#South Korea 🇰🇷
Text
South Korea Is A Test Case On How To Fight An Ecological Disaster
After Two-thirds of the Country’s Tidal Flats Were Lost to Shoreline Development, South Korean Scientists Set Out to Prove Why This Ecosystem is so Essential.
— By Anna Jeanine Kim | Photographs: By Youngrea Kim | August 15, 2023

The sun sets over a tidal flat in Southwestern South Korea. Tidal Flats are a type of Ecosystem that Provide Habitat for Wildlife and help fight climate change—yet many are at risk of disappearing.
Yubudo, South Korea — As Byeongwoo Lee slowly walks across a sandy tidal flat on Yubudo, a small island off the west coast of South Korea, the birding guide does so quietly.
“You can’t see the birds right now,” Lee said. “You can feel them.”
Through the scope, it was just possible to make out their blurry shapes in the dark, and to hear the gentle but powerful “whhhrrr-reet-reet-reet” of tens of thousands of birds as they fed at the shoreline and in the shallow water.
As the sun rose, the tide retreated until it revealed six miles of the muddy sea floor. Channels of water like tree branches crisscrossed mud teeming with crabs, clams, snails, and sea worms.

Top: Depending on the time of day, tidal flats are either completely submerged under water or exposed to the air. Seen here at low tide, tidal channels criss cross an exposed tidal flat neighboring a residential neighborhood in Muan, South Korea.
Bottom: During an annual ceremony that takes place on the first full moon of the Lunar New Year, Gwangho Chu bows before a ceremonial table placed on a tidal flat in Wando, a small island in South Korea. Coastal communities in the Yellow Sea region have continued to honor the centuries-old tradition of celebrating the ancestral spirits of the sea and praying for a good harvest from the tidal flats.
Tidal flats like these are a type of wetland found on coastlines around the world. Korea’s Yellow Sea tidal flats, like those found on Yubudo Island, form the heart of an 18,000-mile route traveled by 50 million shorebirds as they migrate from eastern Russia and Alaska in the summer to Australia and New Zealand in the winter.
Many of them only stop once on their marathon journeys, and the tidal flats of South Korea provide them with essential food and shelter.
Yet despite their critical importance to the environment, many are at risk of disappearing. Some of the most important, and most endangered, are found surrounding the Yellow Sea along the shores of China and the western side of the Korean peninsula.
For decades, people have been transforming them into industrial sites and farms, squeezing them into smaller areas and pushing some species to the brink of extinction. But as science increasingly shows how wetlands like these benefit wildlife and help fight climate change, South Korean scientists and conservationists are gaining momentum in their effort to save and restore what’s left.

Top: From left, Okji Kim, Yangim Kim, and Sunim Bae work together to make gamtae-kimchi, a special type of kimchi made with sea algae instead of cabbage. With limited farmland available, coastal communities have traditionally relied on the abundance of tidal flats, developing a unique culinary culture over thousands of years.
Bottom: A seafood meal is served at a restaurant in Yamido, a small island now connected to the mainland by the construction of the 21-mile-long seawall built as part of the Saemangeum development project. Many of the residents living around the seawall used to make a living working in the seafood industry, but the destruction of nearby tidal flats significantly decreased their harvests, threatening their livelihood.
Why Tidal Flats Are An Environmental Powerhouse
“The tidal flats made the relationship between humans and the sea possible,” said Joon Kim, a senior researcher at the Jeonnam Research Institute who studies the culture around Korean tidal flats.
Since prehistory, South Korea’s coastal communities relied on tidal flats for harvesting clams, crabs, octopus, and seaweed, adjusting their way of life to the tide’s schedule. Their biodiversity and abundance inspired many beloved local cuisines, unique coastal culture, and a fishing economy worth over $330 million U.S. dollars a year.
These same ecosystems are now helping fight climate change.
South Korean universities are partnering with the government to study tidal flats and their ability to clean polluted water, protect shoreline communities from storms, and mitigate climate change by absorbing carbon dioxide.
Korean tidal flats are full of tiny one-celled organisms called benthic diatoms that sink through the mud as they complete their life cycle, burying carbon dioxide in the deep sediment, says Jong Seong Khim, a marine scientist and professor at Seoul National University.

Top: Seoul National University researcher Inok Lee hands a sediment sample to her colleague outside the Saemangeum seawall. Scientists like Lee are studying how the large-scale development project is harming water quality and marine wildlife.
Bottom: People ride recreational boats through a man-made canal at a city park in Songdo, South Korea. Once a thriving tidal flat ecosystem, Songdo was built on reclaimed land and hailed for creating "a city out of nothing." Over the past 70 years, South Korea has lost over two-thirds of its tidal flats due to reclamation projects like these.
The diversity and number of benthic diatoms make South Korean tidal flats unique, as does its thick mud—over 80 feet deep in some tidal flats.
In 2021, Khim and his fellow researchers published a study showing South Korea’s tidal flats and salt marshes absorb 260,000 tons of carbon dioxide annually, equivalent to taking about 110,000 cars off the road every year.
The same year, the South Korean government announced a four-year project to bring back tidal flats and salt marshes to help fight climate change.
Kim hopes that by showing how effectively tidal flats store carbon, governments and conservation groups will recognize them as valuable and save them from being destroyed.
Why Tidal Flats Are In Danger
In the past 70 years, South Korea has transformed from a country devastated by war into a highly developed, industrial nation. During this rapid change, two-thirds of its tidal flats subsequently disappeared.
In a country surrounded by the ocean on three sides, like South Korea, engineering solid, dry land over water-logged terrain, a process referred to as land reclamation, can expand territory or create more farmland.
Of all the threats to tidal flats—such as sea level rise and pollution—land reclamation has led to the most loss.
Scientists are only beginning to understand the true extent of this loss globally, but one recent study suggests 16 percent of the world’s tidal flats have disappeared in the past few decades.
“We are at a point where we should consider what we can do to give back to tidal flats,” said Kim.

Left: In 1989, a satellite image shows what the tidal flats around the Saemangeum development project looked like before construction began in earnest.
Right: By 2018, a satellite image of that same tidal flat reveals the effect of a 21-mile seawall and construction. The 100,000-acre reclamation project is seven times the size of Manhattan. ESA/NASA/USGS
One of the most controversial shoreline developments is Saemangeum, a 100,000-acre reclamation project seven times the size of Manhattan.
Developers first envisioned Saemangeum as a vast agricultural area for rice cultivation, then as the economy changed, they promised to turn it into an industrial corridor.
In 2006, despite lawsuits and protests, a 21-mile-long wall in Saemangeum deprived the ecosystem of the water it needed to exist. Just one part of the region’s transformation, it set the Guinness World Record for the world’s longest sea dam.
Millions of shellfish died when the wall severed the ecosystem from the tide.
Finding no food and no place to land, tens of thousands of migratory birds disappeared. About 90,000 now-endangered great knot birds died, driving their total population numbers down by at least 24 percent.

Top: The 21-mile-long Saemangeum seawall is is the longest such structure in the world. After its construction, tens of thousands of shorebirds disappeared from the area that used to be one of the most important habitats along the Yellow Sea region.
Bottom: As excavators work on tidal flat reclamation in Songdo, shorebirds rest during their annual migration from Australia to the Russian Far East. Developing tidal flats in this region destroys critical habitats for the 50 million migratory birds that fly this route every year.
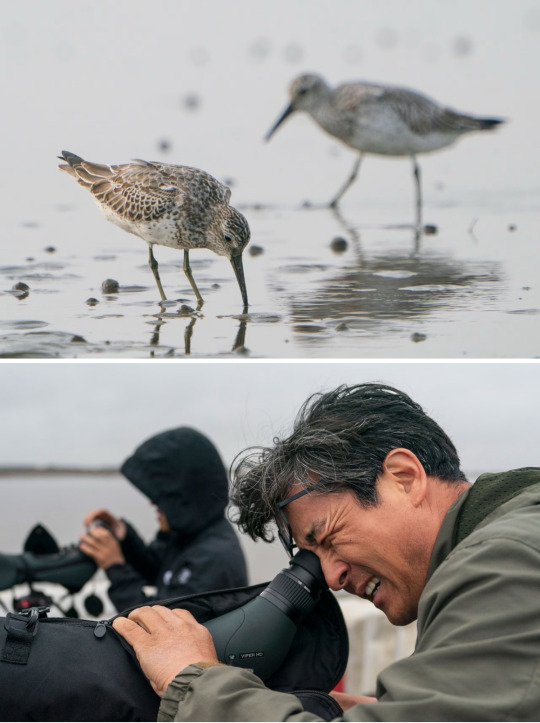

Top: Great knots feed on clams and seaworms at a tidal flat near Yubudo, a small island off the west coast of South Korea. About 80 percent of great knots have disappeared in the last two decades due to habitat loss.
Bottom: Dongpil Oh and his son, Seungjun Oh, conduct monthly surveys of shorebird populations on the the Sura tidal flat found in Gunsan, South Korea. Sura is one of the last remaining tidal flats found within the Saemangeum reclamation site. Dongpil and Seungjun are part of the Saemangeum Citizen Ecology Investigation Team, a grassroots organization that advocates for conservation and documents threats to tidal flats impacted by the Saemanguem.
It wasn’t only wildlife that suffered. Before the wall, the area was known for the nation’s best clams, with a fishing industry supporting around 20,000 people. Nearly all of that disappeared.
And yet despite promises of jobs made to the community, developers have completed less than half of the reclamation, and much of what has been reclaimed are undeveloped empty lots.
Saemangeum developers now plan to build an airport over the last remaining tidal flat, Sura, with construction scheduled to begin in 2024. Activists are suing to stop it, pointing out that the site still provides habitat for endangered species like black-faced spoonbills and Far Eastern curlews.
“It’s painful to remember how much it’s changed. Sometimes you forget how beautiful it was in the past because your eyes adjust to what it looks like now,” said Dongpil Oh, one of the activists involved and leader of the Saemangeum Citizen Ecological Investigation Team.

Left: Halophytes turn red on a tidal flat in Sinan, South Korea. South Korean researchers are studying how salt-tolerant plants like these can boost tidal flats’ ability to fight climate change by absorbing carbon.
Right: A blue-spotted mudskipper jumps during a mating dance at low tide in Sinan. Resting in its burrow at high tide and feeding in the mud when the tide goes out, the unusual, amphibious fish is adapted to the tidal flat’s drastic daily changes.
Bottom: The sun sets over Suncheon Bay Wetland Reserve at low tide. About 16 percent of the world's tidal flats have been destroyed in just the past few decades, but science is increasingly showing how important these ecosystems are for preserving wildlife and fighting climate change.


Top: National Institute of Ecology researchers and local volunteers tag baby black-faced spoonbills with GPS trackers in Incheon, South Korea. Around 90 percent of these endangered shorebirds breed on the country’s west coast. After their worldwide population dropped below 300 in the late 1980s, conservation efforts have brought their numbers to around 5,200. “As a top predator in tidal flats, their health can indicate the health of the overall ecosystem,” researcher Inki Kwon said.
Bottom: Ecotourist guide Sunjeong Heo points out a flock of birds over a tidal flat at Suncheon Bay Wetland Reserve in South Korea. Drawing over six million visitors a year, the UNESCO World Heritage site is a blueprint for the country’s tidal flat conservation and ecotourism.
A New Era of Conservation
After 30 years of construction, Saemangeum has become synonymous with ecological collapse, but it also sparked an environmental movement in South Korea after people witnessed what happens when tidal flats are lost.
Two years after the Saemangeum seawall was finished, in 2008, the South Korean government banned new large-scale reclamation projects—though developments already in progress, like Saemangeum, are still permitted.
And in 2019, reclamation of tidal flats finally plateaued in South Korea, when the net gain from restoration barely surpassed the loss, according to a 2023 report from the International Union for Conservation of Nature.
One of the best places to see the benefit of this kind of conservation is South Korea’s Suncheon Bay Wetland Reserve, on the peninsula's southern edge. The wetland was spared from the threat of development in the ‘90s, when residents and activists protested the government’s plan to mine the land.
Suncheon Bay became the country’s first internationally protected coastal wetland, and its tidal flats were designated a UNESCO World Heritage site in 2021, along with four other tidal flats in South Korea. Every year, over six million tourists visit the wetland and the nearby National Garden to see wildlife like hooded cranes and blue-spotted mud skippers.
With municipal and national funds, the Suncheon Bay Wetland Reserve bought nearby farmland by the coast, restoring the connection with the sea.
Their holistic approach to restoration has introduced organic rice farming to reduce pollution from runoff and educational opportunities for ecotourists, residents, and children in local schools. Suncheon’s success is a blueprint for tidal flat conservation around the world.
“Our focus is on letting the tide flow again, like it always did,” said Sunmi Hwang, a conservationist with the wetland reserve. “And then nature heals itself.”
#Environment#South Korea 🇰🇷#Ecological Disaster#Tidal Flats#Shoreline#South Korean Scientists#Ecosystem#Anna Jeanine Kim#National Geographic#Wildlife Habitat
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
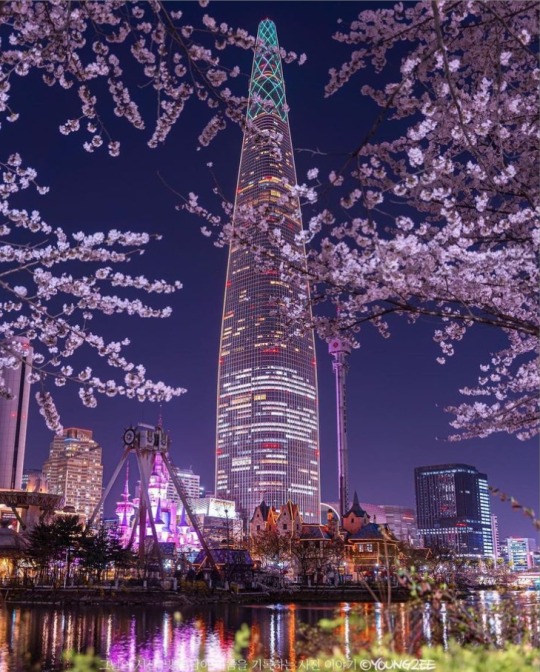




#beauty#city#korean#vogue korea#Korean Street#peace and security#dark moon blg#Cool#nice view#South Korea 🇰🇷
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
35 notes
·
View notes
Text






Cherry Blossom season in SK is officially over, but I wanted to share a few pictures with you guys of my adventures. 🌸
#cherry blossom#cherry blossom season#south korea#South Korea adventures#🇰🇷#sorchathered and demon baby adventures#expatlife
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
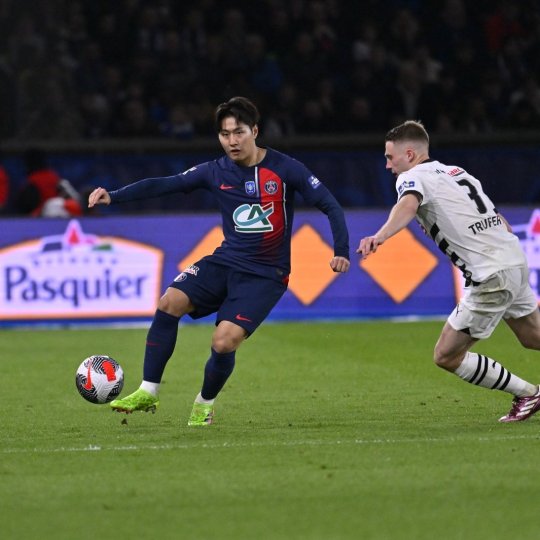

Lee Kang-in
#Lee Kang-in#paris saint germain#psg#football#south Korea#south korea nt#futbol#soccer#away days#player#south Korean international#Asia#🇰🇷#goal#pass#score#fa#champions league#nike#adidas#jordan
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

to the blind hyeonwoo is the light
#jo hyeonwoo#south korea nt#football#HE SAVED TWO PENS LIKE IT WAS NOTHING 😭😭😭😭😭😭🇰🇷🇰🇷🇰🇷🇰🇷🇰🇷#rahul.txt
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
はい、私の性格は少し変わっていますが、大丈夫です。(つ・・)つ

#COMFORTIKS#art#original character#oc art#cat#comfortiks art#catgirl#silly goofy art#idk#korean artist#sanrio#dresses#pink ribbon & cute girl#💝#i love pink#south korea🇰🇷#💗💕💓💞💖💘💝
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

“I believe tears are a language that God not only speaks but also understands.” Esther Fleece Allen
“This whole suffering world is awash with the tears of God and no one cries alone.” Ann Voskamp
#pray for itaewon#pray for Indonesia#pray for South Korea 🇰🇷#and any one#any where#grieving loss#prayer request#my rambles#kinda#oh Jesus#lament#crowd surge#causes#quote#quotes#ann voskamp#Esther fleece Allen#grief#human stampede
7 notes
·
View notes
Text

21/04/2023: first one for today, this one is new. She is one of the contestants from season 1 of 'Physical 100' which is a South Korean physical obstacle course. Network platform is on 'Netflix Korea'
Good news is, heard they maybe a season 2. So it would be interesting to see which contestants from season 1 would return and what kind of events they have. This time round I do hope they make 10 episodes of it at least. Would love to see most of them compete and also have more various event / courses.
Enjoy & good evening from north London.
ref: Song A-Reum (송아름 머슬프로짐 Fitness model 🇰🇷 IFBB BIKINI PRO)
#Song A-Reum#송아름 머슬프로짐 Fitness model 🇰🇷 IFBB BIKINI PRO#Physical 100#k show#obstacle event#south korea#k variety show
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Meet The World’s New Arms Dealers! Where To Buy Drones, Fighters And Tanks On The Cheap
— September 19th, 2023

An aerial view of Kizilelma, Bayraktar TB2, HURKUS, and Akinci surrounded by crowds of visitors at Teknofest in Ataturk Airport, Türkiye 🇹🇷. Image: Getty Images
The sight of North Korea’s chubby leader, Kim Jong Un, shaking hands with Vladimir Putin on September 13th—having travelled by train to a spaceport in Russia’s far east to discuss selling its dictator a stash of Korean weapons—was remarkable both on its own terms and for what it said about the business of selling arms. The world’s five biggest arms-sellers (America, Russia, France, China and Germany) account for more than three-quarters of exports. But up-and-coming weapons producers are giving the old guard a run for their money. They are making the most of opportunities created by shifting geopolitics. And they are benefiting from the Russian invasion of Ukraine.
Mr Kim’s trip to Russia followed a visit to Pyongyang in July by Sergei Shoigu, Russia’s defence minister, who wanted to see if North Korea could provide gear that would help his country’s faltering war effort. North Korea would love to find buyers for its military kit. And few regimes are willing to sell Russia arms. China has so far been deterred from providing much more than dual-purpose chips (although it could yet channel more lethal stuff through North Korea). Only Iran has obliged, selling some 2,400 of its Shahed “Kamikaze” drones.
North Korea could provide a wider range of stuff. As well as drones and missiles such as the kn-23, which is almost a replica of the Russian Iskander Ballistic Missile, it could offer self-propelled howitzers and multi-launch rocket systems. According to sources in American intelligence, North Korea has been delivering 152mm shells and Katyusha-type rockets to Russia for the best part of a year. Russia is shopping in Pyongyang and Tehran because both regimes are already so heavily targeted by international sanctions that they have nothing to lose and much to gain by doing business with Mr Putin’s government. They are not so much an “axis of evil” as a marketplace of pariahs.
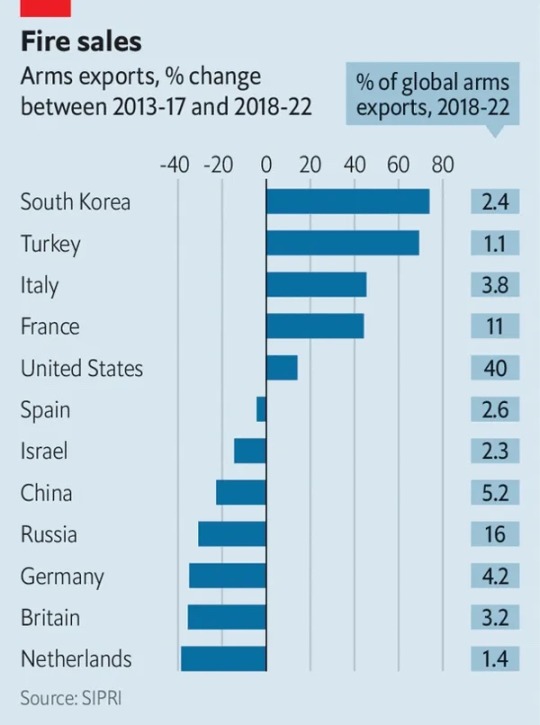
Image: The Economist
If the North Korean arms industry is being boosted by the war in Ukraine, its southern foe is doing even better. South Korea’s arms exporters were cleaning up even before the conflict. In the five years to 2022 the country rose to ninth place in a ranking of weapons-sellers compiled by the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI), a think-tank (See Chart); the government aspires to make South Korea the world’s fourth-largest arms exporter by 2027. Last year it sold arms worth $17bn, more than twice as much as in 2021. Some $14.5bn came from sales to Poland.
The size and scope of the agreements South Korea has reached with Poland, which sees itself as a front-line country in Europe’s defence against a revanchist Russia, is jaw-dropping. The deal includes 1,000 K2 Black Panther tanks, 180 of them delivered rapidly from the army’s own inventory and 820 to be made under licence in Poland. That is more tanks than are operating in the armies of Germany, France, Britain and Italy combined. The package also includes 672 k9 Thunder self-propelled howitzers; 288 K239 Chunmoo Multiple-Rocket Launchers; and 48 Golden Eagle FA-50s, a cut-price fourth-generation fighter jet.
South Korea’s success in the arms business is down to competitive costs, high-quality weaponry and swift delivery, says Tom Waldwyn at the International Institute for Strategic Studies, a think-tank based in London. Its prices reflect Korean manufacturing efficiency. The quality derives from Korea’s experience working with the best American Weaponry, and from its own High-tech Civil Sector. Speedy delivery is possible because the Koreans, facing a major threat across their northern border, run hot production lines that can also ramp up quickly.
Siemon Wezeman, a researcher with sipri’s arms-transfer programme, says wholehearted support from government and attractive credit arrangements are also critical to South Korea’s success. Asian customers like that the fact that it has close ties to America without being America, which is often seen as an unreliable ally. This could also help South Korea clinch a $45bn deal to renew Canada’s ageing submarine fleet. Questions for the future include how far South Korea will go in transferring technology to its customers—a crucial issue for Poland, which sees itself as an exporting partner of South Korea’s, competing with Germany and France in the European market.
If South Korea is the undisputed leader among emerging arms exporters, second place goes to Turkey. Since the ruling ak party came to power in 2002 it has poured money into its defence industry. A goal of achieving near-autarky in weapons production has become more pressing in the face of American and European sanctions—the former imposed in 2019 after Turkey, a nato member, bought Russian s-400 surface-to-air missiles.
Rocket-Fuelled
SIPRI thinks that between 2018 and 2022 Turkey’s weapons exports increased by 69% compared to the previous five-year period, and that its share of the global arms market doubled. According to a report in July by a local industry body, the value of its defence and aerospace exports rose by 38% in 2022, compared with the previous year, reaching $4.4bn. The target for this year is $6bn. Pakistan is receiving modernised submarines from Turkey. And the last of four Corvettes which Turkey has sold to the Pakistan navy was launched last month. More sales to other countries are likely, both because Turkey’s ships are competitively priced and because Turkey has few qualms about who it will sell to.
Yet Turkey’s export charge is led by armed drones. On July 18th Turkey signed a $3bn agreement with Saudi Arabia to supply the Akinci unmanned combat aerial vehicle (UCAV). It was made by Baykar, which also produces the Bayraktar tb2—a drone that has been used in combat by Libya, Azerbaijan, Ethiopia and Ukraine. The tb2 was developed to hunt Kurdish militants after America refused to sell Turkey its Predator drone. More than 20 countries lined up to buy it because it was cheaper and more readily available than the American alternative, and more reliable than the Chinese Unmanned Combat Aerial Vehicles UCAVs that had previously dominated the non-Western market.
The Akinci (pictured right) is more powerful. It can carry lots of big weapons, including air-to-air missiles and the som-a, a stealthy cruise missile with a range of 250km. It will find buyers among several other Gulf countries, such as Qatar, Oman and the UAE, who are keen to hedge against souring relations with America by reducing their reliance on its weaponry. These countries have ambitions to build their own defence industries; they see Turkey as a willing partner and an example to follow.
Turkey’s ambitions are shown by what else is in the pipeline. Its new Navy Flagship, the Anadolu, is a 25,000-ton amphibious assault ship and light aircraft-carrier that will carry Bayraktar ucavs. At least one Gulf country is said to be in talks to buy a similar ship. Turkey’s Fifth-Generation Fighter Jet, the Kaan, in which Pakistan and Azerbaijan are partners, should fly before the end of the year. Developed with help from Britain’s BAE Systems and Rolls-Royce, the Kaan could be seen as a response to Turkey’s ejection from the F-35 partner programme (as punishment for buying the S-400). Turkey will market the plane to anyone America will not sell F-35s to—or who balks at the conditions. Once again, Gulf countries may be first in line.
South Korea and Turkey have benefited from the woes of their main competitors. Russia’s arms exports between 2018 and 2022 were 31% lower than in the preceding four-year period, according to sipri. It is facing further large declines because of the strain its war of aggression is putting on its defence industries, its geopolitical isolation and the efforts of two major customers, India and China, to reduce their reliance on Russian weaponry.
India, previously Russia’s biggest customer, cut its purchases of Russian arms by 37% in the 2018-22 period. It is probably wishing it had gone further: Russia’s largely state-controlled arms industry is having to put its own army’s needs ahead of commitments to customers. Many of India’s 272 Su-30mkis, the backbone of its air force, are kaput because Russia cannot supply parts. Some of Russia’s weapons have performed poorly in Ukraine, compared with nato kit. And sanctions on Russia are limiting trade in things such as microchips, ball-bearings, machine tools and optical systems, which will hinder Russia’s ability to sell combat aircraft, attack helicopters and other lethal contraptions. The longer the war in Ukraine lasts, the more Russia will struggle to claw back its position in the global arms market.
Damp Squibs
As for China, over half its arms exports in the 2018-22 period went to just one country, Pakistan, which it sees as an ally against India. Nearly 80% of Pakistan’s major weapons needs are met by China, according to sipri. These include combat aircraft, missiles, frigates and submarines. Beijing has no interest in its customers’ human-rights records, how they plan to use what China sends or whether they are under Western sanctions.
But China’s arms industry also has its problems. One challenge, says Mr Waldwyn, is that although China set out to dominate the military drone market a decade ago, its customers got fed up with poor quality and even worse support, opening a door for Turkey. A second is that, with the exception of a putative submarine deal with Thailand and a package of weapons for Myanmar, other countries in South-East Asia are tired of Chinese bullying and “won’t touch them”, says Mr Wezeman.
At least China does not have to worry about competition from India. Despite much effort, India’s growth as an arms-exporter has been glacial. The government of Narendra Modi has listed a huge range of weapons parts that must be made in India; it hopes homemade light tanks and artillery will enter service by the end of the decade. But India has relied for too long on the transfer of technology from Russia under production-licensing agreements for aircraft, tanks and warships that have failed to deliver. Investment is wastefully channelled through the state-owned bodies. Red tape suffocates initiative.
Projects such as the Tejas light combat aircraft have taken decades to reach production, and remain fraught with problems. The Dhruv light helicopter, launched in 2002, has crashed dozens of times. After decades in development, the Arjun Mk-2 tank turned out to be too heavy for deployment across the border with Pakistan. Locally made kit is often rejected by India’s own armed forces; “If they don’t want it, exporting it becomes impossible,” says Mr Wezeman. South Korea and Turkey show how countries can build lucrative arms businesses that underpin domestic security. India, for all its bombast, is a lesson in how not to do it. ■
#International#Young Guns 💪#Türkiye 🇹🇷#World’s 🌎 Arm Dealers#Drones | Fighters | Tanks#America 🇺🇸 | Russia 🇷🇺 | France 🇫🇷 | China 🇨🇳 | Germany 🇩🇪#Kim Jong Un | Vladimir Putin#North Korea 🇰🇵 | Pyongyang |#Sergei Shoigu#Ukraine 🇺🇦 | Russia 🇷🇺 | War#Iran 🇮🇷 | Kamikaze Drones#Russian Iskander Ballistic Missile#Katyusha Rockets 🚀#Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI)#K2 Black Panther Tanks#Poland 🇵🇱#Britain 🇬🇧 | Italy 🇮🇹#Tom Waldwyn | The International Institute For Strategic Studies#Siemon Wezeman | Researcher | SIPRI#South Korea 🇰🇷#Canada 🇨🇦 🍁#Türkiye 🇹🇷 | Saudi Arabia 🇸🇦#Pakistan 🇵🇰 | Türkiye 🇹🇷#Gulf Countries | Qatar 🇶🇦 | Oman 🇴🇲 | UAE 🇦🇪#Baykar | Bayraktar#Chinese Unmanned Combat Aerial Vehicles (UCAVs)#Libya 🇱🇾 | Azerbaijan 🇦🇿 | Ethiopia 🇪🇹 | Ukraine 🇺🇦#Turkey’s Fifth-Generation Fighter Jet ✈️ | The Kaan#F-35 | S-400#Myanmar 🇲🇲
0 notes
Text
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
anyway did everyone see my 01z goal against uruguay i thought my 01z goal against uruguay was lovely ☺️🇰🇷
#south korea nt#lee kangin#oh hyeongyu#NO BECAUSE LOOK AT THAAAAAT HOW BEAUTIFUL IS THAT ASSIST AND GOAL 🥺🥺🥺#it was ‘offside’ or whatever. honestly i just think var + ref hated us that day#when this goal happened i was like 대한민국 😭🇰🇷💔😫‼️‼️‼️#so pretty. should’ve been counted. i hate football.#rahul.txt
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
BABYMONSTER-Better up 🔥🔥
0 notes