#Atheroma
Text
Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Atheromas and Cardiovascular Events
There has been a lot of talk about pollution these days, a phenomenon that is also bad for the heart. But how? An Italian study, the first to have identified the presence of microplastics directly in human arteries, highlights a previously underestimated aspect.
After finding them in humans in several organs and tissues, including the placenta, breast milk, liver and lungs, including heart…
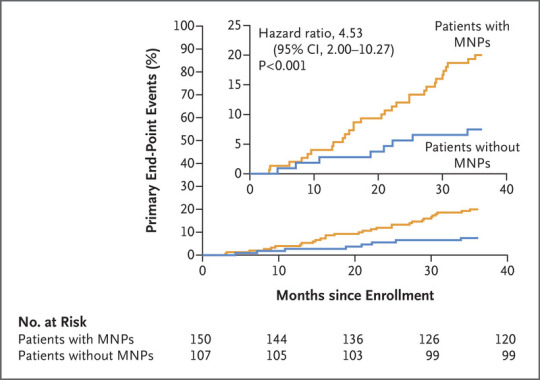
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
New England Journal Of Medicine Microplastics Article Shows Higher Risk Of Heart Attacks, Stroke And Death
The New England Journal Of Medicine, published this article, that was reprinted in Nature. Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Atheromas and Cardiovascular Events In my view, the roll out of the C19 bioweapons need to be included in the discussion. We know that self assembly nanotechnology, made from plastic materials are in the C19 shots, as the Moderna Patent clearly shows. You can see…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Link
Epidermoid cyst, epidermal inclusion cyst, epidermoid cyst treatment, epidermoid cyst pictures, epidermal inclusion cyst pictures, epidermoid cyst removal, epidermoid cyst treatment at home, epidermoid cyst infected.
0 notes
Text
Infinity Care Hospital Director Dr. Abhishek Vikram Singh, explains about Artery Disease
Peripheral artery disease (PAD)
We can also call it peripheral vascular disease. In this condition, fat, along with cholesterol, calcium, etc., starts accumulating inside the arteries in any part of the body. This problem is mainly found in the arteries of the hands and feet. Due to the accumulation of plaque (atheroma) from this asterisk, there is less blood flow throughout the body. PAD usually affects the legs and arms. While awake, it causes pain in the legs, and in severe cases it can lead to depression and even leg amputation.
Dr. Abhishek Vikram Singh, Director of Infinity Care Hospital, Varanasi, says that this disease also depends on age. The risk is higher as you get older. It can happen to both men and women and can run in families. Smoking, diabetes, obesity, and high blood pressure increase the risk of getting PAD.
0 notes
Text
Coronary Heart Disease
youtube
Coronary heart disease (CHD) is when your coronary arteries become narrowed by a build-up of fatty material within their walls. These arteries supply your heart muscle with oxygen-rich blood. CHD is sometimes called ischaemic heart disease.
What is coronary heart disease?
Over time, a fatty material called atheroma can build up inside your coronary arteries. This process is called atherosclerosis. Eventually, your arteries may become so narrow that they can’t get enough oxygen rich blood to your heart.
If a piece of atheroma breaks off, it can cause a blood clot form. This clot can block your coronary arteries and cut off the supply of blood and oxygen to your heart muscle. This is known as a heart attack.
What are the symptoms of coronary heart disease?
Coronary heart disease (CHD) develops slowly over time and the symptoms can be different for everyone. Some people don’t know they have CHD before they have a heart attack.
Angina is the term used to describe the most common symptoms of CHD. These include:
Chest pain
Shortness of breath
Pain travelling through the body
Feeling faint
Nausea
What increases the risk of coronary heart disease?
High blood pressure
High cholesterol
Diabetes
Smoking
Being overweight
Not doing enough physical activity
Risk factors you can’t control include:
Family history
Age
Ethnic background
How is coronary heart disease diagnosed?
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Echocardiogram
Chest x-ray
Coronary angiogram
What is the treatment for coronary heart disease?
Medication - to help control your symptoms
Coronary angioplasty
Heart bypass surgery
Harvard Referencing:
BRITISHHEARTFOUNDATION. (N/A) Coronary heart disease. [Online] Available from: https://www.bhf.org.uk/informationsupport/conditions/coronary-heart-disease [Accessed: 10th November 2023]
www.youtube.com. (2015). Coronary heart disease, clogged arteries and atherosclerosis. [online] Available at: https://youtu.be/y6QJceOAVY0?si=DoFnYIXzLSjPTdyt [Accessed 12 Nov. 2023]
1 note
·
View note
Text
Introduction to HbA1c
Hemoglobin (Hb) that has been chemically bonded to sugar is known as glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c). When present in the bloodstream, the majority of monosaccharides, including glucose, galactose, and fructose, spontaneously and non-enzymatically bind with hemoglobin.
Galactose and fructose are more likely than glucose to do so (13% and 21%, respectively), which is why glucose serves as the main metabolic fuel in humans.
When the sugar-hemoglobin link forms, it means there is too much sugar in the blood, which is frequently a sign of high-concentration diabetes (HbA1c >6.4%). Due to its simplicity of detection, A1C is of great interest. Glycation is the process by which sugars bind to hemoglobin, and the reference system is based on HbA1c, which is defined as a component of beta-N-1-deoxy fructose hemoglobin.
HbA1c is primarily evaluated to identify the three-month average blood sugar level, but it can also be used to diagnose diabetes mellitus and monitor a patient's glycemic control if they already have the disease.
The test is restricted to a three-month average since a red blood cell typically lives for four months. Since different red blood cells have different lifespans, the test is only used with a three-month limit.
A normal amount of glycated hemoglobin is produced by normal glucose levels. The fraction of glycated hemoglobin rises predictably as the average plasma glucose level rises.
Higher levels of glycated hemoglobin in diabetes have been linked to cardiovascular disease, nephropathy, neuropathy, and other complications.
The name HbA1c comes from the cation exchange chromatography separation of hemoglobin type A. HbA0 was given to the first fraction to separate, which was probably thought to be pure hemoglobin A. HbA1a, HbA1b, and HbA1c were given to the subsequent fractions in the order in which they were eluted.
Huisman and Meyering used a chromatographic column to isolate hemoglobin A1c from other types of hemoglobin for the first time in 1958.
In 1968, Bookchin and Gallop classified it as a glycoprotein for the first time. Samuel Rahbar and colleagues initially noted the rise in diabetes in 1969. In 1975, Bunn and his colleagues described the processes that led to its creation.
Anthony Cerami, Ronald Koenig, and colleagues introduced the use of hemoglobin A1c for assessing the level of control of glucose metabolism in diabetic patients in 1976.
Why is it important for managing diabetes?
Cell membranes of red blood cells change as a result of glycated hemoglobin's rise in highly reactive free radicals. As a result, blood viscosity and blood cell aggregation rise, impairing blood flow.
Glycated hemoglobin can also harm cells by causing inflammation, which leads to the development of atherosclerotic plaque (atheroma).
The amount of glucose that binds to hemoglobin in red blood cells increases with the duration of blood hyperglycemia, as does the amount of glycated hemoglobin.
A hemoglobin molecule becomes glycated and stays that way forever. Hence, a buildup of glycated hemoglobin inside the red cell represents the typical level of glucose the cell has been exposed to throughout its life cycle.
Glycated hemoglobin testing evaluates treatment efficacy by keeping track of long-term serum glucose control.
The A1c test measures the weighted average of blood glucose levels throughout the red blood cells' lifetime 117 days for men and 106 days for women. As a result, the level of A1c is significantly influenced more by the glucose levels on days close to the test than by those on days further away.
Data from clinical practice showed a significant improvement in HbA1c levels 20 days following the initiation or intensification of treatment for diabetes.
What do HbA1c test results mean?
Depending on the analytical method, the subject's age, and biological variance between individuals, laboratory results may vary.
Those with
diabetes mellitus or other conditions that cause consistently high blood sugar have higher levels of HbA1c.
Treatment objectives for diabetes patients might vary, but many of them include a target range of HbA1c levels. An HbA1c level that is close to or within the reference range is indicative of a diabetic with good glucose management.
HbA1c values below 6.5% are advised by the International Diabetes Federation and the American College of Endocrinology, however, the American Diabetes Association advises HbA1c values below 7.0 % for the majority of patients.
Patients with an HbA1c greater than 6.5 % had an increased risk of death, according to a retrospective study of type 2 diabetes patients aged 50 and older.
Consistently high blood sugar levels and, consequently, HbA1c)raise the risk of long-term vascular consequences of diabetes, such as gastroparesis, gangrene, coronary disease, heart attack, stroke, heart failure, kidney failure, blindness, and erectile dysfunction.
Moreover, the risk of immediate postoperative problems including slow wound healing is increased by poor blood glucose control.
Those with conditions that cause premature red blood cell death, such as glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, sickle cell disease, or any other ailment, can have lower-than-expected levels of HbA1c.
Red blood cells will be quickly replaced by newly produced ones after blood donation. HbA1c will overestimate the real average levels because these additional RBCs will have only been present for a brief length of time.
In several situations, such as those involving blood loss, surgery, blood transfusions, anemia, high erythrocyte turnover, chronic renal or liver disease, the administration of large doses of vitamin C, or erythropoietin therapy, the results may not be accurate.
The typical reference range found in healthy young people is between 4.9 and 5.2%.
How are HbA1c levels interpreted?
The monitoring of blood sugar control in individuals with more high levels, known as diabetes mellitus, as well as those who may be prediabetic, is advised by glycated hemoglobin testing.
It offers significantly more illuminating data on glycemic behavior for a single blood sample than a fasting blood sugar reading. However, while choosing a course of treatment, fasting blood sugar testing is essential.
Similar to other guidelines, the American Diabetes Association recommends that the glycated hemoglobin test be carried out quarterly in patients with diabetes whose therapy has changed or who are not meeting glycemic goals and at least twice a year in patients with diabetes who are meeting treatment goals and who have stable glycemic control.
When a dietary or medical treatment adjustment has been made within the last six weeks, a glycated hemoglobin measurement is not acceptable.
The HbA1c test is not appropriate for individuals with recent blood loss, hemolytic anemia, or genetic variations in the hemoglobin molecule (hemoglobinopathy), such as sickle-cell disease and other diseases.
.
0 notes
Text
Introduction to HbA1c
Hemoglobin (Hb) that has been chemically bonded to sugar is known as glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c). When present in the bloodstream, the majority of monosaccharides, including glucose, galactose, and fructose, spontaneously and non-enzymatically bind with hemoglobin.
Galactose and fructose are more likely than glucose to do so (13% and 21%, respectively), which is why glucose serves as the main metabolic fuel in humans.
When the sugar-hemoglobin link forms, it means there is too much sugar in the blood, which is frequently a sign of high-concentration diabetes (HbA1c >6.4%). Due to its simplicity of detection, A1C is of great interest. Glycation is the process by which sugars bind to hemoglobin, and the reference system is based on HbA1c, which is defined as a component of beta-N-1-deoxy fructose hemoglobin.
HbA1c is primarily evaluated to identify the three-month average blood sugar level, but it can also be used to diagnose diabetes mellitus and monitor a patient's glycemic control if they already have the disease.
The test is restricted to a three-month average since a red blood cell typically lives for four months. Since different red blood cells have different lifespans, the test is only used with a three-month limit.
A normal amount of glycated hemoglobin is produced by normal glucose levels. The fraction of glycated hemoglobin rises predictably as the average plasma glucose level rises.
Higher levels of glycated hemoglobin in diabetes have been linked to cardiovascular disease, nephropathy, neuropathy, and other complications.
The name HbA1c comes from the cation exchange chromatography separation of hemoglobin type A. HbA0 was given to the first fraction to separate, which was probably thought to be pure hemoglobin A. HbA1a, HbA1b, and HbA1c were given to the subsequent fractions in the order in which they were eluted.
Huisman and Meyering used a chromatographic column to isolate hemoglobin A1c from other types of hemoglobin for the first time in 1958.
In 1968, Bookchin and Gallop classified it as a glycoprotein for the first time. Samuel Rahbar and colleagues initially noted the rise in diabetes in 1969. In 1975, Bunn and his colleagues described the processes that led to its creation.
Anthony Cerami, Ronald Koenig, and colleagues introduced the use of hemoglobin A1c for assessing the level of control of glucose metabolism in diabetic patients in 1976.
Why is it important for managing diabetes?
Cell membranes of red blood cells change as a result of glycated hemoglobin's rise in highly reactive free radicals. As a result, blood viscosity and blood cell aggregation rise, impairing blood flow.
Glycated hemoglobin can also harm cells by causing inflammation, which leads to the development of atherosclerotic plaque (atheroma).
The amount of glucose that binds to hemoglobin in red blood cells increases with the duration of blood hyperglycemia, as does the amount of glycated hemoglobin.
A hemoglobin molecule becomes glycated and stays that way forever. Hence, a buildup of glycated hemoglobin inside the red cell represents the typical level of glucose the cell has been exposed to throughout its life cycle.
Glycated hemoglobin testing evaluates treatment efficacy by keeping track of long-term serum glucose control.
The A1c test measures the weighted average of blood glucose levels throughout the red blood cells' lifetime 117 days for men and 106 days for women. As a result, the level of A1c is significantly influenced more by the glucose levels on days close to the test than by those on days further away.
Data from clinical practice showed a significant improvement in HbA1c levels 20 days following the initiation or intensification of treatment for diabetes.
What do HbA1c test results mean?
Depending on the analytical method, the subject's age, and biological variance between individuals, laboratory results may vary.
Those with
diabetes mellitus or other conditions that cause consistently high blood sugar have higher levels of HbA1c.
Treatment objectives for diabetes patients might vary, but many of them include a target range of HbA1c levels. An HbA1c level that is close to or within the reference range is indicative of a diabetic with good glucose management.
HbA1c values below 6.5% are advised by the International Diabetes Federation and the American College of Endocrinology, however, the American Diabetes Association advises HbA1c values below 7.0 % for the majority of patients.
Patients with an HbA1c greater than 6.5 % had an increased risk of death, according to a retrospective study of type 2 diabetes patients aged 50 and older.
Consistently high blood sugar levels and, consequently, HbA1c)raise the risk of long-term vascular consequences of diabetes, such as gastroparesis, gangrene, coronary disease, heart attack, stroke, heart failure, kidney failure, blindness, and erectile dysfunction.
Moreover, the risk of immediate postoperative problems including slow wound healing is increased by poor blood glucose control.
Those with conditions that cause premature red blood cell death, such as glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, sickle cell disease, or any other ailment, can have lower-than-expected levels of HbA1c.
Red blood cells will be quickly replaced by newly produced ones after blood donation. HbA1c will overestimate the real average levels because these additional RBCs will have only been present for a brief length of time.
In several situations, such as those involving blood loss, surgery, blood transfusions, anemia, high erythrocyte turnover, chronic renal or liver disease, the administration of large doses of vitamin C, or erythropoietin therapy, the results may not be accurate.
The typical reference range found in healthy young people is between 4.9 and 5.2%.
How are HbA1c levels interpreted?
The monitoring of blood sugar control in individuals with more high levels, known as diabetes mellitus, as well as those who may be prediabetic, is advised by glycated hemoglobin testing.
It offers significantly more illuminating data on glycemic behavior for a single blood sample than a fasting blood sugar reading. However, while choosing a course of treatment, fasting blood sugar testing is essential.
Similar to other guidelines, the American Diabetes Association recommends that the glycated hemoglobin test be carried out quarterly in patients with diabetes whose therapy has changed or who are not meeting glycemic goals and at least twice a year in patients with diabetes who are meeting treatment goals and who have stable glycemic control.
When a dietary or medical treatment adjustment has been made within the last six weeks, a glycated hemoglobin measurement is not acceptable.
The HbA1c test is not appropriate for individuals with recent blood loss, hemolytic anemia, or genetic variations in the hemoglobin molecule (hemoglobinopathy), such as sickle-cell disease and other diseases.
.
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
WA 0812-3039-4909, Jual Obat Kista Ganglion Di Tasikmalaya Jawa Barat : British Propolis
KLIK https://wa.me/6281230394909, Jual Obat Kista Ganglion Di Tasikmalaya Jawa Barat : British Propolis, Jual Obat Kista Bartholin Di Tasikmalaya Jawa Barat : British Propolis, Jual Obat Kista Ovarium Di Tasikmalaya Jawa Barat : British Propolis, Jual Obat Kista Ganglion Tasikmalaya Jawa Barat : British Propolis, Jual Obat Kista Atheroma Tasikmalaya Jawa Barat : British Propolis
youtube
BRITISH PROPOLIS Adalah Salah Satu Propolis Terbaik Di Dunia Yang Berasal Dari Bridlington, East Yorkshire, Inggris.
Selama Ini Kita Mengenal Jaguar, Rolls Royce, Range Rover, Mini Cooper, Burberry, Ted Baker, Mark & Spencer, Virgin, Shell, British Petroleum, Dan BBC - Sebagai Global Brand Asal Inggris Yang Identik Dengan Mutu. Demikian Pula British Propolis Yang MENJANJIKAN MUTU Dan Berbagai Khasiat.

Salah Satu KHASIAT yang Banyak Dirasakan Oleh Para Penderita yang Sudah Mengkonsumsi BRITISH PROPOLIS adalah Untuk Pengobatan Penyakit KISTA.
KISTA Adalah Benjolan Di Bawah Kulit Yang Berisi Cairan, Udara, Nanah, Atau Zat Padat Seperti Rambut. Benjolan Ini Dapat Tumbuh Di Bagian Tubuh Mana Pun Dan Umumnya Tidak Bersifat Kanker Atau Tumor Ganas.

Meski Umumnya Tumbuh Di Bawah Kulit, Kista Juga Dapat Tumbuh Di Organ Dalam Tubuh, Seperti Indung Telur (Ovarium). Kista Biasanya Membesar Dengan Lambat Dan Biasanya Tidak Menimbulkan Nyeri. Namun, Nyeri Dapat Timbul Jika Kista Membesar Dan Menekan Organ, Pecah, Terinfeksi, Atau Tumbuh Di Daerah Yang Sensitif.
Penyebab Kista - Tergantung Pada Jenisnya, Kista Dapat Terbentuk Akibat :
Infeksi
Penyumbatan Pada Saluran Di Dalam Tubuh
Peradangan Yang Terjadi Dalam Jangka Panjang (Kronis)
Penyakit Bawaan Lahir
BRITISH PROPOLIS - Cairan Dari Lebah Alami, Yang Mengandung Semua Yang Dibutuhkan Oleh Tubuh, Kecuali Vitamin K. Kandungan Bio-Flavonoid BP 4 - 5 x Lebih Tinggi Dari Propolis Biasa, Karena Berasal Dari Hutan Dengan 4 Musim.
Cara Kerja BP : Meregenerasi Sel-Sel Dalam Tubuh, Alhamdulillah Dengan Izin NYA Telah Terbukti Menyembuhkan Berbagai Penyakit Salah Satunya Penyakit Kista. Kami Sarankan Jangan Dulu Di Operasi Semasih Memungkinkan.
Mengapa Harga BRITISH PROPOLIS Diatas Propolis Rata-Rata ?
Khasiatnya Terasa Dalam 21 Hari Bahkan Kurang
Kandungan Flavonoid 3x Lebih Tinggi Dari Propolis Lain
Mengikuti Standar Inggris dan Satu-Satunya Propolis Asal Inggris Yang Masuk di Indonesia.
Sertifikasi BPOM, MUI dan Non Alkohol
Produk Serta Kemasan Dus Sulit Dipalsukan
Bukan Produk MLM
Pilihan Para Tokoh Dan Artis
Cara Konsumsi :
Teteskan 5 Tetes Propolis Dicampur Dengan 1/2 Gelas Air Hangat - Minum 1x Sehari Saat Sehat Atau 3x Sehari Jika Sedang Kurang Sehat.
Kemasan : Botol Kaca (Seal) Dalam Dus Tersegel Sticker Hologram Dan Wrapping.
Komposisi : Propolis 100% | POM TR : 183610771| Netto 6 ml
NOTE :
Harga Resmi British Propolis Yang Asli Ini Sudah Dinotariskan Alias BERKEKUATAN HUKUM.
Jika Kamu Memukan Ada Yg Menjual Dibawah Harga Tidak Wajar, Kemungkinan Besar Bukan Mitra/Agen Resmi Ippho Santosa Dan Diragukan Keaslian Produknya.
HATI-HATI !! Di Luar Sana Banyak Sekali Propolis Oplosan Yang Dijual Dengan Harga Murah.
Minat Jadi Agen/Reseller Dan Mendapatkan Full Bimbingan Dari Ippho Santosa Sampai Menghasilkan ? Silahkan KUNJUNGI : http://bisnispraktis.id/paktri.bp
SILAHKAN Hubungi : WA – 0812.3039.4909 ( Distributor BRITISH PROPOLIS BLITAR )
#obatkista#obatkistaherbal#obatkistaalami#obatpenyakitkista#obatmiom#obatmioma#obatpenyakitmiom#Youtube
0 notes
Text
Surgery here is not needing.
On my 84 y.old am disability on 2 nd group, on 2009 behind right ear formed atheroma on 5 mm, and am read her calls a cyst. Big are surgeries cure, small are removing. I would agree and for laser, and doctor prescribed me visited for consultation to ENT , and he is prescribed me visited surdologist, that she is shared ,that my atheroma is not surgery needing. Visited oncologist, but he said,that indications for surgery are not having. Am having lots of diseases and am not share are theirs, but on 2009 my ear head bad, does atheroma affect on this, and hot to cure her.
Dear Antonina, answers surgeries Ljubsky , a hard to put diagnosis in absentia is hard, and without atheroma checking , but if this is true atheroma, thus radial cure her is removing.
Atheroma is cyst for sebaceous gland, which are producing fat , as greasing for skin,when fat stopping normally removing outside,she is accumulating inside, forming these atheromas.Atheroma is ability inflaming and infecting, or staying without infecting. And thus atheroma staying into skin, thus not affecting on the hear, but she can too gaping, and not affecting on hear, but this problem finding deeply a scull box. And if atheroma is small, and staying for the long time and not worry you, thus not touching you, but surgery here ambulatory with local anaesthesia. Surgeries instruments are ray for laser, elector current, scalpel, ultrasound affecting .A how to remove atheroma is a not principally ,that importance her need to remove a full as with capsule of sebaceous gland, thus if not, she gives relapse.
from Valga s health news,gardening,and cooking ,and beauty . https://ift.tt/jlomhG9
via https://ift.tt/zSjwZx7
0 notes
Text
Best Interventional Cardiologist In Hyderabad | Dr. Sudheer
Get the Best Cardiology Treatments from Top Cardiologist in Hyderabad - Dr.Sudheer
Dr.Sudheer is one the best Interventional Cardiologists in Hyderabad. With over 15 years of experience in this field, Dr.Sudheer ensures that all of his patients get the treatment they need from the most effective and experienced professionals at his Cardiology clinic in Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
What Is Coronary Artery Disease?
Coronary artery disease is a serious condition where you have reduced blood flow to your heart, which could be due to a narrowing of any one or more of your coronary arteries by fatty substances (atheromas). If not treated, it could lead to heart attack, chest pain that radiates to your arm, neck and jaw on one side and shortness of breath. But with early detection you can prevent or delay its onset. You can get yourself checked at Dr. Sudheer's practice as he is Best Cardiologist in Hyderabad.
Early Detection & Risk Factors
The best way to detect cardiac disease is through a heart health check up, which should be done yearly or every six months. There are many risk factors associated with heart disease, including: family history of atrial fibrillation and stroke, high blood pressure, obesity, diabetes, smoking cigarettes and a sedentary lifestyle. You can find out if you are at risk for cardiac disease by taking the free heart test near me!
Symptoms of CAD
The symptoms of CAD are caused by the buildup of plaque that can restrict blood flow and oxygen to your heart muscle. If you have these symptoms, it is important to get a full evaluation by a cardiologist. Symptoms can include chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, fatigue, and heart palpitations. It is important that you talk to your doctor right away if you experience any of these symptoms so they can determine if it is related to CAD or another condition that requires different treatment options.

Diagnosis Of CAD
Cardiovascular disease is among the most widespread causes of death worldwide. The two main types of cardiovascular diseases are coronary artery disease and heart failure, which are caused by blocked arteries and weakened or damaged heart muscle respectively. CAD, or coronary artery disease, is a narrowing of the large blood vessels that supply blood to your heart muscle, which can lead to chest pain (angina) as well as a potential heart attack. Aortic Regurgitation Valve Replacement is a procedure that replaces an aortic valve with another type of valve.
Treatment Options For Coronary Artery Disease
If you are at risk of a heart attack, here's what you need to do:
1. Visit your doctor and request an EKG (electrocardiogram) test to check for signs of a heart attack
2. Ask your doctor about medication that might help lower your risk of heart disease and/or recurrence of a heart attack if you have already had one, like statins or beta blockers
3. Discuss with your doctor how often they recommend you come back for follow up visits
4. Be sure to take any medications your doctor prescribes as directed
5. Know the warning signs for a second heart attack, including chest pain or pressure, shortness of breath, anxiety or other symptoms
Right Facility Makes A Difference In Recovery
If you're looking for a world-class facility, then look no further than Dr. Sudheer's clinic. He's one of the best cardiologists in Hyderabad with over 15 years of experience and he knows how to offer high-quality care that includes treatments for Bicuspid Aortic Valve Disease Treatment, Aortic Regurgitation Medical Treatment, Heart Imaging and Cardiac Screening Test, Tests to Check Heart Health, Test For Heart Health and more. With so many facilities to choose from near me it can be hard to figure out which one is best for you but don't worry because I'm here to help!
I've been researching all the different facilities in my area and narrowed it down to three choices: Dr.
What To Do After A Heart Attack
If you have had a heart attack or are experiencing chest pain, call emergency services immediately and tell them what is going on. The sooner you receive medical attention, the better your chances of surviving a heart attack. Once you reach the hospital, doctors will perform tests to determine what is going on with your heart and whether or not surgery is needed to repair any damage caused by the heart attack.
Doctors typically use two types of testing for this process: angiograms and cardiac catheterization. An angiogram can be done at an outpatient facility, while a cardiac catheterization typically requires an overnight stay at a hospital or cardiac care centre.
Why Choose Dr. Sudheer As My Heart Doctor?
Dr. Sudheer is a Famous Cardiologist in Hyderabad with over 15 years of experience in this field. He has a huge list of satisfied patients and offers various treatments for your heart health needs, such as coronary artery bypass surgery, peripheral angioplasty, atherectomy and more.
#Best Cardiologist in Hyderabad#Top Cardiologist in Hyderabad#Best Cardiac Surgeon in Hyderabad#Best Cardiologist Doctor in Hyderabad#Famous Cardiologist in Hyderabad#Best Heart Specialist in Hyderabad#Best Interventional Cardiologist in Hyderabad#Heart Check Up#Heart Check Up Test#Cardiac Testing Near Me#Cardio Health Check Up#Heart Health Check Up#Full Heart Check Up#Heart Health Check#Heart Check Up Near Me#Test For Heart Health#Tests to Check Heart Health#Heart Imaging and Cardiac Screening Test#Heart Surgeon Specialist#Free Heart Test Near Me#Aortic Regurgitation Medical Treatment#Bicuspid Aortic Valve Disease Treatment#Aortic Regurgitation Valve Replacement#Supraventricular Tachycardia Treatment#Best Cardiology Hospital in Hyderabad#Coronary Artery Disease Treatment
0 notes
Link
Epidermoid cyst, epidermal inclusion cyst, epidermal inclusion cyst pictures, epidermoid cyst pictures, epidermoid cyst treatment, epidermoid cyst removal, epidermoid cyst treatment at home, is epidermal inclusion cyst dangerous.
0 notes
Text
Black Tea Extracts Market Scope Future Growth Comprehensive Analysis Report 2032
Global black tea extracts demand is anticipated to be valued at US$ 132.2 Million in 2022, forecast to grow at a CAGR of 5.9% to be valued at US$ 210.2 Million from 2022 to 2032. Growth is attributed to the rise in awareness regarding the side effects of synthetic flavors.
Black tea is the most popular tea in the world. Black tea extract is rich in of Vitamin C, zinc, iron, magnesium, copper, manganese, potassium, fluoride and calcium. Black tea extract have more anti-oxidants as compared to green tea, and are anti-allergic, anti-viral and anti-spasmodic. Black tea extract is derived from powdered form powdered leaves of black tea. These leaves come from a plant called Camellia sinesis. Camellia sinensis is the plant from which green tea, oolong, white tea and other forms of tea is derived. Black tea is processed in a different way than green tea.
Green tea comes from ripe, fresh leaves, while black tea is derived from the oxidization of the leaves from the sun gives them their black color, the oxidization process. Black tea extracts consist of various health benefits, and it has also less astringent and had a mellower flavor than other teas. Black tea leaves are rolled and crushed, then allowed to ferment fully. This imparts the dark color and rich characteristic flavor of black tea that ranges from delicate to robust.
The Benefits of black tea are equal to green tea in terms of antioxidant capacities because black tea consists of the aflavins as green tea consist of catechins in the same antioxidant potency.
Black Tea Extracts Market Segmentation
Black Tea Extracts market can be segmented on the basis of form, product type and applications. Based on forms, Black Tea Extracts is segmented into liquid, encapsulated and powder. Most of the powder extracts are spray dried. Based on application, black tea extracts are segmented into functional food, beverages, cosmetics, beauty supplements, dietary supplement & herbal/natural medicine. Black tea extract helps in adjusting blood lipid extraordinarily, blood serum cholesterol, and fights against atheroma hardening, improves blood consistency.
On the basis of product type it is segmented as hot water soluble and cold water soluble extracts.
Black tea may not get have all the benefits that green tea does, but they do come from the same plant and have many of the same properties. Each also has unique properties as a result of processing, which is why it is best when both are used in combination. Green tea can provide powerful antioxidants that black tea cannot, and black tea can fight inflammation with even more efficacy than green tea.
Black Tea Extracts Market Trends and Market Drivers:
Black Tea Extracts market is expected to witness sustained growth over the forecast period. Growth of Black Tea Extracts market is driven by its wide applications in the cosmetics and food additives industry. Other factors attributable to the high growth include rising health conscious consumers, increasing purchasing power, rise in per capita health expenditure. Presence of natural ingredients in Black Tea Extracts coupled with growing awareness regarding its health benefits contributes significantly to its volume growth over the forecast period.
Regional Outlook of Black Tea Extracts Market:
On the basis of geographical market segment, it is segmented into seven different regions: North America, Latin America, and Eastern Europe, Western Europe, and Asia-Pacific region, Japan and Middle East and Africa. In regional segments, North America is projected to hold a relatively high share in terms of market value. Asia Pacific and Europe are expected to witness relatively high growth in the black tea extracts market owing to the rising health consciousness and increasing disposable income in the region.
Black Tea Extracts Market Key Players:
Some of the key players in the Black Tea Extracts market include Finlays, Synthite, Martin Bauer Group, Autocrat LLC, AVT Natural, Phyto Life Sciences P. Ltd, Amax NutraSource, Inc, Teawolf, Cymbio Pharma Pvt. Ltd, Tea&Coffee – Haldin and Blueberry Agro Products Pvt Ltd.
Key Segments Profiled in the Black Tea Extracts Industry Survey
Black Tea Extracts Market by Form:
Liquid Black Tea Extracts
Encapsulated Black Tea Extracts
Powder Black Tea Extracts
Black Tea Extracts Market by Application:
Black Tea Extracts as Functional Food
Black Tea Extracts as Beverages
Black Tea Extracts as Cosmetics
Black Tea Extracts as Beauty Supplements
Black Tea Extracts as Dietary Supplements
Black Tea Extracts as Herbal/Natural Medicine
Black Tea Extracts Market by Product Type:
Hot Water Soluble Black Tea Extracts
Cold Water Soluble Black Tea Extracts
Read More: https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/black-tea-extracts-market
0 notes
Text
The Budding Scavenger-Juvenile Xanthogranuloma
Abstract
Juvenile xanthogranuloma is an uncommon, proliferative, non-Langerhans histiocytic cell disorder arising from dendrocytes. Juvenile xanthogranuloma is commonly discerned in childhood and demonstrates a male predominance. Of obscure aetiology, juvenile xanthogranuloma appears as a consequence of a hitherto uncharted infectious or physical stimulus which engenders a granulomatous histiocytic response. Typically, juvenile xanthogranuloma represents as an asymptomatic, solitary or multiple, firm, yellow, orange or brown papule or nodule. Cutaneous lesions demonstrate an intense infiltration of histiocytic cells within the superficial dermis. Histiocytic cells are intermingled with mature lymphocytes, plasma cells and eosinophils. Also, foam cells, foreign body giant cells and Touton giant cells emerge within mature lesions. Immune reactivity to CD68, vimentin, alpha-1 antichymotrypsin, lysozyme, Factor XIIIa, macrophage inflammatory protein (Ki-MIP) and anti-CD4 is observed. Juvenile xanthogranuloma mandates a segregation from benign and malignant conditions such as Langerhans cell histiocytosis, reticulohistiocytoma, embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma, atheroma, dermatofibroma, xanthoma or lipoma, Conservative management is recommended, and surgical eradication of cutaneous lesion is curative in lesions situated in accessible sites.
Read more about this article: https://juniperpublishers.com/oajs/OAJS.MS.ID.555846.php
Read more Juniper Publishers Google Scholar articles: https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=en&user=sLK6eBEAAAAJ&citation_for_view=sLK6eBEAAAAJ:J_g5lzvAfSwC
#Juvenile xanthogranuloma#Renal parenchyma#Neurofibromatosis#Surgical eradication#Surgical excision.
0 notes
Text
In the alkaline water ionizer machine filtration framework particle charges are utilized to cleanse water. This apparatus is utilized by individuals from one side of the planet to the other. It builds the pH of the drinking water with the utilization of electrolysis and isolates the approaching water stream into Alkaline and acidic parts.
A best ionized alkaline water machine is a little machine that can be kept on the counter of your kitchen. One can likewise introduce these under their sink. It is fueled that drinking alkaline water is great for health and it has astounding advantages.
Advantages Of Ionizer
As referenced before there are a lot of advantages of the Alkaline water ionizer. These advantages are the purposes for its prevalence and use. Alkaline water is supposed to be really great for human health. Following are a portion of the advantages that we get when we use water decontamination frameworks for our homes.
Helps Fight Against Cancer
One of the greatest advantages of alkaline water ionizer machines in India is that they make an effect and prevent disease. Oxygen extremists are the explanations for some substantial tumors that are produced as side-effects of various metabolic frameworks in our body. The extremists are otherwise called unsteady molecules that really hurt the body cells and makes disturbance that makes the phones malignant.
However it is very perilous, the free oxygen revolutionaries battle against the antioxidants that are produced by the Alkaline water ionizer in OH-or Hydroxide particles structure. The Hydroxide particles work similarly to antioxidants in the body like Vitamin C and A. These particles join with the oxygen revolutionaries and structure an oxygen molecule that our body can utilize.
The facts confirm that it's anything but an immediate solution for the disease yet helps in decreasing the gamble of getting malignant growth. In any case, it is a valid justification for you to pick this and put resources into an Alkaline water ionizer as malignant growth is something that nobody needs to have.
Great For Heart Health
The disease isn't simply a solitary issue that free extremists make. With broad exploration, it is been observed that there is likewise a connection between these extremists and cardiovascular health. This is likewise connected with the issues like atherosclerosis. This ends up happening when the inward vessel is totally harmed and gets obstructed because of cholesterol.
This is only the start yet eventually it will be the supporter of heart illnesses, stroke, and heart assault also. This occurs as an enormous number of atheroma develops in the veins and restricted the bloodstream in the body. Atheroma parts likewise separate and it gets caught in the vessel that switches the opens and you get a heart assault.
You can restrict the possibility of experiencing these issues by deciding to have alkaline ionized water. It neutralizes the revolutionaries and furthermore keeps you from the vessel cell assaults to launch the development of atheroma. There are positive consequences of ionized water and it is compelling in diminishing the expected development of atheroma that making it less hazardous when shaped.
Keeps You Hydrated
The Alkaline water ionizer assists in creating watering that keeps you hydrated consistently. This may be a piece odd for you to start with as individuals would feel that faucet water is likewise great for hydration. Nonetheless, it is been found that the course of ionization helps cause molecule bunches in water that self-destructs in little gatherings. Yet, in this cycle the groups are enormous and it contains five H2O molecules rather than typical bunches that contain ten to fifteen.
Really great For Skin
Having alkaline water or cleaning up with this water is really great for your skin also. It will keep your skin perfect and new. You wouldn't see scarcely discernible differences and kinks. It consolidates with the free revolutionaries alongside the Hydroxide particles. Kinks and barely recognizable differences are caused predominantly by these extremists and harm your skin. This can be neutralized when you have alkaline water.
Along these lines get water purifiers that refine water utilizing particles. Have ionized water and get astounding advantages.
#alkaline water ionizer machine#best ionized alkaline water machine#Alkaline water ionizer#alkaline water ionizer machines in India
0 notes
Text
Aerobic Exercise and S-Klotho Effects on Cardiovascular Disease Patients: A Review
Authored by TJ Exford*

Abstract
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the most common type of heart disease progression once major coronary arteries are injured or diseased. When the primary blood arteries which supply the myocardium with blood, oxygen and nutrients is narrowed arterial disease progresses. Plaque buildup in the walls of the arteries from hypercholesterolemia (high blood cholesterol), dyslipidemia, and vascular inflammation contribute to atherosclerosis formation, a primary agent for CAD. Arterial stiffens occurs as a result of the biological aging process and arteriosclerosis. Endothelial dysfunction is characterized by reduced vascular nitric oxide levels. Nitric oxide vascular reductions leads to irregularities in blood artery function. These functional irregularities result from atherosclerosis, causing vasoconstriction of small arteries. Vasoconstriction of smaller arteries is related to hypertension and could possibly influence, left ventricle diastolic dysfunction. There are two forms of klotho; membrane and secreted, membrane klotho acts as co-receptor for fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-23, while secreted klotho (s-klotho) regulates nitric oxide production in the endothelium minimizing endothelial dysfunction. Studies examining the effect of aerobic exercise on blood circulating s-Klotho have demonstrated a fitness dependent response. S-Klotho values have been shown to be significantly higher in trained vs untrained individuals. Aerobic training is an appropriate model for mechanistically probing the role of physical activity on s-Klotho expression. Factors associated with endothelial function improvement; aerobic fitness levels and aerobic training increased s-klotho levels alleviate and attenuate endothelial dysfunction. Aerobic exercise and klotho gene expression is shown to reduce cardiovascular events in patients with prior CAD thereby decreasing mortality risk.
Keywords:Atherosclerosis; Nitric oxide; Reactive oxygen species (ROS); Endothelial dysfunction; Klotho; Coronary artery disease; Oxidative stress
Introduction
Cardiovascular diseases are prevalent in the general population and are the leading cause of death worldwide responsible for 46.2% of noncommunicable deaths [1,2]. Coronary artery disease (CAD) broadly comprises CAD myocardial infarction, vascular stiffening, and left ventricular hypertrophy [3]. CAD regularly advances over long periods and is the most common type of heart disease that progresses once major coronary arteries are injured or diseased. Arterial diseases progress once the main blood arteries that supply the myocardium and the different organs with blood, oxygen, and nutrients is narrowed. Inflammation and cholesterol that creates plaque in the arteries are the cause for arterial diseases [4]. Plaque buildup in the walls of the arteries from hypercholesterolemia, fatty deposits, other substances and inflammatory mechanisms combine dyslipidemia to atheroma development, are usually the main causes for CAD [5]. Once plaque is present, decrement in blood flow to the body’s organs occur which in turn, decrease blood flow causing reduction in oxygen delivery to the tissues and thus, ischemia [6]. The additional arterial tension and subsequent damage due to hypertension cause the coronary arteries to become narrowed from accumulation of fat, cholesterol and other molecules that collectively is the slow process of chronic inflammatory disease [7].
Atherogenesis is the process of forming plaques in the intima layer of arteries. Plaque’s compositions include mainly fat, cholesterol, and calcium [8]. With time, arterial diameter narrows decreasing arterial blood flow. This progression is termed atherosclerosis. Thus, atherogenesis is a multifaceted interface of risk factors with cells of the artery wall, the blood, and molecular communications [9]. Initial atherosclerosis is the consequence of the endothelial cells in the intima layer capturing monocytes along with endothelial permeability aiding the low-density lipoprotein elements to drift into the arterial wall. Myocytes develop and become macrophages that consume the low-density lipoprotein units with apolipoprotein apoB molecule to form foam cells. Oxidative radicals oxidize the apoB molecule, assemble the units mainly designated to be phagocytized by macrophages [10].
Damage progression is the second stage where the migration of the smooth muscle cells from the arterial wall intima layer into the tunica intima. The next stage is the formation of thrombosis. The rupture of the thin cap fibroatheroma that covers the plaque plus the coagulation components of blood interact with the thrombogenic plaque produces thrombi [11]. In addition, risk factors such as, high cholesterol values, hypertension, diabetes, overweight and oxidative radicals affect the early phase of atherogenesis, namely endothelial dysfunction [12,13]. In brief, atherosclerosis develops progressively with inflammation and lipid accumulation. Atherogenesis is the course of creating plaques in the intima coating of arteries. The buildup of lowdensity lipoprotein and the inflammation of the arterial wall are the first phase of atherosclerosis. Atherogenesis results from lipid peroxidation‐derived aldehydes oxidized to carboxylic acids. The pro-inflammatory oxidized phospholipids, resulting of the oxidation of low-density lipoprotein and phospholipids including arachidonic acid, formed in the lipoxygenase and myeloperoxidase pathways, these molecules attract and trigger inflammatory cells, such as monocytes, T-cells, and macrophages. Matrix degradation brings about atherosclerotic as a result of macrophages activation through; cytokines, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and proteolytic enzymes. Oxidative stress is also considered to be a key factor in mechanisms of changes in cell function [14], such as the aging process [15].
Klotho is an anti-aging gene with implications in biological and anatomical processes, mainly in cardiovascular disease [16]. Early human aging involving endothelial dysfunction, vascular calcification and progressive atherosclerosis were seen in mice lacking Klotho [17]. In addition, reduced Klotho levels is observed in coronary artery disease patients, physically inactive individuals and in aging. S-Klotho has a role in the action of fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23), which directly binds to FGF receptors (FGFRs). This, high affinity complex for FGF23 mediates the intracellular effects of metabolism of phosphorus as the required co-receptor [18]. Other mechanisms which s-klotho is involved, include reserve oxidative stress, inflection of inflammation or attenuation of vascular stiffening [19,20]. Therefore, Klotho has been suggested as a master regulator of cardiovascular disease [21].
Aerobic exercise and Klotho gene expression could reduce the risk of cardiovascular events in patients with prior coronary artery disease thus, aerobic exercise may decrease the risk of mortality, incidence and severity of cardiac events [12,15, 22-24]. In addition, in patients with CAD exercise training improves endotheliumdependent vasodilatation both in epicardial coronary vessels and in resistance vessels [24) Patients with significant coronary artery disease present lower soluble concentrations of α-Klotho (s-Klotho) [25], as well as reduced levels of Klotho gene expression in the vascular wall [26]. This protein is related to the attenuation of vascular calcification as well as prevention of cardiac hypertrophy [27]. Reduced serum s-Klotho concentrations and decreased vascular Klotho gene expression were associated with the presence as well as the severity of coronary artery disease independently of other established cardiovascular risk factors [14,23]. S-Klotho is a pleiotropic protein related to longevity, which acts as a co-receptor of the fibroblast growth factor 23 and has been proposed as a key regulator of the development of cardiovascular disease. In the few published clinical studies, an association between low levels of s-Klotho and the occurrence and severity of cardiovascular disease have been reported, as well as a reduction of cardiovascular risk when levels were high [28].
Arterial Endothelial Dysfunction
Arterial endothelium assists vasomotor tone and function by producing and discharging nitric oxide [29]. Arterial endothelium is characterized by cells in the inner layer of all blood arteries and lymphatic system. The inner layer of arteries and veins is the tunica Intima. In arteries, this layer is composed of an elastic membrane lining and smooth endothelium which is a unusual type of epithelial tissue that is covered by elastic tissues. The small thickness of endothelium at the capillaries level permits molecules movements actively and passively as well as ions among blood and lymph by means of the tissues [30]. Following the endothelial layer, elastic fibers thickness varies, which is in a straight line associated to its ability to change vessels’ blood volume, pressure and flow velocity [31]. Arterial endothelium contributes to the regulation of blood coagulation, platelet and leukocyte action, vessel’s tone and inflammatory responses [32]. The endothelium plays an important role in blood vessel functions by producing various signaling molecules [33]. It is a vital regulator of blood flow and blood pressure in the circulatory system. The endothelium is the internal coating of cells that has several critical functions, it controls the correct vessels’ radius namely; constriction or dilation, thus changing rapidly blood’s amount delivered to the various organs. The endothelium also protects the tissues from various toxic substances by: a. coagulation or formation of a fibrin clot, which is a mechanism that blood changes from a liquid to a gel, it includes activation, bond, and accumulation of platelets along with deposition and maturation of fibrin, b. controls the fluid, c. regulates electrolytes’ levels and, d. exchange of numerous substances between the blood and the tissues and Vic versa, and, e. regulates inflammation damages in the tissues. Consequently, Endothelium function is critical for the regular function of the arteries, tissues and organs [34].
Existence of hypertension and dyslipidemia are directly associated to endothelial dysfunction resulting inflammatory and arterial damage [35]. The coronary artery response to acetylcholine rest on the capacity of the endothelium and the endothelial nitric oxide pathway [36]. Arteriosclerosis affects the major elastic and muscular arteries in the extracellular intermediate of arteries elasticity resulting in arterial stiffens [37]. Arterial stiffens outcomes after a deteriorating course affecting mostly the extracellular medium of elastic arteries. It expresses the arterial wall viscoelastic capacity which affects arterial smooth muscle and therefore, the regulation of blood flow, blood pressure, arterial pulse, permeability, and inflammation [38,39]. Changes in extracellular medium proteins and mechanical properties of the arterial wall associated to vessel stiffening can trigger other mechanisms implicated in the progress of atherosclerosis. With time, arterial stiffness increases progressively, exposing the individuals to a greater pressure variation related to increased risk of stroke and renal impairment [40]. Changes in arterial pulsatile lead to an increase in the slow frictional force of blood flow counter to the vessel wall [41]. However, increased wall shear stress reduces nitric oxide production by the endothelial that in turn, increases rate of atheromasias (artery inflammatory) development [42,43]. During aerobic exercise training, systolic blood pressure increases thus, pressure in the artery wall rise resulting in the activation of the autoregulation mechanism and thus, vasodilation, that in turn, improves blood flow [44] and thus, has the potential to minimize these pathological process’ and to reduce the amount of cardiovascular complications [35].
Dysregulation of the nitric oxide normal smooth muscle contraction properties response is usually characterized by endothelial dysfunction, following advanced atherosclerosis and increase oxidative stress [45]. that induces endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis progression by reducing nitric oxide availability [46]. Endothelial dysfunction is a significant moderator in the progress of atherosclerosis and exist long ahead the creation of atherosclerotic plaques [47]. Endothelial dysfunction is mostly triggered by decreased production or action of relaxing mediators. At this point, it is clear that reduced nitric oxide levels cause endothelial dysfunction in blood arterial walls which, leads to vasoconstriction of the artery [48]. and thus, increase blood pressure to high values (hypertension). In addition, it also, activates platelets leading to blood clotting, that increase the stimulation for artery walls inflammation, consequently, arterial walls penetrability to destructive lipoprotein, oxidized free radical species and various toxins is increased.
s-Klotho
α-Klotho protein is found extensively in human tissues of arteries, epithelium, endocrine system, and nerve tissues [49]. Molecular characteristic of Klotho is explained in detail by Martín- Nunez and colleagues, and therefore it is advised to the reader to look into this article [50]. Klotho appears in two forms; membrane and secreted, the membrane klotho acts as an necessitate coreceptor for fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-23, while secreted klotho regulates nitric oxide production in the endothelium. The extracellular domain of Klotho can be cleaved and cut in the circulation as s-Klotho where it may function as a blood vesselprotective hormone possibly by enhancing endothelial function [51,52] or, direct inhibition of arterial calcification [53]. Circulating s-Klotho is produced in the kidney predominantly expressed in renal distal tubular epithelial cells with implications in biological and anatomical processes, mainly in the cardiovascular arterial’s disease [16]. Early human aging that contains endothelial dysfunction, arterial calcification and progressive atherosclerosis were seen in mice lacking Klotho [17]. A reduction in Klotho levels is observed also in aged and physically inactive coronary artery disease patients [26]. These declines are demonstrated by a diminished ability for skeletal muscle to respond to physiological stimuli such as muscle loading or acute injury. Certainly, older adults often exhibit an age-related reduction in the number and size of muscle fibers known as sarcopenia [48]. Klotho appears to apply different functions in distinct cell types as nitric oxidereliant means, Klotho is a putative anti-aging gene, vital cofactor for the linkage of fibroblast growth factor (FGF 23) to its receptor, and thus, acting as a main controller of phosphate balance [18,54]. Studies on mouse genetics have revealed in vivo functions of Klotho (FGF signaling) [55,56].
The Klotho proteins and its connected enzyme β-Klotho apply various influences on the biological regulation of ion transport, energy metabolism, calcium and phosphate mainly by FGF-23 [57] In addition, s-Klotho functions as an obligate co-receptor with fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1) for fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23), a phosphaturic hormone essential for maintaining mineral homeostasis [58] Serum FGF-23 values are related to atherosclerotic problem, endothelial dysfunction, arterial stiffness and vascular calcification [59,60] Therefore, Klotho has been suggested as a master regulator of CAD [20,61]. Klotho inhibited the phosphatidyl nitric oxidesitol 3-kinase (PI3K)-AKT signaling pathway phosphorylation of fork head box protein O3a by improving its connection to the manganese superoxide dismutase supporter. Klotho increased mitochondrial manganese superoxide dismutase, mRNA and protein expression. In addition, Klotho reduce tacrolimus-induced oxidative stress and thus, converse mitochondrial dysfunction, consequently, decrease ROS production [56] Increased cellular levels of ROS result in damage to proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, membranes and organelles, which can lead to activation of cell death processes such as apoptosis. Mice with Klotho-deficiency demonstrate an association with accelerated and enhanced development of vasculopathy [62] and early aging. However, increase Klotho expression increase genetic expression that solve the Klotho-deficient phenotype at baseline [16] and thus, improve mice’s standing against oxidant stress [63] In humans, serum levels of s-Klotho decrease after 40 years of age [25,64] this may be observed in sedentary individuals and patients with several aging-related diseases such as cardiovascular disease, cancer, hypertension, and kidney disease [65,66].
The clinical relations of s-Klotho and cardiovascular diseases were described earlier [67,68] suggesting that, s-Klotho values in the circulating blood in CAD patients are significantly lower compared to healthy matched peers. In addition, in community-dwelling adults higher plasma Klotho concentrations are independently associated with a lower likelihood of having CAD, heart failure, stroke, or peripheral arterial disease. Recently study by Saghiv, et al. [68] demonstrated that circulating s-Klotho levels are significantly higher while IGF-1 are significantly lower in aerobically trained CAD patients compared to untrained CAD patients and inactive healthy counter partners. Genetic variation studies have demonstrated that Klotho gene polymorphisms might be associated with longevity on one hand [16] and CAD on the other hand [69-71]. Previously Arking, et al. [72] suggested that, the functional of KL-VS allele, characterized by six SNPs is related to hypertension and stroke, and thus, it is a self-regulating risk factor for CAD [73].
Atherosclerosis reduction and cell protection occur by some antioxidant’s such as s-Klotho humoral. In addition, arterial stiffening may predispose the intima to atherosclerosis due to injury sustained from increased pulsatile pressure. In mice, klotho through humoral paths guards the arteries by nitric oxide produced in the endothelium [74]. The discovery of Klotho in human vessels tissue [75,76] increased the understanding about the role of the co-expression of two related FGF23 receptors, FGFR-1 and FGFR-3 [76]. Expression of Klotho protein seems to be restricted to arterial intima layer [78]. Yet an argument exists due to inconsistent data regarding Klotho presence in arterial tissue [79]. The connection of Klotho to endothelial dysfunction lays in the attenuation effect on endothelial dysfunction by ways of nitric oxide. Shimada, et al. [80] suggested, that lack of nitric oxide decrease angiogenesis in kl/kl mice and reduced endothelium-derived nitric oxide release, due to increased oxidative stress associated with aerobic exercise and aging. Klotho resists oxidative stress by the expression of manganese superoxide dismutase (Mn-SOD) through activation of FoxO forkhead also known as forkhead in rhabdomyosarcoma transcript factor [81] at the cellular and organismal level in mammals. FoxO forkhead is a human protein encoded by the FOXO3 gene [82] FOXO3 belongs to the O subclass of the forkhead family of transcription factors which are characterized by a distinct fork head DNA-binding domain [83]. Klotho protein stimulates the FoxO forkhead transcription factors that are negatively regulated by insulin/IGF-1 signaling, so bringing about an expression of manganese superoxide dismutase. With this content, Klotho increases nitric oxide formation through c-AMP-PKA-dependent pathway in human umbilical vascular endothelial cells, [19] and decreases (HO)2-prompt apoptosis and cellular senescence [83].
In addition, Klotho reduces oxidative stress production by limiting angiotensin II production [85] While the complete actions of angiotensin II signaling on NADPH oxidase are still under examination, angiotensin II, is an endogens peptide hormone, that has a major role in maintaining homeostasis in the cardiovascular system, as well as an effective stimulator of NADPH oxidase [86]. Recently Six, et al. [87] observed that attenuation of FGF23 or phosphate-induced vasoconstriction mediated by Klotho is eliminated by adding nitro-L-arginine, a competitive inhibitor of nitric oxide. Moreover, they observed that exposure of human umbilical vein endothelial cells to Klotho increased nitric oxide production and induced nitric oxide phosphorylation and the inducible isoform, nitric oxide, involved in immune response expression. Interestingly, Klotho was able to increase (HO)2 production in cultured human vascular smooth muscle cells, which suggests a more complex effect of this protein on the regulation of vascular tone through mediation of a ROS/ nitric oxide balance [87].
Aerobic Exercise
Physical inactivity decreases maximal oxygen uptake, muscle mass (sarcopenia), alters structural and intrinsic muscle cells and changes in energy availability which, decrease further with aging [88, 89]. Cardiac patients in a stage of myocardial deficiency usually lose their muscle mass and muscle strength, due to angiotensin II that directly affects the skeletal muscle and increases protein degradation [90]. Skeletal muscle atrophy is categorized by a reduction in protein contented, fiber width, force generation, and tiredness struggle ability [88]. In addition to angiotensin II, factor such as ROSs cause muscle protein degradation under different situations [88]. The existence of muscle atrophy points out of the rise in ROS production and the inability of antioxidant production to balance it resulting, in a reduced protein synthesis [91]. In addition, genetic factors regardless of lifestyle increase rate of biological aging process thereby, severely limiting elderly’s function, life quality and longevity [89,92]. However, regardless of age, gender or basal work capacity, aerobic exercise training is recommended as a tool to decrease rate of work capacity decline, typically arises as an individual age, being physically inactive or suffers from any cardiovascular disease [93].
Aerobic exercise was suggested as a nonpharmacological intervention in patients with cardiovascular disease in the main prevention and therapy of cardiovascular diseases [94,95]. It is recommended that exercise intensities be above the anaerobic threshold to vigorous exercise [96]. Yet, exercise mechanisms that slow down atherogenic progress have been completely understood. following long-lasting aerobic exercise, significant changes in the vascular are nitric oxide including decreased levels of C-reactive and inflammatory cytokines [97]. Aerobic exercise has the potential to minimize these pathological process’ and to reduce the amount of cardiovascular complications [35]. Effects of chronic aerobic exercise training in CAD and progression of coronary atherosclerosis patients is an increase in myocardial oxygen supply thus, reducing ischemic events. Some indications suggest that long-lasting aerobic exercise may avert loss in endothelium dependent vasodilation and increase levels in sedentary middle to older healthy men. This may represent an important mechanism by which regular aerobic exercise lowers the risk of cardiovascular disease in this population [98]. Aerobic training offers an epigenetic tendency which has benefits in cardiopulmonary and muscular functions, therefore, an individual must interact with environmental factors related to longevity, by exercising at moderate to high level of workloads [99]. In addition, long-lasting aerobic training lessens the decline in maximal oxygen uptake related to physical inactivity and aging [100].
The basic mechanism by which workout triggers genes (epigenetic) includes a stimulus signal to the DNA, then transcript through messenger RNA, and finally conversion into protein [101]. Previously it has been reported that oxidizing free radical species are generated during moderate and high aerobic bouts [102]. ROS production tops cellular defenses, under these conditions, in disease genetic and epigenetic regulation changes gene expression [103]. Skeletal muscle generates superoxide and nitric oxide during aerobic exercise in intensities above the anaerobic threshold [104]. ROS is essential for skeletal muscle force generation, however, ROS in high values may reduce muscle contraction properties and thus, bring about an early exhaustion [105]. There are plentiful indications that exercise can be operative in averting and suspending the result of age on muscle well-being and effectiveness. In addition, chronic exercise training intensifys nitric oxide production, that improves myocardial function due to the increase in coronary blood flow. In addition, nitric oxide has inhibitory effects on platelet and leukocytes well as induces proliferation of arterial smooth fibers [105]. Previous study demonstrate that long-lasting aerobic exercise training reduces cardiovascular risk factors [106]. The nitric oxide synthesis rate seems to be parallel related to increase in amino acid arginine availability [107]. The antithrombotic effect of Aerobic exercise decreases serum levels and activity of inflammatory factors, such as interleukin-6, C-reactive protein, and tumor necrosis factor-α, pointing out about the antithrombotic effect of aerobic exercise [108]. Following aerobic bout, blood pressure decreases to lesser levels than those recorded at rest, identified as post exercise hypotension [109]. This autoregulation mechanism response of aerobic exercise coupled with the nitric oxide vasodilator, affects positively the endothelium function and thus blood flow by decreasing total peripheral resistance [110, 111].
Although the association between s-Klotho and aerobic exercise training is not clear, recently, the α-Klotho gene is circulating in blood as s-Klotho have been related to the aerobic exercise [112,113]. Yet, exercise appears to take a major part on the secreted form of the α-Klotho gene in humans. In addition, α-Klotho gene is associated also with genes: β-Klotho gene and γ-Klotho gene, however, the last two mentioned genes do not have any role during exercise [114]. The increase in s-Klotho following aerobic exercise training may be a response to ROS that increase in muscle cells as a result of aerobic training. s-Klotho reduces apoptosis through the nitric oxide production and thus, suppress oxidative stress [115].
Interplay between Exercise, S-Klotho and Endothelial Dysfunction
Data suggests that endothelium plays a major part in the regulation of arterial stiffness by the action on smooth muscle tone affected by vasoactive intermediaries and, the effect of nitric oxide production on endothelin arterial stiffness [116]. Nitrogen nitric oxide is a soluble gas molecule with the chemical formula for NO. It is continually synthesized by the endothelium: L-arginine in endothelial cells is the precursor for nitric oxide synthesize by calcium-calmodulin-dependent enzyme nitric oxide synthase [117]. Nitric oxide acts as an endothelium-derived relaxing factor [118]. released from endothelial cells and acts as an inhibitor of ROS production, by decrease in L-arginine endogens asymmetric dimethyl-L-arginine ratio connected with endothelial dysfunction [119]. Nitric oxide stimulates phospholipase A2 and inhibitors of lysolecithin acyltransferase inducing smooth muscle tone relaxation by inhibiting low density lipoprotein oxidation [120]. Klotho has been linked to the prevention of muscle atrophy and cardiovascular disease in aged individuals [14]. Circulating s-Klotho acts as a humoral factor, involved in the endothelium production and regulation of nitric oxide. In turn, nitric oxide protects endothelial penetrability, smooth muscles’ contraction by calcium homeostasis and inhibits insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling [121].
Similar to Klotho’s anti-aging impacts have also been attributed to aerobic exercise [114, 122]. In recent years, there are enough studies regarding the effect of aerobic exercise on blood circulating s-Klotho [23,67] Reimers, et al. [123] demonstrated that the response of s-klotho depends on aerobic fitness level. In addition, levels of s-Klotho were significantly higher in trained individuals compared to untrained once [124]. suggesting that long lasting aerobic training may be an appropriate model for mechanistically probing the role of physical activity on s-Klotho expression. Populations aged 0 - 91 years, screened previously by ELISA revealed that the level of human s-Klotho declines with aging [125]. Previously in older mice, it has been demonstrated that low blood serum s-Klotho levels are related to reduced skeletal muscle strength and aerobic capacity [126]. On the other hand, trained elderly with aerobic capacity have longer life expectancies [127] and higher serum s-Klotho values compared to inactive elderly [112].
Moderate aerobic training attenuates aging-induced pathological cardiac hypertrophy at least partially by restoring s-Klotho levels, reduce oxidative stress, and lessening in the phosphorylation of ERK1/2, P38 and fibrosis [128]. The relationships between aerobic exercise, s-Klotho and endothelial dysfunction can be in brief described as follow: previously it has been suggested that s-Klotho and long-lasting aerobic exercise training are factors that may promote and upgrade young adults’ physical performance capacities [129]. Aerobic bout increases s-Klotho levels which in turn, increase FGF23 which promotes nitric oxide synthesis bringing about a, reduction in oxidative stress and ROS in skeletal muscle and accordingly, increase mitochondrial vitality and thus [130] attenuate restore endothelial dysfunction.
Conclusion
Recent developments point out on the effect of aerobic exercise training program as nitric oxide nonpharmacological mean to support in the treatment, prevention, and therapy of patients with cardiovascular diseases. The present review, suggests that aerobically active CAD patients, increase their Klotho gene expression, which may be a primary involvement to slow down endothelial dysfunction course and cardiovascular-related diseases. In addition, moderate aerobic exercise increase Klotho gene expression in muscle cells and decrease ROD production. Future research should examine the relationship between aerobic exercise training and circulating s-Klotho, on cardiovascular arterial stiffness and endothelial dysfunction.
Read More…FullText
For more about Iris Publishers Covid-19 please click on
https://irispublishers.com/COVID-19.php
For more articles in Online Journal of Cardiology Research & Reports (OJCRR) Please click on https://irispublishers.com/ojcrr/
#Iris Publishers#Iris Publishers LLC#Congestive hepatopathy#Cardiac Cirrhosis#Pulmonary hypertension
0 notes