#immunotherapy cancer treatment
Text
Best Lung Cancer Treatment In India
Lung cancer continues to be a significant global health concern, affecting millions of individuals each year. With advancements in medical science and technology, the landscape of lung cancer treatment has evolved, offering patients more effective and innovative options to combat this formidable disease. In India, renowned for its world-class healthcare infrastructure and skilled medical professionals, patients have access to some of the best lung cancer treatment facilities and expertise. Let's delve into the realm of lung cancer treatment in India and explore what makes it stand out on the global stage.
State-of-the-Art Treatment Facilities:
India boasts a vast network of hospitals and cancer centers equipped with state-of-the-art facilities and cutting-edge technology for the diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer. From leading tertiary care hospitals in metropolitan cities to specialized oncology centers, patients have access to a wide range of treatment options tailored to their specific needs.
Multidisciplinary Approach:
One of the hallmarks of the best lung cancer treatment in India is its multidisciplinary approach. A team of highly skilled oncologists, pulmonologists, thoracic surgeons, radiation oncologists, medical oncologists, and other healthcare professionals collaborate closely to formulate comprehensive treatment plans that address the unique aspects of each patient's condition. This collaborative approach ensures holistic care and optimal treatment outcomes.
Advanced Treatment Modalities:
India's top lung cancer treatment facilities offer a comprehensive range of treatment modalities, including surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy treatment, and precision medicine. These facilities are equipped with advanced diagnostic tools such as PET-CT scans, MRI, and genomic profiling, enabling accurate staging and personalized treatment strategies.
Minimally Invasive Surgery:
Minimally invasive surgical techniques, such as video-assisted thoracic surgery (VATS) and robotic-assisted surgery, are widely employed in India for the treatment of lung cancer. These techniques offer several advantages over traditional open surgery, including smaller incisions, reduced postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times.
Comprehensive Support Services:
The best lung cancer treatment centers in India prioritize patient-centric care and offer a wide range of support services to address the physical, emotional, and psychological needs of patients and their families. These services may include counseling, nutritional support, pain management, palliative care, and survivorship programs, ensuring holistic care throughout the treatment journey.
Clinical Trials and Research:
India's leading cancer centers actively participate in clinical trials and research initiatives aimed at advancing the understanding and treatment of lung cancer. Patients may have the opportunity to enroll in clinical trials exploring novel therapies, targeted agents, and immunotherapies, providing access to cutting-edge treatments not widely available elsewhere.
Affordability and Accessibility:
Despite offering world-class treatment facilities and expertise, lung cancer treatment in India remains significantly more affordable compared to many Western countries. Patients from across the globe seek treatment in India due to its cost-effectiveness, high quality of care, and shorter waiting times. Moreover, India's medical tourism industry facilitates seamless travel, accommodation, and logistics arrangements for international patients seeking treatment.
Conclusion:
The best lung cancer treatment in India combines clinical excellence, advanced technology, multidisciplinary expertise, and patient-centric care to deliver superior outcomes and improve the quality of life for patients battling this disease. With a focus on innovation, compassion, and affordability, India's healthcare ecosystem continues to set benchmarks in the field of oncology, offering hope and healing to patients from all walks of life.
#immunotherapy#immunotherapy cancer treatment#immunotherapy treatment#Immunotherapy for Cancer in India#Best Lung Cancer Treatment In India
0 notes
Text
Explore the transformative realm of Immunotherapy for Breast Cancer with Oncarecancer. Uncover breakthroughs, treatment insights, and inspiring stories in our quest for innovative and compassionate breast cancer care.
#immunotherapy for breast cancer#immunotherapy cancer treatment#cancer therapy immunotherapy#immunotherapy treatment#oncarecancer
0 notes
Text
hi so small update 🏥❤️🩹🤞🎗️ i have scans coming up in a couple weeks, which is always really scary 🥲 this will be my 6 months post surgery set of scans. i'm feeling cautiously optimistic as of right now, so hopefully things look clean. if they DO look good, that week is my last week of twice weekly immunotherapy!!! then i only need to come in for treatment once a week (((: really really hoping that happens LMFAO, it'll be a huge help with my energy levels and free time.
so yeah !! i'll almost certainly post more when the time for scans is here (to anxiously crytype lol), so keep me in ur thoughts 💖
oh AND, my birthday is this month! i may share an amazon wishlist if anyone is interested. lmk!!
#cancer fucking sucks but im honestly really looking forward to less treatment 🤞🤞🤞#itll suck if the scans arent clean bc then i have to change my WHOLE regimen#and go back on chemo )): waughhhh chemo is so much fucking worse than immunotherapy#and uh. also the implications for my prognosis would be. bad#so im trying not to think about it!!! i am however planning my birthday (:#i think i wanna go to the aquarium & get kbbq w autumn !!!!#havent had kbbq since before we moved so itll be a nice treat 😌 and also AQUARIUMS 💖💖💖💖#chatter#round 2
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
There's an experimental cancer treatment, that's been over going studies in new York, and so far it has a 100% success rate. And and everyone they've tested on hasn't really had any side effects and and they're in remission and seeming to be staying that way. Their cancer hasn't come back!!
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cancer 101: The Bare Basics to Know if You've Been Diagnosed with Cancer

What is Cancer and How Does It Develop?
Cancer is a complex and multifaceted disease characterized by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells in the body. These cells, known as cancer cells, can invade and destroy surrounding healthy tissues, impairing the normal functioning of organs and systems. Understanding how cancer develops involves diving into the intricate interplay of genetics, hormones, environmental, lifestyle, and immune factors.
At its core, cancer begins when mutations occur within the DNA of normal cells. These mutations can be caused by many factors, including exposure to chemicals and carcinogens, hormone disruptors. ultraviolet radiation, infection, and other stressors that affect the immune system. Additionally, genetic predispositions inherited from one's parents can also contribute to the development of cancer. As a result, cells begin to divide uncontrollably, forming a mass or tumor.
Staging and Grading of Cancer
Staging and grading are essential components of cancer diagnosis and prognosis, providing valuable information about the extent and aggressiveness of the disease.
Staging
Staging refers to the process of determining the extent of cancer spread throughout the body. It involves evaluating the size of the primary tumor, whether it has invaded nearby tissues or organs, and whether cancer cells have spread to regional lymph nodes or distant sites. Staging helps clinicians classify cancer into different categories, each with specific treatment approaches and prognostic implications. The most commonly used staging system is the TNM system, which stands for Tumor, Node, and Metastasis. It assigns a stage based on the size and extent of the primary tumor (T), the involvement of nearby lymph nodes (N), and the presence of metastasis (M). Staging provides valuable information for both treatment planning and prognosis.
Grading
Grading, on the other hand, evaluates the microscopic features of cancer cells and tissues to assess their level of differentiation and aggressiveness. Different cancers have distinct grading systems tailored to their specific characteristics. Typically, cancer cells are graded on a scale from low to high based on how closely they resemble normal cells in terms of structure, organization, and function. Low-grade cancers consist of well-differentiated cells that closely resemble normal tissue and tend to grow and spread more slowly. In contrast, high-grade cancers consist of poorly differentiated or undifferentiated cells with abnormal features and tend to grow and spread more rapidly. Grading helps clinicians predict how aggressively the cancer is likely to behave and guides treatment decisions, with higher-grade cancers often requiring more aggressive therapies.
What is a Tumor Marker and How is It Used?
A tumor marker is a substance produced by cancer cells or by the body in response to cancer. These substances can be found in blood, urine, or tissue samples and can serve as indicators of the presence, progression, or response to cancer treatment. Tumor markers are often proteins, enzymes, hormones, or other molecules that are either produced by cancer cells themselves or released into the bloodstream as a result of the body's immune response to cancer.
While tumor markers are useful in cancer diagnosis and management, it's important to note that they are not always specific to cancer and can also be elevated in other conditions, such as inflammation or benign tumors. Therefore, tumor markers are typically used in conjunction with other diagnostic tests and clinical assessments rather than as standalone tools for cancer diagnosis. Many times they can be used as indicators for whether or not imaging is necessary during or after treatment. They can also be used to monitor recurrence of disease.
What are the Different Kinds of Imaging Used for the Diagnosis and the Continued Evaluation of Cancer?
Imaging plays a crucial role in the diagnosis, staging, and ongoing evaluation of cancer. Different imaging modalities offer unique advantages in visualizing various aspects of cancer, such as the location, size, extent of spread, and response to treatment. Here are some of the most commonly used imaging techniques in cancer diagnosis and evaluation:
X-ray: X-rays are one of the oldest and most widely used imaging techniques. They are particularly useful in detecting abnormalities in bones, such as fractures or bone metastases. X-rays can also provide insights into the presence of lung tumors or abnormalities in the chest cavity.
Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: CT scans use X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body. CT scans are valuable for detecting and characterizing tumors in various organs, including the lungs, liver, pancreas, and abdomen. They can also help in staging cancer by revealing the extent of tumor spread to nearby tissues and lymph nodes.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI uses powerful magnets and radio waves to generate detailed images of soft tissues, such as the brain, spinal cord, muscles, and internal organs. MRI is particularly useful in imaging the brain, spinal cord, prostate, and musculoskeletal system. It provides excellent contrast resolution, making it valuable for detecting and characterizing tumors and assessing their relationship to nearby structures.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scan: PET scans involve the injection of a radioactive tracer, which is taken up by rapidly dividing cells, such as cancer cells. PET scans can detect cancerous lesions anywhere in the body and provide information about the metabolic activity of tumors. When combined with CT (PET-CT), PET scans offer a powerful tool for cancer staging, treatment planning, and monitoring treatment response.
Ultrasound: Ultrasound uses sound waves to create real-time images of internal organs and tissues. It is commonly used to evaluate tumors in the breast, thyroid, liver, kidneys, and reproductive organs. Ultrasound is also used for guiding minimally invasive procedures, such as biopsies or needle aspirations, to obtain tissue samples for further analysis.
Mammography: Mammography is a specialized type of X-ray imaging used for breast cancer screening and diagnosis. It can detect breast tumors at early stages, often before they can be felt during a physical examination. Digital mammography and 3D mammography (tomosynthesis) are advanced techniques that provide higher sensitivity and improved image quality compared to traditional film mammography.
Endoscopy: Endoscopy involves the use of a flexible, lighted tube with a camera (endoscope) to visualize the inside of hollow organs or cavities, such as the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, or urinary tract. Endoscopic procedures, such as colonoscopy, bronchoscopy, or cystoscopy, allow for direct visualization of tumors, tissue sampling (biopsy), and therapeutic interventions.
These imaging modalities, alone or in combination, enable clinicians to accurately diagnose cancer, determine its stage and extent of spread, plan treatment strategies, and monitor response to therapy over time. Each imaging technique has its strengths and limitations, and the choice of imaging modality depends on factors such as the type of cancer, location of the tumor, patient's health status.
Benign versus Malignant
The primary difference between a benign and malignant tumor lies in their behavior and potential to cause harm.
Benign Tumors
Benign tumors are non-cancerous growths that do not invade nearby tissues or spread to other parts of the body.
They typically grow slowly and remain localized, confined to the tissue or organ where they originated.
Benign tumors are usually well-defined and encapsulated, with cells that closely resemble normal cells in structure and function.
While benign tumors may grow and cause symptoms depending on their size and location, they do not have the ability to metastasize or spread to distant sites in the body.
In most cases, benign tumors are not life-threatening, and they can often be removed surgically with minimal risk of recurrence.
Malignant Tumors (Cancer):
Malignant tumors are cancerous growths characterized by uncontrolled cell growth, invasion of surrounding tissues, and the potential to metastasize to distant organs and tissues.
Cancer cells in malignant tumors have undergone genetic mutations that disrupt normal cellular functions, leading to abnormal growth, division, and behavior.
Malignant tumors can invade nearby tissues and organs, infiltrating surrounding structures and impairing their function.
The hallmark of malignancy is the ability of cancer cells to metastasize, spreading to distant sites in the body through the bloodstream or lymphatic system. Metastasis can lead to the formation of secondary tumors in vital organs, complicating treatment and prognosis.
Malignant tumors are often less well-defined than benign tumors, with irregular borders and heterogeneous cell populations.
Cancer is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that requires prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment, which may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, or immunotherapy.
What is Metastatic Disease? Metastatic disease, also known as metastasis, refers to the spread of cancer from its original (primary) site to distant organs or tissues in the body. Metastasis is a hallmark of malignant cancer and significantly impacts prognosis and treatment options.
When cancer cells break away from the primary tumor, they can travel through the bloodstream or lymphatic system to other parts of the body, where they establish secondary tumors. The process of metastasis involves several steps:
Invasion: Cancer cells invade nearby tissues or penetrate blood vessels or lymphatic vessels, allowing them to enter the circulation.
Transport: Cancer cells travel through the bloodstream or lymphatic system to distant sites in the body. The spread of cancer cells to distant organs or tissues can occur early in the disease process, even before the primary tumor is diagnosed.
Colonization: Cancer cells settle and establish secondary tumors in distant organs or tissues. The ability of cancer cells to survive and thrive in a new microenvironment depends on various factors, including interactions with the local tissue environment, immune responses, and the acquisition of specific genetic alterations.
Metastatic disease is a significant concern in cancer management for several reasons:
Prognosis: The presence of metastases is often associated with a poorer prognosis and decreased survival rates compared to localized cancer. Metastatic cancer is generally more challenging to treat and may require more aggressive therapies.
Treatment Considerations: Treatment decisions for metastatic cancer depend on factors such as the location and extent of metastases, the type and stage of the primary tumor, the overall health of the patient, and individual preferences. Treatment goals may focus on prolonging survival, relieving symptoms, maintaining quality of life, or aiming for a cure in select cases.
Multidisciplinary Approach: Managing metastatic cancer often requires a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, including medical oncologists, surgical oncologists, radiation oncologists, pathologists, radiologists, and supportive care specialists. Treatment plans may involve a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and palliative care to address the needs of the patient comprehensively.
While metastatic disease poses significant challenges in cancer care, advances in treatment strategies, including targeted therapies and immunotherapies, have improved outcomes for many patients with metastatic cancer. Research continues to focus on understanding the mechanisms of metastasis, developing new therapeutic approaches, and improving patient outcomes in metastatic disease.
Common Treatments for Cancer
The treatment of cancer often involves a combination of different modalities tailored to the specific type and stage of cancer, as well as individual patient factors such as age, overall health, and preferences. Some of the most common treatments for cancer include:
Surgery: Surgery involves the removal of cancerous tumors and surrounding tissues. It is often the primary treatment for solid tumors that are localized and have not spread to other parts of the body. Surgery may be curative if the cancer is detected early and completely removed, or it may be used to relieve symptoms, improve quality of life, or debulk the tumor before other treatments such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing and dividing. Chemotherapy can be administered orally, intravenously, or through injections and may be given alone or in combination with other treatments such as surgery or radiation therapy. Chemotherapy is commonly used to treat cancers that have spread to other parts of the body (metastatic cancer) or cancers that are sensitive to chemotherapy drugs.
Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy X-rays or other forms of radiation to kill cancer cells or shrink tumors. Radiation therapy may be delivered externally using a machine (external beam radiation) or internally through implants or radioactive substances placed directly into or near the tumor (brachytherapy). Radiation therapy is often used as a primary treatment for localized cancers or in combination with surgery or chemotherapy to improve outcomes.
Targeted Therapy: Targeted therapy targets specific molecules or pathways involved in the growth and spread of cancer cells. Unlike chemotherapy, which affects both cancerous and healthy cells, targeted therapy is designed to selectively target cancer cells while minimizing damage to normal tissues. Targeted therapy drugs may include monoclonal antibodies, small molecule inhibitors, or other targeted agents that interfere with specific cellular processes or signaling pathways.
Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy harnesses the power of the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. Immunotherapy drugs work by enhancing the body's immune response against cancer cells or by blocking immune checkpoints that prevent the immune system from recognizing and attacking cancer cells. Immunotherapy has revolutionized cancer treatment in recent years and has shown promising results in a variety of cancers, including melanoma, lung cancer, and certain types of leukemia and lymphoma.
Hormone Therapy: Hormone therapy is used to treat cancers that are hormone-sensitive, such as breast cancer and prostate cancer. Hormone therapy works by blocking the production or action of certain hormones that stimulate the growth of cancer cells. It may involve the use of hormone-blocking medications or surgical removal of hormone-producing organs (e.g., ovaries or testes).
Bone Marrow Transplantation: Bone marrow transplantation, also known as stem cell transplantation, may be used to treat certain types of cancer, particularly blood cancers such as leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma. It involves replacing diseased or damaged bone marrow with healthy stem cells from a donor (allogeneic transplant) or from the patient themselves (autologous transplant).
These are some of the most common treatments for cancer, but there are other treatment options depending on kind of cancer, stage/grade, etc... In the future, I plan on sharing more about this topic, but for now, I hope this blog has given you a simple breakdown of the disease, how it's diagnosed and evaluated, and the most common types of treatment.
#cancer#chemotherapy#radiationtherapy#immunotherapy#cancer surgery#stem cell treatment#bone marrow transplant#hormonedrivencancer#cancer treatment#eastwestintegrativeoncology#yourcancerguru#cancer diagnosis#integrative oncology
0 notes
Text
Personalized Approaches to Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treatment: Targeting Tumor Diversity
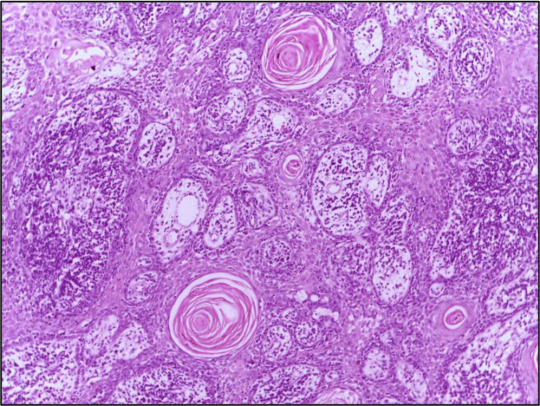
Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma (cSCC) is a heterogeneous disease characterized by diverse clinical and molecular features. Personalized treatment approaches that take into account the unique characteristics of individual tumors have emerged as a promising strategy to improve treatment outcomes and patient survival.
Understanding Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma (cSCC) is a type of skin cancer that arises from the malignant transformation of squamous cells in the epidermis or its appendages. It encompasses a spectrum of disease presentations, ranging from localized lesions to metastatic tumors with varying clinical behaviors.
Tumor Heterogeneity and Molecular Subtypes: Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma (cSCC) exhibits considerable heterogeneity at the molecular level, with distinct genetic alterations and signaling pathways driving tumor progression and metastasis. Molecular subtyping studies have identified different subgroups of cSCC tumors based on their genomic profiles, providing insights into tumor diversity and potential therapeutic targets.
Precision Medicine in cSCC Treatment: Precision medicine approaches aim to tailor treatment strategies to the specific molecular characteristics of individual tumors, allowing for more targeted and effective therapies. By identifying actionable mutations or biomarkers, clinicians can select therapies that are most likely to benefit patients while minimizing the risk of treatment-related toxicities.
Genomic Profiling and Biomarker Identification: Advances in genomic sequencing technologies have enabled comprehensive profiling of cSCC tumors, revealing recurrent mutations in genes involved in cell cycle regulation, DNA repair, and immune evasion. Biomarker identification efforts seek to identify predictive markers of treatment response and prognosis, guiding treatment decisions in personalized medicine.
Get More Insights On This Topic: Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
#Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma#Skin Cancer#Tumor Heterogeneity#Precision Medicine#Molecular Subtypes#Targeted Therapy#Immunotherapy#Biomarker Identification#Personalized Treatment
0 notes
Text
Understanding Immunotherapy for Autoimmune Diseases
Introduction
Immunotherapy, a groundbreaking approach primarily recognized for cancer therapy immunotherapy, is now making significant strides in treating autoimmune diseases. This article delves into how immunotherapy is applied beyond cancer immunology immunotherapy to manage and treat autoimmune conditions.
The Mechanism of Immunotherapy in Autoimmune Diseases
Immunotherapy works by modulating the immune system, enhancing its ability to fight diseases. Unlike in immunotherapy cancer treatment, where the goal is to target and destroy cancer cells, in autoimmune diseases, the therapy aims to recalibrate the immune system to stop attacking the body's tissues.
Types of Immunotherapy for Autoimmune Diseases
There are various types of immunotherapy used to treat autoimmune diseases. These include monoclonal antibodies, cytokine inhibitors, and immune checkpoint inhibitors, each designed to alter specific immune system pathways. While some of these therapies overlap with those used in cancer treatment, their application in autoimmune diseases focuses on immune regulation and suppression of overactive immune responses.
Immunotherapy Medications and Treatments
Immunotherapy medications for autoimmune diseases are tailored to reduce inflammation and curb the immune system's erroneous attacks on healthy cells. The precise medication or combination of therapies depends on the specific autoimmune condition being treated, highlighting the personalized nature of immunotherapy.
The Role of Immunotherapy and Vaccines
Exploring the intersection of immunotherapy and vaccines reveals potential for preventative strategies in autoimmune diseases. Vaccines designed to induce tolerance in the immune system are under research, potentially preventing autoimmune diseases from developing or worsening.
Managing Side Effects and Costs
While immunotherapy offers new hope, it's crucial to consider immunotherapy side effects and immunotherapy cost. Side effects vary widely, from mild to severe, and must be carefully managed under medical supervision. The cost can also be significant, necessitating a discussion about healthcare resources and insurance coverage.
Conclusion
Immunotherapy for autoimmune diseases represents a promising frontier in medical treatment, offering hope for millions suffering from these conditions. As research progresses, it could redefine the therapeutic landscape for autoimmune diseases, much like it has for cancer.
Discovering Excellence in Cancer and Autoimmune Disease Treatment at CBCC India
At the forefront of medical innovation and care, CBCC India stands as one of the leading Cancer Hospital in India, dedicated to eliminating cancer and advancing treatment for autoimmune diseases. Our commitment to innovative research and exceptional care ensures that every patient receives personalized, state-of-the-art treatment. Discover the pinnacle of healthcare excellence at CBCC India, where we strive to conquer cancer and improve the lives of those with autoimmune diseases through cutting-edge immunotherapy and comprehensive care.
#Immunotherapy#Autoimmune diseases#Cancer therapy#Immune system modulation#Monoclonal antibodies#Immune checkpoint inhibitors#Inflammation reduction#Personalized treatment#Vaccines
0 notes
Text
#CTLA-4 Therapies Market#Global Market Trends#Latest Therapeutic Advancements#Innovations in CTLA-4 Therapies#Recent Developments in Immunotherapy#Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors#Cancer Treatment Breakthroughs
0 notes
Text
Unlocking Precision Medicine: Top Treatment Kachiguda TX Hospital's Tailored Approach to Cancer Care

In the pursuit of advancing cancer care, the future is an ever-expanding horizon, filled with possibilities that hold the promise of transformative therapies. At Top Treatment TX Hospital, we stand at the forefront of this frontier, dedicated to exploring and implementing cutting-edge therapies that go beyond the conventional boundaries of oncological treatment. For further information or inquiries, please reach out to us at 9089489089
Unveiling the Future:
In this blog post, we embark on a journey into the future of oncology, where groundbreaking therapies are reshaping the landscape of cancer treatment. At [Top Treatment TX Hospital], we recognize the importance of staying ahead in the quest for more effective, targeted, and personalized approaches to care.
Precision Oncology: Tailoring Treatment to the Individual
One of the cornerstones of our approach is precision oncology. We understand that each patient is unique, and their cancer journey deserves a tailored strategy. Our team of experts utilizes advanced genetic profiling and molecular diagnostics to identify specific genetic alterations driving the cancer, allowing us to prescribe targeted therapies that offer enhanced efficacy with fewer side effects.
Immunotherapy: Empowering the Body's Defense Mechanism
Immunotherapy represents a paradigm shift in cancer treatment, and [Top Treatment TX Hospital] is at the forefront of this revolutionary approach. By harnessing the body's immune system to recognize and combat cancer cells, immunotherapy opens new doors for patients, providing hope where conventional treatments may fall short. Join us as we delve into the success stories and ongoing research initiatives that define our commitment to immunotherapeutic advancements.
Gene Editing Technologies: A Glimpse into the Future of Treatment
As we peer beyond the horizon, gene editing technologies emerge as a promising frontier in oncology. [Top Treatment TX Hospital] is actively exploring the potential of CRISPR and other gene editing tools to precisely modify cancer-related genes, offering unprecedented possibilities for targeted interventions. Discover how these technologies are paving the way for groundbreaking treatments with the potential to revolutionize cancer care.
Patient-Centric Innovation: Putting Individuals at the Heart of Treatment
While our focus is on pioneering technologies, we remain steadfast in our commitment to patient-centered care. Hear directly from patients who have experienced the impact of these future therapies and learn how [Top Treatment TX Hospital] combines cutting-edge science with compassionate support to guide individuals through their unique cancer journeys.
A Call to the Future: Stay Tuned for Ongoing Discoveries
This blog post is just the beginning of our exploration into the future of oncology at [Top Treatment TX Hospital]. As we continue to push boundaries and seek new possibilities, we invite you to stay tuned for regular updates, in-depth insights, and stories of resilience that define our commitment to advancing the field and providing hope to those facing a cancer diagnosis.
The future is bright, and at Top Treatment TX Hospital, we are navigating the uncharted territories of oncology with a vision of better, more effective, and personalized cancer care.
TX Hospitals is one of the best hospitals in Kachiguda, Uppal, and Banjara hills with the largest healthcare facility and the best team of doctors and specialist surgeons to help patients recover fast from health ailments.
Book an Appointment with the Best Doctors in Hyderabad.
#Oncology#Cancer Treatment#Future Therapies#Innovative Technologies#Precision Medicine#Immunotherapy
0 notes
Text
Can Immunotherapy Revolutionize Cancer Treatment?
Cancer is a relentless foe, affecting millions of lives worldwide. Conventional cancer treatments like chemotherapy and radiation therapy have been the primary choices for years, but they often come with severe side effects and limitations. Is there a more effective and less invasive way to combat this deadly disease? That's where cancer immunotherapy comes into play. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the groundbreaking advances in cancer immunotherapy and the challenges it faces, as well as how online resources can enhance the cancer therapy process.
#cancer treatment#immunotherapy#cancer therapy#cancer immunotherapy#CAR T-Cell Therapy#online doctor consultation#online lab test
0 notes
Text
Immunotherapy: Shifting the Landscape of Cancer Care
Discover how immunotherapy is revolutionizing cancer treatment and providing new hope for patients. Learn about the latest advancements and future possibilities in this groundbreaking field.
0 notes
Text
The Power of Immunotherapy in Cancer Treatment
In the fight against cancer, immunotherapy has shown to be an innovative and promising strategy. This innovative therapy has gained a lot of focus over the years because to its potential to strengthen the body's immune system's ability to identify and destroy cancer cells. We'll talk about immunotherapy for cancer and its function in treating cancer, and how it's changing things in this blog article.
What is Immunotherapy?
commonly referred to as biologic therapy, immunotherapy activates the immune system to attack cancerous cells. The immune system can identify and eliminate abnormal cells, including cancer cells, since it was created to protect the body from infections and illnesses. Immunotherapy stimulates or restores the immune system's capacity to identify and combat cancer cells more successfully by using chemicals produced either naturally or in a lab.
Immunotherapy for Cancer Treatment:
Immunotherapy cancer treatment that works to strengthen the defenses of the body so they are able to identify and get rid of cancer cells. Immunotherapy focuses on strengthening the immune system's ability to fight cancer, in contrast to conventional treatments like radiation and chemotherapy, which target cancer cells directly.
There are various types of immunotherapies
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: Checkpoint inhibitors on immune systems prevent proteins that allow immune cells to target cancer cells. The immune system can efficiently identify and target cancer cells for destruction by blocking these proteins.
CAR-T Cell Therapy: The process of CAR-T cell therapy involves modifying a patient's own T cells to express a receptor capable of recognizing and attacking cancer cells. After being reintroduced into the patient's body, these modified CAR-T cells target and eliminate cancer cells.
Cancer Vaccines: The immune system is prompted by cancer vaccines to identify and combat cancerous cells. Proteins, tissues, or even portions of cells can be used to make them.
Monoclonal Antibodies: Monoclonal antibodies are chemicals that are manufactured to reproduce the immune system's defense against infections. These antibodies can be designed to specifically target proteins on cancerous cells, assisting the immune system in identifying and eliminating them.
Pune, a city renowned for its advanced medical facilities and knowledge, has accepted immunotherapy as an essential part of cancer treatment. A variety of immunotherapeutic alternatives are available in Pune from top oncology centers and specialists, each targeted to the specific requirements and cancer type of each patient. Care Speciality Hospital is leading Immunotherapy cancer treatment provided in Pimpri Chinchwad, Pune.
At the cutting-edge of cancer treatment, immunotherapy gives people fighting this terrible illness a ray of hope. The ability of this material to strengthen the body's immune system against cancer cells has pushed it to the center in modern oncology. The use of immunotherapy cancer treatment in Pune is evidence of the city's dedication to offering modern care and promoting a better future for cancer patients. Immunotherapy has promise for changing the face of cancer treatment as research and developments proceed, bringing us closer to a future in which cancer is more successfully controlled and, eventually, defeated.

1 note
·
View note
Text
How does the immune system fight cancer
Cancer can commonly get around many of the immune system’s natural defenses, allowing cancer cells to continue to grow. Some immunotherapy treatments help the immune system stop or slow the growth of cancer cells. Others help the immune system destroy cancer cells or stop the cancer from spreading to other parts of the body. Immunotherapy treatments can be used alone or combined with other cancer treatments.
0 notes
Text
New Cancer Treatment Plan
source unknown
Well, I went and saw my cancer doctor yesterday afternoon. As expected, he changed my treatment plan, with my approval of course. I will now start chemo.
I saw it coming for a while now. I’m not going to lie, chemo scares the crap out of me. I’ve heard so many horror stories about the side effects. I’m going to try anyway. I’ve already had some bad experiences with side effects…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
How Immunotherapy Helps Fight Brain Cancer | Denvax Cancer Care | Dr Aditya Singh Bhati
youtube
Immunotherapy treatments are well known for their effectiveness in treating cancer, but they can also be used to treat other diseases. In the case of brain cancer, immunotherapy is an incredibly effective treatment that works by encouraging your immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells.
Immunotherapy treatments work by targeting and destroying cancer cells by using the patient's own immune system's antibodies to fight against them instead of using toxic chemicals which can be harmful to the body over time. In this video, Dr. Aditya Singh Bhati discusses the role and importance of Immunotherapy in fighting Brain tumors.
0 notes
Text
Colorectal Cancer: Important Types, Risk Factors, Treatment, And Prevention
Colorectal Cancer: Important Types, Risk Factors, Treatment, And PreventionIntroductionWhat is Colorectal Cancer?Types of Colorectal Cancer Adenocarcinomas Carcinoid Tumors Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GISTs) Lymphomas SarcomasRisk Factors for Colorectal Cancer Age and Gender Family History Personal Medical History Lifestyle Factors Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)Symptoms and Early Detection…

View On WordPress
#Adenocarcinomas#Bowel Cancer#Carcinoid Tumors#Chemotherapy for Colorectal Cancer#Colon Cancer#Colorectal Cancer#Colorectal Cancer Awareness#Colorectal Cancer Diagnosis#Colorectal Cancer Prevention#Colorectal Cancer Screening#Colorectal Cancer Staging#Colorectal Cancer Surgery#Colorectal Cancer Treatment#Early Detection of Colorectal Cancer#Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors#Genetic Risk of Colorectal Cancer#Healthy Diet for Colorectal Cancer#Immunotherapy for Colorectal Cancer#Lymphomas#Radiation Therapy for Colorectal Cancer#Rectal Cancer#Risk Factors for Colorectal Cancer#Sarcomas#Symptoms of Colorectal Cancer#Targeted Therapy for Colorectal Cancer
0 notes