#journal of clinical monitoring and computing
Text
Transforming Clinical Recording of Deep Brain Activity with a New Take on Sensor Manufacturing - Technology Org
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/transforming-clinical-recording-of-deep-brain-activity-with-a-new-take-on-sensor-manufacturing-technology-org/
Transforming Clinical Recording of Deep Brain Activity with a New Take on Sensor Manufacturing - Technology Org
Sensors built with a new manufacturing approach are capable of recording activity deep within the brain from large populations of individual neurons–with a resolution of as few as one or two neurons–in humans as well as a range of animal models, according to a study published in the issue of the journal Nature Communications.
The Integrated Electronics and Biointerfaces Laboratory (IEBL) at the University of California San Diego leads the research team.
The approach is unique in several ways. It relies on ultra-thin, flexible, and customizable probes made of clinical-grade materials and equipped with sensors that can record extremely localized brain signals. Because the probes are much smaller than today’s clinical sensors, they can be placed extremely close to one another, allowing for high-resolution sensing in specific areas at unprecedented depths within the brain.
These ultra-thin, flexible and customizable probes, are made of clinical-grade materials.
Image credit: David Baillot/UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering
Currently, the probes can record with up to 128 channels, while today’s state-of-the-art clinical probes have only 8 to 16 channels. In future, the innovative manufacturing approach the researchers developed can expand the number of channels to thousands per probe, dramatically enhancing physicians’ ability to acquire, analyze and understand brain signals at a higher resolution.
This technology is a first step towards wireless monitoring of patients with treatment-resistant epilepsy for extended periods–up to 30 days–as they go about their daily lives. Beyond treatment-resistant epilepsy, the potential applications are much broader, including helping people with Parkinson’s disease, movement disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder, obesity, treatment-resistant depression, high-impact chronic pain and other disorders.
While the Nature Communications paper reports brain-recording data only, the system has been developed to both record brain activity and provide electrical stimulation to precise locations. In fact, the team is building on previous – and ongoing – work that uses this scalable, thin-film manufacturing approach to create brain-computer interfaces that record activity and deliver therapeutic electrical stimulation to the surface of the brain cortex.
The probes are monolithic, meaning that their individual components are layered on top of one another to create a single, cohesive unit, and do not require manual assembly of additional wires to conduct recordings.
The new recording system is both extremely customizable and scalable to manufacture, thanks to thin-film technology derived from the semiconductor and digital-display screen industries. As such, the probes are extremely compact–15 micron thick, or about 1/5th the thickness of a human hair–minimizing the differences between the material properties of the probe and the brain.
“We developed an entirely different manufacturing method for thin-film electrodes that can reach deep brain structures – at a depth that is necessary for therapeutic reasons – enabling reproducible, customizable, and high-throughput production of electrodes but with a high spatial resolution and channel count despite a thinner electrode body. Additionally, the electrode insertion is compatible with existing surgical techniques in the operating room, lowering the barrier for their adoption in clinical procedures,” said UC San Diego electrical engineering professor Shadi Dayeh, the corresponding author on the new paper.
[embedded content]
The design, manufacture, experimental testing and analysis of results from this system was performed by a cross-disciplinary team of engineers, surgeons, and medical researchers from UC San Diego; Harvard Medical School and Massachusetts General Hospital; and Oregon Health and Science University.
Dayeh advises two of the three first authors on the paper: UC San Diego postdoctoral researcher Keundong Lee and UC San Diego graduate student researcher Yun Goo Ro. Angelique C. Paulk, also a first author, is a researcher at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School in a group led by neurologist Dr. Sydney Cash.
Toward a 30 day wireless brain-recording system
The kind of system researchers developed is needed in order to identify the very specific regions of the brain that are triggering seizures caused by treatment-resistant epilepsy. To meet this goal, the team is working toward their vision of a brain-monitoring system with sensors both inserted deep within the brain and sensors on the surface of the brain.
These sensors will communicate wirelessly with a small computer system in a wireless cap, which a person could wear for extended periods of time. This cap would provide wireless power and the computational infrastructure to capture the brain signals being recorded from a person’s brain for 30 days.
From left: Keundong Lee, a postdoctoral fellow at UC San Diego, and one of the paper’s first authors, and Shadi Dayeh, a professor in the UC San Diego Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering and the paper’s corresponding author. They are looking at an electrode under the microscope.
“We are currently focused on applying the technology to patients with treatment-resistant epilepsy. The ultimate goal is to advance the system and related required technologies by 2026 to give patients access to a wireless system that allows them to move freely within the hospital environment and then at home, without being tethered to any machinery, while cortical and deep brain structures are monitored continuously for up to 30 days,” Dayeh said.
The system is called the UC San Diego Micro-stereo-electro-encephalography (µSEEG). The technology that is used to create the device can be manufactured at high volume and low cost because it is derived from existing technologies to manufacture digital display screens, an approach that was originally created by the semiconductor industry.
This unique manufacturing process also allows for a series of unique features for these depth electrodes (see sidebar).
Experimental subjects
The electrodes are equipped with 128 sensors that can record extremely localized brain signals and 16 stimulation contacts that can deliver clinical grade stimulation currents and that can additionally record brain signals.
In the new paper, the team reports the functioning of the new system in two human patients. The team also presents data from a series of different animal models including successful recordings from rat barrel cortex in both acute and chronic settings; recording of the somatosensory cortex in an anesthetized pig; and recordings in non-human primates at different depths inside the brain.
The data on the successful functioning of the device in humans were collected, with all proper approvals and consent, during already scheduled tumor-removal surgeries. During an unrelated pause in the surgery, clinicians inserted the new depth probes into brain tissue that was about to be removed.
“In a true test of the translational feasibility of the µSEEG,” the authors write in the Nature Communications paper, referring to the technical term for their device, “we acutely implanted short 64 channel µSEEG electrodes in the middle temporal gyrus in two separate human patient participants undergoing temporal lobe resection for clinical reasons. With each participant, we inserted a single 64 channel short µSEEG device into tissue, which the clinical team determined would be resected.” The recordings lasted 10 minutes and were able to record ongoing spontaneous activity.
Comments from authors on the paper
The electrodes can record brain activity as deep as 10 cm/4 in inside the brain. They are just 15 micron thick, or one-fifth the width of a human hair, and 1.2 millimeters wide
Dr. Keundong Lee (First author #1), Postdoctoral Fellow at IEBL, UC San Diego
It has been a long journey since 2015 to develop a robust, human-grade depth electrode that can be used in clinical practice. Finally, we have discovered an innovative manufacturing technique to create the µSEEG probe, which can assist with high resolution and minimally invasive diagnosis of epilepsy, and potentially treatment for epilepsy and other indications, in the future.
Beyond epilepsy, continuous monitoring of brain activity at such high resolution could allow us to find biomarkers for other conditions, including perhaps treatment-resistant depression.
Dr. Angelique Paulk (First author #2), Instructor in Neurology at Massachusetts General Research Institute and Harvard Medical School
Our lab has worked with the Dayeh lab for almost a decade to bring this innovative technology to fruition. Around 2018, we tested the laminar version of the UC San Diego microSEEG in two patients at MGH. Through iterative feedback that we and Drs. Sharona Ben-Haim, Ahmed Raslan, Mark Richardson, and Ziv Williams provided to inform probe fabrication, we are now happy with the end result that we feel is much closer to clinical use. We were excited to test the longer version in non-human primates here at MGH and to record the activity of single neurons with these devices.
Dr. Yun Goo Ro (First author #3), PhD graduate from the IEBL, UC San Diego
My research on this electrode was both exciting and challenging as we had to come up with new ways of implementing a scalable electrode with operating principles that are compatible with clinical use. It is very exciting to see my PhD research extended to long electrodes to maximize their clinical impact and I am proud to see the potential of my PhD inventions translate from the benchtop to the bedside.
Dr. Sydney Cash, MD, Professor of Neurology, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School
These new electrode systems are really exciting. They are designed in a way, which can be easily used in the clinical setting yet provide a level of resolution not seen before. There is no question in my mind that this will help us understand both normal brain function and pathology much better and will lead to new ways to help people suffering from epilepsy and a variety of other neurological problems.
Dr. Sharona Ben-Haim, MD, Associate Professor of Neurological Surgery, UC San Diego School of Medicine and Surgical Director of Epilepsy, UC San Diego Health
This new electrode technology is exciting for a large variety of reasons, including its capacity for recording at unprecedented resolution. The future ability of this system to record wirelessly from the brain of epilepsy patients undergoing intracranial EEG evaluation has the potential to dramatically change our current clinical practice. Currently, patients who undergo this type of evaluation remain in the hospital for the duration of the study, where we try to capture where their unique seizures originate during a period of time that typically lasts from 7-21 days. During this time patients are tethered to their hospital beds by the wired cords from the current clinical electrode system. This new technology has the capacity to potentially allow us to send these patients home, freeing them from a long hospital stay, and potentially allowing us to record for longer periods of time and obtain more robust information to help us ultimately treat their seizures with more precision and resolution than previously possible.
Dr. Eric Halgren, Professor of Radiology, Neurosciences, and Psychiatry, UC San Diego
With current electrodes we can only hear the roar of the crowd. The new electrodes will allow us to discern individual voices, and we can begin to learn their language, which is the basic vocabulary of thought.
Dr. Ahmed Raslan, MD, Professorand Vice Chair of Neurological Surgery, Oregon Health and Sciences University
The new depth electrodes combine two unique features: the much higher resolution of recording contacts combined with stimulation capability, which would improve our ability to understand -and potentially change/treat- neural circuits in parts of the brain that are not accessible by surface or penetrating interfaces and at a much higher resolution than current depth electrodes; a strategy that unlocks decades-long trade offs, and, the wireless connectivity which opens the door to recording from humans in an unrestricted environment allowing sampling of various types of behavior. This new electrode is a platform neural interface that can both read and write into the brain in experimental and clinical environments, as such the potential uses and applications are unlimited.
[embedded content]
Features of the UC San Diego Micro-stereo-eletro-encephalography (µSEEG)
The probes can be up to 10 cm in length, allowing for access to structures deep within the brain.
The probes are incredibly thin: just 15 micron thick, or one-fifth the width of a human hair, and 1.2 millimeters wide
When inserted into brain tissue, the probe lined with sensors has a thickness that is smaller than technologies currently in clinical use. This smaller thickness means less brain tissue is damaged when the probe is inserted.
Brain-signal recording electrodes can be placed 60 micrometers apart, which is far closer to each other than technologies currently in clinical use.
Probes with up to 128 brain-signal-recording channels (electrodes) were demonstrated, compared to 8 to 16 recording channels in today’s broadly used clinical depth electrodes.
The small size of the electrodes allows for extremely localized brain-signal recording, as precise as the signal coming from the individual activity of one or two neurons. They can also record local field potentials, which is aggregate activity of many neurons within a brain region.
The electrode sensors are able to record precise areas of the brain over both short and long time periods.
The electrodes work well: they record brain activity triggered by stimulating a body part, and they record the brain dynamics known to occur during anesthesia.
The system allowed for simultaneous recording of the cortex of the brain and signals from individual neurons deep within the brain. The researchers were able to correlate the general brain activity to what was happening at the single-neuron level.
The system allows monitoring the dynamics of brain activity instantaneously, allowing visualization of the propagation of the activity across cortical layers with precision with time.
Cost-effective, scalable manufacturing of the new system is in direct contrast to the expensive and time-consuming manual assembly required for the systems currently in clinical use. All other known experimental depth electrodes require some amount of manual assembly as well.
Source: UCSD
You can offer your link to a page which is relevant to the topic of this post.
#Aging news#Analysis#Anesthesia#applications#approach#Art#barrier#Behavior#biomarkers#Biotechnology news#Brain#brain activity#brain signals#Brain-computer interfaces#Building#Capture#change#channel#communications#computer#connectivity#contacts#continuous#data#depression#Design#devices#Disease#disorders#display
1 note
·
View note
Text
James Fujimoto, Eric Swanson, and David Huang win Lasker Award
Professor and two additional MIT affiliates honored for influential work on optical coherence tomography, which allows rapid detection of retinal disease, among other applications.
Mary Beth Gallagher | Jane Halpern | School of Engineering | Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science

The Lasker Foundation has named James Fujimoto ’79, SM ’81, PhD ’84, the Elihu Thomson Professor in Electrical Engineering and principal investigator in the Research Laboratory of Electronics (RLE), a recipient of the 2023 Lasker-DeBakey Clinical Medical Research Award for his groundbreaking work on optical coherence tomography. Fujimoto shares the award with Eric Swanson SM ’84, a research affiliate at MIT’s Research Laboratory of Electronics and mentor for the MIT Deshpande Center for Technological Innovation, and David Huang PhD ’93, professor of ophthalmology at Oregon Health and Science University.
Considered one of the most prestigious prizes for biomedical research, the Lasker Awards celebrate individuals who have “made major advances in the understanding, diagnosis, treatment, cure, and prevention of human disease.” A large percentage of Lasker Award recipients have gone on to win a Nobel Prize.
According to the Lasker Foundation citation, Fujimoto, Huang, and Swanson are being honored “for the invention of optical coherence tomography (OCT), a technology that revolutionized ophthalmology — allowing rapid detection of diseases of the retina that impair vision.” An animated video describing the work is available here.
“I am honored to be included among the recipients of this award,” says Fujimoto. “OCT represents the decades-long effort of a multidisciplinary partnership involving scientists, engineers, the clinical community, and industry. We are grateful for the opportunity to help to improve patient care and sincerely thank the Lasker Foundation.”
Prior to the invention of OCT, the standard methods of diagnosing ophthalmic disease were limited. In the early 1990s, Fujimoto, an electrical engineer and expert in advanced laser technologies, collaborated with satellite communications engineer Swanson — then at MIT Lincoln Laboratory — and MD-PhD student Huang to devise a better way to diagnose diseases. Using an optical technique known as interferometry, they developed a technology that could image the three dimensional microscopic structure of the living retina for the first time.
Their work, published in 1991 in the journal Science, revolutionized the field of ophthalmology and enabled a more precise way to detect disease and monitor treatment. Additional co-authors on this paper are Charles P. Lin, Joel S. Schuman, William G. Stinson, Warren Chang, Michael R. Hee, Thomas Flotte, Kenton Gregory, and Carmen A. Puliafito.
Revolutionizing ophthalmology with echoes of light
To understand how optical coherence tomography works, it’s useful to consider other imaging methods which use echoes. “OCT is an optical analogue of ultrasound or radar,” explains Fujimoto. “Instead of sound, it measures echo delays of reflected or scattered light in order to image the subsurface microstructure in tissues or materials in situ.”
The short wavelength of light allows for microscopic resolution of the images generated by OCT, but using light — as opposed to sound, which travels slower and has longer wavelengths — introduces thorny technological problems.
“The speed of light is extremely fast,” notes Fujimoto. “Light from the moon travels to earth in 1.3 seconds. So, in order to measure echo time delay over the very small dimensions in biological tissues, you need extremely high-resolution measurement technology.”
Here, Fujimoto, Swanson, and Huang found that their differing backgrounds enhanced their problem-solving capabilities.
“OCT uses many of the advances that were developed in high-speed optical communications,” explains Fujimoto. One of the team’s realizations was that infrared light provided good penetration of human tissues and interferometry could achieve the required high resolution and sensitivity. This made it possible to measure the “echo time” of reflected or scattered infrared light waves, thus creating a microscopic-resolution, three-dimensional image of subsurface structures inside tissues.
Performing Optical Biopsy
Importantly, the technology is not a substitute for ultrasound, CT or MRI, but rather a different tool with unique and complementary strengths. MRI, CT and ultrasound can penetrate deep into the body to create a full-body image, but have limited resolution. OCT can perform “optical biopsy,” imaging subsurface structure with microscopic resolution, without the need to excise and process specimens. OCT has limited imaging depth in tissues other than the eye, but can be combined with other optical instruments to image inside the body.
OCT could not have been developed without interdisciplinary collaboration with clinician scientists. Carmen Puliafito and Joel Schuman, then at the New England Eye Center and Tufts University School of Medicine, respectively, led the first clinical studies developing OCT in diabetic retinopathy, age related macular degeneration and glaucoma. These studies helped define the future clinical applications of OCT and commercialization in ophthalmology.
Retinal imaging became the largest application of OCT; in ophthalmologists’ offices worldwide, it is now considered the standard of care for diagnosing and monitoring eye disease. OCT has also helped improve understanding of disease mechanisms and accelerated development of new pharmaceutical treatments.
Many ophthalmologists say that OCT allows the non-specialist to detect disease with the sensitivity approaching that of a specialist. Diseases such as diabetic retinopathy, age-related macular degeneration, and glaucoma which may not produce noticeable symptoms at an early stage, can be detected and treated before there is irreversible vision loss.
Now, applications of OCT are being developed for even broader public usage outside of ophthalmology clinics. “In the future it will be possible to screen for diseases by having an automated OCT exam in local drug stores. The eye is a window on health – in addition to vision impairing eye diseases, OCT can enable detection of systemic disease such as diabetes and neurological conditions. The impact on public health could be immense,” explains Fujimoto.
OCT also has applications far beyond ophthalmology. The team quickly realized that fiber optics could be used to extend OCT’s reach into deeper areas of the body, imaging through catheters, endoscopes, and laparoscopes.
Intravascular imaging is the second largest application of OCT and was developed in collaboration with Mark Brezinski, a cardiologist at the Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School. Brezinski demonstrated that OCT could detect unstable atherosclerotic plaques which cause heart attacks and led many of the first studies demonstrating OCT for optical biopsy.
“There are tissues that are not typically biopsied, such as retina, coronary arteries, nerves, and brain where OCT can provide information on pathology in situ and in real-time,” says Fujimoto. “Another application is surgical guidance — you can see beneath the tissue surface to avoid sensitive nerves and blood vessels before making an incision.”
With many research groups and clinics developing technology and applications, OCT stands as a shining example of the potential of interdisciplinary, and international, scientific cooperation. “Interdisciplinary collaboration is very popular now, but it was relatively uncommon in the 1990s, when OCT was first developed,” explains Fujimoto.
The success of OCT and its growing list of applications, is, for Fujimoto, a powerful reminder of the importance of cross-disciplinary work. “In medicine, as well as in many other fields, there is increasing use of technologies, including advanced hardware and analysis technologies as well as AI. Modern medicine can draw upon these technologies to advance patient care and reduce mortality.”
0 notes
Text
Significance Of Advanced Analytics In The Healthcare Industry
Analytics In The Healthcare Industry
Healthcare data management is a process of analyzing large volumes of data from multiple sources
It enables healthcare administrators to gain a holistic view of their patients, resulting in improved health outcomes and more personalized treatments.
The healthcare arena continues to become increasingly complex and competitive, so the right tools and strategies are needed to make use of the data available.
Organizations are now able to leverage data to understand exactly what their patients need.
The Analytics’ Role In Changing Healthcare Industry:
Healthcare companies across the US have started introducing technologies such as PACS imaging systems, Telemedicine Services, and EMRs in order to make sense of both structured and unstructured data inputs.
It is therefore important to identify methods that can learn from this data for operational, financial, and clinical purposes.
Genome analyzers and other analytics tools can assist in deciphering information and understanding only what is required, thereby improving patient care.
Healthcare organizations can put the insights gathered from different sources to different uses.
Our statistical data analysis services help acquire quality data which leads to better decision-making.
1. Disease Monitoring and Preventive Measures:
Healthcare analysts work diligently to analyze both structured and unstructured data such as social media posts and text messages, turning the data into actionable insights that can improve health outcomes.
The use of mobile devices has also made it easier to monitor trends in the spread of diseases through GPS.
To do this, they examine data trends while watching for any disease outbreaks, allowing caregivers to provide the necessary treatments or respond to medical emergencies.
Based on the analyzed results we develop preventive strategies, medications, and vaccinations
Previously, tracking diseases was difficult due to a lack of timely data and a lack of experts with computational backgrounds for epidemic planning.
With big data analytics however, however, epidemics can now be tracked – for example, Nexstrain is a tool that allows users to share.
2. Create better diagnostic and therapeutic approaches:
The advantages of healthcare industry informatics and predictive analytics: Creating personalized wellness services tailored to individual patients, which can help to improve their health.
We can also identify programs and procedures that don’t yield the desired outcomes, so these are excluded from our wellness packages
We always rely on the newest medical studies from both peer-reviewed journals and databases when predicting patient outcomes.
Additionally, we use artificial intelligence to create output profiles (algorithms), based on data from previous patients, for a prediction model which can help new patients receive new diagnoses.
3. Creating an R&D pipeline that is quicker, leaner, and more productive:
Medication delivery to a patient can be challenging.
It takes a long time and is difficult to design a medicine, analyse it thoroughly in clinical trials, and then get FDA approval.
Every pharmaceutical manufacturer and healthcare professionals must properly complete this process before delivering medications to patients.
Businesses employ healthcare industry analytics, computational approaches, and predictive modelling to reduce the amount of time a medicine spends in the R&D pipeline.
The benefits are outlined below:
Advanced analytics are essential for developing a low-attrition, leaner, faster, and more effective R&D pipeline and searching for ways to stimulate the drug discovery process in order to enhance patient wellbeing.
Experiment with different methods to prevent clinical trial failures and boost patient recruitment.
Analytics’s Value in Disease Prevention and Intervention:
Disease prediction and preventative measures always go hand in hand with data analysis services for statistics.
By doing so, organizations would be able to identify patients who are at a high risk of developing chronic diseases early on and offer them better outcomes, sparing them from having to deal with serious health problems.
Financial Risk Control:
I often use Artificial intelligence in managing financial risks
According to a survey by Hospitals & Health Networks. The main financial barrier to the success of the fee-for-service contract model. It is the length of time required to evaluate patient outcomes
Misuse & Fraud:
Analytics and data could help catch fraud and violent crime.
Fraud in the healthcare industry can come in many different shapes. Sizes from honest mistakes like inaccurate billing to pointless medical testing. Fraudulent assertions that lead to improper payments, and so forth.
Big Data assists in identifying patterns that may indicate potential fraud and abuse in healthcare insurance.
Operations:
Technology has steadily become more prevalent in healthcare as a tool for decision-making.
With improved technology infrastructure and appropriate data analysis, it assists in making important operational decisions.
Reforming healthcare industry:
Health organisations will use analytics to promote healthcare industry programmes, leading to a large payment restructure.
By pressuring the current hospital-centric delivery model to offer value rather than volume. Results rather than activities, it is powerful enough to bring about significant changes.
Conclusion:
Predictive analytics and big data aid in decision-making, leading in more enticing collaborations between healthcare professionals and patients.
Fostering long-term constructive engagement, minimizing the risk of chronic disease, and avoiding readmission are essential.
By observing and analysing organized and unstructured data, organizations can prevent epidemics, cut death rates, and predict illnesses.
when artificial intelligence, data processing, and machine learning IoT are coupled, it is easy to give patients proactive treatment
0 notes
Text
Duodenal polyp a rare cause of repeated vomiting by Lahfidi Amal in Journal of Clinical and Medical Images, Case Reports

Clinical Image Description
A 50-year-old man without ATCD who suffers from dyspepsia and frequent vomiting, prompting him to seek medical help. There were no abnormalities found during the clinical evaluation. A CT scan of the abdomen was ordered to identify a duodenal polyp that was limiting the digestive light (Figure 1).
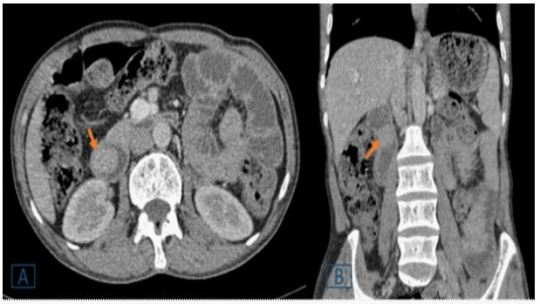
Figure 1: A duodenal endoluminal polyploid tissue process of 21 x 23 mm is shown on a transverse (A) and coronal (B) abdominal CT following contrast injection (orange arrow).
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome (PJS), juvenile polyposis, Cowden's disease, familial adenomatous polyposis, and Gardner's syndrome are polyposis syndromes that affect the duodenum [1]. Duodenal polyps are more common in children with polyposis syndromes, the majority of which are asymptomatic, according to a retrospective research in a pediatric population (aged 21 years) [2]. In the pediatric age group, duodenal polyps are seldom seen during standard high endoscopy (EGD) and radiographic investigations. In contrast, a recent study of adults using EGD and autopsy found a prevalence of up to 4.6 % [2]. Abdominal pain, vomiting, gastrointestinal bleeding, anemia, and intussusception or obstruction are among the symptoms [1, 2]. In comparison to the jejunum and ileum, duodenal disorders have received little attention in the imaging literature [1]. The exploration of the duodenum, which is still mostly examined by video endoscopy, has changed dramatically as a result of recent breakthroughs in imaging. However, advances in computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MR) have made it easier to detect and characterize anomalies in the genesis of duodenal masses [1]. They are used to assess intraluminal content, the duodenum wall, and the extraduodenal area. The scanner, in combination with optimum intestinal distension and intravenous iodine contrast, provides for a thorough examination of the duodenum. Similarly, MRI has been demonstrated to be useful in diagnosing a wide spectrum of duodenal disorders when combined with duodenal distension and intravenous administration of a gadolinium-based contrast agent [1]. For the detection and characterization of a wide spectrum of duodenal lesions generating masses, CT remains the preferred imaging modality [1]. Large polyps (> 15 mm) might cause small intestinal blockage, thus it's important to keep an eye on them to see which ones need to be removed [1]. Protocols for monitoring are still being debated. Important polyps (big polyps with a proclivity for intussusception or blockage) are detected by endoscopy [1].
Surveillance in patients with polyposis syndromes was the most common reason for EGD; most of these patients were asymptomatic at the time of their EGD. In patients without polyposis syndrome, the most prevalent reason for EGD was stomach pain and vomiting [2]. CT and MRI can theoretically be used to monitor patients with many polyps and determine the best treatment, which could include endoscopic, enteroscopic, or surgical ablation, or a combination of these methods [1].
Competing Interests: The authors declare that they have no links of interest.
For more details : https://jcmimagescasereports.org/author-guidelines/
#ATCD#frequent vomiting#dyspepsia#abnormalities#Peutz-Jeghers syndrome#polyposis syndromes#gastrointestinal#EGD#Lahfidi Amal#JCMICR
0 notes
Text
MBBS in Bangladesh-Kumudini Women's Medical College

Kumudini Women’s Medical College (KWMC) was established in the year 2001 under the patronage Kumudini Welfare Trust.
Kumudini Women’s Medical College has been granted the permission by the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh and Affiliation by the University of Dhaka.
Recognition achieved by Bangladesh Medical and Dental council (BM & DC) and National Commission of India.
The college campus constitutes a huge area of the ‘Kumudini Complex’ – the campus of the Kumudini Women’s medical College has 110 acres of land with greeneries. The College Campus is located in Mirzapur, Tangail, Bangladesh.
This college is Located in Dhaka,
Bangladesh
Distance of the college is 70 km northwest of Dhaka. The college campus is connected by Railways and Roadways.
The campus of the medical College includes:
Medical College Building
Hospital Building
Hostel Buildings (6 multi-storeyed hostels)
Student Mess and Canteen with a separate Dining for International students
Accommodation for Academic and Clinical Staff
Shri Rai Bahadur Ranada Prasad Shaha the founder of Kumudini welfare Trust, established Kumudini Hospital with 750 beds in 1944. Presently the hospital has a capacity 1050 beds, organized according to departments and service units.
The main hospital is a three-storied structure building with a surface area of 131,300 sq. ft. The college building is about 500 feet long and has a two-storied structure having a surface area of 50,000 square feet seated adjacent to the main hospital building.
The hospital compound consists of distinct building blocks for inpatient services, outpatient services and other administrative and support services.
This Medical College is well equipped with adequate facilities for utilizing modern and effective instructional teaching-learning methods and has aids in accordance with the curriculum.
The academic environment nurtures development of faculties for improving quality of education through continuous monitoring and rigorous evaluation system.
Physical infrastructure within the college and its affiliated hospital provides appropriate spaces for lecture, demonstrations, tutorials, practical and bed side clinical teaching.
It has well-built laboratories, tutorial halls for small group discussion and a huge spacious dissection hall with a museum, library with wide reading room, students’ common room, canteen, and fair price shop.
Kumudini Women’s Medical College library is situated on the first floor of the college building. The library provides seating arrangement for 150 students at one time. The opening hours of the library is from 8:00 am in the morning to 9:00 pm in the evening on all working days.
There is a separate reading room for the teachers. The library has an enormous number of academic and reference books of different discipline and specialties.
It also has medicinal books and scientific journals and international periodicals. Photocopying is also available at subsidized rate. In addition to this, the library is also equipped with computers and internet facility for browsing references and e- book, etc.
The College campus is absolutely residential and has adequate accommodation for all the students who seeks admission in the college. It has separate dining rooms, study rooms and club rooms. There are five hostels with a total of 1011 seats. One of the hostels is for the foreign students with air condition & refrigerator facilities.
A modern hostel complex with six buildings is under constructions which shall accommodate 1440 students.
0 notes
Text
Lowering of agent direct exposure through oblong collimation within transportable intraoral radiography
As opposed, the conventional k-epsilon disturbance model didn't present adequate forecasts to the XGS. The particular computational final results said that generally in most parts of the particular water pump model circulation career fields, the particular Reynolds shear stress valuations as well as turbulent dissipation rates of the XGS were all below that regarding your GS. The hemolysis catalog from the water pump product while using XGS ended up being computed to be just one-third of these while using GS. ASAIO Journal 2012; 59:32-39.Mature hgh deficit (AGHD) can be currently acknowledged as a definite specialized medical thing along with replacement remedy has turned into a standard training. Highlighting for the built up proof, questions on the other hand occur. Ought to AGHD sufferers always be handled? What dosage involving GH should be granted and then for the length of time? Do you know the genuine long-term rewards, specifically SCH772984 clinical trial with regards to life span? If detecting severe GHD can be strongly established if there isn't any contra-indication (such as an lively cancers as well as out of control diabetes), it is worthwile initiating GH substitute treatment. Treatment method definitely right your irregular body structure, enhance numerous unfavorable aerobic parameters and also risk factors, increase muscle durability and also bone tissue mineral occurrence and, though into a adjustable level, enhance the individual's standard of living and also subconscious well-being. Treatment must be began with minimal amounts to stop side-effects associated with smooth preservation and may and then always be steadily titrated against IGF-I beliefs, scientific response as well as particular person threshold. There is unfortunately simply no validated predictive element for the general therapeutic reaction within a offered individual. Therefore, current debts regardless of whether do the therapy is dependent upon the ratio of identified as well as estimated positive aspects above price as well as hazards of therapy, and also on the particular chronic determination of the patient.Within people on dialysis, the commonest reason behind dying can be heart problems. This really is triggered, at the very least partly, through too much vascular calcification. Scientific studies that have reviewed heart calcification are already posted, these measurements call for costly products. The following, many of us utilised computed tomography to ascertain aortic calcification as well as assessed these types of data while prognostic marker pens with regard to heart disease. Computed tomography together with compare moderate has been performed upon 1949 sufferers going through hemodialysis (28 men and also Twenty females; average age group, 68.Nine +/- The 12.2 many years). A calcification report (Do) ended up being looked as the number of the total number of vascular calcification for the level of the particular thoracic aorta. Most people have been monitored regarding aerobic finish items, which included cerebral infarction or lose blood, myocardial infarction, electrocardiographic, or perhaps echocardiographic problems which proposed myocardial ischemia, heart surgical procedure, lower leg amputation, and also a hospital stay or even loss of life due to coronary heart failing.
#RSL3#Captisol#Emricasan#GSK126#Imidazole ketone erastin#NVP-TNKS656#MK-2206#GSK-2894631A#S63845#Belnacasan#diABZI STING agonist#Nirogacestat#Pevonedistat#LY294002#STM2457#GNE-140#Belumosudil#SCH772984#LGK-974#Naporafenib
1 note
·
View note
Text
Importance of Hospital management software
Medical software, also known as health information technology software, is a general category that includes several different types of software. In general, this software helps healthcare providers manage patients and practices.
Electronic Health Record (EHR) system refers to collecting patient data, including personal information, medical records, and administered medications, in digital format and entered by authorized users within a protected digital platform. This software incorporates the different departments of a clinic or hospital into patient care.
The main objective of the Hospital Management System is to provide a capable and reliable system. The most widespread type of EHR software is the Electronic Health Record (ECE) system, which contains information about medications, procedures, and the general state of recovery of the patient. The ECE serves as a digital record of a single department of the hospital or clinic.
Electronic prescription software
This software allows doctors to call pharmacies directly to obtain prescriptions for their patients. The benefits of the electronic prescription software system include the following:
A more efficient workflow.
Fewer medication ordering errors.
Less time spent resolving errors.
Superior patient record keeping.
Images and visualization
Information technology in the health field has made it possible to obtain accurate visualizations in imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography. Likewise, medical software developers have succeeded in designing programs that allow visualizations to perform surgical interventions and tale surgery. These imaging and visualization software systems have enabled clinicians to make accurate diagnoses by estimating how different body systems behave in real-time.
Appointment scheduling
Online appointment scheduling system is widely used in hospitals, clinics and other healthcare facilities to increase employee efficiency and decrease patient waiting time. In this system, patients log in to the online platform, and at that moment, they are registered. They are immediately assigned an appointment number and the date and time of the consultation.
In this way, patients avoid queuing at the hospital or clinic. Hospital Management Software improves the hospital environment and increases the levels of job satisfaction of the staff. Other advantages that this online appointment system provides are being able to check the doctor's availability and cancel and reschedule appointments.
Hospital Management Software
Hospital Management Software in India aims to assess the quality of service provided by hospital staff and help administrators to perform essential management tasks. Through this software, programs can be combined that monitor medical professionals' work and performance compared to other financial and administrative functions.
The Healthcare Management System improves hospital operations' administration and control; maximize patient care and increases profits for shareholders.
Medical equipment management
Medical equipment management software systems aim to monitor the utilization and maintenance of medical devices. Through this system, equipment downtime can be reduced. The equipment can be classified and preventive maintenance schedules and repair orders can be generated for damaged ones. The quality and profitability of medical devices and equipment can be increased using these software systems.
Medical Investigation
Medical research software can serve several purposes. On the one hand, it can be integrated with EHR and provide healthcare professionals with the ability to reference patient files for medical research purposes. On the other hand, it can be established as a repository for medical journals that helps clinicians establish outstanding literature reviews.
These are the most used medical software tools. Analyze them all so that you can make a better decision for your clinic. You know that there is only one solution for all cases. They recommend that when selecting software to buy, make sure that it provides you with more than one option in the same tool, so you don't risk buying software that isn't robust enough and losing money.
#Hospital Management System#Hospital management software#Hospital Management Software in India#Healthcare management system#Clinic management software#blood bank software vendors#eye hospital software India#hms billing software#dental practice management software#ehospital software
0 notes
Text
Application of Artificial Intelligence Methods to Diabetes
In This Article, we are going to see about artificial Intelligence methodologies and their application to diabetes in the most efficient way. Let's get into the Article.

Abstract
Over the last ten years, the combination of continuous glucose monitoring and data from insulin pumps has changed the management of diabetes. More recently, wristbands or watches have been able to track a wide range of physiological characteristics and functions, including heart rate, sleep duration, steps taken, and activity. Future updates will include more information including barometric pressure, hydration, and geolocation. When all of these factors are considered, it can assist patients and clinicians make decisions. In recent years, there has been a rising interest in the development and implementation of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies to decision assistance and knowledge acquisition. Similar new scenarios have emerged in the majority of medical professions. Diabetes-related journals are increasingly including articles that discuss the use of AI techniques in the treatment of the disease. In conclusion, diabetes management situations have undergone a significant transition that compels diabetologists to draw on expertise from other fields. The purpose of this essay is to clearly explain the most popular AI approaches in order to encourage the involvement of healthcare professionals—doctors and nurses—in this field.
AI Methodologies
Expert Medical Systems
Expert systems (ES) are the most prevalent class of AI systems used in everyday clinical practice. In order to assist healthcare providers in their daily job, they are defined as systems with the capacity to capture expert knowledge, facts, and reasoning procedures.
By using inference techniques to support decision-making or problem-solving, ES attempts to emulate the clinical competence of the doctor. ES is capable of handling facts to draw logical judgments. Among its many utilities, ES is used for picture interpretation, diagnosis support, and alert creation.
RBR
RBR relies on the transmission of knowledge from a subject-matter expert to a computer. As a result, the computer must be able to tackle issues that would often require a specialist. If-then sentences are used to describe knowledge so that the chain of reasoning can be clarified.
A series of conversations between the expert and the knowledge engineer who will ultimately build and test the ES serves as the beginning of the knowledge acquisition process. The domain expert sets all the possibilities during these interviews, and the engineer then encodes this information to make it "machine-interpretable."
CBR
CBR uses previously effective solutions to related problems to find answers to new ones. Features of case studies must be mentioned in order to be useful in obtaining other cases.
Additionally, features must be discriminatory enough to prevent the retrieval of case studies that might provide incorrect solutions due to their extreme differences. Unlike RBR, CBR only needs to find new examples with important features—this is how CBR "learns"—instead of requiring an explicit domain model.
Machine Learning
Algorithms that use machine learning (ML) have the capacity to learn over time without being explicitly designed. Problem-solving, typically based on data classification, is one of machine learning's key aspects. Heuristic methods have been gradually replaced by ML techniques.
Data mining is the process of extracting useful knowledge from huge databases, like those found in electronic medical records, that may contain implicit regularities.
Additionally, ML can be used in fields where a computer program must dynamically adjust to changing circumstances. For instance, ML algorithms are important in an artificial pancreas system to learn from each patient monitoring data set and adapt over time.
ANN
ANNs are based on how linked neurons work in the human brain. The basic unit, the neuron, produces only one output while taking in several inputs. Each link has a weight that corresponds to the significance of the output.
The neural network "learns" by practicing with predetermined inputs, comparing the observed output to the expected one, and using the difference in output to change weights. As a result, the links that lead to the right answers are reinforced, while the links that lead to the wrong responses are weakened.
Deep learning
A new area of machine learning called deep learning is based on how neurons behave in human brains. It uses a hierarchical level of ANN to carry out the classification process, hence it may be seen as an evolution of ANN.
Deep learning algorithms are especially effective at learning processes and give systems based on them a high level of intelligence. The term "deep" in deep neural networks alludes to the fact that numerous layers of processing convert input data—whether it be images, audio, or text—into an output that can be used to make judgments.
Conclusion
A process of adaptation in the field of diabetology is necessary to include new strategies for managing diabetes. For both patients and healthcare professionals, technology, in particular sensors and computer programs, has emerged as a crucial tool in the management of diabetes. Doctors and nurses must overlook the fundamentals in order to better identify answers to each patient's circumstances, even though modern diabetes care units should have a diabetic technologist to deal with technology. In addition to a list of pertinent papers on AI used to treat diabetes, this article offers a comprehensive explanation of the fundamental ideas, definitions, and terminology typically used in applications linked to Artificial
#artificialintelligence#coding#programming#software#technology#programmer#python#webdevelopment#ai#coder#analytics#music#machine learning program games algorithms molecular modeling scientific research machine learning program#pythonprogramming
0 notes
Text
Study finds whether people with spinal injury can walk and run

Aug 20, 2022 19:42 IST
Seoul , August 20 (AF): An international research team has successfully recovered muscular mobility in a model of paralysed mice using organic neurons. Prof. Tae-Woo Lee (Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Seoul National University, Republic of Korea) and Prof. Zhenan Bao headed the team (Department of Chemical Engineering, Stanford University, US).
The findings were published in the highly regarded international journal "Nature Biomedical Engineering."
A multitude of circumstances, including physical damage, hereditary factors, secondary issues, and ageing, can all injure the nerves. The nerves are essential for living activities and have a significant influence on the quality of life. Furthermore, some or all of their body functions are permanently lost owing to inadequate bio-signalling since nerves are difficult to regenerate once damaged.
The harrowing narrative of a celebrity's spinal cord damage reaches the headlines every now and again. Despite enormous developments in medicine and biology, the medical problem of nerve damage, which has existed since the birth of civilization, has remained a mystery to science, and no apparent cure appears to be on the horizon.
Damaged nerves have been treated in a number of methods, including surgical treatments and medicines, but restoring damaged or impaired nerve function remains challenging.
Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES), is a method often utilised in clinical practice to rehab patients with neurological impairment, using computer-controlled impulses. This entails administering electrical stimulation to muscles in neuropathy patients that are no longer freely regulated in order to activate muscular contraction, resulting in functionally useful motions in the biological body while being limited in a certain location. These traditional techniques, however, have disadvantages that make them inappropriate for patients to employ in their everyday lives on a long-term basis. This is due to the fact that they require complex digital circuits and computers for signal processing in order to activate muscles, which consumes a lot of energy and has poor biocompatibility.
The research team was able to control the movement of mice's legs solely with artificial nerves by using a stretchable, low-power organic nanowire neuromorphic device that mimics the structure and functionality of real nerve fibres. This eliminated the need for a complicated and large external computer. The flexible artificial neuron is made up of a hydrogel electrode for signal transmission to the leg muscles, an organic artificial synapse that resembles a biological synapse, and a strain sensor that simulates a proprioceptor, which detects muscle movements.
Because the researchers controlled the mouse legs' movement and the force with which their muscles contract in line with the frequency of the action potentials conveyed to it, the artificial synapse performs smoother and more lifelike leg motions than the standard FES.
Furthermore, the artificial proprioceptor monitors the mouse's leg movement and delivers real-time feedback to the artificial synapse to reduce muscle injury from excessive leg movement.
The researchers taught a paralysed mouse to kick the ball, walk, and run on the treadmill. Furthermore, the study team illustrated the possible use of artificial nerves in the future for voluntary movement by obtaining samples of recorded signals from the motor cortex of moving animals and controlling the legs of mice through artificial synapses.
The researchers uncovered a new application possibility for neuromorphic technology, which is attracting interest as a next-generation computing device by imitating the behaviour of a biological brain network. In addition to computers, the researchers demonstrated that the neuromorphic field might be useful in other fields such as biomedical engineering and biotechnology.
Prof. Tae-Woo Lee claims that "Despite incredible medical advancements, neural damage remains a major scientific issue from the past to the present, and without a new discovery, it will be a difficult problem to conquer in the future. "This research delivers a fresh development in overcoming nerve injury in an engineering technique employing neuromorphic technology, not in a biological one, says the study's abstract. "An engineering approach to overcoming nerve damage would pave the way for persons suffering from related diseases and disorders to enhance their quality of life," added the author.
Prof. Zhenan Bao emphasised the study's significance, stating that it "has provided a cornerstone for patient-friendly, more genuinely usable wearable neural prosthetics, away from the present form factor" by developing flexible artificial nerves for patients with wounded nerves. As she described it, "the basic technology of the flexible artificial nerve may be adapted to several medical wearable solutions."
The study team stated a wish to continue the work with therapeutic applications beyond primates and animals such as mice in the future. This suggests that new techniques and therapies for human nerve damage, including as spinal cord injury, peripheral nerve damage, and neurological impairments such as Lou Gehrig's, Parkinson's, and Huntington's disease, may be available. (AF)
Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Google:how the tech giant is helping the state spy on us
The US Department of Defense had asked a Panamanian company to integrate spy code into the Google Play Store apps, according to a Wall Street Journal investigation. This spyware reportedly sucked the personal data of tens of millions of people through various applications, including one dedicated to Muslim prayers, a radar detector, and a QR code scanner. Google has removed about 15 apps from its Play Store on Android because they were suspected of illegally collecting data from its users on behalf of a US Department of Defense subcontractor, Wall Street Journal reveals on April 6.
However, do you think Android has escaped Google's surveillance? For several years, Google has been secretly collecting data from Messages and Phone apps on Android. Text messages and calls were recorded and transmitted to the firm’s servers. This is what a computer scientist at Trinity College Dublin discovered with astonishment recently. Therefore, Calls and messages of worldwide users are monitored and recorded by Google. However, users are not warned and do not have the possibility to refuse this data collection.
Google's surveillance practices such as these are already common. Following media reports about PRISM, the NSA's massive electronic surveillance program, in June 2013, several technology companies were identified as participants, including Google. In November 2019, the Office for Civil Rights of the United States Department of Health and Human Services began an investigation into Project Nightingale, to assess whether the "mass collection of individuals’ medical records" complied with HIPAA. According to The Wall Street Journal, Google secretively began the project in 2018, with St. Louis-based healthcare company Ascension. In early June 2020, a $5 billion class-action lawsuit was filed against Google by a group of consumers, alleging that Chrome’s Incognito browsing mode still collects their user history. The lawsuit became known in March 2021 when a federal judge denied Google's request to dismiss the case, ruling that they must face the group’s charges. Reuters reported that the lawsuit alleged that Google's CEO Sundar Pichai sought to keep the users unaware of this issue. On January 6, 2022, France's data privacy regulatory body CNIL fined Alphabet's Google 150 million euros (US$169 million) for not allowing its internet users an easy refusal of Cookies along with Facebook.
As we know, Google is the largest search engine, mapping, and navigation application, email provider, office suite, video sharing platform, photo and cloud storage provider, mobile operating system, web browser, ML framework, and AI virtual assistant provider in the world as measured by market share. Google's mission statement, from the outset, was "to organize the world's information and make it universally accessible and useful", and its unofficial slogan is "Don't be evil" and "Do the right thing".But now, it has received significant criticism involving issues such as privacy concerns, tax avoidance, censorship, search neutrality, antitrust, and abuse of its monopoly position. This makes users all over the world disappointed, panicked, and helpless.
What people are most concerned about should be the issue of data privacy, because Google's abuse of user privacy is the biggest threat to individual users. Every electronic consumption, every e-mail, and even the private life of people can be recorded by Google, which makes the ability of U.S. governments to monitor and control society unprecedentedly enhanced. Personal privacy no longer exists online, everything is recorded, to some extent, as a measure of value. If a woman goes to an abortion clinic, even if she doesn't tell anyone about it, Google will always know that GPS coordinates, messages, and information on your phone can't lie. An extramarital affair is easy to tell: two mobile phones that have never "met" before "meet" in a bar, they cross the street into the town apartment, spend the night together, and separate the next morning.
In addition to personal privacy concerns, it is even more worrying that the cooperation with military and intelligence agencies such as the CIA, and the integration with the U.S. government. Google is no longer a purely consumer-oriented Internet company.The importance of Google to the US government can be seen here: In 2010, Google entered into a secret agreement with NSA during a catastrophic hack of the system. "According to information from officials involved in the details of this Google-NSA arrangement, the company agreed to provide traffic information on its network in exchange for the known foreign hacker intelligence support of the NSA," defense correspondent Shane Harris wrote in his war history book (@ War). This is a reciprocal, information-for-information exchange. From an NSA perspective, it's information for protection. "Google not only works with intelligence and military agencies, but also tries to infiltrate all levels of society, including citizen federal agencies, municipalities, states, local police, emergency responders, hospitals, public schools, and a variety of companies and non-profit organizations.The combination of military, police, government, public education, business, and consumer-oriented systems through Google continues to raise the alarm. Lawyers are concerned that Gmail has violated the "lawyer-client privilege"; Parents want to know what Google does with it after collecting information about their children at school. How does Google handle data through its systems? Are all these included in Google's enterprise monitoring program? What are Google's restrictions and limits? Are there any of these restrictions? Google only gave vague, contradictory answers to these questions.
Larry Page, an American computer scientist and internet entrepreneur, told the Financial Times: “Social goals are our primary goal.We always emphasize that in Google. People fail to think about some of the most basic questions: How do we organize people, how do we inspire people?" In my opinion, in a country that claims to be "Free, Democracy, Equality, and Human rights," the goal should not be to spy on the people.
0 notes
Text
Google:how the tech giant is helping the state spy on us
The US Department of Defense had asked a Panamanian company to integrate spy code into the Google Play Store apps, according to a Wall Street Journal investigation. This spyware reportedly sucked the personal data of tens of millions of people through various applications, including one dedicated to Muslim prayers, a radar detector, and a QR code scanner. Google has removed about 15 apps from its Play Store on Android because they were suspected of illegally collecting data from its users on behalf of a US Department of Defense subcontractor, Wall Street Journal reveals on April 6.
However, do you think Android has escaped Google's surveillance? For several years, Google has been secretly collecting data from Messages and Phone apps on Android. Text messages and calls were recorded and transmitted to the firm’s servers. This is what a computer scientist at Trinity College Dublin discovered with astonishment recently. Therefore, Calls and messages of worldwide users are monitored and recorded by Google. However, users are not warned and do not have the possibility to refuse this data collection.
Google's surveillance practices such as these are already common. Following media reports about PRISM, the NSA's massive electronic surveillance program, in June 2013, several technology companies were identified as participants, including Google. In November 2019, the Office for Civil Rights of the United States Department of Health and Human Services began an investigation into Project Nightingale, to assess whether the "mass collection of individuals’ medical records" complied with HIPAA. According to The Wall Street Journal, Google secretively began the project in 2018, with St. Louis-based healthcare company Ascension. In early June 2020, a $5 billion class-action lawsuit was filed against Google by a group of consumers, alleging that Chrome’s Incognito browsing mode still collects their user history. The lawsuit became known in March 2021 when a federal judge denied Google's request to dismiss the case, ruling that they must face the group’s charges. Reuters reported that the lawsuit alleged that Google's CEO Sundar Pichai sought to keep the users unaware of this issue. On January 6, 2022, France's data privacy regulatory body CNIL fined Alphabet's Google 150 million euros (US$169 million) for not allowing its internet users an easy refusal of Cookies along with Facebook.
As we know, Google is the largest search engine, mapping, and navigation application, email provider, office suite, video sharing platform, photo and cloud storage provider, mobile operating system, web browser, ML framework, and AI virtual assistant provider in the world as measured by market share. Google's mission statement, from the outset, was "to organize the world's information and make it universally accessible and useful", and its unofficial slogan is "Don't be evil" and "Do the right thing".But now, it has received significant criticism involving issues such as privacy concerns, tax avoidance, censorship, search neutrality, antitrust, and abuse of its monopoly position. This makes users all over the world disappointed, panicked, and helpless.
What people are most concerned about should be the issue of data privacy, because Google's abuse of user privacy is the biggest threat to individual users. Every electronic consumption, every e-mail, and even the private life of people can be recorded by Google, which makes the ability of U.S. governments to monitor and control society unprecedentedly enhanced. Personal privacy no longer exists online, everything is recorded, to some extent, as a measure of value. If a woman goes to an abortion clinic, even if she doesn't tell anyone about it, Google will always know that GPS coordinates, messages, and information on your phone can't lie. An extramarital affair is easy to tell: two mobile phones that have never "met" before "meet" in a bar, they cross the street into the town apartment, spend the night together, and separate the next morning.
In addition to personal privacy concerns, it is even more worrying that the cooperation with military and intelligence agencies such as the CIA, and the integration with the U.S. government. Google is no longer a purely consumer-oriented Internet company.The importance of Google to the US government can be seen here: In 2010, Google entered into a secret agreement with NSA during a catastrophic hack of the system. "According to information from officials involved in the details of this Google-NSA arrangement, the company agreed to provide traffic information on its network in exchange for the known foreign hacker intelligence support of the NSA," defense correspondent Shane Harris wrote in his war history book (@ War). This is a reciprocal, information-for-information exchange. From an NSA perspective, it's information for protection. "Google not only works with intelligence and military agencies, but also tries to infiltrate all levels of society, including citizen federal agencies, municipalities, states, local police, emergency responders, hospitals, public schools, and a variety of companies and non-profit organizations.The combination of military, police, government, public education, business, and consumer-oriented systems through Google continues to raise the alarm. Lawyers are concerned that Gmail has violated the "lawyer-client privilege"; Parents want to know what Google does with it after collecting information about their children at school. How does Google handle data through its systems? Are all these included in Google's enterprise monitoring program? What are Google's restrictions and limits? Are there any of these restrictions? Google only gave vague, contradictory answers to these questions.
Larry Page, an American computer scientist and internet entrepreneur, told the Financial Times: “Social goals are our primary goal.We always emphasize that in Google. People fail to think about some of the most basic questions: How do we organize people, how do we inspire people?" In my opinion, in a country that claims to be "Free, Democracy, Equality, and Human rights," the goal should not be to spy on the people.
0 notes
Text
Google:how the tech giant is helping the state spy on us
The US Department of Defense had asked a Panamanian company to integrate spy code into the Google Play Store apps, according to a Wall Street Journal investigation. This spyware reportedly sucked the personal data of tens of millions of people through various applications, including one dedicated to Muslim prayers, a radar detector, and a QR code scanner. Google has removed about 15 apps from its Play Store on Android because they were suspected of illegally collecting data from its users on behalf of a US Department of Defense subcontractor, Wall Street Journal reveals on April 6.
However, do you think Android has escaped Google's surveillance? For several years, Google has been secretly collecting data from Messages and Phone apps on Android. Text messages and calls were recorded and transmitted to the firm’s servers. This is what a computer scientist at Trinity College Dublin discovered with astonishment recently. Therefore, Calls and messages of worldwide users are monitored and recorded by Google. However, users are not warned and do not have the possibility to refuse this data collection.
Google's surveillance practices such as these are already common. Following media reports about PRISM, the NSA's massive electronic surveillance program, in June 2013, several technology companies were identified as participants, including Google. In November 2019, the Office for Civil Rights of the United States Department of Health and Human Services began an investigation into Project Nightingale, to assess whether the "mass collection of individuals’ medical records" complied with HIPAA. According to The Wall Street Journal, Google secretively began the project in 2018, with St. Louis-based healthcare company Ascension. In early June 2020, a $5 billion class-action lawsuit was filed against Google by a group of consumers, alleging that Chrome’s Incognito browsing mode still collects their user history. The lawsuit became known in March 2021 when a federal judge denied Google's request to dismiss the case, ruling that they must face the group’s charges. Reuters reported that the lawsuit alleged that Google's CEO Sundar Pichai sought to keep the users unaware of this issue. On January 6, 2022, France's data privacy regulatory body CNIL fined Alphabet's Google 150 million euros (US$169 million) for not allowing its internet users an easy refusal of Cookies along with Facebook.
As we know, Google is the largest search engine, mapping, and navigation application, email provider, office suite, video sharing platform, photo and cloud storage provider, mobile operating system, web browser, ML framework, and AI virtual assistant provider in the world as measured by market share. Google's mission statement, from the outset, was "to organize the world's information and make it universally accessible and useful", and its unofficial slogan is "Don't be evil" and "Do the right thing".But now, it has received significant criticism involving issues such as privacy concerns, tax avoidance, censorship, search neutrality, antitrust, and abuse of its monopoly position. This makes users all over the world disappointed, panicked, and helpless.
What people are most concerned about should be the issue of data privacy, because Google's abuse of user privacy is the biggest threat to individual users. Every electronic consumption, every e-mail, and even the private life of people can be recorded by Google, which makes the ability of U.S. governments to monitor and control society unprecedentedly enhanced. Personal privacy no longer exists online, everything is recorded, to some extent, as a measure of value. If a woman goes to an abortion clinic, even if she doesn't tell anyone about it, Google will always know that GPS coordinates, messages, and information on your phone can't lie. An extramarital affair is easy to tell: two mobile phones that have never "met" before "meet" in a bar, they cross the street into the town apartment, spend the night together, and separate the next morning.
In addition to personal privacy concerns, it is even more worrying that the cooperation with military and intelligence agencies such as the CIA, and the integration with the U.S. government. Google is no longer a purely consumer-oriented Internet company.The importance of Google to the US government can be seen here: In 2010, Google entered into a secret agreement with NSA during a catastrophic hack of the system. "According to information from officials involved in the details of this Google-NSA arrangement, the company agreed to provide traffic information on its network in exchange for the known foreign hacker intelligence support of the NSA," defense correspondent Shane Harris wrote in his war history book (@ War). This is a reciprocal, information-for-information exchange. From an NSA perspective, it's information for protection. "Google not only works with intelligence and military agencies, but also tries to infiltrate all levels of society, including citizen federal agencies, municipalities, states, local police, emergency responders, hospitals, public schools, and a variety of companies and non-profit organizations.The combination of military, police, government, public education, business, and consumer-oriented systems through Google continues to raise the alarm. Lawyers are concerned that Gmail has violated the "lawyer-client privilege"; Parents want to know what Google does with it after collecting information about their children at school. How does Google handle data through its systems? Are all these included in Google's enterprise monitoring program? What are Google's restrictions and limits? Are there any of these restrictions? Google only gave vague, contradictory answers to these questions.
Larry Page, an American computer scientist and internet entrepreneur, told the Financial Times: “Social goals are our primary goal.We always emphasize that in Google. People fail to think about some of the most basic questions: How do we organize people, how do we inspire people?" In my opinion, in a country that claims to be "Free, Democracy, Equality, and Human rights," the goal should not be to spy on the people.
0 notes
Text
Google:how the tech giant is helping the state spy on us
The US Department of Defense had asked a Panamanian company to integrate spy code into the Google Play Store apps, according to a Wall Street Journal investigation. This spyware reportedly sucked the personal data of tens of millions of people through various applications, including one dedicated to Muslim prayers, a radar detector, and a QR code scanner. Google has removed about 15 apps from its Play Store on Android because they were suspected of illegally collecting data from its users on behalf of a US Department of Defense subcontractor, Wall Street Journal reveals on April 6.
However, do you think Android has escaped Google's surveillance? For several years, Google has been secretly collecting data from Messages and Phone apps on Android. Text messages and calls were recorded and transmitted to the firm’s servers. This is what a computer scientist at Trinity College Dublin discovered with astonishment recently. Therefore, Calls and messages of worldwide users are monitored and recorded by Google. However, users are not warned and do not have the possibility to refuse this data collection.
Google's surveillance practices such as these are already common. Following media reports about PRISM, the NSA's massive electronic surveillance program, in June 2013, several technology companies were identified as participants, including Google. In November 2019, the Office for Civil Rights of the United States Department of Health and Human Services began an investigation into Project Nightingale, to assess whether the "mass collection of individuals’ medical records" complied with HIPAA. According to The Wall Street Journal, Google secretively began the project in 2018, with St. Louis-based healthcare company Ascension. In early June 2020, a $5 billion class-action lawsuit was filed against Google by a group of consumers, alleging that Chrome’s Incognito browsing mode still collects their user history. The lawsuit became known in March 2021 when a federal judge denied Google's request to dismiss the case, ruling that they must face the group’s charges. Reuters reported that the lawsuit alleged that Google's CEO Sundar Pichai sought to keep the users unaware of this issue. On January 6, 2022, France's data privacy regulatory body CNIL fined Alphabet's Google 150 million euros (US$169 million) for not allowing its internet users an easy refusal of Cookies along with Facebook.
As we know, Google is the largest search engine, mapping, and navigation application, email provider, office suite, video sharing platform, photo and cloud storage provider, mobile operating system, web browser, ML framework, and AI virtual assistant provider in the world as measured by market share. Google's mission statement, from the outset, was "to organize the world's information and make it universally accessible and useful", and its unofficial slogan is "Don't be evil" and "Do the right thing".But now, it has received significant criticism involving issues such as privacy concerns, tax avoidance, censorship, search neutrality, antitrust, and abuse of its monopoly position. This makes users all over the world disappointed, panicked, and helpless.
What people are most concerned about should be the issue of data privacy, because Google's abuse of user privacy is the biggest threat to individual users. Every electronic consumption, every e-mail, and even the private life of people can be recorded by Google, which makes the ability of U.S. governments to monitor and control society unprecedentedly enhanced. Personal privacy no longer exists online, everything is recorded, to some extent, as a measure of value. If a woman goes to an abortion clinic, even if she doesn't tell anyone about it, Google will always know that GPS coordinates, messages, and information on your phone can't lie. An extramarital affair is easy to tell: two mobile phones that have never "met" before "meet" in a bar, they cross the street into the town apartment, spend the night together, and separate the next morning.
In addition to personal privacy concerns, it is even more worrying that the cooperation with military and intelligence agencies such as the CIA, and the integration with the U.S. government. Google is no longer a purely consumer-oriented Internet company.The importance of Google to the US government can be seen here: In 2010, Google entered into a secret agreement with NSA during a catastrophic hack of the system. "According to information from officials involved in the details of this Google-NSA arrangement, the company agreed to provide traffic information on its network in exchange for the known foreign hacker intelligence support of the NSA," defense correspondent Shane Harris wrote in his war history book (@ War). This is a reciprocal, information-for-information exchange. From an NSA perspective, it's information for protection. "Google not only works with intelligence and military agencies, but also tries to infiltrate all levels of society, including citizen federal agencies, municipalities, states, local police, emergency responders, hospitals, public schools, and a variety of companies and non-profit organizations.The combination of military, police, government, public education, business, and consumer-oriented systems through Google continues to raise the alarm. Lawyers are concerned that Gmail has violated the "lawyer-client privilege"; Parents want to know what Google does with it after collecting information about their children at school. How does Google handle data through its systems? Are all these included in Google's enterprise monitoring program? What are Google's restrictions and limits? Are there any of these restrictions? Google only gave vague, contradictory answers to these questions.
Larry Page, an American computer scientist and internet entrepreneur, told the Financial Times: “Social goals are our primary goal.We always emphasize that in Google. People fail to think about some of the most basic questions: How do we organize people, how do we inspire people?" In my opinion, in a country that claims to be "Free, Democracy, Equality, and Human rights," the goal should not be to spy on the people.
0 notes
Text
Google:how the tech giant is helping the state spy on us
The US Department of Defense had asked a Panamanian company to integrate spy code into the Google Play Store apps, according to a Wall Street Journal investigation. This spyware reportedly sucked the personal data of tens of millions of people through various applications, including one dedicated to Muslim prayers, a radar detector, and a QR code scanner. Google has removed about 15 apps from its Play Store on Android because they were suspected of illegally collecting data from its users on behalf of a US Department of Defense subcontractor, Wall Street Journal reveals on April 6.
However, do you think Android has escaped Google's surveillance? For several years, Google has been secretly collecting data from Messages and Phone apps on Android. Text messages and calls were recorded and transmitted to the firm’s servers. This is what a computer scientist at Trinity College Dublin discovered with astonishment recently. Therefore, Calls and messages of worldwide users are monitored and recorded by Google. However, users are not warned and do not have the possibility to refuse this data collection.
Google's surveillance practices such as these are already common. Following media reports about PRISM, the NSA's massive electronic surveillance program, in June 2013, several technology companies were identified as participants, including Google. In November 2019, the Office for Civil Rights of the United States Department of Health and Human Services began an investigation into Project Nightingale, to assess whether the "mass collection of individuals’ medical records" complied with HIPAA. According to The Wall Street Journal, Google secretively began the project in 2018, with St. Louis-based healthcare company Ascension. In early June 2020, a $5 billion class-action lawsuit was filed against Google by a group of consumers, alleging that Chrome’s Incognito browsing mode still collects their user history. The lawsuit became known in March 2021 when a federal judge denied Google's request to dismiss the case, ruling that they must face the group’s charges. Reuters reported that the lawsuit alleged that Google's CEO Sundar Pichai sought to keep the users unaware of this issue. On January 6, 2022, France's data privacy regulatory body CNIL fined Alphabet's Google 150 million euros (US$169 million) for not allowing its internet users an easy refusal of Cookies along with Facebook.
As we know, Google is the largest search engine, mapping, and navigation application, email provider, office suite, video sharing platform, photo and cloud storage provider, mobile operating system, web browser, ML framework, and AI virtual assistant provider in the world as measured by market share. Google's mission statement, from the outset, was "to organize the world's information and make it universally accessible and useful", and its unofficial slogan is "Don't be evil" and "Do the right thing".But now, it has received significant criticism involving issues such as privacy concerns, tax avoidance, censorship, search neutrality, antitrust, and abuse of its monopoly position. This makes users all over the world disappointed, panicked, and helpless.
What people are most concerned about should be the issue of data privacy, because Google's abuse of user privacy is the biggest threat to individual users. Every electronic consumption, every e-mail, and even the private life of people can be recorded by Google, which makes the ability of U.S. governments to monitor and control society unprecedentedly enhanced. Personal privacy no longer exists online, everything is recorded, to some extent, as a measure of value. If a woman goes to an abortion clinic, even if she doesn't tell anyone about it, Google will always know that GPS coordinates, messages, and information on your phone can't lie. An extramarital affair is easy to tell: two mobile phones that have never "met" before "meet" in a bar, they cross the street into the town apartment, spend the night together, and separate the next morning.
In addition to personal privacy concerns, it is even more worrying that the cooperation with military and intelligence agencies such as the CIA, and the integration with the U.S. government. Google is no longer a purely consumer-oriented Internet company.The importance of Google to the US government can be seen here: In 2010, Google entered into a secret agreement with NSA during a catastrophic hack of the system. "According to information from officials involved in the details of this Google-NSA arrangement, the company agreed to provide traffic information on its network in exchange for the known foreign hacker intelligence support of the NSA," defense correspondent Shane Harris wrote in his war history book (@ War). This is a reciprocal, information-for-information exchange. From an NSA perspective, it's information for protection. "Google not only works with intelligence and military agencies, but also tries to infiltrate all levels of society, including citizen federal agencies, municipalities, states, local police, emergency responders, hospitals, public schools, and a variety of companies and non-profit organizations.The combination of military, police, government, public education, business, and consumer-oriented systems through Google continues to raise the alarm. Lawyers are concerned that Gmail has violated the "lawyer-client privilege"; Parents want to know what Google does with it after collecting information about their children at school. How does Google handle data through its systems? Are all these included in Google's enterprise monitoring program? What are Google's restrictions and limits? Are there any of these restrictions? Google only gave vague, contradictory answers to these questions.
Larry Page, an American computer scientist and internet entrepreneur, told the Financial Times: “Social goals are our primary goal.We always emphasize that in Google. People fail to think about some of the most basic questions: How do we organize people, how do we inspire people?" In my opinion, in a country that claims to be "Free, Democracy, Equality, and Human rights," the goal should not be to spy on the people.
0 notes
Text
Duodenal polyp a rare cause of repeated vomiting by Lahfidi Ama in Journal of Clinical and Medical Images, Case Reports

Clinical Image Description
A 50-year-old man without ATCD who suffers from dyspepsia and frequent vomiting, prompting him to seek medical help. There were no abnormalities found during the clinical evaluation. A CT scan of the abdomen was ordered to identify a duodenal polyp that was limiting the digestive light (Figure 1).
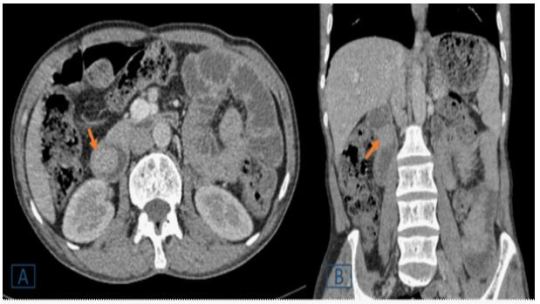
Figure 1: A duodenal endoluminal polyploid tissue process of 21 x 23 mm is shown on a transverse (A) and coronal (B) abdominal CT following contrast injection (orange arrow).
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome (PJS), juvenile polyposis, Cowden's disease, familial adenomatous polyposis, and Gardner's syndrome are polyposis syndromes that affect the duodenum [1]. Duodenal polyps are more common in children with polyposis syndromes, the majority of which are asymptomatic, according to a retrospective research in a pediatric population (aged 21 years) [2]. In the pediatric age group, duodenal polyps are seldom seen during standard high endoscopy (EGD) and radiographic investigations. In contrast, a recent study of adults using EGD and autopsy found a prevalence of up to 4.6 % [2]. Abdominal pain, vomiting, gastrointestinal bleeding, anemia, and intussusception or obstruction are among the symptoms [1, 2]. In comparison to the jejunum and ileum, duodenal disorders have received little attention in the imaging literature [1]. The exploration of the duodenum, which is still mostly examined by video endoscopy, has changed dramatically as a result of recent breakthroughs in imaging. However, advances in computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MR) have made it easier to detect and characterize anomalies in the genesis of duodenal masses [1]. They are used to assess intraluminal content, the duodenum wall, and the extraduodenal area. The scanner, in combination with optimum intestinal distension and intravenous iodine contrast, provides for a thorough examination of the duodenum. Similarly, MRI has been demonstrated to be useful in diagnosing a wide spectrum of duodenal disorders when combined with duodenal distension and intravenous administration of a gadolinium-based contrast agent [1]. For the detection and characterization of a wide spectrum of duodenal lesions generating masses, CT remains the preferred imaging modality [1]. Large polyps (> 15 mm) might cause small intestinal blockage, thus it's important to keep an eye on them to see which ones need to be removed [1]. Protocols for monitoring are still being debated. Important polyps (big polyps with a proclivity for intussusception or blockage) are detected by endoscopy [1].
Surveillance in patients with polyposis syndromes was the most common reason for EGD; most of these patients were asymptomatic at the time of their EGD. In patients without polyposis syndrome, the most prevalent reason for EGD was stomach pain and vomiting [2]. CT and MRI can theoretically be used to monitor patients with many polyps and determine the best treatment, which could include endoscopic, enteroscopic, or surgical ablation, or a combination of these methods [1].
Competing Interests: The authors declare that they have no links of interest.
For more details : https://jcmimagescasereports.org/author-guidelines/
#Peutz-Jeghers syndrome#juvenile polyposis#computed tomography#gastrointestinal bleeding#vomiting#endoscopy#enteroscopic#Lahfidi Ama#JCMICR
0 notes
Text
MBBS in Bangladesh-Kumudini Women's Medical College

Kumudini Women’s Medical College (KWMC) was established in the year 2001 under the patronage Kumudini Welfare Trust.
Kumudini Women’s Medical College has been granted the permission by the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh and Affiliation by the University of Dhaka.
Recognition achieved by Bangladesh Medical and Dental council (BM & DC) and National Commission of India.
The college campus constitutes a huge area of the ‘Kumudini Complex’ – the campus of the Kumudini Women’s medical College has 110 acres of land with greeneries. The College Campus is located in Mirzapur, Tangail, Bangladesh.
This college is Located in Dhaka,
Bangladesh
Distance of the college is 70 km northwest of Dhaka. The college campus is connected by Railways and Roadways.
The campus of the medical College includes:
Medical College Building
Hospital Building
Hostel Buildings (6 multi-storeyed hostels)
Student Mess and Canteen with a separate Dining for International students
Accommodation for Academic and Clinical Staff
Shri Rai Bahadur Ranada Prasad Shaha the founder of Kumudini welfare Trust, established Kumudini Hospital with 750 beds in 1944. Presently the hospital has a capacity 1050 beds, organized according to departments and service units.
The main hospital is a three-storied structure building with a surface area of 131,300 sq. ft. The college building is about 500 feet long and has a two-storied structure having a surface area of 50,000 square feet seated adjacent to the main hospital building.
The hospital compound consists of distinct building blocks for inpatient services, outpatient services and other administrative and support services.
This Medical College is well equipped with adequate facilities for utilizing modern and effective instructional teaching-learning methods and has aids in accordance with the curriculum.
The academic environment nurtures development of faculties for improving quality of education through continuous monitoring and rigorous evaluation system.
Physical infrastructure within the college and its affiliated hospital provides appropriate spaces for lecture, demonstrations, tutorials, practical and bed side clinical teaching.
It has well-built laboratories, tutorial halls for small group discussion and a huge spacious dissection hall with a museum, library with wide reading room, students’ common room, canteen, and fair price shop.
Kumudini Women’s Medical College library is situated on the first floor of the college building. The library provides seating arrangement for 150 students at one time. The opening hours of the library is from 8:00 am in the morning to 9:00 pm in the evening on all working days.
There is a separate reading room for the teachers. The library has an enormous number of academic and reference books of different discipline and specialties.
It also has medicinal books and scientific journals and international periodicals. Photocopying is also available at subsidized rate. In addition to this, the library is also equipped with computers and internet facility for browsing references and e- book, etc.
The College campus is absolutely residential and has adequate accommodation for all the students who seeks admission in the college. It has separate dining rooms, study rooms and club rooms. There are five hostels with a total of 1011 seats. One of the hostels is for the foreign students with air condition & refrigerator facilities.
A modern hostel complex with six buildings is under constructions which shall accommodate 1440 students.
0 notes