#gagauz
Text


Otoyomegatari
#turkic#turkish#traditional#türk#nomad#artwork#art#anime and manga#manga#otoyomegatari#turkmen#turkic culture#kazakh#kyrgyz#azerbaijani#chuvash#gagauz#uzbek#bashkir#girl
39 notes
·
View notes
Text
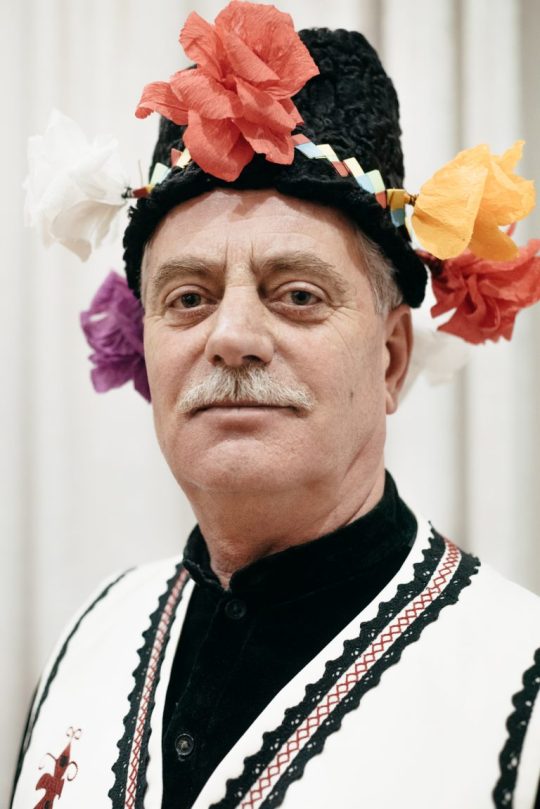

Gagauz man, Moldova, by Gagauzia Dialogue
#gagauz#moldova#europe#eastern europe#traditional clothing#traditional fashion#cultural clothing#folk clothing
102 notes
·
View notes
Text
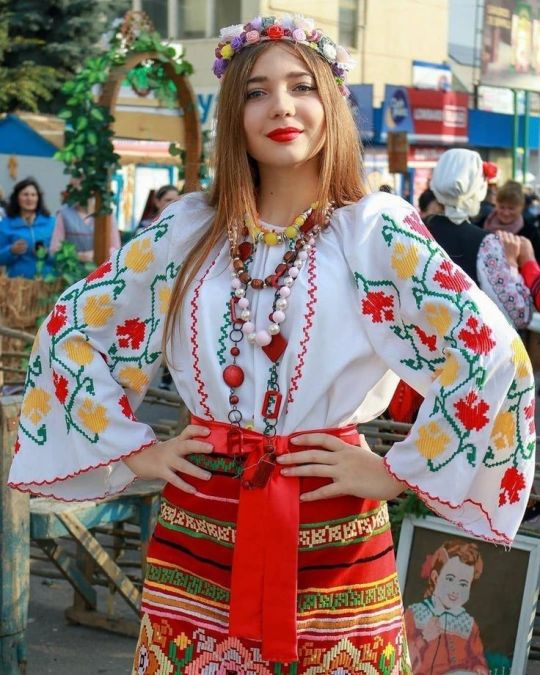

Gagauz girl.
Sourse: https://pinterest.com/pin/1144336586559101624/
1 note
·
View note
Text
In the crowded labyrinth of the open market in downtown Chisinau, the capital city of Moldova, a babble of languages ripples through the throngs of traders hawking a bewildering array of fresh produce, cheap textiles, electronic wares, and much more. A customer may broach the terms of a deal in, say, Ukrainian, and get an answer in Romanian, or propose a price in Romanian and be answered in Russian. Among themselves, the traders from across this diminutive country of 2.5 million, wedged precariously between its outsized neighbors Romania and Ukraine, communicate in other tongues, too.
Moldova is a multiethnic country that wears its patchwork diversity on its sleeve. Particularly in urban centers, the majority Romanians live very much together with Ukrainians, Russians, and the Turkic Gagauz. But the war in Ukraine has completely upended the tenuous status quo that existed before February 2022. The war’s outcome, whether in Ukraine’s or Russia’s favor, has existential consequences for the tiny country nursing aspirations of joining the European Union.
Political convictions in Moldova have long spanned the gamut from aspirations of greater Romanian nationalism to Soviet nostalgia, from pro-Russia patriotism to civic pride in an independent, EU-embedded Moldova. This fractured landscape is also reflected in the country’s geography. Since the first days of its independence in 1991—when the Soviet Republic of Moldova jettisoned Soviet authority and declared statehood, basically for the first time ever—the Republic of Moldova itself has been fractured.
A breakaway, Russia-kowtowing enclave called Transnistria established itself east of the Dniester River—complete with about 1,500 Russian troops that remain there today—while the Gagauz minority, courted by Moscow and Ankara, staked out broad autonomy in the south.
Russian President Vladimir Putin’s first priority is to stop Moldova from joining the EU and integrating with the West, especially since the EU boosted Moldova to candidate status shortly after the onset of the Russia-Ukraine war. But his aspirations may be far wider. Last week, Russia drew the ire of Moldovan authorities by setting up polling stations in Transnistria for its roughly 200,000 residents to vote in the Russian presidential elections held from March 15 to 17. It was a move that harks back to the initial steps taken to absorb occupied territories in Crimea and elsewhere in eastern Ukraine into Russia itself.
“Everything is at stake for Moldova now,” said Alexei Tulbure, the director of the Moldovan Oral History Institute.
If there’s one thing that just about all of Moldova’s peoples agree upon, regardless of political ideology, it is that they have next to no agency to affect the fate of their country—and ultimately, the fate of their own futures. “Moldovans breathe quietly,” according to a Ukrainian saying, mocking the country’s helplessness.
“It’s in the back of our minds,” said Alina Radu, the founder of the independent weekly Ziarul de Garda, of the possibility of the country losing its territory, or autonomy, to Russia. She compared the threat that the country now faces to the first months of the Russia-Ukraine war in 2022, when the Russian military seemed to be on the doorstep of the nearby Ukrainian city of Odesa. Transnistria’s armies seemed to be preparing to lend Russia a hand there. Had they been successful, all of Moldova could have come under Russian domination.
The staging ground for any future assault on Moldova is still likely to be Ukraine. Putin regularly confirms that Odesa is a military priority and has recently stepped up missile attacks there. It is a development that Moldovans are watching with trepidation. It’s one that Moldova’s allies in the West should be watching, too.
Even over its grinding first decades—marred by civil war, raging corruption, abject poverty, and mass emigration—Moldova’s prospects weren’t as starkly imperiled as they are today. Unlike most Ukrainians—who declare that victory over Russia is the only possible outcome—Moldovans have thought through worst-case scenarios.
“If Ukraine is defeated and Russia carves out a land corridor to Transnistria, Moldova will effectively cease to exist as an independent county,” Radu explained. “If they cross the Dniester River to occupy Moldova proper, then most of the population could well flee to Romania and points in Europe.” Her entire editorial staff has fixed plans to relocate to offices in the Romanian cities of Iasi and Bucharest, she said.
This certainly, at the very least, would put an abrupt end to Moldova’s EU and NATO aspirations, which is Washington’s primary concern. Upon signing a security cooperation deal with France on March 7, Moldovan President Maia Sandu—a 51-year-old Romanian-speaking graduate of Harvard University’s Kennedy School of Government—told French President Emmanuel Macron that “our shared security is at stake. If the aggressor is not stopped, he will keep going, and the front line will keep moving closer. Closer to us, closer to you.”
Were Russia to take Moldova, it would open a second frontier with direct access to an EU member state. The United States is obviously aware of this threat and upped its defense assistance to Moldova from $3 million in 2022 to more than $30 million today. The United States and France also provided the country with hundreds of millions to shift its energy supply westward.
Ukraine, according to many Moldovans, including Sandu, is fighting for Moldova’s independence, too. “We’re very grateful to Ukraine,” said Ludmila D. Cojocaru, a historian at the National Museum of History of Moldova in Chisinau. “At the moment, it is the guarantor of our freedom.”
On the other hand, “if Ukraine pushes Russia back,” said Radu, the editor, “the Russian troops will have to leave separatist Transnistria, and it will dissolve.” As far as she is concerned, the peoples of Transnistria—hostages, she called them, to the criminal clique controlling the territory—would be more than welcome to join the Moldovan state in full. As for the alleged gangsters who have lorded over the region for 30 years, they will face justice—if they’re naïve enough to hang around, she said.
Until Russia launched its full-scale attack on Ukraine on Feb. 24, 2022, Moldova’s overwhelming geopolitical preoccupation was with the self-styled Transnistrian Moldovan Republic (PMR)—recognized as a state by no country in the world, not even Russia. Since a brief but bloody civil war in the region that took an estimated 700 lives in 1992, a hard-nosed, Russian-backed mafioso cartel named Sheriff Holding Co. has turned the vertical sliver of land into an entirely captured, one-party authoritarian state that conducts lucrative black-market business from the eastern bank of the Dniester.
The 90-minute minibus trip from Chisinau to PMR’s capital city, Tiraspol, passes a steady flow of traffic in the opposite direction: This workforce, which possesses Moldovan passports, can no longer find employment in Transnistria since its business to the east was cut off abruptly when Ukraine slammed shut the border last year, a body blow to the Sheriff cartel. At the Dniester, a solitary, AK-wielding Russian Army soldier stands in front of a makeshift border, not unlike Checkpoint Charlie in the divided Berlin.
Two flags fly from the checkpoint: the Russian flag and a green-and-red PMR flag that sometimes—but not all the time—sports a hammer and sickle in the upper right-hand corner just as had the flag of the Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic. In the empty, deafeningly quiet streets of Tiraspol, the only image more prevalent than the bust of Soviet leader Vladimir Lenin is the Sheriff logo with its Wild West-inspired star. (“Sheriff” was the nickname of Moldovan police officer Viktor Gushan, who is one of the former Soviet sphere’s wealthiest oligarchs.)
The conflict between Transnistria and the Moldovan state, which never ceded sovereignty over the eastern bank territory, remained largely frozen for years despite international diplomacy to initiate a thawing. As long as the matter remained unsolved, Sheriff’s honchos padded their coffers and Moscow maintained a forward pawn that kept Moldova off balance; through propaganda and puppets, Russia influenced Moldova’s internal politics to the extent that until 2021, all but one Moldovan government reflected positions largely in line with Moscow, much as did in Ukraine until 2014. Interestingly, until the Russian annexation of Crimea in 2014, Ukraine had sided largely with the Transnistrian ruling clique, business and Russian reinforcements flowing over the Ukraine border while Moldova remained tightly in check.
But now it is the Transnistrians who are on the back foot—and not sure how to play it. The narrow lick of land suddenly finds its greatest ally far away, and its residents are well aware that Ukraine could occupy it within a week, Anatolii Dirun, a former Transnistrian politician, told me. Resupply from Russia is blocked by Ukraine. The PMR made a feeble cry to Moscow for help on Feb. 28, but stopped short of calling for it to intervene.
In fact, the gangsters of Transnistria are petrified and thus playing both ends against the middle: Russia and Moldova proper. All of the region’s trade now runs through Moldova proper—and most of that carries on to the EU through Romania. More Transnistrians than ever before work, study, and learn Romanian in Moldova proper, part of a deft strategy by Sandu to integrate Transnistria back into Moldova.
“Transnistria’s leaders are trying to be prudent—as they don’t have much of a choice,” Oazu Nantoi, a member of the Moldovan Parliament who belongs to Sandu’s party, told Foreign Policy.
And yet, the Transnistrian government, in league with the Gagauz and pro-Russian forces in Moldova proper, remains beholden to Moscow and gladly lends it a hand in chipping away at the Moldovan government’s sovereignty.
The fact is, said Alexei Tulbure, an ethnic Ukrainian and the director of the Moldovan Historical Institute, Moldova is an easy target. It remains a very weak state, he noted, and thus wide open to tampering. “We had hoped that the war would consolidate Moldova the way it did Ukraine’s population, bring us all onto the same page. But this didn’t happen,” he said. Polls show that about a quarter of the country is still pro-Russian.
Russia’s chief means to destabilize its targets are bought votes, propaganda, cyberwarfare, and political parties. There are a handful of Russia-friendly (some also Russian-financed) parties that toe Putin’s line to one degree or another. For most of Moldova’s recent history, a combination of these parties had held power. The propaganda is “very strong and very toxic, and it rings like it’s straight from Moscow,” said Mariana Aricova of the Institute of War and Peace Reporting office in Chisinau, whose job is to monitor and counter the Kremlin’s disinformation campaigns.
The Russian campaigns to topple the Sandu government have picked up pace as the Moldovan presidential election, scheduled to take place in autumn along with a referendum on EU membership, grows nearer. And the Sandu government has responded as if its life depends on it, even by banning one of the pro-Russian parties and shutting down six television channels for alleged misinformation.
But “it didn’t really change much because the banned party has regrouped under a new party, and the Russian message gets out through other channels, like the Internet,” Aricova said.
Above all, Moldovans fear being squashed in a power struggle in which they have no say. Many observers see a slow, gentle reintegration of Transnistria into a federally structured Moldova as a first step in the right direction—Sandu’s chosen path. The Sandu government is seizing the moment as a unique opportunity to reconnect with Transnistria—and from there, to bring the entire country, as one, into the EU. The carrots of cross-border employment prospects, full Schengen Area travel rights, European structural and investment funds, minority rights guarantees, and higher wages could be enticing to everyone—save, of course, Transnistria’s criminals.
In terms of a proven mentor, there’s none better than Romania, which has surged to become Eastern Europe’s second-largest economy after Poland. The question is whether Sandu can pull this off without shattering the fragile country in the process. But then, the war raging next door might just take care of that for her.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Kremlin's Plan for Moldova
Greetings everyone.
The RISE investigative journalism agency published a highly detailed account of the Russian efforts to infiltrate Moldovan politics with a comprehensive strategy to integrate the country firmly in the Russian sphere of influence by 2023, with the side effect of completely alienating Moldova from Romania, the EU, NATO and the wider west.
Bellow I took the liberty of translating it into English, and the hyperlink of the Investigation in Romanian.
If you are Moldovan/Romanian, or if you take interest in the regional geo-politics, I highly recommend this read.
Thank you for your attention and time!

A document leaked from behind the scenes of the Kremlin presidential administration reveals Russia's plan to bring Moldova under its own umbrella by 2030.
The document, which has not been made public, is called "Strategic Objectives of the Russian Federation in the Republic of Moldova" and was created in 2021. Several key points of Moscow's strategy have also appeared over the years on the public platforms of pro-Russian parties and in speeches by politicians.
"The document is an interesting one, but it shows that they are one step behind the general situation because of the war in Ukraine and because of the regional capacity of EU countries and other international organisations to mobilise and face Russia's intentions to achieve this," Sergiu Diaconu, head of the Moldovan Prime Minister's Office, told us after we showed him the resulting strategy.
Against the backdrop of the Russian invasion of Ukraine, the government in Chisinau is increasingly promoting Moldova's rapprochement with the European Union. The head of state recently set a deadline for this goal. The year 2030.
This year - 2030, is also included in Russia's strategy as the deadline for gaining control over the Republic of Moldova and moving it away from the EU, NATO and other partners.
The document detailing Moscow's strategy was obtained by RISE Moldova together with an international consortium of journalists including Yahoo News, Delfi Estonia, the London-based Dossier Centre, the Swedish newspaper Exane Westdeutscher, Rundfunk and Norddeutscher Rundfunk, the Polish investigative station Frontstory, the Belarusian Investigative Centre and the Central European news website VSquare.
The document comes from the same Presidential Directorate for Cross-Border Cooperation that produced a similar strategy on Russia's plans to annex the Republic of Belarus. The strategy was drafted in autumn 2021, as was the Belarus strategy, with input from the Russian General Staff and Moscow's special services: the FSB, SVR and GRU. "There is zero percent [chance that] these documents are fake," according to the source who provided us with the documents.
The strategy was built on three spheres of influence: political and military, economic and humanitarian.
PRO-RUSSIAN POLITICAL AND BUSINESS INFLUENCE GROUPS
Strategic objectives in the political, military, military-technical and security spheres
In the short term (until 2022), Russia has set out to open a consulate in ATU Gagauzia, but this has not happened. The idea of opening a Russian consulate in Comrat has been promoted by former head of state Igor Dodon since 2012. At the time, Dodon was a member of parliament.
In 2021, an initiative group started collecting signatures in support of the idea, arguing that "many Gagauz residents have Russian citizenship and go to this country to earn money. Many citizens of the autonomy got married in Russia, have businesses there. We are linked to Russia by many threads".
Mihail Vlah is the chairman of the supervisory board of the public company Teleradio Gagauzia (GRT) and one of the organisers of the rally against price increases in the summer of 2022. His wife, Tatiana Vlah, owns 67% of Bakayan, which is on the list of Moldovan companies that Rosselkhoznadzor allowed to export to Russia in December 2022, after imposing an embargo on all agricultural producers on the right bank of the Dniester in August. Vlah denied at the time any link between obtaining the right to export to Russia and the organisation of the protest.
Mihail VLAH, civic activist from Gagauzia: I think Russia is generally not interested in Moldova. What is happening in the Transnistrian region is very important for Russia, because about 50% of the population there is Russian, they keep their weapons there and there are peacekeepers there.
As far as Moldova as a whole is concerned, I think Russia would naturally like to see Moldova in its sphere of influence. Just as Europe and America would like to see Ukraine, Moldova and Georgia in their sphere of influence.
And from Gagauzia, Russia wants nothing. We live as badly as the whole of Moldova. We pay 30 lei each for gas and electricity. Our products do not reach Russia. We, like our Moldovan brothers, suffer from the fact that there is war in Ukraine and from this relationship between the authorities of the Republic of Moldova and the authorities of the Russian Federation.
Another objective of the Russian Federation is 'Countering Moldova's collaboration with NATO', which it has set itself to achieve by 2025. And in the long term, i.e. by 2030, Russia wants to "form a negative attitude towards NATO in Moldovan society and political circles". This was one of the "10 priority objectives" promoted by the Party of Socialists of the Republic of Moldova (PSRM) in the February 2019 parliamentary elections: "We will not allow NATO membership and we will achieve the closure of the NATO office in Chisinau".

"Countering Romania's expansionist policy in Moldova" - Russia's medium-term goal - by 2025. In the same 2019 elections, the PSRM claimed that if it had a parliamentary majority, it would ban "unionist parties and movements". At the same time, the socialists promised that Moldova would "achieve full membership of the Eurasian Economic Union" (EEU). The objective is also reflected in the Russian Federation's strategy.
Also in the political, military, military-technical and security spheres, Russia wants to "broaden the electoral base of political forces in Moldova that advocate constructive relations with the RF", "create stable pro-Russian groups of influence among the Moldovan political and economic elite", 'developing cooperation in the politico-military sphere, including intensifying Russian-Moldovan contacts between the armed forces and law enforcement institutions' and 'increasing the level of Moldova's participation in CIS activities, including restoring the participation of Moldovan representatives in all Community formats as well as through the EEU'.
Dorin RECEAN, Prime Minister: From a military point of view, at the moment, they do not have the resources and circumstances to do much. They cannot advance on the Transnistrian side. They are not aligned enough.
But in terms of increasing insecurity and fear and anxiety and funding protests and different kinds of destabilization, that's what they're trying to do. And that coincides with the agenda of these groups that normally should be in jail, and their money - recovered by the government, because they stole money from the people.
"Russia sees the Shor Party as a reliable partner"
One party that satisfies the Russian Federation's agenda in Chisinau is Shor. The party led by fugitive Ilan Shor has openly shown sympathy for Moscow.
Alongside socialists and communists, Șor has not once spoken out against NATO, even threatening that our country's rapprochement with the military alliance could lead to war with Russia.
"As if it is not clear how our traditional partners in the East will react to our giving up our neutral status and joining NATO. [...] Do we want war? Maybe we should tell this witch (Maia Sandu - ed.) to stop bringing NATO trouble to our peaceful land," Ilan Shor said in early 2023.
Amid the large-scale war unleashed by Russia, Șor has shown his support for the aggressor state, campaigning against the sanctions imposed by the EU. "In the case of support for sanctions against Russia (by the authorities in Chisinau - ed.), I reserve the right to call people to the streets," Șor said in a Facebook video.
Moreover, back in 2021, the parliamentary party claimed that it aimed to establish cooperation relations with "Edinaia Rossia" (United Russia), the party that has been governing in Russia for more than a decade. A statement published by the Shor Party said that the Chairman of the Foreign Relations Committee of the Russian State Duma, Leonid Slutsky, said that "in recent years, the big problem has been that we have not had a reliable and long-term partner in Moldova for all our big companies. Today, however, we have found this partner in the person of Ilan Shor and the 'Shor' Party."
Ilan Shor and his party have been included on the US sanctions list for representing Russian interests in Moldova.
"Before the 2021 parliamentary elections, Russia was planning [...] to bring Moldova back into its sphere of influence. To support this effort, it worked with Russian citizens to create a political alliance designed to control Moldova's parliament and then support the adoption of a series of legislative acts in the interests of the Russian Federation," a document issued by the US State Treasury in October 2022 said.
We interviewed Marina Tauber in front of the government during the Sunday, 12 March 2023 protest organised by the Shor Party. Tauber denied that she was financed by Russia in any way.
Marina TAUBER, member of the Shor Party: No, we are not financed by Russia in any way. I declare this officially. And when people say or affirm this, please ask them to prove it to you and show you the concrete evidence. Otherwise, sorry, blah, blah, blah. I can't answer for all the people in the world. If they hired some of their employees, they have to answer. Mr Chernăuțan (Viorel Chernăuțeanu, head of the General Inspectorate of Police), as far as I heard from his briefing, said nothing about the Shor political party. If there are provocateurs here, what can I say? How can I tell you? I show you people who came from the district at our invitation. What the others are doing, I can't answer for the whole world.
PRO-RUSSIAN NGOS, CHURCH SUPPORT AND SPECIAL STATUS FOR THE RUSSIAN LANGUAGE
Strategic objectives in the humanitarian sphere
By 2025, Russia aims to create a network of "NGOs promoting the development of Russian-Moldovan relations" in Moldova and to provide "organisational, financial, legal and informational support for Russian-friendly NGOs". Igor Dodon founded such an NGO in 2021.
Transfers to the Moldovan-Russian Business Union
About the former president's "Moldovan-Russian Business Union", RISE Moldova wrote in the "Rubles for Dodon" investigation, in which we showed how from October 2021 to April 2022, i.e. in just seven months, more than 20 million Russian rubles (about five million lei) entered the association's Moldovan account. The money came from the "Delovaia Rossia" organisation in the Russian Federation, financed by businessmen close to the Kremlin and represented in Moldova by Igor Chaika, younger son of Yurii Chaika, Russia's Prosecutor General in 2006-2020.
Also on the humanitarian track, the authors of the plan set as their objectives "ensuring that the Moldovan authorities give up the idea of abolishing the study of Russian in schools" and "reconfirming the status of the Russian language as a language of inter-ethnic communication". The issue of the status of the Russian language on the territory of the Republic of Moldova is also reflected in the political programmes of the Socialist and Communist parties. In the latest political programme, approved in 2021, the PSRM "advocates strengthening the legislative framework on the status of the Russian language as a language of interethnic communication throughout the Republic of Moldova". And the PCRM notes in its electoral programme that "the state authorities will strictly observe the rules stipulating that Russian is the language of interethnic communication on the territory of our country". At the end of 2020, the parliamentary majority made up of socialists and the "For Moldova" Platform (made up of Shor Party MPs and defected MPs) passed a law in Parliament giving the Russian language special status. A month later, the law was declared unconstitutional and subsequently repealed.
Young people are also on the Russian Federation's radar. Russia aims to "expand opportunities for Moldovan students to receive distance education in Russian", to increase the quota allocated by the "Russian government to Moldovan students for studies at Russian universities with budget funding", and to create consortia between "higher education institutions of the two countries", open branches of Russian universities and develop an academic exchange programme.
Sergiu DIACONU, Head of the Prime Minister's Office: Interesting in this document, what we know exactly, but it is just a confirmation that they will put a lot of pressure on the so-called humanitarian and social zone. And here they can really cause some damage, because they are using institutions, including the Russian Cultural Institute here in Moldova, where you can see the permanent presence of the young generation, especially from the socialist side. It's a kind of enclave for the exchange of anything but cultural issues.
And the most interesting thing in the humanitarian sphere is that they want to increase the number of student organizations and the growing presence of the Russian language. They want to increase their media capacity.
The Russians' strategy also targets the church. According to the plan, by 2030 they aim to support "the Russian Orthodox Church in defending the interests of canonical Orthodoxy in the Republic of Moldova".
Mihail VLAH, civic activist from Gagauzia: The European Union is a very big and friendly family. It is like an intellectual, brain, technology. And Russia is Orthodoxy, a shared history of centuries that you cannot break with a pickaxe.
MAINTAINING DEPENDENCE ON RUSSIAN GAS
Strategic objectives in the commercial and economic sphere
"Maintaining the volume and legal framework for Russian natural gas supplies" is the objective with which the plan for the commercial and economic sphere begins.
Sergiu DIACONU, Head of the Prime Minister's Office: I would be very happy if people in Moldova could see this strategy. Because in the second point, in the economic sphere, they set out in the short term that they want to maintain the volume of gas deliveries to Moldova, which they did in 2021. But in this year, 2022, they have cut the supply by 40% and they are keeping us permanently under the prospect of the permanent cessation of gas imports from Russia. Every month we have this problem, that they say we're going to cut gas across the country. So how does what they say here stack up against what they do?
The goal of expanding "Russian-Moldovan cooperation in trade, economic and interregional relations" is similar to the mission of Igor Dodon's organisation. The "Moldovan-Russian Business Union" advocates the development of bilateral relations in the business environment of Moldova and the Russian Federation.
A Moldovan-Russian investment project is also AgroHub Moldova, a business started in Hincesti, which RISE Moldova wrote about last March. Specifically, the investment involved the creation of an agro-industrial and logistics centre, which aims to facilitate the export and import of agri-food and wine products. Worth $55 million, the project was also included in the protocol of the Moldovan-Russian Intergovernmental Commission meeting of 2 October 2020 and, according to the document, the agrohub was "aimed at improving trade relations between the Republic of Moldova and the Russian Federation". Except that, a few months after the publication of the RISE investigation, the lease contract for the public land on which the agrohub was to be built was terminated. Details, HERE
RISE Moldova sent requests for information to the Party of Socialists and the Party of Communists in which we asked them if there is any connection between the political and humanitarian objectives in the parties' programmes of activities and the exact same objectives found in the Russian Strategy. At the time of going to press, I had not received any reply.
Intelligence and Security Service of the Republic of Moldova: A multitude of subversive strategies, scenarios or plans with direct or indirect reference to the Republic of Moldova are circulating in the public space, elaborated by various experts or pseudo-experts. However, in most cases, these have little prospect of materialisation, as they are launched either to attract generous financial resources from sponsors or to manipulate public opinion.
"THE KREMLIN'S 'MOLDOVAN DIVISION
The document "Strategic Objectives of the Russian Federation in the Republic of Moldova" was reportedly drafted under the leadership of Russian Foreign Intelligence Service Colonel Igor Maslov, who headed the Kremlin's so-called "Moldovan Division" until 2021. We talked about this subdivision in the #Kremlinovich series of investigations.
Our partners' sources report that Andrei Vavilov, an employee of the "Moldovan branch", was among the authors of the strategy. Our sources in special services in several countries claim that Vavilov's superior is Victor Lisenko.
Vavilov and Lisenko are not just officials of Putin's administration. They also communicate with FSB General Dmitry Miliutin, who is in charge of the Moldovan-Transnistrian intelligence network. We talked about how Miliutin influences Moldovan politics in the investigation "FSB agents in charge of Moldova".
According to data obtained by RISE Moldova together with the Dossier Centre, from November 2021 to May 2022, Vavilov called Miliutin at least three times, and Lisenco is one of the most frequent phone contacts of the FSB Moldova coordinator. During the period mentioned, Lisenko called the general at least ten times, being surpassed in terms of calls only by Miliutin's wife - Natalia.
If Miliutin came to Moldova in 2016 when Igor Dodon took office as Moldova's president, then Lisenko paid a visit to Chisinau relatively recently. In June 2019, an official Russian government delegation led by Deputy Prime Minister Dmitry Kozak arrived in Moldova. Kozak was also accompanied by Viktor Lisenko, only his presence in the delegation was not made public.
Viktor Lisenko at the meeting between representatives of the Moscow and Chisinau governments. 24 June 2019. Photo:gov.md
In Chisinau, the Russian guests met with Maia Sandu, newly appointed prime minister in a coalition government with the socialists. The incumbent president at the time, Igor Dodon, also met with the Russian delegation. The parties discussed bilateral trade and Moldova's gas supplies, which later became the focus of Russia's ten-year strategy.
RISE Moldova contacted Vavilov on one of his phone numbers just a day before this story was published. As soon as he heard his last name, the man asked:
Andrei Vavilov
- But who is calling?
- This is Vladimir Thorik calling from Moldova.
- About what?
- I'm a journalist with RISE Moldova. I have a question about a document concerning Moldova. We have a document: "Strategic Objectives of the Russian Federation..."
- You... you got the wrong number... Then he hung up.
We sent an official request to the Embassy of the Russian Federation in the Republic of Moldova to find out which of Russia's strategic objectives had been achieved, but until the inquiry was published we had not received a reply.
#politics#moldova#romania#russia#nato#ukraine#maia sandu#putin#political science#kremlin#ukraine war#unionism
46 notes
·
View notes
Video
Kolay Sesleri - Dureriz Dik (Gagauz Türklerinden)
#müzik #şarkı #canlı #akustik #Gagauz #GökOğuz #GagauzTürkleri #KolaySesleri #DurerizDik
Kaynak:
https://youtu.be/YvUa7C_OdVI
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
i love just lyyyying to people about my name no its not a traditional gagauz one mysterious and with hundreds of years of history nah bruv its the #2 most stereotypical jewish name in odessa. its literally jacob. sorry.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text

Ruslar "Din" kardeşimizdi Ancak ,biz ; KAN KARDEŞİMİZ olan Azarbaycan'a destek olmayı tercih ettik. ! Karabağ savaşına katılan Gagauz Türkleri(Gök Oğuz)
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Moldova gagauz régiójának székhelyéről, Comratról remek felhasználói képek találhatóak a google maps-en
5 notes
·
View notes
Text

Everything about Turkic ✨
My Twitter acc https://x.com/TURK1CCULTURE?t=7REqXlqRla9r1OpaHbp-yw&s=09
My Pinterest acc
#turkic#turkish#turkiye#türkiye#traditional#türk#art#nomad#artwork#ottoman#kazakh culture#kazakh#kazakhstan#azerbaijani#azerbaycan#azerbaijan#kyrgyzstan#kyrgyz#chuvash#gagauz#sakha#yakutsk#uzbek#uzbekistan#turkmen#turkmenistan#yurt#yörük#wolf#bashkir
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Modern-day non-Indo-European languages/language families of Europe include:
Uralic languages (Finnish, Estonian, Hungarian, and a number of minority languages)
Kartvelian languages (Georgian, and a number of minority languages)
Northeast Caucasian (Chechen, Avar, and a great number of smaller languages)
Northwest Caucasian (Kabardian, and a number of other smaller languages)
Basque, a language isolate (id est, it belongs to no established language family)
Mongolic (Kalmyk, spoken in the Russian Republic of Kalmykia)
Turkic (Gagauz, Crimean Tatar, and a number of other minority languages)
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Moldova
General Information
Moldova is a country in Eastern Europe. It’s the Eastern part of the historical region of Moldavia. In 1812, it was ceded to Russia. After World War I, it became part of Greater Romania, in World War II, it was turned into a Soviet republic under Russian occupation. In 1991, the independent Republic of Moldova was declared. Today, more than three fourths of the population declare themselves as ethnic Moldovans; Ukrainians, Gagauz, and Russians constitute significant minorities. About 90 % of the 2.5 Million inhabitants are Orthodox Christians. The official language is Moldovan, which is largely considered to be a dialect of Romanian. The capital is Chisinau.

Wine
Moldovans are proud of their winemaking history, which goes back circa 5.000 years. Besides more than 112.000 hectares of the small country consisting of vineyards, Moldova is also home to the world’s largest wine cellar, Mileștii Mici, which holds around two Million bottles. Cricova is also famous for its wine - the wine cellars of this town are so large and numerous that they’re called “an Underground City of wine”. October 3rd and 4th are days dedicated to wine, celebrated by the wineries with special promotions and guided visits.

~ Anastasia
Economy
The economy of Moldova is an upper-middle income economy with a high Human Development Index. Moldova is a landlocked Eastern European country, bordered by Ukraine on the east and Romania to the west. It is a former Soviet republic. Moldova's proximity to the Black Sea gives it a mild and sunny climate. The fertile Chernozem soil supports wheat, corn, barley, tobacco, sugar beet, and soybeans. Beef and dairy cattle are raised, and beekeeping is widespread. Moldova's best-known product comes from its extensive and well-developed vineyards concentrated in the central and southern regions. Moldova produces liqueur and sparkling wine. It is also known for its sunflower seeds, walnuts, apples, and other fruits. This makes the area ideal for agriculture and food processing, which accounts for about 40% of the country's GDP.

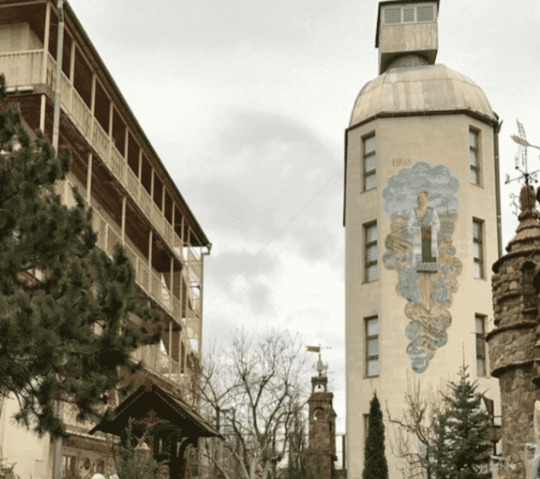
Wine Bottled Building
We know, it’s a question you’ve frequently pondered, just where can I find the largest bottle-shaped building in the world? The answer? The aptly named Strong Drinks Museum, in Tirnauca Village. The 28-metre tall museum-cum-spirit bottle is dedicated to… you guessed it, strong drinks.

~ Damian
Sources:
https://www.britannica.com/place/Moldova
https://passportsymphony.com/fun-facts-about-moldova/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Economy_of_Moldova
https://bigseventravel.com/interesting-facts-moldova/
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Alexandru Musteata, director of the Moldovan Intelligence and Security Service, SIS, said on Tuesday that Russia is involved in a malign operation to compromise Moldova’s EU accession hopes by interfering in its electoral processes.
Musteata said that Moscow first targeted Moldova’s local elections in November 2023 and will now seek to meddle in presidential elections and the country’s EU integration referendum this autumn and parliamentary elections in July 2025.
“Now they are trying to complete the next two stages, to interfere in this year’s electoral processes. We have information that attempts are being implemented to compromise the referendum for European integration, to interfere in the presidential elections, and to denigrate political institutions and candidates that will promote EU accession,” said Musteata.
The head of the SIS explained that Moscow will support various different kinds of political actors under the direct or indirect control of the Russian Federation, who, once elected, will serve the hostile interests of the Kremlin.
“Openly declared pro-Russian political actors, they have direct and confirmed links to Russian special services, political consultants, organised crime groups under Kremlin leadership, oligarchic groups and political actors who declare that they support the state, hiding behind neutral foreign policies, declaring that they defend the national interest, neutrality and statehood, but in fact, their purpose is to serve Moscow in a camouflaged form,” he said.
Musteata named politicians connected to organised crime groups led by fugitive Moldovan oligarchs who are wanted for arrest.
“All of them are planning economic and social crises, social clashes to incite inter-ethnic hatred, security or public order crises, including in the region of UTAG [the pro-Russian region of Gagauzia] or on the left of the Dniester River [the separatist region of Transnistria],” he added.
The SIS chief predicted that the destabilisation attempts will be controlled by the fugitive oligarch Ilan Shor and will be initiated from Gagauzia in the south of Moldova, where Shor is highly influential and spends considerable sums of money on organising protests and violent actions.
“This strategy can already be seen publicly. These forces will promote the false message that the Republic of Moldova’s accession to the EU would affect the country’s sovereignty,” said Musteata.
Musteata also drew attention to the use of the Telegram and TikTok apps to spread disinformation, but also attempts to use TV channels for propaganda.
Moldova has banned the main Russian TV channel alongside domestic TV channels owned by the fugitive oligarchs Shor and Vlad Plahotniuc. But a channel owned by Shor, TV6, which was banned at the national level, has started to broadcast its programmes again via Gagauzian local TV station Gagauz Radio Television, GRT.
The deputy secretary-secretary of NATO, Mircea Geoana, also said on February 15 that Russia will try to obstruct Moldova’s path towards EU membership using hybrid tactics.
“It is clear that in the Russian Federation there is an obvious interest in derailing the pro-Western path of the Republic of Moldova or other candidate countries for EU accession,” Geoana told TVR Moldova.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
UTA Găgăuzia de jure parte integrantă și inalienabilă a Republicii Moldova, de facto tinde spre separatism
Rozovel, Aliona (2024), UTA Găgăuzia de jure parte integrantă și inalienabilă a Republicii Moldova, de facto tinde spre separatism, Cunoașterea Științifică, 3:1, xxx,
UTA Gagauzia, de jure an integral and inalienable part of the Republic of Moldova, de facto tends towards separatism
Abstract
This article is devoted to the Gagauz, those national minorities of the Moldovan state, who, along with…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
KAFKASYA BÖLGESİ DOSYASI /// ÖMÜR ÇELİKDÖNMEZ : Rusya yanlısı Ga gavuz Özerk Cumhuriyeti’ni zor günler bekliyor !!!
ÖMÜR ÇELİKDÖNMEZ : Rusya yanlısı Gagavuz Özerk Cumhuriyeti’ni zor günler bekliyor !!!
27-11-2023
Rusya yanlısı Gagavuz Özerk Cumhuriyeti’ni zor günler bekliyor?
Gagavuz veya Gagauz denilen Ortodoks Türk Halkının büyük çoğunluğu Moldova’da, az bir kısmı Deliorman, Dobruca, Beserabya ve Ukrayna’da yerleşik. Romanya ve Macaristan’a göç eden Türkler olduğu gibi Gök–Oğuzlar da önceleri Romanya–Dobruca…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Antonio Velardo shares: Our Language is Dying by Unknown Author
By Unknown Author
The struggle to save Gagauz, a Turkic tongue
Published: October 4, 2023 at 06:36AM
from NYT World https://ift.tt/pclnNGO
via IFTTT

View On WordPress
0 notes