#Ecology Units
Text
The World's Forests Are Doing Much Better Than We Think

You might be surprised to discover... that many of the world’s woodlands are in a surprisingly good condition. The destruction of tropical forests gets so much (justified) attention that we’re at risk of missing how much progress we’re making in cooler climates.
That’s a mistake. The slow recovery of temperate and polar forests won’t be enough to offset global warming, without radical reductions in carbon emissions. Even so, it’s evidence that we’re capable of reversing the damage from the oldest form of human-induced climate change — and can do the same again.
Take England. Forest coverage now is greater than at any time since the Black Death nearly 700 years ago, with some 1.33 million hectares of the country covered in woodlands. The UK as a whole has nearly three times as much forest as it did at the start of the 20th century.
That’s not by a long way the most impressive performance. China’s forests have increased by about 607,000 square kilometers since 1992, a region the size of Ukraine. The European Union has added an area equivalent to Cambodia to its woodlands, while the US and India have together planted forests that would cover Bangladesh in an unbroken canopy of leaves.
Logging in the tropics means that the world as a whole is still losing trees. Brazil alone removed enough woodland since 1992 to counteract all the growth in China, the EU and US put together. Even so, the planet’s forests as a whole may no longer be contributing to the warming of the planet. On net, they probably sucked about 200 million metric tons of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere each year between 2011 and 2020, according to a 2021 study. The CO2 taken up by trees narrowly exceeded the amount released by deforestation. That’s a drop in the ocean next to the 53.8 billion tons of greenhouse gases emitted in 2022 — but it’s a sign that not every climate indicator is pointing toward doom...
More than a quarter of Japan is covered with planted forests that in many cases are so old they’re barely recognized as such. Forest cover reached its lowest extent during World War II, when trees were felled by the million to provide fuel for a resource-poor nation’s war machine. Akita prefecture in the north of Honshu island was so denuded in the early 19th century that it needed to import firewood. These days, its lush woodlands are a major draw for tourists.
It’s a similar picture in Scandinavia and Central Europe, where the spread of forests onto unproductive agricultural land, combined with the decline of wood-based industries and better management of remaining stands, has resulted in extensive regrowth since the mid-20th century. Forests cover about 15% of Denmark, compared to 2% to 3% at the start of the 19th century.
Even tropical deforestation has slowed drastically since the 1990s, possibly because the rise of plantation timber is cutting the need to clear primary forests. Still, political incentives to turn a blind eye to logging, combined with historically high prices for products grown and mined on cleared tropical woodlands such as soybeans, palm oil and nickel, mean that recent gains are fragile.
There’s no cause for complacency in any of this. The carbon benefits from forests aren’t sufficient to offset more than a sliver of our greenhouse pollution. The idea that they’ll be sufficient to cancel out gross emissions and get the world to net zero by the middle of this century depends on extraordinarily optimistic assumptions on both sides of the equation.
Still, we should celebrate our success in slowing a pattern of human deforestation that’s been going on for nearly 100,000 years. Nothing about the damage we do to our planet is inevitable. With effort, it may even be reversible.
-via Bloomburg, January 28, 2024
#deforestation#forest#woodland#tropical rainforest#trees#trees and forests#united states#china#india#denmark#eu#european union#uk#england#climate change#sustainability#logging#environment#ecology#conservation#ecosystem#greenhouse gasses#carbon emissions#climate crisis#climate action#good news#hope
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
This is from last summer (I found it while trying to clean up browser tabs--oops.) Anyway, it's one of many examples of critically endangered species showing an upturn in population with support. The Devils Hole pupfish is particularly imperiled because it is only found in one flooded cavern in Nevada's Amargosa Desert; the species is likely descended from fish that were washed in there by flooding thousands of years ago, and have managed to eke out a living in the hot, oxygen-deficient water ever since.
This is one of the first species ever listed under the U.S. Endangered Species Act. Devils Hole is threatened by groundwater depletion from well drilling, and after the pupfish's ESA listing there were numerous legal battles between conservationists and farmers over water usage. Water levels reached their lowest point in the early 1970s, but have been slowly rising since then.
Scientists are excited because the current wild population (at least as of last fall) is at 263 fish. That's up from just 35 in 2013, the lowest recorded population ever. There are a few hundred more in captivity, being used to breed more young for reintroduction. The hope is that this fall's wild count will break 300, a good sign for the world's most endangered fish.
By the way, THIS is the entirety of the Devils hole pupfish's habitat, the only place in the world where they are found:
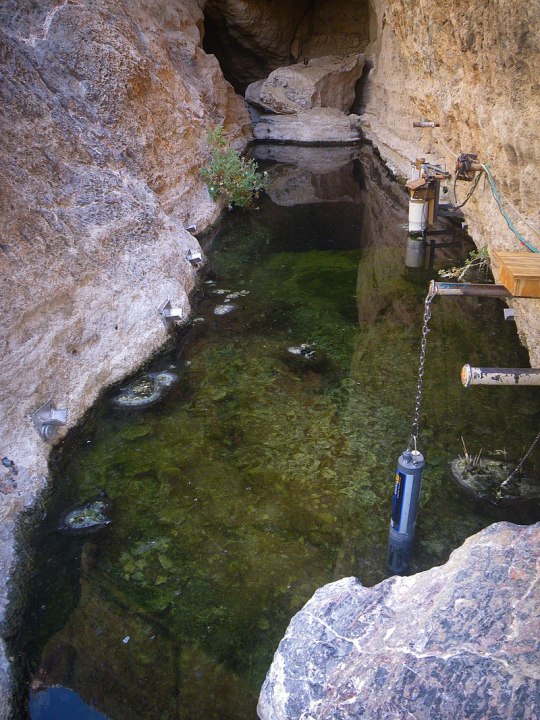

#Devils Hole pupfish#Devils Hole#fish#icthyology#vertebrates#animals#wildlife#endangered species#endangered animals#extinction#nature#ecology#environment#conservation#science#scicomm#Nevada#United States#Endangered Species Act#Endangered Species List
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
It's big, it's strong, its scaly, it's this week's Wet Beast Wednesday topic! An arapaima, also known as a pirarucu or paiche, is any of four species of fish in the genus Arapaima in the order of bony-tongued fish. There is som ongoing debate about the classification of the species, so to keep thing simple, I'm going to use the most common species names of Arapaima gigas (the type species and most well known, and the one with the most confusion about its classification), Arapaima agassizii, Arapaima leptosoma, and Arapaima mapae. Because A. gigas is the most well-studied of the species, unless I say otherwise you can assume everything I say in this post applies to it.

(image: an arapaima)
Arapaimas are bony fish that retain several primitive traits, causing them to sometimes be identified as "living fossils". They are most notable for their size, with A. gigas being a contender for the largest freshwater fish in the world. The maximum recorded size for one was 3.7 meters (10 ft) and 200 kg (400 lbs), but most get to around 2 meters (6.6 ft) long and 200 kg (440 lbs). That average length is decreasing as overfishing of the largest individuals is resulting in a selective pressure for smaller sizes. In addition to their size, they are extremely strong and can move fast if needed. Arapaima are fully capable of leaping out of the water if disturbed or they feel their current pond in unsuitable. Because of their strength, specimens in captivity must be handled with care as they can easy break bones if they slap someone. They live in rivers and lakes in South America, where they are often the top predators.

(image: several anglers with an arapaima)
Arapaimas are obligate air-breathers and will drown if they can't get to the surface to breathe. This is accomplished with a specialized swim bladder. The swim bladder is filled with highly vascularized tissue, letting it act like a lung. This pseudo-lung opens into the mouth using a modified gill arch known as the labyrinth organ. Arapaima gills are too small to sustain them, but they can supplement their oxygen intake with the gills. Juveniles are born exclusively using their gills and transition into air-breathers shortly after hatching. Arapaimas can survive up to a full day out of the water. They typically surface to gulp in air every 15-20 minutes. Breathing makes a loud gulping sound that anglers use to target them.

(image: an arapaima at the surface)
Because of their ability to breathe air, arapaimas are top predators in low-oxygen environments. Non-air breathing fish are forced to slow down in water with low levels of dissolved oxygen as they can't get enough oxygen through their gills. Since Arapaimas breathe air, they can easily chase down lethargic smaller fish. They are especially potent predators during the low season, when water levels lower. A combination of rotting vegetation reducing oxygen levels and ponds getting cut off from rivers and losing a supply of oxygen lets the arapaima reign supreme. Arapaimas are primarily predators that feed on smaller fish, though they will hunt other types of animals and eat fruits and seeds. Even land animals aren't safe as arapaimas have been known to launch themselves out of the water to catch animals near the shore. A combination of sharp teeth and their bony tongues are used to debilitate prey.

(image: an arapaima with its mouth open)
Not content with powerleveling their attack stat, arapaimas also have excellent defense. Their scales have been compared to bullet proof vests. Each has a hard, mineralized outer layer over multiple layers of collagen fibers. These layers are all oriented at an angle to each other to provide extra strength. This orientation of layers is called a Bouligand-type arrangement and is similar to how plywood is assembled. The harder outer layers and flexible inner layers work together to allow for both strength and flexibility. These scales help provide protection form large predators such as caiman and small threats like biting piranha. They also like provide protection from other arapaima, as the fish are aggressive and will fight each other.

(image: a diagram showing the composition of arapaima scales. source)
You probably wouldn't expect a swimming tank of an animal to be a good parent, but you'd be wrong. Arapaimas work together in mated pairs to build nests for their eggs, then cooperate to guard the nest. Once the eggs hatch, the male will practice mouth brooding, keeping his young safe in his mouth. The female will also help by patrolling the area around the male to ward off predators. They secrete pheromones from their heads to ensure the young don't swim too far away. Eggs are laid either in in the low season or as water levels are starting to rise, ensuring that the young become independent during the high season.

(Image: baby arapaimas)
Arapaima are classified as "data deficient" by the IUCN. This means there isn't enough data to properly assess their conservation needs. They are known to be threatened by overfishing. Arapaima make up a large part of the diet of many South American populations. Habitat loss and pollution are also believed to threaten them. They have been introduced to many areas out of their native range and are an invasive species in placed like Florida, Malaysia, and India.

Does anyone else remember these cards? (image: the arapaima card from Weird n' Wild Creatures)
#wet beast wednesday#fishblr#fish#biology#zoology#ecology#animals#aquatic biology#animal facts#absolute unit#arapaima#pirarucu#paiche
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
In the wake of North America's recent solar eclipse, another historic natural event is on the horizon. From late April through June 2024, the largest brood of 13-year cicadas, known as Brood XIX, will co-emerge with a midwestern brood of 17-year cicadas, Brood XIII.
This event will affect 17 states, from Maryland west to Iowa and south into Arkansas, Alabama and northern Georgia, the Carolinas, Virginia and Maryland. A co-emergence like this of two specific broods with different life cycles happens only once every 221 years. The last time these two groups emerged together was in 1803, when Thomas Jefferson was president.
Continue Reading.
185 notes
·
View notes
Text
Russia is bad for the environment




Russians always found ways to slaughter Ukrainians through the whole history. And famines were one of the most popular methods for Russia.
Please don't ignore our fighting, keep spreading our voices, and donate to our army and combat medics (savelife.in.ua, prytulafoundation.org, Serhii Sternenko, hospitallers.life, ptahy.vidchui.org, and u24.gov.ua).
#ukraine#genocide#stop the genocide#russia is a terrorist state#russo ukrainian war#russian invasion of ukraine#russia#ecology#ecocide#united states#united nations#politics#colonial violence#famine#russian war crimes#war crimes#stand with ukraine#arm ukraine#standwithukraine#text post#text#reading#important#signal boost#український tumblr#укртамблер#український блог#укртумбочка#український тамблер#україна
208 notes
·
View notes
Text
Being Ukrainian means fitting your whole life into one backpack.
Kherson. Nova Kakhovka dam. Destroyed by russians. Ecocide, terrorism... Call it whatever you want. I know that right now, there are thousands of Ukrainians that are drowning and hoping for help. But, the part of the Kherson region is still under occupation. And russians don't let them evacuate. The other part, where volunteers, soldiers and civilians are trying to evacuate other people and animals is sheiling by russians.
More than 85 villages will go underwater. Would you happen to know what else it means? People under occupation, people whom the russian occupation authorities imprisoned and tortured in specially designated premises, and dungeons, as was the case in Bucha, Irpin, Izyum and many other cities of Ukraine, are now underwater. Their bodies will be there now until the water goes.
Numbers of endangered species of animals and plants in the South of Ukraine will disappear. And you know what the UN and Red Cross doing? One is celebrating the day of the russian language the other is writing an article about how hard moscow works on the development of humanitarian law. Have any eco-activist, organisations written a word about it? Nothing. No one is helping. No one cares.
Yesterday, I received a letter from an eco-community. About saving bees. Funny things? Ukraine is one of the largest honey-exporting countries. But no one cares what's going on here. Because you all tried to be so good at words, but never at actions. It's easier to close your eyes and tolerate russia. Read their books, listen to their music, learn and celebrate the day of their language. It's easier to block a publication from Ukrainian because they said something bad about big and dear russia, but it's hard to share and speak about all the horrible things they are doing here. So hypocrisy.
I won't be easy in my words, while people here are drowning, being killed and tortured and the whole world is silent because they are scared. I won't ever share a post about plastic, straws and other shit, while there is russia, that can destroy a dam, cause a flood, destroy thousands of lives, kill animals and plants, and get away with it.
I don't believe in this world and in this society. You all have already forgiven russia.





#ukrainian post#ukraine#ukrainian tumblr#post#russia ukraine war#ukranian#russia is a terrorist state#nova kakhovka dam#russian war crimes#kakhovka hpp#ecocide#ecology#world#flood#terrorism tw#red cross#the united nations#organisation#hypocrisy#war crimes#russia war#war#humanity#people#animals#stand with ukraine#fypツ#not all russians#kherson#nova kahovka
169 notes
·
View notes
Text
While on vacation I went to a nature center and they had a trail that followed a path of a tornado that had hit the center a few years ago.
The center had turned the destroyed area in the path of the tornado into an educational trail that teaches about succession :D


Also, take a look at THIS:

You can see where the tornado literally twisted this mature tree like a straw wrapper, and this was only an F1 tornado. *intense fear*
#education#sci comm level 100#succession#gardening#goes in gardening tag bc plonts#plants#trees#ecology#south georgia#southeastern united states
745 notes
·
View notes
Note
Have you thought about collabing with the creators of Clangen?
It would be cool? But from what I know, Clangen really tries to stick close to canon, moreso than I do. They wouldn't be looking to add my clan culture expansions or spirituality overhauls.
So like, sure, if they/a mod maker approached me with an idea or request. Otherwise I'm not sure what we'd collaborate about?
#I want to translate the name file into Clanmew at some point#But another large difference between BB and Clangen is ecological accuracy#Which is something I very intentionally set out to fix#Clangen takes place in a bizarro world mix of the us and uk like canon#The United Statedoms of Englerica#And more specifically canon takes place in the... California/Appalachia/Pennines.#Mostly Appalachia but they mentioned a 'Mountain Vole' in DOTC which is from Cali-fucken-Fornia iirc#Unless it was an accident and they meant ALPINE vole or pygmy vole...#Digressing please do not take any of this as a dig or insult about the ecology stuff. I 10000% understand why they don't do what I do#More than anyone in the world I understand why they would not be super obsessed with ecology#There's absolutely no replacement for coyotes in England. And there is no Gar.#So you can't even do The Garfield Joke if you do what I do#I reintroduced boars so there would be some accurate danger that isn't just offleash dogs#I'm proud of the research I do but it is a lot of work! Work they're already doing on coding a workable game.#Bone babble
69 notes
·
View notes
Text

#animal death#dead animal#deer#white tailed deer#cervids#cervidae#nature#nature photography#naturalist#prairie#vulture culture#grasses#ecology#wildlife biology#wildlife biologist#ecologist#midwest#north America#united states#north american wildlife#mine#bones#skeleton#dead
134 notes
·
View notes
Text

Ecology of the Coyote in Yellowstone, by the National Park Service, 1940
I've only skim read this, but I love it. It focuses primarily on their dietary habits. I really love these older bulletins and want more of them, I know of one other coyote one I really desire but haven't been able to find for sale.
#my library#ecology of the coyote in yellowstone#national park service#united states department of the interior#fauna of the national parks of the united states#coyote book#coyote#ecology#1940#1940s
47 notes
·
View notes
Text
"When considering the great victories of America’s conservationists, we tend to think of the sights and landscapes emblematic of the West, but there’s also a rich history of acknowledging the value of the wetlands of America’s south.
These include such vibrant ecosystems as the Everglades, the Great Dismal Swamp, the floodplains of the Congaree River, and “America’s Amazon” also known as the “Land Between the Rivers”—recently preserved forever thanks to generous donors and work by the Nature Conservancy (TNC).
With what the TNC described as an “unprecedented gift,” 8,000 acres of pristine wetlands where the Alabama and Tombigbee Rivers join, known as the Mobile Delta, were purchased for the purpose of conservation for $15 million. The owners chose to sell to TNC rather than to the timber industry which planned to log in the location.
“This is one of the most important conservation victories that we’ve ever been a part of,” said Mitch Reid, state director for The Nature Conservancy in Alabama.
The area is filled with oxbow lakes, creeks, and swamps alongside the rivers, and they’re home to so many species that it ranks as one of the most biodiverse ecosystems on Earth, such that Reid often jokes that while it has rightfully earned the moniker “America’s Amazon” the Amazon should seriously consider using the moniker “South America’s Mobile.”
“This tract represents the largest remaining block of land that we can protect in the Mobile-Tensaw Delta. First and foremost, TNC is doing this work for our fellow Alabamians who rightly pride themselves on their relationship with the outdoors,” said Reid, who told Advance Local that it can connect with other protected lands to the north, in an area called the Red Hills.
“Conservation lands in the Delta positions it as an anchor in a corridor of protected lands stretching from the Gulf of Mexico to the Appalachian Mountains and has long been a priority in TNC’s ongoing efforts to establish resilient and connected landscapes across the region.”
At the moment, no management plan has been sketched out, but TNC believes it must allow the public to use it for recreation as much as possible.
The money for the purchase was provided by a government grant and a generous, anonymous donor, along with $5.2 million from the Holdfast Collective—the conservation funding body of Patagonia outfitters."
youtube
Video via Mobile Bay National Estuary Program, August 7, 2020
Article via Good News Network, February 14, 2024
#united states#alabama#estuary#wetlands#swamp#river#environment#environmental issues#conservation#video#biodiversity#american south#ecosystems#ecology#conservation news#wildlife conservation#ecosystem#conservation efforts#good news#hope#forest#swampco#re#Youtube
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Good. These things are horrifying for a whole host of reasons. First, it's mind-boggling that the USDA kills as much native wildlife as they do; last year's report showed that they killed over 56,000 (no that's not a typo) coyotes intentionally, over 5,000 of which died via cyanide M-44s. The report lists hundreds of other species, many native, intentionally killed by the USDA, plus a number that were unintentionally killed as well, for a total of 383,731 native wild animals killed by the USDA in 2022.
But M-44s also don't discriminate. Any animal that disturbs one--a pet, livestock, an endangered animal, or a human being--can get a deadly dose of cyanide. They're baited so that animals manipulate them with their mouths, meaning they literally get a mouthful of cyanide.
While the US Forest Service still uses M-44s, they will no longer be used on any Department of the Interior land. Here's hoping the Forest Service will follow suit.
#wildlife#wild animals#animal cruelty#animal welfare#cw animal death#animal death#nature#animals#coyotes#cyanide#poison#environment#conservation#ecology#United States
128 notes
·
View notes
Text
I haven't covered any pinniped pals for Wet Beast Wednesday yet, so for my first one I'm going big. Really big. Elephant seal big. Elephant seals are not only the largest of all pinnipeds, they are the largest of all carnivorans and the largest marine mammals that aren't cetaceans. There are two species: northern (Mirounga angustirostris) and southern (Mirounga leonina), with the southern species being the larger of the two.

AAAAAAAAAAAAAHHHHHHHHH! (image: an elephant seal bellowing)
Elephant seals are true seals (as opposed to sea lions and walruses), meaning they lack external ears and their hind legs have fused into a sort of pseudo-flipper that allows for highly efficient swimming but is of little use when maneuvering on land. While it is common among pinnipeds for males to be larger than females, elephant seals exaggerated that with one of the most extreme size differences between sexes. Females of both species range from around 350 to 900 kg (880 to 1,980 lbs) and 2.5 to 3.6 m (8.2 to 11.8 ft) in length. Male northern seals average between 1,500 to 2,300 kg (3,300 to 5,100 lbs) and 4-5 m (13-16 ft) while southern males break the scale at 1,500 to 3,700 kg (3,300 to 8,200 lbs) and 4.2 to 5.8 m (14 - 19 ft). The southern species has the largest mass difference between sexes of any mammal, with the males averaging 5-6 times the weight of the females.

(image: male and female elephant seals chillaxing on a beach)
In addition to the size difference, the other major form of sexual dimorphism is that the male has his nose elongated into a proboscis. This snout serves two major functions: it amplifies the roars of the male allowing him to be remarkably loud and it traps and reabsorbs moisture when he exhales. This is important as the seals do not eat or drink when on land and recapturing moisture lets him stay hydrated.
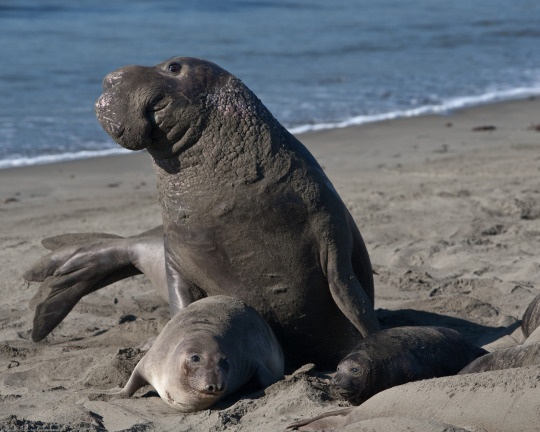

(image: a male[top], female [bottom left] and juvenile [bottom right] northern elephant seal)
Seals are adapted to spend the vast majority of their lives in the water and elephant seals are no different. They spend around 80% of their lives in the water and have many adaptations to aid in their lifestyle. Like most marine mammals, they have a thick layer of fatty blubber that preserves heat in cold water, reduces drag, and provides buoyancy. Like other seals, they can slow their heartbeats and redirect blood flow to the core of their body to avoid losing heat. Another seal adaptation is that veins returning blood to the heart grow near arteries carrying blood from the heart. This allows the cold returning blood to leech some heat from the arteries to avoid cooling down the body's core. They have a lot of blood to store oxygen, allowing for long dives. Elephant seals dive deep (averaging 300-600 m but occasionally much deeper) when searching for food. Females typically go on deeper but shorter dives than males. They can hold their breath for over 100 minutes, longer than nay non-cetacean mammal.. Their eyes are highly adapted to low-light conditions and their whiskers can sense motion in the water, both things that aid in finding food. Elephant seals are very opportunistic predators and will eat a large variety of fish and cephalopods.

(image: a female elephant seal swimming)
The 20% of time not spent at sea is mostly taken up by two yearly periods: the molting and breeding seasons. In both cases, the seal will haul out onto the beach and will not eat or drink until it has finished. Molting season lasts about a month and usually occurs in summer. Elephant seals undergo what are called catastrophic molts, where they not only shed and regrow their fur but their outer layer of skin. During the regrowth of their skin, extra blood has to be directed toward it. In the water, this would cause too much heat loss, so it must be done on land. The skin sheds in large patches and not all at once, resulting in molting seals having a ragged appearance.
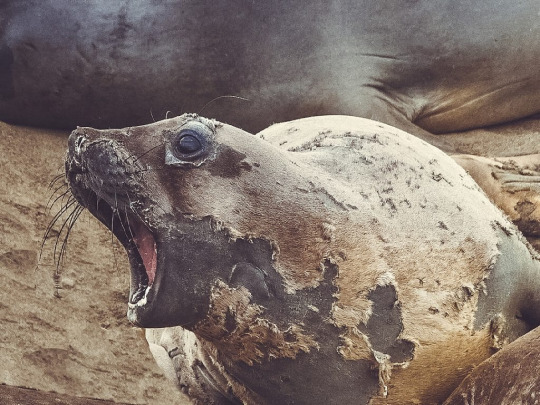

(image: a seal mid-molt)
The longer and more famous time on land is breeding season. In early spring, males will arrive on beaches and fight each other for dominance. In time, a few alpha males will claim most of the beach. These fights last even after the females arrive. Fights are very dramatic, involving posing and bellowing. If one male does not submit, they will fight by biting and slapping each other with their heads. Fights are rarely fatal, but are frequently bloody. Males have thicker skin on their chests to protect them during fights. Alpha males claim the right to mate with the females. Other males are forced to the outskirts of the beach, where they try to mate while the alpha is distracted. Some males will become betas, who help the alpha patrol his territory and drive off competing males. These betas will often try to mate while the alpha is distracted. Only the largest and strongest males can claim alpha status, and usually late in life when they have grown to their largest. After the females arrive, mothers will give birth to their pups. After birth, the female uses unique vocalizations so her pup can always recognize her. They nurse pups for up to 28 days while the males continue to fight. Elephant seal milk is extremely high in fat content, with up to 50% of the milk being fat, compared to 3.5% for cows. Some mothers may adopt the pups of others, especially if their own pup died before weaning. Weaning is very abrupt, after which the females will mate and the adults will return to the sea. The pups are left on land for up to 10 weeks, where they must learn how to swim and hunt while subsisting off the energy stores they built up while nursing. Juvenile mortality is high, with up to 50% of pups dying before reaching maturity. Adults can lose a third of their weight during breeding season.
youtube
(video: a clip from the BBC documentary Seven World One Planet about males fighting fro dominance. warning: there is blood)

(image: a mother seal and pup)
A few pups are known as super weaners because they can grow exceptionally large during nursing. This is usually due to the pup being adopted by an additional female and therefore getting an extra dose of milk or it will steal milk from another pup. In a few cases, the mothers will just wait longer before weaning for unknown reasons. Average pups weigh between 110 and 160 kg (250 - 350 lbs) at weaning while super weaners can weigh up to 270 kg (600 lbs). They can put on so much blubber their ability to move becomes impaired. Super weaners are rarely observed again after leaving the rookery. It has been speculated that their excess blubber makes them exceptionally buoyant, reducing their ability to dive and making it harder to feed, leading to increased mortality.
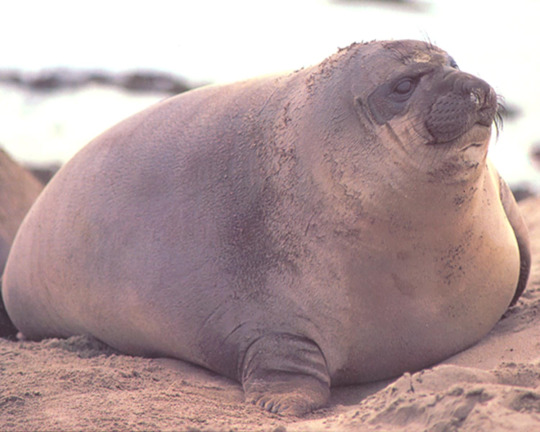

(image: a chonky baby super weaner)
Both species of elephant seal were hunted to near-extinction in the 19th century as their blubber could be used to make exceptionally high-quality oil. After the hunting period ended, their numbers increased to the point both species are classified as least concern by the IUCN, though their populations have never risen to pre-hunting numbers and many areas that were historically occupied are now vacant. Genetic bottlenecks in both species has led to an increase in diseases and birth defects. El Nino is known to have a negative effect on northern seals by drastically increasing pup mortality, so this year was probably a bad one. One major limiting factor in their population growth is a lack of beaches to haul out on and many beaches they use are now protected by local laws or as UNESCO World Heritage Sites.

(Gif: a female versus a car. Round 1, fight!)
#wet beast wednesday#marine biology#biology#zoology#ecology#elephant seal#marine mammals#seal#seals#absolute unit#animal facts#cw animals fighting#chonky#Youtube
277 notes
·
View notes
Text
World hits streak of record temperatures as UN warns of 'climate hell'
https://www.reuters.com/sustainability/world-hits-streak-record-temperatures-un-warns-climate-hell-2024-06-05/
#earth#world#record#temperature#climate change#global warming#united nations#warning#alert#alerta#ausgov#politas#auspol#tasgov#taspol#australia#fuck neoliberals#neoliberal capitalism#anthony albanese#albanese government#climate crisis#climate action#climate justice#climate solutions#climate and environment#ecology#climate catastrophe#climate collapse#climate chaos#environmental
5 notes
·
View notes
Text

Chapter 3--Penguin Family Values: the nature of planetary environmental reproductive justice by Noel Sturgeon
Sturgeon’s article opens in a discussion of the award-winning nature documentary The March of the Penguins and how the animal was simultaneously adopted by “right-wing fundamentalist Christians in the United States as an inspiring example of monogamy, traditional Christian family values, and intelligent design” & was becoming “a symbol of the naturalness of gay marriage” to others(102)—Tango Makes Three (a children’s book based on ‘gay’ penguins at the Central Park Zoo who raised an egg—naturalness and success of gay marriage for raising children). “Queer families turn out to be just the same as straight families. […] they’re determined by nature” 117
Another example of penguins and reproduction in media—Happy Feet—singing/dancing and themes of normalcy. Homosociality and references of homosexuality but “always flavored with the kind of liberal tolerance covering over ultimate rejection that is thin veneer for heterosexist anxiety”. And ultimately, the main character’s differences are settled when he ends up ‘happily ever after’ in a heterosexual and successfully reproductive nuclear family.
“Penguins (along with polar bears) became popular symbols of what we would lose to global warming. Relatively invisible in the public cultural arena in contrast, were the growing and unequal effects of the pollution of our atmosphere on marginalized human beings such as indigenous peoples in the Arctic regions, who are struggling to preserve their cultures and societies in the face of rapid climate change” (102).
The author uses the term “Environmental Reproductive Justice” as a way of connecting environmental issues with social justice issues. This builds off insights by feminists of color and Global South feminists who tend to argue for the term ‘reproductive justice’ over ‘reproductive rights’—not just the ability to control pregnancy but also the need for childcare, health care, prenatal care, freedom from coerced sterilization, healthy environments, clean air, food and water, adequate housing, etc (103)
Living environmentalism-reproduction as necessarily about the intertwined reproduction of the environment, communities, and individuals (Giovanna Di Chiro, 2008)
How we reproduce—whether we are reproducing people, families, cultures, societies, and/or the planet—is politicized in several layered and contradictory ways (103). Gender and sexuality are often ignored as part of explanations when examining contemporary political and economic systems. I.e. when exploring the contradictions inherent in the right-wing—“far right conservatives have been able to mobilize low-income people on their side even though the political and economic policies working-class people are asked to support are contrary to their own class interests” (frank 2004)—gender roles and reproductive labor are not oft explored as ways they've been able to inspire feelings of fear, anger, oppression=abortion, ‘vulgarity’ in popular culture, homosexuality (I would also add transsexuality/transgenderism now), family values…all centered around gender expectations, driven by changes in economic practices in a globalizing economy (104)
“The politics of gender are often both the politics of reproductions and the politics of production—the intertwined ways that people produce more people, manage bringing up children, figure out how to do the work at home at the same time as the work that brings in a paycheck, decide how and where to buy food, clothing, shelter, and transportation, take care of elders, and create and maintain all of the social institutions that surround this work. And all of this is central to whether or not our ways of living cause environmental degradation.” (104)

“Heterosexual culture achieves much of its metacultural intelligibility through the ideologies and institutions of intimacy…First, its conventional spaces presuppose a structural differentiation of ‘personal life’ from work, politics, and the public sphere. Second, the normativity of heterosexual culture links intimacy only to the institutions of personal life, making them the privileged institutions of social reproduction, the accumulation and transfer of capital, and self-development…intimate life is the endlessly cited elsewhere of political public discourse, a promised haven that distracts citizens from the unequal conditions of their political and economic lives, consoles them for the damaged humanity of mass society, and shames them for any divergence between their lives and the imitate sphere that is alleged to be simple personhood” (Berlant and Warner, 1998 553) (105)
Heterosexist arguments are binary (homosexuality vs heterosexuality, ‘opposites attract’, ‘men are from Mars, women are from Venus’) and normative (heterosexuality is better, more natural, more moral, more normal, more wholesome, better for parenting). So social institutions are structured in a way that privileges heterosexual sexual practices and solidifies what a family should look like; who does the domestic work; how women/men should act, look, behave; how life should be maintained (producing heterosexuality) (105) These heterosexist arguments are usually about preserving and reproducing particular forms of family, social power, and economic practice.
Pro-life/pro-family—not just about preventing abortions, but about the reproduction of a certain historically and culturally specific idealized family form; father is authority; mother is helpmate and childcare provider; several children living in a framework of Christian, religious, patriarchal, heterosexual, nationalistic, U.S. and nuclear—right-wing. “The family acts as a miniature welfare state, modulating consumption, curbing excess desires, improvising child care and providing social security—[…]it is the dreamworld conveyed in the…’serious’ media…where the conservative variant of the neoliberal utopia is attributed to the biologically fixed ‘nature’ of desire (Lancaster 2003, 336) (106)
Fear of allowing women (especially young women, especially women of color, especially poor women—ESPECIALLY young, poor, women of color) have access to choices and support for their own reproductive decisions and thus forming families that do not adhere to the right-wing model…..divinely created=natural, normal so all else is unnatural and opposite of divine

This particular family model especially when located in a suburban, consumer economy dependent on extremes of global inequality, might be an important origin of our present environmental problems. (107)
Nuclear family model relies on women’s unpaid domestic labor (childcare, eldercare), using nonrenewable fuel-intensive transportation such as cars and long-distance shipping of consumer products, women as shoppers/consumers—these stores are part of globalized production and distribution chains dependent on exploitation of the labor of the poor (global south and often women) (107)
Environmental health is centrally important to reproduction as well as production (107) Reproduction is a materialist and a planetary issue—all reproduction comes with consequences for the global environment, economies and social practices.
Planetary reproduction and environmental reproductive justice
Deconstructing Polar Opposites: Endangered Peoples, Endangered Cultures, Endangered Natures
Missing from the conversation is the immediate threat to numerous groups of people especially vulnerable to climate change by reason of geography, poverty, or political discrimination (documentaries that use images of penguins and polar bears to dramatize the consequences of melting polar ice fail to mention the impact on Arctic Indigenous peoples…)
Indigenous people are not penguins, endangered tribal cultures are not endangered species—racist and the parallel trope of the ‘disappearing Indian’ discounts and obscures the struggle of real indigenous peoples to exist and successfully transform their cultures strategically for survival. Arctic indigenous tribes may be threatened by climate change but they are resilient and experienced in resisting threats to their people… (119)
“We’ve adapted in the past, which is why we are still here” (Chickaloon Grand Chief Gary Harrison, 2005)
Arctic Indigenous peoples have been addressing the problem and suggesting solutions for many years because they knew the threats they faced were early warnings for the people around the world.
“All of this will have a profound impact on the viability of indigenous cultures throughout the North and further afield. Everything is connected in nature; what happens in Alaska will affect all other places of the world as a cascading effect, as scientists call it, will occur” (Cochran 2007) (120)

The possibility of losing indigenous knowledge along with the animals and ice….Subsistence living is part of cultural survival and an important method for keeping the world in balance (Harry Bower Jr. 121) The environment is part of a larger universe with moral and cultural aspects that are maintained by the practices of indigenous peoples who have lived on the land for thousands of years (121)
The expansive knowledge [indigenous people have] about sustainable practices, whether it was supported by scientific expertise or traditional experience, was knowledge that arose from a particular way of life, one that needed to be respected and maintained. It was not knowledge gained from the mystical identity of being Ecological Indians, but was rather sophisticated information needed now by all those, Indigenous or not, trying to understand and address climate change (121)
The reproduction of industrialized economic systems, particularly by the United States and other Western countries, has consequences for planetary ecological workings on a global scale as well as on the scale of communities, families, and species, determining the ability of animals, families and cultures to reproduce in healthy and sustainable ways (122)
Too Many People, Too Few Penguins

The concept of over-reproduction and over population are inherently problematic. Human reproduction (especially that of the poor, immigrants, and people in the Global South), is depicted as a major environmental problem…some environmentalists argue against having children at all.
The “Other” population is portrayed as the central problem environmentally and socially whereas “Our” society (developed industrialized societies) are made invisible.
We encourage ‘other’ societies to engage in family planning, education for women, birth control access among other things while ignoring how the US often prioritizes abstinence only programs rather than birth control for their own population, among failing to provide support for women when they do become pregnant (this article was written prior to roe v wade being overturned. But I bet that would be in this article now…)

“When environmentalists sound warnings about overpopulation, they are usually expressing fears over the reproduction of (poor) nonwhite people, not of white people, whose populations in all Western countries are in decline (but whose consumption habits generally are not). Calls for educational fixes to inform ‘populations’ about why they should want to bear fewer children advance an imperialist cultural agenda that demands that nonwhite people adopt the cultural, social, and economic practices and systems of organization dominant in Western countries (e.g. the prototypical nuclear family), while blaming the ‘foolishness’ of Third World men and women (since the solution is Western education) for environmental degradation. (Gosine 2005, 80-81) (126)
Environmental Justice Family Values

“We are not outside the earth looking down upon it. Instead, we are inside specific biosystems and complex relationships with other biological entities; we impact and are impacted by the interrelationships of those entities. Responsibility to these ecological niches, networks and dynamics can be brought into view only if we understand ourselves as animals among other animals, with varied sexualities, complicated family relationships, complex political systems, and multiple desires. Perhaps we are peculiar animals with astounding abilities, but we are still part of an interconnected world and thus answerable to it” (129)
#queer ecologies: sex nature politics desire#penguins#arctic life#reproductive justice#overpopulation#malthusian theory#queer ecology#queer theory#ecofeminism#heteronormativity#critical ecology#ecology#environmental politics#colonialism#animal sexuality#media#traditional ecological knowledge#nuclear family#right wing#right wing extremism#united states#environmental justice#environmental reproductive justice#erotophobia#racism#classism#xenophobia#immigration#propaganda
9 notes
·
View notes