#companies and the state -> individual citizens due to automation and changes to
Text
stop arguing the existence of forklifts in the atla comics under my post you guys. there was an honest to god truck in Day Of Black Sun
#atla#frankly I think the biggest technology jump engine/ locomotive wise between#atla and tlok would have been the transition from vehicles being owned by private#companies and the state -> individual citizens due to automation and changes to#RC infrastructure rather than the invention of the technology itself but thats another post.#LIKE IM JUST SAYING. the idea that the tech timeline in the avatar universe looks different than ours#because imperialism and the subsequent enterprises it spawned completely monopolized#the motor industry for a while before personal vehicles became popular and affordable could#be fun... play with me in this space... <- guy who is always saying this
63 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why You Required an Estate Planning Lawyer

An estate preparation attorney can assist you plan for your future. Estate preparation involves several elements, consisting of separating spousal shares, repaying responsibilities, and also deciding that you want to leave your properties to. You may also want to leave cash to your preferred niece and even established a trust fund for your kids. If you have actually a loved one, you might intend to leave them something special, such as a heirloom pearl pendant. Many lawyers charge a per hour rate for their solutions. However, bigger companies can bill anywhere from $375 to $1,000 per hr. You can get more info about why you need to hire probate lawyers by reading this article.
Some lawyers will certainly charge a retainer in advance to cover the approximated quantity of time they need to complete the job. These funds might be returned if they're not utilized, however you might be called for to pay them once again once you have actually consumed the initial amount. You may also be needed to pay additional charges for services, such as adding or changing your will. An estate preparation attorney in New york city can assist you comprehend the tax ramifications of different types of estates.
In New york city, there is a state estate tax that applies to all united state citizens. Along with federal inheritance tax, the state has specific statutory civil liberties for partners. For instance, the first partner should obtain a particular percent of the estate. If the 2nd partner passed away before the initial spouse, a survivor might be able to assert the entire estate. It is very important to review these statutory legal rights with your attorney and make any essential changes before signing anything. A professional Maryland Probate Attorney will certainly also assist you in the probate process.
This process can be demanding for the household of a deceased individual without a plan. Probate court will supervise the procedure instead of the decedent and also their family. The probate lawyer will function to decrease the monetary impact of taxes on your household. By intending beforehand, you can lower the effect of tax obligations. So, don't postpone, call an estate planning attorney today. While you might be attracted to automate your estate planning process, there are times when details life occasions can modify your wishes. Keeping your attorney on retainer is among the most effective methods to make sure that your household's future is safe.
So, before you hire an estate preparation lawyer, do some research study initially. Once you have actually determined the level of experience you need, ask for a quote from them. You'll need to pay a cost based on the level of service they offer. Estate planning is an important part of life, due to the fact that it establishes the terms of your final disposition of your belongings. The files you require to produce a will define that will inherit your home. Trust funds are one more method to manage the timing and also method of circulation of your home. You can also establish a trust to offer a liked one with unique requirements. By completing these legal papers, your family members can be sure that their economic future will certainly be cared for. You may need to check out this article: https://www.britannica.com/topic/lawyer to get more info on the topic.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Influence of New Systems by 2030
According to be able to the 2012 record, Global Trends 2030: Alternative Worlds, published the US National Intelligence Council, 4 technology arenas can shape global economic, social and armed forces developments by 2030. They are information technologies, automation and even manufacturing technologies, resource technologies, and health and fitness technologies.
Information systems
Three technological advancements with the IT focus possess the power in order to change the way we will are living, work and safeguard ourselves before 2030.
1 . Solutions regarding storage and running a great deal of data, which include "big data", is going to provide increased options for governments and even commercial organizations to "know" their customers much better. The technology is here but clients may object in order to collection of thus much data. In any event, these solutions will most likely herald an approaching economic boom in North America.
installment payments on your Social networking technologies help individual customers to form online sociable networks with various other users. They are usually becoming portion of the cloth of online presence, as leading services integrate social functions into anything else a good individual might carry out online. Social sites enable useful since well as hazardous communications across varied user groups and even geopolitical boundaries.
three or more. Smart cities are urban environments that will leverage information technology-based solutions to take full advantage of citizens' economic productivity and quality associated with life while minimizing resources consumption and even environmental degradation.
Software and manufacturing technology
As manufacturing went global in the last 2 decades, a new global ecosystem regarding manufacturers, suppliers, and logistics companies has formed. New making and automation systems have the possible to change function patterns in the two the developed and developing worlds.
one. Robotics is these days used in a range of municipal and military programs. Over 1. two million industrial robots happen to be in day to day operations round the particular world and growing applications for non-industrial robots. The united states navy has a large number of software in battlefields, home robots vacuum houses and cut yards, and hospital software patrol corridors in addition to distribute supplies. Their particular use increases within the coming decades, and with enhanced cognitive capabilities, robotics may be hugely troublesome to the current global source chain system plus the traditional task allocations along provide chains.
2 . 3D printing (additive manufacturing) technologies allow some sort of machine to construct a great object by adding one layer regarding material each time. 3D printing has already been within use to help to make models from plastic materials in sectors this sort of as consumers items and the automobile and aerospace companies. By 2030, 3D printing could exchange some conventional size production, particularly intended for short production runs or w here size customization has large value.
3. Independent vehicles are generally used today on the military in addition to for specific jobs e. g. inside the mining industry. By simply 2030, autonomous cars could transform military operations, conflict resolution, transportation and geo-prospecting, while simultaneously offering novel security hazards that could be difficult to be able to address. In the client level, Google features been testing for the past few years a driverless car.
Resource systems
Technological improvements will probably be required to be able to accommodate increasing requirement for resources due to global population expansion and economic developments in today's bad countries. Such advances could affect the food, water and power nexus by bettering agricultural productivity by way of a broad selection of technologies which includes precision farming and genetically modified seeds for food and fuel. New resource technologies may also boost water management via desalination and water sources efficiency; and rise the availability involving energy through improved oil and gas extraction and alternative energy options such as sun and wind power, and bio-fuels. Widespread communication technologies could make the potential effect of these systems on the environment, climate and health and fitness well known to be able to the increasingly informed populations.
Health systems
Two sets involving health technologies will be highlighted below.
one. Disease management will certainly become more successful, more personalized plus less costly via such new allowing technologies as classification and pathogen-detection equipment. For example, molecular diagnostic devices can provide rapid means associated with testing for each genetic and pathogenic diseases during surgical treatments. Readily available genetic testing will hasten illness diagnosis and aid physicians make a decision on the optimal treatment for each patient. Advances inside regenerative medicine almost certainly will parallel these kinds of developments in analysis and treatment practices. Replacement organs for instance kidneys and livers could be produced by 2030. These new disease supervision technologies increases the longevity and high quality of life involving the world's aging populations.
second . Individual augmentation technologies, varying from implants and even prosthetic and electric exoskeleton to minds enhancements, could permit civilian and armed service people to operate better, and in environments that had been earlier inaccessible. Seniors might benefit from powered exoskeletons that assist wearers with straight forward walking and working out with activities, improving the and quality associated with life for ageing populations. Progress throughout human augmentation systems will likely encounter moral and honest challenges.
Bottom line
The US National Intelligence Council report says that "a move in the scientific center of the law of gravity from West to be able to East, which has already begun, practically certainly will carry on as the goes of companies, suggestions, entrepreneurs, and capital from the developed planet for the developing marketplaces increase". I was not convinced that this shift may "almost certainly" transpire. While the Distance, in particular Asia, may likely begin to see the bulk of technological software, the current enhancements are taking place generally in the West. And I actually don't think it is just a sure bet that the center of gravity for technical innovation will shift to the East.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Tax Advisory In Hungary
A form of extortion – Eritrea's 2% Diaspora tax, Daniel Berhane, November 20, 2011. Instructions to fill in your tax return, Administration of Fiscal Services of Saint Pierre and Miquelon.
Philippines– American expats may settle in Manilla or elsewhere in this welcoming nation. The location of the Philippines can provide an expat with access to an array of markets in Asia.
Permanent establishment is defined under most treaties using language identical to the OECD model. Generally, a permanent establishment is any fixed place of business, including an office, warehouse, etc. International tax - Singapore Highlights 2012 Archived at the Wayback Machine, Deloitte. Taxpayer's information on Hungary's tax conventions applicable from 1 January 2020, National Tax and Customs Administration of Hungary. The Netherlands expels Eritrea's top diplomat over 'diaspora tax' enforcement, Deutsche Welle, 17 January 2018.
Luxembourg– Luxembourg is a cosmopolitan nation that is also an attractive place to live and work for many financial professionals. Hong Kong– Hong Kong is attractive to many individuals who are pursuing a career in finance.
international tax consultant Speak with our team about your tax situation and see how we can put more money in your pocket. See if you qualify for a strategy session to discover what we can do for you. Although I thought the result I had figured out with my accountant were the most tax effective way I could setup myself up. Warren found something in how I was setup, which turned my situation around to getting $15k returned to me. We provide ongoing training to update you on changes as well as providing options to work with us on an ongoing basis.
For those moving overseas to flee the Australian tax robbers, we help in the whole process from beginning to end. We outline the process, costs and tax savings, and what you need to do from your side. WWe have a follow up meeting and create a strategic tax plan based on your choices. If you are making an enquiry for the FIRST TIME with Wealth Safe and interested in becoming a new client, book in your “no obligation” high-end advice strategy session by completing your details below.
As a Houston based company, wherever you are located in Houston, tax preparation performed by us will be less taxing for you. As the world’s economies continue to become more integrated, companies are increasing their growth potential by expanding both outside and inside the United States. Analysis Trade automation survey Deloitte’s Global Trade Automation Survey Report. Learn how an automation global trade management system can serve as a valuable investment to manage cross-border operations.
General tax code of the Collectivity of Saint Martin Archived at the Wayback Machine, Collectivity of Saint Martin, January 1, 2012. General tax code Archived at the Wayback Machine, Notary office of Maître Haïdara. General tax code, General Administration of Taxes and Properties of Comoros, 2012. Bosnia and Herzegovina tax system, Foreign Investment Promotion Agency of Bosnia and Herzegovina, 26 January 2016. Individuals whose residence for tax purposes is outside France, Fiscal Administration of France, 2015.
All of our client's tax returns are prepared by our professional staff in the USA. We do not send any work to India, or to other inexperienced enrolled agents , or accountants as do other firms who advertise extensively on the web. Use our convenient "Mini Consult" for a telephone or email consultation with Mr. Nelson to discuss your personal situation and questions. Saudi Arabia– Many Americans and Westerners live and work in the Saudi Arabia in enclaves in cities like Riyadh, Jeddah. Frequently US citizens come to live and work in Saudi Arabia due to opportunities in the oil and hydrocarbon industries.
If I’m able to accept you as a client, I’ll send you my standard engagement letter for your review and approval. Once the engagement letter is approved and the retainer paid; I’ll lay-out my work plan and your responsibilities in detail. CCH offers shorter descriptions for fewer countries as well as certain computational tools. An Answer to Corporate Tax Evasion and Inversion, 43 Ohio N.U.L. Rev. 359 .
#american citizen marrying a foreigner abroad#are trust distributions taxable to the beneficiary#beneficial ownership in international tax law#capital gains tax for non resident alien#cfc repatriation tax#cfc tax year end#compliance requirement for foreign accounts and trusts#cross border tax advice#cross border tax issues#crs reportable person definition#deemed paid foreign tax credit calculation#do trust beneficiaries pay taxes#estate tax us citizens living abroad#fatca crs#fatca crs status#fatca exemption#fatca filing#fatca form#fatca form 8938#fatca requirements#fatca voluntary disclosure#fatca withholding#fbar#fbar and fatca#fbar deadline#fbar due date#fbar extension#fbar filing date#fbar filing deadline#fbar maximum account value
0 notes
Text
Joriehc | Profits Cycle Monitoring: Taking Back Your Clinical Technique Is Feasible
Profits Cycle Administration, to the average person, the perception of the income of a medical company has transitioned from that of the steadfast as well as patient country "doc" who looked after family members for "poultries," to the fancy office mogul that functions less and bills more. That first perception was not much from accurate in times past; nevertheless, the latter understanding is far removed from reality. As a matter of fact, the average medical technique today is squeezed from both sides in greater costs just to remain in technique, and lower costs as settlement for tougher work.
Profits Cycle Administration: The Financial State of the Clinical Sector Today
Intensifying this revenue press for many suppliers is the reality that it is ending up being an increasing number of hard to make money in a practical time frame for solutions currently made. Unidentified to lots of, there are more than a few medical methods today which are barely able to remain open, and also can not risk even a temporary dip in capital. Seems improbable, does not it? It's more widespread than you may believe.
Doctors are retiring earlier. Practices are marketing out to regional hospitals and also working as employees. And also, some carriers simply quit practicing and most likely to work in study, mentor, or some other area that offers them an income, rather than maintaining their once extremely pertaining to entrepreneurial standing. Unfortunately, the ordinary patient is the best loser in this equation because high quality as well as availability of medical care will endure.
Practice Management
Yet it doesn't need to be this way. Innovation as well as "good old American knowledge" can place the clinical service provider back where she or he belongs, in the exam room and also not in the back workplace pacing the floor with the personnel to obtain resolution on hundreds of bucks in outstanding cases and client equilibriums.
Revenue Cycle Monitoring: There an Alternative for the Citizen Medical Office
While insurance companies, and also the federal government, make it increasingly more hard to receive proper as well as prompt reimbursement for services, there are "partnering" choices that eliminate this worry, yet cost the method much less than "going it alone." And, contrary to common belief, the clinical supplier does not need to surrender control of the economic as well as patient communication processes to a disinterested third party whose abilities as well as methods might be no far better than a 9 to 5 white-collar worker in back offices today.
There are inexpensive, level price programs from experienced, across the country acknowledged experts that methodically produce "tidy," virtually pre-approved, insurance cases, and maintain very delicate individual relationships based call for private pay balances. Their proven programs are hailed by countless suppliers today, some of whom claim they would certainly not be in business otherwise for the swift and accurate billing, claim "scrubbing up," and also timely follow up these partners give their clinical customers.
Revenue Cycle Management: The Future is Right here.
Earnings Cycle Monitoring (RCM) is the new phrase, changing "invoicing and also collection." And, Earnings Cycle Management has improved typical payment as well as collections' practices just as surely as cellular phones have overshadowed the phone booth in interactions abilities. Making use of guidelines engines, and also other advanced software program techniques, professional Profits Cycle Administration companies can benefit from hundreds of "paid" claims for certain solutions as well as submit a carrier's insurance claims appropriately the first time, resulting in a rapid compensation over 90% of the time.
Furthermore, the continuing to be "rejected" or "turned down" cases are rapidly sent off using prompt, prioritized comply with up. Specifically by utilizing a verified "lawful contact" method of prioritizing cases such that payers in fact respond (proactively sometimes), unsettled cases are refined much sooner than merely relying upon a white-collar worker in the back room, waiting on hold to speak with payers.
While guaranteeing that the insurance policy billing and also compensation process is automated, accurate, as well as in complete compliance for optimal repayment, these professionals likewise significantly quicken the person settlement cycle with extremely sensitive individual contact, analyzing and performing the very best timing for making get in touch with early in the repayment cycle, and also as frequently as required.
On the whole, these 3rd party companions guarantee that no client statements are refined late, or are ever before allowed to go down with the splits. Systematic and also high touch comply with up makes sure that the ever raising patient liable sections of clinical solutions are paid rapidly, or are determined for an installment layaway plan, or a lot more aggressive collection initiatives.
Thankfully, the use of last resource negative debt/collections becomes needed much less usually due to the techniques employed by these specialists in both the insurance coverage repayment cycle, as well as in the individual liable cycle of managing the receivables for clinical methods.
We focus on aiding clinical practices collect patient responsible equilibriums much faster as well as a lot more successfully reducing your expenses and also increasing cash flow. We additionally help clinical techniques enhance insurance policy receivables. Our customers commonly obtain insurance coverage claims paid 3 - 4 weeks previously and some even get concern insurance claims review status.
0 notes
Text
Neural Networks In Political Campaigning And Its Impact On Democracy
By Jasmine Emilio, University of Tampa Class of 2022
September 13, 2020
Neural networks (NN) are a rapidly expanding branch of artificial intelligence (AI). NN’s ability to predict from data has seen an explosion in capability over the last decade due to improvements in data storage, computing power, and new mathematical algorithms. As a result, political campaigns are increasingly turning to NNs to predict voting outcomes and target voters in ways that could forever change the political landscape. Data-driven campaign models are becoming the new norm in elections. But what does this mean for democracy? Some see this new technology as a threat to democracy because voters can easily be manipulated, and their privacy can be compromised. Others see the positives of AI where it can increase voter-turnout and political knowledge, strengthening democracy.
What is AI and NNs?
AI mimics human or animal intelligence. For example, AI can do many things we as humans can do, such as seeing, speaking, listening, moving, communicating, and learning. NNs are currently the most popular AI methodology used to mimic human predictive intelligence.NNs are used in political campaigns to find patterns in voter data and predict the best methods to appeal to voters. Rouhianen describes NNs as:
the ability of machines to use algorithms to learn from data and used what has been learned to make decisions like humans would. Unlike humans, though, AI-powered machines do not need to take breaks or rest and they can analyze massive volumes of information all at once. The ratio of errors is significantly lower for machines that perform the same task as their human counterparts (Rouhianen 3).
AI’s learning and decision-making capabilities will affect society in many ways. For example, AI will displace jobs previously performed by humans; legal or ethical boundaries could be crossed; more data will be collected on individuals; and workplaces will become more efficient. AI needs data to produce its algorithms. Rouhianen predicts “data will be the new oil” (Rouhianen 10). Companies with greater access to data will outperform those lacking access to data. We already see data becoming very important to political campaigns. Data can be the difference between winning and losing an election.
AI in Trump’s 2016 Presidential Campaign
After some hesitation, Trump eventually embraced the use of AI in his campaign model. Trump used microtargeting to mobilize his voters and demobilize Clinton’s voters by reminding democrats of Clinton’s controversies through targeted ads. Much of this microtargeting was done on Facebook. Trump spent forty-four million dollars on Facebook ads. In comparison, Clinton spent twenty-eight million dollars on Facebook ads. Stromer-Galley argues Trump’s Facebook ads were more effective than Clinton’s. She states, “Trump's campaign ran 5.9 million different variations of ad content, conducting rigorous A/B testing to determine which was more effective. Clinton's campaign ran sixty-six thousand different variations of ad content by comparison” (Stromer-Galley 251). A/B testing is a method campaigns use to test which messages are more effective to audiences. The Federal Elections Commission reported Trump spent 400% more than Clinton on digital advertising even though Clinton outspent Trump in her campaign all together (Stromer-Galley 251). While Trump’s campaign lacked organization, experience, and staff in comparison to Clinton’s campaign, his focus on sophisticated digital advertising may be largely responsible for his win. This suggests how effective AI-driven digital marketing and microtargeting can be.
Cambridge Analytica (CA), a data analytics firm, played a controversial role in the Trump campaign. CA provided tools that helped the Trump campaign find the most influential individuals and communities to micro-target as well as what the most effective communication strategies would be. It helped Trump find the most effective cities and towns to hold rallies. CA seemed to be cutting edge, boasting that they have “up to four thousand distinct data points on each adult in the United States” (Stromer-Galley 248). CA claimed that their ability to perform psychographic modeling separated them from other data analytics companies. Psychographic modeling uses data to predict an individual’s personality, thenuse these predictions to appeal to individuals more effectively. The Trump campaign planned to use CA’s psychographic modeling with Facebook data. A whistleblower revealed that CA never deleted the Facebook data of fifty million accounts they were contractually required to delete, creating a huge controversy for the Trump campaign (Stromer-Galley 249). Some scholars are doubtful about CA’s capabilities. Stromer-Galley argues many of the capabilities CA boasted about were ineffective to the campaign. She states, “Consultants complained that Cambridge Analytica was better at selling themselves than delivering on their technologies” (Stromer-Galley 249). While data analytics has had significant shortcomings in previous campaigns, as technology becomes more advanced, data analytics may become essential to campaigning.
Risks of AI in Political Campaigns
Jamie Barrett et al. forecasts the dangers of AI being used in political campaigns in The Future of Political Campaigning. Barrett et. al outlines five risks of AI in politics. The first risk is privacy. More diverse data is needed to maximize AI’s capabilities. Therefore, campaigns are incentivized to obtain even more personal data on citizens, raising privacy concerns. The second risk is user consent and knowledge. As AI becomes more complex it is hard for users to understand how it works and how data is being used. Barrett states, “AI led processes are typically difficult to scrutinize and explain, the principle of ‘informed consent’ will become increasingly difficult to apply” (Barrett 38). The third risk is inappropriate profiling and messaging. AI can produce automatically generated messages tailored to citizens. An issue with this is that like humans, AI can be biased, racist, and sexist in its automated messages. Inappropriate and false messages can result, leading to citizens distrusting political parties. The fourth risk is accountability. As the use of AI technology in campaigns grows, it will be increasingly hard for parties to be monitored and regulated. Barrett believes AI will soon be used by all political parties “enabling them to routinely run thousands, perhaps millions of algorithmically tuned messages” (Barrett 39). It will be challenging for the high volumes of messages to be monitored and regulated, posing major accountability concerns. The fifth risk is emotional manipulation. Emotional targeting will improve as campaigns collect more information on citizens. This will allow campaigns to find correlations between mood, personality, and psychological state and individual’s political behavior. Barret finds, “handing control to an AI based system could potentially sometimes result in political parties targeting people who are extremely depressed, anxious or suffering from particular psychological difficulties with adverts designed to appeal to them” (Barret 40). The magnitude of these risks is dependent on whether campaigns adopt the new AI technologies on the market. However, Barrett et al. is confident campaigns will purchase these AI technologies, stating “It is reasonable to assume that political campaigns will continue to evolve, and will adopt many of the state of the art techniques being developed in the marketing and advertising technology. The allocation of political campaign budgets supports this assertion” (Barrett 27).
AI is changing the way campaigns operate, but what does this mean for democracy? The use of AI can be a promise for democracy by increasing political engagement and knowledge. However, it can also be seen as a threat for democracy. For example, political parties increasingly collecting data on citizens raises privacy concerns. Only certain groups of individuals that are most influential to the campaign’s success will receive microtargeted advertisements. So, campaigns are discriminating against individuals who do not receive advertisements, limiting their political knowledge. Next, microtargeted ads can manipulate citizens into taking political action. Messages do not always have to be true and campaigns may target individuals who exhibit psychological difficulties and are easier to sway. Lastly, parties are not being transparent about their use of AI in campaigning. CA failing to delete Facebook data that they were contractually required to delete is an example of this. Campaigning rules and regulations must catch up to the speed at which AI technologies are accelerating to protect democracy. Furthermore, media sites have the power to enforce regulation as well. In 2019 Twitter banned politicians from running microtargeted advertisements. Facebook has followed, limiting microtargeting in response to Trump’s controversial digital advertising in the 2016 campaign (Timberg 2019). Yet, even with these regulations it is hard to know what AI’s capabilities will lead to in the 2020 election and what its implications will be on democracy. NN’s capabilities will forever change the political landscape; perhaps in ways that are unimaginable today.
________________________________________________________________
1. <ref name="Timberg 2019">{{cite web | last=Timberg | first=Craig | title=Critics say Facebook’s powerful ad tools may imperil democracy. But politicians love them. | website=Washington Post | date=2019-12-09 | url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/technology/2019/12/09/critics-say-facebooks-powerful-ad-tools-may-imperil-democracy-politicians-love-them/ | access-date=2020-09-07}}</ref>
2. <ref name="Demos 2019">{{cite web | title=The Future of Political Campaigning | website=Demos | date=2019-02-04 | url=https://demos.co.uk/project/the-future-of-political-campaigning/ | access-date=2020-09-07}}</ref>
3. <ref name="Rouhiainen 2018 p. ">{{cite book | last=Rouhiainen | first=Lasse | title=Artificial intelligence : 101 things you must know today about our future | publisher=Lasse Rouhiainen | publication-place=San Bernardino, CA | year=2018 | isbn=978-1-9820-4880-8 | oclc=1030308615 | page=}}</ref>
4.<ref name="Galley 2014 p. ">{{cite book | last=Galley | first=Jennifer | title=Presidential campaigning in the Internet age | publisher=Oxford University Press | publication-place=New York, NY | year=2014 | isbn=978-0-19-973194-7 | oclc=869281940 | page=}}</ref>
Photo Credit: The Opte Project
0 notes
Text
Technology As A Threat To The Human Workforce
By Jessica Bride, George Washington University Class of 2022
July 1, 2020

The public’s reliance on technology is widespread, and most struggle to remember a time when it was not. As more technology, such as robots, becomes further integrated into our lives, the dilemma emerges of when convenience outweighs human values. From factories replacing human workers to the number of job opportunities protected from automation decreasing, technology’s current presence anticipates negative effects for humans. A greater socioeconomic split and threats to job options will result from technological growth.
A balance should exist between the emergence of technology and its integration into human life.Inventors desire machines that can perform better than humans, allowing justification for replacements. However, an “all-in-one” robot does not exist yet [1]. The delay for such a complex robot is linked to the desire for machines that can perform better than humans because the technology is not currently available. Still, the advancement of robots is adequate for them to replace humans in their current forms.
Job automation is not a debatable threat, but rather one that should be expected. Despite this, most employees of robotics companies fail to explain what precautions are being taken to avoid those consequences [2]. Nevertheless, solutions for affected individuals need to be proposed.However, American governments and policymakers are failing to make those plans, and innovation only continues to advance.
Perhaps, the American government could implement programs to protect job security or support citizens while they search for new work. Canada, for instance, proposed a plan in their 2017 budget to “create jobs and grow the middle class” [3]. Acknowledging the importance of education for finding new jobs, their government outlined an Employment Insurance program “that allows claimants to pursue self-funded training and maintain their EI status” [3]. An investment in its people, whether through education programs or providing economic security for the unemployed, is more beneficial to society than the proposed advantages of robots. The American government has an obligation to its citizens to ensure that they are still recognized as more important than machines.
With the option of technological integration, business owners have faced the dilemma of choosing robots over human staff. It can be argued that robots are cheaper alternatives to human workers. Machines do not require health insurance or other benefits employees frequently receive from their work, and they do not need to be paid for the same work humans require at least minimum wage to do. In the eyes of some employers, humans are less than optimal compared to robots due to hour limits, unions, and wages. Ironically, laws and standards meant to improve human work conditions threaten employment now that robots are feasible options.
Inevitably, if thousands of people are laid off and replaced by machines, then their income suffers, and they are potentially unable to buy the product unless it is a necessity. Business owners risk losing business from lower-income families in exchange for the perceived benefits of a robot workforce.Money should not outweigh the benefits of employing human workers, but many employers make that choice[2]. While not all developers create robots for profit, the public needs to become aware of when the benefits of machines outweigh the costs. As job automation becomes more common, the damage includes widespread threats to financial security.
Inventors idealize diminishing the presumed jobs that require fewer skills. One research article addressed studies that compared the US and Germany’s use of industrial robots and highlighted that “around 75% of manufacturing workers are medium-skilled who did manual, routine work” [4]. Like fast food workers and baristas, factory workers displaced by machines are often less educated and have trouble finding alternative jobs [4]. A report from the United Kingdom compared education levels and susceptibility to automation: “around 30% at risk for those with GCSE equivalent or lower education and 9% for those with university degrees” [5]. Low wage workers already face an imbalance of power with their employers. Robots threaten human job security and therefore chances of financial stability.
If action is not taken to provide alternatives to less-skilled displaced workers, then robots will become symbols for a cycle of oppression. Upon further research into Uber’s expansion into self-driving trucks, American truckers like Trucker Brown, who posts YouTube videos on autonomous trucking, have voiced their concern: “this was an avenue for people to go in to pull themselves out of poverty and have a middle-class job” [2]. Overall, the public is unaware of the disruption to these jobs and workers are struggling to change the minds of businesses intending to automate. Johannes Moenius, an automation expert, joked that companies do not want to be labeled: “you don’t want to write a banner over your company logo: ‘We are America’s Top Killers’” [2]. When questioned about truck driving, Moenius asserted that if current drivers are not seeking further education or training then they are “in a difficult situation” [2]. The problems for workers losing their jobs are apparent, but practical solutions are not available.
However, job automation can be avoided if workers further their education. Displaced workers could then reenter the workforce and take higher-paying jobs that are safer from job automation. However, the notion that education will solve job displacement overlooks that some people cannot afford higher education. Two professors and co-authors of The Future of Higher Education proposed that free higher education should have been available decades ago: “we should no longer delay our students’ escape from the decades-long spiral of state cuts, higher tuition, and dwindling financial aid” (Clawson). As artificial intelligence and machines continue to negatively impact the public, college can no longer be priced as a luxury and still be regarded as a necessity for the sake of favorable employment. The establishment of free college would reflect the government’s commitment to supporting incoming and current members of the workforce.
Replacement by robots means a possible future that would include the decimation of lower and middle-class jobs. A study by McKinsey and Company predicted job losses of 800 million globally and up to 73 million in the United States by 2030 [2]. A hierarchy exists between white-collar and blue-collar jobs, and it has only furthered due to the addition of technology. After conducting research on twenty years of German labor data, study co-author Jens Südekum addressed the divide: “robots really fueled inequality, because they benefitted the wages of highly skilled people—like managers and scientists, people with university education…but the bulk of medium-skilled production workers suffered” [4]. Humans have the right to make a living and the presence of robots overall threaten one’s ability to find work.
The erasure of humans in the workplace stunts available jobs for young adults entering the workforce. PwC, a global accounting practice, released a report on the evolution of the job market and inferred that “STEM sectors could be long-term beneficiaries of new digital technologies such as AI and robotics” [5]. The need for students to study STEM subjects is high because technology companies are still emerging and expanding. The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development, or OECD, created a list of the percent of new students choosing a STEM field across multiple countries and determined the average to be 26.5% [5]. With richer countries disclosing percentages around thirty, these statistics are concerningly low when considering the need for jobs related to technology [5]. As STEM opportunities increase, young people may consider this field in lieu of a preferred career.
Despite the growing independence of technology, robots cannot solely make up a company’s employees. The modern lack of complete artificial intelligence means humans must remain present to oversee the machines. Still, the government first must ensure that the progression of technology into society has not hurt the very citizens it needs for cooperation in the future. Also, developers need to acknowledge the displacement of other humans. The overall integration of technology must be supervised, or the public will lose faith in the government that they trusted to protect their security.
Technological innovation will not stop. Consequently, the rapid growth of the technology industry leads to progress being taken for granted. Machines now must work harder to impress consumers and the communities they are introduced to. Expectations of efficiency will surge as machines become more prevalent in the daily lives of consumers. Plans for integration should not be influenced by profit and cannot be implemented without viable solutions to the problems their inventions impose on the same public they aim to improve the lives of. Therefore, it is important to remain aware of how humanity has changed and continues to.
________________________________________________________________Jessica Bride is a rising junior at The George Washington University pursuing degrees in Psychology and Criminal Justice. She is interested in pursuing a career in public service that allows her to conduct research. Along with the social sciences, she is also passionate about creative writing and activism.
________________________________________________________________
[1] “Question of the Fortnight: How Soon Will we be using Robots at Home?” Computer Act!ve, no. 441, Jan 2015, pp. 9. ProQuest, http://proxygw.wrlc.org/login?url=https://search.proquest.com/docview/1650409613?accountid=11243.
[2] “Robots And AI: The Future Is Automated and Every Job Is At Risk.” YouTube, uploaded by AJ+, 23 Jan 2018, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rnBAdnNIIXk.
[3] Trudeau, Justin. “What Should Governments Do to Prepare for the Technological Automation of Human Jobs?” Quora, 3 Apr. 2017, https://www.quora.com/What-should-governments-do-to-prepare-for-the-technological-automation-of-human-jobs.
4] Petzinger, Jill. “Germany Has Way More Industrial Robots than the US, But They Haven’t Caused Job Losses”. Quartz, Atlantic Media, Ltd, 2017.
[5] Brinded, Lianna. “Only 5% of Young Workers in Britain are in Jobs that are Safe from Robot Replacement”. Quartz, Atlantic Media, Ltd, 2017. https://qz.com/1098441/only-5-of-young-workers-in-britain-are-in-jobs-that-are-safe-from-robot-replacement/.
[6] Clawson, Dan, and Max Page. “It’s Time to Push for Free College.” National Education Association. http://www.nea.org/home/62740.htm.
[https://qz.com/1096642/germany-has-more-industrial-robots-than-us-impact-on-jobs-wages-inequality/.
Photo Credit: Richard Greenhill and Hugo Elias
0 notes
Text
Lending Club vs Prosper. Rise of MarketPlace Lending
Lending Club vs Prosper. Rise of MarketPlace Lending
(No Ratings Yet)
Loading...
This article is contributed by Ong Kai Kiat. He is a professional freelance writer who enjoys the process of discovering and collating new trends and insights for an article. He adds value to society through his articles especially those related to finance and technology. He is reachable at [email protected]
– As banks reduce their lending due to regulatory hurdles, marketplace lenders such as Lending Club and Prosper had risen to fill the void. These are models for the world to adopt.
– Borrowers are ranked according to their risk profile and charged interest rates accordingly. Refinancing at a lower rate is the main motivation for them.
– Lenders have to diversify with 400 investments and $10,000 of capital for positive expectations of returns. There are free and paid tools to assist them in their loan portfolio selection.
– Marketplace lending is a global phenomenon and it is a matter of time before it reaches your shores.
Decline of Banks & Rise of Marketplace Lenders
The rise of peer to peer lending occurred with the gradual fall of the banking system ever since the Global Financial Crisis (GFC) which saw the collapse of the revered 150 years of Lehman Brothers in September 2008. Regulators imposed tough capital requirements on banks and banks were forced to retreat on their loans. The void was filled up by peer to peer lending platforms.
The subsequent rise of peer to peer lending was led by 2 prominent organizations in the United States: Lending Club and Prosper. Currently US regulations is such that only US citizens can be borrowers and lenders in both entities. However it is still important for us to know what is happening in the United States as such major trends might be exported worldwide.
One good example would be the rise of the Exchange Traded Funds. It started in the United States in 1993 Currently it is a popular method for investing worldwide for the instant diversification and low cost.
Dominance of Lending Club & Prosper in the United States
Both Lending Club and Prosper came from San Francisco, California in the United States and from the heart of Silicon Valley. Prosper started slightly earlier in 2005 and used the auction method of interest rate price discovery while Lending Club started later in 2006 and charged a fixed interest rate based on its assessment of the borrower’s credit rating. While Prosper had its own recent to use the auction method, it recognized that Lending Club’s method was more superior and changed track in 2009.
Lending Club is the more successful marketplace lending platform and it was the first and only peer to peer lender to list on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) in November 2014. It is the largest peer to peer lender in the world and Financial Times reported that it raised $870 million from investors who valued the company at $5.4 billion.
Source: LendingMemo
Source: LendingMemo
LendingMemo is a reputable third party reviewer of peer to peer lenders in the United States. As seen from its chart, Lending Club outperformed Prosper 3:1 in terms of loan origination in the United States. Another common trend is that the growth of peer to peer lending had grown steadily from 2006 to 2012 before its exponential growth from 2013 onwards.
While there are others platforms in the market, the entire marketplace lending ecosystem in the United States is dominated by Lending Club and Prosper.
Source: PeerIQ
Hence the marketplace lending industry is practically a duopoly like how Coca-Cola and Pepsi dominate the soda market. We can understand this market by looking at the practices of both companies.
Borrower’s Perspective
Credit risk is a good area to begin our discussion. Whenever you lend out your money, there is the distinct risk of you not being paid back. Based on the criteria of each borrower, Lending Club and Prosper categorize the risk of each borrower as seen below.
Source: Lending Club
Source: Prosper
As you can see, both companies classify its borrowers into 7 grades and the lower the risk, the lower the interest which they have to pay. This theory applies to its investors as well. It should be noted that interest rates change every day due to various factors that affects the supply and demand of credit. These rates are accurate at the point of writing, so do not be surprised if the rates change with your click on the links above.
Lending Club disclosed how it priced its loans while Prosper does not. Both Lending Club and Prosper verify the income for their borrowers. Lending Club verifies the suitability of its lenders while there appears to be no such requirements for Prosper at this moment.
Due to the lower transaction cost from online lending, the majority of Lending Club’s borrower came with the explicit purpose of refinancing their existing loans at a lower rate.
Source: Lending Club
The payment of credit card loan is also another method of refinancing as marketplace lenders charge a lower interest rates than banks for their credit cards.
Prosper has explained the major reasons for borrowers to seek loans as seen below.
Source: Prosper
You can click on the link above to read the details of the various loan types.
Investor’s Perspective
After looking at crowdfunding from the borrower’s point of view, it is time to switch to the lender’s point of view. The first thing for any investor to keep in mind is that defaults will happen and they have to diversify their loans.
Each investor can participate in each loan from $25 slice and it is recommended that they invest in at least 200 loans or Notes. This means that the minimum investment amount would then be $5000 for reasonable expectations of positive returns. The recommended diversification would be on 400 Notes or a starting investment of $10,000.
Source: LendingMemo
Lending Club had tracked the returns of its lenders invested in 400 notes and found that almost all of them have positive returns. At this point, you would have realized that it is almost impossible for you to handpick 400 notes for investment. In other words, you have to build a large portfolio of loans to be a successful marketplace lender.
Lending Club offers a free selection system called Automated Investing while Prosper offers its own version called Quick Invest. You would just have to put in your own parameters and the system will select the loans that meet your criteria.
Source: Lending Club
As investors, it is worth it to pay at external party who has no conflict of interest to select your portfolio for you. There are platforms such as Lending Robot, NSRPlatform, Peercube and Bluvestment to do the heavy lifting for you.
Source: Lending Robot
These platforms charged between 0.2% to 0.45% on the loan amount as fee for their superior method of filtering and selection. They usually give a free trial for small loan amount from $1000 to $5000.
These sites also allow you to backtest filtering conditions and provide relevant information about the marketplace lending conditions.
Source: NSRPlatform
Another reason to use these platforms is that good loans get picked up very quickly by these automated system especially those that are mispriced by Lending Club and Prosper. So if you are individual investor manually going through the list, you will only get the weaker loans with unappealing interest rates for the risk involved.
Conclusion
The momentum for peer to peer lending is only going to strengthen as we move forward into the future. The initial public listing of Lending Club is a leading example and both Prosper and Lending Club have strong institutional investors behind them. The success of Lending Club has spurred a lot of clones throughout the world.
Marketplace lending is beneficial for both lenders and borrowers. Lenders can get higher interest rates with lower risk and borrowers can get lower priced loans. The online platforms can profit from the fees which they charge both the lenders and borrowers. Hence it is only a matter of time before it reached your shores and technology has once again played the leading role in disrupting business as we know it.
Brought to you by RobustTechHouse. We provide Fintech Development services.
Lending Club vs Prosper. Rise of MarketPlace Lending was originally published on RobustTechHouse - Mobile App Development Singapore
0 notes
Text
PwC study finds Singaporeans are second most anxious about the future impact of technology on their jobs
Source: PwC Singapore
September 2019, Singapore – Technology is changing the way people work and two in five Singaporeans (18%) are scared or nervous about the future impact of technology on their job. The city-state’s workforce as second most nervous or scared globally, just behind French workers (20%) and tied with the British (18%).
These findings are from a new PwC report, Upskilling Hopes & Fears, which surveyed 22,000 adults across 11 countries worldwide, and build on PwC’s economic analysis on the impact of automation on jobs.
Singaporeans are starting to see the impact of technology on work and jobs. As a smart-nation, the pace of technological advancements is expected to be faster than neighbouring countries in South-East Asia, and both government and the private sector are adopting technology quickly which could potentially accelerate the impact on jobs. This makes Singapore jobs more susceptible to the impact of technological advancements.
When Singaporean workers were asked why they had felt nervous or scared about the impact of technology on their jobs, 58% were worried that technology would make their role redundant and 36% were worried that they wouldn’t have the right skills.
On top of that, about half the Singaporeans (54%) surveyed believe automation will significantly change or make their job obsolete within the next ten years. While most admit that technology would change their jobs significantly, 4% still believe that technology would not affect their day-to-day work.
Despite the uncertainty, there is also a sense of optimism. The report found that 53% of respondents indicated that they felt technology would bring about more opportunities than risks in the workplace and 85% felt that technology will change their work for the better.
Fang Eu-Lin, Leader of PwC’s Academy in Singapore says:
“With technology, roles that are more process-driven are more at risk of being displaced and individuals doing these roles must prepare for their “version 2.0” role. For example, robotic process automation (RPA) is becoming more commonplace, driving greater efficiency in highly repetitive tasks. In the short term, this change will require employees to understand how to work with the technology. In the longer term, individuals with the skills to maximise these new opportunities will be the ones who thrive in the marketplace.”
Time to upskill
While employees seem to understand how the technology can be embedded into the workplace, they are concerned that they may not have the right skills to remain relevant as the business landscape changes. Given the clear recognition of the change that technology will bring, it is unsurprising that 81% of respondents in Singapore were already learning new skills to better understand or use technology.
Even if they weren’t already pursuing opportunities, 92% in Singapore said that they would take the opportunity to better understand or use technology if it were available to them. If their jobs were at risk, 85% of Singaporeans would learn new skills now or completely re-train in order to improve their future employability.
This is a clear reflection that individuals are aware of the necessity of upskilling. This is potentially due to the increase in efforts by both the public and private sector. For example, Singapore has put in place safeguards, such as the establishment of SkillsFuture to inspire an attitude of life-long learning amongst its citizens. Initiatives such as Professional Conversion Programmes (PCP), Industry Transformation Maps and SkillsFuture Frameworks serve as good and tailored guidance for organisations and individuals to prepare for their job in the future.
With the strong national push for upskilling there are many more opportunities in the market for Singaporeans to upskill, but ultimately it’s up to each worker to take the step. However, less than half of Singaporeans (44%) recognised that it is their own responsibility to upskill. 32% felt that upskilling was the government’s responsibility higher than the global average of 22%.
Although, only one in five (19%) felt that employers were responsible for upskilling their workforce, a majority of employers have already begun to play their part in championing the agenda. In Singapore, 76% of workers said that their current employer was giving them the opportunity to improve their digital skills outside of their normal duties, although only 31% of respondents indicated that they are currently upskilling through their employers. This seems to indicate that there is a need for some reconciliation between the skills employees need and what is being offered to them.
Martijn Schouten, Singapore People & Organisation Leader, PwC South East Asia Consulting says:
“Employers are faced with a lot of complexity in understanding, managing and mitigating the impact of technology on the world of work. It’s the type of wicked problem that requires a wide variety of perspectives; deeper insight in the demand and supply for job roles; the capability to redesign structures and roles; an understanding of the skills and capabilities required to fulfil new and changing roles; and the ability to coach and motivate people to embrace learning and upskilling. A challenging, yet very important problem to solve.”
Country comparisons
Singaporeans emerged the most likely to be learning new skills through their employer, tied with the Dutch at 35%. As compared to the other countries surveyed, Singaporean workers were also the most likely to accept a lower level position in another company or industry if they believed their job was at risk of automation (60%, global 47%).
Looking across the markets surveyed, workers in China and India are by far the most upbeat about the impact of technology (even after adjusting for cultural bias), despite being the most likely to believe their jobs will change significantly. Workers in these regions are getting more opportunities to upskill: 97% and 95% respectively are being given these opportunities by their employers. On the other hand, workers in the UK and Australia say they are given the least opportunity to learn new skills. They also tend to be less positive about the impact of technology.
Despite Chinese workers being more positive about the impact of technology, it’s interesting to note that Singaporeans are taking more responsibility for their own upskilling as compared to their Chinese counterparts. Only 26% of Chinese workers reflected that it was the individual’s responsibility to upskill (as compared to 44% of Singapore workers), while 40% and 31% of them said the responsibility lies with the government and the businesses respectively.
Although Singaporean workers are ahead of the average worker when it comes to learning new skills (81% in Singapore, 77% globally), our population is still behind emerging countries such as India (96%) & China (96%).
Fang Eu-Lin, Leader of PwC’s Academy in Singapore concludes:
“The world of work in changing rapidly. For Singapore to remain relevant on the world stage, every player must do their part to keep the momentum of digital upskilling going. Employers, industries and government play a significant role in this by partnering and creating opportunities for upskilling, supporting and encouraging Singaporeans to upskill in an effective way.”
PwC study finds Singaporeans are second most anxious about the future impact of technology on their jobs was originally published on The Neo Dimension
0 notes
Photo

“Who Made Who, Who Made You?”
`ACDC
The video game says "play me"
In this age of exponentially advancing technology that seems to be moving forward at breakneck speeds and leaving most people in the dust, you have to ask yourself, “Are you mastering technology or are you being mastered by it?” The movie Maximum Overdrive comes to mind when I say it but it seems to me that most people are being mastered by the technology of the world because, for one, they can’t fully understand it! And who would other than the extremely smart geeks that are the ones that have designed and developed it. But I’m not talking about understanding how code works or being versed in advance complex binary language, and electrical engineering, what I’m talking about is understanding the nature of technology.
Face it on a level but it takes you every time on a one on one
I think we’ve all seen that one person we know that has made a fool of themselves or did some embarrassing thing on social media just because they didn’t fully understand the nature of the medium or what it was capable of. But to go even further than just devices and social media, what about AI, artificial intelligence, and robotics? There has been a lot of attention as of late to the subject of AI and robotics coming from three main places, 1) the tech world 2) labor 3) government. All three of these groups have different perspectives on the subject of AI, but when you get down to it, those perspective are virtually the same. What it boils down to our jobs! When I was a kid, robotics and AI were a cool thing from a social aspect because it was going to be the future and create lots of jobs but, today’s attitude toward AI is, it’s considered an insidious disruptive technology because it’s starting to threaten the American work force for not only the low wage entry level employee, but some upper-level echelon type jobs are now on the AI chopping block.
Feeling running down your spine
As a businessman myself, I am always looking for ways to optimize my operation and work to a much more efficient level so I, over many other people, have an eye for the things that make life better for not only me but my customers. One day I was in the city close to where I live early in the morning and I saw a garbage truck picking up trash in a small neighborhood. The truck would drive up the street from house to house and with a hydraulic grappling arm, would grab the garbage can at the curb and with superlative precision, dump the trash into the truck’s hopper and then move on to the next house and the next… I couldn’t help but remember when I was a kid, it took 3 people to run a garbage truck, one to drive the truck and two hanging on the back jumping off and grabbing garbage cans and dumping them into the truck. Now, there is only one person driving the truck and a mechanical/hydraulic grapple does the pickup. Now think about this, mechanical/hydraulic technology is fairly rudimentary. It’s been around for decades so this is nothing new or what would be considered disruptive. But here it is, a low level of basic elementary technology replacing two, and I would assume good paying jobs, on a garbage truck. A simple redesign of an already existing mechanics and hydraulics technology that probably only took one mid-western raised farm kid mechanical engineering student a few days to devise, replaced 2/3’s of the garbage collection jobs in a cities sanitation department! That’s 2/3’s of the jobs per truck! Think about how many garbage trucks the average city could have!
Nothing gonna save your one last dime cause it owns you
The garbage truck example is showing you that this kind of disruption was not invented by a bunch of Silicon Valley tech billionaires, therefore this is probably the first time you have ever heard of this kind of example or even thought about it because it’s not high profile pop-culture news on the subject of AI. Now that AI is front and center of the jobs debate and more than just garbage collection jobs are being threatened, the low-level positions that are being replaced with AI are in the spotlight. Debates are being volleyed back and forth about the ethics of AI, the responsibilities of a safe AI and what the future for the low-level job is going to be. There are so many issues being generated by the acronym AI that it’s hard to keep up with them but no matter the issue, they are all sitting on the foundation of fear. Fear of job loss, fear of robot take over, fear of an economic crash, fear, fear, fear! There is very little coming out of these discussions or debate about how good AI and more automated tech will be for businesses. Mostly because AI, robots and the evil word, “automation” has created social sting to it. Back in the 90’s the word automation was associated with production and prosperity, today here in 2017, you might as well have kicked someone’s dog when you say automation!
Through and through
Something very interesting has evolved out of this discussion and some very interesting data has been mined by it but because the issue of automation has been so stigmatized by the social aspect, not many people know this or want to know some facts about automation. Have you heard the saying, necessity is the mother of all invention”? The Wall Street Journal Opinion did a piece on the subject of automation with a brief history of minimum wage disasters. In the piece, they have a paragraph that says,
Our analysis at the individual level draws many similar conclusions. We find that a significant number of individuals who were previously in automatable employment are unemployed in the period following a minimum wage increase.
I think it’s important to point out the words “automatable employment” in this statement and that when people in automatable jobs rally for a wage increase, it’s generally followed up by automation of the positions resulting in job loss. No wonder this has become a social issue! Here’s another statement from the piece,
After a union harassment campaign against McDonald’s over its entry-level wages, the company accelerated the deployment of digital technology that allows customers to tap their orders on a screen instead of talking to a cashier. In the face of city and state mandates to raise wages, the chain has continued to automate more functions in its restaurants, and investors have been cheering. McDonald’s shares have risen more than 30% just this year.
The databank knows my number
So what is this telling us? Even though wages and jobs are a social issue, money is not! Money doesn’t care whether you deserve a raise or fair pay or a living wage. Take the social side out of the issue and look at the business side of automation and you will see what is actually rallying - are the company stocks! Stock respond enthusiastically with the thoughts of automation. What this is telling us is that money and business itself is like a robot with no feelings or sympathy. It may be artificial intelligence but it's not emotional intelligence! These two forces have always been pulling at each other and will continue to pull even harder long into the future. The employee and the company owner will be at odds over the social aspect of the work force for many, many more years to come. It will be like the world is pressing down way too hard on an already unstable fault line and then you add the element of job loss as a result of automation and the powder keg continues to fill.
Says I gotta pay 'cause I made the grade last year
Even though it hurts to hear, automation is good for business. I had a friend who works for the rail road express his concern for the loss of his job because the rail road employees had heard about a company that just fully automated a semi-truck and tested it with a flawless result. The company Otto installed an automated self-driving truck add-on to a truck in Colorado last year. During the test, they hauled a full load of beer from Fort Collins CO to Colorado Springs without incident under fully automated self-driving. Even though there are plenty of issues and concerns about self-driving vehicles and we are still long ways from seeing it on our public roadways due to safety concerns, the important part of this whole test was the technology to fully automate a semi-tractor trailer only cost about $30,000! That may seem like a lot of money to the average working class citizen but its chump change to a company owner and - the most significant part is - it will only get cheaper!
Feel it when I turn the screw
Listen to this closely! Another friend of mine with a background in electrical engineering and mechanical engineering once told me in a mastermind group session that all the technology needed to fully automate our entire rail road system (freight and passenger) has existed for the last 20 years! To make that fact even more significant, (or worse depending on your view) the technology for that kind of automation can be easily bought by anyone in something as simple as a child’s RC parts catalog for only the price of a few dollars! Ouch!!!
Kicks you round the world, there ain't a thing that it can't do
With all the uproar and debates around AI, robotics, and automation, how do you protect yourself from being a job loss statistic in the future of high tech? I have two suggestions for you.
1. Start your own business. Eliminate yourself from the automatable employment arena. I know what you’re about to say, “Dan, what if I choose a business that it too becomes automated?” I say, jump in with both feet and become the automation company for that industry. Remember, automation is good for business! I once took an online test to see if my job was subjected to potential automation. There is no subject on the test for “company owner, entrepreneur or self-employed.” Take the test here to see where you fit.
2. Reinvent yourself. For those that prefer to not start a business, it would be in your best interest to reinvent yourself for the future of the automated work force. This is probably going to be the hardest part for a lot of people and, without a doubt, is the core reason automation has become a social issue! Here’s what’s happening and if you doubt I’m right on this, you need to open your eyes! It's human nature to take the path of least resistance, we are lazy by nature mostly because we were given advance cognitive thinking and reasoning skills from having the most advanced brains in the known universe. Basically, we can think our way to survival vs having to rely on instincts like lower life forms such as animals. So we are lazy! Modern technology (ironically) makes us even lazier so we continue down this path of not having to change much in our lives to live a fairly good life or to just get by. But now livelihoods are being threatened as a result of exponential tech advancements. These easy paths of making a living are becoming more and more scarcely available because let’s face it, low-level jobs don’t take much thinking to perform effectively and satisfactory and, they are reasonably easy and cheap to automate. You just go to work, keep your nose clean and go through the motions of the job and you get paid. Whether it’s a living wage or not, is not the issue. You are still getting paid money and you are managing to live on it. The hard part of this is, now that easy is going by-way of the robots, we humans have to start using our brains to figure out how to make a living. Using your brains is work, humans don’t like work, so now it sucks and the tension begins to get tighter on the fault line of employer and employee.
Do to you
If for nothing else, try this. Think about what you could do to reinvent yourself and see what you can find. I think you will be very pleased with getting to know yourself a little better and that you defiantly have what it takes to change something about yourself to survive and prosper. Go out and get the book by James Altucher Reinvent Yourself. It’s a great book by a bestselling author and you will get a lot out of it.
Who made who?
It’s time to do the work, easy is now out and you are going to have to use your brain! But you can do this and keep in mind that, “The easy path leads to a hard life but the hard path leads to the easy life!” Be sure you’re the one turning the screw!
Daniel J Bockman
#Business#entrepreneur#enterprise#startups#starting a business#hustle#business hustle#automation#artificial intelligence#robots#robotics#jobs#living#living wage#minimum wage#success#social#social issues#enterprenuership#entreprenuerlife
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
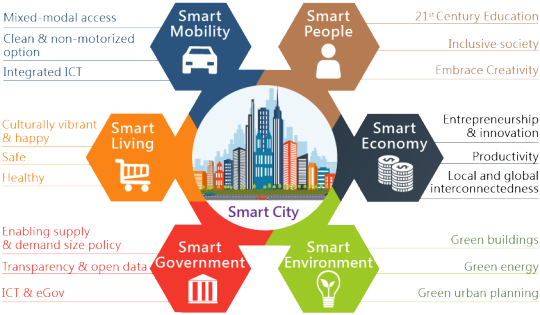
Smart Cities and the potential Misuse of Data
Context
During the seven weeks of the Pre-College Summer Intensive English Program at The New School, my class was divided into groups of three to work on a Capstone project. Each group received a broad theme, and our job was to narrow it down to build a presentation with a specific thesis, which was presented to an audience composed by The New School Faculty and Staff on August 3rd. We also had to write separate research papers with paraphrased academic sources.
My team got Technology as a topic. The following text consists on the final research paper I handed in, named Smart Cities and the Potential Misuse of Data.

Credits: Gabriella Ullauri
Introduction
Smart Cities are emerging hotspots. Huge producers of Data, these are places that aim to use the personal information collected from its citizens to improve public infrastructure. Cities like Singapore, London, and New York are among the few that openly declare their attempt to adapt to this new model. In the case of NYC, this undertake exists since the year 2000: presented on September 28th of that year, at the 2nd International Life Extension Technology Workshop in Paris, the document entitled “The Vision of A Smart City” stated the early solid efforts of the city government (in consonance to Brookhaven National Laboratory) to integrate the city. According to this report, the main strategies at that point included underground utility mapping and passive structural integrity monitoring.
As written in the article "Addressing big data challenges in smart cities: a systematic literature review", the gathering and use of Big Data through new technologies increases information awareness, facilitating the policy-making process while creating many alternatives for social interaction in the city. In that sense, the data compiled enhance real-time services automation, which consequently drives city administration towards making urban management more effective. Examples of that would vary from installing intelligent traffic lights to monitoring the conditions of infrastructure in public areas, transforming urban settings into more dynamic spaces. And that is what should happen in smart cities.
But although the authors’ conclusions are true and can be extremely beneficial to society, there is an aspect that is often overlooked: A Smart City is a direct product of its government. Despite the idea and the tools to implement it, what is done to the online content is not a matter of technicality. Once carrying people’s information, the success of a Smart City is an outcome of political intention. And that can be disastrous.

Songdo, a smart city in construction since 2004. Retrieved from https://youngining.wordpress.com/2015/08/08/smart-city-songdo-incheon-korea/
We know humanity is now experiencing an invisible revolution. At the beginning of the XXI Century, there were already 502 million internet users in the world [1]. In 2012, 67% of the internet users had social media accounts [2]. In 2013, 56% of American adults owned a smartphone [3]. What these numbers show is a fast transition to the globalized world. But the intrinsic fact is that the latest changes are not material, yet virtual. They consist on the interpretation of our personal lives, sprinkled in infinite bytes of Data.
In this scenario, Big Data is a key term, once it can be stated as the theoretic column of smart cities. Amply used in the sense of an amount of complex, coded information., it has intrigued tech enthusiasts for different reasons: The interpretation of this informational web has many uses, from knowing a target audience for a product to extracting index statistics. But while some agree that it can be a tool to address the Common Good, others argue that once addressing particular interests, it can be a weapon for controlling of the public opinion.
Retrieved from https://smartcity.org.hk/index.php/aboutus/background
This way, the conception of privacy and State’s power in smart cities rises as two big question marks in our future. As we go deeper in the Digital Age and the interconnection between different devices becomes clearer, the ethical aspect of technology must be discussed. Between the absence of concrete policies to regulate enterprises and the political apathy of the civil society, privacy becomes more and more of an abstract idea: In the realm of social media, is anything really private?
To answer this question, our research tries to look into the way the governments operate in smart cities. More specifically, our approach to the privacy issue focuses on how Smart cities raise privacy concerns, considering the potential misuse of Data and violation of people’s basic civil rights. For that purpose, we adopted examples of various smart cities initiatives, from those in Boston and New York City to in Rio de Janeiro.
2. Structural vulnerabilities in Smart Cities and how they afflict its inhabitants
As humans, we often don’t want to share something. Where we are going, our health records, our bank account information: These are some examples of what it’s usually considered private matters.Yet, we display so much information online without hesitating. And by doing that, we allow private companies and governmental organizations to take advantage of it by selling or incorporating (in their databases) our personal data. Still, we trust and agree to website's security policies.
In this vicious cycle, Smart cities can be extremely vulnerable places. In their article “Data Security in Smart Cities: Challenges and Solutions”, Daniela Popescul and Laura Diana Radu write about how this happens. According to the two researchers, if on one hand the use of smart objects - that is “objects connected in order to provide seamless communication and contextual services”- enables the collection, transmission, and processing of huge amounts of Data; on the other hand, it needs to be constantly protected. These devices have multiple resource-constraints, such as network requirements, hardware limitations or software restrictions, which is an obstacle to the installation of security mechanisms. Due to these difficulties, software designers often overlook the issue of device security and prioritize other aspects of the product, such as performance and energy consumption. That seems like a way to deceive the consumer: The best-ranked tech products on the market cannot guarantee your safeness in the virtual world, and they are sold as they could.
Another factor that weakens Smart Cities’ structure is the lack of regulations. Our Capstone group had the opportunity to interview New School’s Director of Information and online security, David Curry. When asked “how secure is our Data?”, Mr. Curry said: “ In Europe, particularly, and some would say in Latin America, [...] there are very specific laws about when you collect private Data you have to say exactly what is it used for, and you’re not allowed to use it for something you didn’t say you’re going to use it for. In the United States, that’s a little squishy. As for smart cities and that kind of thing, that is a real concern: What kind of Data is being collected by what? Who has access to it? It’s the whole notion of the Internet of Things. ”
Besides not being able to guarantee information security, the smart city system doesn’t make the city accessible to all citizens. In the November edition of Fordham Urban Law Journal, the authors Kelsey Finch and Omer Tene argue that, despite the nature of government’s intentions, services offered by smart cities often impact individuals in a discriminatory way. According to Finch and Tene, that happens because the system automatically favors those used to technological devices. For example, when looking closely at the case of the Street Bump app, which was an initiative aimed to report to Boston’s Public Works Department the location of potholes and road castings, it is possible to affirm that the younger and wealthier areas of the city benefited the most. By that we can infer that people who are less likely to carry smartphones, such as seniors, were indirectly excluded from the perks of such in the same manner others did.

Retrieved from https://www.bu.edu/systems/2014/12/18/boston-is-becoming-a-smart-city-with-eng-support/
This problem appears in other social and infrastructural projects. For instance, take Singapore’s regulated Electronic Road Pricing (ERP) scheme. Once the toll booth system was installed in a single cordon area, dramatic changes in traffic happened. According to the book “Transport Economics”, within few months, the percentage of carpooling with less than four passengers dropped from 48 to 21, while the use of public transportation rose from 41 to 62 percent. Despite that, the average number of cars during rush hours also declined, but the traffic after ERP’s functional hours peaked. What these numbers show, in fact, is that those who could not afford the extra fee were indirectly prevented from accessing some parts of the city. As we can see, technology itself is not inclusive, and often perpetuate the status quo.

Retrieved from https://www.lta.gov.sg/content/ltaweb/en/roads-and-motoring/managing-traffic-and-congestion/electronic-road-pricing-erp.html
3. Governance vulnerabilities in Smart Cities and how it affects individual liberties
The complete eradication of privacy in Smart Cities by the government is also a risk to the current democratic system. By exchanging our information for security and practicality, we allow the government to not only know about us but also to profile us and even forecast our actions. In her article, " Legislating Privacy: Technology, Social Values, and Public Policy", Priscilla M. Regan, Professor at George Mason University, writes about the implications of new technologies in Public Policy. According to Regan, while the use of digital media devices by enterprises is usually classified as an invasion of privacy, it usually makes the organization even more powerful over individuals. That is, the online information turns into a new source of mass control, once that by accessing it, they can know one's history, activities, and proclivities.
In this scenario, minorities are groups of special interest. Historically underrepresented in public matters and often the target of authoritarian measures, this part of the population is more exposed than any other. One key factor to explain this is society’s tendency to generalize. Although the United States of America Civil Rights Act states that “All persons shall be entitled to the full and equal enjoyment of the goods, services, facilities, and privileges, advantages, and accommodations of any place of public accommodation, as defined in this section, without discrimination or segregation on the ground of race, color, religion, or national origin”[4], ethnicity, nationality, and religion continue to result in stereotypes and hate crimes. Take terrorism as an example. After the 9/11 attacks in New York, more muslims started to be selected for security checks at airports, despite the fact that most of them were peaceful individuals. Simultaneously, less of them were accepted in the U.S. as immigrants and tourists [5]. Statistically speaking, when the numbers prove that there is a profile for people that commit certain crimes, it is almost impossible to assure that there won’t be reprisals to this particular group.
Indeed, as technology makes these kinds of web intelligence acts evident, it also broadens its scope. In that sense, one concern about the interconnection of databases is shown in the forensic use of DNA. While the use of DNA samples to identify criminals boosts the efficiency of the judicial system, it also makes us question whether this measure leads to wrongful convictions. According to the article “Building a Face, and a Case, on DNA”, some researchers doubt the accuracy of the technology used in the recreation of facial images. The argument is that such techniques could stimulate racial profiling among law enforcement agencies, consequently affecting individual privacy and resulting in a violation the Fourth Amendment, which states: “The right of the people to be secure in their persons, houses, papers, and effects, against unreasonable searches and seizures, shall not be violated, and no warrants shall issue, but upon probable cause, supported by oath or affirmation, and particularly describing the place to be searched, and the persons or things to be seized.”[6]

Retrieved from http://nuffieldbioethics.org/project/bioinformation
Another example of how good ideas can become dangerous is seen in New York City. Recently, the City Hall opened the possibility to its citizens of avoiding bureaucracy when registering to its Supplemental Nutritional Assistance Program through an app called HRA Mobile. Instead of handing documents directly to a social services office, applicants can quickly upload them using the platform. According to Nina Stewart, the reporter behind the New York Times’ headline “Those Needing Food Stamps Find City App Eases the Path”, from March to June 2017, more than a million documents were posted. What is not said in the news, however, is what else these Data can be used for. From mere statistic purposes to profiling people to make use of populist measures, there are unlimited possibilities.
Unfortunately, one of the effects of Big Data usage by the government can be the perpetuation of tyranny. When it comes to an actual vigilance mechanism, the lack of privacy that is characteristic of Smart Cities becomes a dangerous threat to freedom of thought and expression. In the article “The watchers”, the author, Jonathan Shaw, argues that the mere awareness of surveillance reshapes people's behavior. This happens because, once you know you are constantly being watched, you tend to be more careful in your actions. According to the text, many governments use this kind of self-censorship to perpetuate its values. One example of this comes from China. By basing its system in 24/7 vigilance and rigorous repression, the Chinese government manages to keep its population following the rules. The understanding behind this approach is that, in the words of Bruce Schneider, one of the experts working in the cybersecurity program at Kennedy School’s Belfer Center, “if you don’t know where the line is, and the penalty for crossing it is severe, you will stay far away from it.”
In smart cities, surveillance is a vivid reality. Both New York and London have special departments to deal with the information gathered from security cameras - the Department of Information Technology and Telecommunications (DoITT) and Government Communications Headquarters (CCHQ), respectively. And even not so developed cities seem to be heading in the same direction. In the online article “The truth about smart cities: ‘In the end, they will destroy democracy'”, Steven Poole mentions Rio de Janeiro’s center of operations. In Poole’s view, “One only has to look at the hi-tech nerve center that IBM built for Rio de Janeiro to see this Nineteen Eighty-Four-style vision already alarmingly realized. It is festooned with screens like a Nasa Mission Control for the city.” The journalist also highlights what Anthony Townsend writes about the building in “Smart Cities: Big Data, Civic Hackers, and the Quest for a New Utopia”: “What began as a tool to predict rain and manage flood response morphed into a high-precision control panel for the entire city.” They both make use of a quote of Rio’s mayor, Eduardo Paes, when he affirms that “The operations center allows us to have people looking into every corner of the city, 24 hours a day, seven days a week.”

Rio’s Center of Operatios (Centro de Operações da Prefeitura do Rio). Retrieved from http://www.metropolismag.com/cities/big-data-big-questions-data-smart-cities/
4. Conclusion
To sum up, although Smart Cities seem to be a strong tendency for the future, they still must overcome many issues. The matter of whether technology should influence in policy-making – and more importantly, remain under the realm of already rich and powerful institutions such as governments – has to be addressed in the next years. In that sense, awareness of the population over the matter needs to increase, and is, therefore, one of the goals of this paper.
In the original online survey conducted by this Capstone group, the subjects were asked to briefly tell us about their background with social media. But we included an extra question. By the end of the form, we simply put “What is Big Data?” as an optional part. From the 779 responses, we obtained only 65 answers to this particular inquiry. And even between these few, many included variations of “I don’t know.” The outcome of the process described was clarifying, even though it was somewhat expected. Living immerse in a technological environment, we understand that the loss of privacy often seems natural and that concepts like Big Data are not really discussed. What surprised us, however, was the unwillingness of people to find more about it. Most of the participants didn’t even try to google the term, they just jumped the question. And that is worrying.
Translated from Portuguese: “ Have you ever heard of Big Data?” In red, “no”; in blue, “yes”; and in orange, “maybe”.
So, the best way to address the privacy issue is to invest in ways to inform the population about it. Once we are all aware of the complexity of Smart Cities and understand the possible consequences of it, we can demand our governments to be more transparent and to formulate concrete online privacy policies. Anyway, the future is uncertain, but it is possible to minimize its risks.
References (in order of appearance):
Hall, E. (2000). The Vision of a Smart City. Retrieved from: https://ntl.bts.gov/lib/14000/14800/14834/DE2001773961.pdf
Chen, W. & Wellman, B. (2004). The Global Digital Divide. IT&Society (1) 19. [1]
Duggan, M. & Brenner, J. (2013). The Demographics of Social Media Users – 2012. Pew Research Center. 2. [2]
Smith, A. (2013). Smartphone ownership – 2013 Update. Pew Research Center. 2. [3]
Chauhan, S.; et al (2016) Addressing Big Data challenges in smart cities: a systematic literature review. The Journal for Policy, Regulation and Strategy for Telecommunications, Information and Media. 2, 2-5.
Popescul, D. & Radu, L. (2016). Data Security in Smart Cities: Challenges and Solutions. Informatica Economica. 30.
Finch, K. & Tene, O. (2013). Fordham urban Law Journal. 41. 1602-1604.
Oum Hoon, T.; et al. (1999). Harwood Academic Publishers. 289.
Regan, P. (1995). Legislating Privacy: Technology, Social Values, and Public Policy. University of North Carolina Press. 74-75.
The United States Civil Rights Act (1965). Retrieved from https://www.ourdocuments.gov/doc.php?flash=false&doc=97&page=transcript [4]
Abbas (2007); Croucher & Cronn-Mills (2011); Gonzàlez, Verkuyten, Weesie, & Poppe (2008). [5]
Pollack, A. (February, 2015). Building a Face, and a Case, on DNA. New York Times: D1
Retrieved from https://www.law.cornell.edu/constitution/fourth_amendment [6]
Stewart, N. (2017). Those Needing Food Stamps Find City App Eases the Path. The New York Times. Published on July 25th, 2017.
Shaw, J. (2017). The Watchers. Harvard Magazine. 119 (3), 56.
Poole, S. (2017). Retrieved from https://www.theguardian.com/cities/2014/dec/17/truth-smart-city-destroy-democracy-urban-thinkers-buzzphrase [7].
1 note
·
View note
Photo

Researching cybersurveillance, I stumbled upon the Citizen Lab, and subsequently upon Deibert’s book, Black Code. First book to have read on Kindle, and there’s irony in this, as the more I read, the more data I produced to be collected and analyzed.
A few of the main ideas: To start with, code is law. As Marshall McLuhan postulated that the medium is the message and Harold Innis showed the bias of communications, we must understand that instructions encoded in software regulate what we can do. Second, a recent change is the movement away from searching the WWW to a push notifications environment where „information is delivered to us” through apps. Third, while in the beginning the internet seemed like a free place, hard to regulate, right now, many countries use censorship and block Twitter, Facebook, Youtube, etc. Internet censorship went from being regulated – like usual things – through law, to being regulated through code and software, and responsibility is put directly on the service providers. For example, China has a particular way of doing this: it sends back to the user an error message, as if the content itself doesn’t exist (Google found a way around this, suggesting users alternate spellings). We must begin to understand and connect the dots, as users and as citizens: the internet is international, but its cables are everywhere, its central nodes are everywhere – but mostly around the US – and the devices we use are from specific nations – bending to specific national laws. From a lawless place, it has became a place of many, many laws. Fourth, the future is at least partly out of the West’s hands. The growing populations of the rest of the world will have access to the net, along with living in increasing inequality due to climate change and capitalism’s mechanism, so the question Deibert asks is, what kind of web will they craft? As the author shows, in some countries governments outsource to extra-legal intervention groups to deal with unrurly citizens. Coming back to corporations, Google has started issuing transparency reports, showing the number of requests it has received from governments to censor or remove content, and highlighting those it complied with or turned down (most requests are „other requests”, not issued through a court order). Most companies don’t tell users if their data is asked for by the government. In 2002 and 2004, Chinese government requested information on two dissidents from Yahoo!, who complied. When being sued by the families in the US, the company testified that it was following local law. Skype, as well, uses content filtering for China, and can be intercepted, although it promises end to end encryption. After 9/11, a key point in the cybersurveillance debate, governments felt entitled to more and more of citizen’s information, creating the false tradeoff: privacy vs security. Human Rights Watch found that the UN passed several resolutions urging member states to pass laws that expand government powers to „investigate, arrest, detain, and prosecute individuals at the expense of due process”. With enough data, a Minority Report future isn’t just dystopian fiction anymore – politically inclined individuals can be monitored before they do anything. Researcher Chris Soghoian pointed out that some companies even charge fees for „lawful access”, with automated process. Cybercrime is real, and just like most crime, its structure is knotted in complicated patterns and networks – many „cyberweapons” (spying software, malware for breaking in, or just hiring a black hat to hack someone) are cheap and easy to buy on the internet, and, as Deibert puts it, how can the West condemn the Syrian Electronic Army when it openly markets computer network attack products at trade shows? Besides, when cyberweapons are perceived as clean, there might be „strong pressures to adopt military over diplomatic solutions”. Technology is multi-puroposed, and the same is used for surveillance of dangerous targets or of peace activists. Hacking used to have a more positive value – „of experimentation and exploration of limits and possibilities”. Technology can be seen not as a thing, but as a craft, inherently political. In the context of our constant connectedness, the increasing restrictions on cyberspace „are alarming”. The closing off of hardware and software and putting on copyright or other laws to diminish access to them are not only barriers to our freedoms, but ultimately to our security as well. The Electronic Frontier Foundation has found laws (in debate – Article 3 of DAAIS in Europe) that limit the publishing of research on security flaws. The denial of access to knowledge is increasing, together with the tools to dismantle it. One solution could take the form of a distributed model: mixture of multiple actors with governance roles, division of control with cooperation and consent, and restraint. Without humans „cyberspace would not exist”. Deibert pushes for a position of joint custodianship: we either degrade cyberspace, or we extend it. The responsibility is inter-generational.
I also finished Program or be programmed by Rushkoff. It’s a kind of manifesto for the digital age, with ten main “commandments”, which I quite enjoyed - an easy read, fast and recommended for anyone interested in what it means to live online. Rushkoff is a character, writing that “instead of optimizing our machines for humanity ... we are optimizing humans for machinery”. The base for the ten commands are the biases inherent in the technology we use. First, ‘do not always be on’, as machines live beyond time, from decision to decision, while we live in the present, continuously flowing, so, “by becoming “always on”, we surrender time to a technology that knows and needs no such thing”. Second, ‘live in person’, be local, be there, where you are - technology is biased towards distance, non-space, and scaling. Third, ‘you may always choose none of the above’, as technology draws lines that are too simple, categorizing or binary through our lives, we can refuse all options, or label freely, with tags. Fourth, ‘you are never completely right’, because, “thanks to its first three biases, digital technology encourages us to make decisions, make them in a hurry, and make them about things we’ve never seen ourselves up close”. It is “biased towards a reduction of complexity”. Rushkoff stresses that we should opt for a world in which we learn about our technology, not a world in which it learns about us. Fifth, ‘one size does not fit all’, because this hyper-abstracted model of internet business doesn’t work for smaller start-ups. Sixth, ‘be yourself’, because while anonymity can protect you, it can also make people behave irresponsibly, facilitating angry and revengeful mobs. Seventh, ‘do not sell your friends’, exposes the internet’s bias towards connection rather than content, and how businesses are making money off it. Eighth, ‘tell the truth’, “because this will increase our value to others”, and besides, lies don’t last long. Ninth, ‘share, don’t steal’, shows how our belief in open sharing has lead to the current business model based on ads, and how we should support the work we consume directly. Tenth, and most importantly, ‘program or be programmed’, because if you don’t understand the inner workings, or at least the superficial biases of the technology you use, it will bias you towards certain things, and you’ll never know why.
When I find the time, I plunge into Haruki Murakami’s short story collection, Men without Women - a gift from my cousin. I re-read the first story, which I hear a few years ago at a “Vocea cititorului” meeting - “Drive my car”. This time, I enjoyed it more. I guess I read the book with a kind of nostalgia, but also detachment. Murakami used to be a favorite of mine in high school, and although I’ve always sensed his novels are far better than his short stories, I have a feeling now I wouldn’t like those as much as I did back then. Men without women is a collection of stories about exactly this - lonely men, left by women in one way or another. I think they’re a bit like writing exercises, in which Murakami tries this and that, typical characters and settings of his, on jazz or Beatles music. None of them contain anything too surreal, maybe just a smokey atmosphere. “Yesterday” is about the narrator’s relationship with his peculiar friend and his girlfriend, “The independent Organ” is about a doctor that is constantly in romantic relationships, for short time and without engagement, with married women, “Sheherezade” contains a woman taking care of a man who can’t go out for some mysterious reason and telling him stories of her youth, “Kino” is about a man whose wife cheats on him so he leaves and opens a bar, “Samsa in love” is, well, a bug turned into a man, and “Men without women” is the narrative of a man who gets a phone call about the death of a love from his youth. I most liked “Kino”, for its emotional, fantastic ending, and “Samsa in love”, because it’s such a nice stretch of the imagination, and kind of lovely all in all.
#summer reads#cyberspace#cybersurveillance#finished book#kindle#citizen lab#black code#deibert#rushkoff#murakami
0 notes
Text
How Twitter took on Trump's Twitter bot army—and won
Image: Bob Al-Greene/Mashable
By Louise Matsakis2017-02-02 18:42:04 UTC
Just around dawn, on Tuesday, at 6:21 a.m., President Donald Trump tweeted.
He mocked Congressional Minority Leader Nancy Pelosi and New York Senator Chuck Schumer's protests against his recent executive order on immigration, which banned citizens from Muslim-majority countries from entering the United States.
Nancy Pelosi and Fake Tears Chuck Schumer held a rally at the steps of The Supreme Court and mic did not work (a mess)-just like Dem party!
— Donald J. Trump (@realDonaldTrump) January 31, 2017
Over 39,000 tweets were sent in response to the president’s words. But for many users, it was a thread mocking Trump—from New Yorker and television writer Bess Kalb—that soared to the top of his replies.
She pointed out how Trump failed to criticize the reason lawmakers protested, and instead, focused on calling them names.
Kalb’s responses—and the ones by other writers, activists, comedians, and media companies who tweet at the president—are getting seen because of a quiet change Twitter made to the way that replies work on mobile, back in November.
Two months ago, if you looked at the same Tweet on mobile, you would've never seen Kalb’s tweets. After all, she sent her first reply more than three hours after the president first sent his.
It didn’t matter: Kalb’s dissident tweets became some of the most seen and replied to on that thread, an experience she’s likely used to.
Since the election, Kalb's tweeted at the president dozens of times. Her sarcastic responses frequently find their way to the top of Trump’s replies, aided by a sizable fan club cheering her on. (When contacted, Kalb declined to speak on the matter for this story.)
Before November, on mobile (where the majority of Twitter activity happens) replies appeared in chronological order. It gave users thirsty to be seen by Trump’s followers an incentive to write computer scripts capable of auto-replying to Trump’s tweets far faster than anybody thumbing away at a mobile keyboard ever could.
If you got there first, your tweet was prominently displayed right below Trump's, garnering hundreds of thousands—if not millions—of views.
Over the course of his campaign, Trump’s replies and Twitter as a whole ballooned with fake Trump supporters. The fake "bot" accounts were made to look like genuine citizens, but were actually created en masse, and ran on software programs.
It's not clear who's behind the bots, though researchers speculated they might be the creation of individual tech-savvy voters, or political action committees (PACs) in support of the president. For their part, the Trump campaign's denied that they created or paid for the bots.
It's been estimated that up to 80 percent of Trump’s Twitter traffic is perpetuated by bots, singing his praises, hawking Trump-related merchandise. The most famous item they sold was a now-infamous "Liberal Tears" mug.
Tolulope Edionwe at The Outline uncovered that the mugs were a scam, with many customers never receiving their much-desired liberal-shaming swag.
Still, the mug's become so ubiquitous that Slate figured out how long a liberal would actually have to cry to fill such a cup. That notoriety, in other words, is also a testament to how valuable being high up in Trump’s mentions can be.
As Edionwe noticed, though, the mug seems to have all but vanished from the top of Trump’s replies.
While that’s at least partially due to the fact that creating automated spambots violates Twitter’s terms of service, the bots more likely disappeared because it no longer matters if you’re the first to reply to a Trump tweet on mobile.
When asked about the matter, a Twitter spokesperson told us: what now determines whether a reply is featured is if the person is in your network (meaning you follow them, or know someone who follows them) or if the original tweet's author has replied.
The number of likes and responses a tweet get also likely factors in, at least according to the experience of users who've reached the top of Trump's replies.
Some users also said they think being a user who's been verified by Twitter, blue checkmark and all, might help. It'd make sense: verified accounts are almost never bots, and thus, are safer to bump toward the top.
Twitter’s change has since substantially raised the visibility of legitimate people's responses in mentions, as opposed to bots and spammers. They're making their way into Trump's replies to promote their own organizations, and to influence the president's followers for the first time.
"I couldn’t be happier that normal humans are getting heard," David G. McAfee, the founder of The Party of Reason and Progress, (PORP) an organization dedicated to promoting reason and sound decision-making in politics said.
"My entire philosophy revolves around exposing all ideas to scrutiny, and that doesn't work if anonymous twitter bots are dominating the conversation with a pro-Trump agenda," McAfee said.
McAfee cleverly started replying to Trump in order to promote PORP’s values, and his tweets are frequently displayed right below the president's. His approach is free, of course, and arguably much more effective than purchasing advertisements.
Image: Screenshot/twitter
"We would normally do this via other more traditional channels, but this isn’t a traditional president. We have to take the fight to Twitter because it’s the only way to guarantee we reach him and his supporters," McAfee explained.
Media companies have also noticed how valuable it can be to score a prominent spot right below Trump's words. "It's like digital town hall sometimes," Katrine Dermody, the Director of Social Media for Fusion said.
"A lot of people were surprised with the election results," she explained. "“We started asking ourselves more critically how we could expand beyond what people call the echo chamber of media."
One way was to tweet articles and videos at the president that contradict or disagree with what he says, in the hopes of reaching people who agree with Trump, or don't know much about what he says. "We had to figure out how to rebut what he was saying," Dermody said.
Trump's replies will continue to be an important space in a media landscape that's increasingly fractured along partisan lines. It's one of the only places left where you can find people who voted both ways.
Regular citizens like Justin Hendrix, a New York City resident that works in tech and media, have also seen their responses hit a chord with Trump's followers.
"As someone who disagrees vehemently with this person [Trump] I feel it’s valuable to respond to him," Hendrix said. "It’s like a media channel, and you can literally get right in there."
He admitted that although tweeting at the president "sometimes seems to have the effect of spreading information," it also means having to deal with the wrath of Trump's supporters.
Every user we spoke to that's tried to reach the top of Trump’s replies said that they're the victim of relentless abuse. They’ve received death threats, been doxxed, and have discovered malicious impersonators pretending to be them on other sites like 4chan.
Still, for some, the abuse is worth weathering.
"People say Trump doesn't read the replies," Hendrix said, "In my heart I don't believe that."
"I can't imagine that he doesn't occasionally scroll through those responses."
BONUS: Here's a clip of Kellyanne Conway's previous (and mercifully brief) career in stand-up comedy
Let's block ads! (Why?)
- Repost from: mashable Post
0 notes
Text
COVID-19 outbreak tracker. Interview with Cotiviti’s Jordan Bazinsky
Cotiviti EVP, Jordan Bazinsky
Healthcare analytics company Cotiviti has launched a COVID-19 tracker to predict infection outbreaks based on insurance claims data. It says its model has a high degree of accuracy and is useful for health ecosystem players and government authorities that need to decide where to allocate resources.
In this interview, I asked Cotiviti EVP, Jordan Bazinksy to explain.
What are the needs for COVID-19 tracking in the US?
To make decisions on how to best protect their citizens and employees while also limiting harm to their economies, policymakers and business leaders need accurate and timely data about how far COVID-19 has spread in their communities. But unfortunately, we’ve seen that in too many areas, COVID-19 tests are not being administered to everyone who should receive one due to lack of resources. Therefore, in the absence of this testing, we sought to develop a model that would help to forecast which geographic areas were likely to see a substantial number of COVID-19 cases using other factors such as flu testing and flu diagnoses.
How could this model impact/shift the U.S. approach to combating this health crisis (at private, federal, and state/local levels)?
We’re already seeing many states and local governments move to re-open their economies even as COVID-19 testing remains scarce. While this is understandable given the economic devastation this pandemic has caused for many, these decisions should be guided by accurate data to protect those who are most vulnerable. We hope this approach will encourage everyone to proceed with the utmost caution as they make decisions that could have far-reaching impacts.
What is the unmet need you saw at Cotiviti? And what approach are you taking to address it?
This project originated the same day the WHO declared COVID-19 a pandemic. We assembled a team to explore how Cotiviti could help respond to the outbreak by using our Caspian Insights data and analytics platform. The team began examining leading indicators such as telemedicine, rapid flu testing, and chest x-rays, that can help predict potential areas of concern before COVID-19 testing takes place.
The primary deficiency we are aiming to solve is the widespread lack of COVID-19 testing resources, which has left states unable to confirm the true impact and reach of the virus in their communities. Instead, our approach relies on other leading indicators of COVID-19, such as flu testing and diagnosis. By comparing current flu testing data seen in the CPT codes processed through our systems against confirmed flu diagnoses seen in ICD-10 codes, we can spot significant discrepancies that could indicate a “hidden outbreak” is occurring.
What are the use cases? Are people using it for purposes beyond what you originally envisioned?
Our focus is on helping all healthcare stakeholders to prepare for what’s ahead given the unpredictable nature of this virus. As healthcare organizations seek to gain more data and use that data to extract meaningful insights, we are offering this resource to supplement their existing resources.
We have fielded questions recently regarding how this data may support contact tracing. We have also had inquiries from retailers wanting to use this data to inform decisions about when to open stores in various parts of the country. While neither of these were uses we initially envisioned, they reflect the need from all stakeholders to have access to reliable, timely COVID-19 data.
Now that states are looking at loosening their social distancing mandates and re-opening previously shuttered businesses, Cotiviti has unveiled a second map that shows which states have seen a downward trend of influenza-like illness and COVID-like syndromic cases to aid in decision making. It will be critical to maintain active surveillance of any early spikes that may be predictive of COVID-19 resurgence.
How does it compare with other initiatives, like the Johns Hopkins model?
While Johns Hopkins has assembled an excellent, informative COVID-19 dashboard that aggregates data to track cases around the world and show trends over time, it specifically focuses on confirmed cases, which can only be identified through COVID-19 testing. Similar dashboards and tracking tools released by other organizations are also limited to tracking confirmed cases. Our approach looks at where there are a significant population of unconfirmed but likely cases to help forecast the hidden impact of this outbreak.
What are the data sources? How did Cotiviti ensure data quality and accuracy?
Our data source is Cotiviti’s Caspian Insights data and analytics platform—the engine behind our healthcare analytics solutions—which processes millions of claims per day and comprises longitudinal data for more than 130 million Americans. It combines financial and clinical information alongside a multitude of other healthcare data types, such as social determinants of health, medical records, pharmacy, dental, and lab information to give health plans and providers actionable information at their fingertips.
We have both automated data quality standards and rigorous processes to ensure data quality and accuracy at all levels. For example, healthcare data is known to be inconsistent across disparate systems—the same individual might be listed by different names in the different data feeds we receive. To overcome this challenge, we leverage a unique combination of probabilistic and deterministic models to establish linkages between data sources, while also ensuring the data is de-identified. Finally, we have a strong organizational commitment to quality at all levels of Cotiviti.
How accurate are the predictions? How is that changing?
We made our first forecast on March 12, and 80 percent of our predictions were realized by March 22. We have continued to maintain this level of accuracy while refining our data and algorithms, and we continue to see indications of potential hidden outbreak in certain states. However, as COVID-19 testing becomes more available, we know that hidden outbreaks will diminish and transition to confirmed outbreaks. Therefore, our team is preparing to shift to a more sophisticated modeling approach that identifies “COVID-like illness” based on the unique care pattern of COVID-19 that can be seen in the claim, clinical, prescription, and lab data for a patient. This approach will allow continued monitoring of the virus until a vaccine is available.
By healthcare business consultant David E. Williams, president of Health Business Group.
The post COVID-19 outbreak tracker. Interview with Cotiviti’s Jordan Bazinsky appeared first on Health Business Group.
0 notes
Text
New UK Points-Based Immigration System
New UK The Government has laid out its plans for the new UK points-based immigration system which is to apply from 1 January 2021.
In a policy paper published on 18 February 2020, the Government confirms that the new system will apply to both EU and non-EU citizens in the same way.
The changes outlined in the paper centre on economic and work immigration only, and do not impact existing routes for students, families or asylum seekers. Further changes in these areas may transpire as the Government seeks to “transform the way in which all migrants come to the UK to work, study, visit or join their family”.
A new UK points-based system
The Government’s overriding vision is “to reduce overall levels of migration and give top priority to those with the highest skills and the greatest talents”.
The changes will affect anyone coming to the UK from 2021 to work.
EU free movement will end on 31 December 2020. Nationals of EEA countries looking to come to the UK to work from 1st January 2021 must attain the required points and apply for a visa under the new immigration system. EU citizens currently in the UK are required to register under the EU settlement scheme to secure their immigration status.
For UK employers, the impact of the reforms cannot be underestimated. The new system has been designed to move the UK economy away from a “reliance on cheap labour from Europe”, and will drive fundamental shifts in how workforce needs are met across sectors and skill levels.
While some measures are to be introduced to ease the transition for scientists, graduates, NHS workers and those in the agricultural sector, the Government has stated these will be short term. The message to employers is that they have no choice but to “adjust” to the new world.
With changes to the definition and scope of skilled workers and removal of any lower-skilled work visa, there is a lot for employers to absorb and respond to, and a fast-approaching deadline of 1 January 2021 to be ready by.
We summarise the changes employers need to be aware of.
UK work visas
The new points-based system will offer immigration routes for highly skilled workers, skilled workers, students and other specialists such as global leaders and innovators.
Visitors will in most cases be able to come to the UK for up to six months without a visa, but will not have the right to work. Those who come to the UK as a visitor will need to leave the country before making an application to another route.
Points requirements
Non-UK nationals will have to attain 70 points to qualify for a UK work visa.
There are three mandatory requirements: having an offer of a job with a sponsored employer; having a job at the appropriate skill level; speaking English to the required level. These total 50 points, and applicants must then make up their points to the 70 points threshold from the remaining characteristics, which include salary level, shortage occupation and education qualification.
Requirement Tradeable? Points Offer of job by approved sponsor No 20 Job at appropriate skill level No 20 Speaks English at required level No 10 Salary of £20,480 (minimum) – £23,039 Yes Points Salary of £23,040 – £25,599 Yes Points Salary of £25,600 or above Yes Points Job in a shortage occupation (as designated by the MAC) Yes Points Education qualification: PhD in subject relevant to the job Yes Points Education qualification: PhD in a STEM subject relevant to the job Yes Points
The policy paper also indicated that points allocations will remain subject to review and may be “refined” to improve flexibility, such as including new characteristics or amending tradeable attributes.
Skilled workers
Under the plans, the definition of skilled workers is being expanded and the skill level reduced from level 6 (degree) to level 3 (A-level), ie those educated to A-level/Scottish Highers-equivalent standard and not just graduate level, as is currently the case.
In a welcome move, there will no longer be a cap on the number of skilled worker visas that can be issued to qualifying individuals.
The minimum salary threshold for skilled workers is to be lowered from £30,000 per annum to £25,600, and in some cases £20,480 for shortage occupations, which currently include nurses, civil engineers and individuals with a PhD relevant to a specific job.
The Migration Advisory Committee is being commissioned by the Government to devise the shortage occupation list for the new skilled worker route.
Low skilled workers
There will be no work visas for general low-skilled or temporary workers under the new points-based immigration system. This means roles that do not require A-level qualifications or higher will not qualify under the new rules.
This will be hugely problematic for UK employers that rely heavily on ‘low-skilled’ and/or low paid workers such as farms, restaurants, hotels and care homes.
While sectors such as health & social care, agriculture, construction, retail and leisure have been vocal in their concerns about cutting off the supply of low skilled migrant labour, the Government has stated its position with the new rules is to shift the economy away from a dependence on unskilled European workers, in favour of the domestic labour market and innovation, automation and technological solutions.
This will be a painful transition, particularly for employers reliant on human resources to perform critical work deemed unskilled under the new system.
The Government has said the EU settlement scheme has provided employers with some reprieve in allowing EU citizens who have applied to stay in the UK to help meet short-term labour demands.
In addition, it has also referred to additional sector-focused schemes to alleviate labour shortages, for example seasonal agricultural workers and youth mobility programmes (currently under Tier 5) allowing 20,000 young people to come to the UK each year.
Affected employers will, however, need to take action now to reassess and remodel their recruitment strategies and workforce planning to take them into 2021 and beyond.
DM comment
So how much is going to change with the new points-based immigration system?
The Government has worked hard to distance the new rules from the existing points-based system for work visas; the policy paper avoids referring to ‘tiers’ as per the current system and the routes themselves also differ, with the skills level being lowered.
The biggest shock to the system – both economically, culturally and socially – will be the end of EU free movement coupled with no general UK work visa for lower skilled roles.
We expect the Government may get creative in providing sector or role-specific concessions, and may well use such schemes as leverage in trade negotiations.
The functional aspects of the new system, from the detail so far released, appear not to be too dissimilar to how the current UK points-based system for work visas operates. In any event, the reform certainly does not go as far as the Australian-style system which affords considerably more flexibility for work visa applicants in attaining the required points.
Practical detail still eludes, however, in many areas, with the policy paper stating further detail on the points-based system is to be released in due course.
Frustratingly, this leaves very little time for employers to digest the new rules and to take action in readiness for the new system going live on 1st January 2021.
If you are concerned about the impact of the changes on your company and its ability to meet its workforce needs from 2021, DavidsonMorris can help. As employer solutions lawyers, we bring together specialist UK immigration lawyers with experts in employment, HR and global mobility to provide advice, strategy and implementation support across all your people requirements.
UK points-based immigration system FAQs
How does a points based immigration system work?
Individuals wanting to come to the UK work will need to apply for a visa by showing they have enough points to meet the requirements of the immigration route. Work visa applicants will need a minimum of 70 points, from a combination of mandatory and tradeable characteristics.
Does the UK have a points based immigration system?
The UK currently operates a points-based system applicable to non-EEA workers. From 1 January 2021, a new immigration system will be introduced requiring all non-UK nationals to apply for a visa to work in the UK. To be eligible for a UK work visa, applicants will need to attain a minimum of 70 points.
Can I move to the UK without a job?
Free movement rules still apply to EU nationals until 31 December 2020. After this date, all EU citizens and non-EEA nationals will have to apply for permission to the work in the UK under an appropriate immigration route. Under the new points-based immigration system, applicants will need to be sponsored by an employer, in addition to meeting other requirements to attain the required 7- points. Unsponsored routes are also available eg Global Talent visa, for individuals possessing specific skills or level of standing within their profession.
How can DavidsonMorris help with the new points-based immigration system?
DavidsonMorris’ specialists bring together expertise in UK immigration law, employment, HR and global mobility. We are working with companies across all areas of the UK economy to advise on the implications of the new points-based system on recruitment and workforce planning. We also advise individuals on immigration routes and applications, alleviating the stress and improving your prospects of securing a visa.
{ "@context": "https://schema.org", "@type": "FAQPage", "mainEntity": [ { "@type": "Question", "name": "How does a points based immigration system work?", "acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "text": "Individuals wanting to come to the UK work will need to apply for a visa by showing they have enough points to meet the requirements of the immigration route. Work visa applicants will need a minimum of 70 points, from a combination of mandatory and tradeable characteristics. " } } , { "@type": "Question", "name": "Does the UK have a points based immigration system?", "acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "text": "The UK currently operates a points-based system applicable to non-EEA workers. From 1 January 2021, a new immigration system will be introduced requiring all non-UK nationals to apply for a visa to work in the UK. To be eligible for a UK work visa, applicants will need to attain a minimum of 70 points. " } } , { "@type": "Question", "name": "Can I move to the UK without a job?", "acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "text": "Free movement rules still apply to EU nationals until 31 December 2020. After this date, all EU citizens and non-EEA nationals will have to apply for permission to the work in the UK under an appropriate immigration route. Under the new points-based immigration system, applicants will need to be sponsored by an employer, in addition to meeting other requirements to attain the required 7- points. Unsponsored routes are also available eg Global Talent visa, for individuals possessing specific skills or level of standing within their profession. " } } , { "@type": "Question", "name": "How can DavidsonMorris help with the new points-based immigration system? ", "acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "text": "DavidsonMorris’ specialists bring together expertise in UK immigration law, employment, HR and global mobility. We are working with companies across all areas of the UK economy to advise on the implications of the new points-based system on recruitment and workforce planning. We also advise individuals on immigration routes and applications, alleviating the stress and improving your prospects of securing a visa. " } } ] }
The full policy paper can be found here.
Last updated: 20 February 2020
New UK Points-Based Immigration System published first on https://ordergcmsnotescanada.tumblr.com/
0 notes
Text
Self Driving Cars and Auto Accidents – Top Houston Car Crash Lawyers
Self Driving Cars and Auto Accidents – Top Houston Car Crash Lawyers
youtube
Many men and women continue to be suspicious of the life-threatening potential that self-driving cars have, pointing to the fatalities that involve this kind of vehicle.
Whether it is because of driving, driving under the influence, road anger, substance abuse, drowsy driving, speeding or only a bad decision at the incorrect moment, most severe car accidents are brought on by a human error. According to an NHTSA study, up to 94% of crashes are brought on by drivers, the remainder of them being credited to the vehicles, surroundings or other conditions.
These statistics sparkle an exciting debate, especially now that self-driving cars are being analyzed in real life conditions and driving together regular vehicles. If we want to anticipate a future with much more autonomous cars, could that mean that the data will change quite shortly?
A lot of men and women continue to be suspicious of their life-saving potential that self-driving cars have, pointing to the fatalities that involve this kind of vehicle. However, even if autonomous cars do wreck, as it turns out, human error is frequently to blame. Human operators are yet to pass the full responsibilities to their machinery, and self-driving car manufacturers constantly advocate taking over in the event of a critical situation
Among the most recent mishaps and possibly the most famous one is that the Tesla crash. The car had been driving in fully autonomous mode, killing its driver on the scene. Self-driven cars aren’t equipped to avoid any scenario fully, and also the board computer instructs the human operator to take over when the road conditions are too unpredictable. Also, as a method of precaution, the driver must keep his hands on the steering wheel and observe the road, even when the car is fully autonomous.
However, the analysis showed that the driver didn’t hold the wheel and ignored the board computer warnings that instructed him to take over. Simply put, even this mishap is a consequence of human error.
The issue of safety and self-driving cars is not new. Governments around the world are fighting to keep up and establish legal frameworks that would maintain security standards.
Back in April 2018, Tesla was removed from the official evaluation into the Autopilot deadly crash in Mountain View, California, for violating its legal arrangement with the NTSB by publicly commenting on the continuing investigation. Tesla stated it voluntarily left the investigation, but the NTSB published an official announcement denying this fact.
According to the Society of Automotive Engineers automation 6-level framework, the Autopilot matches to the level 2 category. The machine can manage speed and steering under some conditions, but still needs drivers to be careful and require control.
Autopilot functions also fit this description, as it alerts drivers any time they take their hands off the steering wheel. In reaction to this crash, Tesla reinforced this fact and stated many times that their system depends on the driver who is responsible for everyone’s security, including his own. However, if you look at their advertisements, the Autopilot seems to perform higher than the usual level 2 automation, leaving many people wondering that side of the story is accurate.
Nonetheless, it’s quite probable that even if the present amount of Autopilot doesn’t allow for a completely automated driving experience, Tesla and other businesses are currently at work to make that occur. If it does, it will most likely make an extremely debatable task at the legislative end.
We are living exciting times as technology is taking over and making our lives more comfortable than ever before in several ways. At precisely the same time, this requires new regulations and legislation. It is going to probably be some time until there will be autonomous cars on the street. Until then, the rules we have now can not cover most of the situations involving self-driving cars.
In the rare cases when technology fails, who’d be responsible for the damage: the car producer or the software creator? It’s still uncertain how to approach such a change of paradigm.
Many people are wondering if autonomous cars may detect the nuances in situations involving individuals. For instance, will a self-driving vehicle be able to detect a pedestrian who is consumed by their mobile phone, or a kid who’s unaware of their surroundings?
These questions will probably dominate the new era of the autonomous car and form the future of road safety and driving expertise.
It is best to consult an experienced Houston car accident attorney to get help in seeking the claim. Call Houston car crash lawyers RJ Alexander Law, PLLC at (832) 458-1756 to request a free case evaluation.
Houston Car Accident Glove Compartment Guide
var cpm_language = {"lng":"en"};var cpm_api_key = 'AIzaSyDFbtrFxyyzE-4VAR8QQTYd1ZDuXlR45vw'; var cpm_global = cpm_global || {}; cpm_global['cpm_P7uxT2'] = {}; cpm_global['cpm_P7uxT2']['zoom'] = 10; cpm_global['cpm_P7uxT2']['dynamic_zoom'] = false; cpm_global['cpm_P7uxT2']['markers'] = new Array(); cpm_global['cpm_P7uxT2']['display'] = 'map'; cpm_global['cpm_P7uxT2']['drag_map'] = true; cpm_global['cpm_P7uxT2']['highlight_class'] = 'cpm_highlight'; cpm_global['cpm_P7uxT2']['marker_title'] = 'title'; cpm_global['cpm_P7uxT2']['highlight'] = true; cpm_global['cpm_P7uxT2']['type'] = 'ROADMAP'; cpm_global['cpm_P7uxT2']['show_window'] = true; cpm_global['cpm_P7uxT2']['show_default'] = true; cpm_global['cpm_P7uxT2']['mousewheel'] = true; cpm_global['cpm_P7uxT2']['zoompancontrol'] = true; cpm_global['cpm_P7uxT2']['fullscreencontrol'] = true; cpm_global['cpm_P7uxT2']['typecontrol'] = true; cpm_global['cpm_P7uxT2']['streetviewcontrol'] = true; cpm_global['cpm_P7uxT2']['trafficlayer'] = true;
codepeople-post-map require JavaScript
Houston Car Accident Lawyer Injury Resources
Ankle Injury From Car Accident
Annular Disc Tear
Anosmia from Automobile Accident
Arthritis After Car Accident
Brain Injury from Car Accident
Brain Injury in Child
Broken Arm Accident
Broken Bones in Car Accident
Broken Femur Car Accident
Broken Nose in Car Accident
Broken Rib from Car Accident
Burn Victim Car Accident
Car Accident Back Injury
Car Accident Brain Hemorrhage
Car Accident Death
Car Accident Eye Injury
Car Accident Head Injury
Car Accident Nerve Damage
Car Accident Paralysis
Car Accident Spine Injury
Car Accident Wrist Injury
Car Accident Wrongful Death
Catastrophic Injury
Cervical Spine Injury
Chronic Neck Injury After Car Accident
Chronic Pain After Accident
Collarbone Pain After Car Accident
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome After Car Accident
Connective Tissue Injury
Crush Injury Car Accident
Delayed Pain After Car Accident
Diffuse Axonal Injury
Emotional Pain and Suffering
Face Injury Accident
Fatal Car Accident
Foot Injury Car Accident
Headache after Car Accident
Heart Damage after Car Accident
Herniated Disc Car Accident
Impacted Fracture
Internal Bleeding Due to Car Accident
Internal Injuries from Car Accident
Joint Injury Car Accident
Leg Injuries from Car Accident
Mental Distress During Accident
Multiple Spinal Fractures
Neck Fusion from Car Accident
Neck Injuries after Car Accident
Pain and Suffering Car Accident
Permanent Injury Car Accident
Pre Existing Injury Auto Accident
PTSD After Car Accident
Scarring Cause by Car Accident
Shoulder Injury from Car Accident
Soft Tissue Injury Car Accident
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage from Car Accident
Tibia Fibula Fracture
Tinnitus Car Accident
Traumatic Brain Injury from Car Accident
Unborn Baby Injured in a Car Accident
Vocal Cord Damage
Whiplash from Car Accident
Houston Car Crash Lawyers – Driver Involved in Accident Resources
Aggressive Driving
Buzzed Driving
Carpool Car Accident
Child in Car Accident
Designated Driver in Car Accident
Distracted Driver Accident
Drowsy Driving Accident
Drugged Driving Accident
Drunk Driving Accident
Elderly Car Accident
Employee Car Accident
Family Member Car Accident
Friend Driving Car Accident
Lease Car Accident
Line of Duty Accident
Low Speed Car Accident
Obesity and Car Accidents
Passenger in Car Accident
Pedestrian Accident
Phantom Vehicle Accident
Pregnant Car Accident
Reckless Driving Accident
Rental Car Accident
Seat Belt Accident
Senior Citizen Driving Accident
Speeding Car Accident
Teen Car Accident
Houston Car Accident Lawyer – Type of Car Accident Resources
Head-on Collision
Hit and Run Accident
Fender Bender
Low Impact Car Accident
Low Speed Car Accident
Side Swipe Car Accident
Side Impact Car Accident
Rear End Car Accident
Roll Over Car Accident
T-Bone Car Accident
Houston Car Accident Lawyer – Location of Your Car Accident Resources
Accident at Intersection
Bridge Car Accident
Car Accident Close to Home
Highway Accident
Parking Lot Accident
Railroad Crossing Accident
School Zone Accident
Stop Sign Accident
Traffic Accident
Houston Car Crash Lawyers – Car Accident Cause Resources
Car Backing Up Accident
Chain Reaction Car Accident
DWI Accident
Eating and Driving Car Accident
Left Turn Car Accident
Negligent Car Accident
Night Time Car Accident
Partial Fault Car Accident
Passing Car Accident
Red Light Car Accident
Right Hand Turn Car Accident
Right of Way Car Accident
Selfie While Driving Accident
Teen Driver Car Accident
Texting While Driving Car Accident
Wrong Way Driving Accident
Houston Car Accident Lawyer Lawsuit Resources
Accident Reconstruction
Chose Correct Venue
Contingency Fee Arrangement
Defense Appeals to Jury Verdict
Deposition
Documenting a Car Accident
Expert Testimony
Importance of Credibility
Obtaining a Police Report
Obtaining Medical Records
Police Report
Protect Your Financial Interest
Protect Your Rights
Proving Alcohol Intoxication
Role of a Jury
Stranded on the Highway
Sympathetic Plaintiff
Traffic Control Devices
Houston Car Accident Lawyer Resources
Boating Accident Lawyer Houston
Bus Accident Lawyer Houston
Company Car Auto Accident Lawyer Houston
Bike Accident Lawyer Houston
Detached Trailer Accident Lawyer Houston
Dog Bite Lawyer Houston
Dump Truck Accident Lawyer Houston
Emergency Vehicle Accident Lawyer Houston
Forklift Accident Lawyer Houston
Garbage Truck Accident Lawyer Houston
Lyft Accident Lawyer Houston
Motorcycle Accident Lawyer Houston
Multi-vehicle Accident Lawyer Houston
Non-traffic Related Vehicle Accident Lawyer Houston
Off-road Vehicle Accident Lawyer Houston
Passenger Van Accident Lawyer Houston
Personal Injury Attorney Houston
School Bus Accident Lawyer Houston
Single Vehicle Accident Lawyer Houston
Taxi Accident Lawyer Houston
Test Drive Accident Lawyer Houston
Truck Accident Lawyer Houston
Uber Accident Lawyer Houston
Houston Car Accident Lawyer Insurance Claim Resources
Accident Damages
Accident Injury Claim
Another Person Driving Claim
Auto Accident Claim
Bad Faith Insurance Claim
Car Accident Compensation
Car Accident Medical Bills
Car Accident Medical Restrictions
Car Accident Not Your Fault
Car Accident Occupational Rehab
Car Accident Passenger Claim
Car Accident Punitive Damages
Car Accident Settlement
Car Accident Sudden Medical Emergency
Car Insurance Claim Denial What Next
Car Insurance Liability Limit
Car Insurance Premium
Car Insurance Settlement Offer Too Low
Claim Exceeds Policy Limits
Claim on Behalf of a Minor
Compensation Damage to Car
Future Medical Bills
ICU Insurance Claims
Insurance Claim Totaled Car
Life Care Planner
Loss of Companionship Claim
Loss of Use Claim
Lost Wages Claim From Car Accident
Maximum Medical Improvement
No Health Insurance in Car Accident
Ongoing Medical Care After Car Accident
Sue for Car Accident
Sue for My Child
Total Loss Claim
Truck Accident Claim
Underinsured Motorist Claim
Uninsured Motorist Claim
Wrongful Death Claim
Houston Car Accident Lawyer Road Accident Resources
I-45 Car Accident Lawyer Houston
I-10 Car Accident Lawyer Houston
I-69 Car Accident Lawyer Houston
610 Loop Car Accident Lawyer Houston
Beltway 8 Car Accident Lawyer Houston
Highway 6 Car Accident Lawyer Houston
US 290 Car Accident Lawyer Houston
US 90 Car Accident Lawyer Houston
US 59 Car Accident Lawyer Houston
SH 249 Car Accident Lawyer Houston
SH 6 Car Accident Lawyer Houston
SH 146 Car Accident Lawyer Houston
SH 99 Car Accident Lawyer Houston
SH 225 Car Accident Lawyer Houston
FM 2920 Car Accident Lawyer Houston
FM 1764 Car Accident Lawyer Houston
FM 518 Car Accident Lawyer Houston
Spur 5 Car Accident Lawyer Houston
Spru 527 Car Accident Lawyer Houston
Spur 330 Car Accident Lawyer Houston
Westpark Tollway Car Accident Lawyer Houston
Hardy Toll Car Accident Lawyer Houston
Fort Bend Tollway Car Accident Lawyer Houston
Sam Houston Tollway Car Accident Lawyer Houston
Bammel North Houston Road Car Accident Lawyer Houston
Clay Road Car Accident Lawyer Houston
Antoine Car Accident Lawyer Houston
Bissonnet Street Car Accident Lawyer Houston
Westheimer Road Car Accident Lawyer Houston
Hardy Road Car Accident Lawyer Houston
W. Little York Car Accident Lawyer Houston
Crosby Freeway Car Accident Lawyer Houston
Gessner Road Car Accident Lawyer Houston
Veterans Memorial Drive Car Accident Lawyer Houston
Main Street Car Accident Lawyer Houston
John F. Kennedy Car Accident Lawyer Houston
Greens Road Car Accident Lawyer Houston
NASA Parkway Car Accident Lawyer Houston
Hammerly Blvd Car Accident Lawyer Houston
Louetta Road Car Accident Lawyer Houston
Pearland Car Accident Lawyer Houston
Tidwell Car Accident Lawyer Houston
Hollister Car Accident Lawyer Houston
Wallisville Car Accident Lawyer Houston
West 42nd Street Car Accident Lawyer Houston
Houston Car Accident Resources
Houston Automobile Accident Attorney
Houston Automobile Accident Lawyer
Houston Auto Wreck Attorney
Houston Auto Injury Lawyer
Houston Auto Crash Lawyer
Houston Accident Lawyer
Houston Auto Crash Attorney
Houston Auto Accident Attorney
Car Accident Lawyer Near Me
Car Accident Lawyer Houston
Houston Galleria Car Accident Lawyer
Rice Village Car Accident Lawyer Houston
Cypress Car Accident Lawyer
Galveston Car Accident Lawyer
Fort Bend Car Accident Lawyer
Jersey Village Car Accident Lawyer
Clear Lake Car Accident Lawyer
Sugar Land Car Accident Lawyer
Humble Car Accident Lawyer
Katy Car Accident Lawyer
Conroe Car Accident Lawyer
Spring Car Accident Lawyer
Houston Car Wreck Lawyer
Houston Car Injury Attorney
Houston Car Wreck Attorney
Houston Car Crash Lawyer
Houston Car Collision Lawyer
Houston Car Accident Attorney
North Houston Car Accident Lawyer
Northwest Houston Car Accident Lawyer
Wrongful Death Houston Car Accident Attorney
Houston Car Accident Death Lawyer
Houston Motor Vehicle Accident Lawyer
Texas Car Accident Lawyer
Harris County Accident Lawyer
Houston Car Injury Lawyer
Houston Car Crash Attorney
Houston Auto Wreck Lawyer
Houston Automobile Crash Lawyer
Houston Auto Injury Attorney
Houston Auto Accident Lawyer
Houston Accident Attorney
Texas City Car Accident Lawyer
League City Car Accident Lawyer
Hempstead Car Accident Lawyer
West Houston Car Accident Lawyer
Pasadena Car Accident Lawyer
Baytown Car Accident Lawyer
Pearland Car Accident Lawyer
Tomball Car Accident Lawyer
The Woodlands Car Accident Lawyer
North Houston Car Accident Lawyer
Accident Lawyer in North Houston
Home Visit Houston Car Accident Lawyer
Houston Energy Corridor Car Accident Lawyer
Downtown Houston Car Accident Lawyer
The post Self Driving Cars and Auto Accidents – Top Houston Car Crash Lawyers appeared first on Houston Car Accident Lawyer.
source https://rjalexanderlaw.com/self-driving-cars-and-auto-accidents-top-houston-car-crash-lawyers/
0 notes