#activitypub
Text
If Staff ever implements the editing method from Mastodon, we'd be fucked.
Currently, on Tumblr, if you edit a post, all the former reblogs stay exactly the same.
On Mastodon, editing a post changes all the boosts and simply notifies the people who interacted with the post prior to the edit.
Now, can you imagine that on Tumblr?
Surely giving the OP the ability to edit their post after hundreds of thousands of people have reblogged it would be a perfectly balanced feature that I'm sure the Tumblr' userbase has never abused before.
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
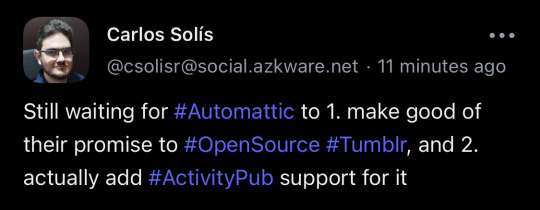
hey staff, how’s it going with this? it has been 4 years. can we hang out with my fediverse friends?
#image description in alt#automattic#tumblr staff#a&m#open source#oss#technology#fediverse#federate#mastodon#activitypub
840 notes
·
View notes
Text
A quick example of the current state of Goblin:
I imported my following list from mastodon and started following everyone with my goblin.band account too, so I basically read all my mastodon content from there already. Even if no one but me using the tumblr-like features I'm adding, I already enjoy Goblin more than Mastodon.
Things that I've added since my last post:
Integration with mastodon (and well, any other fediverse platform that use plain text instead of html)
Copy/pasting images in the editor
Sanitized html input when saving & updating posts
Improved the landing page
Cleaned the menus and improved the UI in general
Current "next" to-do list:
Fix posts displaying images twice when you paste an image
Fix RSS feed including the inline files again after the post
Sanitize html inputs on incoming federated posts
fix several style issues around different settings sections (black texts on dark blue background, white text over white background, etc)
Figure out if I can create a tumblr-api app so the posts from goblin can be automatically shared here without having to go through Zappier.
Figure out what kind of server I need to run a, let's say, 500 people server.
Find someone to do some security review of my server (Long story short, I've only a very slim idea of what I'm doing when configuring a server and I'm sure I've left some huge security holes around).
This is happening, folks. I think Goblin is going to be a reality. At least https://goblin.band will be.
282 notes
·
View notes
Text

257 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why you should make a Misskey/Shonk.Social/Mastodon account.
Hi lol. As a trans artist who has been incredibly frustrated with tumblr censoring lgbt content and general transphobia. Eat shit Matt.🔨🚗💥 I wanted to offer a small guide about activitypub servers. Considering Tumblr and Threads wish to integrate with activitypub services.
It truly doesn't matter what instance or server you pick. There are a lot of them that within each individual one hosts thousands of smaller communities. You can also make your own servers and instances!
Other good servers.
Point of the matter is, you can follow anyone from any instance and have them on our dashboard. You can follow someone from mastodon and still use misskey.io Or (eventually) follow someone from tumblr on shonk.social.



Or even make your own instance. The best part is say one of these sites has another CEO meltdown, or they have harmful policies, you can migrate to another instance without losing followers or our posts.

From our experiences Misskey.io is similar to twitter AO3 and deviantart with no censorship regarding artwork (so long as you mark it as explicit). Which is good and bad. That means they allow drawn nsfw lgbt content and sex work. However being a japanese instance they allow drawn loli shota and noncon. Therefore I highly recommend using an instance blocklist and blocking any terms or words in relation. There are hatespeech instances and conspiracy instances of course. And it is always good to be aware of when a server becomes toxic. Luckily with instances and account migration we can pack up and leave. The reason I'm on Misskey currently is because its the biggest server and there are more utilities than shonk such as animated banners, decorations, and community outreach.
Mastodon works but the UI is incredibly bland and uncustomizable. It also feels mostly dead.
Shonk.Social is a fork of Misskey that is a safe lgbt space. It is a very small server currently but the people who code it are incredibly passionate. Their boosts and global timelines are really good ways to keep up to date on other servers.
You've also got custom emojis, lists, channels, antennae.

There's also cookie clicker LOL

But all the same I highly recommend it. If tumblr decides to feature activitypub integration we could eventually follow people from tumblr on any instances without all of the Transphobic ceos and app breaking ads.
#misskey#misskey.io#activitypub#shonk.social#lgbt#hammer car explosion#fediverse#mastodon#tumblr alternative#trans rights
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
What the fediverse (does/n't) solve

No matter how benevolent a dictatorship is, it’s still a dictatorship, and subject to the dictator’s whims. We must demand that the owners and leaders of tech platforms be fair and good — but we must also be prepared for them to fail at this, sometimes catastrophically.
That is, even if you trust Tim Cook to decide what apps you are and aren’t allowed to install — including whether you are allowed to install apps that block Apple’s own extensive, nonconsensual, continuous commercial surveillance of its customers — you should also be prepared for Cook to get hit by a bus and replaced by some alt-right dingleberry.
What happens next is a matter of technology and law. It’s a matter of whether you have to give up your media and your apps and your data to escape the no-longer-benevolent dictatorship. It depends on whether the technology is designed to let you move those things, and whether the law protects you from tech companies, or whether it protects tech companies from *you, by criminalizing jailbreaking, reverse engineering, scraping, etc.
As thorny as this is, it’s even harder when we’re talking about social media, because it’s social. Sociability adds a new and pernicious switching cost, when we hold each other hostage because we can’t agree on when/whether to go, and if we do, where to go next. When the management of your community goes septic, it can be hard to leave, because you have to leave behind the people who matter to you if you do.
We’ve all been there: do you quit your writers’ circle because one guy is being a jerk? Do you stop going to a con because the concom tolerates a predator? Do you stop going to family Thanksgiving because your racist Facebook uncle keeps trying to pick a fight with you? Do you accompany your friends to dinner at a restaurant whose owners are major donors to politicians who want to deport you?
This collective action problem makes calamity of so long life. At the outer extreme, you have the families who stay put even as their governments slide into tyranny, risking imprisonment or even death, because they can’t bear to be parted from one another, and they all have different views of how bad the situation really is:
https://www.theatlantic.com/books/archive/2022/12/the-oppermanns-book-holocaust-nazi-fascism/672505/
The corporate person is a selfish narcissist, a paperclip-maximizing artificial lifeform forever questing after its own advantage. It is an abuser. Like all abusers, it is keenly attuned to any social dynamic that it can use to manipulate its victims, and so social media is highly prized by these immortal colony-organisms.
You can visit all manner of abuses upon a social network and it will remain intact, glued together by the interpersonal bonds of its constituent members. Like a kidnapper who takes your family hostage, abusers weaponize our love of one another and use it to make us do things that are contrary to our own interests.
In “Stop Talking to Each Other and Start Buying Things: Three Decades of Survival in the Desert of Social Media,” Cat Valente is characteristically brilliant about this subject. It is one of the best essays you’ll read this month:
https://catvalente.substack.com/p/stop-talking-to-each-other-and-start
Valente is on the leading edge of creators who were born digital — whose social life was always online, and whose writing career grew out of that social life. In 2009, she posted her debut novel, “The Girl Who Circumnavigated Fairyland in a Ship of Her Own Making” to the web for free. Two years, and many awards, later, Macmillan brought it out in hardcover:
https://memex.craphound.com/2011/05/10/valentes-girl-who-circumnavigated-fairyland-sweet-fairytale-shot-through-with-salty-tears-magic/
“Stop Talking to Each Other” is a memoir wrapped around a trenchant, take-no-prisoners critique of all the robber-barons who’ve made us prisoners to one another and fashioned whips out of our own affection for one another and the small pleasures we give each other.
It begins with Valente’s girlhood in the early 1990s, where Prodigy formed a lifeline for her lonely, isolated existence. Valente — a precocious writer — made penpals with other Prodigy users, including older adults who assumed they were talking to a young adult. These relationships expanded her world, uplifting and enriching her.
Then, one day, she spotted a story about Prodigy in her dad’s newspaper: “PRODIGY SAYS: STOP TALKING TO EACH OTHER AND START BUYING THINGS.” The headline floored her. Even if Valente wanted to buy the weird grab-bag of crap for sale at Prodigy in 1991, she was a 12 year old and had no way to send internet money to Prodigy. Also, she had no money of any sort.
For her, the revelation that the owners of Prodigy would take away “this one solitary place where I felt like I mattered” if she “didn’t figure out how to buy things from the screen” was shocking and frightening. It was also true. Prodigy went away, and took with it all those human connections a young Cat Valente relied on.
This set the pattern for every online community that followed: “Stop talking to each other and start buying things. Stop providing content for free and start paying us for the privilege. Stop shining sunlight on horrors and start advocating for more of them. Stop making communities and start weaponizing misinformation to benefit your betters.”
Or, more trenchantly: “Stop benefitting from the internet, it’s not for you to enjoy, it’s for us to use to extract money from you. Stop finding beauty and connection in the world, loneliness is more profitable and easier to control. Stop being human. A mindless bot who makes regular purchases is all that’s really needed.”
Valente traces this pathology through multiple successive generations of online community, lingering on Livejournal, whose large community of Russian dissidents attracted Russian state-affiliated investors who scooped up the community and then began turning the screws on it, transforming it into a surveillance and control system for terrorizing the mutual hostages of the Russian opposition.
Valente and her friends on the service were collateral damage in the deliberate enshittification of LJ, band the Russian dissidents had it worse than they did, but it was still a painful experience. LJ was home to innumerable creators who “grew audiences through connections and meta-connections you already trusted.”
Most importantly, the poisoning of LJ formed a template, for how to “[take] apart a minor but culturally influential community and develop techniques to do it again, more efficiently, more quickly, with less attention.”
It’s a template that has been perfected by the alt-right, by the Sad Puppies and the Gamergaters and their successor movements. These trolls aren’t motivated by the same profit-seeking sociopathy of the corporate person, but they are symbiotic with it.
Valente lays out the corporate community’s lifecycle:
Be excited about the internet, make a website!
Discover that users are uninterested in your storefront, add social features.
Add loss-leaders to “let users make their own reasons to use the site” (chat, blogs, messaging, etc), and moderate them “to make non-monster humans feel safe expressing themselves and feel nice about site.”
The site works, and people “[use] free tools to connect with each other and learn and not be lonely and maybe even make a name for themselves sometimes.”
The owners demand that users “stop talking and start buying things.”
Users grow disillusioned with a site whose sociability is an afterthought to the revenue-generation that is supposed to extract all surplus value from the community they themselves created.
The owners get angry, insult users, blanket the site with ads, fire moderators, stoke controversy that creates “engagement” for the ads. They sell user data. They purge marginalized community that advertisers don’t like. They raise capital, put the community features behind a paywall, and focus so hard on extraction that they miss the oncoming trends.
“Everyone is mad.”
“Sell the people you brought together on purpose to large corporation, trash billionaire, or despotic government entity who hates that the site’s community used those connective tools to do a revolution.”
The people who “invested their time, heart, labor, love, businesses and relationships” are scattered to the winds. Corporate shareholders don’t care.
Years later, the true story of how the site disintegrated under commercial pressures comes out. No one cares.
The people who cashed out by smashing the community that created their asset are now wealthy, and they spend that wealth on “weird right-wing shit…because right-wing shit says no taxes and new money hates taxes.”
This pattern recurs on innumerable platforms. Valente’s partial list includes “Prodigy, Geocities, collegeclub.com, MySpace, Friendster, Livejournal, Tumblr,” and, of course, Twitter.
Twitter, though, is different. First, it is the largest and most structurally important platform to be enshittified. Second, because it was enshittified so much more quickly than the smaller platforms that preceded it.
But third, and most importantly, because Twitter’s enshittification is not solely about profit. Whereas the normal course of a platform’s decline involves a symbiosis between corporate extraction and trollish cruelty, the enshittification of Twitter is being driven by an owner who is both a sociopathic helmsan for a corporate extraction machine and a malignant, vicious narcissist.
Valente describes Musk’s non-commercial imperatives: “the yawning, salivating need to control and hurt. To express power not by what you can give, but by what you can take away…[the] viral solipsism that cannot bear the presence of anything other than its own undifferentiated self, propagating not by convincing or seduction or debate, but by the eradication of any other option.”
Not every platform has been degraded this way. Valente singles out Diaryland, whose owner, Andrew, has never sold out his community of millions of users, not in all the years since he created it in 1999, when he was a Canadian kid who “just like[d] making little things.” Andrew charges you $2/month to keep the lights on.
https://diaryland.com/
Valente is right to lionize Diaryland and Andrew. In fact, she’s right about everything in this essay. Or, nearly everything. “Almost,” because at the end, she says, “the minute the jackals arrive is the same minute we put down the first new chairs in the next oasis.”
That’s where I think she goes wrong. Or at least, is incomplete. Because the story of the web’s early diversity and its focus on its users and their communities isn’t just about a natural cycle whereby our communities became commodities to be tormented to ruination and sold off for parts.
The early web’s strength was in its interoperability. The early web wasn’t just a successor to Prodigy, AOL and other walled gardens — it was a fundamental transformation. The early web was made up of thousands of small firms, hobbyists, and user groups that all used the same standard protocols, which let them set up their own little corners of the internet — but also connected those communities through semi-permeable membranes that joined everything, but not in every way.
The early web let anything link to anything, but not always, which meant that you could leave a community but still keep tabs on it (say, by subscribing to the RSS feeds of the people who stayed behind), but it also meant that individuals and communities could also shield themselves from bad actors.
The right of exit and the freedom of reach (the principle that anyone can talk to anyone who wants to talk to them) are both key to technological self-determination. They are both imperfect and incomplete, but together, they are stronger, and form a powerful check on both greed and cruelty-based predation:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/12/19/better-failure/#let-my-tweeters-go
Small wonder that, from the beginning, the internet has been a fight between those who want to build a commons and those who wish to enclose it. Remember when we were all angry that the web was disappearing into Flash, the unlinkable proprietary blobs that you couldn’t ad-block or mute or even pause unless they gave you permission?
Remember when Microsoft tried, over and over again, to enclose the internet, first as a dial-up service, then as a series of garbage Windows-based Flash-alikes. Remember Blackbird?
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blackbird_(online_platform)
But standard protocols exert powerful network effects on corporations. When everyone is adhering to a standard, when everything can talk to everything else, then it’s hard to lure users into a walled garden. Microsoft coerced users into it by striking bargains with buyers at large companies to force its products on all their employees, and then by breaking compatibility with rival products, which made it hard for those employees to use another vendor’s products in their personal lives. Not being able to access your company email or edit your company documents on your personal device is a powerful incentive to use the same product your company uses.
Apple, meanwhile, seduced users into its walled garden, promising that it would keep them safe and that everything would just work, and then using its power over those customers to gouge them on dongles and parts and repair and apps.
Both companies — like all corporations — are ferocious rent-seekers, but both eventually capitulated to the internet — bundling TCP and, eventually, browsers with their OSes. They never quit trying to enclose the web, via proprietary browser extensions and dirty tricks (Microsoft) or mobile lock-in and dirty tricks (Apple). But for many years, the web was a truly open platform.
The enclosure of online communities can’t be understood without also understanding the policy choices that led to the enclosure of tech more broadly. The decision to stop enforcing antitrust law (especially GWB’s decision not to appeal in the Microsoft antitrust case) let the underlying platforms grow without limits, by buying any serious rival, or by starving it out of existence by selling competing products below cost, cross-subidizing them with rents extracted from their other monopoly lines.
These same policies let a few new corporate enclosers enter the arena, like Google, which is virtually incapable of making a successful product in-house, but which was able to buy others’ successes and cement its web dominance: mobile, video, server management, ad-tech, etc.
These firms provide the substrate for community abusers: apps, operating systems and browser “standards” that can’t be legally reverse-engineered, and lobbying that strengthens and expands those “Felony Contempt of Business Model” policies:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2017/09/open-letter-w3c-director-ceo-team-and-membership
Without these laws and technologies, corporations wouldn’t be able to block freedom of exit and freedom of reach. These laws and technologies let these corporations demand that the state obliterate anyone who gives users the tools to set their own terms for the communities they built.
These are the laws and technologies that transform network effects from a tool for openness — where even the largest, most vicious corporations must seek to pervert, rather than ignore, standards — into a tool for enclosure, where we are all under mounting pressure to move inside a walled garden.
This digital feudalism is cloaked in the language of care and safety. The owners of these walled gardens insist that they are benevolent patriarchs who have built fortresses to defend us from external threats, but inevitably they are revealed as warlords who have built prisons to keep us from escaping from them:
https://locusmag.com/2021/01/cory-doctorow-neofeudalism-and-the-digital-manor/
Which brings me to the Fediverse. The Fediverse’s foundation is a standard called ActivityPub, which was designed by weirdos who wanted to make a durably open, interoperable substrate that could support nearly any application. This was something that large corporations were both uninterested in building and which they arrogantly dismissed as a pipe dream. This means that Activitypub is actually as good as its architects could make it, free from boobytraps laid by scheming monopolists.
The best-known Fediverse application is Mastodon, which has experienced explosive growth from people who found Musk’s twin imperatives to cruelty and extraction sufficiently alarming that they have taken their leave of Twitter and the people they cared about there. This is not an easy decision, and Musk is bent on making it harder by sabotaging ex-Twitter users’ ability to find one another elsewhere. He wants the experience of leaving Twitter to be like the final scene of Fiddler On the Roof, where the villagers of Anatevka are torn from one another forever:
https://doctorow.medium.com/how-to-leave-dying-social-media-platforms-9fc550fe5abf
With Mastodon’s newfound fame comes new scrutiny, and a renewed debate over the benefits and drawbacks of decentralized, federated systems. For example, there’s an ongoing discussion about the role of quote-tweeting, which Mastodon’s core devs have eschewed as conducive to antisocial dunks, but which some parts of Black Twitter describe as key to a healthy discourse:
https://www.tbray.org/ongoing/When/202x/2022/12/21/Mastodon-Ethics
But quote tweeting wasn’t initially a part of Twitter. Instead, users kludged it, pasting in text and URLs for others’ tweets to make it work. Eventually, Twitter saw the utility of quote-tweeting and adopted it, making it an official feature.
There is a possibility that Mastodon’s core devs will do the same, adding quote-tweet to the core codebase for Mastodon. But if they don’t, the story isn’t over. Because Mastodon is free software, and because it is built on an open standard, anyone can add this feature to their Mastodon instance. You can do this yourself, or you can hire someone else to do it for you.
Now, not everyone has money or coding skills — but also, not everyone has the social clout to convince a monolithic, for-profit corporation to re-engineer its services to better suit their needs. And while there is a lot of overlap between “people who can code,” and “people who can afford to pay coders” and “people whom a tech company listens to,” these are not the same population.
In other words: Twitter is a place where you get quote-tweeting if the corporation decides you need it, and Mastodon is a place where you get quote-tweeting if the core devs decide you need it, or if you have the skills or resources to add it yourself.
What’s more, if Mastodon’s core devs decide to take away a feature you like, you and your friends can stand up your own Mastodon server that retains that feature. This is harder than using someone else’s server — but it’s way, way easier than convincing Twitter it was wrong to take away the thing you loved.
The perils of running your own Mastodon server have also become a hot topic of debate. To hear the critics warn of it, anyone who runs a server that’s open to the public is painting a huge target on their back and will shortly be buried under civil litigation and angry phone-calls from the FBI.
This is: Just. Not. True. The US actually has pretty good laws limiting intermediary liability (that is, the responsibility you bear for what your users do). You know all that stuff about how CDA230 is “a giveaway to Big Tech?” That’s only true if the internet consists solely of Big Tech companies. However, if you decide to spend $5/month hosting a Mastodon instance for you and your community, that same law protects you.
Indeed, while running a server that’s open to the public does involve some risk, most of that risk can be contained by engaging in a relatively small, relatively easy set of legal compliance practices, which EFF’s Corynne McSherry lays out in this very easy-to-grasp explainer:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2022/12/user-generated-content-and-fediverse-legal-primer
Finally, there’s the ongoing debate over whether Mastodon can (and should) replace Twitter. This week on the Canadaland Short Cuts podcast, Jesse Brown neatly summarized (and supported, alas) the incorrect idea that using Mastodon was no different from using Gab or Parler or Post.
https://www.canadaland.com/podcast/843-god-save-the-tweets/
This is very, very wrong. The thing is, even if you like and trust the people who run Gab or Parler or Post, you face exactly the same risk you face with Twitter or Facebook: that the leadership will change, or have a change of heart, and begin to enshittify your community there. When they do, your only remedy will be the one that Valente describes, to scatter to the winds and try and reform your community somewhere else.
But that’s not true of the Fediverse. On Mastodon, you can export all your followers, and all the people who follow you, with two clicks. Then you can create an account on another server and again, with just two clicks, you can import those follows and followers and be back up and running, your community intact, without being under the thumb of the server manager who decided to sell your community down the river (you can also export the posts you made).
https://codingitwrong.com/2022/10/10/migrating-a-mastodon-account.html
Now, it’s also true that a particularly vindictive Mastodon server owner could summarily kick you off the server without giving you a chance to export your data. Doing so would arguably run afoul of the GDPR and state laws like the CCPA.
Strengthening these privacy laws would actually improve user rights — unlike abolishing CDA 230, which would simultaneously make the corporate owners of big services more trigger-happy when it comes to censoring content from marginalized groups, and make it all but impossible for those groups to safely run their own servers to decamp to when this happens.
Letting people set up their own communities, responsible to one another, is the tonic for Valente’s despair that the cycle of corporate predation and enshittification is eternal, and that people who care for one another and their communities are doomed to be evicted again and again and again and again.
And *federating these communities — creating semi-permeable membranes between them, blocking the servers for people who would destroy you, welcoming messages from the like-minded, and taking intermediate steps for uneasy allies — answers Brown’s concern that Twitter is the only way we can have “one big conversation.”
This “one conversation” point is part of Brown’s category error in conflating federated media with standalone alternatives to Twitter like Post. Federated media is one big conversation, but smeared out, without the weak signal amplification of algorithms that substitute the speech of the people you’ve asked to hear from with people who’ve paid to intrude on your conversation, or whom the algorithm has decided to insert in it.
Federation is an attractive compromise for people like Valente, who are justly angry at and exhausted by the endless cycle of “entrepreneurs” building value off of a community’s labor and then extracting that value and leaving the community as a dried-out husk.
It’s also a promising development for antitrust advocates like me, who are suspicious of corporate power overall. But federation should also please small-government libertarian types. Even if you think the only job of the state is to enforce contracts, you still need a state that is large and powerful enough to actually fulfill that role. The state can’t hold a corporation to its promises if it is dwarfed by that corporation — the bigger the companies, the bigger the state has to be to keep them honest.
The stakes are high. As Valente writes, the digital communities that flourished online, only to be eradicated by cruelty and extraction, were wonderful oases of care and passion. As she says, “Love things. Love people. Love the small and the weird and the new.”
“Be each other’s pen pals. Talk. Share. Welcome. Care. And just keep moving. Stay nimble. Maybe we have to roll the internet back a little and go back to blogs and decentralized groups and techy fiddling and real-life conventions and idealists with servers in their closets.”
“Protect the vulnerable. Make little things. Wear electric blue eyeshadow. Take a picture of your breakfast. Overthink Twin Peaks. Get angry. Do revolutions. Find out what Buffy character you are. Don’t get cynical. Don’t lose joy. Be us. Because us is what keeps the light on when the night comes closing in.”
Image:
Cryteria (modified)
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
Heisenberg Media (modified)
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Elon_Musk_-_The_Summit_2013.jpg
CC BY 2.0
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/deed.en
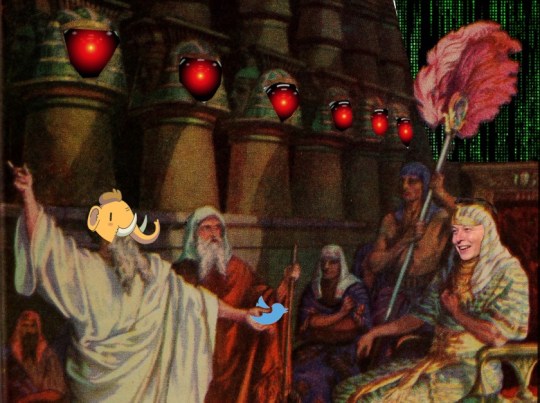
[Moses confronting the Pharaoh, demanding that he release the Hebrews. Pharaoh's face has been replaced with Elon Musk's. Moses holds a Twitter logo in his outstretched hand. Moses's head has been replaced with the head of Tusky, the Mastodon mascot. The faces embossed in the columns of Pharaoh's audience hall have been replaced with the menacing red eye of HAL9000 from 2001: A Space Odyssey. The wall over Pharaoh's head has been replaced with a Matrix 'code waterfall' effect.]
#pluralistic#prodigy#standards#activitypub#tumblr#federation#fediverse#mastodon#jesse brown#canadaland#cat valente#twitter#yasnses#social media#freedom of exit#section 230#cda 230#intermediary liability
142 notes
·
View notes
Text
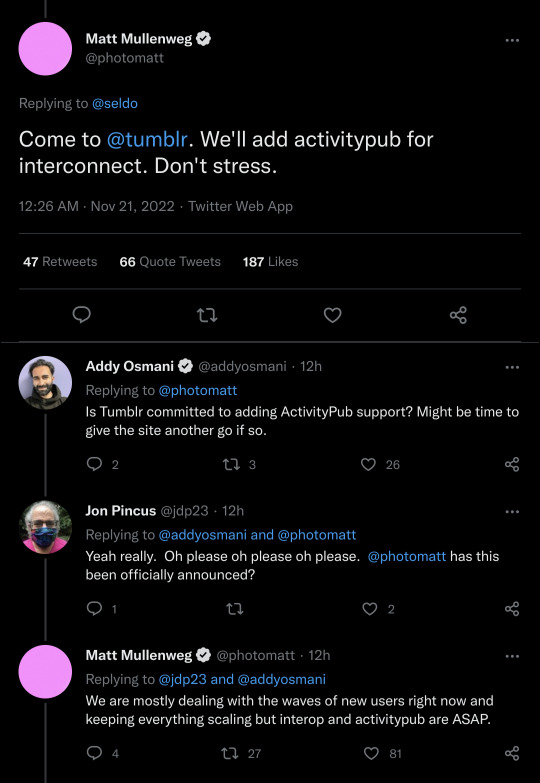
Tumblr will add support for ActivityPub, the open, decentralized social networking protocol that today is powering social networking software like Twitter alternative Mastodon, the Instagram-like Pixelfed, video streaming service PeerTube, and others. The news was revealed in response to a Twitter user’s complaint about Mastodon’s complexities. Automattic CEO Matt Mullenweg — whose company acquired Tumblr from Verizon in 2019 — suggested the user “come to Tumblr” as the site would soon “add activitypub for interconnect.”
“Don’t stress,” he said, before clarifying that Tumblr first has to deal with the waves of new users coming in right now from Twitter but that support for “interop and activitypub” were due to come “ASAP.”
In short, this announcement means Tumblr would move from being only a niche blogging platform to becoming a part of a larger, decentralized social network of sorts — and one whose user base has grown in size in recent days as people flee Elon Musk’s Twitter in search of new communities.
#activitypub#tech memes#tech news#technology#open source#decentralization#twitter#news#techcrunch#computers#software engineering
137 notes
·
View notes
Text

I typed a message to the @tumblr team about copying a feature from @wordpress & @wordpressdotcom that allows the latter two to automatically post snippets with links to Mastodon.
I know activating ActivityPub within Tumblr is currently expensive…
…so a better option would be to flirt with the Fediverse instead via auto share. At least until ActivityPub support comes to the Tumblverse (I still believe ActivityPub activation should be a premium feature for those with custom domains as an anti-spam measure).
It would also be cool if Tumblr could embrace other platforms beyond Mastodon such as:
Misskey
Pleroma
Firefish
Threads (in the future)
…but that might be asking too much. Maybe…it would be cool if they supported the others though.
#fediverse#activitypub#mastodon#tumblr#automattic#social networks#tech#pleroma#firefish#misskey#threads#meta
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
so was the “we’re adding activitypub!” thing just a complete lie or is that somehow still in the works?
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
A warning to anyone trying out the fediverse/Mastodon
There's a large cluster of people who are basically an alliance of photomatts and (if you're on Twitter) Jai orbiters who try to police the various servers to isolate people they deem to be undesirables.
They are deeply transmisogynistic and unhinged, in ways that make photomatt's recent behaviour seem downright enlightened in comparison.
A recent good summary of what's going on is posted here.
A much lengthier history of this drama (which has been going on for years) has been put up by a kindly anon here.
The fediverse isn't all like this, but you do need to watch out which server you make your account on.
General red flags to avoid:
any involvement with "The Bad Space"
mastodon.art
users who frequently post to the #FediBlock hashtag
use of automated or shared blocklists (these are for entire servers blocking other servers, not individual accounts)
reasons for blocking a server mentioning "oliphaunt" or "tier" anything
As a general rule, you will want to coordinate with your mutuals which servers you go to as much as possible, to minimize the chances that you end up on different instances and end up getting cut off from each other until at least one of you makes an alt so you're both on servers that communicate with each other. This takes a bit of trial and error but unfortunately that is the nature of a decentralized social networking system.
So all that said... I really hope staff smarten up, Matt gets put in his place by his and Tumblr's lawyers and we can all stay where we are.
#mastodon#activitypub#fediblock#the bad space#pleroma#akkoma#mastodon.art#misskey#sharkey#gotosocial#pixelfed#a lot of people will warn you to avoid mastodon.social which isn't bad advice#but frankly even m.s would be vastly preferable to the creepy totalitarian policing you see from admins who think TBS is good
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Since Tumblr is planning on implementing ActivityPub in order to federate with Mastodon, I can’t help but wonder how the 4,000,000 character limit on here will affect the protocol and Mastodon users looking in from the outside.
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
now seems like a decently good time to mention that I have vague plans to start using activitypub
though that probably won't happen for at least a few months, mainly because I want to run my own server
regardless, if I do make the switch, I will be using the same name (probably under a domain like "tokinanpa.dev" or similar); again, haven't planned much yet
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Changelog 6/3/2024
Well friends, I come to you bringing some great news!
Not only @sirilyan has set-up a second Goblin server (https://kobold.page), but after a few adjustments and fixes, now Goblin is fully working as a tested multi-server network! Someone using an account based on a server (let's say, Kobold,page) is able to follow and see posts from someone in a different server (for example, Goblin.band) not only keeping all the formatting, but also the entire reblog chain.
I know this may sound like technical gibberish, but it means that the idea of a federated version of Tumblr is finally taking shape and... it works. It actually works. And it's beautiful.
144 notes
·
View notes
Text
When Meta announced opening Threads to ActivityPub, I thought this could be a great thing for decentralised, people-owned and free platforms like Mastodon, because it would bring attention to this anti-capitalist form of social media.
But after reading this, I changed my mind. Meta, Alphabet and all the other fucking horrible capitalist kraken will never play nice. They are inherently evil.
Find me in the Fediverse:
Take social media back! Don't let your data get sold to the government and people who think you are just a cow to milk.
18 notes
·
View notes
Photo
A bit excited about this promise from @photomatt! ActivityPub, for those not in the know, is a decentralized social networking protocol. (Its best-known implementation is in Mastodon.) With the murder implosion of Twitter, this has not only cross-platform posting and viewing implications, but also the potential for self-hosted Tumblr servers. Fascinating.
121 notes
·
View notes
Text
Solving the Moderator's Trilemma with Federation

The classic trilemma goes: “Fast, cheap or good, pick any two.” The Moderator’s Trilemma goes, “Large, diverse userbase; centralized platforms; don’t anger users — pick any two.” The Moderator’s Trilemma is introduced in “Moderating the Fediverse: Content Moderation on Distributed Social Media,” a superb paper from Alan Rozenshtein of U of Minnesota Law, forthcoming in the journal Free Speech Law, available as a prepub on SSRN:
https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4213674#maincontent
If you’d like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here’s a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/03/04/pick-all-three/#agonism
Rozenshtein proposes a solution (of sorts) to the Moderator’s Trilemma: federation. De-siloing social media, breaking it out of centralized walled gardens and recomposing it as a bunch of small servers run by a diversity of operators with a diversity of content moderation approaches. The Fediverse, in other words.
In Albert Hirschman’s classic treatise Exit, Voice, and Loyalty, stakeholders in an institution who are dissatisfied with its direction have two choices: voice (arguing for changes) or exit (going elsewhere). Rozenshtein argues that Fediverse users (especially users of Mastodon, the most popular part of the Fediverse) have more voice and more “freedom of exit”:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Exit,_Voice,_and_Loyalty
Large platforms — think Twitter, Facebook, etc — are very unresponsive to users. Most famously, Facebook polled its users on whether they wanted to be spied on. Faced with overwhelming opposition to commercial surveillance, Facebook ignored the poll result and cranked the surveillance dial up to a million:
https://www.nbcnews.com/tech/tech-news/facebook-ignores-minimal-user-vote-adopts-new-privacy-policy-flna1c7559683
A decade later, Musk performed the same stunt, asking users whether they wanted him to fuck all the way off from the company, then ignored the vox populi, which, in this instance, was not vox Dei:
https://apnews.com/article/elon-musk-twitter-inc-technology-business-8dac8ae023444ef9c37ca1d8fe1c14df
Facebook, Twitter and other walled gardens are designed to be sticky-traps, relying on high switching costs to keep users locked within their garden walls which are really prison walls. Internal memos from the companies reveal that this strategy is deliberate, designed to keep users from defecting even as the service degrades:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2021/08/facebooks-secret-war-switching-costs
By contrast, the Fediverse is designed for ease of exit. With one click, users can export the list of the accounts they follow, block and mute, as well as the accounts that follow them. With one more click, users can import that data into any other Fediverse server and be back up and running with almost no cost or hassle:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/12/23/semipermeable-membranes/
Last month, “Nathan,” the volunteer operator of mastodon.lol, announced that he was pulling the plug on the server because he was sick of his users’ arguments about the new Harry Potter game. Many commentators pointed to this as a mark against federated social media, “You can’t rely on random, thin-skinned volunteer sysops for your online social life!”
https://mastodon.lol/@nathan/109836633022272265
But the mastodon.lol saga demonstrates the strength of federated social media, not its weakness. After all, 450 million Twitter users are also at the mercy of a thin-skinned sysop — but when he enshittifies his platform, they can’t just export their data and re-establish their social lives elsewhere in two clicks:
Mastodon.lol shows us how, if you don’t like your host’s content moderation policies, you can exercise voice — even to the extent of making him so upset that he shuts off his server — and where voice fails, exit steps in to fill the gap, providing a soft landing for users who find the moderation policies untenable:
https://doctorow.medium.com/twiddler-1b5c9690cce6
Traditionally, centralization has been posed as beneficial to content moderation. As Rozenshtein writes, a company that can “enclose” its users and lock them in has an incentive to invest in better user experience, while companies whose users can easily migrate to rivals are less invested in those users.
And centralized platforms are more nimble. The operators of centralized systems can add hundreds of knobs and sliders to their back end and twiddle them at will. They act unilaterally, without having to convince other members of a federation to back their changes.
Centralized platforms claim that their most powerful benefit to users is extensive content moderation. As Tarleton Gillespie writes, “Moderation is central to what platforms do, not peripheral… [it] is, in many ways, the commodity that platforms offer”:
https://yalebooks.yale.edu/book/9780300261431/custodians-of-the-internet/
Centralized systems claim that their enclosure keeps users safe — from bad code and bad people. Though Rozenshtein doesn’t say so, it’s important to note that this claim is wildly oversold. Platforms routinely fail at preventing abuse:
https://www.nbcnews.com/nbc-out/out-news/sexual-assault-harassment-bullying-trans-students-say-targeted-school-rcna7803
And they also fail at blocking malicious code:
https://www.scmagazine.com/news/threats/apple-bugs-ios-macos_new_class
But even where platforms do act to “keep users safe,” they fail, thanks to the Moderator’s Trilemma. Setting speech standards for millions or even billions of users is an impossible task. Some users will always feel like speech is being underblocked — while others will feel it’s overblocked (and both will be right!):
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2021/07/right-or-left-you-should-be-worried-about-big-tech-censorship
And platforms play very fast and loose with their definition of “malicious code” — as when Apple blocked OG App, an Instagram ad-blocker that gave you a simple feed consisting of just the posts from the people you followed:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/02/05/battery-vampire/#drained
To resolve the Moderator’s Trilemma, we need to embrace subsidiarity: “decisions should be made at the lowest organizational level capable of making such decisions.”
https://pluralistic.net/2023/02/07/full-stack-luddites/#subsidiarity
For Rozenshtein, “content-moderation subsidiarity devolves decisions to the individual instances that make up the overall network.” The fact that users can leave a server and set up somewhere else means that when a user gets pissed off enough about a moderation policy, they don’t have to choose between leaving social media or tolerating the policy — they can simply choose another server that’s part of the same federation.
Rozenshtein asks whether Reddit is an example of this, because moderators of individual subreddits are given broad latitude to set their own policies and anyone can fork a subreddit into a competing community with different moderation norms. But Reddit’s devolution is a matter of policy, not architecture — subreddits exist at the sufferance of Reddit’s owners (and Reddit is poised to go public, meaning those owners will include activist investors and large institutions that might not care about your little community). You might be happy about Reddit banning /r_TheDonald, but if they can ban that subreddit, they can ban any subreddit. Policy works well, but fails badly.
By moving subsidiarity into technical architecture, rather than human policy, the fediverse can move from antagonism (the “zero-sum destructiveness” that dominates current online debate) to agonism, where your opponent isn’t an enemy — they are a “political adversary”:
https://www.yalelawjournal.org/article/the-administrative-agon
Here, Rozenshtein cites Aymeric Mansoux and Roel Roscam Abbing’s “Seven Theses On The Fediverse And The Becoming Of Floss”:
https://test.roelof.info/seven-theses.html
For this to happen, different ideologies must be allowed to materialize via different channels and platforms. An important prerequisite is that the goal of political consensus must be abandoned and replaced with conflictual consensus…
So your chosen Mastodon server “may have rules that are far more restrictive than those of the major social media platforms.” But the whole Fediverse “is substantially more speech protective than are any of the major social media platforms, since no user or content can be permanently banned from the network and anyone is free to start an instance that communicates both with the major Mastodon instances and the peripheral, shunned instances.”
A good case-study here is Gab, a Fediverse server by and for far-right cranks, conspiratorialists and white nationalists. Most Fediverse servers have defederated (that is, blocked) Gab, but Gab is still there, and Gab has actually defederated from many of the remaining servers, leaving its users to speak freely — but only to people who want to hear what they have to say.
This is true meaning of “freedom of speech isn’t freedom of reach.” Willing listeners aren’t blocked from willing speakers — but you don’t have the right to be heard by people who don’t want to talk to you:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/12/10/e2e/#the-censors-pen
Fediverse servers are (thus far) nonprofits or hobbyist sites, and don’t have the same incentives to drive “engagement” to maximize the opportunties to show advertisements. Fediverse applications are frequently designed to be antiviral — that is, to prevent spectacular spreads of information across the system.
It’s possible — likely, even — that future Fediverse servers will be operated by commercial operators seeking to maximize attention in order to maximize revenue — but the users of these servers will still have the freedom of exit that they enjoy on today’s Jeffersonian volunteer-run servers — and so commercial servers will have to either curb their worst impulses or lose their users to better systems.
I’ll note here that this is a progressive story of the benefits of competition — not the capitalist’s fetishization of competition for its own sake, but rather, competition as a means of disciplining capital. It can be readily complemented by discipline through regulation — for example, extending today’s burgeoning crop of data-protection laws to require servers to furnish users with exports of their follow/follower data so they can go elsewhere.
There’s another dimension to decentralized content moderation that exit and voice don’t address — moderating “harmful” content. Some kinds of harm can be mitigated through exit — if a server tolerates hate speech or harassment, you can go elsewhere, preferably somewhere that blocks your previous server.
But there are other kinds of speech that must not exist — either because they are illegal or because they enact harms that can’t be mitigated by going elsewhere (or both). The most spectacular version of this is Child Sex Abuse Material (CSAM), a modern term-of-art to replace the more familiar “child porn.”
Rozenshtein says there are “reasons for optimism” when it comes to the Fediverse’s ability to police this content, though as he unpacked this idea, I found it much weaker than his other material. Rozenshtein proposes that Fediverse hosts could avail themselves of PhotoDNA, Microsoft’s automated scanning tool, to block and purge themselves of CSAM, while noting that this is “hardly foolproof.”
If automated scanning fails, Rozenshtein allows that this could cause “greater consolidation” of Mastodon servers to create the economies of scale to pay for more active, human moderation, which he compares to the consolidation of email that arose as a result of the spam-wars. But the spam-wars have been catastrophic for email as a federated system and produced all kinds of opportunities for mischief by the big players:
https://doctorow.medium.com/dead-letters-73924aa19f9d
Rozenshtein: “There is a tradeoff between a vibrant and diverse communication system and the degree of centralized control that would be necessary to ensure 100% filtering of content. The question, as yet unknown, is how stark that tradeoff is.”
The situation is much simpler when it comes to servers hosted by moderators who are complicit in illegal conduct: “the Fediverse may live in the cloud, its servers, moderators, and users are physically located in nations whose governments are more than capable of enforcing local law.” That is, people who operate “rogue” servers dedicated to facilitating assassination, CSAM, or what-have-you will be arrested, and their servers will be seized.
Fair enough! But of course, this butts up against one of the Fediverse’s shortcomings: it isn’t particularly useful for promoting illegal speech that should be legal, like the communications of sex workers who were purged from the internet en masse following the passage of SESTA/FOSTA. When sex workers tried to establish a new home in the fediverse on a server called Switter, it was effectively crushed.
This simply reinforces the idea that code is no substitute for law, and while code can interpret bad law as damage and route around it, it can only do so for a short while. The best use of speech-enabling code isn’t to avoid the unjust suppression of speech — it’s to organize resistance to that injustice, including, if necessary, the replacement of the governments that enacted it:
https://onezero.medium.com/rubber-hoses-fd685385dcd4
Rozenshtein briefly addresses the question of “filter bubbles,” and notes that there is compelling research that filter bubbles don’t really exist, or at least, aren’t as important to our political lives as once thought:
https://sciendo.com/article/10.2478/nor-2021-0002
Rozenshtein closes by addressing the role policy can play in encouraging the Fediverse. First, he proposes that governments could host their own servers and use them for official communications, as the EU Commission did following Musk’s Twitter takeover:
https://social.network.europa.eu
He endorses interoperability mandates which would required dominant platforms to connect to the fediverse (facilitating their users’ departure), like the ones in the EU’s DSA and DMA, and proposed in US legislation like the ACCESS Act:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2022/04/eu-digital-markets-acts-interoperability-rule-addresses-important-need-raises
To get a sense of how that would work, check out “Interoperable Facebook,” a video and essay I put together with EFF to act as a kind of “design fiction,” in the form of a user manual for a federated, interoperable Facebook:
https://www.eff.org/interoperablefacebook
He points out that this kind of mandatory interop is a preferable alternative to the unconstitutional (and unworkable!) speech bans proposed by Florida and Texas, which limit the ability of platforms to moderate speech. Indeed, this is an either-or proposition — under the terms proposed by Florida and Texas, the Fediverse couldn’t operate.
This is likewise true of proposals to eliminate Section 230, the law that immunizes platforms from federal liability for most criminal speech acts committed by their users. While this law is incorrectly smeared as a gift to Big Tech, it is most needed by small services that can’t possibly afford to monitor everything their users say:
https://www.techdirt.com/2020/06/23/hello-youve-been-referred-here-because-youre-wrong-about-section-230-communications-decency-act/
One more recommendation from Rozenshtein: treat interop mandates as an alternative (or adjunct) to antitrust enforcement. Competition agencies could weigh interoperability with the Fediverse by big platforms to determine whether to enforce against them, and enforcement orders could include mandates to interoperate with the Fediverse. This is a much faster remedy than break-ups, which Rozenshtein is dubious of because they are “legally risky” and “controversial.”
To this, I’d add that even for people who would welcome break-ups (like me!) they are sloooow. The breakup of AT&T took 69 years. By contrast, interop remedies would give relief to users right now:
https://onezero.medium.com/jam-to-day-46b74d5b1da4
On Tue (Mar 7), I’m doing a remote talk for TU Wien.
On Mar 9, you can catch me in person in Austin at the UT School of Design and Creative Technologies, and remotely at U Manitoba’s Ethics of Emerging Tech Lecture.
On Mar 10, Rebecca Giblin and I kick off the SXSW reading series.
[Image ID: A trilemma Venn diagram, showing three ovoids in a triangular form, which intersect at their tips, but not in the middle. The ovoids are labeled 'Avoid angering users,' 'Diverse userbase,' 'Centralized platforms.' In the center of the ovoids is the Mastodon mascot. The background is composed of dead Twitter birds on their backs with exes for eyes.]
#pluralistic#cda#cda230#section 230#content moderation#federation#intermediary liability#mastodon#fediverse#protocols not platforms#activitypub#moderator's trilemma#agonism#subsidiary
93 notes
·
View notes