#U.S. Chief Justice John Roberts
Text
Congress Fails To Adopt Important Immigration Legislation
Congress Fails To Adopt Important Immigration Legislation
Previous posts documented Congress’ earlier failure this Session to adopt (a) the Afghan Adjustment Act to improve the legal status of Afghan evacuees in the U.S. and (b) important bipartisan immigration reform, one of which was offered by Senators Kyrsten Sinema (ex-Democrat & now Independent) and Thom Tillis (Rep., NC) that would have addressed the legal fate of so-called Dreamers and provided…
View On WordPress
#Afghan Adjustment Act#Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA)#Greisa Martinez Rosas#Homeland Security Secretary Alejandro Mayorkas#Omnibus Bill#President Joe Biden#Title 42#Trump Administration#U.S. Chief Justice John Roberts#U.S. Department of Homeland Security#U.S. Justice Amy Barett#U.S. Justice Bret Kavanaugh#U.S. Justice Clarence Thomas#U.S. Justice Elena Kagan#U.S. JUstice Ketanji Jackson#U.S. Justice Neal Gorsuch#U.S. Justice Samuel Alito#U.S. Justice Sonia Sotomayor#U.S. Senator Kyrsten Sinema#U.S. Senator Mike Lee#U.S. Senator Tester#U.S. Senator Thom tillis#United We Dream#Wall Street Journal#White House Press SecretaryKarine Jean-Pierre
0 notes
Text
Don't Be Fooled!
Long overdue headlines yesterday:
Supreme Court Adopts Ethics Code After Reports of Undisclosed Gifts and Travel (New York Times)
Supreme Court, under pressure, issues ethics code specific to justices (The Washington Post)
Supreme Court adopts modified ethics code after pressure from Hill Dems (Fox ‘News’)
The Supreme Court adopts first-ever code of ethics (NPR)
Under fire, US Supreme Court…

View On WordPress
#Chief Justice John Roberts#ethics code#Harlan Crow#Justice Clarence Thomas#Justice Samuel Alito#Leonard Leo#Robert Reich#U.S. Supreme Court
0 notes
Text
Joan McCarter at Daily Kos:
The U.S. Supreme Court heard Donald Trump’s immunity claim in his federal criminal trial for trying to overturn the 2020 election Thursday, and the conservative majority is likely going to give Donald Trump what he wants: a delay of the trial until after the election. If Trump wins again, the conservatives have essentially signaled that they would be open to blanket immunity for him against any future criminal charges.
The fact that Supreme Court justices are suggesting that the president is above the law proves why the court must be reformed.
Four of the justices—Clarence Thomas, Samuel Alito, Brett Kavanaugh, and Neil Gorsuch—even went so far as to suggest that special counsel Jack Smith’s entire prosecution is unconstitutional, and they reinforced Trump’s argument that the president is immune.
Kavanaugh even told Michael Dreeben, a lawyer from Smith’s office, that it’s a “serious constitutional question whether a criminal statute can apply to the president’s criminal acts.”
That would be the ultimate get-out-of-jail-free card for the chief executive, rubber stamped by the highest court of the land.
It’s worth remembering that Thomas refused to recuse himself from this—and most of the Trump election interference cases—despite the fact that his wife, Ginni Thomas, was deeply involved in Trump’s coup attempt. When she testified to the Jan. 6 special congressional committee, she maintained that the election was stolen.
His failure to recuse himself comes after a new ethics code has supposedly been enforced, saying that “a Justice should disqualify himself or herself in a proceeding in which the Justice’s impartiality might reasonably be questioned, that is, where an unbiased and reasonable person who is aware of all relevant circumstances would doubt that the Justice could fairly discharge his or her duties.”
So much for that suggestion from Chief Justice John Roberts. His code has no teeth, which is yet another reason why ethics reform—and indeed court reform and expansion—is essential.
Joan McCarter writes in Daily Kos that the Trump v. United States "immunity" case is a good reason to reform and expand SCOTUS.
114 notes
·
View notes
Quote
Sen. Elizabeth Warren (D-MA) criticized Chief Justice John Roberts’ fixation on the “fairness” of the Biden administration’s student debt relief plan Thursday, which he and his right-wing peers brought up repeatedly during oral arguments earlier this week.
“When Justice Roberts asks about fairness rather than focusing on statutory interpretation or constitutional issues, he’s becoming a super legislator. That’s not his job,” Sen. Elizabeth Warren (D-MA) told TPM. “It is not the role of the United States Supreme Court to make those judgements.”
“And that means this Court is trying to pull more power into itself and away from the elected officials whose jobs it is to make those decisions,” she added. “This is not about a Court that is promoting small government. This is about a Court that is promoting big court.”
Roberts, joined by Justices Samuel Alito and Neil Gorsuch, repeatedly asked the U.S. Solicitor General about the fairness of the plan, with Roberts conjuring up a hypothetical person who forewent college to start a lawn care business to torque up the sympathy.
Warren Accuses John Roberts Of Acting As ‘Super Legislator’ During Student Debt Oral Arguments
Expand the court and impeach the illegitimate Trump appointees.
940 notes
·
View notes
Text
Do they ever give up? Those looking to divvy up Americans by race, that is.
In California they tried to get race preferences approved in a 2020 referendum, but voters rejected it 57.2% to 42.8%. This was a stunning rebuke, not only because the rejection came from residents of a blue state but because the losing side had outspent opponents something like 14 to 1.
In 2023 the Supreme Court weighed in with a landmark ruling that barred colleges from treating people as members of a racial group instead of as individuals—and cast constitutional doubt on all race-based preferences. “Eliminating racial discrimination means eliminating all of it,” Chief Justice John Roberts wrote. Couldn’t be clearer, right?
Not in California. Undaunted state Assemblyman Corey Jackson is pushing a bill called ACA7. It takes aim at the state ban on race preferences that voters put in the constitution in 1996 when they passed Proposition 209. Californians reaffirmed Proposition 209 three years ago at the ballot box.
The language the voters agreed to and the activists hate reads as follows: “The state shall not discriminate against, or grant preferential treatment to, any individual or group on the basis of race, sex, color, ethnicity, or national origin in the operation of public employment, public education, or public contracting.”
Unlike the 2020 effort, the new bill would leave that language intact. Instead, it would add a provision allowing the governor to create “exceptions.” Effectively that would gut the ban.
Apparently, the lesson the advocates of state-sponsored discrimination have taken from their defeat is that if at first you don’t succeed, try something sneakier.
Here is Mr. Jackson’s press release summarizing the bill: “ACA7 will allow . . . the Governor to issue waivers to public agencies that wish to use state funds for research-based, or research-informed and culturally specific interventions to increase life expectancy, improve educational outcomes, and lift people out of poverty for specific ethnic groups and marginalized genders.”
Gail Heriot is a University of San Diego law professor who sits on the U.S. Commission on Civil Rights and was a leader of both Proposition 209 and the “no” effort on the 2020 referendum. She has launched a petition with Extremely Concerned Californians at change.org opposing the measure.
“ACA7’s proponents are hoping that voters will be fooled into thinking that it is just a small exception,” Ms. Heriot says. “In fact, it gives the governor enormous power to nullify Proposition 209.”
Edward Blum agrees. As the founder of Students for Fair Admissions, he spearheaded the lawsuits against Harvard and the University of North Carolina that killed race preferences in college admissions.
“Racial preferences are never legally justified because some specious ‘research’ report concludes it would be beneficial to a certain race,�� says Mr. Blum. “This exemption will trigger endless litigation that will polarize California citizens by race.”
But sowing discord is a feature, not a bug. As the bill was making its way through the Assembly, Mr. Jackson got in a spat with Bill Essayli—a Republican who is also the first Muslim elected to the Assembly. Mr. Essayli pointed out that the majority of Californian voters disagree with state-sanctioned discrimination. “I fundamentally disagree with this backwards policy,” he later tweeted.
Mr. Jackson responded in his own tweet: “This is a perfect example how a minority can become a white supremacist by doing everything possible to win white supremacist and fascist affection.”
ACA7 passed the state Assembly in September. If it passes the Senate, it will be on the ballot in November. If Californians vote yea, it will become part of the constitution.
But all is not lost. The 2020 referendum awakened a sleeping giant: the Asian-American community. Asian-Americans quickly realized (as the Harvard case drove home) that they and their children are the primary victims whenever race is substituted for merit. Asian-Americans are more aware and organized than they were in 2020. They aren’t likely to be fooled by talk of “exceptions” based on “research.”
It also isn’t a given that ACA7 will make it through the state Senate. Though Democrats enjoy a 32-8 majority, polls consistently show race preferences are unpopular. Gov. Gavin Newsom’s support will be crucial.
Though he has no formal role in the constitutional process, some think the bill will go nowhere if Mr. Newsom doesn’t want it to. If it does make it to the ballot this November, he’ll be under immense pressure to endorse it. That’s another reason the Senate should kill ACA7 now, Ms. Heriot says.
“California voters need to make sure their state senators know where they stand—through emails, phone calls, letters, and petitions,” Ms. Heriot says. “Once the senators understand that, they will realize putting ACA7 on the ballot is not in their interest.”
92 notes
·
View notes
Text
"The Supreme Court on Thursday issued a surprising 5-4 ruling in favor of Black voters in a congressional redistricting case from Alabama, with two conservative justices joining liberals in rejecting a Republican-led effort to weaken a landmark voting rights law.
Chief Justice John Roberts and Justice Brett Kavanaugh aligned with the court’s liberals in affirming a lower-court ruling that found a likely violation of the Voting Rights Act in an Alabama congressional map with one majority Black seat out of seven districts in a state where more than one in four residents is Black. The state now will have to draw a new map for next year’s elections.
The decision was keenly anticipated for its potential effect on control of the closely divided U.S. House of Representatives. Because of the ruling, new maps are likely in Alabama and Louisiana that could allow Democratic-leaning Black voters to elect their preferred candidates in two more congressional districts.
The outcome was unexpected in that the court had allowed the challenged Alabama map to be used for the 2022 elections, and in arguments last October the justices appeared willing to make it harder to challenge redistricting plans as racially discriminatory under the Voting Rights Act of 1965...
The case stems from challenges to Alabama’s seven-district congressional map, which included one district in which Black voters form a large enough majority that they have the power to elect their preferred candidate. The challengers said that one district is not enough, pointing out that overall, Alabama’s population is more than 25% Black.
A three-judge court, with two appointees of former President Donald Trump, had little trouble concluding that the plan likely violated the Voting Rights Act by diluting the votes of Black Alabamians. That “likely” violation was the standard under which the preliminary injunction was issued by the three-judge panel, which ordered a new map drawn.
But the state quickly appealed to the Supreme Court, where five conservative justices prevented the lower-court ruling from going forward. At the same time, the court decided to hear the Alabama case.
Louisiana’s congressional map had separately been identified as probably discriminatory by a lower court. That map, too, remained in effect last year and now will have to be redrawn.
The National Redistricting Foundation said in a statement that its pending lawsuits over congressional districts in Georgia and Texas also could be affected."
-via AP, June 8, 2023
#scotus#supreme court#united states#us politics#voting#voting matters#voting rights#voting rights act#racial justice#gerrymandering#alabama#louisiana#georgia#texas#good news#hope#also Pat Robertson died today - good news really is coming in threes!
212 notes
·
View notes
Text
By Jessica Corbett
Common Dreams
April 24, 2024
"At its core, this Supreme Court decision will reflect who we are becoming as a society."
Less than a month after a key abortion pill hearing, the right-wing U.S. Supreme Court on Wednesday heard arguments for another major reproductive rights case—one out of Idaho that could impact healthcare for pregnant women and people across the country.
Idaho is among the over 20 states that have tightened restrictions on abortion since the high court's right-wing majority reversed Roe v. Wade nearly two years ago with Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health Organization. Since August 2022, abortions have been banned in the state except for reported cases of rape or incest or when "necessary to prevent the death" of the pregnant person.
"If the court does not uphold emergency abortion care protections, this ruling will have devastating consequences for pregnant people."
Before Idaho's near-total ban on abortion took effect, U.S. District Judge B. Lynn Winmill barred enforcement of it to the extent that it conflicts with the Emergency Medical Treatment and Labor Act (EMTALA), a 1986 federal law requiring emergency departments that accept Medicare to provide "necessary stabilizing treatment" to any patient with an emergency medical condition.
The Biden administration argues that such care includes abortion; Idaho's Republican policymakers—backed by the far-right Christian Alliance Defending Freedom—disagree. The U.S. Supreme Court in January paused Winmill's order and agreed to hear arguments in Moyle v. United States and Idaho v. United States.
As The New York Times reported Wednesday:
In a lively argument, questions by the justices suggested a divide along ideological lines, as well as a possible split by gender on the court. Justice Amy Coney Barrett, a conservative, appeared skeptical that Idaho's law, which bars doctors from providing abortions unless a woman's life is in danger or in specific nonviable pregnancies, superseded the federal law.
The argument also raised a broader question about whether some of the conservative justices, particularly Justice Samuel A. Alito Jr., may be prepared to embrace language of fetal personhood, that is, the notion that a fetus would have the same rights as a pregnant woman.
Also noting Barrett's apparent alignment with the three liberal women on the court, Law Dork's Chris Geidner predicted "it comes down to" Chief Justice John Roberts and fellow right-winger Brett Kavanaugh.
"Already, we see women miscarrying and giving birth to stillborn infants in restrooms and in their cars after hospitals have turned them away, and medical professionals put in impossible positions by extremist lawmakers," said MomsRising executive director and CEO Kristin Rowe-Finkbeiner, citing Associated Pressreporting from last week.
"Of all the horrors SCOTUS unleashed with its appalling, dangerous, massively unpopular ruling overturning Roe v. Wade, the threat that pregnant people—most of whom are moms—will be denied emergency medical care is among the worst," she asserted. "An adverse ruling in this case will mean emergency rooms can deny urgently needed care to people experiencing serious pregnancy complications that can destroy their health, end their fertility, and take their lives."
Alexa Kolbi-Molinas, deputy director of the ACLU Reproductive Freedom Project, similarly stressed that under a decision that favors the Idaho GOP, "pregnant people will suffer severe, life-altering health consequences, and even death."
"We're already seeing the devastating impact of this case play out in Idaho, where medical evacuations to transport patients to other states for the care they need have dramatically spiked since the Supreme Court allowed state politicians to block emergency abortion care," she noted.

The has also been an exodus of healthcare providers. Pointing out that those who violate Idaho's ban face five years in prison, The Guardian reported Wednesday that "between 2022, when Roe was overturned, and 2023, about 50 OB-GYNs moved out of the state."
As Republican lawmakers in various states have ramped up attacks on reproductive freedom since Dobbs, states that still allow abortions have seen an influx of "healthcare refugees." A Planned Parenthood spokesperson confirmed in January that about 30% of its abortion patients in Nevada—which borders Idaho—are from other states.
"With several of Nevada's bordering states enforcing abortion bans, pushing many people seeking care to our state, we've seen firsthand the devastation that anti-abortion policies are already wreaking," Reproductive Freedom for All director of Nevada campaigns Denise Lopez said Tuesday. "The Supreme Court must not allow us to spiral further into this healthcare crisis."
If the high court rules in favor of Idaho's Republican lawmakers, she warned, "all states will be impacted, even in places like Nevada with more than 4 in 5 voters supporting reproductive freedom."
Destiny Lopez, acting co-CEO of the Guttmacher Institute, declared that "at its core, this Supreme Court decision will reflect who we are becoming as a society: Are we okay with requiring pregnant individuals who face severe complications to suffer life-threatening health consequences rather than granting them access to abortion? Are we okay with forcing doctors to choose between violating federal law by not providing emergency abortion care or violating state law if they do?"
"If the court does not uphold emergency abortion care protections, this ruling will have devastating consequences for pregnant people—particularly Black and Brown folks, immigrants, people with lower incomes, those without health insurance, and LGBTQ+ communities—while further emboldening extremists," she emphasized.
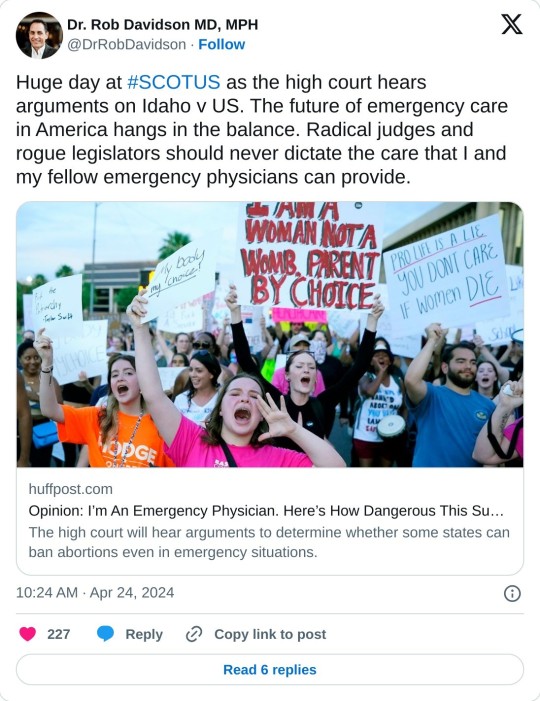
Arguments in the case have sparked multiple demonstrations, from a weekend rally in Boise, Idaho to a Wednesday gathering outside the U.S. Supreme Court in Washington, D.C., where Women's March organized a die-in to highlight the potential consequences of the forthcoming ruling.
"It's a horrifying time to be someone who needs critical abortion care in America right now," said Women's March executive director Rachel O'Leary Carmona. "The GOP is chipping away at women's bodily autonomy and livelihoods one illegitimate court case at a time—from fast-tracking a case on the authorization of a medication that's been safely administered for decades last month, to now bringing the fate of emergency abortion care to a Supreme Court captured by their radical, anti-choice agenda."
"We know what these cases really are: They're part of a series of efforts by Christian nationalist politicians to do anything they can to control women's bodies and cut back women's decisions about their healthcare, their family planning, and their lives," she added.
Similar warnings about far-right Christian nationalist attacks on a range of rights have dominated political contests this cycle—including the race for the White House. In November, Democratic President Joe Biden, who supports access to abortion care, is set to face former Republican President Donald Trump, who brags about appointing three of the six justices who reversed Roe.
The case has renewed arguments for considering changes to the country's top court, which over the past few years has not only seen plummeting levels of public trust but also been rocked by repeated ethics scandals.
"Idaho's abortion ban is a direct consequence of the court's radical decision to overturn Roe v. Wade and allow partisan state legislatures to determine Americans' access to abortion care," said Stand Up America managing director of policy and political affairs Brett Edkins. "If the Supreme Court once again sides with anti-abortion extremists, it will be further proof that this court is radically out of touch with the American people and must be reformed."
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Supreme Court on Monday said Idaho can enforce a law banning gender transition care for minors, stepping into the debate over an issue that has divided lower courts.
The court did so over the objections of the three liberal justices.
It’s the first case about restrictions on puberty blockers and hormone therapy for transgender people under age 18 that the court has acted on. But it does not get to the underlying legal questions of the ban itself, an issue that has divided lower federal courts and is part of a wave of conservative legislation and litigation aimed at transgender Americans.
Justice Kentanji Brown Jackson, writing for herself and Justice Sonya Sotomayor, criticized the majority for granting Idaho’s request through its “emergency” route, rather than letting it proceed through the regular channels.
“This Court is not compelled to rise and respond every time an applicant rushes to us with an alleged emergency, and it is especially important for us to refrain from doing so in novel, highly charged, and unsettled circumstances,” Jackson wrote.
But Justice Neil Gorsuch, joined by Justices Samuel Alito and Clarence Thomas, said the district court went further than it should have when it blocked the state from enforcing any aspect of the law while it’s being litigated. That decision threatened to suspend the law indefinitely because it can take years to reach final judgment, Gorsuch wrote.
Justice Brett Kavanaugh wrote his own defense of the majority’s order in a concurrence joined by Justice Amy Coney Barrett.
Chief Justice John Roberts did not make his position public.
The court could also decide soon whether it will review such bans in Tennessee and Kentucky. That election-year decision would come as transgender issues have become an increasingly potent political issue.
Passed last year, Idaho’s law is being challenged by the families of two transgender teenagers.
After lower courts temporarily blocked enforcement, Idaho asked the Supreme Court to let it go into effect with an exception carved out for the challengers.
The American Civil Liberties Union, which is representing the two Idaho families, said that option won't protect the teenagers as medical providers won't want to risk triggering a law that could put them behind bars for a decade. Also, the teens would have to give up their anonymity.
AN 'AWFUL RESULT FOR TRANSGENDER YOUTH'
The ACLU called the Supreme Court's decision an "awful result for transgender youth and their families across the state."
"Today's ruling allows the state to shut down the care that thousands of families rely on while sowing further confusion and disruption," the group said in a statement.
Praising the court's decision, Idaho Attorney General Raúl Labrador said the law ensures minors will not be subjected to life-altering drugs and procedures.
"Denying the basic truth that boys and girls are biologically different hurts our kids," he said in a statement.
Filed as an emergency request, Idaho’s appeal to the high court is a prelude to the larger pending issue: Whether the justices will uphold such bans, which have proliferated in recent years.
KENTUCKY, TENNESSEE TRANSGENDER CASES MAY COME NEXT
Families of transgender children have asked the Supreme Court to overturn a ruling by the Cincinnati-based U.S. Court of Appeals for the 6th Circuit allowing Kentucky and Tennessee to ban gender-affirming medical care for minors.
The Justice Department has weighed in on the side of the families, telling the court that its input is “urgently needed” to definitively resolve whether the bans are discriminatory.
“These laws, and the conflicting court decisions about their validity, are creating profound uncertainty for transgender adolescents and their families around the nation,” Solicitor General Elizabeth Prelogar said in a filing.
The court could announce as early as this month if they will hear the appeals.
Combined with other state actions to restrict the bathrooms transgender students can use and what sports teams they can join, the laws are expected to be a major issue in this year’s elections.
TRUMP SAYS HE WILL PUSH TO BAN GENDER-AFFIRMING CARE FOR MINORS
Former President Donald Trump, the presumptive GOP nominee, has said he will press Congress to pass a law banning gender-affirming care for minors and will cut federal funding for schools pushing “transgender insanity” if he returns to the White House.
President Joe Biden has boasted about steps he’s taken to strengthen the rights of “transgender and all LGBTQI+ Americans.”
The issue has gained prominence with startling speed, despite the tiny fraction of Americans who are transgender.
Since 2022, the number of states taking steps to limit access to gender-affirming care for minors has grown from four to 23, according to the nonpartisan health research organization KFF. Restrictions were fully in effect in 17 states as of January.
That’s despite the fact that most major medical groups support youth access to gender-affirming care.
The American Medical Association has called the state bans a “dangerous intrusion of government into the practice of medicine and the criminalization of health care decision-making.”
“Gender-affirming care is medically necessary, evidence-based care that improves the physical and mental health of transgender and gender-diverse people,” Dr. Michael Suk, a member of the AMA board, said when the group reinforced its opposition to state bans in 2021.
DEPRESSION, ANXIETY AND SELF-HARM
One of the transgender teenage girls challenging Idaho’s law suffered from depression, anxiety and self-harm before starting gender-affirming medical care, according to filings. The mental health of the other teen likewise deteriorated as puberty began.
Their parents have told the courts they’re terrified about the impact on their daughters’ health and lives if they can’t continue treatment.
Labrador, Idaho's attorney general, argued the law is needed to protect “vulnerable children” from what he called “risky and dangerous medical procedures.”
“Idaho should be able to protect children from experimental medical procedures that cause irreversible and life-long harms,” Labrador wrote in his appeal to the Supreme Court.
Originally scheduled to go into effect in January, Idaho's law was temporarily blocked by a district court judge in Idaho while it’s being litigated. The San Francisco-based U.S. Court of Appeals for the 9th Circuit upheld that decision in January.
Despite the litigation swirling around transgender minors, the Supreme Court has largely been silent on the issue. In April, the high court sided with a 12-year-old transgender girl who was challenging a West Virginia ban on transgender athletes joining girls sports teams, temporarily blocking the state from enforcing the prohibition. The ruling came on the court's emergency docket and did not resolve the underlying questions in the case.
In January, the Supreme Court declined to decide whether schools can bar transgender students from using a bathroom that reflects their gender identity, leaving in place a lower court ruling that allowed a transgender middle school boy in Indiana to use the boys' bathroom.
#us politics#news#us supreme court#idaho#Kentucky#Tennessee#2024#gender affirming care#trans rights#reproductive health#reproductive rights#bodily autonomy#Justice Kentanji Brown Jackson#Justice Sonya Sotomayor#Justice Neil Gorsuch#Justice Samuel Alito#justice Clarence Thomas#Justice Brett Kavanaugh#Justice Amy Coney Barrett#Justice John Roberts#American Civil Liberties Union#Raúl Labrador#6th Circuit US Court of Appeals#Elizabeth Prelogar#president joe biden#donald trump#American Medical Association#9th Circuit US Court of Appeals
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Stalking is so closely correlated with lethal violence that experts refer to it as “slow motion homicide”: More than half of all female homicide victims in the U.S. were stalked before they were killed. Despite the terrifying and dangerous consequences, many victims of stalking do not report the abuse to law enforcement for fear they will not be taken seriously.
The reasonableness of that fear was vividly illustrated by the Supreme Court oral arguments in Counterman v. Colorado on Wednesday morning, as members of the highest court of the land joked about messages sent by a stalker to his victim, bemoaned the increasing “hypersensitivity” of society, and brushed aside consideration of the actual harm of stalking to focus on the potential harm of stalking laws.
For nearly two years, Billy Raymond Counterman sent thousands of unsolicited and unwanted Facebook direct messages to C.W., a local musician, ultimately driving her to abandon her career and leave the state. Counterman, who had previously served time in federal prison for making violent threats against his ex-wife and her family, argues that his conduct towards C.W. was free speech protected by the First Amendment. Counterman maintains, supported by amicus briefs from influential civil libertarian organizations such as the ACLU, the EFF, and FIRE, that stalking cannot be criminally prohibited except when the government can prove that the stalker subjectively intended to terrify his victim. The state of Colorado, supported by amicus briefs from First Amendment scholars, stalking experts, and domestic violence victim advocates, argues that it is enough to prove that the stalking would be terrifying to a reasonable person in light of the totality of the circumstances. If the court rules in Counterman’s favor, delusional stalking—no matter how objectively terrifying or threatening—will be transformed into an inviolable constitutional right.
During oral argument, Chief Justice John Roberts quoted a handful of the thousands of unsolicited messages Counterman sent to C.W. “Staying in cyber life is going to kill you,’” Roberts read aloud. After a pause, he joked, “I can’t promise I haven’t said that,” prompting laughter from other justices and the audience. Picking out another message, which he described as an “image of liquor bottles” captioned as “a guy’s version of edible arrangements,” Roberts challenged Colorado Attorney General Phil Weiser to “say this in a threatening way,” leading to more laughter from the court. And the laughs didn’t stop there: Counterman’s attorney, John Elwood, shared with the court that his mother would routinely tell him to “drop dead” as a child, but “you know, I was never in fear because of that.”
(continue reading)
#politics#scotus#john roberts#stalking#femicide#misogyny#rape culture#war on women#counterman v colorado#stalkers
46 notes
·
View notes
Note
Has any president ever not been given the oath of office by the chief justice of the supreme court
Yes. The Constitution does not specify who must administer the oath of office to the President and government officials who are required to swear (or affirm) an oath can essentially be sworn in by any federal or state judge or even a notary public.
The oath of office has been administered eight times by someone other than the Chief Justice of the United States -- usually when a Vice President has assumed office upon a President's death and it was necessary to quickly locate somebody who could administer the oath. George Washington was also sworn in by someone other than the Chief Justice at both of his inaugurations. In fact, not only was there no Chief Justice at the time of Washington's first inauguration but there was literally no federal judiciary (and, obviously, no federal judges). The Judiciary Act establishing the Supreme Court wasn't enacted until September 1789 -- almost five months into President Washington's first term -- and that's when the first members of the Supreme Court were nominated and confirmed.
Of course, the Chief Justice of the United States has been the person swearing in the President the vast majority of the time. John Marshall, the longest-serving Chief Justice in American history (1801-1835), administered the oath of office more times than anyone else -- nine times to five different Presidents. However, Chief Justice Roger B. Taney (served from 1836-1864) administered the oath to more individual Presidents than anyone else -- seven times to seven different Presidents. The nation's first two Chief Justices -- John Jay (1789-1795) and John Rutledge (August-December 1795) -- are the only two Chiefs who never administered the oath to a President.
Here is the list of Presidential Inaugurations not conducted by the Chief Justice of the United States along with the person who administered the oath of office:
•GEORGE WASHINGTON's 1st Inauguration (April 30, 1789):
Robert Livingston, Chancellor of New York (The Chancellor of New York was the presiding judge of the New York Court of Chancery, the highest court in New York State from 1701-1847)
•GEORGE WASHINGTON's 2nd Inauguration (March 4, 1793):
William Cushing, Associate Justice of the U.S. Supreme Court
•JOHN TYLER's Inauguration (April 4, 1841):
William Cranch, Chief Judge of the U.S. Circuit Court of the District of Columbia (Tyler assumed office upon the death of President William Henry Harrison. Interestingly, Cranch was the nephew of John and Abigail Adams.)
•MILLARD FILLMORE's Inauguration (July 9, 1850):
William Cranch, Chief Judge of the U.S. Circuit Court of the District of Columbia (Fillmore assumed office upon the death of President Taylor.)
•CHESTER A. ARTHUR's Inauguration (September 20, 1881):
John R. Brady, Justice of the New York State Supreme Court (Arthur assumed office upon the death of President Garfield. Brady was the first judge that could be tracked down to administer the oath at Arthur's home in New York City after notification of Garfield's death arrived shortly after midnight on Sept. 20, 1881. After returning to Washington, D.C. on September 22, 1881, Arthur was administered the oath of office again in a formal ceremony by Chief Justice Morrison Waite.)
•THEODORE ROOSEVELT's 1st Inauguration (September 14, 1901):
John R. Hazel, Judge of the U.S. District Court for the Western District of New York (Roosevelt assumed office upon the death of President McKinley.)
•CALVIN COOLIDGE's 1st Inauguration (August 3, 1923):
John Calvin Coolidge Sr., Justice of the Peace and Notary Public in Plymouth, Vermont (Coolidge assumed office upon the death of President Harding. Coolidge was staying at his father's home in Vermont when he was notified shortly after midnight on August 3, 1923 that President Harding had died a few hours earlier in San Francisco. Since Coolidge's father was a Notary Public, he administered the oath of office to his son in the sitting room of the family home. After being sworn in by his father, President Coolidge promptly went back to sleep.)
•LYNDON B. JOHNSON's 1st Inauguration (November 22, 1963):
Sarah T. Hughes, Judge of the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of Texas (Johnson assumed office upon the death of President Kennedy. Johnson was in Dallas with Kennedy when the President was assassinated, and he was sworn in as President aboard Air Force One on the airport tarmac of Love Field before leaving Texas to return to Washington with Kennedy's body.)
#History#Presidents#Presidential Oath of Office#Oath of Office#Presidential Inaugurations#Inaugurations#Swearing-in the President#Presidential Oath#Politics#Chief Justice of the United States#Supreme Court#Chief Justice#Constitution#POTUS#Presidents and Chief Justices#Judiciary#SCOTUS
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Washington-based married couple's challenge to an obscure provision of the 2017 Republican tax law has the potential to become "the most important tax case in a century," with far-reaching implications for federal revenues, key social programs, and Congress' constitutional authority to impose levies on income.
That's according to a new report released Wednesday by the Roosevelt Institute and the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy (ITEP).
The policy groups estimated that if the conservative-dominated U.S. Supreme Court sides with the plaintiffs in Moore v. United States—which the justices are set to take up in December—nearly 400 multinational corporations could collectively receive more than $270 billion in tax relief, further enriching behemoths such as Apple, Microsoft, Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, and Google.
The Roosevelt Institute and ITEP also found that Chief Justice John Roberts and Associate Justice Samuel Alito own stock in 19 companies that are poised to receive a combined $30 billion in tax breaks if the judges strike down the 2017 law's mandatory repatriation tax, a one-time levy targeting earnings that multinational corporations had piled up overseas.
But the case could have impacts well beyond a repeal of the repatriation tax, which was projected to generate $340 billion in federal revenue over a decade.
Depending on the scope of the justices' decision, the new report argues, the Supreme Court could "suddenly supplant Congress as a major American tax policymaker, putting at legal jeopardy much of the architecture of laws that prevent corporations and individuals from avoiding taxes, and introducing great uncertainty about our democracy's ability to tax large corporations and the most affluent."
"At the best of times, blowing a $340 billion hole in the federal budget would be catastrophic," Matt Gardner, a senior fellow at ITEP and a co-author of the new report, said in a statement. "And if the court invalidates the transition tax in its Moore decision, that's exactly what would happen: possibly the costliest Supreme Court decision of all time. And it would be hard to identify a less deserving set of tax cut beneficiaries than the companies that would reap at least $271 billion from repealing this tax."
"The Roberts Court could decide with the stroke of a pen to simultaneously forgive big business decades of tax dues."
Charles and Kathleen Moore brought their challenge to the repatriation provision after they were hit with a roughly $15,000 tax bill stemming from their stake in an Indian farm equipment company. As the Tax Policy Center recently observed, the Indian firm is a "controlled foreign corporation (CFC), or a foreign corporation whose ownership or voting rights are more than 50% owned by U.S. persons who each own at least 10%."
The Moores' cause has been championed by billionaire-backed organizations and corporate lobbying groups, including the Manhattan Institute–which is chaired by billionaire hedge fund mogul Paul Singer—and the powerful U.S. Chamber of Commerce.
"That such a case involving such modest sums would make it all the way to the high court indicates that there is much more at play than a single family's tax refund," ITEP's Gardner and Spandan Marasini and the Roosevelt Institute's Niko Lusiani note in the new report.
The plaintiffs' legal team argues that because the Moores' shares in the Indian firm were not "realized"—they did not sell or receive a distribution from the company—they should not have been on the hook for the repatriation tax.
"The government, on the other hand, argues that almost a century of tax law precedent has established Congress' broad authority to decide when and how to tax income, even without a specific realization event," the new report explains. "What's more, the income was clearly realized by the corporation, which is sufficient for income taxation of shareholders under various provisions of the existing tax code."
While it's possible that the Supreme Court will rule narrowly on the specifics of the Moores' situation, the report authors cautioned that the justices "could also issue a broad decision that taxing income—of an individual or a corporate shareholder—requires realization, and that income taxation on multiple years of accrued income is unconstitutional."
Such a sweeping ruling could preemptively ban a wealth tax—an outcome that right-wing supporters of the Moores have explicitly advocated.
"This case presents the court with an ideal opportunity to clarify that taxes on unrealized gains, such as wealth taxes, are direct taxes that are unconstitutional if not apportioned among the states," the Manhattan Institute declared in a May amicus brief.
A broad ruling by the high court could also imperil key elements of the existing tax code, according to ITEP and the Roosevelt Institute.
"One of the most established of these pillars is known as Subpart F, which was enacted in 1962 to prevent American corporations from avoiding taxation through offshore entities or controlled foreign corporations," the new report says. "Provisions related to Global Intangible Low-Taxed Income (GILTI), the branch profits tax; tax treatment of corporate debt; and others could be uprooted by five justices."
"The Corporate Alternative Minimum Tax—enacted as part of the Inflation Reduction Act to create a basic corporate tax floor—as well as international efforts to curb international tax avoidance could be made constitutionally invalid," the report adds.
The analysis stresses that the consequences of a broad ruling in the upcoming case would be profound, affecting more than just a handful of corporate tax provisions.
"In Moore," the report warns, "the Roberts Court could decide with the stroke of a pen to simultaneously forgive big business decades of tax dues, increase the federal deficit over the long run, jeopardize future public revenue and essential social programs, escalate these multinational companies' already sizeable after-tax profits, and further enrich their shareholders."
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
June 29, 2023
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
JUN 30, 2023
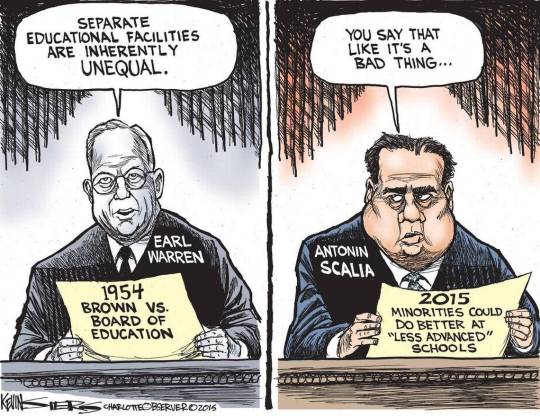
Today the Supreme Court handed down a decision in Students for Fair Admissions, Inc., v. President and Fellows of Harvard College. Students for Fair Admissions is an organization designed to fight against affirmative action in college admissions, and today it achieved its goal: the Supreme Court decided that policies at Harvard and the University of North Carolina that consider race as a factor in admissions are unconstitutional because they violate the guarantee of equal protection before the law, established by the Fourteenth Amendment.
The deciding votes were 6 to 2 in the case of Harvard—Justice Ketanji Brown Jackson recused herself because she had been a member of Harvard’s board of overseers—and 6 to 3 in the case of the University of North Carolina.
In the case of the two schools at the center of this Supreme Court decision, admissions officers initially evaluated students on a number of categories. Harvard used six: academic, extracurricular, athletic, school support, personal, and overall. Then, after the officers identified an initial pool of applicants who were all qualified for admission, they cut down the list to a final class. At Harvard, those on the list to be cut were evaluated on four criteria: legacy status, recruited athlete status, financial aid eligibility, and race. Today, the Supreme Court ruled that considering race as a factor in that categorical fashion is unconstitutional.
The court did not rule that race could not be considered at all. In the majority decision, Chief Justice John Roberts wrote that “nothing in this opinion should be construed as prohibiting universities from considering an applicant’s discussion of how race affected his or her life, be it through discrimination, inspiration, or otherwise.”
How much this will matter for colleges and universities is unclear. Journalist James Fallows pointed out that there are between 3,500 and 5,500 colleges in the U.S. and all but 100 of them admit more than 50% of the students who apply. Only about 70 admit fewer than a third of all applicants. That is, according to a study by the Pew Research Center, “the great majority of schools, where most Americans get their postsecondary education, admit most of the people who apply to them.”
The changing demographics of the country are also changing student populations. As an example, in 2022, more than 33% of the students at the University of Texas at Austin, which automatically admits any Texas high school student in the top 6% of their class, were from historically underrepresented populations. And universities that value diversity may continue to try to create a diverse student body.
But in the past, when schools have eliminated affirmative action, Black student numbers have dropped off, both because of changes in admission policies and because Black students have felt unwelcome in those schools. This matters to the larger pattern of American society. As Black and Brown students are cut off from elite universities, they are also cut off from the pipeline to elite graduate schools and jobs.
More is at stake in this case than affirmative action in university admissions. The decision involves the central question of whether the law is colorblind or whether it can be used to fix long-standing racial inequality. Does the Fourteenth Amendment, ratified in 1868 to enable the federal government to overrule state laws that discriminated against Black Americans, allow the courts to enforce measures to address historic discrimination?
Those joining the majority in the decision say no. They insist that the framers of the Fourteenth Amendment after the Civil War intended only that it would make men of all races equal before the law, and that considering race in college admissions undermines that principle by using race in a negative manner, involving racial stereotyping (by considering race by category), and lacking an endpoint. “Many universities have for too long wrongly concluded that the touchstone of an individual’s identity is not challenges bested, skills built, or lessons learned, but the color of their skin. This Nation’s constitutional history does not tolerate that choice,” the majority opinion reads.
In a concurring opinion, Justice Clarence Thomas wrote that affirmative action actually made racial tensions worse because it “highlights our racial differences with pernicious effect,” prolonging “the asserted need for racial discrimination.” He wrote: “under our Constitution, race is irrelevant.” “The great failure of this country was slavery and its progeny,” Thomas wrote. “And, the tragic failure of this Court was its misinterpretation of the Reconstruction Amendments.”
Those justices who dissented—Justices Sonia Sotomayor, Elena Kagan, and Ketanji Brown Jackson—pointed to the profound racial discrimination that continued after the Civil War and insist that the law has the power to address that discrimination in order to achieve the equality promised by the Fourteenth Amendment. “The Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment enshrines a guarantee of racial equality,” Sotomayor’s opinion begins. “The Court long ago concluded that this guarantee can be enforced through race-conscious means in a society that is not, and has never been, colorblind.”
In her concurring opinion concerning the UNC case, Jackson noted that “[g]ulf-sized race-based gaps exist with respect to the health, wealth, and well-being of American citizens. They were created in the distant past, but have indisputably been passed down to the present day through the generations. Every moment these gaps persist is a moment in which this great country falls short of actualizing one of its foundational principles—the ‘self-evident’ truth that all of us are created equal.”
If this fight sounds political, it should. It mirrors the current political climate in which right-wing activists reject the idea of systemic racism that the U.S. has acknowledged and addressed in the law since the 1950s. They do not believe that the Fourteenth Amendment supports the civil rights legislation that tries to guarantee equality for historically marginalized populations, and in today’s decision the current right-wing majority on the court demonstrated that it is willing to push that political agenda at the expense of settled law. As recently as 2016, the court reaffirmed that affirmative action, used since the 1960s, is constitutional. Today’s court just threw that out.
The split in the court focused on history, and the participants’ anger was palpable and personal. Thomas claimed that “[a]s [Jackson] sees things, we are all inexorably trapped in a fundamentally racist society, with the original sin of slavery and the historical subjugation of black Americans still determining our lives today.” Her solution, he writes, “is to unquestioningly accede to the view of elite experts and reallocate society’s riches by racial means as necessary to ‘level the playing field,’ all as judged by racial metrics…. I strongly disagree.”
Jackson responded that “Justice Thomas’s prolonged attack…responds to a dissent I did not write in order to assail an admissions program that is not the one UNC has crafted.”
She noted that Black Americans had always simply wanted the same right to take care of themselves that white Americans had enjoyed, but it had been denied them. She recounted the nation’s long history of racial discrimination and excoriated the majority for pretending it didn’t exist. “With let-them-eat-cake obliviousness, today, the majority pulls the ripcord and announces ‘colorblindness for all’ by legal fiat. But deeming race irrelevant in law does not make it so in life. And having so detached itself from this country’s actual past and present experiences, the Court has now been lured into interfering with the crucial work that UNC and other institutions of higher learning are doing to solve America’s real-world problems.”
“Today, the Supreme Court upended decades of precedent that enabled America’s colleges and universities to build vibrant diverse environments where students are prepared to lead and learn from one another,” the Biden administration said in a statement, warning that “the Court’s decision threatens to move the country backwards.” In a speech to reporters, Biden called for new standards that take into consideration the adversity—including poverty—a student has overcome when selecting among qualified candidates, a system that would work “for everyone… from Appalachia to Atlanta and far beyond.”
“While the Court can render a decision, it cannot change what America stands for.”
—
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
#Kevin Siers#history#Brown vs Board of Education#minorities#racism#injustice#affirmative action#heather cox richardson#Letters From An American
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Supreme Court on Thursday issued a surprising 5-4 ruling in favor of Black voters in a congressional redistricting case from Alabama, with two conservative justices joining liberals in rejecting a Republican-led effort to weaken a landmark voting rights law.
Chief Justice John Roberts and Justice Brett Kavanaugh aligned with the court’s liberals in affirming a lower-court ruling that found a likely violation of the Voting Rights Act in an Alabama congressional map with one majority Black seat out of seven districts in a state where more than one in four residents is Black. The state now will have to draw a new map for next year’s elections.
The decision was keenly anticipated for its potential effect on control of the closely divided U.S. House of Representatives. Because of the ruling, new maps are likely in Alabama and Louisiana that could allow Democratic-leaning Black voters to elect their preferred candidates in two more congressional districts.
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Every conservative justice on the Supreme Court bowed out of deciding a case stemming out of Texas.
In a rare move, Chief Justice John Roberts and Justices Clarence Thomas, Samuel Alito, Neil Gorsuch, Brett Kavanaugh and Amy Coney Barrett all sat out deciding whether to hear MacTruong v. Abbott, a case arguing that the Texas Heartbeat Act (THA) is constitutional and that the state law violates federal law. The six justices were named as defendants in the case. They did not give a detailed justification as to why they chose not to weigh in, and are not required to do so.
Monday's order list from the Supreme Court states that the six conservatives on the bench "took no part in the consideration or decision of this petition." Because there were not enough justices for a quorum—the court needs at least six and only Justices Elena Kagan, Sonia Sotomayor and Ketanji Brown Jackson remained—the court affirmed the judgment of a lower court to dismiss the lawsuit.
The case was brought by MacTruong, a U.S. citizen who resides in New Jersey, against the six conservative justices, Texas Governor Greg Abbott, Texas Lieutenant Governor Dan Patrick, Speaker of the Texas House of Representatives Dade Phelan and former President Donald Trump. MacTruong alleges the defendants were involved in either passing, enacting or upholding the THA because he believes the Dobbs decision was incorrectly decided and thus, Roe v. Wade is still law.
In June 2022, the Supreme Court overturned Roe in Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health Organization, ending federal access to abortion.
Judicial politics expert Alex Badas told Newsweek that the justices may be ineligible to partake in the decision because of the court's recent statement on its ethics. "A Justice should disqualify himself or herself in a proceeding in which the Justice's impartiality might reasonably be questioned, that is, where an unbiased and reasonable person who is aware of all relevant circumstances would doubt that the Justice could fairly discharge his or her duties," the statement said.
"I believe being named in the suit falls into this category of disqualification," Badas said.
Affirming the decision from the Fifth Circuit, which ruled against MacTruong and decided that he did not have standing to sue, the Supreme Court effectively tossed the suit altogether.
"The Fifth Circuit was unanimous against MacTruong," Badas said. "It is worth noting that two of the three judges who heard the case were appointed by Democratic presidents. These judges may be sympathetic to his claim that Dobbs was incorrectly decided but it shows that his legal case for standing is very weak that they vote against him."
Badas noted that MacTruong has other pending cases involving the same issue, but it is likely that they will end like this case, "with him losing and the courts issuing decisions arguing that he lacks standing."
Other plaintiffs named in the suit include the Planned Parenthood Federation of America, Senators Elizabeth Warren and Amy Klobuchar, Cory Booker and Bernie Sanders, Representative Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez, President Joe Biden, California Governor Gavin Newsom, actors George Clooney, Brad Pitt and Angelina Jolie, Tesla Founder Elon Musk, singer Britney Spears and media expert Norah O'Donnell.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Supreme Court Decides 5-4 to Watch ‘Legally Blonde’ at Monthly Movie Night

The U.S. Supreme Court defied its usual 6-to-3 conservative/liberal split in an important decision on Wednesday. They decided 5-4 to watch the Reese Witherspoon comedy “Legally Blonde” at their monthly movie night. Lately the movie night decisions have been dominated by the conservative majority, but this decision marked an end to the usual 6-3 split. “I’m glad we could introduce a little variety into our movie night decisions,” said Justice Elena Kagan who wrote the majority opinion in favor of watching “Legally Blonde.” Joining Kagan's opinion were Chief Justice John Roberts, and Justices Clarence Thomas, Sonia Sotomayor, Amy Coney Barrett, and Ketanji Brown Jackson. Dissenting were Justices Brett Kavanaugh, Samuel Alito, and Neil Gorsuch. “I wanted to watch ‘Homeward Bound,’ but whatever,” said a miffed Gorsuch.
10 notes
·
View notes