#Lecture4
Quote
[...] vieillir est une chose merveilleuse, car cela signifie que nous avons la possibilité , chaque jour, de vivre une vie pleine et heureuse. [...] Les mots sont importants. Quand ils parlent d'une femme de plus de quarante ans, les gens ont tendance à dire : "Elle est splendide... pour son âge." La prochaine fois que vous vous surprendrez à vouloir prononcer cette formule, envisagez la possibilité de dire simplement : "Elle est splendide." [...] Il ne s'agit pas de prétendre que tout est formidable dans le fait de vieillir ; mais il faudrait arrêter de considérer la vie comme une colline dont on se met à dévaler la pente en roue libre à partir de trente-cinq ans."
[Lecture #4] ~ Sorcières, la puissance invaincue des femmes (p.149) - Mona CHOLLET (2018)
4 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Lecture #4: Abstract Thinking
Principles of Visual Composition (part and whole, figure and ground, frame of reference)
Assignmet #2: Lift me Up! A Paper Relief
In this assignment, we rediscovered the kaleidoscope we created in assignment 1, this time in three dimensions. We have created combining our composition using geometric shapes (triangle, square, circle, rectangle) and we determined how many of these shapes will be.
While creating my composition, I paid attention to the relationship between figure and ground, the frame of reference, depth, and craftsmanship. I tried to pay attention to this composition to be better and understandable than the previous kaleidoscope.
Used materials:
1mm gray cardboard
The utility knife
The glue
Ruler
The aim of this study is to add volume to the kaleidoscope by improving and renewing our previous kaleidoscope work.
25.10.2020
0 notes
Text
Lecture 4 Reflection
(22 January 2019)
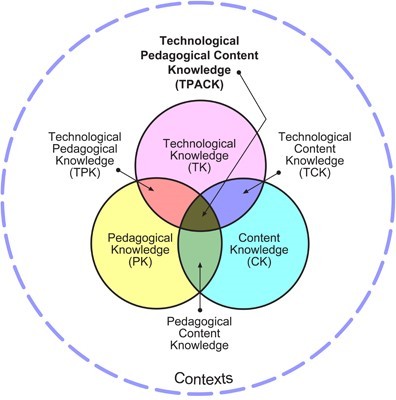
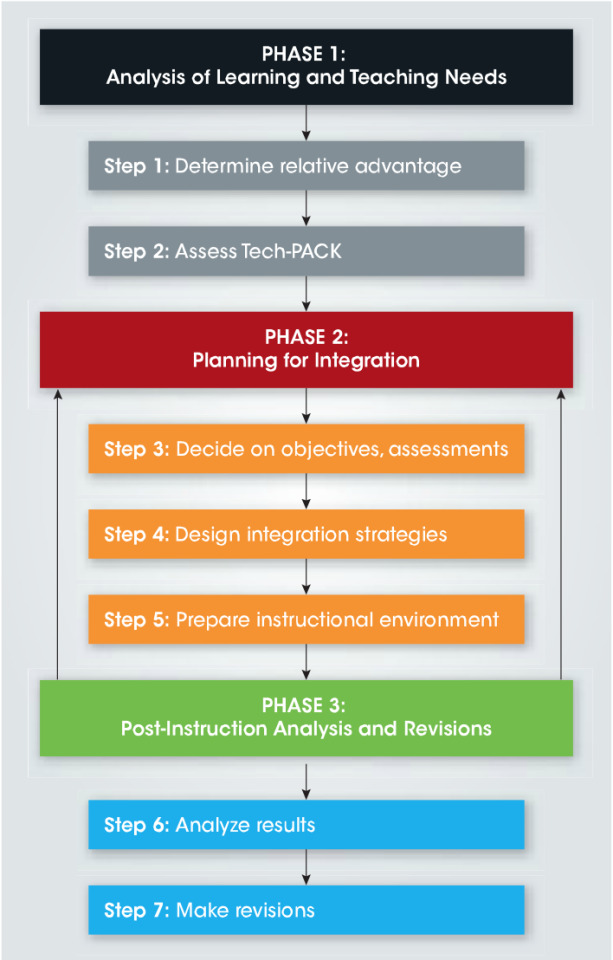
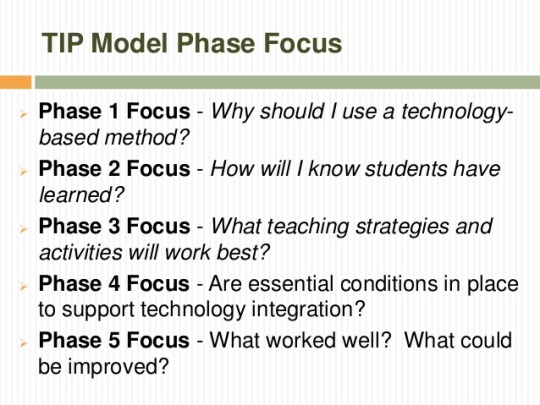
In week 4, the class started off in a unique way. Before the lesson begins, each of us were given a few minutes to think of our own theme song. This task was then remained as a secret which creates the feeling of curiosity in me. We are only able to know the purpose of this task in the next lesson. We were introduced to the TechPack, TIP model and 4 new educational tools.
The TIP model is a method allows educator to integrate technology into teaching meanwhile the TechPack model is a method used by educators to design a lesson for each class. Here are the 4 technological tools with its potential benefits and drawbacks that is introduced in class today:
1. Geoguesser.com
It is a web-based geographic discovery game.
It allow you to learn more about places.
It can be an ice-breaking game for the starter of the geography class.
2. Webjets.io
This tool is a similar tool to a blog that allows you to collect, organise and share everything.
Students are able to express themselves freely.
It also helps students to organise things.
Students tend to get carried away.
3. Noisli.com
It is an application that have a range of fantastic background noise and colour generator for working and relaxing.
It helps individuals to relax and boost their productivity.
It also brings benefits to individuals who are in the spectrum.
4. Prowritingaid.com
It is a personal writing coach that helps you with grammar check, style editor and writing mentor.
It helps students to organised and improve their writing.
It helps students in their teacher-grading.
As an advance learner, these educational tools are benefits my daily tasks. As a student who constantly does a writing assignment, “prowritingaid.com” is able to be my writing mentor tool. “noisli.com” helps me to boost my productivity and reduces my stress and anxiety with its relaxing background noise. “webjets.io” is able to help me in terms of collecting and organizing my daily class or meeting schedules and some important information that is shared in class.
Multimedia Artifact
Acknowledgement
Ijbrideson. (2010) Research Journal 1, Entry 4, “Building Teacher ICT Knowledge…” [online] available from <https://ljbrideson.wordpress.com/tag/tip-model/> [22 January 2019]
Childress, M. (2012) Meda5400TechnologyIntegrationPlanning(TIP)Model [online] available from <https://www.slideshare.net/vatechnoteacher/meda5400technologyintegrationplanningtipmodel> [22 January 2019]
Educational Technology EEC 334 (n.d.) E. TIP Model [online] available from <https://sites.google.com/site/educationaltechnologyeec344/home/e-tip-model> [22 January 2019]
0 notes
Text
Tutorial - Lecture 4 (cn)
Briefly describe FIVE (5) main issues that must be addressed when designing computer networks.
Addressing – The message be specific where it will be send to . Such as by IP address.
Error control – Makes sure the message is send to the receiver.
Flow control – Matching the speed of the sender and receiver of the message so they have the same speed.
Multiplexing – (Multi-sending) Dividing the messages from the senders so it can be received by receivers together and in the same time.
Routing – Using different paths but still have the same destination.
Briefly explain why networks are modeled as a stack of layers.
: The networks are modeled as stack of layers because the process of the network work in layer from bottom layer to top layer, and it will process each on of the layer without any skip. Each layer had protocols (rules) and own well defined function.
Briefly describe the role of an interface when modeling a network as stack layers.
: The role of an interface when modeling a network as stack layers is providing end-user meaning it’s user-friendly.
Explain the role played by a session in a network connection.
: Role of session in network connection is to establishing process of communication between network hosts. (Multiplexing). Such as inter-host connection.
State the SEVEN (7) layers of the OSI Reference Model in the correct order and briefly state the purpose of each layer.
Physical Layer - Transmitting bits (1s and Os) over communication channels. For example, 0110110110.
DataLink Layer - Establishing paths for data transfer through the network(routing). Such as logical Addressing.
Transport Layer - Delivering message between network hosts.
Session Layer - Establishing process to process communication between the network hosts.
Presentation Layer - Defining syntax which two network use to communication such as Operating System (OS)
Application Layer - Providing end-user devices for user interaction.
1 note
·
View note
Photo
EXPLAINING THE PLANCK’S CURVE OF THE BLACK-BODY RADIATIONPosted on
21st June 2019
by
theshan_weerasinghe
In this article, we will study the properties of Planck’s Intensity-Wavelength Curve of Black-Body Radiation. As usual, I will try to give more of a conceptual explanation rather than mathematical. But keep in mind that, in physics, especially in Quantum Mechanics, the involvement of mathematics is inevitable.
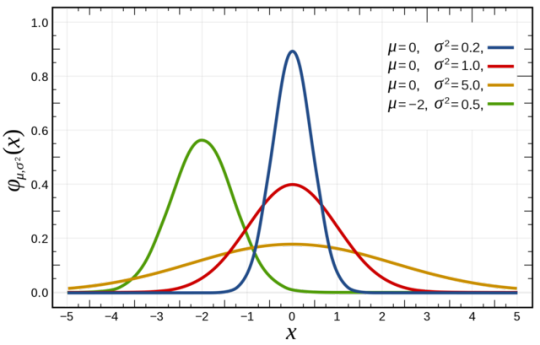
Now, If you take a look at the given figure, it is conspicuous that this curve is approximately a ‘Normal Distribution’. (Statistically)
If you’re familiar with the idea of a ‘Normal Distribution’, this article will be a piece of cake for you. But since everyone should be considered, we will first get familiar with the idea of a normal distribution.
What is a normal distribution?
An ideal normal distribution is shown below.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Normal_distribution#/media/File:Normal_Distribution_PDF.svg
Above picture implements 3 ‘Probability Density Functions’ which gives out 3 normal distributions. Check out this awesome website for more info. Probability Density Function @mathinsight
An ideal normal distribution would consist of the following characteristics.
The mean, median and the mode are the same in the distribution. Here, it’s situated at the peak.
So obviously the graph is symmetric around the mean. That means, the areas right to the peak and left to the peak each represents 50% of the samples(whatever results of the experiment we implemented in the function).
Many numbers of these samples or experimental results are concentrated around the mean value and at the extremes, the numbers fall drastically. (we will discuss that later in the article)
Theoretically. the graph extends to infinity.
Alright, that would be enough for the discussion here.
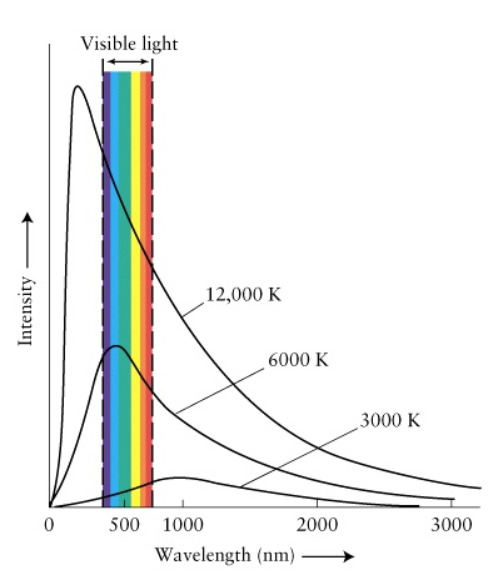
Here, in the Planck’s Black-Body Radiation distribution, the graph is drawn between the Intensity of the radiation and wavelength of that radiation for specific temperatures. For different temperatures, you get different graphs of the same family. Check out the picture below.
Source: https://sites.ualberta.ca/~pogosyan/teaching/ASTRO_122/lect4/lecture4.html
Here, you will see that at higher temperatures, the peak of the curve moves toward the lower wavelengths (higher frequencies). Also, the peak gets higher and higher when the temperature is high while increasing the area of the graph too. Why is that?
As more and more energy is supplied, the Black-Body gets warmer and warmer (emits more energy). As it’s temperature goes higher, the radiation it emits goes to higher frequencies. (more energetic radiation is emitted) So, with common sense, we can expect the peak to move towards the lower wavelength side. This was explained mathematically by Wilhelm Wien. (For the mathematical explanation go to http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/wien.html)
Also, when more and more energy is supplied, the emission of radiation in numbers also increases. Therefore, at higher temperatures, we must expect the graph to increase in area.
The reason for the peak to be broader at lower temperatures and higher at higher temperatures is also a characteristic of a normal distribution. To explain the situation in a more understandable way, consider the Maxwell-Boltzmann curve of gas molecules. When the temperature goes high, you will see that the number of molecules that achieve those speeds within some range will be reduced. (Not every molecule can achieve that energy when the energy is higher). The same thing happens in Plank’s distribution too. Though the energy goes high, the number of peak radiations become lower in a specific range.
According to Planck, the energy must absorb and emit in discrete values called ‘quanta’. His idea was that the energy of these discrete ‘quanta’ was proportional to frequency. In the last article, we saw how Planck developed his theory. Now we will see how his idea explained the graph.
At that time, as far as I know, even though the electron was discovered, scientists did not have a clear idea about how it was situated or, how atoms absorb energies. Also, they argued about the wave and particle natures of the light. So the explanation of how atoms absorb and emit energy could not be explained very well even by Planck at that time. Anyhow, he said, according to his findings, the atoms must absorb and emit radiation in discrete numbers, not in a continuous manner. That means you can keep directing some source of energy towards a sample, but not until it receives some specific energy, will it absorb what you supply.
But now we believe that electrons absorb energies from ‘photons’ in specific numbers and achieve higher energy states and even get themselves removed from their atoms sometimes. The above curve gets its shape because the energy an electron can absorb and emit is limited. With that limitation at some point, it would stop absorbing and emitting energy. (we haven’t experienced that yet) But at this point, we consider the Black-Bodies would absorb and emit radiation of wavelengths or frequencies of infinite and infinitesimal discrete values.
Even though Plank’s formula explained the Black-Body radiation and everything in thermodynamics, there was still an unexplained phenomenon called ‘Photoelectric Effect’ which, even Plank couldn’t explain with his idea of ‘quanta’ which was really close to a little modification which Einstein did, which could’ve given the whole glory to Planck himself if he had realized it.
At that time, whether if the light was a wave or a particle was doubtable for scientists. (Like we’re in doubt with relativity and quantum mechanics where both of them explain different phenomena.) It was called ‘The wave-particle duality‘. (Guess what would be my next article. LOL)
Planck’s theory’s drawback was that it couldn’t explain a model for ‘quanta’. He only explained the phenomenon of Black-Body radiation but didn’t try to give a physical interpretation of how these energy transfers of quanta would happen.
Then came Einstein into play where he took over everything and invented a particle which has both wave and particle natures that solved everything that was in doubt, successfully interpreting quanta as particles of energy.
That will be for another day.
Until then keep reading stuff.
Will see you soon with another article.
#Quantum Theory#quantum physics#quantum mechanics#quantum#physics#chemistry#science#technology#innovation#education#thequantuminsight
1 note
·
View note
Text
5 Best ways to make bells in Animal Crossing
CHAPTERS: 0:00 Intro 0:26 Bell Vouchers 1:26 Fossils and Art 2:15 Selling NMT 3:18 Nookazon 4:05 Nookazon Safty Lecture ...
via YouTube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yZ0DVIzpN6Y
0 notes
Text
Strong & Weak Forms
In term of finite element, strong form (or classical form) is differential equations (DEs) that are said to state a problem in. whereas, weak form (variational methods of approximation, e.g. Ritz, Galerkin, least-quares, collocation, or in general, weighted-residual methods) is an integral expression (functional) which implicitly contains a DEs.
The name originates from the fact that solutions to the weak form (aka. virtual work, or virtual displacement in mechanics) need not be as smooth as solutions of the strong form, i.e. they have weaker continuity* requirements.
A weak form is defined to be a weighted-integral statement of a differential equation in which the differentiation is transferred from the dependent variable to the weight function such that all natural boundary conditions of the problem are also included in the integral statement [Reddy].
The strong form states conditions that must be met at every material point, whereas weak form states conditions that must be met only in an average sense.
In linear elasticity (multi-dimensional vector field problem), strong and weak form are developed from three basic equation: equilibrium, kinematic (strain-displacement relation) and constitutive (stress-strain relation) equation.
sumber:
https://web.iitd.ac.in/~hegde/fem/lecture/lecture4.pdf
Fish and Belytschko, page 49, 223
Hughes, page 2
Reddy 2006, page 58
Cook 2001, page 136
0 notes
Photo

#Lecture4
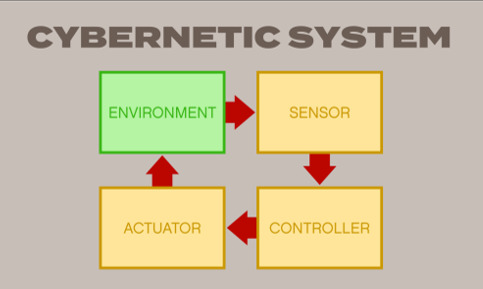
Looking at Lecture 4, we have been analysing how Cybernetics and positive & negative feedback would be impacting our game. A successful game would be described by the explanation above, one which creates suspense and releases adrenaline and reward at the end. Taking this into account, we decided to incorporate riddles into the game to either frustrate or reward the user. This would enable both positive and negative feedback to be upfront in our game.
0 notes
Photo

✨✨✨ 未来をたのしくサバイブするトーク祭@ヒカリエ \ オンラインアーカイブ化 決定! / http://www.d-department.com/jp/archives/people/48669 ・ 行きたいのに遠方でどうにもいけない。 ゆっくり聞きたいけど子どもがいるからなぁ。 そに日はすでに予定があって... などなど、全国から寄せられるあらゆる声に答えまして、 10回通しパスポート購入で、 オンラインアーカイブも完備します〜! トーク開催日の翌々日までにUPして、 URLとパスワードをメールでお送りする予定です! これがあれば、会場でも、オンラインでも楽しめます。 ・ Off-Grid Life PASSPORT ¥8000-です。 ・ すでに、単品購入されている方も、 パスポートにアップグレードできますので、 会場で追加の5500円払っていただく OR 10月の分だけ購入してて9月のアーカイブみたい方の対応を今検討中なので、 ちょっとお待ちください!(><) ・ ////////// ・ よく目を凝らすと、世の中捨てたもんじゃないなぁ、 未来って楽しみだなぁ、ってことが たくさんある。 ・ 暮らしかた冒険家の仕事って、 そういう未来のかけらを集めて歩いたり、 つくっていくことだと思ってます。 ・ 未来を楽しくサバイブするための 《思想》と《哲学》を満タンなトークでお待ちしています。 ・ エコハウスや食べ物の話なんかは、 とてつもなく身近なトピック。 快適だし、おいしいし、勉強すると暮らしは必ず豊かになる。 ・ ////////// ・ ◉Lecture1 わざわざ行く店 渡邉麻里子(タルマーリー)× 宮本篤(USHIO CHOCOLATL ) ・ わざわざ行かないと行かない人気店ってなんなんだ。 それで儲かってるんなら、そっちの方が利益率高くってしあせじゃないですか? という仮説の元、いろいろ聞いてみようと思います。 ・ 《暮らしかた冒険家的詳細解説→ https://goo.gl/AVCo9Y 》 ・ ・ ◉Lecture2 ゴミをいかして未来をつくる 東野唯史・華南子(ReBuilding Center JAPAN)× 野原健史(のはら農研塾) ・ 暮らしかた冒険家とは家族のような付き合いの2組。 ゴミとマジメとセンスがマリアージュした時に起こる、 すんげー未来の景色を垣間見たとき、 きっとみなさんも、ゴミがゴミに見えなくなるはず。 ・ 《暮らしかた冒険家的詳細解説→ https://goo.gl/vrr6Sq 》 ・ ・ ◉Lecture3 まちの空気をつくる小商い 本郷紘一(SENDAI COFFEE STAND)× 立道嶺央(POMPON CAKES) ・ コーヒー屋さんのようで、コーヒー屋さんだけでは語れない。 ケーキ屋さんのようで、ケーキ屋さんだけでは語れない。 彼らの仕事にはまちや仕事がどう映っているのか、 まちと自分の関わりかたの新たな視点が生まれるかも!? ・ 《暮らしかた冒険家的詳細解説→ https://goo.gl/r1ZpNu 》 ・ ・ ◉Lecture4 これからの暮らしかたって何だ? 田中辰幸(ツバメコーヒー)× 小倉ヒラク(発酵デザイナー) ・ 見えない事象を言語化したり、見える化するのが、得意な2人。 今回の《これからの暮らしかた》って 言葉にするとなんだろう?を2人の力を借りて紐解きたい! みなさん、言語化の瞬間に立ち会ってください。 ・ ・ ◉Lecture5 可能性を見つめ直して仕事をつくる 森下静香(Good Job! Center KASHIBA)× 阿部裕志(巡の環) ・ 障害がある人がどう働くか、 離島でどう仕事をつくるか、 効率重視の社会では光が当たりにくかったことに価値を見出し 仕事をつくっている発想の転換力や行動力が気になるところ。 ・ ・ ◉Lecture6 快適でかっこいい、家づくり最前線 佐藤欣裕(もるくす建築社)× 高岡文紀(アーキテクト工房Pure) ・ 快適でカッコよくってエコ。 もはや選ばない理由がなく、間違いなく未来の家はこっち!と 竹内と伊藤が断言できる家づくりを地方都市で進めるお2人に これからの住宅がどうなっていくのかを聞いてみます。 これから、家づくりするみなさん、絶対、聞いた方がいい。 ・ ・ ◉Lecture7 これからのエネルギー 井筒耕平(あわくら温泉 元湯)× 中嶋健造(土佐の森・救援隊) ・ 林業にまつわることを、普通に暮らしていると耳にしない。 森林を活用すれば《日本は資源大国》という可能性と そこに立ちはだかる壁について、 バイオマスボイラーの活用と林業の現場から、 語ってもらいます。 全てのトークはウェブから。 #d47これからの暮らしかた展 #暮らしかた冒険家 #のはら農研塾
3 notes
·
View notes
Quote
Faibles de corps et d'esprit, animées par un insatiable désir de luxure, [les femmes] sont censées faire des proies faciles pour le Diable. Dans les procès [pour sorcellerie], elles ont représenté en moyenne 80% des accusés et 85% des condamnés. Elles étaient aussi plus démunies face à la machine judiciaire [...] Alors qu'auparavant les tribunaux refusaient leur témoignage, les Européennes n'accédèrent au statut de sujets à part entière aux yeux de la loi que pour être accusées en masse de sorcellerie. La campagne menée entre 1548 et 1593 dans vingt-deux villages des environs de Trèves, en Allemagne - lieu d'apparition et épicentre, avec la Suisse, des chasses aux sorcières -, fut si féroce que, dans deux d'entre eux, elle ne laissa plus qu'une femme encore en vie ; en tout on en avait brûlé 368. Des lignées féminines entières furent éliminées : les charges contre Magdeleine Denas, brûlée dans le Cambrésis en 1670, à l'âge de soixante-dix-sept ans, n'étaient pas très claires, mais on avait déjà exécuté sa tante, sa mère et sa fille, et on pensait que la sorcellerie était héréditaire.
[Lecture #4] ~ Sorcières, la puissance invaincue des femmes (p.16) - Mona CHOLLET (2018)
8 notes
·
View notes
Link
How to Create Passport size photo in Photoshop cc Lecture # 4 in Urdu/Hindi Tutorial
#instapassport #urdu #hindi #graphics #language #passport #size #adobe #tutorial #create #lecture4 #passportsize
0 notes
Video
youtube
#RRClasses #ReetaRukhaya #Class12th #Lecture4 #BusinessStudies #commerce #OrganisationalStructure #Organizing #bcom #mcom #cbse #hbse
In this course, the educator covered the topic of Organisational structure of Unit Organizing. The class will be beneficial for Class 12th, B.COM, and M.COM students.
Welcome to RR Classes - RR Classes मे आपका स्वागत है !!!
Hey !! This is Reeta Rukhaya.
Here you find the video of content and World-Class interaction with students.
0 notes
Text
Topic 2. Lecture 4. Internet (cn)
1. Give the difference between a MAC and an IP address.
Media Access Control Address (MAC) - It’s an identifier for the specific hardware and known as physical address or hardware address. It had its own unique address and be easily identified the network that may use your device’s address.
Internet Protocol (IP) - It’s an identifier that’s labeled numerically to a particular device on the network that uses TCP/IP to interact, and the address that uses the network can not be identified outside the network.
2. Explain each section of the IP Address Header
VERs - A 4-bit field that identifies the IP version being used. The current version is 4, and this version is referred to as IPv4.
HLEN - A 4-bit field containing the length of the IP header in 32-bit increments. The minimum length of an IP header is 20 bytes, or five 32-bit increments. The maximum length of an IP header is 24 bytes, or six 32-bit increments. Therefore, the header length field should contain either 5 or 6.
SERVICE TYPE - The 8-bit ToS uses 3 bits for IP Precedence, 4 bits for ToS with the last bit not being used. The 4-bit ToS field, although defined, has never been used.
TOTAL LENGTH - Specifies the length of the IP packet that includes the IP header and the user data. The length field is 2 bytes, so the maximum size of an IP packet is 216 – 1 or 65,535 bytes.
INDETIFICATION, DF, MF and FRAGMENT OFFSET - As an IP packet moves through the Internet, it might need to cross a route that cannot handle the size of the packet. The packet will be divided, or fragmented, into smaller packets and reassembled later. These fields are used to fragment and reassemble packets.
TIME TO LIVE - It is possible for an IP packet to roam aimlessly around the Internet. If there is a routing problem or a routing loop, then you don't want packets to be forwarded forever. A routing loop is when a packet is continually routed through the same routers over and over. The TTL field is initially set to a number and decremented by every router that is passed through. When TTL reaches 0 the packet is discarded.
PROTOCOL - In the layered protocol model, the layer that determines which application the data is from or which application the data is for is indicated using the Protocol field. This field does not identify the application, but identifies a protocol that sits above the IP layer that is used for application identification.
HEADER CHECKSUM - A value calculated based on the contents of the IP header. Used to determine if any errors have been introduced during transmission.
SOURCE ADDRESS - 32-bit IP address of the sender.
DESTINATION ADDRESS - 32-bit IP address of the intended recipient.
IP OPTIONS and DATA - A field that varies in length from 0 to a multiple of 32-bits. If the option values are not a multiple of 32-bits, 0s are added or padded to ensure this field contains a multiple of 32 bits.
List the different IP Address classes within its corresponding details
Class A, 1.0.0.1 to 126.255.255.254
Class B, 128.1.0.1 to 191.255.255.254
Class C, 192.0.1.1 to 223.255.254.254
Class D, 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255
Class E, 240.0.0.0 to 254.255.255.254
3. Identify the IP version 4 public addresses and IP version 4 private addresses
IP version 4 public addresses:
Private Class A range 10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255
Private Class B range 172.16.0.0-172.31.255.255
Private Class C range 192.168.0.0-192.168.255.255
Loopback Addresses 127.0.0.0-127.255.255.255
IP version 4 private addresses:
1.0.0.0 - 9.255.255.255
11.x.x.x - 126.255.255.255
129.0.0.0 - 169.253.255.255
169.255.0.0 - 172.15.255.255
172.32.0.0 - 191.0.1.255
192.0.3.0 - 192.88.98.255
192.88.100.0 - 192.167.255.255
192.169.0.0 - 198.17.255.255
198.20.0.0 - 223.255.255.255
4. Identify the difference between IP version 4 and IP version 6 addresses
IPv4 addresses are 32 bit length. IPv6 addresses are 128 bit length.
IPv4 addresses are binary numbers represented in decimals. IPv6 addresses are binary numbers represented in hexadecimals.
No packet flow identification. Packet flow identification is available within the IPv6 header using the Flow Label field.
Checksum field is available in IPv4 header No checksum field in IPv6 header.
Options fields are available in IPv4 header. No option fields, but IPv6 Extension headers are available.
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is available to map IPv4 addresses to MAC addresses. Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is replaced with a function of Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP).
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is used to manage multicast group membership. IGMP is replaced with Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) messages.
Broadcast messages are available. Broadcast messages are not available. Instead a link-local scope "All nodes" multicast IPv6 address (FF02::1) is used for broadcast similar functionality.
Manual configuration (Static) of IPv4 addresses or DHCP (Dynamic configuration) is required to configure IPv4 addresses. Auto-configuration of addresses is available in IPv6.
5. Give the differences between TCP and UCP
TCP stands for “Transmission Control Protocol” while UDP stands for “User datagram Protocol”.
TCP is connection oriented protocol while UDP is connectionless protocol.
TCP is more reliable than UDP.
UDP is more faster for data sending than TCP.
UDP makes error checking but no reporting but TCP makes checks for errors and reporting.
TCP gives guarantee that the order of data at receiving end is same as on sending end while UDP has no such guarantee.
Header size of TCP is 20 bytes while that of UDP is 8 bytes.
TCP is heavy weight as it needs three packets to setup a connection while UDP is light weight.
TCP has acknowledgement segments but UDP has no acknowledgement.
TCP is used for application that require high reliability but less time critical whereas UDP is used for application that are time sensitive but require less reliability.
6. Explain what is a subnet and subnet addressing.
A subnet is an identifiably separate part of an organization's network. A portion of a network that shares a common address component. On TCP/IP networks, subnets are defined as all devices whose IP addresses have the same prefix.
Subnet addressing known as a subnet mask because it is used to identify network address of an IP address by performing a bitwise AND operation on the netmask. A Subnet mask is a 32-bit number that masks an IP address, and divides the IP address into network address and host address.
Explain VLSM and identify its purpose.
A Variable Length Subnet Mask (VLSM) is a numerical masking sequence, or IP address subset, based on overall network requirements. A VLSM allows a network administrator to use long masks for networks with few hosts and short masks for networks with multiple hosts. A VLSM is used with a VLSM router and must have routing protocol support.
Reference
Theydiffer.com. (2017). Mac Address vs IP Address - What's the difference?. [online] Available at: http://theydiffer.com/difference-between-a-mac-address-and-an-ip-address/ [Accessed 20 Apr. 2017].
Parkhurst, W. (2017). IP Header Format > Internet Addressing and Routing First Step. [online] Ciscopress.com. Available at: http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=348253&seqNum=4 [Accessed 20 Apr. 2017].
Computerhope.com. (2017). What is IP (Internet Protocol)?. [online] Available at: http://www.computerhope.com/jargon/i/ip.htm [Accessed 23 Apr. 2017].
Inetdaemon.com. (2017). Private IPv4 Addresses - InetDaemon's IT Tutorials. [online] Available at: http://www.inetdaemon.com/tutorials/internet/ip/addresses/private_addresses.shtml [Accessed 23 Apr. 2017].
Inetdaemon.com. (2017). Public IP Addresses - InetDaemon's IT Tutorials. [online] Available at: http://www.inetdaemon.com/tutorials/internet/ip/addresses/public_addresses.shtml [Accessed 23 Apr. 2017].
Omnisecu.com. (2017). Differences Between IPv4 and IPv6. [online] Available at: http://www.omnisecu.com/tcpip/ipv6/differences-between-ipv4-and-ipv6.php [Accessed 23 Apr. 2017].
Difference Between. (2015). Difference between TCP and UDP. [online] Available at: http://www.differencebtw.com/difference-between-tcp-and-udp/ [Accessed 23 Apr. 2017].
SearchNetworking. (2017). What is subnet (subnetwork)? - Definition from WhatIs.com. [online] Available at: http://searchnetworking.techtarget.com/definition/subnet [Accessed 23 Apr. 2017].
Iplocation.net. (2017). What is a Subnet Mask?. [online] Available at: https://www.iplocation.net/subnet-mask [Accessed 23 Apr. 2017].
Techopedia.com. (2017). What is Variable Length Subnet Mask (VLSM)? - Definition from Techopedia. [online] Available at: https://www.techopedia.com/definition/25932/variable-length-subnet-mask-vlsm [Accessed 23 Apr. 2017].
0 notes