#¤°'~Heated
Text
ⓘ This user is desperate for hot makeout sessions w inappropriate touching
#bd/sm puppy#ftm bottom#ftm puppy#ftm sub#puppy sub#subby puppy#bitch in heat#breeding k1nk#ftm ns/ft#dumb puppy#slutty puppy#puppyboy#stupid puppy
23K notes
·
View notes
Text
magic system where “dark magic” and “light magic” are literal terms - dark magic consumes photons, making an area around the spell visibly darker, sometimes to an Extreme extent, and light magic releases photons.
because of this most dark mages tend to work in very brightly-lit areas (either artificial light or outside in the daytime) to fuel their spells and wear and use lightly coloured clothes and tools so that they’re easier to see in the dimness their spells create, whereas light mages wear heavy, sometimes leaden robes (depending on the work being done) and the magical equivalent of welding masks to protect themselves from what can be an extreme amount of light, and sometimes other kinds of electromagnet radiation!
needless to say this is incredibly confusing for anyone unfamiliar with the culture
#light mage about to unleash an absurd amount of infrared radiation wearing those heat suits volcanologists use:#of course many light mages dabble in dark magic as extra layers of protection#and vice versa - dark mages using light magic to light up their work spaces#though most specialize#sadly all theories of perpetual spell craft - light spell powering a dark spell#have been proven to not be feasable
48K notes
·
View notes
Text

you dont see brave writing like this in tv shows anymore
17K notes
·
View notes
Text
"With “green corridors” that mimic the natural forest, the Colombian city is driving down temperatures — and could become five degrees cooler over the next few decades.
In the face of a rapidly heating planet, the City of Eternal Spring — nicknamed so thanks to its year-round temperate climate — has found a way to keep its cool.
Previously, Medellín had undergone years of rapid urban expansion, which led to a severe urban heat island effect — raising temperatures in the city to significantly higher than in the surrounding suburban and rural areas. Roads and other concrete infrastructure absorb and maintain the sun’s heat for much longer than green infrastructure.
“Medellín grew at the expense of green spaces and vegetation,” says Pilar Vargas, a forest engineer working for City Hall. “We built and built and built. There wasn’t a lot of thought about the impact on the climate. It became obvious that had to change.”
Efforts began in 2016 under Medellín’s then mayor, Federico Gutiérrez (who, after completing one term in 2019, was re-elected at the end of 2023). The city launched a new approach to its urban development — one that focused on people and plants.
The $16.3 million initiative led to the creation of 30 Green Corridors along the city’s roads and waterways, improving or producing more than 70 hectares of green space, which includes 20 kilometers of shaded routes with cycle lanes and pedestrian paths.
These plant and tree-filled spaces — which connect all sorts of green areas such as the curb strips, squares, parks, vertical gardens, sidewalks, and even some of the seven hills that surround the city — produce fresh, cooling air in the face of urban heat. The corridors are also designed to mimic a natural forest with levels of low, medium and high plants, including native and tropical plants, bamboo grasses and palm trees.
Heat-trapping infrastructure like metro stations and bridges has also been greened as part of the project and government buildings have been adorned with green roofs and vertical gardens to beat the heat. The first of those was installed at Medellín’s City Hall, where nearly 100,000 plants and 12 species span the 1,810 square meter surface.
“It’s like urban acupuncture,” says Paula Zapata, advisor for Medellín at C40 Cities, a global network of about 100 of the world’s leading mayors. “The city is making these small interventions that together act to make a big impact.”
At the launch of the project, 120,000 individual plants and 12,500 trees were added to roads and parks across the city. By 2021, the figure had reached 2.5 million plants and 880,000 trees. Each has been carefully chosen to maximize their impact.
“The technical team thought a lot about the species used. They selected endemic ones that have a functional use,” explains Zapata.
The 72 species of plants and trees selected provide food for wildlife, help biodiversity to spread and fight air pollution. A study, for example, identified Mangifera indica as the best among six plant species found in Medellín at absorbing PM2.5 pollution — particulate matter that can cause asthma, bronchitis and heart disease — and surviving in polluted areas due to its “biochemical and biological mechanisms.”
And the urban planting continues to this day.
The groundwork is carried out by 150 citizen-gardeners like Pineda, who come from disadvantaged and minority backgrounds, with the support of 15 specialized forest engineers. Pineda is now the leader of a team of seven other gardeners who attend to corridors all across the city, shifting depending on the current priorities...
“I’m completely in favor of the corridors,” says [Victoria Perez, another citizen-gardener], who grew up in a poor suburb in the city of 2.5 million people. “It really improves the quality of life here.”
Wilmar Jesus, a 48-year-old Afro-Colombian farmer on his first day of the job, is pleased about the project’s possibilities for his own future. “I want to learn more and become better,” he says. “This gives me the opportunity to advance myself.”
The project’s wider impacts are like a breath of fresh air. Medellín’s temperatures fell by 2°C in the first three years of the program, and officials expect a further decrease of 4 to 5C over the next few decades, even taking into account climate change. In turn, City Hall says this will minimize the need for energy-intensive air conditioning...
In addition, the project has had a significant impact on air pollution. Between 2016 and 2019, the level of PM2.5 fell significantly, and in turn the city’s morbidity rate from acute respiratory infections decreased from 159.8 to 95.3 per 1,000 people [Note: That means the city's rate of people getting sick with lung/throat/respiratory infections.]
There’s also been a 34.6 percent rise in cycling in the city, likely due to the new bike paths built for the project, and biodiversity studies show that wildlife is coming back — one sample of five Green Corridors identified 30 different species of butterfly.
Other cities are already taking note. Bogotá and Barranquilla have adopted similar plans, among other Colombian cities, and last year São Paulo, Brazil, the largest city in South America, began expanding its corridors after launching them in 2022.
“For sure, Green Corridors could work in many other places,” says Zapata."
-via Reasons to Be Cheerful, March 4, 2024
#colombia#brazil#urban#urban landscape#urban planning#cities#civil engineering#green architecture#green spaces#urban heat#urban heat island effect#weather#meteorology#global warming#climate change#climate hope#climate optimism#climate emergency#climate action#environment#environmental news#city architecture#bicycling#native plants#biodiversity#good news#hope#solarpunk#ecopunk#hopepunk
12K notes
·
View notes
Text
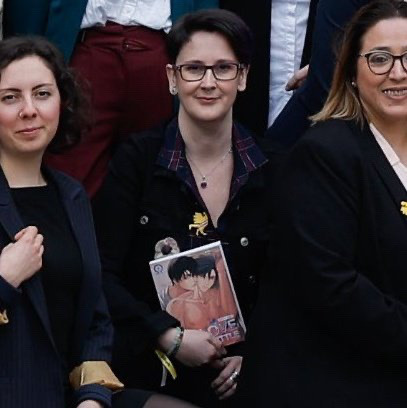





liberté, egalité, fraternité et yaoi
#love shuttle……. it’s the millennium of omegaverse#a win for fujoshi everywhere#had to look her up and that’s noemie the founder of nao studio publishing#also calling it bl is putting it so delicately#this is full on squelchy invisidick yaoi#anyway if you’re looking for shamelessly id-fulfilling manhwa this is it#it’s love shuttle by aeju#man who has never gone into heat his entire life and insists he is FINE with it#suddenly spontaneously keeps slipping into heat every time a certain alpha is around#and then they fuck nasty in almost every chapter#love shuttle#omegaverse#manga#manhwa#twitter#yaoi#art
9K notes
·
View notes
Text
"summer is the worst" "no winter is!!!" actually both are. down with Big Temperature. spring and autumn for the win
#one thing about me is i hate an extreme temperature#high heat makes me feel physically ill and low cold hurts my body#it should be 55-75 fahrenheit year round
59K notes
·
View notes
Text
PSA: i keep seeing posts about staying cool in extreme heat that include advice like "gatorade is bad actually!" and "don't drink fruit juice it'll just dehydrate you!" and neither of these are true!
regarding fruit juice: there's apparently a misconception that Any Sugar At All will dehydrate you, and that's simply not true. yes, sugar will make you pee more when consumed in large amounts, but 1) the natural sugar in fruits won't do this to you 2) great news! a lot of fruit juices exist without any added sugar in them! 3) honestly even having a glass of the fruit juice with added sugar won't completely dehydrate you as long as you're also drinking water throughout the day. if its hot you deserve a cold treat of a drink!!! can't go wrong with fruit juice!!!
regarding gatorade: maybe this isn't an every day drink, but guess what: if it's 110F/40C or hotter outside, and you don't have AC, or you're moving around a lot outside of the AC, and you're sweating buckets: that's when you drink a gatorade.
gatorade exists to replenish all the electrolytes (salt) and glucose (sugar) that you sweat out. YES it is meant for athletes to drink during intensive work outs and not necessarily for people who aren't doing that kind of exercise. BUT GUESS WHAT! when you're sweating buckets because you had to walk to the bus in extreme heat, that's intensive exercise. please feel free to drink a gatorade after that! that's its intended use case!!!!
no: neither of these drinks should be a total replacement for water. but drinking a lot of water and then treating yourself to a fruit juice with lunch is a good idea!!! drinking a gatorade becuase you just had to walk for 20 minutes in the heat is a good idea!!!
Please Stop Spreading Misinformation About Drinks!!! It's fine if you drink things that aren't water!!!! Yes you should probably always be drinking water but drinking something else As Well isn't going to hurt you!!!! okay!!!! its fine!!!!!!
honestly so long as you are consistently getting Any (non-alcoholic) fluids in you, you're doing great!!!!!! okay!!!! i love you stay safe <3
#also: drinking A Soda or A Coffee isn't going to completely dehydrate you if you're drinking other fluids tbqh!!!#its fine!!!!! its fine!!!!!#drinks#heat#dehydration#this post exists because i'm mad at misinfo but also#this is for my homies who hate the taste of water and struggle to stay hydrated#because people have told them over and over again You Must Absolute Drink Water And Nothing Else and so they just don't drink anything#listen!! hey!!! whoever told you that was lying!!!!#drinking Any Fluids At All (yes even with caffeine!!) is better than Not Drinking Anything#please hydrate!!!! it's okay if that hydration isn't water!!!!#honestly i tried to be extremely non confrontational in this post but im pretty sure i've seen people suggest flavored water packets#but say no fruit juice ever. and that's insane.#it's all fluids baby!!!!!!!!!!!!!!#so long as you are drinking fluids you are combatting dehydration#YES water is the best option HOWEVER. if you drink things that aren't water that's also okay! i promise!!!!!!!!
41K notes
·
View notes
Text

Mother of Pearl
#artists on tumblr#seahorses are cute aren't they#how are we coping with the heat wave everyone?#i'm too busy having like three different kind of existential crises#to worry about it being too hot#hot girl summer more like nonstop anxiety summer#pondering the fact that nothing is permanent#can't rely on anything to last#life is just#drifting in a sea of uncertainty#but anyway#happy pride month#be gay#eat ice cream#don't think about your mortality
29K notes
·
View notes
Text
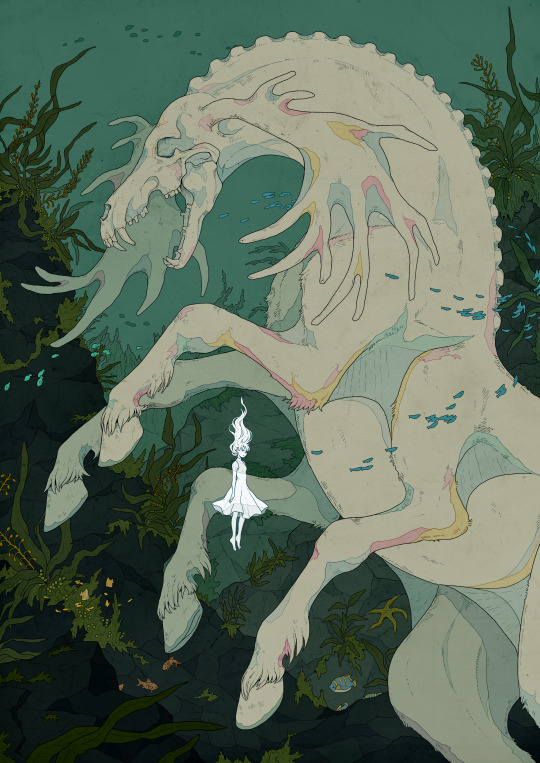
So I was scrolling and saw this image in an article about the European heat wave,
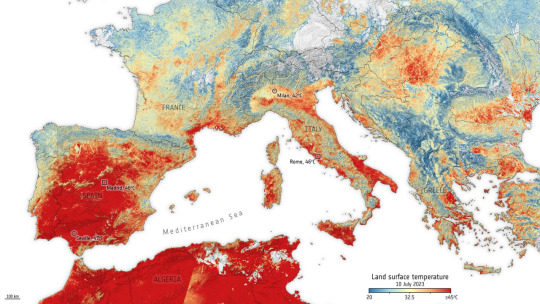
And was like, uh, are you missing something there, buddy? Like all that red in northern Africa? Because that's a lot of red.
And I was going to give them the benefit of doubt, since I don't know much about the climate in Northern Africa, aside from Morroco and Egypt, which seem like really hot places, so you know, maybe it's normal there?
But nope, that's not the case:
Some selections from the article:
"The region has been experiencing some of the most intense heat waves in recent years, but in many cases they’ve been under-reported due to misconceptions about Africans’ ability to withstand them.
“Africa is seen as a sunny and hot continent,” said Amadou Thierno Gaye, a research scientist and professor at Cheikh Anta Diop University in Dakar, the capital of Senegal. “People think we are used to heat, but we are having high temperatures for a longer duration. Nobody is used to this.”
"The Sahel, for instance, has been heating at a faster pace than the global average despite being hot already. Burkina Faso and Mali, both in West Africa’s Sahel, are among countries that are set to become almost uninhabitable by 2080, if the world continues on its current trajectory, a UK university study found. Its people are especially vulnerable due to shrinking resources, such as water, and poor amenities, and a dearth of trees and parks means there are few options for places to cool off."
23K notes
·
View notes
Text

take a jacket just in case
#it's true i use a world meteorological map to see if my ex is in a heat wave lol out of love#ive had this idea in my head forever#my art#digital artists#artists on tumblr#queer art#all my love alright all of it!
36K notes
·
View notes
Text

My slut jacket
#trans nsft#butch nsft#queer nsft#dyke nsft#butch bottom#trans butch#bd/sm community#bd/sm kink#bd/sm blog#bd/sm puppy#butch pup#butch dog#trans pup#trans dog#pup sub#pup in heat#butch dyke#dykeposting#butch4butch#dyke pup#trans t4t#t4t nsft#t4t ns/fw#t4t puppy#t4t yearning#t4t lesbian
10K notes
·
View notes
Text
i never thought global warming wasn't real but it really hits when it's winter and i'm out here in summer clothes 🤡🤡🤡

21K notes
·
View notes
Text
Ancient redwoods recover from fire by sprouting 1000-year-old buds

Article | Paywall free
When lightning ignited fires around California’s Big Basin Redwoods State Park north of Santa Cruz in August 2020, the blaze spread quickly. Redwoods naturally resist burning, but this time flames shot through the canopies of 100-meter-tall trees, incinerating the needles. “It was shocking,” says Drew Peltier, a tree ecophysiologist at Northern Arizona University. “It really seemed like most of the trees were going to die.”
Yet many of them lived. In a paper published yesterday in Nature Plants, Peltier and his colleagues help explain why: The charred survivors, despite being defoliated [aka losing all their needles], mobilized long-held energy reserves—sugars that had been made from sunlight decades earlier—and poured them into buds that had been lying dormant under the bark for centuries.
“This is one of those papers that challenges our previous knowledge on tree growth,” says Adrian Rocha, an ecosystem ecologist at the University of Notre Dame. “It is amazing to learn that carbon taken up decades ago can be used to sustain its growth into the future.” The findings suggest redwoods have the tools to cope with catastrophic fires driven by climate change, Rocha says. Still, it’s unclear whether the trees could withstand the regular infernos that might occur under a warmer climate regime.
Mild fires strike coastal redwood forests about every decade. The giant trees resist burning thanks to the bark, up to about 30 centimeters thick at the base, which contains tannic acids that retard flames. Their branches and needles are normally beyond the reach of flames that consume vegetation on the ground. But the fire in 2020 was so intense that even the uppermost branches of many trees burned and their ability to photosynthesize went up in smoke along with their pine needles.
Trees photosynthesize to create sugars and other carbohydrates, which provide the energy they need to grow and repair tissue. Trees do store some of this energy, which they can call on during a drought or after a fire. Still, scientists weren’t sure these reserves would prove enough for the burned trees of Big Basin.
Visiting the forest a few months after the fire, Peltier and his colleagues found fresh growth emerging from blackened trunks. They knew that shorter lived trees can store sugars for several years. Because redwoods can live for more than 2000 years, the researchers wondered whether the trees were drawing on much older energy reserves to grow the sprouts.
Average age is only part of the story. The mix of carbohydrates also contained some carbon that was much older. The way trees store their sugar is like refueling a car, Peltier says. Most of the gasoline was added recently, but the tank never runs completely dry and so a few molecules from the very first fill-up remain. Based on the age and mass of the trees and their normal rate of photosynthesis, Peltier calculated that the redwoods were calling on carbohydrates photosynthesized nearly 6 decades ago—several hundred kilograms’ worth—to help the sprouts grow. “They allow these trees to be really fire-resilient because they have this big pool of old reserves to draw on,” Peltier says.
It's not just the energy reserves that are old. The sprouts were emerging from buds that began forming centuries ago. Redwoods and other tree species create budlike tissue that remains under the bark. Scientists can trace the paths of these buds, like a worm burrowing outward. In samples taken from a large redwood that had fallen after the fire, Peltier and colleagues found that many of the buds, some of which had sprouted, extended back as much as 1000 years. “That was really surprising for me,” Peltier says. “As far as I know, these are the oldest ones that have been documented.”
... “The fact that the reserves used are so old indicates that they took a long time to build up,” says Susan Trumbore, a radiocarbon expert at the Max Planck Institute for Biogeochemistry. “Redwoods are majestic organisms. One cannot help rooting for those resprouts to keep them alive in decades to come.”
-via Science, December 1, 2023
#redwoods#california#wildfire#climate change#extreme heat#natural disasters#botany#plant biology#photosynthesis#santa cruz#hopepunk#sustainability#climate hope#united states#good news#hope
11K notes
·
View notes
Text
This is going to be an unpleasant post but I need to talk to y’all about heat stroke in dogs. I am an ER vet and I am seeing firsthand the death toll that this heat wave is taking on our pets. In the past two weeks, for every single weekend shift I have worked, we have had at least one DOA with a body temperature over 107 degrees. One of them had simply been on a 20 minute walk at 5pm. All of them were brachycephalic (short faced breeds like pugs and french bulldogs). Their owners were in shock that this could happen so quickly, and their grief lingers with me.
If you have a dog, and especially if you have a brachycephalic dog, you need to familiarize yourself with the signs of heat stroke. Do not take your dogs out in the heat of the day, be aware of the pavement temperature, and always have fresh water available for them. When I am outdoors with my dog I am checking on him constantly. This heat wave is extremely serious; I need you to keep yourself and your pets safe.
17K notes
·
View notes
Text
For those with homes built to keep heat in, not let it out: aluminum foil your windows, shiny side out. Cover the window, tape up the sides, maybe tape cardboard behind it to help insulate from the heat outside and absorb heat that gets through the foil.
Love, a former Californian, whose had to keep houses cool without any electricity.
P.S. this is a method endorsed by FEMA and the Department of Energy, so if you need more than anecdotal evidence, there ya go.
19K notes
·
View notes
Text


Shoutout to all fanfics that have my sweet soft boys sleep like this! <33 You're so real for that!
(also, if you have fanfic recs that feed me this well do tell me!)
#Zukka#prince zuko#sokka#snuggling all..platonically........#just boys being boys#sharing body heat#in the middle of the earth kingdom#atla#avatar the last airbender
13K notes
·
View notes