#Emmanuel Morales
Photo
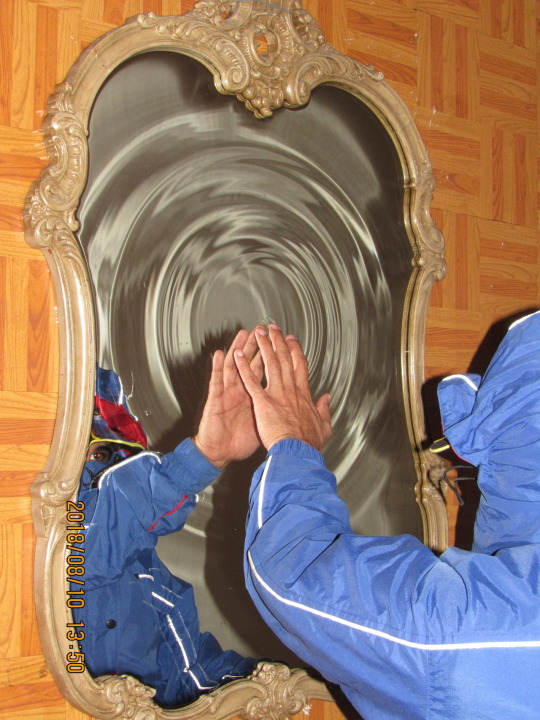

Emmanuel Morales ― mon Dieu Adore
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

By Emmanuel Morales
#I was sooo sad when he deactivated#but thankful I still could find his pictures on his website#still am#I’m obsessed with all of his work#Emmanuel morales#fav#mirror#hand#reflection#ripples#flash#2018#windbreaker#jacket#portal#reflective#photography#flash photography#dreamcore#upload#blue#aesthetic#fav ever
40 notes
·
View notes
Text




You need to see this.
#ramsey fast and furious#deckard shaw#fast x#fate of the furious#megan ramsey#fast and furious#ramsey is deck's morality pet write home about it#she's his favorite! he's her favorite!#flashing //#jason statham#nathalie emmanuel#genuinely he saves her life after knowing her 2 seconds after making a speech about not caring about anyone... she reminds him of his siste
257 notes
·
View notes
Text

— Morality, An Introduction To Ethics by Bernard Williams
#bernard williams#when school reading makes you <3 abt being human#humanity#emmanuel#quote#morality an introduction to ethics
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
My plan of shipping an OC with Ashley to cope with my crush on her has failed, I want them both now
#the coffin of andy and leyley#ashley graves#tcoaal oc#gabriel emmanuel#oc x canon#*flips table*#GODDAMMIT—#Curse you pretty men with long hairrrr#and morally dubious women
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Scrooge and Johnny from the latest Duck Avenger story... just how many times did they get kicked out of the Club exactly? 🤦

Scrooge: Unlike yours, Rookie, my fortune grows during night time!

John: Wanna see how you're gonna grow bumps?
Scrooge: Bring it on, bonsai size billionaire!
Club President: Enough with this undignified show off!
John: He started it!
Scrooge: He carried it on!

Club president: Silence! You're suspended for a day!
And they go on! XD
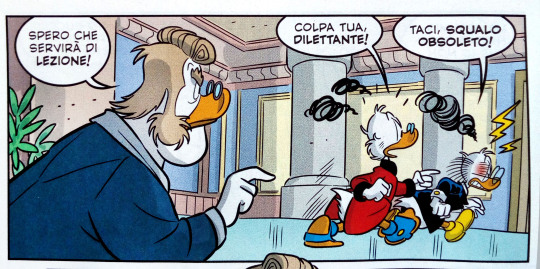

Club president: And let that be a lesson!
Scrooge: This is all your fault, amateur!
John: Shut your prehistoric mouth!
Paperinik e la torre d'oro (2022)
Club president: Though I highly doubt it!
Scrooge: Take your shot, hat-eater!
John: You asked for it, moth-eaten Top Hat!
#whoever is the president they really need some moral support...#respect#can we take a minute to appreciate baccinelli's rockerduck?#he looks so good! :D <3#john d. rockerduck#scrooge mcduck#scrooge vs rockerduck#scrooge and rockerduck epic quarrels#duckburg billionaires club#duck avenger#alex bertani#marco gervasio#emmanuele baccinelli#from this week topolino#topolino magazine
52 notes
·
View notes
Text

«Ahora bien, la fuerza se caracteriza por otro tipo de propagación. El que la ejerce no la abandona. La fuerza no se pierde entre los que la padecen. Se adhiere a la personalidad o a la sociedad que la ejerce, que la expande subordinando al resto. Aquí el orden universal no se establece como corolario de la expansión ideológica, sino que es esa misma expansión la que constituye la unidad de un mundo de señores y esclavos. La voluntad de poder de Nietzsche, que la Alemania moderna redescubre y glorifica, no es sólo un nuevo ideal, es un ideal que al mismo tiempo aporta su propia forma de universalización: guerra y conquista».
Emmanuel Levinas: Reflexiones sobre la filosofía del hitlerismo. Alpha Decay, pág. 35. Barcelona, 2023.
TGO
@bocadosdefilosofia
@dias-de-la-ira-11
#emmanuel levinas#levinas#reflexiones sobre la filosofía del hitlerismo#hitlerismo#universalidad#expansión#fuerza#ideología#expansión ideológica#orden universal#orden#nazismo#señores y esclavos#moral de los señores#moral de los esclavos#voluntad de poder#nietzsche#ideal#guerra#poder#conquista#propagación#teo gómez otero
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Okay, so I just watched The Invitation on Netflix and I got some stuff to say
First off....
Thomas. Doherty.
He is honestly so good looking and his smirk kills me every time. I loved him when I was younger watching Descendants, and I need more movie recs with him in it cause damn. Man’s hot.
That ending was AMAZING *spoiler free post, slight spoiler in tags*. Totally badass. My mom and I called the ending, but it was so satisfying.
Also, Oliver is/was a total sweetheart. His face reminds me of Matt Smith.
If you love Vamp movies, you’ll probably like this one. I did love it, but if you like pining vampires, you aren’t getting that here.
10/10 would recommend giving it a try tho. I loved it
#ok but I didn't want Walt to die until he made that racist comment tho#murderous vampire? yes#racist? no#Morals? gray and twisted#hotel? trivago#the invitation#thomas doherty#nathalie emmanuel
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
highlife in the city
Wenn er nicht zugegen war, spielte ich in frühen Tagen eine Platte auf dem Plattenspieler meines Vaters; dann hörte ich den Titel 'highlife in the city'. Ich verstand die Liedzeile "das Ding hat er ausgemistet und sich darin eingenistet" als Handlungsaufforderung.
Als unpraktisch veranlagter Mensch hatte ich aber keine Idee, wo ich ein Autowrack auf einem Wiesengrundstück finden könnte.
Und warten wollte ich auch nicht.
Also hielt ich mich an die Grundlagen ("er laß Hemingway, Karl May und Sigmund Freud") und wünschte mir von meinen Eltern zu Weihnachten - von Karl May hatte ich schon an die dreißig Bände gelesen - entweder ein Buch von jenem Hemingway oder aber von Freud.
Meine Eltern wunderten sich, zu Weihnachten gab es für mich “Die Traumdeutung“, aus dem Fischerverlag, von Sigmund Freud (zu erst erschienen im Jahr 1900). Sechzhundertvierundfünfzig Seiten.
So las ich das erste Sachbuch meines Lebens.
Zwar beanspruchte es mich ein ganzes Jahr, mehr und mehr fand ich aber Gefallen. Meine Erkenntnis: Durch nüchterne Beobachtung und vor allem der Kraft zur Analyse - also durch Denken - ist die chaotisch und bedrohlich wirkende Praxis zu durchkämpfen und auch zu bestehen. Genauer, indem man sie sachgemäß ordnet... und dies klappt sogar bis in das Reich jenseits des Eigentlichen. Also bis hinein in das Reich des Morpheus, das Reich des Uneigentlichen.

In diesem Jahr war der Samen dafür für mich gesät, die Schreckgespenster meines Alltags mit einem geisteswissenschaftlichen Studium beikommen zu wollen.
Dem Umstand, dass Freud Jude war, hatte ich keine Bedeutung zugemessen. Ich dachte, das sei die Aufdeckung der Psychologie. Als ich dann viele Jahre später, während der Spätphase meines Studiums, auf jüdischstämmige Philosophen des 20. Jahrhunderts aufmerksam gemacht wurde, dachte ich, mich tritt ein Pferd. Diese Denker hatten eine Weise die Praxis zu erfassen, die nicht nur das mir bis dahin übliche aufklärerische Denken als beleidigend beschränkt vorkommen lies, sondern mich augenblicklich und wehmütig an meinen Ausgangspunkt erinnerte. Die Traumdeutung. Von Sigmund Freud. Als ich diese Denker etwas näher kennenlernte, stellte ich immer wieder fest, dass diese sich mit dem Talmud beschäftigt hatten.
Von den Denkern, die man mir damals anvertraute, wurde mir Emmanuel Levinas am vertrautesten.

Seine Hauptwerke erschienen auf deutsch unter:
Totalität und Unendlichkeit. Versuch über die Exteriorität, im frz. Original 1961.
Jenseits des Seins oder anders als Sein geschieht, im frz. Original 1974.
Unter anderem hat er sich auch mit dem Talmud beschäftigt, in so genannten Talmudlesungen. Hier exemplarisch vier Titel: Dem Anderen gegenüber - Die Versuchung der Versuchung - Gelobtes Land oder Erlaubtes Land - So alt wie die Welt?
Levinas arbeitete, indem er die gebräuchliche ontologische Semantik (also die Beschreibungen von Daseinsformen des Seins) in Begriffen des Moralischen wendete, und ihre - Bedeutung - abtastete.
Oder wie es Susanne Dungs mit den Begriffen Levinas pointiert zusammenfasst: „Thema der Lévinasschen Philosophie ist die schonungslose Ausgesetztheit an das Verletztwerden durch die Transzendenz des Anderen und zwar in Art eines Empfangens, das passiver ist als irgendeine Rezeptivität, so dass sich keinerlei immanentes Wissen daraus ableiten lässt. Sie führt zu einer Verantwortung, in der ich mich ebenso wenig vertreten lassen kann wie im eigenen Sterben“ (Susanne Dungs, Bildlichkeit bei Emmanuel Levinas, auf: http://www.theomag.de/25/sd1.htm)
Levinas hat es in seinem zweiten Hauptwerk 'Jenseits des Seins, oder anders als Sein geschieht' so zu erklären versucht: „Es heißt, die Möglichkeit einer – schmerzlichen – Trennung vom sein denken.“ (Lévinas, Jenseits des Seins..., S.35)
Das für mich Unerhörte dieser Art sich auszudrücken, bedeute, "daß an mich eine Anordnung ergeht, die mich an das Gesicht des Anderen weist. Aufgrund dieser Anordnung, die einer Weihe gleichkommt, ist die Nicht-Gegenwart des Unendlichen kein Ausdruck negativer Theologie. Alle negativen Attribute, die das Jenseits-des-sein aussagen, werden zu Positivität in der Verantwortung – einer Antwort, die einer nicht thematisierbaren Provokation antwortet und daher (...) Verletzung ist“. (Lévinas, Jenseits des Seins... S.43f)
Auf den Punkt gebracht:
Erstens: Eine Annäherung an den Anderen. (Wobei der Annähernde gegenüber dem Anderen eine Offenheit gewähren muss, die einer Bestürzung gleichkommt.)
Zweitens: Die Übernahme von Verantwortung für den Anderen.
Drittens: Bis hin zur Stellvertretung für den Anderen, um dem Anderen nah sein zu können.
Zum Abschluss: „Das Gesicht, dem man sich nähert, die Berührung einer Haut: das Gesicht unter der zunehmenden Last der Haut und die Haut, in der, bis hin zur Obszönität, das veränderte Gesicht atmet.“ (Levinas, Jenseits des Seins..., )
#gerhard schöne#highlife#hemingway#karl may#freud#plattenspieler#traumdeutung#sachbuch#emmanuel levinas#levinas#andere#gesicht#moral#jenseits#sein#talmud
1 note
·
View note
Text
Struggling as a single mother in 1967 to raise a son on scant funds while teaching 10 college courses a year, Helen Vendler realized that “the only way I could make my life easier was to give up writing” — something she couldn’t face.
" ‘They can’t make me,’ I said to myself in panic and fear and rage. ‘They can’t make me do that,’ " she recalled in an essay decades later. “I suppose ‘They’ were the Fates, or the Stars, but I knew that to stop writing would be a form of self-murder.”
As she had done before and would do again, Professor Vendler found a path through that crisis. And soon she published the second of some 30 books of poetry criticism she wrote or edited while becoming one of the most influential and esteemed figures in her field.
[...] “I believe poetry is for everybody,” Professor Vendler, who was still writing and publishing essays, said in an interview for this obituary as her health was failing.
“Helen understood that all poets needed what she did so they could take the next step,” said Jorie Graham, a Pulitzer Prize-winning poet who had barely heard of Professor Vendler when she reviewed Graham’s earliest work for The New York Times in the early 1980s.
“I encountered the most lucid account of what I was doing that I could ever hope for,” Graham, who became a friend and Harvard colleague, said of those first reviews. “She certainly taught me right away that there was more to a poem than I could fathom on my own.”
Seamus Heaney, the late Nobel Prize-winning poet whose work Professor Vendler championed early on, once said that “she is like a receiving station picking up on each poem, unscrambling things out of word-waves, making sense of it and making sure of it. She can second-guess the sixth sense of the poem.”
“I do understand, I think, what it feels like to be a poet, even though I’m not one,” Professor Vendler told the Harvard Gazette afterward. “I was born with a mind that likes condensed and unusual language, which is what you get from poetry.”
[...] At Emmanuel College, from which she graduated summa cum laude, Professor Vendler decided against studying literature — taught there, she wrote, “as a branch of faith and morals.”
Majoring in chemistry, she found science crucial to her intellectual development.
“I think it’s the base of everything I do,” she said in a 2004 National Endowment for the Humanities interview. “You have to be exact in all your writing in science: your flow chart has to go from beginning to end with all the steps accounted for, and all the equations have to balance out. Evidence has to be presented for each step of your reason.”
[...] At Harvard, Professor Vendler also taught a celebrated core course, “Poems, Poets, Poetry,” which was aimed at non-humanities majors.
“I thought — and still think — that all people would like poetry if they were only brought up with it and shown how easily it is entered into and what enormous solace it has to offer,” she wrote in a 1994 essay.
Poems offered vital comfort and support to her as well.
“Helen needed poetry to live by,” Graham said. “She fashioned and honed her moral sense not through the church, but through the church of poetry — the whole history of poetry. I can’t imagine a poem that she didn’t know.”
Helen Vendler, a towering presence in poetry criticism, dies at 90
103 notes
·
View notes
Text
Frev friendships — Fouché and the Robespierre siblings

A circumstance relating to one of the most important crises of my life must here be mentioned. By a singular chance, I had been acquainted with Maximilian Robespierre, at the time I was professor of philosophy in the town of Arras, and had even lent him money, to enable him to take up his abode in Paris, when he was appointed deputy to the National Assembly.
Memoirs of Fouché (1825), volume 1, page 12. Fouché first arrived in Arras in 1788.
Robespierre didn’t like science, but he thought it useful for his vanity to research Fouché and to annoy him several hours per day in his office in order to acquire the reputation of scholar. Often, in order to appear intelligent, he interrupted his physics demonstrations to reproach him for being a materialist.
Note written by Barère, probably shortly after thermidor. Cited in Fouché: les silences de la pieuvre (2014) by Emmanuel de Waresquiel.
Fouché’s first need […] was to tell me his entire life story, a recital that I find in my notes written down that very day as it seemed interesting for me to keep: […] I (Fouché) had known [Robespierre] since our youth, we had belonged to the same academy. I then had occasions to prove to him his inadequacy, a relative insufficiency because he was judged poorly. He had some talent, a strong, persevering will; simplicity, no greed; but he was all puffed up with a pride that I had humiliated.
De 1800 à 1812. Un aide de camp de Napoléon. Mémoires du général compte de Ségar (1894), page 438. According to Robespierre (2014) by Hervé Leuwers, it would not appear Fouché joined the arrageois literary society Rosati of which Robespierre was a member, a claim which is nevertheless often invoked.
Fouché had shown the most ardent patriotism, the most sacred devotion since the beginning of the revolution. My brother, who believed him sincere, had accorded him his friendship and his esteem; he spoke to me of him as a proven democrat, and introduced him to me in praising him and asking me to give him my esteem. Fouché, after having been introduced to me by my brother, came to see me assiduously, and had those regards and attentions that one has for a person in whom one is particularly interested. Fouché was not handsome, but he had a charming wit and was extremely amiable. He spoke to me of marriage, and I admit that I felt no repugnance for that bond, and that I was well enough disposed to accord my hand to he whom my brother had introduced to me as a pure democrat and his friend. I did not know that Fouché was only a hypocrite, a swindler, a man without convictions, without morals, and capable of doing anything to satisfy his frenzied ambition. He knew so well how to disguise his vile sentiments and his malicious passions in my eyes as in my brother’s eyes, that I was his dupe as well as Maximilien. I responded to his proposition that I wanted to think about it and consult my brother, and I asked him the time to resolve myself. I spoke of it, effectively, to Robespierre, who showed no opposition to my union with Fouché.
Mémoires de Charlotte Robespierre sur ses deux frères (1834) page 122-123. Charlotte places the courtship in the midst of the revolution, which can hardly be accurate given the fact Fouché was already married by then, but it does sound likely for it to have happened somewhere between 1788 and 1790, when both of them were unmarried and lived in Arras.
When [Robespierre and I] again met at the Convention, we, at first, saw each other frequently; but the difference of our opinions, and perhaps, the still greater dissimilarity of our dispositions, soon caused a separation. One day, at the conclusion of a dinner given at my house, Robespierre began to declaim with much violence against the Girondins, particularly abusing Vergniaud, who was present. I was much attached to Vergniaud, who was a great orator, and a man of unaffected manners. I went round to him, and advancing towards Robespierre, said to him, "Such violence may assuredly enlist the passions on your side, but will never obtain for you esteem and confidence." Robespierre, offended, left the room; and it will shortly be seen how far this malignant man carried his animosity against me.
Memoirs of Fouché (1825), volume 1, page 12
Lamartine, in the first edition of his Girondins, wrote the following: ”A very small number of friends of Robespierre and Duplay were one after another taken into this intimity: sometimes the Lameths; Le Bas, Saint-Just, always; Panis, Sergent, Coffinhal, Fouché, who liked Robespierre’s sister and who Robespierre didn’t like, Taschereau, Legendre, Le Boucher, Merlin de Thionville, Couthon, Pétion, Camille Desmoulins, Buonarotti, roman patriot… […]” On the placard corrected by the widow and son of Philippe Le Bas, these words are replaced by the following ones: ”The Lamenths and Pétion in the early days, quite rarely Legendre, Merlin de Thionville and Fouché, who liked Robespierre’s sister and who Robespierre didn’t like, often Taschereau, Desmoulins and Teault, always Lebas, Saint-Just, David, Couthon and Buonarotti.”
Le conventionnel Le Bas: d’après des documents inédits et les mémoires de sa veuve (1901) page 83-84. This could be read as Élisabeth Le Bas confirming, or at least not denying, that there existed links between Charlotte and Fouché.
…The representatives of the people in Commune-Affranchie, using the powers entrusted to them for the surrounding departments, have already purged several administrations in the department of Allier. So consult with your colleagues by going to Commune-Affranchie. The instructions that Fouché has acquired relative to the department of Allier, where he resided for a long time, will be all the more useful to you since, animated by the same principles, the same effects must result from your common energy.
Letter from the CPS to Petitjean, written by Robespierre, January 8 1794
The Committee of Public Safety decides 1, that citizen Reverchon immediately travels to Ville-Affranchie to organise revolutionary government and that he, together with Méaulle, takes all the measures that the interests of the republic need. 2, that the representative Fouché immediately travels to Paris to give to the Committee of Public Safety the neccesary clarifications about the affairs in Ville-Affranchie 3, that all procedurs against the popular society in Ville-Affranchie, and especially against the patriots that were subjected to persecution under the reign of Précy and the federalistes, are suspended. The representative Reverchon and his colleges will severely persecute the enemies of the Republic, protect the true friends of the Republic, help the patriots in need and assure the triumph of liberty through a constant and inflexible energy.
Committee of Public Safety decree recalling Fouché from Lyon, written by Robespierre (and signed by him, Collot d’Herbois, Billaud-Varennes, C-A Prieur, Carnot and Barère) on March 27 1794
The Committee of Public Safety, alarmed by the fate of patriots in Commune-Affranchie, considering that the oppression of a single one of them would be a triumph for the enemies of the Revolution and a mortal blow to freedom, orders that all proceedings against the Popular Society of Commune-Affranchie, and particularly against the patriots who were persecuted under the reign of the federalists and Precy, will be suspended: it further orders that the representative of people Fouché immediately travels to Paris to give to the Committee of Public Safety the neccesary clarifications about the affairs in Ville-Affranchie.
Committee of Public Safety decree recalling Fouché from Lyon, written by Robespierre (and signed by him, Collot d’Herbois, Billaud-Varennes, C-A Prieur, Carnot, Barère, Saint-Just and Couthon) on March 27 1794 (don’t know why there exists two seperate decrees)
I have since learned that the step I took opposite Robespierre - viz, of calling upon him - was attempted about the same time, and with as little success, by Tallien and Fouché, each of them on his own part. I have learned that their eloquence likewise struck against a determined deaf-mute, and that to all their gentle, forcible, friendly, respectful, and feeling words Robespierre vouchsafed no other answer than an obstinate silence, an expressionless physiognomy, and neither word nor sign. There is in a like silence, on the part of a man wielding the scep tre of death, something more fearful to the imagination than uttered threats.
Memoirs of Barras, member of the Directorate (1895) page 206
It is known well enough in what way [Collot and Fouché] conducted themselves [in Lyon]; it is known that they made blood flow in torrents, and plunged the second city of the republic into fright and consternation. Robespierre was outraged by it. […] I was present for the interview that Fouché had with Robespierre upon his return. My brother asked him to account for the bloodshed he had caused, and reproached him for his conduct with such energy of expression that Fouché was pale and trembling. He mumbled a few excuses and blamed the cruel measures he had taken on the gravity of the circumstances. Robespierre replied that nothing could justify the cruelties of which he had been guilty; that Lyon, it was true, had been in insurrection against the National Convention, but that that was no reason to have unarmed enemies gunned down en masse. From that day forth, Fouché was the most irreconcilable enemy of my brother, and joined the faction conspiring his death. I would only learn this later. Fouché never again set foot in my apartment, but I met him from time to time on the Champs-Elysées, where walked almost every day. He addressed me as if nothing had happened between him and my brother. When I learned that he was Maximilien’s declared enemy, I no longer wanted to talk to him. Despicable words have been spoken about me on the subject of that man, some have dared to say that I was his mistress before and after 9 Thermidor; this is an abominable calumny! Never did Fouché cease to have the greatest respect for me; and if in his discourse he had included any words tending to make me neglect my duty, I would have left him that very instant. Besides, Fouché had only sought my hand because my eldest brother occupied premier place on the political stage. That honorific of Robespierre’s brother-in-law flattered his pride and his ambition; to judge by that man’s conduct since, everything was a calculation with him, and, if he pretended to love me, that’s because he saw it was in his interest. What would have become of me if I had married such a being?
Mémoires de Charlotte Robespierre sur ses deux frères (1834)
Robespierre murmured a lot about the forms that we had established in Lyon for the execution of decrees: he constantly repeated that there was no reason to judge the guilty when they are outlawed. He exclaimed that we had let the families of the condemned go free; and when the commission sent the Convention and the committee the list of its judgments, he was not in control of his anger as he cast his eyes on the column where the names of the citizens who had been acquitted were written. Unable to change anything in the forms of judgment, regulated according to the decrees and approved by the committee, he imagined another system; he questioned whether the patriots of Commune-Affranchie were not vexed and under oppression. They were, he said, because the property of the condemned being specially intended, by article IV of the decree of July 12, to become their patrimony, we had greatly reduced their claims, not only by not judging only a quarter of the number of conspirators identified by Dubois-Crancé on 23 Vendémiare, or designated by previous decrees, but also by establishing a commission which appeared willing to acquit two thirds, as it happened. Through these declamations Robespierre wanted to entertain the patriots of whom he spoke, with the most violent ideas, to throw into their minds a framework of extraordinary measures, and to put them in opposition with the representatives of the people and their closest cooperators: he made them understand that they could count on him, he emboldened them to form all kinds of obstacles, to only follow his indications which he presented as being the intentions of the Committee of Public Safety.
Collot d’Herbois’ explanation of Robespierre’s dislike for his and Fouché’s Lyon activities in Défense de J-M. Collot, répresentant du peuple. Éclaircissemens nécessaires sur ce qui s’est passé à Lyon (alors Commune-Affranchie), l’année dernière; pour faire suite aux rapports des Répresentants du peuple, envoyés vers cette commune, avant, pendant et après le siège (1794), somewhat the polar opposite of Charlotte’s version.
Robespierre accused Fouché of having dishonored the Revolution by exaggerating all measures and erecting atheism as a doctrine. ”No, Fouché," he said to him in the hall of the Jacobins, ”death is not an eternal sleep." Besides, to use his own expression, he believed he "held him in his power in the matter of honesty,” as Fouché had been charged with not having been any too strictly faithful on the occasion of his mission to Lyons, where, outstripping his epoch in those early days, he was believed to have enjoyed a foretaste of that corrupt century. Reports, possibly mendacious, had reached Robespierre, according to which Fouché is said to have, in the midst of the demolition of the dwellings in the town doomed to endure his cruelty, behaved somewhat like the incendiaries who carry on their business by the light of the flames. It is that which caused Robespierre to assume so lofty a manner against Fouché, because Fouché was supposed to have begun "to make money" at a time when no one in the Republic had so far dreamed of doing such a thing, either because of the Terror, which was not disposed to indulgence towards thieves, or because of a sentiment of genuine honesty which dominated men whose sole thought was the defence of the Republic.
Memoirs of Barras, member of the Directorate (1895) page 208-209
Fouché reads a report regarding Commune-Affranchie, where he was sent. After having brought up the slander repeated against the representatives sent to this commune, he proves by several observations the need of the measures that they took and the punishments that they handed out. He proves that the blood of crime fertilizes the soil of liberty and consolidates its power on unshakeable foundations. He also develops through much reflection the measures he was obliged to take in the last moments.
A citizen demands the floor in order to speak against Fouché.
Robespierre, after having declared that Fouché’s report is incomplete, pays homage to the patriotism of this representative and to the citizen who presented himself to speak against him. He presents some observations on what has gone down in Commune-Affranchie, and announces that the patriots, the friends of Chalier, and the companions of his suffering have been too modest against the schemers who put themselves in their place, and who introduced themselves among the patriots sent from Paris. He protests that without the schemers, the true patriots already would have plunged the whole conspiracy into nothingness. He recognizes that they have legitimate complaints to make, but he assures that the Committee of Public Safety, which is aware of them, has taken all the necessary measures to establish liberty in these unfortunate countries. Consequently, he invites the patriot who wants to speak, to put aside any kind of bitterness, to develop the facts and to give the knowledge that he considers useful.
I recognize, says this citizen, the validity of the principles of Robespierre, you will subsequently know all the facts. The truth will pierce through all the clouds; I’m backing down. (applauds)
Robespierre and Fouché at the Jacobins, April 8 1794
Sure of having sown the seed, I had the courage to defy [Robespierre], on the 20th Prairial (June 8 1794), a day on which, actuated with the ridiculous idea of solemnly acknowledging the existence of the Supreme Being, he dared to proclaim himself both his will and agent, in presence of all the people assembled at the Tuileries. As he was ascending the steps of his lofty tribune, whence he was to proclaim his manifesto in favour of God, I predicted to him aloud (twenty of my colleagues heard it) that his fall was near.
Memoirs of Fouché (1825) page 20
A deputation from the Society of Nevers presents itself at the tribune in order to repel charges directed against it. After having summarized the things done for the public sake by the Society which has sent him, the orator announces that the patriots have their souls broken and compromised in Nevers, because of atrocious persecutions of which they are every day the unfortunate victims.
Fouché (currently serving as president of the Jacobins): Your society deserves severe reproaches. If it is true to say that the impure breath of Chaumette could not exert its disastrous influence there during his stay in Nevers, it seems at least certain that the shadow of this conspirator hovers there today. Imprisoned suspects were released, and your Society made no complaint. Ardent and pure patriots, true sans-culottes, were slandered by federalist lawyers, and your Society remained silent. Finally, its correspondence is insignificant, it is null. As the Jacobins do not know how to disguise any truth, I make it my duty, on their behalf, to point out some false and very weak ideas that you have just expressed. The patriots, you say, have their souls compromised at this moment in Nevers. Citizens, strong hearts can never be compromised; Republicans know how to die for the truth as well as for liberty, and the perfidious person who tells you that he is not free to express his thoughts is a coward; the crime is in his heart, he complains of not being able to produce it. You hand us, as proof of your opposition to the maxims of the conspirators, the celebration that you are preparing for the Supreme Being; but in this you are only obeying the impulse given to nature. Add to this natural impulse the strength and courage to dedicate yourself to the defense of patriots and the annihilation of their oppressors; the exercise of democratic virtues. Brutus paid homage worthy of the Supreme Being by bringing the blade into the heart of the one who conspired against the liberty of his homeland.
I don't know, says Robespierre immediately, if the Society understood the motive and the object of the approach of the members of the Society of Nevers; I ask if the president's response can shed some light on this point. For my part, I assure you that I don't understand anything about it. If the president knows everything that concerns morals, it is his duty to explain. Everyone knows that Nevers was one of the main centers of the conspiracies hatched by Chaumette, in concert with the supporters of the foreign faction. We must remember that he abandoned his post as national agent, near the Paris Commune where he appeared to play a major role, to go, under a frivolous pretext, to plot in the commune of Nevers: it is important that we learn from what we were able to discover on such a journey. I ask that the president explain his response to us, and tell us frankly what he thinks.
Fouché takes the floor to give clarifications. He announces that, having served as representative of the people in the department of Nièvre at the time when the scoundrel Chaumette arrived in Nevers under the pretext of enjoying the native air, he didn’t hear from his mouth any counterrevolutionary expression; that he only saw him while in public, that, the popular society believing this Chaumette to be a zealous defender of liberty, it took him in without difficulty and without defiance. Fouché thinks that this immoral man hid away, because he saw the constitutional authorities strongly attached to good principles, and that he conspired in secret, and then returned to Paris to there continue his execrable profession of assassin of all public and private morality. As for the deputation that has just been heard, Fouché declares that, as the Society of Nevers has been indirectly attacked, it will send a deputation of its members to respond to the imputations that have been made against it, that there was a time when suspicious people, arrested, then released, and finally imprisoned again, managed to obtain an arrest order against the patriots. “This,” he says, “is all I know; I reproached the deputation on the weakness of the letters written by the Society of Nevers, and on the insignificance of its correspondence. The deputation presented its address to me when it entered, and it is on that I’m basing my answer.
Robespierre is surprised that the president and the delegation only say insignificant things that cannot enlighten the Society. He declares that Chaumette having hatched his plots in Nevers, it is impossible that neither the representative nor the Société populaire had knowledge of some of the maneuvers he employed. He recalls that at the moment when the Convention took a vigorous decision against the infernal plot of Chaumette, the Society of Nevers sent the Convention an address in which the decree was faulted.
Fouché observes that this adress wasn’t from the Society of Nevers, but from that of Moulins.
Robespierre replies that the latter is right next to to the other, that both corresponded to each other and that the information must have been the same; he continues by maintaining that the Society is isn’t instructed by the details that have just been given to it, and one has not sufficiently characterized the men who are called patriots, and those who are declared triumphant aristocrats. He is surprised to hear congratulations on the decree issued yesterday, mixed with observations presented by the Society of Nevers, as if this society could be aware of this decree. It is not by sentences, as he observes, but by conduct and facts that one must judge men: instead of stopping at the language of the deputation, one must ask the Society of Nevers if it fought Chaumette and foiled his horrible schemes? Very often the greatest enemies of the people use republican expressions, to better deceive unsuspecting citizens. It is not a question, he says, of throwing mud on the grave of Chaumette, when this monster has already perished on the scaffold. For a long time people have done evil while speaking the language of republicans. Today someone is spewing imprecations against Danton, who until recently was his accomplice. There are others who appear all fired up to defend the Committee of Public Safety, and who then sharpen daggers against it. The enemies of liberty have retained the same audacity, they have not changed their system; they do not want to appear to separate themselves from the patriots; they praise and flatter them; they even make vague imprecations against tyrants, and at the same time they conspire for their cause! It is to their friends the conspirators that they give the name of patriots; and it is the latter that they designate by the name of aristocrats: they surround the Committee of Public Safety and the representatives of the people only to intrigue, to lead them astray and thus destroy the Revolution. There are still two parties within the Republic: on the one hand patriotism and probity; on the other, the counter-revolutionary spirit, the crookedness and the improbity which are bent on the ruin of empires and the virtue of humankind. Patriots, you who in the career of the Revolution have only sought the public good, you who did nor go into it to serve a criminal faction, be more than ever on your guard; evil men use all imaginable artifices to destroy the Convention and slaughter the defenders of the homeland. Do not fall asleep in a false security, do not abandon the Convention and the government of which it is the center: let courageous voices be raised to make the truth known, stifle the clamors of the intriguers who surround us daily, who change patriotism into aristocracy, and reciprocally aristocracy into patriotism. Do not tire of instructing us, rest assured that the wish to sacrifice ourselves for all patriots is always deeply engraved in our hearts, that we are resolved to defend persecuted virtue with all our power, and to fight with strength and constancy the enemies of liberty and patriotism. This is the wish that I address, on behalf of the representatives, to the oppressed patriots; it is not natural that we remain indifferent on their account: the first of the republican virtues is to watch over innocence. Pure patriots, one is waging a war to the death against you, save yourselves, save with you all the friends of liberty.
Robespierre’s speech is followed by the liveliest applause.
Fouché observes that he hasn’t wanted to reproach the Society of Nevers for not having denounced Chaumette. This society didn’t know him as a conspirator, it wouldn’t have been late to accuse him warmly, had it suspected him of this.
Robespierre and Fouché at the Jacobins, June 11 1794
Five days after (June 12) in full committee, [Robespierre] demanded my head and that of eight of my friends, reserving to himself the destruction of twenty more at a later period. How great was his astonishment, and what was his rage, upon finding amongst the members of the committee an invincible opposition to his sanguinary designs against the national representation! It has already been too much mutilated, said they to him, and it is high time to put a stop to a deliberate and progressive cutting-down, which at last will include ourselves. Finding himself in a minority, he withdrew, choked with rage and disappointment, swearing never to set foot again in the committee, so long as his will should be opposed. He immediately sent for St. Just, who was with the army, rallied Couthon under his sanguinary banner, and by his influence over the revolutionary tribunal, still made the Convention, and all those who were operated on by fear, to tremble.
Memoirs of Fouché (1825), volume 1, page 20
Robespierre: The example of Commune-Affranchie can explain a theory that I have already noted. The patriots defend the patriots with all their means; they give no rest to the intriguers and traitors, they constantly badger and fight them; aristocrats do precisely the opposite. I knew Chalier at a time when the patriotic representatives of the people were themselves persecuted. It was he who first discovered Roland's perfidy, and denounced him to me for keeping an immense store of libels at his home, directed against the Mountain and against me. Chalier had no sooner known this conspiring minister than he abandoned him and renounced the justice he had come to demand from him, not wanting to owe anything to a traitor who sought to ignite civil war in France.
[Robespierre] adds that since this moment he has only known Chalier through the acts of heroism and virtue which immortalized his name. The enemies of the people were only able to establish their triumph through the assassination of this man, as patriotic as he was intrepid. He recalls the courage of this republican at the time of his torture, prolonged by the villainy of the aristocrats of Lyon who brought the ax down on his head four times, which he raised each time, crying out in a dying voice: Long live the Republic, attach the cockade to me.
After this touching story, Robespierre goes into detail about the services rendered by Chalier's friends; he knows them all, he also knows their persecutors. The fate of the former was to be oppressed by all the factions that succeeded one another. They opposed these tyrannical and unprecedented vexations with a calm and patience of which it is impossible to find an example in the history of any people.
When the overly prolonged siege of Lyon was over, and this commune had been returned to the power of the Republic, the friends of Chalier were not restored to the goodness that they had so well deserved by their constant virtue. One took care to make sure Précy and all the other conspirators escaped, although one went so far as to making the trick of the Committee the supposed remains of this monster. The gate of Lyon was opened to them at the very moment when the Republican army entered, and they left through the gate where the army corps commanded by Dubois-Crancé was, which remained motionless.
Another cause of the impunity of the conspirators is that national justice has not been exercised with the degree of force and action that the interests of a great people require and command. The temporary commission initially displayed energy, but soon it gave way to human weakness which too soon tires of serving the homeland, and it lost with all its courage, its devotion and its purity. After having given in to the insinuations of the perverse aristocrats, the persecution was established against the patriots themselves: the cause of this criminal change can be found in the seduction of certain women, and it is to these terrible maneuvers that we can attribute the despair that led Gaillard to kill himself.
Reduced to escape, the patriots come to submit their complaints to the Committee of Public Safety, which rescues them from persecution, and suppresses their odious persecutors with fear. Thus, virtue will be eternally exposed to the traits of two factions which, opposed in apperance, always rally to sacrifice the patriots. Here [Robespierre] swears to avenge Chalier, Gaillard and all the victims of the infamous aristocracy.
The speaker's principles are to stop the shedding of human blood caused by crime: the authors of the plots denounced, on the contrary, only aspire to immolate all patriots and especially the National Convention, since the Committee indicated the vices from which it must purge itself. Who are those who have constantly distinguished error from crime, and who have defended lost patriots? Isn’t it the members of the Committee? Those who demand justice can only be formidable to the leaders of the factions, and those who want to destroy the members of the Committee in public opinion can have no other intention than to serve the projects of the tyrants interested in the fall of a Committee which disconcerts them and will soon destroy them.
Robespierre ends by denouncing the author of all these maneuvers who is the same one who persecuted the patriots at Commune-Affranchie, with a cunning, a perfidy as cowardly as it is cruel: the Committee of Public Safety was not his dupe. He asks, finally, that justice and virtue triumph, that innocence be peaceful and the people victorious over all their enemies, and that the Convention puts all petty intrigues under its feet.
Couthon, who had interrupted Robespierre in order to cite charges against Dubois-Crancé regarding the siege of Commune-Affranchie, proposes that he be struck from the club’s list of members (adopted).
At the suggestion of Robespierre, Fouché is invited to come and exonerate himself of the reproaches which have been addressed to him before the Society.
Robespierre at the Jacobins, July 11 1794
One reads a letter from Fouché, in which he asks the Society to suspend their judgement up until the Committees of Public Safety and General Security have made their report on his private and public conduct.
Robespierre: I begin by making the declaration that I am not interested in the individual Fouché at all. I could be connected to him because I thought him a patriot. When I denounced him here, it was less because of his past crimes than because he hid away in order to commit others, and because I regarded him as the leader of the conspiracy which we have to thwart.
I examine the letter which was just read out, and I see that it is written by a man who, being accused for crimes, refuses to justify himself before his fellow citizens. This is the beginning of a system of tyranny. He who refuses to answer to a Popular Society whose member he is, is a man who attacks the institution of Popular Societies. This contempt for the Society of the Jacobins is all the more inexcusable as Fouché himself has not refused his suffrage when he was denounced by the patriots from Nevers, and as he even took refuge on the [president’s] seat of the Jacobins. He was placed there because he had agents in this Society, who had been at Commune-Affranchie. He delivers a great speech to you on his conduct in the mission with which he had been charged. I will not seek to analyse this speech. The Society has judged that Fouché does not want to say anything, as his reflections are insignificant.
It is surprising that the one who, at the time of which I speak, craved the approval of the Society, neglects it when he is denounced, and that he seems to implore, so to speak, the aid of the Convention against the Jacobins. Does he fear the eyes and ears of the people? Does he fear that his sad face visibly presents crime, that six thousand looks fixed on him discover his entire soul in his eyes, and that, in spite of nature which has hidden them, one reads his thoughts there? Does he fear that his speech reveals the embarrassment and the contradictions of a culprit? A reasonable man has to judge that fear is the only motive of Fouché’s conduct ; well, the man who fears the looks of his fellow citizens is a culprit. He uses [the fact] as a pretext that his denunciation is sent to the Committee of Public Safety ; but is he forgetting that the tribunal of the public conscience is the most infallible? Why does he refuse to present himself here?
The obligation to give an account of his mission to the Committees of Public Safety and of General Security, which are the government, and to the Convention, which is its source or, rather, which is the government by definition, this obligation, I say, does not destroy the one of appearing respectable in the eyes of a Society, and does not excuse appearing to put it in contradiction with the Convention. A representative is responsible for his actions to the Convention; but a good citizen does not discard appearing before his fellow citizens. If the system of Fouché could dominate, it would follow that those who have denounced schemes outside of the Convention have committed a crime. This was the conduct of all conspirators, who, from the moment onwards when one has wanted to judge them, shunned this Society and denounced it to the different National Assemblies as a gathering of factious [persons].
I here call Fouché into judgement. He shall respond and he shall say who, among him and us, has borne the rights of the representatives of the people with more dignity, and struck down all factions with more courage? Was it him who unveiled the Héberts and the Chaumettes, when they hatched assassination plots and wanted to debase the Convention? No! It was us who, on this tribune, when the Hébertists claimed to be more patriotic than us, unmasked them openly. It was us who silenced the false denunciations.
They shall say if they would have been listened to here, these men who had only served the Revolution in order to dishonour it and to make it turn to the benefit of the foreign [powers] and of the aristocracy! All the vile agents who have conspired did not see their likes unveiled and punished sooner than they seemed to abandon their cause ; and, because we had dismissed the perfidiously spread calumnies against the Convention, they extended this principle onto themselves in such a way as to render it tyrannical. The slightest words against this kind of men have been regarded as crimes by them; terror was the means which they used in order to force the patriots into silence. They threw those into prison who had the courage to break it; and this is the crime for which I reproach Fouché!
He will not say that it were the principles of the Convention that he has professed ; the intention of the Convention is not to throw terror into the soul of the patriots, nor to carry out the dissolution of the Popular Societies. Which means would thus remain to us, if, while plotters conspire and prepare daggers in order to assassinate us, we could not speak in the presence of the Friends of Liberty?
Robespierre then declares that Fouché is a vile and despicable impostor ; that his move is the confession of his crimes and that the action which he takes is similar to the one of the Brissots and of the other crooks who slander the Society as soon as they are chased from it. He assures that virtue will never sacrificed to baseness, nor [will] liberty [be sacrificed] to men whose hands are full of rapines and crimes. I do not want to add anything, he says while closing; Fouché himself has characterised himself enough. I have made all these observations, so that the conspirators know once and for all that they must never hope to escape the surveillance of the people.
A citizen from Commune-Affranchie reports some serious facts against Fouché. The Society sends them to the Committee of Public Safety and, upon the motion of a member, Fouché is excluded from the Society.
The citizens Tolède and Dessyrier, who found themselves at Commune-Affranchie in the days of Fouché, and who claim to be accused, mount the tribune.
Robespierre observes that these two citizens divert, without wanting it, the attention away from Fouché, and that his cause must not be common with theirs. He recalls that the conspirators have always sought to save themselves by placing themselves beside pure patriots ; he hence invites Tolède and Dessyrier not to interrupt a discussion wherein they are not involved. – After members did justice to the patriotism of these citizens, they descend from the tribune.
Robespierre at the Jacobins, July 14 1794
They are strange accomplices of Robespierre, those who, against his will, made a political report on the religious troubles, sheltered from all research in this matter the representatives of the people sent on mission in the departments, defended Tallien, Dubois-Crance, Fouché, Bourdon de l'Oise, and other representatives whom he relentlessly pursued.
Réponse des membres des deux anciens Comités de Salut Public et de sûreté générale aux imputations renouvelées contre eux par Laurent Lecointre, de Versailles, et déclarées calomnieuses par décret du 13 fructidor dernier, à la Convention Nationale (1795) by Barère, Collot d’Herbois, Vadier and Billaud-Varennes
One man alone in the Convention appeared to enjoy an inexpugnable popularity: this was Robespierre, a man full of pride and cunning; an envious and vindictive being, who was never satiated with the blood of his colleagues; and who, by his capacity, steadiness, the clearness of his head, and the obstinacy of his character, surmounted circumstances the most appalling. Availing himself of his preponderance in the Committee of Public Safety, he openly aspired, not only to the tyranny of the decemviri, but to the despotism of the dictatorship of Marius and Sylla. One step more would have given him the masterdom of the revolution, which it was his audacious ambition to govern at his will; but thirty victims more were to be sacrificed, and he had marked them out in the convention.
He well knew that I understood him; and I, therefore, was honoured by being inscribed upon his tablets at the head of those doomed to destruction. I was still on a mission, when he accused me of oppressing the patriots and tampering with the aristocracy. Being recalled to Paris, I dared to call upon him from the tribune, to make good his accusation. He caused me to be expelled from the Jacobins, of whom he was the high-priest; this was for me equivalent to a decree of proscription. I did not trifle in contending for my head, nor in long and secret deliberations with such of my colleagues as were threatened with my own fate. I merely said to them, among others to Legendre, Tallien, Dubois de Crancé, Daunou and Chénier: “You are on the list, you are on the list as well as myself, I am certain of it!” Tallien, Barras, Bourdon de l'Oise and Dubois de Crancé evinced some energy. Tallien contended for two lives, of which one was then dearer to him than his own: he therefore resolved upon assassinating the future dictator, even in the Convention itself. But what a hazardous chance was this! Robespierre’s popularity would have survived him, and we should have been immolated to his manes. I therefore dissuaded Tallien from an isolated enterprise, which would have destroyed the man, but preserved his system.
Convinced that other means must be resorted to, I went straight to those who shared with Robespierre the government of terror, and whom I knew to be envious or fearful of his immense popularity. I revealed to Collot d'Herbois, to Carnot, to Billaud-Varennes, the designs of the modern Appius; and I presented to each of them separately, so lively and so true a picture of the danger of their situation, I urged them with so much address and good fortune, that I insinuated into their breasts more than mistrust, but the courage of henceforth opposing the Tyrant in any further decimating of the Convention.
"Count the votes,” said I to them, “in your committee, and you will see, that when you are determined, he will be reduced to the powerless minority of a Couthon and a Saint-Just. Refuse him your votes, and compel him to stand alone by your vis inertiæ.” But what contrivances, what expedients were necessary to avoid exasperating the Jacobin club, the Seides, and the partisans of Robespierre.
My eye was on him; and seeing him reduced to a single faction, I secretly urged such of his enemies who still clung to the committee, at least to remove the artillery from Paris, who were all devoted to Robespierre and the Commune, and to deprive Henriot of his command or at least to suspend him. The first measure I obtained, thanks to the firmness of Carnot, who alleged the necessity of sending reinforcements of artillery to the army. As to depriving Henriot of his command, that appeared too hazardous; Henriot remained, and was near losing all, or rather, to speak the truth, it was he, who on the 9th Thermidor (the 27th July) ruined the cause of Robespierre, the triumph of which was for a short time in his power. But what could be expected from a drunken and stupid ci-devant footman.
What follows is too well known for me to dwell upon it. It is notorious how Maximilian the First perished; a man whom certain authors have compared to the Gracchi, to whom he bore not the slightest resemblance, either in eloquence or elevation of mind. I confess that in the delirium of victory, I said to those who thought that his views tended to the dictatorship: "You do him too much honour; he had neither plan, nor design: far from disposing of futurity, he was drawn along, and did but obey an impulse he could neither oppose nor govern." But at that time I was too near a spectator of events justly to appreciate their history. The sudden overthrow of the dreadful system which suspended the nation between life and death, was doubtless a grand epoch of liberty; but, in this world, good is ever mixed with evil. What took place after Robespierre's fall? that which we have seen to have been the case after a fall still more memorable. Those who had crouched most abjectly before the decemvir, could, after his death, find no expression strong enough to express their detestation of him.
Memoirs of Fouché (1825), volume 1, page 18-22
…The fact is that, sent [to Lyon], after the sack of this city, I (Fouché) returned in revolt, with a report against Robespierre, and that, from this moment up until Thermidor, I was his declared rival! Robespierre had established himself at the Jacobins, and I in the Committees, from where I expelled him; you'll see! I was a Jacobin myself, but there were two kinds. As for us, we were not popular; we talked about equality, but deep down we were aristocrats! Yes, more aristocratic than anyone perhaps! The Jacobins of the opposite party, such as Hullin, paved the way; they would shout in the crowd on the floor; we only saw them in the stands. It was Robespierre’s henchmen who flattered this populace; Robespierre was its leader, its soul, attempting to reign through them and crush the Convention! But we were his antagonists there, me at the head! He feared me. […] [The fact that I had humiliated his pride] was enough to be certain that he would be my mortal enemy, his hateful and envious character would never forgive me for it, no more than Lacuée who, if it wasn’t for Carnot, he would have had guillotined! […] I understood that you couldn’t go and fight such a man in his club; that I there would be dominated, crushed, and that to resist it, it was necessary to choose another terrain, that is to say the Convention itself and its Committees. It was therefore there that, on my return from Lyon, I began with a report on what needed to be done to stop the complete disorganization of this province, of which I accused Robespierre. People were surprised and terrified by my audacity, Carnot among others, who in his emotion embraced me, praising my courage, but warning me that it would cost me my head! This did not stop me, I persisted; and, addressing all the enemies of the Dictator, either separately or in meetings that I convened as head of public education, I reassured them, encouraged them, and got the Committee to call Robespierre before it to defend itself. It was putting him in a false position, he did not accept it; he refused to present himself and confined himself to the Jacobins, where I proposed to have him attacked, seized as a rebel and thrown into the river! We were preparing the means when the 9th of Thermidor arrived, the day when Tallien, single-handedly, unexpectedly, without having warned us, without knowing our project, warning us, denounced Robespierre as the tyrant of his colleagues! He cited me in support of this questioning, to which Robespierre replied that this was a duel between him and me! You know the rest. But what we don't know is that, under the Directory, it was again me who destroyed the tail of this party, after having thus fought its head!
De 1800 à 1812. Un aide de camp de Napoléon. Mémoires du général compte de Ségar (1894), page 437-438
The primary object of [Robespierre’s] ambition seemed to be to strike, in the first place, what remained or what might spring up again of those he looked upon as his personal enemies, of whom in his hatred he never lost sight. At the head of those he had marked for death stood Fouché, and as, in view of the point his personal quarrel with Robespierre had reached, he could not but succumb within a very short time, it had been concluded therefrom that he was to be one of those who would deal the first blows at Robespierre.
But the arguments brought into play to convince Fouché of his danger were not sufficient to inspire him with courage. He had certainly been at all times an ultra-Revolutionist, and had shown what he was made of in his support of the system of terror; but he had not exactly hit the idea of Robespierre, or rather he had become his rival, and had given him offence by going even further than he did. Fouché's position was therefore not one to afford him opposite his enemy a frank and clearly defined character enabling him to attack him openly. Robespierre had told Fouché that his face was the expression of crime. Fouché, far from replying, took it as a matter of course; expelled from the Jacobins, he had not been able to return to the fold; he no longer dared show himself even in the Convention, but busied himself actively and with a will with intrigues and machinations of the lowest kind. I sent him hither and thither to inform our friends of what we knew of the intentions of Robespierre, Saint-Just, and Couthon. His personal dread of the triumvirs served but to increase in his eyes the idea of their hostile plans. Everything that he already dreaded most sincerely was artfully exaggerated by him when seeking to stimulate those whom he sought to induce to make up their minds to action. Rising at early morning, he would run round till night calling on deputies of all shades of opinion, saying to each and everyone, "You perish tomorrow if he does not.” To those who mourned Danton, and who were threatened with the resentment of his executioners, Fouché said: ”We may, if we see fit, be avenged tomorrow, and tomorrow only will we be safe.”
In order to instil fresh courage into minds so stricken with fright more than one speech was required to place the question before each and every one in such a way that he should see his own interests in it. Hence it cannot be denied that Fouché, gathering together by his clever intriguing all sentiments against Robespierre, was a genuine resource in the midst of the elements extant ready to make a decisive move against the oppressors of the Convention. […] Matters were growing worse apace; no longer was there any possibility of a reconciliation, even under the mask of mutual deceit. Not only had hostilities been declared, but a war to the knife proclaimed. In spite of all Fouché's prudence, a letter written in his own hand had been intercepted, containing particularly the following line addressed to a colleague in the Convention: ”Ere a fortnight has rolled over us either Maximilien or we shall have ceased to exist." Hence the quarrel could end only by the destruction of one side or the other; nothing was left but to conquer or die.
Even at a time when he was brought face to face with the necessity of defending himself, it was not in Fouché to do so aboveboard. Indirect means, those of ceaseless and underground intrigue, in which he had served his apprenticeship at the Oratory, he was familiar with; and just as everything comes handy in a household, so in a conspiracy, which is itself but an intrigue more serious than others, skill and manoeuvring constitute the necessary elements; and it will be seen that Fouché was to be, if not by his courage, at least by his doings, a useful cooperator in what was about to take place. He has, in later days, boasted that he dealt mortal blows to Robespierre; the fact is that in order to flee from his wrath and, if he could have done so; from his relentless memory, Fouché no longer appeared at the National Convention nor slept at home; it was at night alone that, under various disguises, he would go the rounds of such of his colleagues as were busily engaged in preparing means of defence against Robespierre, and bring and carry from one to the other every particular as to what was taking place, and go on the errands it was requisite should be dextrously done in order to cement the alliances we were forming pending the moment, impossible to positively determine, when the decisive blow was to be struck.
Memoirs of Barras, member of the Directorate (1895) page 207-214
Legendre: […] I did not see Fouché during his missions, but I saw him at the Jacobins; he surrounded himself with all the men who, before the 9th of Thermidor, were preparing for this great day. There he openly attacked Robespierre who, wanting to manage him or give himself the means to destroy him, had him named president of the Jacobins. Fouché seized this post to attack Robespierre more openly, and in his responses he designated this tyrant whom it was necessary to strike. I declare that I see Fouché as one of the elements of the day of 9 Thermidor.
Tallien: On Germinal 12, at the time when I believed I saw in Fouché a man linked to the conspirators, I had the courage to denounce him. Since that time, I have had no relationship with him, but it is my duty to defend him by attesting to the facts that are within my knowledge. Fouché was proscribed by Robespierre, because he had opposed the measures taken by Collot in Lyon. Fouché courageously unmasked Robespierre, and declared that, even if his head fell, he would make this dictator known to the people. Every day Fouché came to report to us what was happening at the Committee of Public Safety, and the day before the 9th of Thermidor he told us: “The division is complete, tomorrow we must strike.” The next day, the tyrant was no more. Fouché, at the same time, wrote to his sister: “In a short time the tyrant shall be punished. Robespierre only have a few days left to reign.” This letter was intercepted by Bô, who sent it to Robespierre. These are the facts I had to make known.
Legendre and Tallien at the Convention, August 9 1794
Madame Collot (d’Herbois)
Mademoiselle Robespierre
(their titles are common as well as their distress)
Per month: 200 pounds
Per year: 2400 pounds
for special help.
Collective decree granting Charlotte a pension from Minister of Police Fouché dated February 8 1805, cited in Charlotte Robespierre et ses amis (1961) by Gabriel Pioro and Pierre Labracherie.
#fouché wanting to throw robespierre into the seine😂😭#fouché#robespierre#maximilien robespierre#charlotte robespierre#joseph fouché#frev friendships#frev#french revolution
110 notes
·
View notes
Text
From Taiwan and Finland in January to Croatia and Ghana in December, one of the largest combined electorates in history will vote for new governments in 2024. This should be a cause of celebration and a vindication of the power of the ballot box. Yet this coming year is likely to see one of the starkest erosions of liberal democracy since the end of the Cold War. At their worst, the overall results could end up as a bloodbath or, marginally less bleakly, as a series of setbacks.
At first glance, the stats are impressive. Forty national elections will take place, representing 41 percent of the world’s population and 42 percent of its gross domestic product. Some will be more consequential than others. Some will be more unpredictable than others. (You can strike Russia and Belarus from that list.) One or two may produce uplifting results.
However, in the United States and Europe, the two regions that are the cradles of democracy—or at least, that used to project themselves as such—the year ahead is set to be bracing.
It is no exaggeration to say that the structures established after World War II, and which have underpinned the Western world for eight decades, will be under threat if former U.S. President Donald Trump wins a second term in November. Whereas his first period in the White House might be regarded as a psychodrama, culminating in the paramilitary assault on Congress shortly after his defeat, this time around, his menace will be far more professional and penetrating.
European diplomats in Washington fear a multiplicity of threats—the imposition of blanket tariffs, also known as a trade war; the sacking of thousands of public officials and their replacement with politicized loyalists; and the withdrawal of remaining support for Ukraine and the undermining of NATO. For Russian President Vladimir Putin, the return of Trump would be manna from heaven. Expect some form of provocation from the Kremlin in the Baltic states or another state bordering Russia to test the strength of Article 5, the mutual defense clause of the Western alliance.
More broadly, a Trump victory would arguably mark the final dismantling of the credibility of Western liberal democracies. From India to South Africa and from Brazil to Indonesia, countries variously called middle powers, pivot countries, multi-aligned states—or, now less fashionably, the global south—will continue the trend of picking and choosing their alliances, seeing moral equivalence in the competitive bids on offer.
The greatest effect that a Trump return could have would be on Europe, accelerating the onward march of the alt right or far right across the continent. Yet that trend will have gained momentum long before Americans go to the polls. French President Emmanuel Macron and German Chancellor Olaf Scholz are looking over their shoulders as the second wave of populism affects the conduct of government.
The wedge issue that is threatening all moderate parties is immigration, just as it did in 2015, when former German Chancellor Angela Merkel allowed in more than 1 million refugees from the Middle East in what is now seen as the first wave of Europe’s immigration crisis. This time around, the arguments propagated by the AfD (the far-right Alternative for Germany party), Marine Le Pen’s National Rally in France, and similar groups across the continent have permeated the political mainstream.
The past 12 months have seen European Union decision-making constantly undermined by Prime Minister Viktor Orban in Hungary, particularly further support for Ukraine. For the moment, he stands alone, but he is likely to be joined by others, starting with the newly returned Prime Minister Robert Fico in Slovakia. Italian Prime Minister Giorgia Meloni has struck a tacit deal with Brussels, remaining loyal on supporting Ukraine (against her instincts and previous statements) in return for effectively being given carte blanche in Italy’s domestic politics.
In September, Austria seems almost certain to vote in a coalition of the far right and the conservatives. A country that has (ever since the withdrawal of Soviet forces in 1955) prized its neutrality and been keen to ingratiate itself with Moscow has already been uncomfortable giving full-scale support to Kyiv. We can expect that support to soon be scaled back.
One of the few countries with a center-left administration, Portugal, will see it join the pack of the right and far right when snap elections are held in March. The previous incumbent, the Socialist Party’s outgoing Prime Minister Antonio Costa, was forced to quit amid a corruption investigation.
The most explosive moment is likely to occur in June, with the elections to the European Parliament. This reshuffling of the Euro-pack, which happens once every four years, was always seen in the United Kingdom as an opportunity to behave even more frivolously than usual. In 2014, the British electorate, in its inestimable wisdom, put Nigel Farage and his U.K. Independence Party in first place, setting in train a series of events that, two years later, led to the referendum to leave the EU.
Having seen the damage wrought by Brexit, voters in the remaining 27 EU member states are not angling for their countries to go it alone. However, many will use the opportunity to express their antipathy to mainstream politics by opting for a populist alternative. Some might see it as a low-risk option, believing that the European parliament does not count for much.
In so doing, they would be deluding themselves. It is entirely possible that the various forces of the far right could emerge as the single biggest bloc. This might not lead to a change in the composition of the European Commission (the diminished mainstream groupings would still collectively hold a majority), but any such extremist upsurge will change the overall dynamics across Europe.
Far-right parties in charge of governments will see themselves emboldened to pursue ever more radical nativist policies. In countries in where they are junior members of ruling coalitions (such as in Sweden), they will apply further pressure on their more mainstream conservative partners to move in their direction.
Conversely, countries that saw a surprising resurgence of the mainstream in national elections this year are unlikely to see that trend maintained. Spanish Prime Minister Pedro Sánchez’s success in staving off the right was achieved only by cutting a deal with Catalan separatists. This led to protests by Spanish nationalists and a situation that is anything but stable.
Prime Minister Donald Tusk’s victory in Poland was at least as remarkable because the far-right Law and Justice party (PiS) government had used its years in government to try to skew the media and the courts in its direction. Expect PiS gains in June.
The most alarming result of 2023 was the return to prominence, and the verge of power, of Geert Wilders. The Dutch elections provide a how-not-to guide for mainstream politicians. The willingness of the center-right party of the outgoing Prime Minister Mark Rutte to contemplate a coalition with Wilders’s Party for Freedom emboldened many voters who had assumed their vote would be disregarded.
In Europe’s biggest economy, Germany, the so-called firewall established by the main parties to refuse to govern with the AfD is beginning to fray. Already, the conservative Christian Democratic Union (CDU) is working with them in small municipalities. Friedrich Merz, the CDU leader, has dropped hints that such an option might not be out of the question at the regional level.
If the AfD gains the largest number of seats in the June European Parliament elections (opinion polls currently put it only marginally behind the CDU and ahead of all three parties in Scholz’s so-called traffic light coalition), then the momentum will change rapidly. It could go on to win three of the states in the former communist east—Thuringia, Saxony, and Brandenburg—next autumn. Germany would enter unchartered territory.
These dire predictions could end up being overblown. Mainstream parties in several countries may defy the doom merchants and emerge less badly than forecast. Given recent trends, however, optimism is thin on the ground.
There is one election, however, due to take place in the latter part of 2024 that could produce not just a centrist outcome, but one with a strong majority in its parliament. Britain, the country that left the heart of Europe, the island that until recently was run by a clown, could emerge as the lodestar for modern social democracy. The irony would be lost on no one.
79 notes
·
View notes
Text
As early as 1700, Samuel Sewall, the renowned Boston judge and diarist, connected “the two most dominant moral questions of that moment: the rapid rise of the slave trade and the support of global piracy” in many American colonies [...]. In the course of the eighteenth century, [...] [there was a] semantic shift in the [literary] trope of piracy in the Atlantic context, turning its [...] connotations from exploration and adventure to slavery and exploitation. [...] [A] large share of Atlantic seafaring took place in the service of the circum-Atlantic slave trade, serving European empire-building in the Americas. [...] Ships have been cast as important sites of struggle and as symbols of escape in [...] Black Atlantic consciousness, from Olaudah Equiano’s Interesting Narrative (1789) and Richard Hildreth’s The Slave: or Memoir of Archy Moore (1836 [...]) to nineteenth century Atlantic abolitionist literature such as Frederick Douglass’s My Bondage and My Freedom (1855) or Martin Delany’s Blake (1859-1862). [...] Black and white abolitionists across the Atlantic world were imagining a different social order revolving around issues of resistance, liberty, (human) property, and (il)legality [...].
---
Using black pirates as figures of resistance [...], Maxwell Philip’s novel Emmanuel Appadocca (1854) emphasizes the nexus of insatiable material desire and its conditions of production: slavery. [...] [T]he consumption of commodities produced by slave labor itself was delegitimized [...]. Philip, a Trinidadian [and "illegitimate" "colored" child] [...], published Emmanuel Appadocca as a protest against slavery in the United States [following the Fugitive Slave laws of 1850.]. [...] [The novel places] at its center [...] a heroic non-white pirate and intellectual [...] [whose] pirate ship [...] [is] significantly named The Black Schooner [...]. One of the central discourses in [the book] is that of legitimacy, of rights and lawfulness, of both slavery and piracy [...]. About midway into the book, Appadocca gives a [...] speech in which he argues that colonialism itself is a piratical system:
If I am guilty of piracy, you, too [are] [...] guilty of the very same crime. ... [T]he whole of the civilized world turns, exists, and grows enormous on the licensed system of robbing and thieving, which you seem to criminate so much ... The people which a convenient position ... first consolidated, developed, and enriched, ... sends forth its numerous and powerful ships to scour the seas, the penetrate into unknown regions, where discovering new and rich countries, they, in the name of civilization, first open an intercourse with the peaceful and contented inhabitants, next contrive to provoke a quarrel, which always terminates in a war that leaves them the conquerors and possessors of the land. ... [T]he straggling [...] portions of a certain race [...] are chosen. The coasts of the country on which nature has placed them, are immediately lined with ships of acquisitive voyagers, who kidnap and tear them away [...].
In this [...], slavery appears as a direct consequence of the colonial venture encompassing the entire “civilized world,” and “powerful ships” - the narrator refers to the slavers here - are this world’s empire builders. [...] Piracy, for Philip, signifies a just rebellion, a private, legitimate [resistance] against colonial exploiters and economic inequality - he repeatedly invokes their solidarity as misfortunate outcasts [...].
---
All text above by: Alexandra Ganser. “Cultural Constructions of Piracy During the Crisis Over Slavery.” A chapter from Crisis and Legitimacy in the Atlantic American Narratives of Piracy: 1678-1865. Published 2020. [Bold emphasis and some paragraph breaks/contractions added by me.]
#abolition#its first of february#caribbean#maxwell philip was trinidadian#tidalectics#archipelagic thinking
65 notes
·
View notes
Text
good evening everybody i have a question for you:
IMPORTANT NOTE: i do not give a shit about the morality of any of these men. ‘oh rochester locked his wife in the attic’ yeah sure but does he eat pussy. ‘m. paul is a misanthropic misogynist’ cool whatever are we re-enacting fleabag s2 or what. ‘heathcliff and cathy were in a toxic relationship’ i do not caaaaaaaare this post is about which of these men you find the most fuckable, not which of them you’d actually want to put up with for longer than one night. now go fucking wild idc
#jane eyre#villette#wuthering heights#the tenant of wildfell hall#charlotte bronte#anne bronte#emily bronte#listen i know i just said go wild but if anyone genuinely picks gilbert markham as a fuckable man i genuinely want to study your brain#also there is a correct answer to this poll just fyi
326 notes
·
View notes
Text
i have this excerpt from Notes from the Warsaw Ghetto: The Journal of Emmanuel Ringelblum printed and framed
Like, I paid an etsy seller to print it for me on the nicest cardstock with the best ink, and then I waited in line and paid a stupid amount of money to have it framed at the Michael's custom framing counter. And I have zero regrets. I've probably posted this excerpt here before but I don't care. It is everything.
The heroic girls, Chajke and Frumke—they are a theme that calls for the pen of a great writer. Boldly they travel back and forth through the cities and towns of Poland. They carry “Aryan” papers identifying them as Poles or Ukrainians. One of them even wears a cross, which she never parts with except when in the Ghetto. They are in mortal danger every day. They rely entirely on their “Aryan” faces and on the peasant kerchiefs that cover their heads. Without a murmur, without a second’s hesitation, they accept and carry out the most dangerous missions. Is someone needed to travel to Vilna, Bialystok, Lemberg, Kowel, Lublin, Czestochowa, or Radom to smuggle in contraband such as illegal publications, goods, money? The girls volunteer as though it were the most natural thing in the world. Are there comrades who have to be rescued from Vilna, Lublin, or some other city?— They undertake the mission. Nothing stands in their way, nothing deters them. Is it necessary to become friendly with engineers of German trains, so as to be able to travel beyond the frontiers of the Government General of Poland, where people can move about with special papers? They are the ones to do it, simply, without fuss, as though it was their profession. They have traveled from city to city, to places no delegate or Jewish institution had ever reached, such as Wolhynia, Lithuania. They were the first to bring back the tidings about the tragedy of Vilna. They were the first to offer words of encouragement and moral support to the surviving remnant of that city. How many times have they looked death in the eyes? How many times have they been arrested and searched? Fortune has smiled on them. They are, in the classic idiom, “emissaries of the community to whom no harm can come.” With what simplicity and modesty have they reported what they accomplished on their journeys, on the trains bearing Polish Christians who have been pressed to work in Germany! The story of the Jewish woman will be a glorious page in the history of Jewry during the present war. And the Chajkes and Frumkes will be the leading figures in this story. For these girls are indefatigable. Just back from Czestochowa, where they imported contraband, in a few hours they’ll be on the move again. And they’re off without a moment’s hesitation, without a minute of rest.
He only namechecks Chaike Grossman and Frumka Plotnicka here, but I can tell you for a fact that he's also referring to Tossia Atlman, Tema Schneiderman, and Lonka Kozybrodska. At least.
So far the count of Jewish women (that I'm aware of) who have responded to "They are a theme that calls for the pen of a great writer" with a book (or long-planned book) are three: me, Dr. Lenore Weitzman (who won't return any of my emails) and Judith Batalion (who did return my emails, had lunch with me, and told me that Dr. Weitzman wouldn't respond to her emails either). I hope more Jewish women--in and out of the academe--continue to take up this call, and I hope they keep getting published and aren't rejected because it's "too similar" to mine and Batalion's.
No like seriously like two months after I signed with my agent, and one month after I got my book deal, I received a rejection from a lit agent saying that my book was "too similar" to Batalion's. Ok first of all it's not. I read Batalion's the day it came out, and they're very different books with very different focuses, goals, and approaches; the only thing they have in common is that they're both about this underserved, underappreciated group of amazing women. There SHOULD be multiple books about each and every one of them. There SHOULD be multiple books about one day Tossia spent in Vilna. Every white man who looked sideways at WW2 and the American Civil War have like, 87 terrible books dedicated to them, and I DEMAND at least 3 for each of these women. And 17 for Queen Zivia. (Who does have a biography, written by Bella Gutterman). Plus a biopic.
So this post went in a direction.
tl;dr:

#epica's cover of the pirates of the caribbean theme came on shuffle while i was writing this#it was awesome
103 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Best News of Last Week - December 12, 2022
1. Big cats: US Senate unanimously passes bill to curb private ownership

A bill to restrict the private ownership of big cats like lions and tigers in the US has passed by unanimous consent in the Senate. The Big Cat Public Safety Act would stop people from keeping the animals as pets and from them being exposed to public petting and photo opportunities.
Efforts to curb private ownership have increased in the wake of the Netflix documentary series Tiger King.
The bill now needs to be signed into law by President Joe Biden.
2. New Mexico voted a child care guarantee into its constitution.

New Mexico in May became the first state to offer free child care to most of its residents. Now, after a November referendum, it’s also the first state to enshrine child care funding in its constitution, effectively making the service a universal right – and perhaps offering a model for how other states could serve their youngest residents and working parents.
3. Rare good news from the Amazon: Gigantic fish are thriving again

Thanks to sustainable fishing programs that combine education with strict rules and quotas, the pirarucu, one of the world's largest freshwater fish it's now making a comeback.
"The pirarucu population has recovered," says Ana Claudia Torres, who runs the sustainable fishing program for the Mamirauá Institute, which manages a vast nature reserve covering 4,300 square miles of jungle in northern Brazil.
4. Dog reunited with family 7 days after falling from cliff on Vancouver Island

A beloved pet that went missing in the Highlands area of Vancouver Island was found seven days later by an army of volunteers. Luna, was found desperately clinging to a narrow ledge on a cliff, and was reunited with her owner after a heroic rescue last month.
It's believed that Luna had chased an animal out of her yard and got lost, somehow falling off a cliff and landing on a two-foot wide ledge. She remained there, alone, as her owner and searchers frantically looked for her.
5. Iran Shutting Down Morality Police, Official Says, After Months of Protests

Iran has scrapped its morality police after more than two months of protests triggered by the death of Mahsa Amini following her arrest for allegedly violating the country's strict female dress code, local media said Sunday, citing a single Iranian official.
"Morality police have nothing to do with the judiciary and have been abolished," Attorney General Mohammad Jafar Montazeri was quoted as saying by the ISNA news agency.
6. Condoms to be free for young people in France, Macron says

Young people in France will be able to get condoms free of charge from next year in an effort to reduce the spread of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), President Emmanuel Macron said on Thursday.
"In pharmacies, condoms will be free for those aged 18 to 25 from January 1," Macron told reporters during an event about young people's health.
7. One-eared rescue dog Van Gogh paints his way into adoption

A former bait dog in a North Carolina dogfighting ring "paints" artwork for charity and is living his best life in Connecticut.
. . .
That’s it for this week. If you liked this post you can support this newsletter with a small kofi donation:
Buy me a coffee ❤️
Have a great week ahead :)
325 notes
·
View notes