Text
Zen Buddhism on guilt
Passage from Nothing Special, by American Zen teacher Charlotte Joko Beck:
"STUDENT: I frequently feel guilty that I’m not spending enough quality time with my parents. I have watched myself do this over and over again; yet I keep doing it.
JOKO: You are measuring yourself against a mental ideal. When you are with your parents, just be with them and see what comes up. That’s all. The rest is a fantasy about how you should be. Who knows how you should be? We simply do our best, over and over and over. In time, we lose all interest in our past."
0 notes
Text
You're allowed to be inconsistent (while you work to articulate your logic / principles)
Basically, your actions are not limited to only those that can be justified with explicit logic / principles.
Give yourself some leeway / grace to act when your intuition is niggling at you, even if you can't articulate the exact values / principles underlying the intuitions yet. Going from inexplicable to explicit takes time. In the meantime, you're allowed to be inconsistent.
---
"The False Consistency error is committed when someone has conflicting desires, thoughts, or beliefs, and bludgeons all but one of them into silence, in the name of "consistency." This has the effect of robbing that person of the ability to use inarticulable intuition and gut-level analysis, and I suspect that it leads to the accumulation of resentment and frustration.
Bob doesn't want to, but can't quite articulate why not. Bob reflects, and decides that he doesn't endorse this difficult-to-articulate feeling, and he doesn't feel he has the social affordance to say "no" if he can't provide clear reasoning as to why. ... That difficult-to-articulate feeling remains, festering and causing Bob frustration.
Now, I'm all for internal consistency. Consistency is a virtue.
It's fine to be uncomfortable in the face of inconsistency. The trouble occurs when you respond to that discomfort with internal violence, by bludgeoning part of yourself into submission.
With practice, it's also possible to become better at articulating the inarticulable concerns. In the interim, you're allowed to be inconsistent.
You don't need to ignore concerns that you have just because you can't articulate them. If your actions today are inconsistent with your actions yesterday, and you know how to dialog between the conflicting parts of yourself but you haven't had the time to do that yet, then you don't need to be consistent at the moment."
0 notes
Text
Minding Our Way: do the hard things
Roundabout ways of basically saying:
"Do something that your future self will thank you for."
"We can do hard things."
"Embrace the suck."
Flow state is when you work on something befitting your abilities. Challenging enough, but not excessively so.
"Sometimes the only way out is through."
Enjoying the feeling of agency
an "ugh field", and these things occur whenever it becomes difficult to think about doing something because the very thought of the thing is unpleasant. ... There is a lot of power to be had in training yourself to notice ugh fields.��... once you notice that you're avoiding a thought ... think the thought.
Say that you've noticed an ugh field ... Now what? Do you force yourself to [do the thing] now? Because I am not a fan of forcing oneself to act. Willpower is a stopgap measure; any plan that requires continuous application of willpower is doomed.
Instead, my suggestion is this: install a part of yourself that enjoys doing things that are supposed to be difficult.
agency is not the human default. For me, [doing the difficult thing] is a power signal, a reminder that I can act where others fail to, a reminder that I can cause the world to be a little more how I want it to be, even in the face of mental inertia that many find difficult to overcome.
If you have the opportunity to [exercise your agency], take it — and appreciate it. It is a rare thing.
Moving toward the hard parts
Imagine you have a group of friends who have stereotyped you into a social role you dislike. You find yourself acting in ways you don't endorse when among this group of friends. Maybe you're meaner than you'd like, or meeker than you'd like, or you give into peer pressure and hate it. And yet, every time you fulfill their expectations, the expectations get stronger, and the rut gets deeper. ...
Most people can recognize the ruts they're in, they can see the social and mental chains that bind them there, but seeing isn't enough to free them. In my experience, many people deal with these problems via either denial or resignation. If instead you have a part of yourself that enjoys finding ways to break the pattern, that enjoys causing social disruption and paying upfront costs to escape bad outcomes, then for you, situations such as the above can only ever be temporary.
have a part of yourself that sees the problem, sees how the solution involves going through a hard part (such as overcoming akrasia or going against the social grain), and enjoys the opportunity. And now we've come full circle: this is enjoying the feeling of agency, but at the level where you enjoy solving any problem that matches the pattern above.
0 notes
Text
Article: One BIG Difference Between ENFP & INFP
Spoiler: it's risk aversion
"one big difference I’ve noticed between the INFP and ENFP personality types."
The ENFP personality tends to take that leap earlier, whereas I’ve noticed – and again, it’s not everyone I’ve worked with – but I’ve noticed the INFP personality tends to be a lot more risk-averse.
Ultimately, the two personality types have a very similar goal, but INFP people have more difficulty pushing themselves to take a big risk, to quit their job or change directions, and actually go for it.
Whereas with the ENFP Campaigner maybe it’s the shiny object syndrome or we’re just a little crazy, but we’re more likely to actually just go for it and take that big risk.
Now, what’s interesting is what happens maybe six months or a year after that initial change and that’s some of those patterns I’ve noticed with ENFPs and INFPs as well a bit.
The ENFP sometimes sticks to it and kicks ass, becomes very successful at what they’re doing and other times they get off course, so ultimately, it’s fear coming in for both the ENFP and INFP. ... with the ENFP personality type that fear tends to push us towards shiny object syndrome ... Whereas the INFP Mediator type I’ve noticed more tends to backtrack a bit to this safer route and lose some of that interest a bit quicker.
it’s normal to have that feeling of fear. but what I’ve noticed some INFPs will do is then either backtrack and get another job that really isn’t the thing they wanted to be doing.
Or go back to something like education, which is generally a safety net. ... especially in Europe, where education is free, basically, or very cheap, is it can be used as something that feels safer.
And so when we’re starting our own business or some kind of creative pursuit that makes us feel uncomfortable, stressed, and a little worried, then we can think:
Oh, I’ll go back to school! That’s socially acceptable to do, whereas [X thing I want to do] maybe isn’t as socially acceptable."
1 note
·
View note
Text
youtube
youtube
Murder case of Tristyn Bailey.
Testimony by families of both the perpetrator and victim. The thought occurs to me that this seems like an unnecessary appeal to pathos where facts should preside & decide. But it's important to humanize both sides. So that neither victim nor perpetrator become a simple statistic. In sentencing, we (as a society, and the justice system) should feel the emotional weight of our decisions. That discomfort should spur us to improve society over time so that these occurrences become less necessary in the future.
Interest in this stems from morbid curiosity: learning about societal threats, how they compare to myself & others who generally have a higher intrinsic capacity for empathy.
0 notes
Note
Do you see a correlation with astrology and MBTI type?
If you’re asking about the MBTI types most likely to believe in astrology, yes, overwhelmingly feelers over thinkers, strongly intuitives over sensors, and slightly xxFPs over xxFJs.
As for my theory of why this is the case: feelers have low thinking cognitive functions and astrology is an external system of logic with its own evidence based model. This external system compensates for their low thinking functions to provide understanding for causal relationships and provide explanations for events in the world.
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
ENTJ Humor: Self-Deprecating, Dark & Absurd Humor
"When it comes to humor not everyone appreciates the same style, and so this can make for a lot of misunderstandings. ... At times this can be challenging for the types with a darker sense of humor, as they don’t always feel free expressing this without receiving judgement.
ENTJs definitely appreciate humor, especially dark or sarcastic types of humor. They enjoy being able to use their wit in order to give a more biting response. ... They can actually be over the top at times, wanting to push the envelope and see how much their humor can shock people. This is often surprising to people, as ENTJs are focused and driven people who at times can seem rather serious. That doesn’t mean they don’t have a playful side, and this is often where their humor is expressed.
... they enjoy when things push certain boundaries. Sometimes the appeal to dark jokes is that they can be rather shocking, ... ENTJs aren’t afraid of crossing certain lines, especially when they are around friends. ... For the ENTJ it can be fun and entertaining just to see how others will react to some of their darker or more shocking jokes. ... Sometimes ENTJs enjoy pushing their buttons, even mocking or teasing people they care about. It can seem weird to some people, as they don’t understand why the ENTJ can be so mocking towards their loved ones. It is purely for the sake of being funny and playful, as the ENTJ [is] extremely loyal to those close to them, ... They sometimes enjoy making a joke which can confuse people or make them question just how serious they actually are.
Sometimes comedy which is a bit darker is also entertaining for the ENTJ because it has more thought put into it. Intelligent or witty humor gets them more intrigued and leaves them feeling like not just anyone can appreciate the joke. They enjoy when people use their minds as a means of stating certain truths and bringing them to light. That can be one of the most appealing things about dark humor for the ENTJ, that it might cross lines but that it can also be extremely honest. The more straightforward and totally sincere dark humor is going to really hit home to the ENTJ. When it is shedding light on something people might be afraid to admit to or accept, it definitely draws them in. Sometimes the truth can be dark or make people uncomfortable, but ENTJs are rarely afraid of feeling uncomfortable over these types of things. ENTJs are definitely drawn to sarcasm as well, ... especially when not everyone really understands them or the joke they are making. For the people who do appreciate it, it can actually give the ENTJ a better idea of which people they feel more connected to based on that.
ENTJ Self-Deprecating or Absurd Humor
ENTJs can certainly have moments of self-deprecating humor, but only if it is very funny. They don’t like people who do this constantly, as it just starts to feel like they are actually down on themselves. To the ENTJ it is more fun to banter back and forth with someone and see how the other person can come at them. Being too self-deprecating makes them feel like people are going to see them as weak and use that to their advantage. ENTJs don’t like showing vulnerabilities, and so they can avoid using too self-deprecating humor too frequently. On occasion when they are around people they trust they might poke fun at themselves for the sake of making someone laugh.
ENTJs can certainly have absurd or over the top humor sometimes, especially if it goes against people’s expectations. This is more for the sake of poking at people and seeing just how they will respond ... It is all done in jest and not meant to actually upset anyone, ENTJs will respect boundaries if people clearly set them. They just want to know where people stand, and how far they can take more offensive humor before the people around them get bothered by this. For the ENTJ it can be a lot about reading and understanding people, and at the same time still be funny. ENTJs do enjoy people who can follow along with their sense of humor, and who don’t seem to get offended all that easily."
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Introduction to Cognitive Functions (Socionics)
Function #1 – leading, program, primary, base, or dominant function. This is the strongest conscious function, and the most utilized function of the psyche. A person’s outlook and role in life is largely determined by the nature of this function. One is generally very confident in the use of this function, and may defend it when challenged. According to Bukalov, this is a 4D function.
Function #2 – creative or secondary function, is second in influence only to the dominant function. It assists the dominant function in achieving its essence. One is generally less confident with the use of this function than with his dominant function. As a result, the creative function is sometimes less instrumental when a person is challenged or threatened, or when dealing with new and complex tasks and data. This function is 3D or time invariant, because it produces something new which may never exist before.
Function #3 – role function, is a weak but conscious function. One generally tries to be at least adequate in areas where use of the role function is necessary. Moreover, one generally uses it in situations of social adaptation (e.g. introducing themselves to an unknown person). However, generally one has very little control or confidence over the role function, and criticism is painfully acknowledged with respect to it. Tactful assistance is required from someone else’s strong function to overcome the problems associated with the role function. This function is 2D or situation invariant, because it cannot adapt to the unusual situation beyond social norms.
Function #4 – the vulnerable function, or place of least resistance, is a weak and conscious function, in addition to being the weakest function of the psyche. One painfully perceives his complete inability to use this function, and reacts negatively to its imposition upon him. Tactful assistance is required from someone else’s strong function (preferably the Function 8) to overcome the problems associated with this function. This function is 1D (i.e. only personal experience is collected here, and it cannot be adapted even to the social norms.)
Function #5 – suggestive function, is a weak and unconscious function which is largely lacked.
One requires assistance from somebody confident in this function in order to overcome the difficulties it presents. When left to ones own devices, the suggestive function goes unnoticed. This function is 1D too, and one must be careful not to become subject of manipulation because of misuse of this function. Discussing aspects of this function makes person happy and trustful. (That’s why it’s called suggestive.)
Function #6 – mobilizing function. This is a weak and unconscious function which one often understands poorly.
Nonetheless, this function has a strong influence over one’s actions. Individuals requires assistance from someone who uses it confidently in order to understand it. Often an individual is only aware that they are totally unaware of how to use this function. At the same time, it’s a 2D function, so it’s capable of collecting a number of easy receipts for daily needs. Being successful in aspects of this function makes one happy and motivated. (That’s why it’s called mobilizing.)
Function #7 – observant, or ignoring, or restricting function, the function of personal knowledge.
This is a strong (3D) but unconscious function. One generally has a good grasp of this function, but attempts to limit its use considerably. Individuals will disregard this function when an argument calls for restraint or when it will be difficult to indulge in its essence. At the same time one uses this function to restrict somebody’s intervention to their privacy or territory, or other unsolicited interaction.
Function #8 – demonstrative or background function.
This function is so deeply rooted into the psyche that one is usually not consciously aware of its existence or utilization. It is as strong as the leading function (4D) and it tends to act silently to protect the weakest point of the dual person (see below). It can sound in situations of extreme irritation when the restricting function fails to break the unsolicited influence.

STRONG AND WEAK
Depending on our type, certain kinds of information metabolism will be strong or weak, meaning we find it easy or difficult to act on that kind of information effectively.Bukalov introduced the idea of Strength/Weakness being divided into four levels, known as Dimensionality which varies from One-Dimensionality (Experience) to having all Four Dimensions (Experience, Normativity, Situation and Time):
One-Dimensionality (1D) – Very Weak. These IM Elements can only be metabolised at the most basic and rudimentary level, meaning we are only open to our own Experience of that information and will thus come across as inept and indecent when using it ourselves
Two-Dimensionality (2D) – Weak. We have to work at these IM Elements to achieve adequacy in them. Usually their use will be tiring to maintain. We are exposed to the Normativity of this sort of information and thus are able to conform to basic standards and expectations but as a result will be rather conservative and stiff in its use.
Three-Dimensionality (3D) – Strong. We can easily and readily metabolise these IM Elements, acting on them as and when we wish. An experience of Situation allows us to make judgement calls on this sort of information, knowing when it is best to adhere to basic standards and when to be more creative.
Four-Dimensionality (4D) – Very Strong. These kinds of information are so prevalent in us that they strongly dictate how we move and communicate in the world. Such information carries its own sense of development over Time with decisions being made as numerous, specific instances on a global scale in the greater interest of that IM Element. People can easily be recognised by the IM Elements assigned to these strongest functions.
VALUED & SUBDUED
Depending on our type, certain kinds of information metabolism will be valued or subdued (not valued), meaning we will appreciate those kinds of information in our surroundings or reject/avoid them. By combining the Strong/Weak and Valued/Subdued dichotomies, we form the four blocks which the eight functions can be separated into:
Ego – Mental, Strong and Valued. The most apparent part of our personality. IM Elements in the Ego Block are those which we actively bring to the world, conducting ourselves and affecting our surroundings according to them.
Super Ego – Mental, Weak and Subdued. The painful expectations of society on us. IM Elements in the Super-Ego Block are those which we are expected by others to use but which we have no wish for and no ability to deliver. As a result, these kinds of information are a constant source of neurosis.
Super Id – Vital, Weak and Valued. The unconscious needs we find help with from others. IM Elements in the Super-Id Block are those which we are generally blind to but which we find ourselves being drawn to when supplied by others. We enjoy these kinds of information and find ourselves appreciating people who readily provide them.
Id – Vital, Strong and Subdued. The rejected approaches. We look down upon IM Elements in the Id Block as the alternative but incorrect ways of doing what we accomplish in our Ego. Instead of pursuing these kinds of information, we unconsciously carry them out as side effects of our natural motives, fulfilling the need with proficiency but without appreciation.
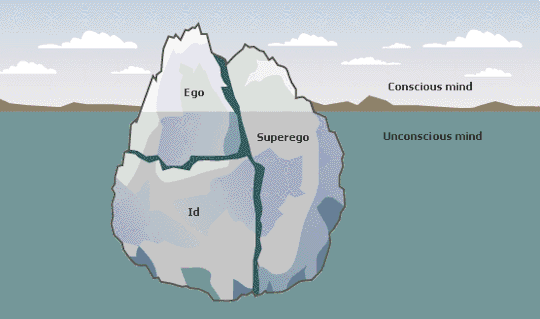
INFORMATION METABOLISM (IM)
These are theoretical constructs that convert (metabolise) certain kinds of information into behaviour. Each is geared towards a certain kind of information which is then acted upon via the process of Information Metabolism.
Ne (Extroverted Intuition) - Intuition of Ideas : Considers the essence of objects and the multiple possibilities contained within. This instils an attitude of opportunity-seeking, pursuing freedom of choice and maximising the possibilities as well as tolerance of multiple, alternative viewpoints.
Ni (Introverted Intuition) – Intuition of Time: Focuses on the likely flow of causes and effects from the past through to the future. This instils an attitude of foresight and prediction, attempting to conceive of how events will develop over the long term and adapting oneself to benefit from these predictions.
Se (Extroverted Sensation) – Sensation of Force. Scans the environment for items of desire and motivates assertive action towards claiming those items. This instils an attitude of lust and combat, pursuing one’s ambitions in the real world and conquering threats to gain more territory.
Si (Introverted Sensation) – Sensation of Senses. Refines sensory experiences down to those that are most enjoyable, seeking to increase pleasure in the moment. This instils an attitude of aesthetic and comfort, adjusting oneself to the environment and making small changes to the environment so that it is most pleasing to the senses.
Te (Extroverted Thinking) – Logic of Procedures. Actively develops methods by which processes work more productively. This instils an attitude of efficiency, readily absorbing relevant information and using that information to make the environment work better and instructing others on how to do things that lead to profitable effects.
Ti (Introverted Thinking) – Logic of Laws. Orders and structures the environment according to rules and principles, creating classificatory systems wherein objects are granted logical meaning. This instils an attitude of consistency and principle, adhering to one’s principles and avoiding situations where these rules might be compromised.
Fe (Extroverted Feelings) – Ethics of Emotions. Actively expresses emotions in order to affect the mood of the people in the area, instilling enthusiasm to create group cohesion. This instils an attitude of dramatic expression and group motivation, readily making people feel the way they should be feeling.
Fi (Introverted Feelings) – Ethics of Relations. Consults one’s personal sentiments in relation to external stimuli, ascertaining whether the thing is ‘good’ or ‘bad’ and being able to pick up on similar sentiments in others to form meaningful relationships. This instils an attitude of sincerity, requiring one to act true to one’s personal feelings on matters.
Summarised from: Source 1 , Source 2, Source 3
803 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Privilege That Is Inherent To Each Myers-Briggs Personality Type
(Written by Heidi Priebe)
What is natural to the point of being obvious to one type is often completely and utterly unconsidered by another. Our natural methods of processing information often put us at a specific advantage that we are not always aware of – to the point where we can almost call our ability to consider information in a specific manner a privilege.
ENFP and ENTP: The ability to fathom a plethora of different solutions to any given problem.
Being a type that leads with extroverted intuition means that you are naturally able to tap into the wide scope of possibilities that exist in your external environment. While other types may get stuck in stagnancy and lack the ability to see a way out of the ruts that they get stuck in, you are naturally creative and adaptable. You can usually think of approximately fifty solutions to any given problem, which means you never stay helpless for long.
INTJ and INFJ: The ability to envision and consider multiple opposing points of view simultaneously.
Being a type that leads with introverted intuition means that you are naturally able to see and consider various different viewpoints simultaneously. While other types may struggle to understand things that are outside the scope of what they’ve been taught or what they believe, you are naturally adept at seeing where others are coming from and understanding how all different points of view all fit into a bigger picture. You can effortlessly consider multiple various perspectives and understand what’s behind them, which gives you the leg up on making the best of all possible decisions.
ESFJ and ENFJ: The ability to naturally understand the needs of a group and connect with others.
Being a type that leads with extroverted feeling means that you are naturally able to pick up on how others are feeling and what needs to be done in order to maintain interpersonal harmony. While many types struggle to relate to and work cohesively alongside others, this skill comes naturally to you. You are able to communicate effectively with those around you and understand how your actions have the potential to affect others. This makes you an excellent coworker, a reliable friend or family member and a natural leader in almost any situation.
ESFP and ESTP: The ability to think on your feet and react quickly and effectively to changing circumstances.
Being a type that leads with extroverted sensing means that you are naturally in tune with your environment and the possibilities that are immediately present within it. While other types require extensive amounts of time to mull things over before reacting to a change in circumstance, you are always quick to re-evaluate, pick out the best of all options that are available to you and directly pursue it. More often than not, you’re busy getting ahead while others are at home deliberating over their options.
ISFP and INFP: The ability to deeply understand the underlying causes and motivations behind human behavior.
Being a type that leads with introverted feeling means that you are able to understand emotional processes on a deep and intuitive level. While others are struggling to make sense of the seemingly illogical human behavior that drives relationships, politics, economics and just about everything else human beings engage in, you are able to take a step back and put yourself in others shoes with terrifying accuracy and clarity. Your understanding of the human condition is as impressive as it is effortless and it allows you to understand the truths and intricacies of the world in the ways that logic cannot explain.
ESTJ and ENTJ: The ability to clearly identify the most beneficial solution to a given problem and how to implement it.
Being a type that leads with extroverted thinking means that you are ceaselessly focused on results – and you are able to clearly evaluate various courses of action based on their potential outcomes. While other types are caught up in trying to decipher how they feel or which goals will launch them down which paths, you are able to quickly pinpoint which actions will lead to the the results that you want. This regularly puts you ahead of the game in terms of productivity and progression.
INTP and ISTP: The ability to pinpoint shortcuts that exist within systems and understand how you can manipulate those systems to your advantage.
Being a type that leads with introverted thinking means that you are constantly looking at the bigger picture of how things logically work in relation to one another. Consequently, you are also able to quickly pick up on potential shortcuts or hacks that exist within just about any logical system. While other types are busy plugging away at jobs and situations that are barely benefiting them, you are able to quickly see how you can manipulate a system to your advantage, and achieve maximum results with minimum effort.
ISTJ and ISFJ: The ability to naturally maintain your focus and work steadily towards goals.
Being a type that leads with introverted sensing means that you feel comfortable maintaining a routine that optimizes your productivity and moves you steadily toward your goals. While other types are growing restless and flaking halfway through projects or relationships, you aren’t afraid to stick it out to get to what matters. You find comfort in commitment and security, which means you naturally attract quality in every area of your life.
807 notes
·
View notes
Text
the difference between analysts and researchers is that analysts look at existing data to develop useful findings.
According to [Towards Data Science], a data analyst might be given an extensive database featuring past results and analyze this information to compile a report. (x)
Data analysts are professionals who collect, process, and perform statistical analyses on large datasets to extract meaningful insights and inform business decisions. They use various tools and techniques to clean, transform, and visualize data, and create reports and dashboards that communicate their findings to stakeholders. Data analysts work across industries, ... and are often responsible for monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs), identifying trends and patterns, and providing recommendations for improvement.
Research scientists, on the other hand, are professionals who design, develop, and test new algorithms, models, and systems that solve complex problems ... They work on cutting-edge projects that require a deep understanding of mathematical and computational concepts, and use advanced programming languages and tools to build and evaluate prototypes. Research scientists work in academia, industry, and government, and are often responsible for publishing research papers, presenting their work at conferences, and collaborating with other experts in the field.
Responsibilities
The responsibilities of data analysts and Research scientists differ significantly, as outlined below:
Data Analyst
Collect, clean, and process data from various sources
Analyze data using statistical methods and tools
Create reports and dashboards that communicate insights to stakeholders
Identify trends and patterns in data
Monitor KPIs and provide recommendations for improvement
Collaborate with other teams to ensure Data quality and accuracy
Stay up-to-date with industry trends and best practices
Research Scientist
Design and develop new algorithms, models, and systems
Test and evaluate prototypes using simulations and real-world data
Conduct experiments and analyze results
Write research papers and present findings at conferences
Collaborate with other researchers and experts in the field
Stay up-to-date with the latest research and developments
Apply for grants and funding for research projects
Required Skills
While both roles require a strong foundation in Mathematics, statistics, and data analysis, research scientists need more advanced skills in programming, machine learning, and data modeling.
Data Analyst
Strong analytical and problem-solving skills
Proficiency in statistical methods and tools
Knowledge of Data visualization and reporting tools
Familiarity with databases and SQL
Excellent communication and presentation skills
Attention to detail and accuracy
Ability to work in a team environment
Research Scientist
Strong programming skills in languages such as Python, R, and Java
Knowledge of Machine Learning algorithms and frameworks
Familiarity with data modeling and simulation tools
Experience with big data technologies such as Hadoop and Spark
Strong mathematical and statistical skills
Excellent problem-solving and critical thinking skills
Ability to work independently and collaboratively
Educational Backgrounds
Data analysts often have degrees in fields such as statistics, mathematics, Economics, or Computer Science, while research scientists typically have advanced degrees in computer science, mathematics, statistics, or a related field.
Data Analyst
Bachelor's degree in statistics, mathematics, economics, or Computer Science
Master's degree in a related field (optional)
Certifications in data analysis or Business Intelligence (optional)
Research Scientist
Master's or PhD degree in computer science, mathematics, statistics, or a related field
Experience conducting research and publishing papers
Experience with programming and machine learning projects
Data analysts and research scientists use a variety of tools and software to perform their jobs. Data analysts typically use tools such as Excel, Tableau, and SQL to analyze and visualize data, while research scientists use programming languages such as Python, R, and Java, and frameworks such as TensorFlow and PyTorch to build and test algorithms and models.
Data Analyst
Excel
Tableau
SQL
SAS
R
Python
Research Scientist
Python
R
Java
TensorFlow
PyTorch
Hadoop
Spark
Practical Tips for Getting Started
If you are interested in pursuing a career as a data analyst or research scientist, here are some practical tips to help you get started:
Data Analyst
Take courses in Statistics, data analysis, and visualization
Learn SQL and database management
Gain experience with Excel and Tableau
Build a portfolio of data analysis projects
Network with professionals in the field
Research Scientist
Pursue a master's or PhD degree in computer science or a related field
Learn programming languages such as Python and R
Gain experience with machine learning algorithms and frameworks
Participate in research projects and publish papers
Attend conferences and network with other researchers
Conclusion
Data analysis and research are both important fields in AI, ML, and Big Data, but they require different skills, educational backgrounds, and responsibilities. Data analysts are responsible for analyzing data and providing insights to inform business decisions, while research scientists are responsible for developing new algorithms and models to solve complex problems. (x)
0 notes
Text
rejection + resilience + survivorship bias

Case studies of seeming outsider success can be both inspiring and misleading. They should not be taken out of context to serve as the primary basis of decision making / risk-taking.
Einstein's bad recommendation
The story has become lore.
Albert Einstein was a rebellious student who chafed against traditional schooling and earned bad grades. After his university education, his brilliance was overlooked by a conformist academy who refused to give him a professorship. Broke and unemployed, Einstein settled for a lowly job as a patent clerk.
But this turned out to be a blessing in disguise. Free from the bonds of conventional wisdom, he could think bold, original thoughts that changed the world of physics.
The reality, of course, is more complicated.
Einstein was a rebellious student, but he always received exceptional marks in math and physics in school and on entrance exams.
Einstein did struggle after college, but he wasn’t turned down for professorships. What he failed to obtain after graduation was a university assistantship — which is, roughly speaking, a way to fund a graduate student while he or she works on a doctoral dissertation (like what we now call a research assistantship in American graduate education).
This was not a case of his brilliance being ignored, because Einstein was too early in his education to have done anything brilliant yet (the paper on capillary action he published the year after his graduation was mediocre). The main reason for his assistantship rejection was a bad recommendation letter from a professor who didn’t like him.
The key detail often missed in this story is that while Einstein was a patent clerk, he was continuing to work toward his doctoral degree. He had an adviser, he was reading and writing, he met regularly with a study group (pictured above).
The same year Einstein published his ground breaking work on special relativity (1905) he also submitted his dissertation and earned his PhD. Soon after he received professorship offers, and his academic career took off.
In other words, Einstein had to work a job to support his family while earning his PhD (an exhausting turn of bad luck), but his career from university to graduate degree to professorship still followed a pretty standard trajectory and timeline.
The reason I’m telling this story is because it underscores a common habit: we like to cast innovators as outsiders who leverage their freedom from tradition-bound institutions to change the world.
In reality, innovation almost always requires long periods of quite traditional training.
Einstein was brilliant and original, but until he finished a full graduate education, he didn’t know enough physics to advance it.
The same story can be told of many other innovators.
Take Steve Jobs: the Apple II was lucky timing; Jobs didn’t become a great CEO until after spending decades struggling to master the world of business. Once his skills were honed, however, he returned to Apple and his brilliance had an outlet.
This is the hard thing about innovation. If we want to encourage people to change the world, we have to first encourage them to buckle down and work inside the box.
The tricky part is embracing this necessary conformity while somehow keeping that spark to think different alive long enough for you to get good enough to do good.
the fetishization of the “lone maverick” who works outside the system.
our culture’s interest in the storyline of outsiders bucking tradition as the source of innovation. (x)
Deng Xiaoping's factory job
having saved some money from his job and having received a small sum from his father, he resigned from the factory and tried to enroll at a nearby college ... it turned out, however, he did not have enough funds. Three months later he returned to work at [the factory.] After he left the company a second time, in March, the company records report that he "refused to work" and that he "would not again be given work there."
After his last effort to find an opportunity to study failed, Deng devoted himself to the radical cause.
-Deng Xiaoping and the Transformation of China, by Ezra Vogel
Inspiring b/c he had little qualms about making a bad impression with his factory supervisors. Working a factory job was not his real goal/path, so he ultimately cared little about burning bridges there. He had faith in where he was going.
0 notes
Text
data analytics
the science of analyzing raw data to make conclusions about that information.
Data analytics help a business optimize its performance, perform more efficiently, maximize profit, or make more strategically-guided decisions. (x)
public interest technology
strives to encourage interoperability between technology, policy and society. PIT puts people at the center of policy making and improving community-driven problem-solving through the use of design, data and delivery skills and draws from technical fields like computer science, data science, and engineering, along with law, public policy, movement-building, philosophy, the social sciences, the arts and humanities, and more. (x)
public interest technology” and “civic technology” stand at odds with the first theme we discuss in this report, something we heard in virtually every interview: It’s not about technology. Or, rather, not only about technology. Or always about technology. And thus, neither are the people doing the work.
“For me, ‘technology in the public interest’ brings up associations of like open data, hackathons, and easy and useful greenfield projects,” said one designer. “‘Civic tech’ brings up a lot of similar associations. I occasionally use it as a hashtag on my tweets. But the real thing underneath it is organizational and procurement change inside government. That's not sexy. That's not easily consumable by the public. So, I say ‘government digital transformation’ is the space I'm in.” (x New America, a left-of-center think tank)
0 notes
Text
417 enneagram tritype
Difference between Six and Seven - Core fears: 6 - Abandonment and betrayal.
7 - Entrapment and boredom.
One flavoured with seven makes it a lot more lighter and playful as opposed to Six which just plays up the anxious perfectionism.
Also, 416 (The Philosopher) is capable of producing original works of profound analysis and critique of systems. 417 (The Visionary) would be better at creating systems for the betterment of society or people, whatever their profession may be. (x)
The Visionary (417) is original, intellectual and motivated to cause change. Morally focused, then tend to have big ideas and strong will to change the world around them. They tend to want to try to do something new, set a trend, or otherwise be as original as possible in their ideas. They are very intuitive and extremely creative. The blindspot is that the identification with the high ideals can create a sense of being inflexible in standards and rigid. This is the type most likely to alternate between being the life of the party and feeling inhibited and needing to be appropriate. The life mission is to bring visualize ways to create meaningful change and teach or inspire others toward higher values of excellence. They are highly opportunistic and focused on the vision, creativity and the magical. Your emotional energy goes towards seeking ideal relationships and circumstances. You want fulfilling experiences, relationships and environments. You tend to be fussy and easily frustrated and/or disenchanted with less than ideal relationships or situations. You are quite discriminating and tend to compare yourself to others. Overall, you want a sense of idealistic perfection. (x)
471: More of a happy go lucky [4] due to 7, intense emotions but imbues them with positivity, and even possibly avoids negative ones. Energetic and enthusiastic, inquisitive, curious, ready to take action, somewhat flighty and impulsive while still maintaining a set of convictions and values from 1 and experiencing a deep well of emotion in their activities from 4. Openness to experience, adventurous but still somewhat reserved. Though they enjoy social activities, they may tire after a while and withdraw. Probably come off reserved at first, but reveal a playful nature as you get to know them, while still experiencing deep emotions. Can avoid emotions they don’t like though, and nit pick through, seeming oblivious to a very obvious crisis. Self controlled. Willing to teach others, easy team player though they still feel something is different or off about them, wise in a playful yet honest manner. (x)
0 notes
Text
Reuters: America now in prolonged state of political violence
Fatal political violence more tied to right-wing ideology
Destruction of property more tied to left-wing ideology
0 notes
Text
Party attendance & friendship quality
The way I see it, 1:1 time is more likely to include depth connection, parties are more for breadth/group/crowd connection. The makeup/purpose of the party and one’s familiarity with the people involved help determine your experience of breadth vs. depth connection. Most parties end up being for a) finding and experiencing new connections with (or just ‘watching’) people you don’t know well – but who may be somewhat ‘vetted’ through shared friends or interests and/or (breadth) b) places to have followup connection or maintenance/renewal catchup with a subset of friends, which is especially useful if you’re crunched for time. (combo breadth+depth)
I so highly value un-noisy depth over breadth (and most parties are the latter, even among friends) that parties have often become a net negative, unless they’re heavily weighted toward a high potential for deep friend-connections (even new ones), and/or are a place with quieter nooks/crannies to have real conversation (the joy of spontaneous 1:1 spark within a crowd is awesome).
I so highly value my work & my sparse one-on-one time with others that my just _showing up_ to a party, even or especially on the late side, is a sign that I really highly value your friendship and/or the people you might bring to it. This is partially because the only people I want to hang out with when I’m tired late at night, or risk tilting my sleep schedule for, are the ‘real’ friends I don’t have to be perfectly ‘on’ for. ... Plus, it sucks to throw a party and [be] so tuckered from the work involved that you don’t enjoy it as much – ...This is mitigated by good pre-party planning, and some of my friends get around this by having stuff catered. Not everyone has that luxury, though… and you *can* make party prep spontaneously fun. =) (x)
100% this.
0 notes
Text
Is an online master's degree respected?
As many as 83% of business leaders see an online degree at a “well-known” institution as having the same value as an on-campus degree. If they are not familiar with a school, however, or the institution isn't known for producing prepared graduates from its programs, your degree may not be seen as having the same value. (Northeastern University)
The Department of Education found that “students in online conditions performed modestly better, on average, than those learning the same material through traditional face-to-face instruction.” In addition, “the effectiveness of online learning approaches appears quite broad across different content and learner types.”
0 notes
Text
Journaling When Mad (x)
A structured thought journal where you practice expressive writing can help you understand and manage anger. It allows you to identify what triggered your anger, why, and how to respond to it.
You can note situations where you feel frustrated or struggle with anger. This practice can help you make a concerted effort to change your behavior.
Here's an example template:
Event: Write down the event where you felt angry.
Thought: What was your immediate reaction to the event? Describe your reactionary thoughts to the event.
Behavior: What did you do next? Did you yell back at your boss? Did you cry in the bathroom?
Feeling: How do you feel after your response to the event? Maybe you feel embarrassed or hurt, for example.
Actions: It can be helpful to write down what you do when you become angry. Understanding why you're taking the actions you take can help you learn and grow.
Consequences: What happens due to these thoughts, feelings, and actions?
Another exercise you can use to try shifting your reactions is the dialectical behavioral therapy (DBT) skill called REST. (x)
Relax: Take a breath, pause, step away, count to 10, do whatever you have to do to help yourself calm down. Sometime saying “Stop” or “Relax” out loud can help this. Also, if you already have a self-soothing skill such as deep breathing this can be a great time to implement it.
Evaluate: Now that you’ve calmed down a bit, look more closely at yourself and at the situation that caused the distress. What happened? How do you feel? Is there anything else going on?
Set an intention: Come up with a plan to address the situation. Maybe it's thinking of the appropriate response to someone or recognizing that you need a longer break before going back to studying. This could also be more long term, such as learning better communication styles or a new study technique.
Take Action: When you feel prepared, set your plan into motion.
Also, remember that sometimes things don’t go as planned once you Take Action, so feel free to take a second or third REST as needed.
0 notes