#Abnormal RDW levels
Text
Explore a comprehensive guide to understanding RDW in blood tests, also known as red cell distribution width. Learn about its significance in diagnosing anemia and other blood disorders, as well as its correlation with hematocrit levels. Discover the normal range of RDW and what abnormal levels may indicate for your health. Gain insights into interpreting your blood test results and the importance of monitoring hematological parameters for overall well-being. https://www.manipaltrutest.com/blogs/understanding-rdw-in-blood-test-a-comprehensive-guide
#RDW in blood test#Red cell distribution width#Hematological parameters#Normal RDW range#Abnormal RDW levels
0 notes
Note
I had abnormal red blood cell counts on tests like CBC panels where the RDW and such would come back funny for literally YEARS until a doctor bothered to listen to me and run my feratin at which point it was a 3 and I needed infusion therapy... So yeah definitely make sure y'all get your iron checked especially if RBC counts are funny on other tests!
yes!!!! literally!! if you're able to access the numerical results for your blood tests yourself I would recommend it because then *you* can look at what's going on there. Having looked at my CBC results from the past few years, my MCHC (concentration of hemoglobin (an iron rich protein) in red blood cells) is either in the low range or below the range reccomended but it's never been flagged up. And I only even got most of my CBCs because they're required for my testosterone prescription.
Get your iron and ferritin levels checked!!
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
Exploring Your Blood Composition: The Complete Blood Picture (CBP)
The Complete Blood Picture (CBP), also referred to as a Complete Blood Count (CBC), serves as a fundamental diagnostic tool in modern medicine. By analyzing various components of the blood, this test offers invaluable insights into an individual's health status, aiding in the diagnosis and management of numerous medical conditions. Let's delve into the intricacies of the CBP, exploring its significance, components, and clinical applications.
Significance of the Complete Blood Picture:
The Complete Blood Picture (CBP) test, holds immense significance in healthcare due to its ability to provide comprehensive information about the composition and functionality of blood. This test aids healthcare professionals in assessing overall health, diagnosing disorders, and monitoring treatment responses. By evaluating key parameters within the blood, the CBP offers valuable clues regarding the presence of infection, inflammation, anemia, clotting disorders, and various systemic illnesses.
Components of the Complete Blood Picture:
The CBP encompasses a range of blood components, each offering unique insights into an individual's physiological state:
1. Red Blood Cells (RBCs):
Red blood cells, also known as erythrocytes, are responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to tissues throughout the body. The CBP measures parameters such as RBC count, hemoglobin concentration, hematocrit level, and mean corpuscular volume (MCV), providing crucial information about oxygen-carrying capacity and the presence of anemia.
2. White Blood Cells (WBCs):
White blood cells, or leukocytes, play a vital role in the body's immune response, defending against infections and foreign invaders. The CBP assesses WBC count and categorizes different types of white blood cells, such as neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils, aiding in the detection of infections, inflammatory conditions, and immune system disorders.
3. Platelets:
Platelets, also called thrombocytes, are essential for blood clotting and wound healing. The CBP measures platelet count, helping identify potential bleeding disorders, thrombocytopenia (low platelet count), or thrombocytosis (high platelet count).
4. Other Parameters:
In addition to RBCs, WBCs, and platelets, the CBP may include assessments of mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC), mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH), and red cell distribution width (RDW), providing further insights into the characteristics and morphology of blood cells.
Clinical Applications of the Complete Blood Picture:
The CBP finds extensive applications across various medical specialties and clinical scenarios:
1. Diagnosis of Anemia:
By evaluating RBC indices and hemoglobin levels, the CBP helps diagnose different types of anemia, including iron deficiency anemia, vitamin B12 deficiency anemia, and hemolytic anemia.
2. Detection of Infection and Inflammation:
Abnormalities in WBC count and differential count can indicate the presence of bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic infections, as well as inflammatory conditions such as autoimmune diseases and allergic reactions.
3. Monitoring Disease Progression:
The CBP facilitates the monitoring of certain chronic conditions, including leukemia, lymphoma, and myeloproliferative disorders, by tracking changes in blood cell counts and morphology over time.
4. Assessment of Bleeding and Clotting Disorders:
Platelet count and other clotting parameters assist in diagnosing and managing bleeding disorders such as thrombocytopenia, hemophilia, and von Willebrand disease.
5. Evaluation of Overall Health:
The CBP serves as a routine screening tool during general health check-ups, enabling early detection of underlying health issues and facilitating timely interventions.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Complete Blood Picture (CBP) is an indispensable tool in modern medicine, providing valuable insights into blood composition and function. By evaluating key parameters such as red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and hemoglobin levels, the CBP aids in the diagnosis, monitoring, and management of various medical conditions, ultimately contributing to improved patient care and outcomes.
0 notes
Text
Complete Blood Count (CBC) Test Price in Jammu
Introduction
A CBC test, known as a complete blood count analysis, provides crucial insights into the different types of cells present in your blood. This test aids healthcare providers in evaluating general health and diagnosing specific symptoms or conditions like anemia and infections. Additionally, it helps determine the need for further investigations.
This comprehensive test examines various blood cell parameters such as red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. In addition to aiding in the diagnosis of different conditions, it helps assess the effectiveness of treatments and medications.
Test Criteria
To determine your eligibility for a CBC test in Jammu or any other location, consider the following:
Eligibility for CBC Test
Suitable for individuals of any age, gender, or demographic to evaluate general health.
Useful in diagnosing health conditions like infections, anemia, blood cancers, and more.
Recommended if you experience symptoms such as easy bruising, fatigue, signs of bleeding, infections, or inflammation.
Prescribed when a disease affecting blood cells or related parameters is suspected.
Utilized to assess the effectiveness of ongoing treatments like radiation or anemia management.
Why Take the CBC Test?
Consider taking the CBC test for the following reasons:
As part of your routine health checkup
To determine the cause of fatigue, weight loss, or fever
To check for anemia or abnormal bleeding
In the case of infections or during pregnancy
To monitor your response to certain drugs or treatments like radiation
Prior to undergoing surgery
To diagnose blood diseases such as leukemia or chronic inflammation
In many other health conditions
What are the Benefits of the CBC Test at O-Lab?
At O-Lab, we offer tailored test packages to cater to individual needs. Our lab ensures quick results with a high level of accuracy. With the best CBC test price in Jammu, we provide convenient options such as home collection and walk-in services. By opting for our accredited lab, you can benefit from early detection of various health conditions, facilitating timely and appropriate treatment. Our trained staff and phlebotomists prioritize your safety, comfort, and reliability throughout the testing process. Feel free to reach out to us for further information.
Preparation
No special preparation or fasting is required for the CBC test. However, if you are undergoing other tests that necessitate fasting, such as LFT or lipid profile, fasting may be necessary.
Test Parameters
The CBC test includes essential parameters that vary slightly based on the lab's methodology. Here are the important parameters typically included:
Haemoglobin (Hb)
RBC (Red Blood Cell) Count
WBC- TLC (Total Leucocytes Count)
Absolute Basophil Count, blood
Absolute Eosinophil Count, blood
Absolute Lymphocyte Count, blood
Absolute Monocyte Count, blood
Absolute Neutrophil Count, blood
Neutrophils
Eosinophils
Lymphocytes
Monocytes
Basophils
MCH (Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin)
MCHC (Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration)
MCV (Mean Corpuscular Volume)
MPV (Mean Platelet Volume)
PCV Hematocrit (Packed Cell Volume)
PDW (Platelet Distribution Width)
RDW (Red Cell Distribution Width)
Platelet Count/Thrombocyte Count
0 notes
Text
Complete Blood Count
What Is a Complete Blood Count?
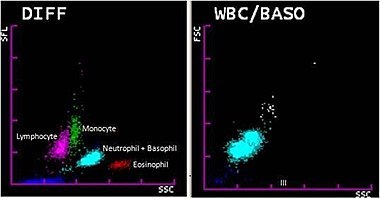
Benefits of a Complete Blood Count
A complete blood count (CBC) is an important diagnostic and screening tool used by healthcare providers to evaluate a patient’s overall health. It can help detect a variety of conditions, such as infections, anemia, diseases of the immune system, and more. The CBC measures the number, size, and types of cells in your blood. It looks at red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Red blood cells carry oxygen throughout the body while white blood cells help fight infection. Platelets are responsible for helping with clotting when bleeding occurs.
A CBC can be done as part of a routine checkup to screen for problems or because someone isn't feeling well. An abnormal result from a complete blood count test can alert healthcare providers to potential issues that may need further investigation or treatment. It can also provide valuable information about how your body is functioning overall so that any changes that arise over time can be tracked and monitored accordingly.
How Is the Test Performed?
A Complete Blood Count (CBC) is a common test performed by your healthcare provider to measure different parts and features of your blood. The CBC can help detect anemia, infection, inflammation, and many other disorders. To perform the test, a sample of blood is taken from your arm or finger and analyzed using an automated hematology analyzer that counts cells and collects information on their size and structure. It also measures the concentration of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, hemoglobin levels, hematocrit levels, mean corpuscular volume (MCV), mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH), mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC), and red cell distribution width (RDW). A CBC with differential is also known as a blood differential test because it includes further evaluation of the types of white blood cells present in the sample. This type of testing may be ordered as part of a routine exam or if there are signs or symptoms suggesting an underlying medical condition. To prepare for the CBC test, you should fast for 8-10 hours before having your blood drawn so that accurate results can be obtained. The skin at the puncture site will also be cleansed with antiseptic before taking a sample to reduce potential risk of infection.
0 notes
Link
Posted by Masswithclass on Musclesci
Bloodwork Knowledge
Blood tests
You just had some blood work done, and the friggin' doctor or his nurses are guarding the results as if they're state secrets. However, after much cajoling and explaining that you'd like to at least be an informed partner in your own goshdarn health care, they begrudgingly give you a copy of your lab tests.
Trouble is, as much as you've been posturing about how you've had more than a smattering of medical education, you still can't figure out what half the tests are for and whether or not those abnormal values are anything to worry about.
Well, in the following article, I'm going to go over each of the most common tests. I'll include why it's performed, what it tells you, and what the typical ranges are for normal humans. That way, you'll have something more to go on in assessing your health other than your family doctor saying, "Well, these few values are a little worrisome, but you'll probably be okay."
One note, though, before I get started. The values I'll be listing are merely averages and the ranges may vary slightly from laboratory to laboratory. Also, if there's only one range given, it applies to both men and women.
Lipid Panel — Used to determine possible risk for coronary and vascular disease. In other words, heart disease.
HDL/LDL and Total Cholesterol
These lipoproteins should look rather familiar to most of you. HDL is simply the "good" lipoprotein that acts as a scavenger molecule and prevents a buildup of material. LDL is the "bad" lipoprotein which collects in arterial walls and causes blockage or a reduction in blood flow. The total cholesterol to HDL ratio is also important. I went in to detail about this particular subject — as well as how to improve your lipid profile — in my article "Bad Blood".
Nevertheless, a quick remonder: your HDL should be 35 or higher; LDL below 130; and total to HDL ratio should be below 3.5. Oh and don't forget VLDL (very low density lipoprotein) which can be extremely worrisome. You should have less than 30 mg/dl in order to not be considered at risk for heart disease.
On a side note, I'm sure some of you are wishing that you had abnormally low plasma cholesterol levels (as if it's something to brag about), but the fact is that having extremely low cholesterol levels is actually indicative of severe liver disease.
Triglycerides
Triglycerides are simply a form of fat that exists in the bloodstream. They're transported by two other culprits, VLDL and LDL. A high level of triglycerides is also a risk factor for heart disease as well. Triglycerides levels can be increased if food or alcohol is consumed 12 to 24 hours prior to the blood draw and this is the reason why you're asked to fast for 12-14 hours from food and abstain from alcohol for 24 hours. Here are the normal ranges for healthy humans.
16-19 yr. old male
40-163 mg/dl
Adult Male
40-160 mg/dl
16-19 yr. old female
40-128 mg/dl
Adult Female
35-135 mg/dl
Homocysteine
Unfortunately, this test isn't always ordered by the doctor. It should be. Homocysteine is formed in the metabolism of the dietary amino acid methionine. The problem is that it's a strong risk factor for atherosclerosis. In other words, high levels may cause you to have a heart attack. A good number of lifters should be concerned with this value as homocysteine levels rise with anabolic steroid usage.
Luckily, taking folic acid (about 400-800 mcg.) as well as taking a good amount of all B vitamins in general will go a long way in terms of preventing a rise in levels of homocysteine.
Normal ranges:
Males and Females age 0-30
4.6-8.1 umol/L
Males age 30-59
6.3-11.2 umol/L
Females age 30-59
4.5-7.9 umol/L
>59 years of age
5.8-11.9 umol/L
The Hemo Profile
These are various tests that examine a number of components of your blood and look for any abnormalities that could be indicative of serious diseases that may result in you being an extra in the HBO show, "Six Feet Under."
WBC Total (White Blood Cell)
Also referred to as leukocytes, a fluctuation in the number of these types of cells can be an indicator of things like infections and disease states dealing with immunity, cancer, stress, etc.
Normal ranges:
4,500-11,000/mm3
Neutrophils
This is one type of white blood cell that's in circulation for only a very short time. Essentially their job is phagocytosis, which is the process of killing and digesting bacteria that cause infection. Both severe trauma and bacterial infections, as well as inflammatory or metabolic disorders and even stress, can cause an increase in the number of these cells. Having a low number of neutrophils can be indicative of a viral infection, a bacterial infection, or a rotten diet.
Normal ranges:
2,500-8,000 cells per mm3
RBC (Red Blood Cell)
These blood cells also called erythrocytes and their primary function is to carry oxygen (via the hemoglobin contained in each RBC) to varioustissues as well as giving our blood that cool "red" color. Unlike WBC, RBC survive in peripheral blood circulation for approximately 120 days. A decrease in the number of these cells can result in anemia which could stem from dietary insufficiencies. An increase in number can occur when androgens are used. This is because androgens increase EPO (erythropoietin) production which in turn increases RBC count and thus elevates blood volume. This is essentially why some androgens are better than others at increasing "vascularity." Anyhow, the danger in this could be an increase in blood pressure or a stroke.
Androgen-using lifters who have high values should consider making modifications to their stack and/or immediately donating some blood.
Normal ranges:
Adult Male
4,700,000-6,100,000 cells/uL
Adult Female
4,200,000-5,400,000 cells/uL
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is what serves as a carrier for both oxygen and carbon dioxide transportation. Molecules of this are found within each red blood cell. An increase in hemoglobin can be an indicator of congenital heart disease, congestive heart failure, sever burns, or dehydration. Being at high altitudes, or the use of androgens, can cause an increase as well. A decrease in number can be a sign of anemia, lymphoma, kidney disease, sever hemorrhage, cancer, sickle cell anemia, etc.
Normal ranges:
Males and females 6-18 years
10-15.5 g/dl
Adult Males
14-18 g/dl
Adult Females
12-16 g/dl
Hematocrit
The hematocrit is used to measure the percentage of the total blood volume that's made up of red blood cells. An increase in percentage may be indicative of congenital heart disease, dehydration, diarrhea, burns, etc. A decrease in levels may be indicative of anemia, hyperthyroidism, cirrhosis, hemorrhage, leukemia, rheumatoid arthritis, pregnancy, malnutrition, a sucking knife wound to the chest, etc.
Normal ranges:
Male and Females age 6-18 years
32-44%
Adult Men
42-52%
Adult Women
37-47%
MCV (Mean Corpuscular Volume)
This is one of three red blood cell indices used to check for abnormalities. The MCV is the size or volume of the average red blood cell. A decrease in MCV would then indicate that the RBC's are abnormally large(or macrocytic), and this may be an indicator of iron deficiency anemia or thalassemia. When an increase is noted, that would indicate abnormally small RBC (microcytic), and this may be indicative of a vitamin B12 or folic acid deficiency as well as liver disease.
Normal ranges:
Adult Male
80-100 fL
Adult Female
79-98 fL
12-18 year olds
78-100 fL
MCH (Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin)
The MCH is the weight of hemoglobin present in the average red blood cell. This is yet another way to assess whether some sort of anemia or deficiency is present.
Normal ranges:
12-18 year old
35-45 pg
Adult Male
26-34 pg
Adult Female
26-34 pg
MCHC (Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration)
The MCHC is the measurement of the amount of hemoglobin present in the average red blood cell as compared to its size. A decrease in number is an indicator of iron deficiency, thalassemia, lead poisoning, etc. An increase is sometimes seen after androgen use.
Normal ranges:
12-18 year old
31-37 g/dl
Adult Male
31-37 g/dl
Adult Female
30-36 g/dl
RDW (Red Cell Distribution Width)
The RDW is an indicator of the variation in red blood cell size. It's used in order to help classify certain types of anemia, and to see if some of the red blood cells need their suits tailored. An increase in RDW can be indicative of iron deficiency anemia, vitamin B12 or folate deficiency anemia, and diseases like sickle cell anemia.
Normal ranges:
Adult Mal
11.7-14.2%
Adult Female
11.7-14.2%
Platelets
Platelets or thrombocytes are essential for your body's ability to form blood clots and thus stop bleeding. They're measured in order to assess the likelihood of certain disorders or diseases. An increase can be indicative of a malignant disorder, rheumatoid arthritis, iron deficiency anemia, etc. A decrease can be indicative of much more, including things like infection, various types of anemia, leukemia, etc.
On a side note for these ranges, anything above 1 million/mm3 would be considered a critical value and should warrant concern and/or giving second thoughts as to whether you should purchase a lifetime subscription to Muscle Media.
Normal ranges:
Child
150,000-400,000/mm3
(Most commonly displayed in SI units of 150-400 x 10(9th)/L
Adult
150,000-400,000/mm3
(Most commonly displayed in SI units of 150-400 x 10(9th)/L
ABS (Differential Count)
The differential count measures the percentage of each type of leukocyte or white blood cell present in the same specimen. Using this, they can determine whether there's a bacterial or parasitic infection, as well as immune reactions, etc.
Pt. 2
Neutrophils
As explained previously, severe trauma and bacterial infections, as well as inflammatory disorders, metabolic disorders, and even stress can cause an increase in the number of these cells. Also, on the other side of the spectrum, a low number of these cells can indicate a viral infection, a bacterial infection, or a deficient diet.
Percentile Range:
55-70%
Basophils
These cells, and in particular, eosinophils, are present in the event of an allergic reaction as well as when a parasite is present. These types of cells don't increase in response to viral or bacterial infections so if an increased count is noted, it can be deduced that either an allergic response has occurred or a parasite has taken up residence in your shorts.
Percentile Range:
Basophils
0.5-1%
Eosinophils
1-4%
Lymphocytes and Monocytes
Lymphocytes can be divided in to two different types of cells: T cells and B cells. T cells are involved in immune reactions and B cells are involved in antibody production. The main job of lymphocytes in general is to fight off — Bruce Lee style — bacterial and viral infections.
Monocytes are similar to neutrophils but are produced more rapidly and stay in the system for a longer period of time.
Percentile Range:
Lymphocytes
20-40%
Monocytes
2-8%
Selected Clinical Values
Sodium
This cation (an ion with a postive charge) is mainly found in extracellular spaces and is responsible for maintaining a balance of water in the body. When sodium in the blood rises, the kidneys will conserve water and when the sodium concentration is low, the kidneys conserve sodium and excrete water. Increased levels can result from excessive dietary intake, Cushing's syndrome, excessive sweating, burns, forgetting to drink for a week, etc. Decreased levels can result from a deficient diet, Addison's disease, diarrhea, vomiting, chronic renal insufficiency, excessive water intake, congestive heart failure, etc. Anabolic steroids will lead to an increased level of sodium as well.
Normal range:
Adults
136-145 mEq/L
Potassium
On the other side of the spectrum, you have the most important intracellular cation. Increased levels can be an indicator of excessive dietary intake, acute renal failure, aldosterone-inhibiting diuretics, a crushing injury to tissues, infection, acidosis, dehydration, etc. Decreased levels can be indicative of a deficient dietary intake, burns, diarrhea or vomiting, diuretics, Cushing's syndrome, licorice consumption, insulin use, cystic fibrosis, trauma, surgery, etc.
Normal range:
Adults
3.5-5 mEq/L
Chloride
This is the major extracellular anion (an ion carrying a negative charge). Its purpose it is to maintain electrical neutrality with sodium. It also serves as a buffer in order to maintain the pH balance of the blood. Chloride typically accompanies sodium and thus the causes for change are essentially the same.
Normal range:
Adult
98-106 mEq/L
Carbon Dioxide
The CO2 content is used to evaluate the pH of the blood as well as aid in evaluation of electrolyte levels. Increased levels can be indicative of severe diarrhea, starvation, vomiting, emphysema, metabolic alkalosis, etc. Increased levels could also mean that you're a plant. Decreased levels can be indicative of kidney failure, metabolic acidosis, shock, and starvation.
Normal range:
Adults
23-30 mEq/L
Glucose
The amount of glucose in the blood after a prolonged period of fasting (12-14 hours) is used to determine whether a person is in a hypoglycemic (low blood glucose) or hyperglycemic (high blood glucose) state. Both can be indicators of serious conditions. Increased levels can be indicative of diabetes mellitus, acute stress, Cushing's syndrome, chronic renal failure, corticosteroid therapy, acromegaly, etc. Decreased levels could be indicative of hypothyroidism, insulinoma, liver disease, insulin overdose, and starvation.
Normal range:
Adult Male
65-120 mg/dl
Adult Female
65-120 mg/dl
BUN (Blood Urea Nitrogen)
This test measures the amount of urea nitrogen that's present in the blood. When protein is metabolized, the end product is urea which is formed in the liver and excreted from the bloodstream via the kidneys. This is why BUN is a good indicator of both liver and kidney function. Increased levels can stem from shock, burns, dehydration, congestive hear failure, myocardial infarction, excessive protein ingestion, excessive protein catabolism, starvation, sepsis, renal disease, renal failure, etc. Causes of a decrease in levels can be liver failure, overhydration, negative nitrogen balance via malnutrition, pregnancy, etc.
Normal range:
Adults
10-20 mg/dl
Creatinine
Creatinine is a byproduct of creatine phosphate, the chemical used in contraction of skeletal muscle. So, the more muscle mass you have, the higher the creatine levels and therefore the higher the levels of creatinine. Also, when you ingest large amounts of beef or other meats that have high levels of creatine in them, you can increase creatinine levels as well. Since creatinine levels are used to measure the functioning of the kidneys, this easily explains why creatine has been accused of causing kidney damage, since it naturally results in an increase in creatinine levels.
However, we need to remember that these tests are only indicators of functioning and thus outside drugs and supplements can influence them and give false results, as creatine may do. This is why creatine, while increasing creatinine levels, does not cause renal damage or impair function. Generally speaking, though, increased levels are indicative of urinary tract obstruction, acute tubular necrosis, reduced renal blood flow (stemming from shock, dehydration, congestive heart failure, atherosclerosis), as well as acromegaly. Decreased levels can be indicative of debilitation, and decreased muscle mass via disease or some other cause.
Normal range:
Adult Male
0.6-1.2 mg/dl
Adult Female
0.5-1.1 mg/dl
BUN/Creatinine Ratio
A high ratio may be found in states of shock, volume depletion, hypotension, dehydration, gastrointestinal bleeding, and in some cases, a catabolic state. A low ratio can be indicative of a low protein diet, malnutrition, pregnancy, severe liver disease, ketosis, etc. Keep in mind, though, that the term BUN, when used in the same sentence as hamburger or hotdog, usually means something else entirely. An important thing to note again is that with a high protein diet, you'll likely have a higher ratio and this is nothing to worry about.
Normal range:
Adult
6-25
Calcium
Calcium is measured in order to assess the function of the parathyroid and calcium metabolism. Increased levels can stem from hyperparathyroidism, metastatic tumor to the bone, prolonged immobilization, lymphoma, hyperthyroidism, acromegaly, etc. It's also important to note that anabolic steroids can also increase calcium levels. Decreased levels can stem from renal failure, rickets, vitamin D deficiency, malabsorption, pancreatitis, and alkalosis.
Normal range:
Adult
9-10.5 mg/dl
Liver Function
Total Protein
This measures the total level of albumin and globulin in the body. Albumin is synthesized by the liver and as such is used as an indicator of liver function. It functions to transport hormones, enzymes, drugs and other constituents of the blood.
Globulins are the building blocks of your body's antibodies. Measuring the levels of these two proteins is also an indicator of nutritional status. Increased albumin levels can result from dehydration, while decreased albumin levels can result from malnutrition, pregnancy, liver disease, overhydration, inflammatory diseases, etc. Increased globulin levels can result from inflammatory diseases, hypercholesterolemia (high cholesterol), iron deficiency anemia, as well as infections. Decreased globulin levels can result from hyperthyroidism, liver dysfunction, malnutrition, and immune deficiencies or disorders.
As another important side note, anabolic steroids, growth hormone, and insulin can all increase protein levels.
Normal range:
Adult
Total Protein: 6.4-8.3 g/dl
Albumin: 3.5-5 g/dl
Globulin: 2.3-3.4 g/dl
Albumin/Globulin Ratio:
Adult
0.8-2.0
Bilirubin
Bilirubin is one of the many constituents of bile, which is formed in the liver. An increase in levels of bilirubin can be indicative of liver stress or damage/inflammation. Drugs that may increase bilirubin include oral anabolic steroids (17-AA), antibiotics, diuretics, morphine, codeine, contraceptives, etc. Drugs that may decrease levels are barbiturates and caffeine. Non-drug induced increased levels can be indicative of gallstones, extensive liver metastasis, and cholestasis from certain drugs, hepatitis, sepsis, sickle cell anemia, cirrhosis, etc.
Normal range:
Total Bilirubin for Adult
0.3-1.0 mg/dl
Alkaline Phosphatase
This enzyme is found in very high concentrations in the liver and for this reason is used as an indicator of liver stress or damage. Increased levels can stem from cirrhosis, liver tumor, pregnancy, healing fracture, normal bones of growing children, and rheumatoid arthritis. Decreased levels can stem from hypothyroidism, malnutrition, pernicious anemia, scurvy (vitamin C deficiency) and excess vitamin B ingestion. As a side note, antibiotics can cause an increase in the enzyme levels.
Normal range:
16-21 years
30-200 U/L
Adult
30-120 U/L
Pt. 3
AST (Aspartate Aminotransferase, previously known as SGOT)
This is yet another enzyme that's used to determine if there's damage or stress to the liver. It may also be used to see if heart disease is a possibility as well, but this isn't as accurate. When the liver is damaged or inflamed, AST levels can rise to a very high level (20 times the normal value). This happens because AST is released when the cells of that particular organ (liver) are lysed. The AST then enters blood circulation and an elevation can be seen. Increased levels can be indicative of heart disease, liver disease, skeletal muscle disease or injuries, as well as heat stroke. Decreased levels can be indicative of acute kidney disease, beriberi, diabetic ketoacidosis, pregnancy, and renal dialysis.
Normal range:
Adult
0-35 U/L (Females may have slightly lower levels)
ALT (Alanine Aminotransferase, previously known as SGPT)
This is yet another enzyme that is found in high levels within the liver. Injury or disease of the liver will result in an increase in levels of ALT. I should note however, that because lesser quantities are found in skeletal muscle, there could be a weight-training induced increase . Weight training causes damage to muscle tissue and thus could slightly elevate these levels, giving a false indicator for liver disease. Still, for the most part, it's a rather accurate diagnostic tool. Increased levels can be indicative of hepatitis, hepatic necrosis, cirrhosis, cholestasis, hepatic tumor, hepatotoxic drugs, and jaundice, as well as severe burns, trauma to striated muscle (via weight training), myocardial infarction, mononucleosis, and shock.
Normal range:
Adult
4-36 U/L
Endocrine Function
Testosterone(Free and Total)
This is of course the hormone that you should all be extremely familiar with as it's the name of this here magazine! Anyhow, just as some background info, about 95% of the circulating Testosterone in a man's body is formed by the Leydig cells, which are found in the testicles. Women also have a small amount of Testosterone in their body as well. (Some more than others, which accounts for the bearded ladies you see at the circus, or hanging around with Chris Shugart.) This is from a very small amount of Testosterone secreted by the ovaries and the adrenal gland (in which the majority is made from the adrenal conversion of androstenedione to Testosterone via 17-beta HSD).
Nomal range, total Testosterone:
Male
Age 14
<1200 ng/dl
Age 15-16
100-1200 ng/dl
Age 17-18
300-1200 ng/dl
Age 19-40
300-950 ng/dl
Over 40
240-950 ng/dl
Female
Age 17-18
20-120 ng/dl
Over 18
20-80 ng/dl
Normal range, free Testosterone:
Male
50-210 pg/ml
LH (Luteinizing Hormone)
LH is a glycoprotein that's secreted by the anterior pituitary gland and is responsible for signaling the leydig cells to produce Testosterone. Measuring LH can be very useful in terms of determining whether a hypogonadic state (low Testosterone) is caused by the testicles not being responsive despite high or normal LH levels (primary), or whether it's the pituitary gland not secreting enough LH (secondary). Of course, the hypothalamus — which secretes LH-RH (luteinizing hormone releasing hormone) — could also be the culprit, as well as perhaps both the hypothalamus and the pituitary.
If it's a case of the testicles not being responsive to LH, then things like clomiphene and HCG really won't help. If the problem is secondary, then there's a better chance for improvement with drug therapy. Increased levels can be indicative of hypogonadism, precocious puberty, and pituitary adenoma. Decreased levels can be indicative of pituitary failure, hypothalamic failure, stress, and malnutrition.
Normal ranges:
Adult Male
1.24-7.8 IU/L
Adult Female
Follicular phase: 1.68-15 IU/L
Ovulatory phase: 21.9-56.6 IU/L
Luteal phase: 0.61-16.3 IU/L
Postmenopausal: 14.2-52.3 IU/L
Estradiol
With this being the most potent of the estrogens, I'm sure you're all aware that it can be responsible for things like water retention, hypertrophy of adipose tissue, gynecomastia, and perhaps even prostate hypertrophy and tumors. As a male it's very important to get your levels of this hormone checked for the above reasons. Also, it's the primary estrogen that's responsible for the negative feedback loop which suppresses endogenous Testosterone production. So, if your levels of estradiol are rather high, you can bet your ass that you'll be hypogonadal as well.
Increased estradiol levels can be indicative of a testicular tumor, adrenal tumor, hepatic cirrhosis, necrosis of the liver, hyperthyroidism, etc.
Normal ranges:
Adult Male
10-50 pg/ml
Adult Female
Follicular phase: 20-350 pg/ml
Midcycle peak: 150-750 pg/ml
Luteal phase: 30-450 pg/ml
Postmenopausal: 20 pg/ml or less
Thyroid (t3, T4 Total and Free, TSH)
T3 (Triiodothyronine)
T3 is the more metabolically active hormone out of T4 and T3. When levels are below normal it's generally safe to assume that the individual is suffering from hypothyroidism. Drugs that may increase T3 levels include estrogen and oral contraceptives. Drugs that may decrease T3 levels include anabolic steroids/androgens as well as propanolol (a beta adrenergic blocker) and high dosages of salicylates. Increased levels can be indicative of Graves disease, acute thyroiditis, pregnancy, hepatitis, etc. Decreased levels can be indicative of hypothyroidism, protein malnutrition, kidney failure, Cushing's syndrome, cirrhosis, and liver diseases.
Normal ranges:
16-20 years old
80-210 ng/dl
20-50 years
75-220 ng/dl or 1.2-3.4 nmol/L
Over 50
40-180 ng/dl or 0.6-2.8 nmol/L
T4 (Thyroxine)
T4 is just another indicator of whether or not someone is in a hypo or hyperthyroid state. It too is rather reliable but free thyroxine levels should be assessed as well. Drugs that increase of decrease T3 will, in most cases, do the same with T4. Increased levels are indicative of the same things as T3 and a decrease can be indicative of protein depleted states, iodine insufficiency, kidney failure, Cushing's syndrome, and cirrhosis.
Normal ranges:
Adult Male
4-12 ug/dl or 51-154 nmol/L
Adult Female
5-12 ug/dl or 64-154 nmol/L
Free T4 or Thyroxine
Since only 1-5% of the total amount of T4 is actually free and useable, this test is a far better indicator of the thyroid status of the patient. An increase indicates a hyperthyroid state and a decrease indicates a hypothyroid state. Drugs that increase free T4 are heparin, aspirin, danazol, and propanolol. Drugs that decrease it are furosemide, methadone, and rifampicin. Increased and decreased levels are indicative of the same possible diseases and states that are seen with T4 and T3.
Normal ranges:
0.8-2.8 ng/dl or 10-36 pmol/L
TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone)
Measuring the level of TSH can be very helpful in terms of determining if the problem resides with the thyroid itself or the pituitary gland. If TSH levels are high, then it's merely the thyroid gland not responding for some reason but if TSH levels are low, it's the hypothalamus or pituitary gland that has something wrong with it. The problem could be a tumor, some type of trauma, or an infarction.
Drugs that can increase levels of TSH include lithium, potassium iodide and TSH itself. Drugs that may decrease TSH are aspirin, heparin, dopamine, T3, etc. Increased TSH is indicative of thyroiditis, hypothyroidism, and congenital cretinism. Decreased levels are indicative of hypothyroidism (pituitary dysfunction), hyperthyroidism, and pituitary hypofunction.
Normal ranges:
Adult
2-10 uU/ml or 2-10 mU/L
Knowing how to interpret these tests can be a very valuable tool in terms of health and your body building and athletic progress. Use your new knowledge wisely.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Identify conditions associated with abnormal LOW levels of each of the following labs (if applicable) Identify conditions associated with abnormal HIGH levels of each of the following labs (if applicable)
Identify conditions associated with abnormal LOW levels of each of the following labs (if applicable) Identify conditions associated with abnormal HIGH levels of each of the following labs (if applicable)
Identify conditions associated with abnormal LOW levels of each of the following labs (if applicable) Identify conditions associated with abnormal HIGH levels of each of the following labs (if applicable)
Components of a CBC WBC, Hemoglobin, Hematocrit (Hgb/Hct), RBCs, MCV: What is Normocytic, Microcytic, Macrocytic. RDW, Reticulocyte count, Platelets, and differential Components on a…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
ABIM: Hematology
ABIM syllabus can be found here
Let me know if you find any errors
Sources: UWorld, MKSAP 16/17, Rizk Review Course, Louisville Lectures, Knowmedge (free version)
Hypoproliferative anemia
Aplastic anemia:
- associated with autoimmune diseases, thymomas <-- need CT chest, Tx with resection
- Tx all patients with PPx anticoagulation + iron + folic acid; if <40yo: stem cell transplant
- associated with PNH: pancytopenia/hemolytic anemia with need for transfusions + Budd-Chiari/venous thrombosis/CVA/MI + morning hematuria/iron deficiency, associated with AML; Dx: flow cytometry shows lack of CD55, CD59; Tx: iron + Eculizumab to decrease need for transfusions (AE of Eculizumab is increased risk of meningococcal infections) +/- (if thrombus) warfarin; if <40yo: allogenic BMT
Iron deficiency anemia:
- decreased iron, ferritin, transferrin; increased TIBC, RDW
- associated with gastric surgery, restless leg syndrome
- colon cancer until proven otherwise
- also seen in:
(1) Celiac disease: IBS Sx with iron deficiency that is unresponsive to oral supplementation; Dx: tissue transglutaminase Ab --> if neg: small bowel biopsy
(2) Plummer-Vinson: esophageal webs, glossitis; associated with squamous cell esophageal carcinoma
(3) Osler-Weber-Rendu/Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia: lip/oral telangiectasias + epistaxis + +FOBT associated with hemoptysis/brain bleed
- Tx iron deficiency: PO supplementation x6mo or IV iron gluconate (dextran is associated with anaphylaxis)
Sideroblastic anemia:
- ringed sideroblasts/basophilic stippling on PBS seen in EtOH, lead toxicity (Burton line on teeth, deposition in metaphysis, RTA type II (hypokalemia, glucosuria)), copper deficiency, and use of INH (from B6 deficiency), chloramphenicol, Linezolid
- Tx hereditary sideroblastic anemia with pyridoxine/B6
Megaloblastic anemia: MCV>100, hypersegmented PMNs, associated with EtOH use
(1) B12 deficiency: peripheral paresthesias; associated with strict vegetarians and Crohn’s disease (terminal ileum disease), elevated methylmalonic acid > homocysteine
(2) Pernicious anemia: anti-IF antibodies causing B12 deficiency; associated with autoimmune diseases and increased risk of gastric cancer
(3) folate deficiency: no paresthesias; associated with pregnancy, EtOH, and Bactrim use; elevated homocysteine only
Pure red cell aplasia: associated with AIDS + Parvovirus B19; Dx: flow cytometry shows monoclonal CD57+ T-cells; Tx: IVIg and check for thymoma with CT chest
Hemolytic anemia
- PBS shows schistocytes (vs. dacryocytes/tear drop cells with 2 line involvement in Myelodysplastic syndrome)
- appropriate reticulocyte response = >100,000/uL
- Tx chronic hemolytic anemia with folate
- Scleroderma renal crisis (HTN, AKI, MAHA): Tx with ACEi (Captopril) even iff pregnant
- MAHA in the setting of mechanical heart valve needs emergent TEE to check for leak/regurg
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency:
- remember food: fava beans, bite cells, Heinz bodies (red spots in RBCs; looks kind of like a pink boob with 1 or more red nipples)
- associated with sulfa drugs, infection, and DKA --> hemolysis
- has decreased glutathione levels
Pyruvate kinase deficiency: Tx with PRN transfusions --> severe?: splenectomy
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia: Coomb’s/DAT positive
(1) warm immunoglobulins:
- IgG, DAT+ with spherocytosis
- associated with autoimmune (SLE, UC), HIV, CLL
- Tx steroids --> splenectomy --> refractory Tx: IVIg, AZT, cyclophosphamide, Rituximab
(2) cold:
- IgM (Mmm cold ice cream), occurs in cold temperatures
- associated with malignancies, mono, mycoplasma
- Tx: avoid the cold, Rituxan
Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia: Tx: plasma exchange +/- corticosteroids
- Sx: “FAT RN” (fever, anemia, thrombocytopenia, renal failure, neuro sx)
- Dx: normal coags, D-dimer, fibrinogen (vs. DIC = elevated coags and D-dimer; decreased fibrinogen, platelets)
*FYI: ITP, TTP/HUS, and HELLP all have normal coags
(1) TTP: primarily neurologic symptoms
- increased vWF multimers/decreased ADAMSTS13 (NOT needed for diagnosis)
- associated with tacrolimus, cyclosporine, plavix/ticlodipine, quinine
- Tx: plasmapheresis
*if >20 weeks pregnant, this is TTP and does NOT resolve with delivery
(2) HUS: primarily renal symptoms
- associated with E.coli/Shigella diarrhea and cyclosporine
- Tx: discontinue cyclosporine!, supportive, plasmapheresis
Hereditary spherocytosis:
- jaundice from unconj/indirect hyperbilirubinemia, pigmented gallstones, splenomegaly, leg ulcers
- PBS shows spherocytes and Howell-Jolly bodies (blue dot in RBC seen in splenectomy); DAT negative (vs. DAT+ in warm hemolytic anemia; see above)
- Dx: osmotic fragility test --> flow cytometry
- Tx: splenectomy
Wilson’s: young patient with hemolytic anemia + psychosis + transaminitis
Hemoglobinopathies and thalassemias
- present as microcytic anemias: MCV <80; target cells
Alpha thalassemia: has normal Hb electrophoresis
--, -x = HbH: hemolysis, splenomegaly, Heinz body
- --,-- = Barts / Hydrops fetalis (dies before birth)
Beta thalassemia: abnormal Hb electrophoresis
- minor: elevated HbA2 (alpha 2 gamma 2) and HbF
- intermedia: elevated HbA2 only; Tx: intermittent transfusion +/- iron chelation if Fe>1000
- Major: elevated HbF, decreased HbA; Tx: splenectomy and allogenic stem cell transplant
Hemoglobinopathy: severe disease requires stem cell transplant
Leukocyte disorders
(1) AML: t(15;17)
- associated with PCV, Fanconi’s, Down’s, Klinefelter’s, CML, XRT/chemo, benzenes, MDS
- presents acutely as sepsis (decreased PMNs, anemia, thrombocytopenia)
- pallor, gingival hypertrophy (M5), fatigue, easy spontaneous bleeding/purpura (due to thrombocytopenia), and NO hepatosplenomegaly or lymphadenopathy
- M3 (Auer rods) associated with DIC Tx: ATRA
*ATRA AE: after 1-3 weeks --> fever, leukocytosis, pulmonary infiltrates/hypoxemia; Tx: dexamethasone
*prevent TLS (hyperkalemic paresthesia/weakness, hypocalcemic tetany, bronchospasm, AKI) with Allopurinol BEFORE chemo --> Rasburicase
(2) CML: t(9;22)/BCR-ABL, decreased LAP
- asymptomatic splenomegaly with elevated WBC (symptomatic when >200) with increased Eosinophils and Basophils
- Tx: Imatinib/Gleevec (TKI)
(3) ALL: TdT, anterior mediastinal mass (thymoma <-- chest CT)/bulky mediastinal lymphadenopathy with bone pain and CNS involvement
- increased blasts (>30%)
- Tx: combo chemo (intrathecal if CNS involvement) +/- XRT if bulky disease --> stem cell
(4) CLL: B2microglobulin; CD5, CD23 B-cells; smudge cells
- asymptomatic, lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, lymphocytosis, thrombocytopenia
- Tx: watchful waiting if asymptomatic; Bendamustine+Rituxan > Fludarabine + Bactrim PPx
*AE: Richter’s syndrome: transformation into aggressive large cell lymphoma
*Evan’s syndrome: AIHA + ITP
(5) Hairy cell: older patient with pancytopenia, splenomegaly, dry fibrotic bone marrow
- associated with PAN
- Dx: flow-cytometry: CD11c, CD103+; +TRAP
- Tx: Cladribine
Platelet disorders
*Rule of thumb: transfuse if Plt <10 or if ICH/pulm hemorrhage <40-50; 1 bag of platelets corrects by 25k
*give IVIg + steroids if pregnant with Plt <50
*Plt >50 = okay for surgery
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: diagnosis of exclusion
- Dx: PBS, DAT+ (don’t order anti-Plt antibodies)
- Tx (if symptomatic or Plt <15): steroids --> IVIg/Rhogam --> refractory: splenectomy, Rituxan
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT):
- 4T’s: thrombocytopenia (2pts: >50%, 1pt: 30-50, 0pt: <30), timing (>5days, ?>5, <4), thrombosis (+, ?, -), no other cause (yes, maybe, no); score 6-8 = high, 0-3 low
- Dx: PF4, SRA
- Tx: stop Heparin (warfarin is NOT contraindicated!); switch to Argatroban
Essential thrombocythemia:
- “Jack et Vera are Buddies” (”et” in Latin is “and”): Jak2 mutations are associated with ET, polycythemia Vera, and Budd-Chiari”
- JAK2, CALR, BCR-ABL, NPL1
- Plt >600 --> livedo reticularis, erythromelagia (painful red hands/feet, Tx: ASA), headache, vision changes
- Tx: ASA + (if symptomatic) Hydroxyurea +/- (if TIA/CVA/MI/GIB) pheresis
Other platelet dysfunction: increased bleeding time; bleeding from small injuries, epistaxis, menorrhagia
(1) vWF: increased PTT/low-normal VIII corrected with mixing study; Dx: vWF Ag; Tx: pre-dental DDAVP or for active bleed, recombinant factor VIII
(2) Bernard-Soulier: X glycoprotein Ib --> thrombocytopenia
(3) Glanzmann (~Abciximab/Eptifibatide): X gpIIb-IIIa --> normal platelet counts
Coagulation factor disorders and thrombotic disorders
Rule of Thumb:
PeT PiTTbull
- PT extrinsic pathway (VII, X)
- PTT intrinsic pathway (VIII, IX, XI, XII)
*mixing studies correct = deficiency --> present as bleeding into muscle/joint; Tx with DDAVP for mild disease or missing factor for active bleed
*mixing studies don’t correct =
(1) if there is bleeding: presence of factor antibody: Tx with recombinant FVII
(2) if there is no bleeding: antiphospholipid Ab
Coagulation factor deficiencies:
- VII: elevated PT (it’s pretty much the only one that isn’t elevated PTT), presents as ICH, Tx: rfVII
- VIII/Hem A: elevated PTT, bleeding into muscles/joints, no excessive bleed after minor cuts; Tx: DDAVP before dental work, fVIII
- acquired VIII: elevated PTT that doesn’t correct, Tx: rFVII (<--yes, Tx is rf7, NOT 8)
- IX/Hem B: elevated PTT, bleeding into muscles/joints, no excessive bleeding after minor cuts; Tx: fIX
- XI/Rosenthal: elevated PTT in Ashkenazi Jews; Tx: FFP prior to major surgeries
- XII: asymptomatic and totally benign elevated PTT
- XIII: coags look normal, but has severe post-op bleed; Dx: urease clot dissolves; Tx: Qmonthly FFP
- acquired X/AL amyloid: elevated INR with postural hypotension, macroglossia, heart failure, and proteinuria/kidney failure; Dx: serum/urine electrophoresis, free light chain assay, BMB, fat pad aspirate
vs. vWF: increased bleeding time, normal/elevated PTT that corrects with mixing stud
- Dx: vWF Ag, vWF activy assay, VIII, level, subtype multimer study
- Sx: gingival/mucocutaneus bleed, menorrhagia, easy bruising
- Tx: DDAVP prior to dental work, active bleed: rfVIII
Thrombophilia: DVT/PE’s
(1) Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome: anti-beta2glycoprotein I Ab
- blood clots, miscarriage; associated with SLE
- apTT doesn’t correct with mixing study --> Dx: anticardiolipin IgG/IgM ELISA
(2) Factor V Leiden: most common
- Dx (check months after DVT): clotting assay (resistance to Protein C) --> genetic prothrombin G20210A mutation
Porphyria
-morning hematuria, blistering photosensitive rash, abdominal pain, nausea/vomiting, HTN, tachycardia, psychosis, seizures all exacerbated by EtOH, smoking, stress, sulfa drugs
- increased risk of HCC, lymphoma
- Dx: elevated urine uroporphyrinogen (urine turns purple in sunlight) --> check for Hep C and hemochromatosis
- Porphyria cutanea tarda: associated with HIV, Hep C; Tx: phlebotomy to decrease iron stores
Myeloproliferative disorders
Polychythemia vera and other erythrocytosis: JAK2V617F, associated with Budd-Chiari, facial plethora, pruritus with hot baths
- BMB is hypercellular, decreased EPO levels
- Tx: ASA and phlebotomy to Hct <45 +/- Hydrea
- also Tx hyperuricemia with allopurinol, pruritus with antihistamines
Essential thrombocythemia: JAK2, decreased EPO levels; associated with vWF disease (more info under Platelet Disorders above); Tx: ASA + Hydroxyurea +/- pheresis if TIA/CVA/MI/GIB
Agnogenic myeloid metaplasia and myelofibrosis:
- splenomegaly, dacryocytes, giant megakaryocytes/platelets, BM fibrosis
- portal HTN
- Tx: supportive (NOT splenectomy); if <60yo, stem cell transplant
Myelodysplastic syndrome
- cytopenia of 2 cell lines + tear drop cells + nucleated RBCs, elevated MVC
- r/o B12 deficiency (PBS macrocytosis)
- BMB shows ringed sideroblasts, Pseudo Pelger-Huetz cell (looks like 2-lobed PMN or cell wearing blue sunglasses)
- Tx: Azacitidine to keep Plt >100k, Epo, GCSF; if young: stem cell transplant
- 5q-subtype Tx (best prognosis): Thalidomide (AE: rash, peripheral neuropathy), Lenalidomide (AE: less neuropathy, but more decr PMN, thrombocytopenia)
Hematologic malignancies
Acute and chronic leukemias (see Leukocyte Disorders above)
Hodgkin’s disease: B-symptoms, non-tender contiguous nodes with Reed-Sternberg (owl-eye) B-cells, associated with EBV; Dx: full excision of lymph node + pan-CT + PET + BMB if Bsx or stage III/VI; Tx: ABVD + rads if same side of diaphragm --> screen for breast cancer 8 years after XRT or at 40yo
Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: multiple nodes with extranodal involvement, B>T cells, associated with autoimmune dz (Sjogrens: parotid MALT), HIV
(1) Indolent:
(a) Follicular: painless swelling in neck, armpit, groin; Tx: watchful waiting, but if symptomatic: XRT if limited, Bendamustine-Rituxan or R-CHOP if outside XRT field
(b) MALT: Tx H.pylori
(2) Aggressive:
(a) Diffuse large B-cell: B-symptoms; Dx: biopsy, Tx: CHOP --> R-CHOP --> XRT
(b) AIDs-associated lymphoma: EBV in CSF --> primary cerebral lymphoma
(c) Burkitt’s lymphoma: African jaw mass/U.S.A. abdominal mass, associated with EBV, increased LDH, starry sky
(3) Cutaneous T-cell (CD4): Sezary/Mycosis Fungoides: plaque --> nodular lesions with cerbriform nuclei (epidermis: Pautrier microabscess)
Plasma cell disorder / Multiple Myeloma:
- “CRAB” hypercalcemia, renal injury, anemia, lytic bone lesions
- >3gM protein, >10% plasma cells in BM, normal ALP, discrepancy between urine protein and urine dipstick (due to inability to detect light chains)
- Dx: BMB, XR>bone survey; serum and urine electrophoresis Q6 months
- Tx:
(1) <75yo: Lenalidomide/Thalidomide + Dexamethasone --> stem cell transplant --> Bortezomib
(2) can’t or >75yo: Melphalan + Prednisone
vs. Smoldering MM: MM without Sx
vs. Plasmacytoma: solitary lytic bone lesion; Dx: tissue Bx; Tx: follow
vs. MGUS: no CRAB, few clonal plasma cells, serum monoclonal protein <3g
*AE of Thalidomide = DVTs
Transfusion medicine
Indications for transfusion: Hb <7 or <10 for acute MI
Complications of transfusion:
(1) ABO/acute hemolytic transfusion: fever, flank pain, tachycardia, hypotension --> stop transfusion
(2) Delayed: elevated bili and LDH, decreased Hb and Haptoglobin, increased retic
(3) Post-transfusion purpura: within 1 week, anti-HPA-1a Ab; Tx: IVIg and watch for transfusion-induced thrombocytopenia with next transfusion
(4) TRALI (ARDs picture with hypotension after transfusion; Tx: vent/supportive fluids) vs TACO (hypertension; Tx: diuretics)
Other
Sickle Cell:
- may present as diffuse pulmonary infiltrates that mimic PE/PNA/appendicitis, but with >2g/dL Hb drop and elevated LDH/retic
- acute chest syndrome --> Tx: exchange transfusion if Hb <10
- associated with pulmonary HTN and increased risk for CVA (BUT DO NOT NEED PLAVIX; instead CVA PPx with monthly 2 unit transfusions)
- Dx: Hb electrophoresis
- chronic Tx with 2 pain crisis/year or h/o ACS: hydroxyurea (but CI in pregnancy and AKI)
*vs Fat embolus (long bone fx): fever, CP, thrombocytopenia, multiorgan failure; BAL shows fat bodies
*vs. Aplastic crisis (Parvovirus/B19): low retic count
Plasma exchange indications:
(1) Guillain Barre (symmetric ascending flaccid paralysis with reduced DTRs)
(2) Myasthenia gravis (ocular-->facial -->proximal muscle weakness that doesn’t fatigue)
(3) TTP (neurologic symptoms with hemolytic anemia and thrombocytopenia)
(4) Goodpasture (anti-GBM nephritis (hematuria, hypertension) with hemoptysis)
(5) Cryoglobulinemia (cold-induced nephritis, low complements, associated with HCV)
*AE of plasma exchange = hypocalcemia from citrate: perioral numbness, tingling, anxiety/vomit; Tx: calcium gluconate
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Menstrual problems in adolescence: relationship to serum vitamins A and E, and systemic inflammation.
PMID: Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2019 Nov 16. Epub 2019 Nov 16. PMID: 31734759 Abstract Title: Menstrual problems in adolescence: relationship to serum vitamins A and E, and systemic inflammation. Abstract: BACKGROUND: Vitamin status and inflammatory mechanisms may be related to menstrual cycle abnormalities. We investigated the associations between serum fat soluble vitamin (vitamins A and E) concentrations and biomarkers of inflammation and antioxidant status with menstrual characteristics, primary dysmenorrhea (PD) and premenstrual syndrome (PMS) in healthy adolescents.METHODS: A total of 897 adolescent girls either suffering from PMS (n = 134), PD (n = 322), PMS and PD (n = 293) or healthy adolescents (n = 148) were recruited. Serum vitamin A and E, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), antibody titers to Hsp27 (anti-Hsp27), serum prooxidant-antioxidant balance (PAB), WBC, mean platelet volume (MPV), and platelet distribution width (PDW) and RBC distribution width (RDW) were measured. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) and RDW-to-platelet ratio (RPR) were calculated.RESULTS: Girls with long bleeding periods had lower concentrations of serum vitamin E compared to those who reported a normal period duration. There were significantly differences between the groups reporting oligomenorrhea, regular menses and polymenorrhea with respect to NLR, RPR, MPV and PDW. Logistic regression demonstrated that the presence of both PMS and PD was positively related to higher serum hs-CRP, PAB and NLR, while serum vitamin A level was inversely related to the presence of PMS.CONCLUSIONS: We found that serum vitamin A, hs-CRP, PAB and NLR are significantly associated with the presence of PMS and PD. Inflammatory processes may contribute to the etiology, symptoms and severity of menstrual disorders. Prospective studies are needed to elucidate the possibility of targeting oxidative stress and inflammatory process for the amelioration of menstrual symptoms.
read more
0 notes
Link
Cancer Blood Test Options
There are often certain blood tests that may prove to be helpful for some people with a cancer diagnosis. This list of different tests, though not completely comprehensive, is a general guide that patients may follow to help them understand the benefits of specific testing. No one test will be best for all people with a given type of cancer and not everyone will show positive cancer markers or other blood markers so testing is not relevant for everyone.
Bone Specific Alkaline Phosphatase (BAP) Test
This test measures blood levels of a form the enzyme Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) which is produced by the skeletal system. Different types of ALP are produced by various systems throughout the body. Bone ALP levels increase when the bones are growing. Children who are still growing normally have higher levels of ALP as do people who are healing from one or more broken bones. Abnormal Bone ALP levels are often associated with a number of disorders including Osteoporosis, Bone Cancer, and Paget’s disease.
Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP)
The Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP) blood test can be used to screen or monitor treatment for certain types of cancer. Elevated AFP levels in men and non-pregnant women are often indicative of cancers in the testicles, ovaries, stomach, pancreas, or liver. Measuring AFP levels can help determine if a person has cancer, gauge how far along it is, or determine how effective their treatment is. It is important to note that not all people will develop elevated AFP levels so negative results should not be considered definitive proof that a person is cancer free. AFP may also be elevated in people with liver diseases such as Hepatitis or Cirrhosis.
Blood samples are on a laboratory form for Finding out the blood values
Amylase Blood Test
This test measures the level of Amylase in the blood. Amylase is an enzyme produced by the pancreas, which aids in digestion. Elevated levels of Amylase can indicate a number of conditions such as pancreatitis, pancreatic tumor, or gallstones blocking the pancreatic duct.
Amylase testing is typically ordered when a person is experiencing symptoms of a pancreatic disorder such as abdominal or back pain, fever, loss of appetite or nausea. It can also be used to monitor treatment for pancreatitis or pancreatic cancer or after having a gallstone removed.
Amylase testing is often done with a Lipase test.
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) Blood Test
This test measures the level of Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) in the blood. Antidiuretic Hormone is also known as Arginine Vasopressin (AVP). ADH is a hormone, which helps to regulate how much water the kidneys absorb. Typically, the body produces ADH in response to increased blood osmolality. Osmolality refers to the amount of dissolved particles in the blood. ADH production causes the kidneys to conserve water rather than release it from the body in urine. The increased water causes the blood to be diluted which decreases osmolality. Normal ADH production helps maintain a healthy water balance in the body. ADH deficiency can result in frequent urination, dehydration, excessive thirst, and high sodium levels. Excessive ADH levels can cause increased blood pressure, nausea, lethargy, disorientation, and low sodium levels. Irregular ADH levels can be caused by a number of conditions including several types of diabetes and various forms of cancer.
An ADH test may be ordered when someone has symptoms such as headache, nausea, confusion, excessive thirst, or frequent urination. It may be done as a follow-up to low blood sodium levels. ADH is often measured along with osmolality.
Beta 2 (B2) Microglobulin Blood Test
This test measures the level of Beta-2 Microglobulin in the blood. B2 Microglobulin is a protein found on the surface of many types of cells in the body. B2 levels are often increased in people with certain types of cancers such as Multiple Myeloma and Lymphoma. Other conditions such as HIV or Cytomegalovirus may also increase B2-Microglobulin levels. B2 is most often used as a tumor marker. While it is not used as a screening, measuring B2 levels can help assess the severity of a person’s cancer. It is also used in some cases to measure how effective someone’s treatment has been.
B2-Microglobulin testing is typically ordered after a person has been diagnosed with cancer such as Multiple Myeloma to determine what stage of the disease they are in.
CBC with Differential Blood Test
A Complete Blood Count (CBC) with Differential is a broad screening test which can aid in the diagnosis of a variety of conditions and diseases such as Anemia, Leukemia, bleeding disorders, and infections. This test is also useful in monitoring a person’s reaction to treatment when a condition, which affects blood cells, has been diagnosed.
A CBC includes the following measurements:
White Blood Cell Count (WBC) WBC’s protect the body against infections.
Red Blood Cell Count (RBC) RBC’s carry oxygen throughout the body.
Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW) is the variation in size of the RBC’s.
Hematocrit measures the percentage of blood made of up red blood cells.
Hemoglobin is a protein, which carries oxygen in the blood.
Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV) measures the average size of RBC’s.
Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (MCH) measures the average amount of hemoglobin in a red blood cell.
Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration (MCHC) is the average percentage of hemoglobin in a red blood cell.
Platelet Count measures cell fragments, which are vital for proper blood clotting.
Percentage and absolute differential count for types of WBC’s including neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils.
A CBC is often ordered as part of a routine health examination. It is also ordered when someone has symptoms, which may indicate a condition which affects the blood cells or is undergoing treatment such as chemotherapy which affects blood cells. A CBC is often ordered with other common blood tests such as a comprehensive metabolic panel.
CEA (Carcinoembryonic Antigen) Blood Test
This test measures the level of Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA) in the blood. CEA is a protein which is often elevated in people with certain types of cancer. CEA is used as a tumor marker for a variety of cancers including colon, breast, rectum, liver, pancreas, stomach and ovaries. This test is not typically used as a screening for cancer because not all cancer cases will show elevated CEA and CEA can be elevated in other conditions such as cirrhosis, inflammation, ulcers, emphysema and benign breast disease as well as in people who smoke.
CEA is usually measured when a person is diagnosed with cancer and then subsequently to monitor their response to treatment. While CEA is not typically used as a screening, it can be ordered when a person is suspected of having cancer but has not been diagnosed if a doctor determines it is relevant.
Calcitonin Blood Test
This test measures levels of Calcitonin in the blood. Calcitonin is a hormone produced by the Thyroid Gland. Calcitonin production helps regulate the body’s levels of calcium and phosphate. In most cases, having a deficiency or overload of calcitonin does not cause any negative health effects. For this reason, there is still a lack of research on the exact purpose calcitonin serves.
A rare form of thyroid cancer which affects the C-cells, the same cells which produce calcitonin, may cause levels to be elevated. A calcitonin test may aid in the diagnosis when a person is suspected of having this form of cancer. Calcitonin may also be used to treat people with osteoporosis or Paget’s disease. In these cases, monitoring Calcitonin levels can help determine how well they are responding to therapy or find the optimal dosage.
Calcium Blood Test
This test measures Calcium levels in the blood. Calcium is a mineral which is important for healthy functioning of the heart, muscles and nervous system as well as proper bone formation. The body will pull calcium from the bones to maintain blood levels when a person is not ingesting enough calcium or has a disorder which prevents proper absorption.
Calcium testing is frequently part of a general health screening. It may also be ordered when someone has kidney disease, thyroid disease, cancer, malabsorption or malnutrition.
A Calcium test is also included as part of a Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP), Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP), and Renal Function Panel.
This test measures total calcium levels, which include both free and bound. An Ionized Calcium Serum test is available for those who wish to only measure the free or unbound portion of calcium and can be beneficial to measure destruction of bone.
Cancer Antigen (CA) 15-3 Blood Test
The Cancer Antigen 15-3 test is typically used to monitor people who have been diagnosed with Breast Cancer. CA 15-3 is a protein which is typically elevated in people with cancerous breast tumors. CA 15-3 may also be elevated in other types of cancer such as lung, pancreas, prostate, ovary and colon. People with benign diseases of the liver and breast as well as other condition such as Cirrhosis or Hepatitis or even people who are healthy may see elevated CA 15-3 levels as well. While CA 15-3 is not typically sensitive or specific enough to be used as a screening for breast cancer, it can be helpful for monitoring response to treatment or to look for a recurrence of cancer.
This test is typically ordered when a person has been diagnosed with Breast Cancer to determine how advanced it is as a monitoring test – though again, NOT all with breast cancer will show positive. It may also be ordered periodically during treatment or when checking to see if the cancer had returned.
Cancer Antigen CA 19-9 Blood Test
The Cancer Antigen (CA) 19-9 test is often used to aid in the diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer. CA 19-9 is a protein found on the surface of some cancer cells. CA 19-9 is elevated in about 70-95% of pancreatic cancer cases. It can also be elevated in cases of colorectal cancer, lung cancer and gallbladder cancer. While a CA 19-9 test can be used to differentiate types of cancer or monitor response to treatment, it is not sensitive enough to be used as an initial screening by itself.
A CA 19-9 test is often ordered with other tests such as a CEA, Hepatic Function, or Bilirubin when a person is experiencing symptoms associated with Pancreatic Cancer. It is also used to monitor how well a person is responding to treatment for pancreatic cancer. Because not every person with pancreatic cancer will show elevated levels of CA 19-9, this test will not always be an effective tumor marker.
Cancer Antigen CA 27.29 Blood Test
The Cancer Antigen (CA) 27.29 test is used to monitor people with Breast Cancer. CA 27.29 in a protein that is used as a tumor marker to gauge how advanced a person’s cancer is. This test can also be used to determine how well a person is responding to treatment or therapy. The CA 27.29 is not intended to be used as a screening. This test is not considered specific enough to accurately determine if an undiagnosed person has breast cancer. It is important to consult your doctor in determining the appropriate testing to aid in making a diagnosis.
Please note that test results from different labs and/or testing methods should not be used interchangeably.
This test may be ordered when a person has been diagnosed with Breast Cancer or to monitor their response to treatment.
Cancer Antigen 125 (CA 125) Blood Test
This test measures Cancer Antigen (CA) 125 in the blood. CA-125 is a protein which is present on the surface of most ovarian cancer cells. Elevated levels of CA-125 are often present in women with ovarian cancer. CA-125 testing is typically done to monitor treatment for ovarian cancer or to periodically check someone who is in remission to see if the cancer may have come back. This test is also used to screen women who have a high risk of developing ovarian cancer due to family history.
It is important to note that other conditions such as pregnancy, menstruation or pelvic inflammatory disease may also cause elevated levels of CA-125. For this reason, CA-125 testing is not typically used as a general screening. In some cases, even when someone has ovarian cancer, they may not show elevated CA-125. In such cases, CA-125 is not a useful marker for monitoring treatment.
Comprehensive Metabolic Panel Blood Test
A Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP) is a broad screening test which is used to evaluate organ function and electrolyte balance as well as aid in the diagnosis of conditions such as diabetes, liver disease, and kidney disease. This test is also useful for monitoring people receiving treatment for conditions which affect the liver or kidneys. The CMP contains all of the measurements in a Basic Metabolic Panel and most of the same measurements as a Hepatic Function Panel and a Renal Function Panel.
A CMP includes the following tests:
Glucose: Abnormal blood sugar levels can indicate a number of conditions including Diabetes.
BUN (Blood Urea Nitrogen): Used to evaluate kidney function.
Creatinine: Used to Evaluate Kidney Function.
BUN/Creatinine Ratio: This calculation is only provided if the measurements for BUN or Creatinine are out of range or if the person tested is under the age of 19.
Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR): Used to screen for and detect early kidney damage.
Sodium, Potassium, Chloride, Carbon Dioxide, Total: An improper electrolyte balance can indicate a number of conditions including dehydration, Addison’s disease, kidney disease, and Diabetes.
Calcium: Normal levels are important for healthy bones, heart, nerves, kidneys, and teeth.
Protein, Total: Aids in measuring Liver and Kidney function as well as nutritional status.
Albumin: A protein important for healthy liver and kidney function.
Globulin: A protein that helps the body fight infection and the blood to clot properly.
Albumin/Globulin Ratio: Can help identify various liver problems when combined with other test results.
Bilirubin, Total: Helps to identify conditions such as anemia, sickle cell, hepatitis, cirrhosis, alcohol, and drug abuse.
Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP): Used to detect liver disease or bone disorders.
Aspartate Amino Transferase (AST): Used to evaluate liver function, very high levels often indicate Hepatitis
Alanine Amino Transferase (ALT): Used to help identify liver damage.
A CMP is usually ordered as part of a routine health check. It may also be ordered when someone is experiencing symptoms which may indicate conditions affecting the liver or kidneys.
HTLV 1&2 Antibodies Blood Test
This test looks for antibodies which the body develops in response to infection with the Human T-Cell Lymphotropic Virus (HTLV). HTLV infects white blood cells which are important to the body’s immune system. HTLV infection can be responsible for the development of a number of conditions including Leukemia, Lymphoma, and nervous system disorders. The HTLV 1&2 Abs test detects and differentiates both type 1 and type 2 HTLV infections.
An estimated 15-20 million people worldwide suffer from HTLV infections. HTLV is typically spread through sexual contact and exposure to infected blood, especially through intravenous drug use. Infected mothers can spread the infection to their infants during pregnancy or breast feeding. After infection, HTLV will remain in the body for life. Some people will develop HTLV related illnesses months or years after their initial exposure. Most HTLV infections show no symptoms. An infected person can spread the virus to others even if they are asymptomatic.
Risk factors for HTLV infection include:
Having multiple sexual partners
Being an IV drug user
Having a history of blood transfusions
Living in or having a sexual partner from parts of the world where HTLV is prevalent such as Southwestern Japan, parts of Africa, the Caribbean, and the Southeastern U.S.
HTLV testing is typically ordered to help identify or rule out HTLV as the cause of conditions such as Leukemia, Lymphoma, or nervous system disorders. It can also be ordered by people who are concerned they have had an exposure to HTLV especially if they have been with someone who has also tested positive for HTLV antibodies.. Due to the common lack of symptoms, testing is recommended for anyone who engages in high risk activities.
Hemoglobin Blood Test
This test measures Hemoglobin in the blood. Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells which enables them to bind with oxygen and carry it throughout the body. Hemoglobin levels are affected by conditions which cause a rise or drop in red blood cell levels. Low hemoglobin is often indicative of anemia which can be caused by excessive blood loss, nutritional deficiencies such as iron or B12, bone marrow disorders or kidney damage. Higher than normal hemoglobin can be caused by dehydration, lung disease, heart disease or kidney tumors
Hemoglobin is often measured as part of routine general health blood work. It is also measured when a person is suspected of having anemia due to symptoms such as fatigue, lack of energy, paleness, shortness of breath or fainting. It can also be ordered to monitor treatment for anemia.
Hemoglobin is also part of a Complete Blood Count (CBC).
Hepatic Function Blood Test
The Hepatic Function test (Liver Function Panel) is a common health screening that can help to identify conditions affecting the liver. This test is also used to monitor people who are being treated for liver disease.
The Hepatic Function Panel includes the following tests:
Alanine Amino Transferase (ALT): An enzyme produced by the liver which is typically elevated in cases of liver damage.
Aspartate Amino Transferase (AST): A liver enzyme which is typically elevated in cases of liver damage or Hepatitis.
Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP): An enzyme found in the liver and bones which is increased when there is liver or bone damage.
Protein, Total: A measure of albumin and all other proteins on the blood.
Albumin: The main protein produced by the liver.
Bilirubin, Total: Helps to identify conditions such as anemia , sickle cell, hepatitis, cirrhosis, alcohol and drug abuse.
Bilirubin Direct: Used in conjunction with Total Bilirubin to aid in the diagnosis of liver disorders.
Globulin (calculated) and Albumin/Globulin ratio
Bilirubin, Indirect calculated
A Hepatic Function Panel is usually ordered as a general health screening. It can also be ordered when someone is experiencing symptoms associated with liver disorders or has risk factors for Liver Disease. Risk factors can include heavy alcohol use, diabetes, possible exposure to Hepatitis viruses, a family history of liver disease, high blood pressure, and taking medications which may damage the liver.
Immunoglobulin Antibody Blood Test IgA IgG IgM
This Immunoglobulin test measures levels of 3 classes of immunoglobulins in the blood. Results will include measurements for Immunoglobulin A (IgA), Immunoglobulin G (IgG) and Immunoglobulin M (IgM). Immunoglobulins, or antibodies, are an important part of the immune system which fight off bacteria, viruses and other foreign organisms. Measuring Immunoglobulin levels can help evaluate a person’s immune system.
This test may be ordered when a person is suffering from chronic infections, especially of the lungs or gastrointestinal tract. It can also help to diagnose various conditions resulting in excess or deficiencies in one or more types of antibodies. Abnormal results will typically need to be followed up with further testing.
Insulin-like Growth Factor IGF 2 Test
This test measures levels of Insulin-like Growth Factor 2 (IGF-2) in the blood. IGF-2 is a hormone produced by the liver. Its primary function is to regulate the production of Growth Hormone (GH) during growth and development of a fetus during gestation. IGF-2 is also linked to the production of other hormones including Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1), Luteinizing Hormone (LH), Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) and Progesterone. Deficiency in IGF-2 can contribute to growth problems in children. Certain types of tumors can produce an excess of IGF-2. As a result, measuring IGF-2 levels can be useful in the diagnosis or monitoring of treatment for some types of cancer including prostate, colon, breast and colorectal.
Lactic Acid Dehydrogenase Blood Test
This test measures Lactic Acid Dehydrogenase (LDH) in the blood. LDH is an enzyme found in most cells in the body. Typically, only a small amount of LDH is detectable in the blood. When cells are damaged, LDH is released into the blood causing levels to rise. Measuring LDH levels can indicate if there is tissue damage somewhere in the body. Conditions which can result in elevated LDH levels include anemia, meningitis, mononucleosis, HIV, sepsis, liver disease, kidney disease, muscle injury, broken bones and some types of cancers.
An LDH blood test is typically ordered along with a Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP) when a person is suspected of having a disease which causes tissue damage. Because an LDH test cannot identify where in the body the damage is, follow up testing will usually be necessary. LDH may also be used to monitor treatment for conditions such as cancer.
Natural Killer Cell and Activated T-Cell Test
This test provides several measurements related to the immune system including Natural Killer Cells (NK). Natural Killer Cells (NK Cells) are a type of lymphocyte, or white blood cell, which play an important role in the body’s immune system. NK cells help to kill tumor cells or cells infected with a virus. NK cells are identified and differentiated from other types of immune cells by certain antigens called CD proteins. NK cells are CD56 positive and CD3 negative. The measurements in this test can help assess the level of NK cells as well as their state of activation. Results for this test should be interpreted by a person’s doctor.
This test includes:
Percentage CD3+
Absolute CD3+
Percentage CD3+CD25+ (IL-2 Receptor)
Absolute CD3+CD25+
Percentage CD3-CD56+ (NK)
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
This test can be useful in diagnosing or monitoring treatment to conditions such as leukemia, viral hepatitis, and HIV.
Occult Blood Fecal Test
A Fecal Occult Blood Test looks for the presence of microscopic or invisible blood in the stool. Blood in the stool can be a sign of a number of conditions such as
Abnormal growths or polyps in the colon
Cancer in the colon or rectum
Anemia
Hemorrhoids
Intestinal infections
Ulcers
Crohn’s Disease
Diverticular Disease
This test is commonly ordered as a routine screening to aid in the early detection of Colon Cancer. Yearly testing is recommended for people age 50 and above. This test may also be ordered by people experiencing symptoms of anemia.
Because certain conditions may cause intermittent bleeding, results from multiple specimens may be required for results to be conclusive. If blood is detected, it is important that a doctor is consulted to determine a diagnosis. Additional procedures such as a colonoscopy may be required.
PSA Ultrasensitive Blood Test
The PSA Ultrasensitive Test measures the level of Prostate Specific Antigen in the blood. PSA is a protein produced by the prostate gland. Typically, elevated PSA levels are indicative of an increased risk of having Prostate Cancer. This test is more sensitive than a regular PSA test and is able to detect PSA in smaller amounts. This test is typically used to monitor men who are receiving treatment or have had surgery for Prostate Cancer. The PSA Ultrasensitive Test is not typically used as an initial screening for Prostate Cancer. For this purpose, most customers order the Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test.
PSA – Prostate Specific Antigen Test
The Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) test is a common screening for prostate cancer. This test measures a protein that is produced by the prostate gland. Elevated PSA levels may indicate a higher likelihood of having prostate cancer. The PSA test is also used to monitor a person’s response to cancer treatment.
It is important to note that not all cases of prostate cancer will show elevated total PSA levels and there are other conditions which may cause higher PSA levels besides cancer.
Prostate Specific Antigen Free: Total Ratio Test
The Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Free:Total Ratio provides several measurements which help to screen for prostate cancer. This test includes measurements for PSA, Free PSA and % Free PSA. PSA is a protein produced by the prostate gland. Elevated PSA levels may indicate a higher likelihood of having prostate cancer. However, not all cases of prostate cancer will cause elevated PSA levels and there are conditions other than cancer which may cause elevated PSA.
Free PSA is the portion of PSA which is not bound to other proteins in the blood. Generally, men with lower levels of Free PSA have a higher likelihood of having Prostate Cancer. Free PSA measurements are useful for people with borderline or moderately increased total PSA levels. A test which includes Free PSA is often ordered as a follow up to a high PSA test.
Total Protein Blood Test
This test measures Protein levels in the blood. Proteins are an essential part of the tissues and cells that make up the body. This test measures the total amount of all proteins (including albumin and globulins) in a person’s blood. Measuring protein is a part of most routine general health checks. Protein measurements are a reflection of a number of health conditions including nutritional status, liver and kidney function.
Protein testing is often done as part of routine blood work for general wellness. It may also be used to aid in diagnosing or monitoring liver and kidney disease. It may be used to evaluate nutritional status when someone has experienced unexplained weight loss or shows signs of malnutrition.
A Protein test is also included in a Comprehensive Metabolic Panel and a Hepatic Function test.
Renal (Kidney) Function Panel
A Renal Function Panel (Kidney Function Test) is a common health screening used to help detect conditions affecting the kidneys. It can also be used to monitor people who are receiving treatment for illnesses affecting the kidneys.
A Renal Panel includes the following tests:
Glucose: Abnormal blood sugar levels can indicate a number of conditions including Diabetes. Over time, high glucose levels can damage the kidneys.
BUN (Blood Urea Nitrogen): A waste product filtered through the kidneys. Used to evaluate kidney function.
Creatinine: A waste product produced by the muscles which is filtered through the kidneys. Used to Evaluate Kidney Function.
BUN/Creatinine Ratio: This measurement can indicate kidney disease or conditions such as dehydration or intestinal bleeding.
Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR): The amount of blood filtered by the kidneys. Used to screen for and detect early kidney damage.
Calcium: Normal levels are important for healthy bones, heart, nerves, kidneys, and teeth.
Sodium, Potassium, Chloride, Carbon Dioxide, Total: An improper electrolyte balance can indicate a number of conditions including dehydration, Addison’s disease, kidney disease, and Diabetes.
Albumin: A protein important for healthy liver and kidney function.
Phosphorus/Phosphate: Low levels of phosphorus can be indicative of a number of illnesses while high levels may be a symptom of kidney failure.
This panel is typically ordered as part of a general health screening. It may also be ordered when someone has symptoms which may indicate kidney disease or is being treated for kidney disease.
Vitamin D, 1, 25-dihydroxy Blood Test
This test is used to measure Vitamin D levels in the blood. The Vitamin D 25-Dihydroxy test measures the active form of Vitamin D which is produced in the liver and kidneys through the conversion of Vitamin D 25-Hydroxy. This test is not typically used as a routine measurement to assess if a person has a vitamin D deficiency because it may show normal results even if a person has an overall deficiency. It is more useful when a person is suspected of having a condition which is producing an excess of vitamin D such as Sarcoidosis or certain types of Lymphoma. This test may also be ordered to aid in the diagnosis or Parathyroid disorder or kidney failure.
For a test which is more commonly used to detect if a person may be suffering from a Vitamin D Deficiency, customers may order the Vitamin D 25-Hydroxy Test.
Vitamin D, 25-Hydroxy Blood Test
This test is used to measure the level of Vitamin D in the blood. Vitamin D is necessary for the proper growth and health of teeth and bones. It also helps in the healthy developments of the immune system as well as various tissues throughout the body. Vitamin D typically comes from 2 sources. D3 (cholecalciferol) is produced by the body when the skin is exposed to sunlight. For many people, D3 makes up the majority of the vitamin D in their body. D2 (ergocalciferol) is found in certain foods as well as vitamins and supplements. This test provides a combined measurement for D2 and D3.
Vitamin D deficiency is typically caused by someone not getting enough sun exposure. While Vitamin D is found in some foods such as fatty fish, egg yolks, milk and cheese, the majority of people do not get sufficient vitamin D from their diet so exposure to sunlight is the primary source. Symptoms of vitamin D deficiency can include tiredness, weakness, aches and pains and frequent infections. Conditions such as Cystic Fibrosis and Crohn’s Disease which interfere with the body’s ability to absorb fat and fat-soluble vitamins can also cause vitamin D deficiency.
This test is typically ordered when someone had signs of vitamin D deficiency which can include conditions affecting the bones such as Rickets or Osteoporosis.
Patients may also order a Vitamin D, 1, 25-Dihydroxy Test which can aid in the diagnosis of conditions which cause excessive vitamin D production.
For more information on running different tests, we suggest you ask your local doctor or contact our clinic.
Dr. Kevin Conners, D.PSc., FICT, FAARFM
Dr. Conners graduated with his doctorate from Northwestern Health Sciences University in 1986 and has been studying alternative cancer care for over 20 years. He holds AMA Fellowships in Regenerative & Functional Medicine and Integrative Cancer Therapy.
He is the author of numerous books including, Stop Fighting Cancer and Start Treating the Cause, Cancer Can’t Kill You if You’re Already Dead, Help, My Body is Killing Me, Chronic Lyme, 3 Phases of Lyme, 23 Steps to Freedom, and many more you can download for FREE on our books page.
via News
0 notes
Text
Best hemogram test in Pune-Indocare diagnostics
Haemogram additionally cited as complete blood count or complete haemogram check may be a cluster of checkperformed on a sample of blood. Haemogram is broad screening panel that checks for the presence of any diseases and infections within the body. Haemogram tests in the main the 3 elements of the blood specifically Red Blood Cells, White Blood Cells and Platelets.
The checks performed beneath these 3 classes embrace a good array of test namely; Total WBC Count (TLC), Total red blood count (RBC), hemoglobin (HGB). Haematocrit (HCT), Mean Cell Volume (MCV), Mean Cell hemoglobin (MCH), Mean Cell hemoglobin Concentration (MCHC), platelets count, RDW-SD (RBC Distribution Width-Standard Deviation), Neutrophils, Lymphocytes, Monocytes, Eosinophils, Basophils, PCV (Packed Cell Volume), P/S (Peripheral Smear) Examination, , RDW-CV (RBC Distribution Width-Coefficient Of Variation), PDW (Platelet Distribution Width), MPV (Mean platelet Volume), P-LCR (Platelet giant Cell Ratio), pct (Platelet Crit), Absolute Neutrophils Count, Absolute Lymphocytes Count, Absolute Monocytes Count, Absolute Eosinophils Count, Absolute Basophils Count, And ESR (Erythrocyte sedimentation Rate).
The main advantage of Haemogram check is that it detects the slightest of abnormality gift within the blood and offers crucial data concerning the medical cause.
The haemogram check needs no special preparation and is conducted on a sample of blood. There square measurefew factors that may alter the check results then ought to be notified to the doctor. These factors square measureas follows;
Certain medications like diuretics, antibiotics, steroids, etc
Pregnancy
Certain kind of allergies
High triglyceride level
Smoking, stress, vigorous exercise
https://indocare.in
https://www.instagram.com/indocarediagnostics/
https://www.baazarpeth.com/2019/06/01/indocare-diagnostics-pune/
https://www.facebook.com/IndocareDiagnostic/
0 notes
Text
Complete Blood Count Test in Vadodara
An aggregate blood check, or CBC, is a key and astoundingly standard test that screens for particular issue that can affect your prospering. A CBC picks whether there are any extensions or diminishments in your platelet checks. Standard regards change subordinate upon your age and your sexual introduction.Your lab report will uncover to you the solid regard go for your age and sex.An whole blood check test measures a few zones and features of your blood, including:
Red platelets, which pass on oxygen White platelets, which fight sickness Hemoglobin, the oxygen-passing on protein in red platelets Hematocrit, the level of red platelets to the fluid piece, or plasma, in your blood Platelets, which help with blood coagulating Abnormal developments or diminishments in cell join as revealed an aggregate blood count may demonstrate that you have a noteworthy therapeutic condition that calls for help assessment.
Use OF COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT
You may get a CBC as a section of your yearly enrollment. Your lord may in like way diagram it to: See in case you have another recovering issue or to clear up reactions like weakness, fever, hurting, or feeling tired Keep an eye on a blood condition you starting at now have See how meds or pharmaceuticals like chemotherapy are impacting your blood
System for Complete Blood Count Test
A band is wrapped around the arm, 3– 4 crawls over the party site (shallow vein that exists in the elbow pit) A 70% alcohol pad is used to clean the skin A needle is then continued as exhibited by and installed into a vein that can be seen from the skin The blood is dragged out from the needle by a gush, saved in a vessel and settled with your name The depiction is then taken to a lab for examination
It’s to a psyche boggling degree clear and takes just a few minutes. A mending escort or lab tech will take an occasion of blood by embeddings a needle into a vein in your arm. She’ll send it to the lab for survey. You can leave and get faultless back to your standard timetable.
System REQUIREMENT
Outline →Whole blood
Volume →Fill tube to oblige.
Holder →Lavender-top (EDTA) tube.
The blood test drawn for a total blood combine is poor down a strong research center. The total blood tally examination is routinely and tirelessly done by systems for robotized machines in various examination working conditions. A little instance of the blood drawn from a man is empowered into the machine and inside a few minutes, the estimations of the parts of the entire blood check are showed up and printed for survey. This is known as a robotized cell check and differential.
The standard method to investigate these information is to get a little case of the collected blood and place it on a glass slide for visual examination under an opening up motivation behind combining. This is generally done by a prepared lab technologist or a specialist. This framework is still broadly utilized when yielded aftereffects of a total blood check require likewise concentrate to express certain bewildering respects, or a master needs to perceive how the platelets look (for instance, if any unpredictable highlights are open which would not be tended to by a mechanized finish blood tally). This is known as the manual differential examination.
Relationship of the entire blood check are far reaching. Right when all is said in done, the entire blood think about should be possible piece of routine flourishing exam and general screening by an ace. It might be requested if an ailment or sickliness is suspected. It might in like way be requested to study sporadic kicking the holder.
As picked already, a move of the white platelet check or an assortment from the standard of the white platelet differential might be suggestive of a disease or aggravating. A high or a low white platelet fuse could like way be an indication of central change, for example, leukemia or lymphoma.
A low red platelet or hemoglobin tally dependably displays press require (low blood). Whiteness, frequently observed as low hemoglobin or low hematocrit on the total blood tally, deduces that a covered infection and it isn’t a perplexity itself. Delicacy can have differing causes including blood hardship, bone marrow issues, sound inadequacies, natural hemoglobin imperative or sensible issues , or kidney disappointment. These are just the most refreshing explanations behind iron insufficiency, and the layout of all reasons for whiteness is extraordinarily wide. Need found in an entire blood check might be suggestive of pushing moderate blood inconvenience and, as needs be, can be utilized to see malignancies, for example, colon tumor. In the event that sickliness is seen, when in doubt the MCV and RDW give some extra indications concerning the conceivable illustrations behind whiteness.
A low platelet fuse may like way be found in the total blood check. This might be an aftereffect of bone marrow issues, two or three pharmaceuticals or over the best liquor utilize, immunologic or acquired issues, affected liver malady, or tumors, for example, leukemia. The MPV may display how quickly platelets are made in the bone marrow and discharged into the course structure. A high platelet check may in like way be suggestive of an aggravation or ragged looking, for example, leukemia and lymphoma.
Baroda Clinical Laboratory — Gorwa, Vadodara
Now you can get away with the trouble of finding an accurate diagnostic lab, Baroda Clinical Laboratory is now available in Gorwa area, Vadodara. With accreditation from NABL and a number of well experienced staff and technicians it gives you accurate and detailed reports.
Jhaveri Pathology Laboratory — Manjalpur, Vadodara
Jhaveri Pathology Laboratory provides diagnostic test services at attractive rates, with a guarantee to deliver reports within 72 hrs based on the test conducted. You can book majority of known tests like HB electrophoresis, SGPT, Anti Thyroglobulin, SGOT and Bicarbonate, Bilirubin. It provides comprehensive range of lab tests covering more than 75 tests.
0 notes
Text
Complete Blood Count Test in Thane
An aggregate blood check, or CBC, is a key and astoundingly standard test that screens for particular issue that can affect your prospering. A CBC picks whether there are any extensions or diminishments in your platelet checks. Standard regards change subordinate upon your age and your sexual introduction. Complete Blood Count Test in Faridabad Your lab report will uncover to you the solid regard go for your age and sex.An whole blood check test measures a few zones and features of your blood, including:
Red platelets, which pass on oxygen White platelets, which fight sickness Hemoglobin, the oxygen-passing on protein in red platelets Hematocrit, the level of red platelets to the fluid piece, or plasma, in your blood Platelets, which help with blood coagulating Abnormal developments or diminishments in cell join as revealed an aggregate blood count may demonstrate that you have a noteworthy therapeutic condition that calls for help assessment.
Use OF COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT
You may get a CBC as a section of your yearly enrollment. Your lord may in like way diagram it to: See in case you have another recovering issue or to clear up reactions like weakness, fever, hurting, or feeling tired Keep an eye on a blood condition you starting at now have See how meds or pharmaceuticals like chemotherapy are impacting your blood
System for Complete Blood Count Test
A band is wrapped around the arm, 3– 4 crawls over the party site (shallow vein that exists in the elbow pit) A 70% alcohol pad is used to clean the skin A needle is then continued as exhibited by and installed into a vein that can be seen from the skin The blood is dragged out from the needle by a gush, saved in a vessel and settled with your name The depiction is then taken to a lab for examination
It’s to a psyche boggling degree clear and takes just a few minutes. A mending escort or lab tech will take an occasion of blood by embeddings a needle into a vein in your arm. She’ll send it to the lab for survey. You can leave and get faultless back to your standard timetable.
System REQUIREMENT
Outline →Whole blood
Volume →Fill tube to oblige.
Holder →Lavender-top (EDTA) tube.
The blood test drawn for a total blood combine is poor down a strong research center. The total blood tally examination is routinely and tirelessly done by systems for robotized machines in various examination working conditions. A little instance of the blood drawn from a man is empowered into the machine and inside a few minutes, the estimations of the parts of the entire blood check are showed up and printed for survey. This is known as a robotized cell check and differential.
The standard method to investigate these information is to get a little case of the collected blood and place it on a glass slide for visual examination under an opening up motivation behind combining. This is generally done by a prepared lab technologist or a specialist. This framework is still broadly utilized when yielded aftereffects of a total blood check require likewise concentrate to express certain bewildering respects, or a master needs to perceive how the platelets look (for instance, if any unpredictable highlights are open which would not be tended to by a mechanized finish blood tally). This is known as the manual differential examination.
Relationship of the entire blood check are far reaching. Right when all is said in done, the entire blood think about should be possible piece of routine flourishing exam and general screening by an ace. It might be requested if an ailment or sickliness is suspected. It might in like way be requested to study sporadic kicking the holder.
As picked already, a move of the white platelet check or an assortment from the standard of the white platelet differential might be suggestive of a disease or aggravating. A high or a low white platelet fuse could like way be an indication of central change, for example, leukemia or lymphoma.
A low red platelet or hemoglobin tally dependably displays press require (low blood). Whiteness, frequently observed as low hemoglobin or low hematocrit on the total blood tally, deduces that a covered infection and it isn’t a perplexity itself. Delicacy can have differing causes including blood hardship, bone marrow issues, sound inadequacies, natural hemoglobin imperative or sensible issues , or kidney disappointment. These are just the most refreshing explanations behind iron insufficiency, and the layout of all reasons for whiteness is extraordinarily wide. Need found in an entire blood check might be suggestive of pushing moderate blood inconvenience and, as needs be, can be utilized to see malignancies, for example, colon tumor. In the event that sickliness is seen, when in doubt the MCV and RDW give some extra indications concerning the conceivable illustrations behind whiteness.
A low platelet fuse may like way be found in the total blood check. This might be an aftereffect of bone marrow issues, two or three pharmaceuticals or over the best liquor utilize, immunologic or acquired issues, affected liver malady, or tumors, for example, leukemia. The MPV may display how quickly platelets are made in the bone marrow and discharged into the course structure. A high platelet check may in like way be suggestive of an aggravation or ragged looking, for example, leukemia and lymphoma.
Shree Pathology Laboratory — Ulhasnagar, Thane
Shree Pathology Laboratory ( Dr Lal PathLabs ) is a well known diagnostic laboratory situated in Ulhasnagar, Thane. Shree Pathology Laboratory ( Dr Lal PathLabs ) offers a wide range of diagnostic tests for both blood and urine, with a total number of 58 tests including tests like SGOT AST Aspartate Transaminase, BETA HCG Total Quantitative Maternal, ABO Group and Rh Type Forward and Reverse Grouping, Blood Urea Nitrogen BUN and Sodium Serum, C Reactive Protein CRP. It also provide complete body scan and major scans at highly competitive prices.
Relief Laboratory — Ulhasnagar, Thane
Relief Laboratory is a well known diagnostic laboratory situated in Ulhasnagar, Thane. Relief Laboratory offers a wide range of diagnostic tests for both blood and urine, with a total number of 20 tests including tests like Bilirubin, Blood Group, Cholesterol Total, Complete Blood Count and Blood Sugar, Iron Test. It also provide complete body scan and major scans at highly competitive prices.
0 notes
Text
Complete Blood Count Test in Nashik
An aggregate blood check, or CBC, is a key and astoundingly standard test that screens for particular issue that can affect your prospering. A CBC picks whether there are any extensions or diminishments in your platelet checks. Standard regards change subordinate upon your age and your sexual introduction. Complete Blood Count Test in Faridabad Your lab report will uncover to you the solid regard go for your age and sex.An whole blood check test measures a few zones and features of your blood, including:
Red platelets, which pass on oxygen White platelets, which fight sickness Hemoglobin, the oxygen-passing on protein in red platelets Hematocrit, the level of red platelets to the fluid piece, or plasma, in your blood Platelets, which help with blood coagulating Abnormal developments or diminishments in cell join as revealed an aggregate blood count may demonstrate that you have a noteworthy therapeutic condition that calls for help assessment.
Use OF COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT
You may get a CBC as a section of your yearly enrollment. Your lord may in like way diagram it to: See in case you have another recovering issue or to clear up reactions like weakness, fever, hurting, or feeling tired Keep an eye on a blood condition you starting at now have See how meds or pharmaceuticals like chemotherapy are impacting your blood
System for Complete Blood Count Test
A band is wrapped around the arm, 3– 4 crawls over the party site (shallow vein that exists in the elbow pit) A 70% alcohol pad is used to clean the skin A needle is then continued as exhibited by and installed into a vein that can be seen from the skin The blood is dragged out from the needle by a gush, saved in a vessel and settled with your name The depiction is then taken to a lab for examination
It’s to a psyche boggling degree clear and takes just a few minutes. A mending escort or lab tech will take an occasion of blood by embeddings a needle into a vein in your arm. She’ll send it to the lab for survey. You can leave and get faultless back to your standard timetable.
System REQUIREMENT
Outline →Whole blood
Volume →Fill tube to oblige.
Holder →Lavender-top (EDTA) tube.
The blood test drawn for a total blood combine is poor down a strong research center. The total blood tally examination is routinely and tirelessly done by systems for robotized machines in various examination working conditions. A little instance of the blood drawn from a man is empowered into the machine and inside a few minutes, the estimations of the parts of the entire blood check are showed up and printed for survey. This is known as a robotized cell check and differential.
The standard method to investigate these information is to get a little case of the collected blood and place it on a glass slide for visual examination under an opening up motivation behind combining. This is generally done by a prepared lab technologist or a specialist. This framework is still broadly utilized when yielded aftereffects of a total blood check require likewise concentrate to express certain bewildering respects, or a master needs to perceive how the platelets look (for instance, if any unpredictable highlights are open which would not be tended to by a mechanized finish blood tally). This is known as the manual differential examination.
Relationship of the entire blood check are far reaching. Right when all is said in done, the entire blood think about should be possible piece of routine flourishing exam and general screening by an ace. It might be requested if an ailment or sickliness is suspected. It might in like way be requested to study sporadic kicking the holder.
As picked already, a move of the white platelet check or an assortment from the standard of the white platelet differential might be suggestive of a disease or aggravating. A high or a low white platelet fuse could like way be an indication of central change, for example, leukemia or lymphoma.
A low red platelet or hemoglobin tally dependably displays press require (low blood). Whiteness, frequently observed as low hemoglobin or low hematocrit on the total blood tally, deduces that a covered infection and it isn’t a perplexity itself. Delicacy can have differing causes including blood hardship, bone marrow issues, sound inadequacies, natural hemoglobin imperative or sensible issues , or kidney disappointment. These are just the most refreshing explanations behind iron insufficiency, and the layout of all reasons for whiteness is extraordinarily wide. Need found in an entire blood check might be suggestive of pushing moderate blood inconvenience and, as needs be, can be utilized to see malignancies, for example, colon tumor. In the event that sickliness is seen, when in doubt the MCV and RDW give some extra indications concerning the conceivable illustrations behind whiteness.
A low platelet fuse may like way be found in the total blood check. This might be an aftereffect of bone marrow issues, two or three pharmaceuticals or over the best liquor utilize, immunologic or acquired issues, affected liver malady, or tumors, for example, leukemia. The MPV may display how quickly platelets are made in the bone marrow and discharged into the course structure. A high platelet check may in like way be suggestive of an aggravation or ragged looking, for example, leukemia and lymphoma.
Nirnay Computerised Clnical Laboratory
Khutwad Nagar, Nashik
Nirnay Computerised Clnical Laboratory is a well known diagnostic laboratory situated in Khutwad Nagar, Nashik. Nirnay Computerised Clnical Laboratory offers a wide range of diagnostic tests for both blood and urine, with a total number of 191 tests including tests like Acid phosphatase, Acid phosphatase, ADA, HB ELECTROPHORESIS and SGPT, Albumin. It also provide complete body scan and major scans at highly competitive prices.
Clinipath Computerised Laboratory
Canada Corner, Nashik
Now you can get away with the trouble of finding an accurate diagnostic lab, Clinipath Computerised Laboratory is now available in Canada Corner area, Nashik. With accreditation from and a number of well experienced staff and technicians it gives you accurate and detailed reports.
0 notes
Text
Complete Blood Count Test in Hyderabad
A total blood check, or CBC, is a key and astoundingly standard test that screens for specific issue that can impact your flourishing. A CBC picks whether there are any expansions or diminishments in your platelet checks. Customary respects change subordinate upon your age and your sexual presentation. Finish Blood Count Test in Faridabad Your lab report will reveal to you the reliable respect go for your age and sex.An entire blood check test measures a couple of zones and highlights of your blood, including:
Red platelets, which pass on oxygen White platelets, which battle disease Hemoglobin, the oxygen-passing on protein in red platelets Hematocrit, the level of red platelets to the liquid piece, or plasma, in your blood Platelets, which help with blood coagulating Abnormal expansions or diminishments in cell join as uncovered a total blood tally may show that you have a major remedial condition that calls for help evaluation.
Utilization OF COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT
You may get a CBC as a fragment of your yearly enlistment. Your master may in like way outline it to: See on the off chance that you have another recuperating issue or to clear up responses like shortcoming, fever, harming, or feeling tired Keep an eye on a blood condition you beginning at now have See how meds or pharmaceuticals like chemotherapy are influencing your blood
Framework for Complete Blood Count Test
A band is wrapped around the arm, 3– 4 slithers over the get-together site (shallow vein that exists in the elbow pit) A 70% liquor cushion is utilized to clean the skin A needle is then proceeded as demonstrated by and embedded into a vein that can be seen from the skin The blood is dragged out from the needle by a spout, spared in a vessel and settled with your name The portrayal is then taken to a lab for examination
It’s to a mind boggling degree clear and takes only a couple of minutes. A healing escort or lab tech will take an instance of blood by embeddings a needle into a vein in your arm. She’ll send it to the lab for review. You can leave and get immaculate back to your standard timetable.
Framework REQUIREMENT
Diagram →Whole blood
Volume →Fill tube to oblige.
Holder →Lavender-top (EDTA) tube.
The blood test drawn for an aggregate blood merge is poor down a supportive research focus. The aggregate blood count examination is routinely and persistently done by strategies for robotized machines in different examination working environments. A little case of the blood drawn from a man is enabled into the machine and inside a couple of minutes, the estimations of the parts of the whole blood check are showed up and printed for review. This is known as a robotized cell check and differential.
The standard technique to research these data is to get a little example of the assembled blood and place it on a glass slide for visual examination under an opening up purpose of merging. This is for the most part done by a readied lab technologist or an expert. This system is still extensively used when conceded results of an aggregate blood check require also study to express certain astounding regards, or a specialist needs to see how the platelets look (for example, if any irregular features are accessible which would not be addressed by an automated complete blood count). This is known as the manual differential examination.
Associations of the whole blood check are expansive. Right when all is said in done, the whole blood consider ought to be conceivable bit of routine thriving exam and general screening by a pro. It may be asked for if an infirmity or sickliness is suspected. It may in like way be asked for to survey sporadic kicking the holder.
As chose previously, a move of the white platelet check or a variety from the standard of the white platelet differential may be suggestive of an illness or compounding. A high or a low white platelet incorporate could like way be an indication of focal change, for instance, leukemia or lymphoma.
A low red platelet or hemoglobin count reliably exhibits press require (low blood). Whiteness, often saw as low hemoglobin or low hematocrit on the aggregate blood count, infers that a concealed disease and it isn’t a perplexity itself. Delicacy can have diverse causes including blood hardship, bone marrow issues, sound insufficiencies, innate hemoglobin important or sensible issues , or kidney frustration. These are only the most appreciated elucidations behind iron inadequacy, and the outline of all purposes for paleness is uncommonly broad. Lack found in a whole blood check may be suggestive of pushing moderate blood trouble and, accordingly, can be used to perceive malignancies, for instance, colon tumor. In case sickliness is seen, if all else fails the MCV and RDW give some additional hints concerning the possible elucidations behind whiteness.
A low platelet incorporate may like way be found in the aggregate blood count. This may be a result of bone marrow issues, a couple of pharmaceuticals or over the best alcohol use, immunologic or inherited issues, influenced liver disease, or tumors, for instance, leukemia. The MPV may exhibit how rapidly platelets are made in the bone marrow and released into the course framework. A high platelet check may in like way be suggestive of an irritation or blood shot, for instance, leukemia and lymphoma.
Pathcare — Nampally Station Road, Hyderabad
Pathcare is one of the leading diagnostic chains in India offering best-in-class laboratory testing services in Nampally Station Road, Hyderabad. Pathcare is well known for their professional and cost effective services and is accredited by CAP NABL, etc. With a team of well trained technicians they provide high quality and error free reports.
Thyrocare — Nampally Station Road, Hyderabad
Thyrocare provides diagnostic test services at attractive rates, with a guarantee to deliver reports within 72 hrs based on the test conducted. You can book majority of known tests like SCL 70 Antibody, Serum, Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH), Triiodothyronine (T3), Total Thyroxine (T4) and 1,25-Di Hydroxy Cholecalciferol, Glycosylated Hemoglobin (HbA1c).
0 notes
Text
Complete Blood Count Test in Faridabad
An aggregate blood check, or CBC, is a key and astoundingly standard test that screens for particular issue that can influence your thriving. A CBC picks whether there are any extensions or reductions in your platelet checks. Regular regards change subordinate upon your age and your sexual introduction. Complete Blood Count Test in Faridabad Your lab report will uncover to you the consistent regard go for your age and sex.An whole blood check test measures a few areas and features of your blood, including:
Red platelets, which pass on oxygen White platelets, which fight ailment Hemoglobin, the oxygen-passing on protein in red platelets Hematocrit, the level of red platelets to the fluid piece, or plasma, in your blood Platelets, which help with blood coagulating Abnormal extensions or diminishments in cell join as revealed an aggregate blood count may exhibit that you have a fundamental therapeutic condition that calls for help appraisal.
Usage OF COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT
You may get a CBC as a segment of your yearly enrollment. Your lord may in like way design it to: See in case you have another healing issue or to clarify reactions like weakness, fever, hurting, or feeling tired Keep an eye on a blood condition you starting at now have See how meds or pharmaceuticals like chemotherapy are affecting your blood
System for Complete Blood Count Test
A band is wrapped around the arm, 3– 4 crawls over the social event site (shallow vein that exists in the elbow pit) A 70% alcohol pad is used to clean the skin A needle is then continued as indicated by and implanted into a vein that can be seen from the skin The blood is dragged out from the needle by a gush, saved in a vessel and settled with your name The depiction is then taken to a lab for examination
It’s to an incredible degree clear and takes just a few minutes. A remedial escort or lab tech will take a case of blood by embeddings a needle into a vein in your arm. She’ll send it to the lab for overview. You can leave and get perfect back to your standard timetable.
Outline REQUIREMENT
Outline →Whole blood
Volume →Fill tube to oblige.
Holder →Lavender-top (EDTA) tube.
The blood test drawn for a total blood consolidate is broke down a helpful research center. The total blood tally examination is routinely and continually done by methods for robotized machines in various investigation workplaces. A little instance of the blood drawn from a man is empowered into the machine and inside a few minutes, the estimations of the parts of the entire blood check are showed up and printed for audit. This is known as a robotized cell check and differential.
The standard procedure to investigate these information is to get a little instance of the gathered blood and place it on a glass slide for visual examination under an opening up point of convergence. This is generally done by a prepared lab technologist or an ace. This framework is still broadly utilized when deferred outcomes of a total blood check require moreover survey to state certain amazing respects, or an expert needs to perceive how the platelets look (for instance, if any abnormal highlights are available which would not be spoken to by a mechanized finish blood tally). This is known as the manual differential examination.
Organizations of the entire blood check are broad. Right when all is said in done, the entire blood think about should be possible piece of routine flourishing exam and general screening by a specialist. It might be requested if an ailment or sickliness is suspected. It might in like way be requested to assess sporadic kicking the container.
As decided beforehand, a climb of the white platelet check or an assortment from the standard of the white platelet differential might be suggestive of a disease or worsening. A high or a low white platelet include could like way be an indication of central improvement, for example, leukemia or lymphoma.
A low red platelet or hemoglobin tally consistently demonstrates squeeze need (low blood). Whiteness, frequently observed as low hemoglobin or low hematocrit on the total blood tally, implies that a hid illness and it isn’t a confusion itself. Delicacy can have different causes including blood hardship, bone marrow issues, sound inadequacies, hereditary hemoglobin principal or sensible issues , or kidney disappointment. These are just the most comprehended clarifications behind iron insufficiency, and the synopsis of all reasons behind pallor is exceptionally extensive. Deficiency found in an entire blood check might be suggestive of propelling moderate blood difficulty and, thusly, can be utilized to recognize malignancies, for example, colon tumor. On the off chance that sickliness is seen, when in doubt the MCV and RDW give some extra intimations concerning the conceivable clarifications behind whiteness.
A low platelet include may like way be seen in the total blood tally. This might be a consequence of bone marrow issues, a few pharmaceuticals or over the best liquor utilize, immunologic or hereditary issues, affected liver ailment, or tumors, for example, leukemia. The MPV may demonstrate how quickly platelets are made in the bone marrow and discharged into the course system. A high platelet check may in like way be suggestive of an aggravation or blood chance, for example, leukemia and lymphoma
Pathcare — NHPC Chownk, Faridabad
Pathcare is one of the leading diagnostic chains in India offering best-in-class laboratory testing services in NHPC Chownk, Faridabad. Pathcare is well known for their professional and cost effective services and is accredited by CAP NABL, etc. With a team of well trained technicians they provide high quality and error free reports.
Thyrocare — NHPC Chownk, Faridabad
Thyrocare provides diagnostic test services at attractive rates, with a guarantee to deliver reports within 72 hrs based on the test conducted. You can book majority of known tests like SCL 70 Antibody, Serum, Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH), Triiodothyronine (T3), Total Thyroxine (T4) and 1,25-Di Hydroxy Cholecalciferol, Glycosylated Hemoglobin (HbA1c). It provides comprehensive range of lab tests covering more than 242 tests.
0 notes