#but anyways both of my english accents are rhotic so there is no way i wouldve figured this out
Text
i was today years old when i learned that eeyore from winnie the pooh is named that bc that’s the sound a donkey makes if you speak english with a non-rhotic accent
#same thing with er and erm cause i read that and was like ok i guess that’s how british people say it#but no that’s just uh and uhm#but higher in vowel space#but anyways both of my english accents are rhotic so there is no way i wouldve figured this out#personal post
10 notes
·
View notes
Note
PLEASE watch summercamp island its so good its so silly its got that thang where random stuff in the first season is built upon and makes a complex lore, theres a he/him lesbian, mini stories, all sorts of stuff. i still have to find where to watch the last season because hbo max nixed it before it released, but its so good
!!! it sounds so lovely!!! i cant believe i put off watching it a few years ago (some guy called it ugly.. not even true. i love looking at it i think the way they developed julia pott's style for animation is really cute and charming. same thing happened for clarence but now sometimes i see clips of it and its genuinely funny idk what the hate was for). i watched some episodes last night and the pacing is so light and refreshing and nonserious and sincere all at once.. it's a nice breath of fresh air since i havent watched cartoons in a while. it reminds me so much of adventure time and over the garden wall (particularly the animal school and greg's dreams! super whimsical and offbeat and straightforward. how we see the world when we're children)
and thank god:

i felt a hyperfixation forming for this show before i even watched it but i've seen how many people love susie and she does deserve it. my first impression was that she was a kind of over-it 20-something who just wants the kids at her camp to not die but she is perpetually 15 and an utter bitch (who genuinely thinks her meanness is charming) god bless. i believe it's also julia pott who voices her and she does a brilliant job. her voice stands out where most of the main cast are american (and because i'm an accent freak i find hers interesting it's sort of a mix of a standard london accent but instead of pronouncing the t in a word like "better" or dropping it for "be' er" she uses a slightly more american "bedder" while still not swapping the -uh sound on the end for a more rhotic -err). anyway she's the high-maintenance butch representation we need in media, i LOVE her eyebrows, & i cant wait to see her get more complex and sympathetic as time goes on.
going back to the main characters, oscar and hedgehog are the best protagonists!! he's incredibly nervous! she's an academic weapon! they grew up together and are the perfect vessel for these silly stories to be told. i appreciate your wisdom and i will definitely be watching more of it!! i will have more to say about it and might end up doing some art for it because the charm of this show is irresistible.
as for places to watch... i heard they got major fucked over by HBO max.. even if it was all on there i wouldnt be able to watch since i'm in the uk. i wish i could stream it somewhere where i could fully support it, but for situations like this, these two are my secret weapons - there are little to no adverts and none of them are gross or for nsfw sites. they're both clean and they WORK:
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
Making the Draenei Language - Part 2
Part 1 | Part 3
First off, thanks to all the people who’ve expressed interest in this project! It makes me super happy that people think what I’m doing is interesting :D
Anyway, last time I went through and got a basic idea of the structure of the language, this time we’re diving into WHAT 👏 THAT👏 MOUTH👏 DO (and also spelling)

... and by that I of course mean phonetics (the study of the sounds produced in speech), phonology (the study of which sounds differentiate meaning) and phonotactics (how sounds are put together).
Phonetics and Phonology
Before we can even consider choosing some sounds for the language lets take a moment to consider those TEEF!
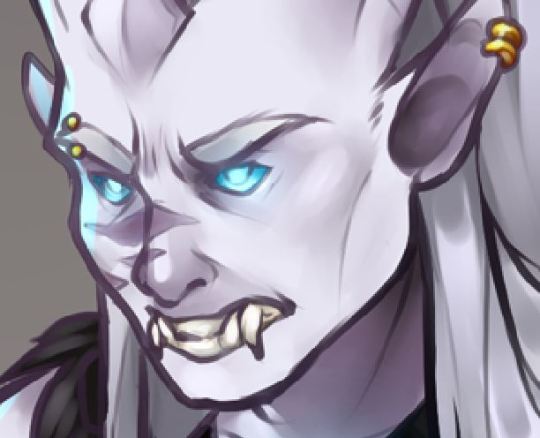

Taking my main boy Aegagrus (drawn by the wonderful @rurukatt, definitely didn’t put this in here cuz I still love this pic) as a model for my headcanon of Draenei teeth, we can see how those might get in the way of some sounds... but just like, specifically [f] and [v] (sounds in square brackets represent sounds not the letters, to hear what they sound like go here!) Both of those sounds involve making the same shape with your mouth - touching your bottom lip to your top teeth, but when you got some real long or pointy teeth, that might be a little bit hard to do! (or an accident waiting to happen if they’re sharp enough)
There’s only a small problem with this though, we have some canon words that use these sounds e.g “Pheta vi acahaci” - Light give me strength. I’m gonna explain this away by saying that we’re dealing with an approximate transcription using the Latin alphabet and English spelling conventions, which definitely wasn't designed to write down languages outside of well.. ideally Latin. I mean there’s a reason why English spelling is the way it is and one of those reasons comes down to using an alphabet too small for the number of sounds in the language.
Tangent aside, this means those two sounds are probably something like [ɸ] (again click here to hear these) for f and [β~ʋ] for v. These are sounds similar to [f] and [v] but they don’t involve teeth touching lips, check, and they’re probably what human transcribers misheard as [f] and [v].
Going through the other transcriptions in the data and making some guesses as to what they could be, we end up with something like this:

and huh that seems familiar... wait a second!
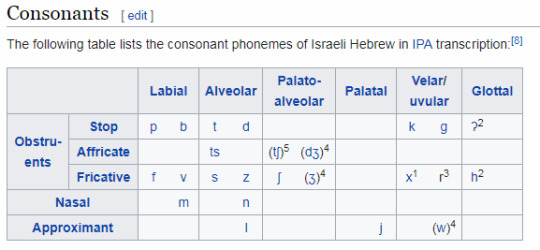
Yeah that’s just Hebrew without voiced fricatives, affricates or the sound [j] (the ‘y’ sound in English), and a bonus rhotic. I mean that’s probably to be expected as Draenei are heavily coded to be Jewish (a good post on that), so it makes sense that the sounds are also similar. It’s a shame to have such quote-unquote normal sounds (the th sound [θ] in ”thin” and “ether” is only in 4% of the worlds languages!) but that’s what you get when English devs make a game for a western audience, you get... ~~the fantasy accent~~ a.k.a discount slavic/germanic accents.
By the way [r] is the ‘trilled’ or ‘rolled’ r and [ɾ] is a ‘tapped’ r like in Spanish "por favor”.
Also, as another side note, this sound [ʔ] - the glottal stop is present in English too but you probably don’t recognise that it’s there. It’s the ‘-’ break in between “uh-oh”, and its also present in some dialects of American and British English where the [t] in words like “bottle” (bo’el) and “water” (wa’er) are replaced with the glottal stop.
Anyway, onto vowels! And yet again we come back to the problems of English spellings. English has approximately... too many vowels. In my dialect of Australian Standard English there’s up to 20 different vowel sounds depending on how you count. I mean all things considered we've done pretty well with the 5 vowel symbols we've got but good luck trying to accurately represent all this:
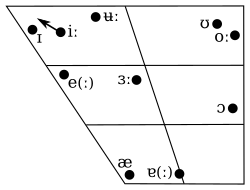
(not to mention the diphthongs) with just a e i o u. Most languages only have ~5 vowels so that’s about what I’m looking for. Taking into consideration all the English wackiness in spelling, we end up with what I think are 7 vowels (the pronunciation examples are definitely not gonna be spot on due to regional differences, learn the IPA its good):
[i] - meat, me, three, e-mail
[ʊ] - (short though) good, should, wood
[ʊ:] - (same as above but long)
[e] - bed, head, red
[ɔ~o] - (somewhere between the vowels in) bought, bot (those of you with the cot-caught merger are having real fun now)
[ɐ] - (this one is really only in Australian English) but, strut, bud
[ɐ:] - (same as above but long) bard, palm, start, hard
The two vowels with long forms are the interesting ones. All throughout the canon text we see ‘aa’ and ‘uu’ popping up again and again in things like “Maraad”, “Sayaad”, “Enkaat”, “Vaard”, “Tuurem” and “Krokuun”. Now this could just be stylistic choices made by the dev team to make the language seem more ~exotic~ but I think that it is definitely a case of phonemic vowel length. That’s where distinctions in words are made by elongating a vowel - something Latin had. But it’s not to be confused with what English calls ‘long vowels’, which are really the leftovers from actual vowel length after everyone in 1500 decided to pronounce every vowel just... completely different for some reason. The Great Vowel Shift is an interesting read). Anyway, it makes these double letters make sense, and is way more interesting than random double vowels. It’s also interesting that it’s not perfectly symmetric either, not all the vowels have this distinction, which is cool and perfectly natural for languages to do!
What is weird is that [ɔ~o] doesn’t have this feature, because in our vowel system, it’s almost directly in the middle of our two long/short vowels so it would probably assimilate and end up doing the same thing! So, going off that I’m going to simulate the beginning of language evolution, where the [ɔ~o] sounds is in the process of diverging into [o:] (oar, caught, thought) when it’s followed by ‘r, t, d, k or g’ and [ɔ] (lot, pot) everywhere else.
So, now we have the sounds for our language, how are they used? (dw hardcore conlanging people, I’ve worked out the rest of the allomorphy rules for the consonants but this post is already loooong)
Phonotactics
Phonotactics is largely about how syllables are formed and what sounds are allowed where. In an effort to try and not make the language *too* similar to English I want these rules to differ from English. Luckily, that’d really easy to do because yet again, English is a statistically weird language!
Syllables are divided into 3 parts - The onset, The nucleus and the Coda. For simplicities sake this corresponds to the consonants before the vowel, the vowel, and the consonants after the vowel. English lets wayyyyy too many consonants on either side ending up with abominations like “strengths” having 3 sounds before the nucleus and 3 after, or crimes against god like “twelfths” with 4 sounds after the coda.
Draenei on the other hand seems to be at most (C)(L)V(C). The brackets mean a sound is optional, C’s being consonants, L being ‘liquids’ like [l] and [r] (and [ʋ]) and V of course being vowels. Now going through the data (plus some creative input) we end up with some rules as to what can go where...

but we’ll leave the details of that for the final documentation and head onto...
Spelling! Everyone’s favourite...
There have been countless forum posts about how to pronounce ‘Draenei’ and even between developers at different panels there doesn't seem to be a consensus. This is probably due to the inconsistent spellings used throughout the lexicon so far - draenei and auchenai rhyme (I think) but they’re spelt with different endings!
With the language I have a few main goals
- Make it match as closely as reasonable with canon and common interpretations
- Have the spelling be consistent (same letters should always produce the same sound)
- In line with the first one, keep as much of the spelling the same as possible
- Make it as alien as possible within reason (sadly phonetics and phonology will not be the place to do that)
So coming to a word like “Draenei”, I have to break at least one thingon that list. Personally I want it to be pronounced [drɐ.naɪ] (druh-nai). So, to be consistent with the sounds from before it should be spelt ‘Dranai’ but that definitely won’t do, or I could keep the spelling and pronounce it literally [drɐ.e.ne.i] (druh-eh-ne-ey to give a rough guide for that), which is... equally bad.
The compromise I'm going with is keeping the spelling of Draenei but making the [aɪ] (ai) sound spelt ‘ei’ across the language. Meaning is gonna be Auchenei. Well, not really because there’s still a bunch of other spellings that need standardising.
the ‘ch’ in “Auchenei” is pronounced with a [k], so is the ‘c’ in “Dioniss aca”. Going through and standardising things like ‘ph’ -> ‘f’, ‘ch’ -> ‘k’ or ‘sh’ depending and rewriting vowels to match the phonology we end up with something that preserves most of the identity and look of the language but just makes more sense! Aukenei would then be the spelling I’m using in the lexicon, probably with a little note for the canon spelling.
So, from now on I'm going to be using the reformed spelling TM, which hopefully will mean anyone attempting to speak this language will have an easier time getting what I'm envisioning, cuz everything is now consistant.
That about does it for this post. Yet again if you made it all the way to the bottom, congratulations! Hopefully the next posts will be a bit more interesting (I’m so fucking pumped for how the culture will impact the grammar and vocabulary holy shit) but I gotta get this one out of the way.
Next time, we’ll be doing word-building - the morphology of the language, Thanks for reading!
#draenei#wow#World of Warcraft#lorecraft#headcanon#theorycrafting#language#conlang#linguistics#draenei language#not art
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
Transcript Lingthusiasm Episode 6: All the sounds in all the languages - The International Phonetic Alphabet
This is a transcript for Lingthusiasm Episode 6: All the sounds in all the languages - The International Phonetic Alphabet. It’s been lightly edited for readability. Listen to the episode here or wherever you get your podcasts. Links to studies mentioned and further reading can be found on the Episode 6 show notes page.
[Music]
Gretchen: Welcome to Lingthusiasm, the podcast that's enthusiastic about linguistics. I'm Gretchen McCulloch.
Lauren: and I'm Lauren Gawne. And today we're going to be talking about the International Phonetic Alphabet. But first -- it was International Mother Language Day in February and even though it was a couple of weeks ago now on February the 21st, I think it's still worth saying a belated 'Happy Mother Language Day' to you Gretchen!
Gretchen: Happy Mother Language Day to you! Which we are wishing in our of mother languages of English, which is kind of boring.
Lauren: Both wishing it our mother languages. Do you have any other heritage languages that you wish to acknowledge?
Gretchen: I mean, technically Scottish Gaelic is probably a long time ago a mother language for me, but my ancestors were lowland Scots so it's a really long time ago.
Lauren: Well happy Scots Gaelic day
Gretchen: Do you have any other?
Lauren: My grandmaternal language is Polish and thanks to generally typical Australian attitudes towards non-English speaking in the 1960s that wasn't passed on to any of my mother's generation at all. So yeah it's still a very recent part of our family history. I'm the only grandchild who ever learnt enough Polish to speak with my grandmother in her mother tongue
Gretchen: Oh that's cool
Lauren: Which is cool, I wish I still spoke that much
Gretchen: Well I mean it's cool that you learned it, it's not cool that no one else did
Lauren: It's probably questionable how much Polish I remember today. And yeah, I always like to think of my Nan and my lack of opportunities to learn Polish on February 21st. What have you been up to or what's coming up?
Gretchen: Well, by the time this episode goes out I will have been to South by Southwest, where I will have done a panel with Erin Mckean and Jane Solomon and Ben Zimmer
Lauren: How are you not going to like die of fangirling at people?!
Gretchen: Because I've already met all of them anyway?
Lauren: Awwww I'm so jelly
Gretchen: But they're really cool and I'm really excited to be on a panel with them! We're going to be talking about 'Word curation: Dictionaries, tech, and the future' which will happen by the time you guys get this episode so you can check out the hashtag that I'm sure will have some action on it and we'll link to that in the show notes.
Lauren: I'm really excited for that panel. I'm looking forward to it hopefully - is it going to be recorded? Am I going to be able to see it as a non South by Southwest attendee?
Gretchen: I think there's going to be an audio recording on soundcloud that South by Southwest is going to put up online because they've done that for previous years. So I can't promise that they'll do that again but they seem to like doing it in previous years, I don't know why they wouldn't do it again so we'll link to that if we have it.
Lauren: Yay, excellent!
[Music]
Gretchen: So there's a problem when you learn to spell English, which is that it's really hard to spell English.
Lauren: It's really a lifelong learning process as far as I'm concerned
Gretchen: It's a lifelong learning process. You know, some languages don't have spelling bees because their spelling systems are so consistent they don't need them - we can only wish! So, the English spelling system is especially ridiculous, it's got silent letters, it's got something around 14 vowels but only five letters to write them in.
My favorite demonstration of this is that there's a phrase that has all of the English vowels and the phrase goes - I have to have to say it in a non-rhotic accent because it only works that way - the phrase goes 'Who would know aught of art must learn, act and then take his ease'. And each of those words has a different vowel in it.
Lauren: Cool!
Gretchen: And that's one way of remembering the vowels
Lauren: That's a nifty sentence!
Gretchen: Yeah, but if you try to write that down in English it's hard
Lauren: With the English orthography that we have, or the English writing system - orthography - that we have
Gretchen: And spelling systems are also inconsistent across different languages. Even languages that are consistent in themselves are often inconsistent when you compare them with each other. So, some languages use the letter J for the /dʒ/ sound [as in Jane], some languages use it for the /ʒ/ sound like French [Jean], some languages use it for the 'y' /j/ sound like German as in 'Jan' or 'Johann Sebastian Bach', some languages use it for the /x/ sound as in Spanish like 'Juan'. There's a whole bunch of different sounds you can use the same letter for depending on your language
Lauren: There's a really great tumblr post that kind of encapsulates this variety in the ways different alphabets that are based on the same alphabet English is based on, use their orthographies in different ways which we'll link to. When I first read this I was like oh look someone's just posting in Norwegian or Danish or something, but then if you sit there and read it and you know the orthographic conventions in different languages it says something along the lines of 'I wonder if English speakers will notice that I'm writing this in English but using the spelling conventions of my language'
Gretchen: And yeah a whole bunch of people have certain different versions of it - there's a Finnish one which is pretty good, there's an Irish one which is fantastic
Lauren: It's good, because once you know what the phrase is that gives you a feel for what the conventions are in different languages. For example I found the Polish one really easy to read and then for some of the others I was just basically guessing because I knew what the sentence was, and it really nicely illustrates this problem that we have that we all learn different spelling conventions for different languages
Gretchen: And we're not the first people to have noticed this problem! In fact people have been realizing this problem for quite a long time, as long as people have been writing with different systems. And it became especially apparent as writing systems became standardised in the 1700s and 1800s, when dictionaries are becoming popular and people were starting to write in a standardised sort of way and looking at other languages and realising that their standardisations were converging on something different
Lauren: I really love that historically there was no consistent spelling conventions, and so in Old English text we actually have a good idea of the different common literate dialects of people who lived in Mercia or people who live in Cumbria and because the way that they wrote English really reflected the way their accent worked. Once spelling systems became standardized that stopped being the case
Gretchen: It also became really difficult people for who are trying to learn English because even if you learn the spelling systems, then you pronounce the words the way they look and people look at you like "that's not actually how it's pronounced" and you're like "how was I supposed to remember that?" Various people came up with various proposals for spelling reform for either just like a more phonetic way of writing English in total, or for ways of adapting English words so that it could be used for specialised purposes like people who are learning the language, or people who want to write down specific things and annotate exactly how they're said
Lauren: And some people went for massive 'let's create an entirely new alphabet', some people just wanted some small reforms. So Noah Webster is probably one of the people who had the most impressive effect on English especially on American English. It was Webster who decided to take and consistently use conventions like 'i-z-e' instead of 'i-s-e' and using words like colour without the 'u' instead of with the 'u' as part of this attempt to make English spelling more realistically reflect the language that was being spoken
Gretchen: Yeah and there were other British reformers that were trying to do this, so there was a guy named Henry Sweet who came up with an alphabet called the Romic /ɹomɪk/ alphabet or the Romic /ɹɑmɪk/ alphabet, I'm not actually sure how to pronounce the name of this alphabet, which...
Lauren: If only was written down some where in a consistently pronounceable script!
Gretchen: If only! He didn't seem to actually write the name of his own alphabet anywhere in a consistent script so that's a shame. And that was based on mostly Roman letters but with adaptations for sounds that English had and Latin hadn't. And then there was Alexander Ellis who was apparently the real-life origin of Henry Higgins from 'My Fair Lady'
Lauren: Really?!
Gretchen: I dunno, that's what Wikipedia says!
Lauren: Okay, because I'm going to invoke the supremacy of David Crystal, if that's okay. I don't know if Crystal officially trumps Wikipedia, but in his book called 'Wordsmiths and Warriors' he says if Higgins is anyone it has to be Daniel Jones who is a phonetician who is very influential in terms of like codifying the vowel system. So what we think of is the modern International Phonetic Alphabet vowel space kind of started with Daniel Jones' cardinal vowels
Gretchen: I mean I don't know it could have been a composite or something
Lauren: I think to be honest that the most likely is that there was a genre of gentleman academic at the time who's very interested in these topics. Anyway, there was a lot of work being invested in generating some kind of writing system that accurately reflected speech
Gretchen: Yeah and so they made the International Phonetic Association in the late 1800s, which confusingly enough also has the acronym IPA, and they had some meetings and they were like, “yeah, we need to come up with a system for this”
Lauren: So the IPA is where the IPA was created
Gretchen: Yeah I hope they were all drinking IPA but I can't guarantee that
Lauren: In our reenactment that is definitely what's happening
Gretchen: Yeah, when we when we all get dressed up in historic costume (bagsies Henry Sweet), then we will all drink IPA
Lauren: I'm Daniel Jones apparently - no wait, I'm going to dress up as Cardinal Vowel, I always thought that would be a great linguist costume
Gretchen: Ah that's great! Were cardinal vowels invented yet?
Lauren: Well it was Daniel Jones who did that, I don't know when he was working
Gretchen: Oh ok good
Lauren: I mean we'll have to have a whole episode just talking about vowels and how they work, but that was kind of a thing that was figured out at the time
Gretchen: Yeah and they came up with some principles for future development of this International Phonetic Alphabet and these were: each symbol should have its own distinctive sound and the same symbol should be used for the same sound across all languages
Lauren: So instead of having the J sound sounding like /dʒ/ or /ʒ/ or /j/ or /x/ across different languages, every time that sound was used it would be used for exactly the same sound
Gretchen: Every time that *symbol* was used
Lauren: Yes sorry every time that symbol was used it would be used for the same sound
Gretchen: They also came up with some principles that influenced which symbols ended up being chosen for which sounds. So they decided to use as many ordinary Roman letters as possible and to have a very minimal number of new letters, and to use what they called quote unquote “international” usage to decide the sound for each symbol
Lauren: So they wouldn't like, take the symbol that we have for 's' and decide 'oh we're going to make that the sound for 'l' because we're crazy people'
Gretchen: Yeah, they didn't do that. But the other thing is, so if we look at the vowels, the IPA vowels look kind of weird from an English perspective. So the IPA uses the letter that we think of as 'i' to represent the 'ee' /i/ sound and uses the letter we think of as 'e' to represent the 'eh' /e/ sound and so on. And this doesn't make sense for English, but it does make sense when you look at a whole bunch of other languages like Spanish and Italian, and the way the Roman alphabet has been used for non-European languages generally falls along these principles as well. So they said, “Look, even though we're English speakers we're going to not do the English things”
Lauren: Okay, so they really did go with this kind of international general preference
Gretchen: Yeah, I mean, they're still eurocentric, they're still starting with European languages and kind of working their way outwards, but they were at least not completely Anglo-centric, which is helpful here, because English does some weird stuff with its sounds
Lauren: Yeah and we only have 26 letters in the English alphabet, a few more if we kind of pull everything from across European languages, and there are so many more sounds that the world's languages can make, so once we've run out of kind of standard letters where do we go from there?
Gretchen: Where we are from there is often Greek letters or Latinised looking versions of Greek letters because those were familiar to these creators. Another thing that they did was they would rotate letters. and this was partly because the shapes are still familiar if you do that and partly because this is the 1800s and people were typing with metal bits of type. So if you just take a lowercase 'e' and turn it upside down, you can just print your new character by flipping or rotating an existing metal type bit rather than casting a new one
Lauren: I have a really nice example from Australia, so I was at a workshop the other day and a colleague was showing me a booklet of Kamilaroi, so it's a language from the New England area of New South Wales in Australia, and William Ridley was working on this language in 1856. So this is even before the IPA was codified. And these languages have a sound like an English sound but you may not notice it in English because it's a sound at the end of words like 'sing' or 'bring', that /ŋ/ sound, but that sound can occur anywhere so you can have it at the start of the word as well as at the end. This /ŋ/ sound now has a symbol in the IPA that looks like an 'n' with a little tail and it's called an 'engma'
Gretchen: Yeah kind of like an 'n' with a 'g' tail shoved on it
Lauren: Yeah, and Ridley is one of the first people who adopted this symbol for use in his describing languages work in the 1850s, which was before the 1880s when the IPA was established. But this symbol had begun to be used for this /ŋ/ and it makes sense because it's like an 'n' and a 'g' squashed together. But when he sent it to the typesetters for his booklet they didn't have a /ŋ/ and so they just turned a capital 'G' upside down which sounds a bit crazy and it looks a bit crazy it looks like it's just full of upside down 'G's, but it meant that that was a way that they could represent this /ŋ/ sound. Apparently he sent it to some other journal in Europe and they just turned it all into a 'z'
Gretchen: Wow, a 'z'!
Lauren: Yeeeah
Gretchen: Wow, that's really bad! So I guess that's why it's good that another principle the IPA had was that the look of the new letters should suggest the sound they represent, so once you've learned the kind of basic ones and if you see a couple languages and you have a sense of what's used in other languages then you can often guess fairly accurately what an IPA letter is going to be like. So it's better to have a symbol for /ŋ/'that looks like an 'n' and a 'g' shoved together because that's how it's often written in different languages, a bit like an 'n' sound, a bit like a 'g' sound.
Another one of their principles was that diacritics should be avoided where possible. So adding extra little like accent marks or other types of small bits on top of letters was something that they tried to avoid for their basic sounds. Diacritics were only was supposed to be for if there's a modified version of a sound, but not for basic sounds in general. So in the current IPA, you still get these rotated letters, which must make the IPA very difficult for people who are dyslexic; you get small capitals; you get Greek stuff like the Greek letter theta is used for the 'th' /θ/ sound, and the runic and ultimately Icelandic sound /ð/ -- so the symbol that looks like an 'o' with kind of a cross above it, that’s from Icelandic and it used to be in English before the Normans came, that got borrowed back in -- so borrowing from other established systems. Because then you could just go to Iceland and grab some of their metal type bits, I don't know, or go to Greece and get some from them
Lauren: It's something that was a problem with the original metal type but it's also been a problem for a long time with modern software. So for a long time computers didn't really have fonts that expanded beyond the kind of really basic font set of like English and French and some diacritics and some special things. If you have some older software or if you look at older digital documents you have, y’know, people using capital 'A' for particular vowel sounds, vowel characters in the IPA that are symbols in the IPA that aren't in regular type or y’know schwa would be a capital 'E' for example
Gretchen: Yeah you can even see this on some old websites, people will use a different system that only uses the basic 26, plus capitals to do the extra stuff or maybe some places use like an 'at' sign @ to indicate a schwa, because we've also had a different version of this encoding problem with technology
Lauren: So it's not just the metal type it's also modern computing
Gretchen: It's also the byte! It's the type and the byte!
Lauren: The type and the byte have been a problem, it's getting better
Gretchen: It's getting better thanks to Unicode, thanks Unicode! So yeah the first version from 1887 was designed to work for sounds in English, French, and German because that's what they were doing at the time. It's a bit weird compared to the modern IPA because we're used to seeing it as a chart and they just gave a list of symbols and keywords that stuff was found in for various languages. So they'd say something like okay this 'a' symbol is going to be like the sound in English 'father' or this symbol is going to be like the sound in German 'Bach' and they just give the keywords like sometimes you see in the front of the dictionary. And then later, so they kept on working on it in the late 1800s and then by the year they expanded, published a version that included Arabic and a few other languages’ sounds, that’s when they finally publish it as a table for the first time
Lauren: So why would it be in it table, for people who aren't familiar with the International Phonetic Alphabet?
Gretchen: The cool thing about the table is -- so our English alphabet that you learn as a kid is 'ABCD' in no particular order, that's just the order it is, that's just for historical reasons -- but the table is ordered based on how the sounds are produced. So sounds get produced with constriction in various parts of the mouth and with different degrees of constriction once you're in that place
Lauren: So it's a nice feature based table of all the kind of combination of features in particular places
Gretchen: Yeah, exactly. If you superimpose a mouth onto that table, it looks a bit weird but you can kind of do it and you can see where each of the sounds is produced
Lauren: I have a link somewhere to an audible IPA chart so you can click on the sounds and hear what they sound like, but the ones on the very left side are all produced with just the lips like /p/, and the very front of the mouth. And then the ones at the very right edge are all the way back at the far back of the mouth, and that's things like your velar sounds like /g/ get made with that soft bit there or your uvula like right down in the very far back in the mouth
Gretchen: Yeah, it goes from your lips, through your mouth along the roof of your mouth and back into your throat. And the weird thing about this version from 1900 is that it's a mirror image of that so it has 'p' and 'b', your labial sounds on the right instead of on the left
Lauren: Oh no, that would confuse me so much
Gretchen: You can see an image of it on Wikipedia, it's all like typewritten, we'll link to that
Lauren: Wow, awesome
Gretchen: But it looks really weird, and they also have the vowel chart and the consonant chart on the same chart
Lauren: Right, okay!
Gretchen: They just have like a really wide section where the vowels go
Lauren: How weird!
Gretchen: Yeah, which is something else that changed later
Lauren: So there's now a table for the consonants, there's a few consonants that don't even fit, and then there's a vowel chart that's a separate thing, but it's very similar principle like it starts at the front of the mouth and goes back
Gretchen: Yeah, and what's cool is that the version that we use today is actually very very similar to the version that was solidified in 1932, which was quite a while ago. There were some adjustments made in 1989 and then after that it's just like 'oh well we need to add this one symbol because we found some languages that use it' but pretty much it stays very similar for quite a long time once it's established
Lauren: Nice. So it goes from left to right all the different places in the mouth, and then from top to bottom there are different ways just looking at the consonants, the ways to pronounce different consonants so you have the very plosive sounds like /b/, /k/, /d/, /t/ - we call them stops - along one row and your nasal sounds, so your /m/, /n/, /ŋ/, sounds along another row...
Gretchen: It kind of goes in order of how much you need to drop your jaw. So if you think about the sounds in the top row, your mouth is the most closed when you're making like a 'p' or a 'b'. You have to literally close your mouth for a second, you have to close your lips to make those sounds. Whereas if you're making a sound like 'r' /ɹ/ you don't have to actually close anything you're letting the sounds kinda come through. So the 'r' /ɹ/ sounds are near the bottom, but the /p, b/ sounds are near the top
Lauren: I mean that's the thing I found super neat about it when I was studying the IPA in undergrad was just how elegantly it captures all these different parameters in one table
Gretchen: Yeah, just to realize that someone has thought this through, thinking 'ok what are all the permutations you could put your mouth in and which ones do people actually use and let's organize this'
Lauren: And English just uses one subset of it
Gretchen: Yeah, every language is going to pick some subset of the sounds in this table, or if it doesn't we have to add something. So one of the cool things that you can do with the IPA because it's based on different positions the mouth can be in is adapt it to other mouth stuff. For example, Lauren Ackerman, who has the linguistics blog 'Wug Life', has made a table of emoji with their mouth positions as if they're making sounds in the IPA. So you can look at this table and she has things like the surprised emoji, which has kind of a round mouth and so that's like an 'oo' /u/ sound because you have to round your lips for that, and the 'ee' /i/ is kind of like a smile, and it is completely ludicrous but also great
Lauren: These are the important things that linguists do with their downtime
Gretchen: Yeah and the other cool thing you can do with the IPA is because you can use it to represent mouth sounds is you can write beatboxing in IPA, because beatboxing is done with the mouth
Lauren: Oh yeah, that must look amazing!
Gretchen: It looks so cool! I have a picture of it, of a chart that some beatboxing linguist researchers made
Lauren: That is awesome
Gretchen: So we'll link to that too
Gretchen: I mean we both have a lot of love for the International Phonetic Alphabet, obviously it's something we engage with a lot in all varieties of linguistic work. I think it's worth mentioning though that like, it's not perfect for everything, it can get really annoying sometimes.
Gretchen: Yes!
Lauren: Particularly, as I mentioned in terms of the fact that font encoding on computers is still a problem, you still occasionally will get proofs back from a publisher for a journal article and all the engma, they're all mysteriously like really ugly still, we haven't quite got there with them being part of the font set for every single font
Gretchen: Yeah and it can be hard to write on a normal keyboard
Lauren: Yeah it's also really annoying to write on a normal keyboard sometimes. Also especially in the vowels, like I get a bit of like IPA anxiety when I use IPA and share it with people publicly, especially for long passages of text it's not always that easy to transcribe things
Gretchen: Yeah, and as fluent writers we've gotten used to the Byzantine nature of the English spelling system and we we also know how to talk, but thinking about how you talk in a more conscious way to say 'what sound am I saying here, what sound am I saying there' -- that’s different. So it can be hard to write extended passages in IPA. I know if I make a blog post that has an English sentence or two in IPA, I'll inevitably get some corrections from a linguist or something that says “I think you're probably producing this sound here” and I'm like “Oh yeah you're right” because there's no spellcheck for IPA
Lauren: Yeah and also even if there were a spellcheck, you and I would produce different IPA transcriptions for our own pronunciation of things
Gretchen: Yeah and we're pretty good with understanding people's different pronunciations of things when we're hearing them, because I guess humans have a lot of evolutionary practice at that, but for reading things we have a fairly standardised system. I remember when I was still a young linguist back when John Wells's phonetic blog was active. He's a well-known British linguist who's involved in some of the history of the IPA and he used to keep a blog and he would sometimes write full posts in IPA. And they were really interesting for me to read, to practice but I also found them very difficult because he would be transcribing his own accent. And he was British and so he wouldn't write all these 'r' /ɹ/ after vowels that I would, so I had to figure out where all these /ɹ/ were supposed to be. I'd end up reading his post out loud to myself and hearing the British accent being like “oh yeah this is what he's trying to say”
Lauren: You would be saying it in his accent?
Gretchen: Yeah, I'd be saying it in his accent, because you can write someone's accent, which is the cool thing but also the more challenging thing about reading IPA
Lauren: Linguists also talk about broad IPA and narrow IPA transcription - so like, you can do a kind of rough-and-ready, mostly correct transcription, or actually if you are a phonetician and you're looking really closely at how people actually articulate things, you discover all kinds of things that you need to transcribe to capture the correct and accurate transcription but which people don't hear kind of consciously or would find really weird when you've represented it to them
Gretchen: Yeah or don't notice
Lauren: And there's often like phonological processes, like when you tell people that the vowel that they use in the middle of 'handbag' is actually, for native speakers if they say it quickly, it often becomes 'hambag'
Gretchen: 'hambag', like a ham sandwich
Lauren: Yeah, like a bag-o-ham. If you write it out in IPA, people are like ‘that's incorrect,’ and you're like 'well that's what you said'
Gretchen: There's a fun story about that, so English speakers also often say 'sammich' instead of 'sandwich' because the 'm' the like the nasal sound becomes like the 'w'. Except for Anglo-Italians; so in Canada there's like Italian Torontonians and Italian Montrealers and people who grew up in those communities often have a particular accent. So in that accent they say 'sangwich' instead of sammich' because in Italian the 'w' sound is kind of more velar whereas in English it's more labial and so it like pulls the nasal along with it to be a different sound
Lauren: And when you start transcribing things in really close IPA you can see those distinctions, it's really cool
Gretchen: Yeah and we often just reduce the vowels in words that we’re saying quickly or in the small unimportant function words we often reduce the vowels all to schwa or something like that
Lauren: I still remember in in my undergraduate class learning that English vowels will often change into schwa, this is the /ə/ sound in unstressed syllables and it just made me realize that for a certain set of words, that's why I was really bad at spelling them. Because you sit there and you're like 'is it amu... amuni ammunition?'. I mean, is it ammunitiON or is it ammunitiAN? That’s not a great word to use as an example but it's the first one that came to mind. For certain vowels, because it's unstressed and it's a schwa, it’s possible that any of the vowel letters could be used to spell it. So you just have to memorize what the spelling is because your pronunciation doesn't help you. And that's why I tell people I'm bad at English spelling - it’s not my fault, it's the fault of my stress system and orthography!
Gretchen: The other thing is, is sometimes English orthography gives you useful cues to distinguish between certain words or when a suffix who's added sometimes the stress changes and you have to recover vowels that are kind of there but had turned into schwa. So if you take a word like 'electric' which becomes 'electricity' - in some senses it's weird that it's spelled with a 'c' and not with a 'k' or an 's' because 'c' is completely redundant, it always makes one of those two sounds, but it does reflect that when it's 'electric' with the 'k' sound and then when you add an '-ity' to it, the 'k' sound becomes an 's' sound because that's what happens with 'c', but it doesn't happen with 'k'. Or the vowels also change - with 'electric', 'electricity' you get different sorts of vowels. So it's kind of useful to have some of this stuff there that was historically there and has changed in its sound. But it also creates this extra layer of complication. Or you can get used to speed reading because a word always looks like the same in spelling whereas if you had to speed read a whole bunch of different accents then an unfamiliar accent might be harder to speed read, but then again it's harder to learn spelling in the first place if you have an accent that's less similar to the spelling system
Lauren: But we still love the IPA for all of the occasional detriments that occur
Gretchen: We still love it and it's still useful to have it as an option to write something very specifically even if you don’t want to do that all the tim. I find if I'm meeting somebody and they have a name I haven't heard before, then I write it in IPA and then I can pronounce it correctly when I'm talking back to them. People like it when you pronounce their names correctly.
Lauren: That's handy. The Journal of the International Phonetic Association used to accept articles written in IPA, which blows my mind. So people would write about some feature of phonetics and they would do the whole thing in the IPA. I think it very quickly became apparent that that was more labour both to produce and to consume than there was any benefit in doing that, for many of the reasons that we've already mentioned
Gretchen: Like, 'hi I'm going to write about like long vowels in Sussex' or something and that whole thing would be in IPA
Lauren: Yes, I think academics clearly had more time on their hands 50 years ago.
Gretchen: I mean, to be fair, I have played IPA Scrabble, which is like Scrabble, but you do it in IPA
Lauren: Do you just kind of argue for your own pronunciation or do you have to do it in your own dialect?
Gretchen: The way that I've done it is I combined IPA Scrabble with Descriptivist Scrabble, which is a little bit like those bluffing games, so as long as you can convince other people that it's a word then it's a word
Lauren: Ah, I like that
Gretchen: Yeah, because like, dictionaries are arbitrary authorities anyway, so with Descriptivist Scrabble you can just use whatever means you have at your disposal to convince people that it's a word. Of course choosing an obvious word like dog or something is going to be easier to convince people than saying--
Lauren: blergh?
Gretchen: Yeah, than saying “blerg is a word, honestly it means a colour kind of like grey and blue at the same time” but you can try!
Lauren: There are heaps of cool things people have done with the IPA including someone has made a set of IPA Scrabble
Gretchen: Yeah so I posted on All Things Linguistic a set of frequencies and scores that you can use for IPA Scrabble tiles, because I made it with a friend in undergrad and we had figured this out. We just cut out bits of cardboard to make them, and then some undergrads at Yale came across this post and decided to get their friend who has like a wood cutting machine to cut these out of these gorgeous wood tiles and they sent me some photos which I've also posted. You can see those on the blog, they're amazing, so yeah so someone has made a wooden IPA set that I still have not played but it’s really cool
Lauren: IPA characters also make for popular tattoos because they're quite beautiful, so I've definitely seen a schwa tattoo and I've seen a glottal stop which is a little bit like a question mark - it's our logo!
Gretchen: It is also our logo. Do people get whole words in IPA or like phrases in IPA tattooed on them?
Lauren: Mmm I haven't seen any but if anyone has we will definitely be interested in seeing it
Gretchen: If you know any IPA tattoos please send them to us
Lauren: Well I've seen a couple but not that long
Gretchen: There's also a whole version of Alice in Wonderland that's published in IPA - so this takes us back to the Journal of Phonetics - and she's like talking to the Mad Hatter and so on and it's all in IPA. The weird thing about this particular version is that this publisher decided to also have capital letters
Lauren: Huh, interesting
Gretchen: And of course they had to make capital versions for all of the IPA letters
Lauren: Wow, that's commitment
Gretchen: Because you know if you think about it capitals are redundant, they don't add any extra phonetic information to a sound, so the IPA doesn't use them. And sometimes the IPA uses small cap versions of a letter to indicate a different sound because it's an extra symbol. And so instead this person decided that no, if I'm going to write it as a book I'm going to make capitals and so yeah it's very interesting how they decided them.
Lauren: Yeah, there you go. My IPA nerd craft activity was to cross stitch the consonant chart, I did that quite a few years ago and it's a very useful adornment in the office when you just need to quickly refer to some of the symbols. I also was going to do the vowel chart but the modern vowel chart is very very complicated and messy which is why I went with Jones's much more elegant original cardinal vowels
Gretchen: Ahh so you did a simplified version
Lauren: Yep I'll put links to those in the show notes
Gretchen: And you also did a cookie cutter, right?
Lauren: Oh yeah! I made a schwa cookie cutter for Christmas last year, just what you need, and it's a 3D printable cookie cutter, so you can also download that design and print your own and make your own gingerbread schwa or shortbread schwas.
Gretchen: That's great. There's also an IPA version of the game 2048, which came out when the game 2048 was popular - so that's the one where you like slide the tiles around and you try to combine to make bigger and bigger things. And so you start with a schwa and then you combine them to make an engma, which makes no sense phonetically, and then you combine them to make an esh. Again, this won't teach you anything about phonetics
Lauren: But it goes into more and more elaborate and less frequent forms
Gretchen: Yeah it does get to more and more elaborate stuff, like you end up with like a glottalised bilabial click or something like that
Lauren: Right, it doesn't officially teach you anything about the IPA but it is a good excuse for a distraction
Gretchen: You should not do it if you're a student and you're about to write an exam on the IPA, this is not a good way to procrastinate
Lauren: Official warning!
Gretchen: Instead you should play IPA scrabble
Lauren: Much better way!
Gretchen: Which will teach you some more about the IPA
Lauren: Or read Alice in Wonderland
Gretchen: There's also a fun sketch from the sketch comedy show John Finnemore's Souvenir Programme, which is a sketch where some characters encounter some skeletons and the skeletons are pirates but these skeletons cannot tell you that there are pirates because they don't have any lips, so they cannot produce the 'p', sound so they call themselves 'kirates',
Lauren: Awww
Gretchen: And the characters who encounter them are very confused, like 'what are you?' 'we're kirates, I said we're kirates!'. Anyway, I am probably not doing it justice but you should listen to it, we have a link to that as well
Lauren: Excellent
Gretchen: Although they don't make the point which I kept thinking, which was like 'Well, if the don't have any lips, they probably don't have any tongues either, so they probably can't produce any sounds because they're skeletons'
Lauren: They probably don't have any kind of pulmonic air flow ability
Gretchen: Like all they can do is clack
Lauren: Yup, Morse code?
Gretchen: Yeah! So skeletons can communicate with us in Morse code, there we go
Lauren: Yeah. I was going to say sign language just because I always seem to want to mention sign languages because they're always cool
Gretchen: Oh yeah please do
Lauren: it's worth pointing out that like obviously the IPA is for all spoken languages, if you haven't figured that out by this point in the podcast, I'll just make that abundantly clear. It’s for all oral languages. In individual sign languages people talk about like phonemes and morphemes in terms of hand shapes so there are some hand shapes that are possible in some sign languages that don't occur in others. And so you have a similar kind of basic feature sets that you can refer to in in sign languages. But because it uses a more complex modal articulation system and it isn't just limited to the mouth, then it's a bit more complicated cross-sign-linguistically, but they do have their own kind of equivalent of phonemes or phonetics
Gretchen: There's a couple different standardised sign transcription systems, I don't know if any of them have caught on at an international level in the same way to the IPA has, I mean to be fair there there are other phonetic transcription systems that aren't the IPA, it's just the IPA has caught on more than the others. But you can transcribe signs, there's a couple different ways of doing that. There's also the fact that sign languages have alphabets that they use to borrow words in from spoken languages among other functions and within that there are sign equivalents of at least some IPA characters, which I know because I've been to linguistics conferences and seen interpreters signing talks and they will sign a particular IPA symbol when the person who's giving the presentation is talking about that particular IPA symbol
Lauren: There you go
Gretchen: Yeah, I cannot recite any of them for you, but I remember noticing it and thinking 'huh, ok I guess that's what they're doing’
Lauren: Man, awesome!
[Music]
Lauren: For more Lingthusiasm and links to all the things mentioned in this episode go to Lingthusiasm dot com. You can listen to us on iTunes, Google Play Music, SoundCloud or wherever else you get your podcasts. You can follow at @Lingthusiasm on Twitter, Facebook and Tumblr. I tweet and blog as Superlinguo
Gretchen: And I can be found as @GretchenAMcC on Twitter and my blog is All Things Linguistic dot com. Lingthusiasm is created and produced by Gretchen McCulloch and Lauren Gawne, our producer is Claire and our music by The Triangles. Stay Lingthusiastic!
[Music]

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
#linguistics#ipa#International Phonetic Alphabet#phonetics#phonology#lingthusiasm#episode 6#transcript#transcripts#podcast#accessibility
94 notes
·
View notes