#Beta hCG Levels in Pregnancy
Text
What is the Beta hCG Test and How it Relates to Pregnancy
For many women, the journey to parenthood starts with a simple yet significant question: “Am I pregnant?” Then, it starts a series of pregnancy tests and various hormone checks. The beta-human chorionic gonadotropin or Beta hCG test is crucial among these. But what exactly is this test, and how does it relate to pregnancy?
This article delves into the science behind the beta hCG test, its role in confirming pregnancy, and its wider applications in understanding fetal development and potential complications.

#beta hCG test#HCG Test#hCG Blood test#hCG test price#Beta hCG Levels in Pregnancy#Quantitative blood pregnancy test#Quantitative hCG test#Quantitative serial beta-hCG test#Repeat quantitative beta-hCG test
0 notes
Text
Fighting Choriocarcinoma: Advanced Treatment at Dr. Chandrakanta’s Gynae-Oncology Center in Jaipur
In the landscape of gynaecological cancers, choriocarcinoma stands out as a rare but aggressive condition that demands prompt and specialized care. Located in the heart of Jaipur, Dr. Chandrakanta’s Gynae-Oncology Center is dedicated to providing comprehensive treatment for choriocarcinoma in Jaipur , offering hope and healing to patients facing this challenging diagnosis.
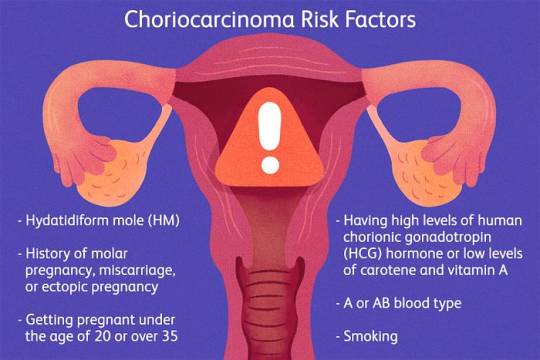
Choriocarcinoma is a type of gestational trophoblastic disease that develops from abnormal placental tissue following a molar pregnancy, miscarriage, or rarely, a normal pregnancy. This malignant tumor arises from the cells that would normally develop into the placenta during pregnancy. While the exact causes remain unclear, certain risk factors such as previous molar pregnancies or a history of choriocarcinoma may increase the likelihood of developing this condition.
Symptoms:
Choriocarcinoma often presents with symptoms that mimic those of pregnancy-related conditions, making diagnosis challenging. Common symptoms may include:
1. Vaginal bleeding, which may be irregular or heavy
2. Pelvic pain or discomfort
3. Enlarged uterus, disproportionate to the stage of pregnancy or absence of pregnancy
4. Elevated levels of beta-hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) in the blood
5. Symptoms of metastasis, such as shortness of breath, chest pain, or neurological symptoms if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body
Prevention:
Since choriocarcinoma often occurs following a molar pregnancy, prevention strategies focus on early detection and management of molar pregnancies. Regular prenatal care, including ultrasound examinations and monitoring of beta-hCG levels, is essential for identifying molar pregnancies and preventing complications such as choriocarcinoma.
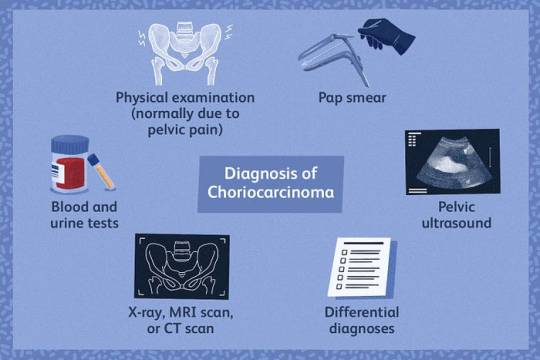
The treatment approach for choriocarcinoma typically involves a combination of chemotherapy, surgery, and close monitoring. At Dr. Chandrakanta’s Gynae-Oncology Center, we offer comprehensive choriocarcinoma treatment tailored to each patient’s individual needs, including:
1.Chemotherapy: The primary treatment for choriocarcinoma involves administering chemotherapy drugs to kill cancer cells and prevent them from spreading. Chemotherapy may be given in cycles, with regular monitoring of beta-hCG levels to assess response to treatment.
2. Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the primary tumor or metastatic lesions, particularly if the cancer has spread to other organs such as the lungs or brain.
3. Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy may be used in combination with chemotherapy to target and shrink tumors, particularly in cases where the cancer has spread to the brain or other sensitive areas.
Comprehensive Care and Support:
At our center, we understand the physical and emotional toll that choriocarcinoma can take on patients and their families. That’s why we offer comprehensive care and support services to address the holistic needs of our patients. From counseling and fertility preservation to pain management and palliative care, we are committed to guiding our patients through every step of their cancer journey with compassion and expertise.now the best Choriocarcinoma Treatment in jaipur.
Conclusion:
Choriocarcinoma may be rare, but with early detection and expert treatment, patients can achieve favorable outcomes and regain their health and well-being. At Dr. Chandrakanta’s Gynae-Oncology Center in Jaipur, we are dedicated to providing cutting-edge treatment and unwavering support to patients facing this challenging diagnosis. With our multidisciplinary approach and personalized care, we offer hope and healing to those affected by choriocarcinoma, empowering them to face their diagnosis with courage and resilience.
Choriocarcinoma is a rare and aggressive form of cancer that happens in your uterus or ovaries. The most common type, gestational choriocarcinoma is a type of gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD). GTD is a group of rare conditions that happens in pregnancy when tumors form from the placenta. The placenta provides oxygen and nutrients to a fetus through the umbilical cord.
Choriocarcinoma is most common in people who have a molar pregnancy (when the sperm and egg join incorrectly and make a hydatidiform mole). It can also happen after an ectopic pregnancy, a pregnancy that ends in miscarriage or even after a full-term pregnancy resulting in a birth.
#choriocarcinomatreatment in jaipur#dr chandrakanta gynae oncology in jaipur#cervical cancer treatment in jaipur#gynae oncologist in jaipur#endometrial cancer treatment in jaipur#gynae cancer doctor in jaipur#gynaecological cancer in jaipur#gynaecological surgeries in jaipur#gynaecological oncologist near me
0 notes
Text
Double Marker Test in Pregnancy in Pune - Dr. Tejash Tamhane
Pregnancy is a joyous journey filled with anticipation and excitement. However, it also comes with its share of concerns, especially regarding the health and well-being of both the mother and the unborn child. In Pune, expectant mothers have access to advanced medical care, including specialized tests like the best double marker test pregency in Pune, thanks to experts like Dr. Tejash Tamhane.
Understanding the Double Marker Test
The double marker test is a prenatal screening test performed during pregnancy to assess the risk of certain chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome (trisomy 21) and Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18). It involves measuring two specific substances in the mother's blood: beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (beta-hCG) and pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A).
Importance of the Double Marker Test
Early detection of chromosomal abnormalities is crucial for appropriate counseling and decision-making regarding the pregnancy. The double marker test helps identify pregnancies at a higher risk of chromosomal abnormalities, allowing healthcare providers to offer further diagnostic testing or interventions as needed.
When is the Double Marker Test Done?
The double marker test is typically performed between the 9th and 13th weeks of pregnancy, making it an early screening test for chromosomal abnormalities.
How is the Double Marker Test Performed?
The double marker test is a simple blood test performed on the mother. A small sample of blood is drawn from the mother's arm and sent to the laboratory for analysis. The levels of beta-hCG and PAPP-A in the blood sample are measured, and the results are interpreted to assess the risk of chromosomal abnormalities.
What do the Results Mean?
The results of the double marker test provide an estimation of the risk of chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus. A low-risk result indicates a lower likelihood of chromosomal abnormalities, while a high-risk result suggests a higher probability of such conditions.
Accuracy and Reliability
While the double marker test is a valuable screening tool, it's important to note that it does not provide a definitive diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities. In some cases, further diagnostic testing, such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling, may be recommended for confirmation.
Interpretation of Results
Interpreting the results of the double marker test requires expertise and experience. Dr. Tejash Tamhane, with his extensive knowledge in fetal medicine, provides comprehensive counseling and support to patients, helping them understand the implications of the test results and guiding them through the next steps.
Why Choose Dr. Tejash Tamhane?
Experience and Expertise
Dr. Tejash Tamhane is a renowned specialist in fetal medicine with years of experience in prenatal screening and diagnostic procedures. His expertise ensures accurate assessments and personalized care for expectant mothers.
Patient-Centric Approach
Dr. Tamhane is known for his compassionate and patient-centric approach to care. He takes the time to listen to his patients' concerns, address their questions, and provide them with the support they need throughout their pregnancy journey.
Conclusion
In Pune, the double marker test in pune is an essential component of prenatal care, offering valuable insights into the health of the fetus. With the expertise of Dr. Tejash Tamhane, expectant mothers can trust in accurate assessments, personalized care, and compassionate support for a healthy pregnancy.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What does a high-risk result on the double marker test mean? A high-risk result indicates an increased likelihood of chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus, warranting further diagnostic testing and counseling.
2. Is the double marker test mandatory during pregnancy? The double marker test is not mandatory but is recommended for all pregnant women, especially those with risk factors such as advanced maternal age.
3. Can the double marker test detect all chromosomal abnormalities? While the double marker test is effective in screening for common chromosomal abnormalities like Down syndrome and Edwards syndrome, it may not detect all genetic conditions.
4. How long does it take to get the results of the double marker test? The results of the double marker test are usually available within a few days after the blood sample is collected.
5. Are there any risks associated with the double marker test? The double marker test is a safe and non-invasive procedure, and the risks associated with it are minimal, similar to any other blood test.
0 notes
Video
youtube
How reliable are Pregnancy Tests
Home pregnancy test is the very first test a woman who suspect pregnancy takes. The accuracy and reliability of home pregnancy test have always been in discussion. Doctors usually advise to opt for a blood test to confirm pregnancy after you have taken home pregnancy test. The home pregnancy test examines the presence read more here and density of human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) in the body to confirm pregnancy. If hCG is present in your body, you have conceived otherwise you have not. The reliability of pregnancy test largely depends on the displayed result.
If you've been tested positive for pregnancy then it is more reliable than a negative result. This is because home pregnancy test detects pregnancy, even if your body doesn't have the considerable amount of HCG. It is advisable that you consult a gynaecologist/obstetrician immediately to confirm your pregnancy and start taking necessary preventive measures and medical help.
Negative result in Home pregnancy test If you are suspecting pregnancy and the pregnancy test has shown a negative result then it becomes less reliable than positive result. This is because, at times, the level of HCG in your urine isn't high enough to give the accurate result. This usually occurs in those cases when a woman has taken home pregnancy too early. A woman should wait for two to seven days after her missed cycle to take a pregnancy test.
As your pregnancy test can detect positive result even if your urine doesn't have accurate level of HCG, it can pronounce a negative result in the same condition. Therefore, you should thoroughly read the label of the test kit to determine the sensitivity of your pregnancy test. In case you doubt the results of your pregnancy test, consult your obstetrician at the earliest and go for a blood test, which is more accurate than home pregnancy test.
Home pregnancy test is considered 97 per cent accurate when conducted as per the instructions given on the kit; however, the blood test for pregnancy confirmation remains the most accurate test. The blood test is generally called beta hCG test (also called quantitative blood test). It accurately evaluates the levels of HCG in blood. This indicates that blood test can detect even the minimal levels of HCG. Another blood test called qualitative hCG test has a simple system that detects pregnancy by giving a yes if you have conceived and no you have not conceived.
1 note
·
View note
Text
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): What to Expect from the Process
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is a groundbreaking fertility treatment that has provided hope and joy to countless individuals and couples. Understanding what to expect from the IVF process is essential for those embarking on this transformative journey. In this comprehensive guide, we unravel the key stages and intricacies of the IVF process.

1. Initial Consultation and Assessment:
Comprehensive Evaluation: The IVF journey begins with an initial consultation and a thorough assessment of both partners' reproductive health.
Individualized Treatment Plan: Our expert fertility specialists create a personalized treatment plan based on the evaluation, addressing specific fertility challenges.
2. Ovulation Stimulation:
Ovarian Stimulation Medications: Fertility medications are prescribed to stimulate the ovaries, promoting the development of multiple eggs.
Monitoring and Adjustments: Regular monitoring through blood tests and ultrasound scans ensures optimal egg maturation. Medication adjustments are made as needed.
3. Egg Retrieval:
Surgical Procedure: Once the eggs reach maturity, a minor surgical procedure known as egg retrieval is performed.
Minimally Invasive: Egg retrieval is a minimally invasive procedure conducted under sedation, and it typically takes about 20-30 minutes.
4. Sperm Collection and Fertilization:
Sperm Sample Collection: On the same day as egg retrieval, a sperm sample is collected.
Fertilization Process: In the laboratory, eggs and sperm are combined through conventional insemination or Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) to facilitate fertilization.
5. Embryo Culture and Development:
Embryo Monitoring: Fertilized eggs develop into embryos, which are cultured and monitored in the laboratory for several days.
Quality Assessment: Embryo quality is assessed, and the most viable embryos are selected for transfer.
6. Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT):
Optional Testing: In certain cases, Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Aneuploidy (PGT-A) or Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Monogenic or Single Gene Defects (PGT-M) may be recommended.
Enhanced Selection: PGT allows for the selection of embryos with the best chance of a successful pregnancy.
7. Embryo Transfer:
Transfer Process: One or more selected embryos are transferred into the uterus during a brief and relatively painless procedure.
Post-Transfer Rest: After the transfer, a short period of rest may be advised to enhance implantation.
8. Luteal Phase Support:
Hormonal Support: Medications are prescribed to support the luteal phase, promoting a receptive uterine environment for embryo implantation.
Monitoring Progress: Hormone levels and ultrasound scans are used to monitor the progression of the early stages of pregnancy.
9. Pregnancy Test and Follow-up:
Beta hCG Test: A blood test measures the level of beta hCG to determine pregnancy.
Follow-up Consultation: A follow-up consultation is scheduled to discuss results, provide support, and plan for ongoing care.
10. Emotional Support and Counseling:
Psychological Well-Being: Emotional support and counseling are integral throughout the IVF process.
Support Groups: Our center offers access to support groups and resources to help individuals and couples navigate the emotional aspects of fertility treatment.
Conclusion:
Embarking on the In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) journey is a significant decision, and knowing what to expect can alleviate uncertainties. At the best IVF center in Indore, our dedicated team is committed to guiding individuals through each stage of the IVF process with compassion, expertise, and a focus on achieving the dream of building a family.
0 notes
Text
Does Stress Affect My IVF Outcome?

Your family and friends may have told you countless times to “stop stressing out” and that “it would improve your chances of success” with in vitro fertilization (IVF) if you were less stressed. This may be completely inaccurate and probably makes you even more stressed. While stress may affect your production of stress hormones, the regularity of your menstrual cycles, and ultimately fertility itself, the relationship of stress with IVF outcome is unproven. In IVF, ovaries are stimulated and eggs are mechanically retrieved without relying on your natural menstrual cycle. Many studies have looked at the relationship between stressand IVF outcome and the results are mixed at best…the same way you would get a 50/50 result when tossing a coin. A Swedish study followed 166 women after their first IVF cycle and found no association between outcome and stress levels1.
I have had many patients who conceived that were emotional wrecks during the ten-day waiting time prior to their beta hCG pregnancy test results. Conversely, many who were calm did not conceive. While stress is a natural coping mechanism for infertility and IVF treatments, it does not affect the quality of your eggs at the molecular level. In the end, the ultimate limiting factor in reproduction is the stability of your eggs’ DNA, not your emotional state. Of course, stress is bothersome to most and it is helpful to learn coping strategies to suppress it and improve your quality of life. It will not, however, affect your IVF outcome. It is important to avoid feeling guilty, convinced that somehow you were responsible for any bad outcome of your IVF treatment. If history has taught us anything, it’s that high stress levels do not affect human fertility. Fertility or miscarriage rates are not affected by events around us. War prisoners, for example, do not have a higher chance of miscarriage or infertility than the non-prisoner population, and this is clearly a high stress environment. In the end, the “seeds” decide the outcome. I find that counseling my patients about the lack of negative effects actually helps reduce their stress level. In the end, stress declines to a large extent once the pregnancy is going well and a nice fetal heartbeat is detected at your six-and-a-half week ultrasound.
#fertility clinic dallas#fertility center dallas#fertility doctor dallas#ivf clinic dallas#best ivf doctors in dallas
0 notes
Text
Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia
Understanding and Managing a Unique Pregnancy-Related Condition
Introduction:
Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia (GTN) is a rare group of tumors that develop from abnormal growth of cells in the uterus during pregnancy. While most pregnancies progress without any complications, GTN can occur in a small percentage of cases. Understanding GTN, its subtypes, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is crucial for early detection and effective management. In this blog, we will explore the world of Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia and shed light on this unique pregnancy-related condition.
Understanding Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia:
Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia refers to a group of tumors that arise from the placental trophoblast cells, which normally support the growth of the embryo during pregnancy. The different subtypes of GTN include Hydatidiform Mole (complete or partial), Invasive Mole, Choriocarcinoma, Placental Site Trophoblastic Tumor, and Epithelioid Trophoblastic Tumor. These tumors have distinct characteristics and can range from benign to malignant.
Causes and Risk Factors:
The exact cause of GTN is still not fully understood. However, certain factors can increase the risk of developing GTN:
Previous history of molar pregnancy: Women who have had a previous molar pregnancy are at a higher risk of developing GTN in subsequent pregnancies.
Age: Women younger than 20 or older than 40 years have a slightly higher risk of GTN.
Previous miscarriage or stillbirth: A history of recurrent miscarriages or stillbirths may slightly increase the risk of GTN.
Recognizing the Symptoms and Diagnosis:
The symptoms of GTN can vary depending on the subtype and stage of the tumor. Common symptoms may include:
Vaginal bleeding or spotting during or after pregnancy
Enlarged uterus or a rapidly growing abdomen
Severe nausea and vomiting (hyperemesis gravidarum)
Pelvic pain or discomfort
Anemia (low red blood cell count) or fatigue
If GTN is suspected, a series of diagnostic tests will be conducted, including:
Ultrasound: An ultrasound examination can help visualize the uterus and detect any abnormal growths or masses.
Beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (β-hCG) blood test: β-hCG levels are typically elevated in GTN. Serial measurements can help monitor the response to treatment and detect any recurrence.
Tissue biopsy: A biopsy of the suspected tumor may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and determine the subtype of GTN.
Treatment Options for GTN:
The treatment approach for GTN depends on various factors, including the type and stage of the tumor, the patient's desire for future pregnancies, and overall health. The primary treatment options include:
Surgery: In cases of localized GTN, surgery may be performed to remove the tumor and surrounding affected tissues. This is often the preferred option for non-metastatic GTN.
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is the mainstay of treatment for GTN. It involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells and prevent their spread. Chemotherapy is highly effective in treating GTN, even if it has spread to other organs or if the tumor is malignant.
Radiation therapy: In some cases, radiation therapy may be used to target and destroy cancer cells. It is typically used in combination with chemotherapy for advanced or persistent GTN.
Follow-up and monitoring: Regular follow-up visits, including β-hCG testing, are essential to monitor the response to treatment, detect any recurrence, and provide ongoing support and counseling.
Prognosis and Future Pregnancies:
The prognosis for GTN is generally good, especially when detected and treated early. The majority of women with GTN can be cured, and the chances of having a successful future pregnancy are usually excellent. However, close monitoring and appropriate follow-up are crucial to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Conclusion:
Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia is a unique group of tumors that can develop during pregnancy. Early detection and appropriate management are essential for a positive prognosis. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking timely medical attention, women and healthcare professionals can work together to effectively treat GTN and support future pregnancies. With advancements in diagnostic techniques and treatment options, the outlook for individuals affected by GTN continues to improve, offering hope and reassurance to those facing this rare pregnancy-related condition.
0 notes
Text
Molar Twin Deliveries with Coexisting Fetus at Term: Concerning Two Uncomplicated Cases of Gestational Trophoblastic Tumor, From 2015-2021, In Conakry, Guinea
Abstract
The coexistence of a molar pregnancy with a live fetus is a rare entity of difficult diagnosis and treatment. Continuation of the pregnancy until full-term delivery is possible. We report two cases of twin molar deliveries observed empirically from 2015-2021, in the gynecology-obstetrics department of the Donka national hospital and in the maternity ward of the Jean Paul II hospital in Conakry. The discovery was made on ultrasound of the first trimester of pregnancy and macroscopic examination of the placenta. One of the neonates was alive, a healthy female and the other was polymal formed with facial dysmorphism, omphalocele and sexual ambiguity, fresh stillborn. There was no maternal complication towards a gestational trophoblastic tumor (T.T.G) in both cases. Efforts must be made in the prevention of T.T.G. by screening for twin molar pregnancies with healthy fetuses on transvaginal ultrasound in the first trimester, the dosage of HCG in the face of unexplained metrorrhagia, macroscopic observation of the placenta after each delivery and biopsy sampling of any suspicious placenta.
Introduction
Complete moles with a coexisting fetus, evolving at term with spontaneous vaginal delivery, without fetal and maternal complications, are rare. Early diagnosis of this association leads in the majority of cases to termination of pregnancy on the one hand because of the frequency of triploidy and on the other hand because of the maternal risk and the possibility of progression to persistent trophoblastic disease [1]. We report two particular cases of twin molar deliveries at term without fetal complication and without progression to maternal gestational trophoblastic disease in the gynecology-obstetrics department of the Donka national hospital, the Teaching Hospital (C.H.U) of Conakry and in the maternity ward of the Jean Paul II hospital in Conakry.
Patients and Observations
Case 1
This was Mrs. D.F.B, aged 19, primigravida and primiparous, with no particular history, admitted while in labor at the gynecology- obstetrics department of Donka National Hospital, Conakry Teaching Hospital, with two results of ultrasound performed with a transparietal probe during her pregnancy. These results did not mention any notion of hydatidiform mole or associated congenital malformation. The pregnancy would have progressed normally until its term without maternal or fetal complications. It was only after the delivery of a fresh stillborn, polymalformed (with facial dysmorphism, omphalocele and sexual ambiguity) child, that the macroscopic examination of the placenta made it possible to make the diagnosis of presumptive mole twin by the presence of a normal placenta attached to a vesicular mass characteristic of a mole. The biopsy sample allowed the histological diagnosis of a complete mole. The post molar follow- up had been organized without maternal complication 61 days before the closure of the service for renovation, on October 5, 2015.
Case 2
This was Mrs. H.C, seamstress, 30 years old, gravidity of 5 and parity of 5 including a twin birth and a laparotomy for ruptured ectopic pregnancy (GEU), who came on her own for a consultation for incoercible vomiting, physical asthenia on a menorrhea of 3 three months, June 19, 2020. The clinical examination had objectified a uterine height greater than the age of amenorrhea and dating ultrasound had made it possible to observe, intrauterine, a normal eutrophic fetus of 13 weeks – Amenorrhea (W.A) and a poorly vascularized heterogeneous multicystic mass. The beta HCG serum marker level was 16000IU/l. We had concluded a twin molar pregnancy and animated counseling on the interest of a medical termination of pregnancy to avoid the risks associated with serious maternal complications of trophoblastic tumor including choriocarcinoma. The couple, after a delay of two weeks, had opted to continue the pregnancy until its term. A pregnancy monitoring and childbirth preparation plan had been drawn up with the pregnant woman, whose morphological ultrasound at the 23rd W.A of the second trimester carried out on 03/09/2020, which had objectified a mass of 81 x 97 mm, in previa position. The pregnancy had progressed, without fetal and maternal complications, at 40 WA 2 days and ended with a vaginal delivery of a normal female child, alive and weighing 2830 grams. The woman had benefited from active management of the third stage of labor (TSLM) and digital uterine dissection to confirm the uterine cavity. Macroscopic examination of the adnexa had confirmed the presence of two separate placentas, joined together (Figure 1), one of which appeared normal and linked to the umbilical cord and had a histologically confirmed vesicular mass of “complete mole”. The planned post-molar follow-up was regular with progressive regression of the beta HCG level until negativity on the fortieth day of delivery without any clinical particularity on the closing date of January 31, 2021.
Discussion
The diagnosis of the association of a live fetus with a normal karyotype with a hydatidiform mole is often difficult, especially in the absence of revealing clinical signs [2,3]. The diagnostic modalities of molar twin pregnancy associating a complete mole with a healthy fetus were different due to the early ultrasound detection in the first trimester and the observation of the placenta. The lack of diagnosis of the coexisting mole during pregnancy despite the two ultrasound examinations in the first case would be linked to the age of the ultrasound scanners, which are often second-hand, the technique used (endovaginal in the first trimester or transparietal) and of the operator’s experience in the first observation. Early ultrasound detection made it possible to develop a follow-up plan for pregnancy, childbirth and postpartum in the second case. In the event of a twin pregnancy associating a live fetus and a molar pregnancy, the pregnancy can be continued until term if the patient wishes after having been informed of the risks and the most frequently reported complications (hemorrhages, late miscarriage, fetal death in utero and preeclampsia) [3]. Evacuation of the pregnancy is required only in cases of fetal anomalies or deterioration of the maternal condition [4]. The probability of obtaining a live birth varies between 16 and 56% [5] or 16 and 60% [4] deliveries. The continuation of the pregnancy is against payment given the risks of immediate and distant maternal complications. Close monitoring of the mother and fetus can help achieve a favorable outcome [4]. We accepted monitoring despite the maternal risks for one of our two pregnant women. The two pregnancies resulted spontaneously in the normal delivery at term of a healthy living fetus and another which would have succumbed to its multiple malformations per partum. The most feared complication is progression to gestational trophoblastic disease [1]. The diagnosis of postmolar Gestational Trophoblastic Tumor (G.G.T.) can be made according to criteria such as the persistence of h.C.G detectable more than 6 months after uterine evacuation and the histological diagnosis of choriocarcinoma [5]. According to Ikram Boubess et al., who adopted termination of two of these pregnancies, one remotely progressed to an invasive mole [6]. Regular monitoring of h.C.G levels throughout pregnancy and the postpartum period is necessary to detect GTN [7]. For Suksai M et al., a pregnancy with an initial serum h.C.G level of less than 400,000m.U.I/ml is a good candidate for the continuation of the pregnancy and the achievement of fetal viability [8]. The incidence of post-molar GTN is higher in twin pregnancies combining a complete hydatidiform mole (CHM) and a normal fetus than in single CHM [9].
Conclusion
Spontaneous evolution of the association of molar pregnancy with a live-to-term fetus, without immediate fetal and maternal complications, is possible. The most formidable complication, gestational trophoblastic tumor, choriocarcinoma, was not observed during the study period. The prevention of this complication requires the training of providers in endovaginal ultrasound, its systematic practice in the first trimester of pregnancy, ultrasound and biological monitoring of suspected cases during pregnancy, systematic macroscopic examination of the placenta with biopsy of cases suspect for histological confirmation.
0 notes
Text
Fetal Medicine Specialist - A Glimpse Into A Fascinating Field Of Medicine

Pregnancy is also referred to as gestation. It is a period in which a fetus or baby grows inside the uterus of a woman. A missed menstruation cycle or period is the most common indication of a pregnancy. A few women show other indications such as weakness, back pain, and nausea. A maternal fetal medicine specialist or a fetal medicine expert is a doctor who has the expertise in helping and taking care of the women with high-risk pregnancies.
These doctors are also known as obstetricians who have also completed three additional years of training in high-risk pregnancy. Specialists for fetal medicine are also referred to as a perinatologist.
No matter if it is your very 1st pregnancy or 3rd one, hearing your obstetrician, midwife or nurse practitioner say that your pregnancy is high risk can feel concerning. High-risk pregnancy is a team that can be a symbol of a wide range of common conditions. A lot of them are associated with pre-existing conditions you may have had prior to turning out to be pregnant or conditions that you may have developed at the time of being pregnant or during delivery.
A high-risk pregnancy does not essentially signify that your pregnancy will be more challenging or difficult as compared to the pregnancy with low risks. However, at times, it does signify that you will need to have a word with a reputed and experienced maternal fetal medicine doctor in Alain and go through more monitoring as compared to a person with low-risk pregnancy.
Roles and responsibilities of a fetal medicine doctor
One will carry out routine pregnancy, non-invasive tests such as routine screening tests and ultrasound, and invasive tests such as amniocentesis and CVS (chorionic villus sampling)
One will help keep an eye on a pregnant woman who may fall at high risk of developing pre-eclampsia
One will help manage the prevailing conditions of a pregnant mom such as hypertension or diabetes
One will provide routine antenatal care for the ones with high-risk pregnancies
Tests that a pregnant woman has to go through in routine during pregnancy
The very 1st test is to confirm a pregnancy. It is simple urine pregnancy test that can be carried out with the help of a general kit at home, or it can even be performed at a lab. You will also need to go through checking the Beta HCG levels in a laboratory. After this, a woman goes through a transvaginal scan, which is also referred to as a dating scan, to check for the position of the embryo.
The doctor can find out whether the implantation has taken place and check for the fetal heartbeat by means of a transvaginal scan. In general, this scan takes place between four to six weeks of gestation.
The following are the two pregnancy tests:
Screening Tests
Confirmatory Tests
Screening tests help to find out the risk of recognizing a genetic abnormality or chromosomal abnormality with the help of ultrasound tests or blood tests. Screening tests are non-invasive tests, at the same time as confirmatory tests are invasive tests.
Let us begin with screening tests that are carried out as per the gestation period.
Combined 1st Trimester Screening (NT Scan and Double Marker)
In order to measure the biochemical approximation of two parameters – Beta HCG and pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A), combined 1st trimester screening is carried out. This screening is performed along with an ultrasound examination of Nuchal Translucency (NT). Depending on the age and level of PAPP-A, Beta HCG, and NT, the risk is projected with the help of making use of Astria or Lifecycle platforms. It is carried out from 11 - 13.6 weeks of gestation. The sensitivity and specificity for this testing are 85% - 90%.
Quadruple Marker Test
In general, a quadruple marker test is carried out between fifteen to eighteen weeks of gestation. The specialist for maternal fetal medicine normally checks four biomarkers:
Inhibin A,
Estriol (uE3),
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG), and
Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)
Depending on the levels of these biomarkers, the test can help evaluate the risk for Trisomy 13, 18, 21, and NTD (Neural Tube Defects).
Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing
Also known as NIPS (non-invasive prenatal screening) non-invasive prenatal testing helps to screen chromosomal aneuploidies. It is a plain blood test that a pregnant woman can go through from the tenth weeks of gestation. The specificity and sensitivity of NIPS for Trisomy21 are more than 99% at the same time as the specificity and sensitivity for Trisomy 13 and 18 are 93% - 95%. For sex chromosomes, the specificity and sensitivity are 85%.
TIFFA(Targeted Imaging for Fetal Anomalies)
Every pregnant woman goes through a thorough head-to-toe checkup of the fetus around the eighteenth week of gestation. An expert for fetal medicine checks for structural abnormality in a fetus by making use of an ultrasound. TIFFA scan is normally carried out from 18 - 23 weeks of gestation. Every major organ is imagined and inspected in this scan. This scan is also used to find out congenital anomalies such as movement of the fetus, septum defects, clubfoot, and a lot more.
If any of the test mentioned above are high risk, invasive testing such as amniocentesis or CVS (chorionic villus sampling) is recommended to a pregnant woman.
Amniocentesis - It is an ultrasound-guided invasive procedure. A fetal medicine expert initially checks for the position of the fetus by making use of an ultrasound, and about 20 ml of amniotic fluid is gathered with the help of a sterile syringe. Amniocentesis is carried out from sixteen to eighteen weeks of gestation. There is a risk for miscarriage from one to two percent.
CVS (Chorionic Villus Sampling) - It is an ultrasound-guided invasive procedure. An expert for fetal medicine collects a sample either from the abdomen or from the cervix, known as transcervical, known as transabdominal. It is carried out from ten to twelve weeks gestation. Chorionic villus sampling can be performed in order to find out any type of chromosomal aneuploidies or for any single-gene disorders such as Thalassemia. There is a risk for miscarriage from one to two percent. This is for the reason that this is an invasive procedure.
Will all my future pregnancies be high risk?
Having a high-risk pregnancy does not signify that all your future pregnancies will be deemed high risk as well. You may have a fetal complication to take place in one pregnancy that would not be in another, and certain health conditions may change in the fullness of time.
However, if you have had a pregnancy that ended in preterm delivery, you are at greater risk or having preterm labor at the time of your next pregnancy. If this takes place, your obstetric provider will manage the pregnancy with the help of medication, and a specialist for maternal fetal medicine will keep an eye on the cervical length with ultrasound surveillance.
Ultimately, the most important thing to keep in mind regarding having a high-risk pregnancy is that your specialists for maternal fetal medicine and OB/GYN have the experience and knowledge necessitated to keep you and your baby as healthy as possible. If you are also in search of a specialist for maternal fetal medicine near me, look no further than visiting Mothers and Fetuses!
0 notes
Text
Screen marker

#Screen marker free
We also show multiple markers were equally expressed in all cell populations (e.g. We identified 35 surface marker proteins expressed on normal breast epithelial and/or stromal subpopulations that were previously unreported. To determine the differences in expression of a range of uninvestigated cell surface markers between the normal breast cell subpopulations, primary human breast cells were analysed using high-throughput flow cytometry for the expression of 242 cell surface proteins in conjunction with EpCAM/CD49f staining. However, the majority of cell surface maker expression of primary breast cells have not been investigated. Investigation of surface marker expression provides a valuable approach to resolve complex cell populations. Delineating the spectrum of cellular heterogeneity will provide new insights into normal cellular properties within the breast tissue that might become dysregulated in the initial stages of cancer. They’re all calculated together to produce your baby’s potential risk of Down syndrome, trisomy 13, or trisomy 18.Normal human breast tissues are a heterogeneous mix of epithelial and stromal subtypes in different cell states. These measurements are combined with your blood results and age-related risk. Your doctor will also assess the development of the nasal bone, which may be another indicator of a trisomy. It’s performed around the same time as your double marker test.Īt that point in pregnancy - late in the first trimester - your healthcare provider can measure the size of the clear area on the back of your baby’s neck. The NT scan allows your healthcare provider to use sound waves to collect a real-time image of your baby. When performed without the double marker test, the NT scan is less effective at detecting potential abnormalities. The information gathered from both tests is what gives the result of a low-, moderate-, or high-risk of abnormalities. It’s all about personal choice and your own health history, so there’s really no right or wrong answers to your questions.įor the most accurate results, the double marker test (blood test) and NT scan (ultrasound) are used together in the first trimester screening. Would the results change how you’d manage your pregnancy?.Would you want to go for more invasive testing if you receive a result that indicates heightened risk?.Would knowing about possible abnormalities ease or worsen your anxiety?.It doesn’t definitively determine whether your baby has any abnormalities.īefore deciding whether you want a double marker test, you might ask yourself what the results would mean to you in the long run. It’s important to remember that the result only tells you whether there’s an increased risk of trisomies. That said, the screening (and others like the cell-free DNA test) is recommended if you’re over the age of 35 or may have an elevated risk of chromosomal issues, such as if you have a family history of certain conditions. The first trimester screening - double marker test and NT scan - isn’t mandatory. Instead, the blood test is used along with an ultrasound called a nuchal translucency (NT) scan, which examines the clear tissue at the back of your baby’s neck. However, blood levels alone don’t produce your results. Levels of hCG and PAPP-A may be either higher or lower than “normal” in pregnancies with these chromosomal abnormalities. These common chromosomal abnormalities involve an extra copy of chromosome 18 (Edward’s syndrome) or chromosome 13 (Patau’s syndrome). This common trisomy is also referred to as trisomy 21 because there’s an extra copy of chromosome 21. In a typical pregnancy, there will be either 22 pairs of XX chromosomes in female fetuses or 22 pairs of XY chromosomes in male fetuses.Ī trisomy is a chromosomal condition in which there are extra chromosomes, such as the following:
#Screen marker free
Specifically, this test screens for blood levels of both free beta-human chorionic gonadotrophin (beta-hCG) and pregnancy-associated plasma protein A (PAPP-A). Instead, it’s classified as a predictive test, which means its results report the likelihood of chromosomal abnormalities. The double marker test, also known as maternal serum screening, is part of a more comprehensive screening called the first trimester screening.

0 notes
Text
Ectopic Pregnancy: Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
It's important to note that ectopic pregnancies are extremely rare but pose serious health risks when they do occur. When a fertilised egg implants itself somewhere other than the uterus, usually in a tube, the resulting pregnancy is known as an ectopic. Therefore, the embryo will not be able to develop into a baby because the Fallopian tubes are too small.
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when an egg fails to make it to the uterus because of a faulty or damaged Fallopian tube. Initial symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy are similar to those of a normal pregnancy, making early diagnosis challenging. Because an ectopic pregnancy can be fatal to the mother if left untreated, treatment must begin as soon as possible after the diagnosis is made.
What is the causes of an ectopic pregnancy?
In many cases, it is unclear what triggers an ectopic pregnancy. However, there are a number of external factors that play a role in triggering this condition.
Damage to the fallopian tubes caused by scarring or inflammation, which can be the result of a previous medical condition, an infection, or even surgery.
Hormonal factors of various kinds can also play a role.
This condition may also arise from inherited abnormalities.
A woman's reproductive organs, including her Fallopian tube, can be altered in appearance and health by a number of medical conditions.
The problem, though, is that not every situation is the same. See a doctor right away if you experience any of the signs and symptoms of this condition.
Ectopic pregnancy symptoms
It's not uncommon for early signs of an ectopic pregnancy to mirror those of a normal pregnancy. Tenderness in the breasts and feeling sick are symptoms similar to those of a missed period. Additionally, a positive pregnancy test is confirmed. However, symptoms of ectopic pregnancy become more obvious as the embryo grows in a restricted space.
Mild vaginal bleeding and pelvic pain are the first symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy. The woman may also experience stomach cramps or shoulder pain. When and where an embryo implants can cause pain.
The fallopian tube or other reproductive organs may burst if the developing embryo grows too large. Heavier-than-usual blood loss occurs, along with possible dizziness, fainting, and shock. Another sign of an ectopic pregnancy is pain or pressure in the pelvic region, especially the shoulder. If any of these things happen to you, please see a doctor right away.
Lower abdominal pain could be experienced after a ruptured tube. You need to get in touch with your doctor or head to the ER right away; this is a medical emergency.
If you are currently using an intrauterine device (IUD) or have had your tubes tied in the past (either surgically or at the time of a C-section), you should talk to your doctor as soon as possible if you become pregnant. This is a high-risk group for ectopic pregnancies.
How is an ectopic pregnancy diagnosed?
Ectopic pregnancies are typically identified during routine doctor visits. Your doctor will perform several tests to first confirm a pregnancy, and then look for the ectopic pregnancy. The following are some examples of these examinations:
A urine test is performed by urinating into a cup or onto a test strip (typically in the shape of a stick) at home or in the office of your healthcare provider.
A blood test can determine the amount of the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) present in the body. Pregnancy triggers the production of this hormone. Your serum beta-hCG level may also be referred to in this context.
Examination via ultrasonic means: An ultrasound is a type of imaging test that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce an image of the organs and tissues inside of a patient's body. Pregnancies typically involve the use of an ultrasound. This test will help your doctor determine where in your uterus the fertilised egg has taken root.
After a pregnancy has been confirmed and the site of embryonic implantation has been identified, your healthcare provider can begin formulating a treatment strategy. Ectopic pregnancies are life-threatening and require immediate medical attention.
Fallopian tube rupture necessitates immediate medical attention at an emergency room. There would be no time to schedule an appointment if a crisis arose.
Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment
Because a fertilised egg cannot develop normally outside of the uterus, an ectopic pregnancy always ends in failure. Treatment for ectopic pregnancies should begin as soon as possible after diagnosis, as delaying care may increase the risk of complications. Medicine and surgery are both viable options.
Medicine
Methotrexate is the medication that will be prescribed by your doctor. The treatment will soon be over. Once an egg is fertilised, its cells cease dividing and are absorbed by the body. The Fallopian tubes are spared.
Surgical Procedures
In this method, a procedure called laparoscopy is used to end the pregnancy. In this procedure, the doctor makes a small cut near the belly button and pulls out the pregnancy. This is done with the help of a small camera on a surgical tool. This is what most people do. In some cases, this surgery causes scarring in the fallopian tube, so the fallopian tube needs to be removed.
Ectopic Pregnancy and Successful Conception
It's similar to experiencing a miscarriage at a very early stage of pregnancy, and that's always a tough pill to swallow. But the good news is that more than half of all women who have it can go on to have one or more healthy pregnancies in the future, despite the risk of having another one.
Your overall health and the state of your fallopian tubes are the two most important factors in determining your fertility and the likelihood of a healthy pregnancy.
All of your questions and concerns about ectopic pregnancies and infertility can be answered by Dr. Poonam S. Upadhyaya, a renowned Obstetrician, Gynec Endoscopic Surgeon & Infertility Specialist.
0 notes
Text
What Is A Double Marker Test?
A Double Marker Test is a type of test that in mainly given to pregnant women to determine any chromosomal malformation in the foetus. This test also plays a vital role in the detection of any kind of neurological conditions in the foetus, such as down’s syndrome or Edward’s Syndrome. Chromosomal abnormalities in foetus can result in serious developmental deformities and lead to various health problems in the child post birth, but such abnormalities are extremely rare. The Double Marker Test is especially given to pregnant women above 35 years of age and those who have a family history of birth defects and history insulin – dependent type 1 diabetes.
Preparation Of Double Marker Test
The Double Marker Test is a simple blood test and does not require any preparations. However, the doctor must be intimidated about the medications being taken prior to taking the test.
Uses Of Double Marker Test
The varied uses of the Double Marker Test are as follows;
It helps in assessing whether the unborn baby is at risk for any mental disorder
It is used primarily for the detection of Down syndrome
Double Marker Test also helps to detect Trisomy 18, that results in mental retardation and severe birth defects
It also helps in the detection of Trisomy 21.T, which cause mental disorders, heart disorders and other health conditions affecting vital organs
Double Marker Test Procedure
A Double Marker Test is done with an ultra – sound test and is done with a blood sample. The Double Marker Test looks for two markers namely Free Beta hCG (human chorionic gonadotrophin) and PAPP – A (Pregnancy associated plasma protein A).
Free Beta hCG is a glycoprotein hormone produced by the placenta during pregnancy. It’s high level is indicative to a higher risk of Trisomy 18 and Down’s syndrome.
PAPP – A is a vital plasma protein. A low level of plasma protein is indicative of the risk of down syndrome.
The test readings are signified in terms of screen positive, high risk and screen negative.
Double Marker Test Normal Value
The Double Marker Test normal value of hCG in pregnant women is 25700-288000 mIU/ml for all age groups, while the Double Market test normal value for PAPP – A is 1 MoM (multiple of median) for the female gender across all age groups.
Double Marker Test Cost
The Double Marker Test Cost varies due to various factors like city, quality and availability of the test, since this test is available in only select cities. The average Double Market Test Cost usually averages on the higher side and is quite expensive. The Double Market Test Cost in Bangalore averages anywhere between 2,500 to 3,500 rupees. But, these prices are only indicative and actual prices could vary.
Sunrise Diagnostic Center
Address: Ground Floor, Shop No. 2, Business Hub Building Opp. Mirch Masala Hotel, Near Vandevi Mandir Karve Road, Karvenagar, Kothrud, Pune, Maharashtra 411038
Mobile Number: 9028801188, 9028566644, 9028566611
Timing: Monday to Saturday: 7:00 am to 9:00 pm
Sundays: 7:00 am to 2:00 pm
Find us here: Get Direction
0 notes
Note
Hi Aly, thanks for allowing anons to ask you questions. I love the show but I’m too lazy to create an account. About bout last episode, I think Park is pregnant. The results given to Ressler showed cancer because the lab thought they were testing urines from a man. Pregnancy tests are based on the level of Beta-hCG. High urine levels mean pregnancy for a woman and testicular cancer for a man. There’s still a possibility it’s cancer for Park.
Hi there. As soon as the "pee swap" became known, everyone I was watching the show with assumed we'd hear that Park was pregnant so it wouldn't surprise me if they still find a way to make that happen. Either way, sick - pregnant - they can't come up with a better storyline for her? Doesn't inspire much faith that they have gotten any better at handling their female characters.
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
Beta Levels
4w1d - 839 mIU/mL
4w3d - 1790 mIU/mL
4w5d - 4260 mIU/mL
So happy to be getting such great numbers! They said my first ultrasound will be week 6 in early October.
Also, can you believe it's nearly October already? Can't wait! 🍁🎃
5 notes
·
View notes
Text

Beta hcg levels throughout pregnancy
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
rating movies by how accurately they portray blood tests
THE INVISIBLE MAN 2020 0/10
Wow where to even begin with this one! Blood test results are quite a big plot point of the movie (they are how we find out cecelia is pregnant and has also been drugged against her knowledge) but gets them very WRONG😡😡
You can detect both pregnancy and diazepam overdose with a blood test this is true. BUT in both these cases you have to test for something specific. Firstly, pregnancy; in order to identify pregnancy you have to test for beta hcg (human chorionic gonadotropin but that’s actually not important). Hcg levels would only be tested if pregnancy is already suspected - which is not the case for cecelia like at all. Cecelia TO HER KNOWLEDGE has been using birth control and has not been sexually active for at least 2 weeks so even if the doctor requesting her tests suspected pregnancy (which they wouldn’t. If you’ve ever been a woman and gone to the doctor about anything you will know that they will blame everything on anaemia. I’ve been in cecelias exact situation recently - unexplained fainting episode that I followed up with a blood test. All they really look for is iron levels, thyroid function, liver and kidney function too just as a nonspecific monitor or to identify low sodium) then it would have been ruled out by her medical history. Unfortunately, you cannot test everyone for everything - it would be too expensive and time consuming. A patient deemed to be of “child bearing potential” (aka having a uterus and being under 60 years old) who is of uncertain pregnancy status might be tested for serum hcg if they’re about to go for emergency surgery or treatment but otherwise clinicians are always going to use urine tests instead because they’re easier and quicker to obtain. What I’m saying is : you cannot identify early stage pregnancy if you’re not already LOOKING for it, and in cecelia’s case they would not be looking for it.
Secondly the diazepam: again, to identify a diazepam overdose, you have to specifically test for it, and being as cecelia DOESNT KNOW she has been drugged, there would be no reason to test for it. If the doctor asked if she’s on any medication, her answer would be no and that would be the end of that line of questioning. Idrk if diazepam overdose would cause sufficiently deranged ec’s and liver function to necessitate further investigation but even if it did and they requested a repeat blood sample from cecelia (repeats to make sure the result is genuine is usually the first step in investigating an unexpected result), then her results would be back to normal by then as all the sources ive found have said that diazepam only lasts 48 hours in the blood stream.
I guess ultimately it comes down to the fact that our healthcare systems aren’t really set up to deal with patients who have been unknowingly drugged and are unknowingly pregnant. Rlly good film tho
1 note
·
View note