#Federation of American Scientists
Text
Three years ago, Donald Trump tweeted an image that left intelligence experts gobsmacked.
The picture was of a rocket that had exploded on a launch pad deep inside of Iran. It was so crisp, that some initially thought it may not have been taken by a satellite.
"This picture is so exquisite, and you see so much detail," says Jeffrey Lewis, who studies satellite imagery at the Middlebury Institute of International Studies at Monterey. "At first, I thought it must have been taken by a drone or something."
But aerospace experts quickly determined it was photographed using one of America's most prized intelligence assets: a classified spacecraft called USA 224 that is widely believed to be a multibillion-dollar KH-11 reconnaissance satellite.
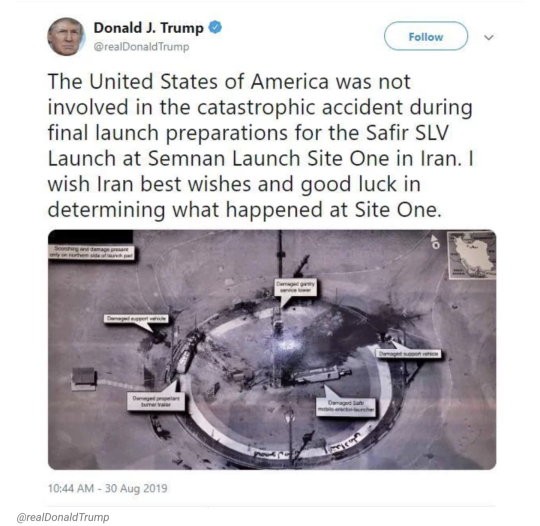
Now, three years after Trump's tweet, the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA) has formally declassified the original image. The declassification, which came as the result of a Freedom of Information Act request by NPR, followed a grueling Pentagon-wide review to determine whether the briefing slide it came from could be shared with the public.
Many details on the original image remain redacted – a clear sign that Trump was sharing some of the U.S. government's most prized intelligence on social media, says Steven Aftergood, specialist in secrecy and classification at the Federation of American Scientists.
"He was getting literally a bird's eye view of some of the most sensitive US intelligence on Iran," he says. "And the first thing he seemed to want to do was to blurt it out over Twitter."
The revelation comes just days after Trump announced his bid to run for president in 2024. It also follows the FBI's seizure in August of 33 boxes filled with over one hundred classified records, stored at Trump's Mar-a-Lago resort in Florida. Some of those documents were reportedly related to Iran, according to the Washington Post.
The NGA, which produced the image Trump used in his 2019 tweet, is the government's clearing house for much of its intelligence. The agency collects images from drones, spy planes and satellites and turns them into information that can be used by decision-makers.
It's not uncommon for those people to want to declassify what they see, says Robert Cardillo, who served as director of the NGA from 2014 to 2019. Often, he says, he would suggest that the government release a lower-resolution image from a commercial satellite instead. "That was done from time-to-time as a way to protect that source, but then also get the information out," Cardillo says.
He says he cannot ever recall seeing the authorized release of an image such as the one tweeted by President Trump.
According to reports, Trump first saw the image as part of a daily intelligence briefing on the morning after the Iranian launch failure. In the most complete account of what happened next, published last year by Yahoo! News, President Trump asked to keep a copy of the photo, which was from a KH-11 series satellite. An hour later, he sent it out to more than 60 million followers on Twitter.
NPR has not independently verified that reporting, but what is clear is that the image in the tweet was a photograph of a sheet of physical paper, Lewis says. Visible at the center of Trump's tweet is the shine of overhead lights or a flash, and a shadow, possibly from Trump or an aid, photographing the image with a camera.

A portion of the text tweeted by the president also used the exact wording of the then-classified caption to the image, indicating his tweet was based on the NGA briefing document released to NPR.
After he tweeted the image, Trump said that he did nothing wrong. "We had a photo and I released it, which I have the absolute right to do," he told reporters at the time. The president has ultimate authority over what material is classified, and Aftergood says that he was probably within his legal rights to publicize the image.
Cardillo, who now works as a senior executive for the commercial satellite company Planet, says that imagery is no longer as secret as it once was. The proliferation of commercial imaging satellites means that the public now has regular access to overhead views that are comparable, if not quite as good, as U.S. government satellites. Over his career, he saw the levels of classification for spy satellite images loosen up.
"Because there is so much commercial imagery out there, I feel like there's less sensitivity," he says.
But this image was still classified, and Lewis says that seeing it released probably stung for the intelligence agencies involved.
"The entire US intelligence community is incredibly averse to letting this information out," Lewis says. "The idea that the president would just scream 'YOLO!', photograph it and tweet it--is really hard to take."

Cardillo says he is certain that other countries have used Trump's tweeted image to learn more about what U.S. spy satellites can do. If, for example, Putin had tweeted a photo from a Russian satellite, he says that the U.S. would have assembled a task force to learn everything they could from the image.
In the case of Trump's tweet: "my assumption is that Russia would have done the same thing and Iran would have done the same thing," he says.
Aftergood says the latest release "confirms a kind of recklessness on the part of former President Trump and also a disrespect for the rather astonishing intelligence that he was receiving."
For Lewis, the incident is telling about Trump's abilities to handle classified documents as he heads into the 2024 presidential race.
"I wouldn't tell this man any information that I wanted to remain private," Lewis says. "The idea that he could again have access to classified information is unnerving."
#us politics#news#donald trump#trump administration#twitter#tweet#republicans#conservatives#2022#2019#iran#satellite images#classified intelligence#russia#National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency#Freedom of Information Act#npr#Steven Aftergood#Federation of American Scientists#Robert Cardillo#Jeffrey Lewis#Middlebury Institute of International Studies#USA 224#KH-11 reconnaissance satellite
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
'Christopher Nolan will be honored by the Federation of American Scientists for his cinematic portrait of J. Robert Oppenheimer in Universal’s Oppenheimer this November. The five-time Oscar nominee will be bestowed with the org’s Public Service Award which recognizes outstanding work in science policy and culture.
The awards ceremony, which will take place in Washington D.C next month, revives a decades-long tradition that began in 1971, which honors the contributions of a diverse group of scientists, policymakers, and tastemakers in pursuit of advancements in science and technology.
“Nolan’s film depicts the scientists who formed FAS in the fall of 1945 as the ‘Federation of Atomic Scientists’ to communicate the dangers of nuclear weapons to the public. We continue to pursue their vision of a safer world, especially as current events remind us that those dangers are real and resurgent,” FAS CEO Daniel Correa said.
Nolan tells Deadline, “I am especially honoured to be recognized by the Federation of American Scientists, a body formed to give scientists a voice in policy making during the very period we attempt to portray in Oppenheimer.”...
Oppenheimer is the third highest grossing movie of 2023 to date at $939.1M worldwide, an unprecedented achievement for a three-hour feature drama movie, in particular one that opened on the same weekend with the year’s highest grossing movie, Barbie, which counts $1.43 billion global.'
0 notes
Text
Eugene Rabinowitch remembers:
Apart from the preparation of Bertrand Russell's statement, the programme of the London conference was rather improvised, and no personal invitations were extended to scientists most likely to contribute to it – one reason being that the actual organization of the conference was in the hands of people unfamiliar with the world of science, and the other, that practically no funds were available for travel expenses. Invitations were sent to the rectors or presidents of all universities in the world, with the request to transmit them to interested faculty members. It was hoped that atomic physicists on their way to Geneva would stop in London; but Professor Marcus Oliphant of Australia proved to be the only prominent atomic physicist from outside England who availed himself of this opportunity. My own attempt to inform the Federation of American Scientists of the conference and to induce some individual American atomic scientists who were going to Geneva to stop over in London came too late to influence already fixed travel plans.
"Brighter than a Thousand Suns: A Personal History of the Atomic Scientists" - Robert Jungk, translated by James Cleugh
#book quotes#brighter than a thousand suns#robert jungk#james cleugh#nonfiction#eugene rabinowitch#bertrand russell#conference#london#geneva#marcus oliphant#invitations#federation of american scientists#travel expenses
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Defense Intelligence Agency disclosed this week that it had funded research on warp drive, invisibility cloaking, and other areas of fringe or speculative science and engineering as part of a now-defunct program to track and identify threats from space.
From 2007 to 2012, the DIA spent $22 million on the activity, formally known as the Advanced Aerospace Threat Identification Program. It was apparently initiated at the behest of then-Senate Majority Leader Harry Reid, with most of the funding directed to a Nevada constituent of his. See “Glowing Auras and ‘Black Money’: The Pentagon’s Mysterious U.F.O. Program” by Helene Cooper, Ralph Blumenthal and Leslie Kean, New York Times, December 16, 2017.
Yesterday, the DIA released a list of 38 research titles funded by the program, many of which are highly conjectural and well beyond the boundaries of current science, engineering — or military intelligence. One such title, “Traversable Wormholes, Stargates, and Negative Energy,” was prepared by Dr. Eric Davis, who has also written on “psychic teleportation.”
0 notes
Text
youtube
Christopher Nolan at the 2023 FAS Awards: "Science is truth"
#Nolan brings in so many mind boggling concepts in his work. so pleased he is recognized by scientists#a true gift to cinema#Federation of American Scientists 2023#Oppenheimer#christopher nolan#Youtube
0 notes
Text
The Best News of Last Year - 2023 Edition
Welcome to our special edition newsletter recapping the best news from the past year. I've picked one highlight from each month to give you a snapshot of 2023. No frills, just straightforward news that mattered. Let's relive the good stuff that made our year shine.
January - London: Girl with incurable cancer recovers after pioneering treatment
A girl’s incurable cancer has been cleared from her body after what scientists have described as the most sophisticated cell engineering to date.
2. February - Utah legislature unanimously passes ban on LGBTQ conversion therapy

The Utah State Legislature has unanimously approved a bill that enshrines into law a ban on LGBTQ conversion therapy.
3. March - First vaccine for honeybees could save billions

The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) has approved the world’s first-ever vaccine intended to address the global decline of honeybees. It will help protect honeybees from American foulbrood, a contagious bacterial disease which can destroy entire colonies.
4. April - Fungi discovered that can eat plastic in just 140 days
Australian scientists have successfully used backyard mould to break down one of the world's most stubborn plastics — a discovery they hope could ease the burden of the global recycling crisis within years.
5. May - Ocean Cleanup removes 200,000th kilogram of plastic from the Pacific Ocean

The Dutch offshore restoration project, Ocean Cleanup, says it has reached a milestone. The organization's plastic catching efforts have now fished more than 200,000 kilograms of plastic out of the Pacific Ocean, Ocean Cleanup said on Twitter.
6. June - U.S. judge blocks Florida ban on care for trans minors in narrow ruling, says ‘gender identity is real’

A federal judge temporarily blocked portions of a new Florida law that bans transgender minors from receiving puberty blockers, ruling Tuesday that the state has no rational basis for denying patients treatment.
7. July - World’s largest Phosphate deposit discovered in Norway

A massive underground deposit of high-grade phosphate rock in Norway, pitched as the world’s largest, is big enough to satisfy world demand for fertilisers, solar panels and electric car batteries over the next 50 years, according to the company exploiting the resource.
8. August - Successful room temperature ambient-pressure magnetic levitation of LK-99

If the claim by Sukbae Lee and Ji-Hoon Kim of South Korea’s Quantum Energy Research Centre holds up, the material could usher in all sorts of technological marvels, such as levitating vehicles and perfectly efficient electrical grids.
9. September - World’s 1st drug to regrow teeth enters clinical trials

The ability to regrow your own teeth could be just around the corner. A team of scientists, led by a Japanese pharmaceutical startup, are getting set to start human trials on a new drug that has successfully grown new teeth in animal test subjects.
10. October - Nobel Prize goes to scientists behind mRNA Covid vaccines

The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine has been awarded to a pair of scientists who developed the technology that led to the mRNA Covid vaccines. Professors Katalin Kariko and Drew Weissman will share the prize.
11. November - No cases of cancer caused by HPV in Norwegian 25-year olds, the first cohort to be mass vaccinated for HPV.
Last year there were zero cases of cervical cancer in the group that was vaccinated in 2009 against the HPV virus, which can cause the cancer in women.
12. December - President Biden announces he’s pardoning all convictions of federal marijuana possession

President Joe Biden announced Friday he's issuing a federal pardon to every American who has used marijuana in the past, including those who were never arrested or prosecuted.
------
And there you have it – a year's worth of uplifting news! I hope these positive stories brought a bit of joy to your inbox. As I wrap up this special edition, I want to thank all my supporters!
Buy me a coffee ❤️
Merry Christmas and Happy New Year!
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
the author of the death and life of the great lakes is releasing another book about phosphorus (which like a half chapter ish of the book was about wrt lakes and agriculture specifically) thats set to release start of march omgggg
#okayyyy <3 literally i cannot wait omfg#like. idk i cannot explain how good and esp readable his death and life was.#im emotionaly abt anything and everything when it comes to humans but beyond that like. how do you open with just describing the history#of canals opening in the states and make it so so interesting and like. idk he def has a way with ordering stuff idk#what specfically but im reading the source abt rivers in america rn and its a bit jumping back and fourth#compared to how good death and life was written. and stuff like i knew nothing about alewives and hes describing these fish and their#population in the lakes over the decades and he keeps building onto it talking abt the introduction of salmon talking about the rise in#native species in relation and like. all interspersed w interviews of scientists and locals and business owners who all#are affected or know abt this stuff#the source by martin doyle is good too so far btw a lot about american government in relation to rivers canals etc#on the first part which is abt its relation to federalism and how power was handed back to federal government w rivers#as international transit systems and all that#very cool like genuinly interesting stuff#my take away is everyone should start reading books about rivers and lakes ^_^
1 note
·
View note
Text
Zakharova said the main issue was that Israel appeared to have admitted that it had nuclear weapons.
Israel does not publicly acknowledge it has nuclear weapons though the Federation of American Scientists estimates Israel has about 90 nuclear warheads.
"Question number one - it turns out that we are hearing official statements about the presence of nuclear weapons?" Zakharova said.
If so, she said, then where are the International Atomic Energy Agency and international nuclear inspectors?[...]
"The UN Security Council and the International Atomic Energy Agency must take immediate and uninterrupted action to disarm this barbaric and apartheid regime. Tomorrow is late," Iranian Foreign Minister Hossein Amirabdollahian said on platform [Twitter] on Monday.
7 Nov 23
1K notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
Corporations Have Been Salivating Over This SCOTUS Decision
The Supreme Court seems to have no problem regulating women’s bodies. But when it comes to regulating big business, they may be ready to end 40 years of established law. Let me explain.
The Court is hearing a pair of cases that could upend federal regulations designed to protect us. At risk is the Biden Administration’s entire climate agenda, the power of the government to approve and regulate drugs, and even the safety and quality of the food we eat, the water we drink, and the air we breathe.
And big corporations are salivating for a ruling that goes their way.
So what’s putting all of this at risk? It’s a challenge to something known as the “Chevron” Doctrine, a legal precedent established by the Supreme Court’s ruling in the 1984 case Chevron v. Natural Resources Defense Council. That case held that whenever any regulation in a law is unclear, it should be the federal agencies, not the courts, that interpret and implement it. This makes sense because unlike courts, federal agencies are staffed with scientists, researchers, and engineers — actual experts in the fields they’re regulating.
But now, a pair of Supreme Court cases challenging the doctrine could shift this power to the courts, stripping federal agencies of this key role of interpreting and implementing our nation’s laws.
If non-expert courts become the sole interpreters of the nation’s laws, a single activist judge, carefully selected by plaintiffs, could invalidate all the regulations of a federal agency charged with protecting the public.
No wonder the big banks, fossil fuel companies, and pharmaceutical giants, who hate the power of federal agencies to limit their profits, have been trying for years to end the Chevron Doctrine. And this time, they think they have the votes on the Supreme Court to do it.
If agencies are stripped of their power to regulate, the big losers will be the American public. We need real experts tackling today’s complicated problems, not judges who think they know better.
We also need to see the potential fall of the Chevron Doctrine for what it is: a power grab by corporate interests, allowing them to shop for judges who will strip agencies of their power to protect the public.
440 notes
·
View notes
Text
American workers are dying, local businesses are reporting a drop in productivity, and the country's economy is losing billions all because of one problem: the heat.
July was the hottest month on record on our planet, according to scientists. This entire summer, so far, has been marked by scorching temperatures for much of the U.S. South, with the thermometer reaching triple digits in several places in Texas between June and July.
In that same period, at least two people died in the state while working under the stifling heat enveloping Texas, a 35-year-old utility lineman, and a 66-year-old USPS carrier. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, there were 36 work-related deaths due to environmental heat exposure in 2021, the latest data available. This was a drop from 56 deaths in 2020, and the lowest number since 2017.
"Workers who are exposed to extreme heat or work in hot environments may be at risk of heat stress," Kathleen Conley, a spokesperson for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), told Newsweek. "Heat stress can result in heat stroke, heat exhaustion, heat cramps, or heat rashes. Heat can also increase the risk of injuries in workers as it may result in sweaty palms, fogged-up safety glasses, and dizziness. Burns may also occur as a result of accidental contact with hot surfaces or steam."
While there is a minimum working temperature in the U.S., there's no maximum working temperature set by law at a federal level. The CDC makes recommendations for employers to avoid heat stress in the workplace, but these are not legally binding requirements.
The Biden administration has tasked the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) with updating its worker safety policies in light of the extreme heat. But the federal standards could take years to develop—leaving the issue in the hands of individual states.
Things aren't moving nearly as fast as the emergency would require—and it's the politics around the way we look at work, the labor market, and the rights of workers in the U.S. that is slowing things down.
949 notes
·
View notes
Text
"A federal judge has ruled that artwork created solely by artificial intelligence cannot be copyrighted because “human authorship is an essential part of a valid copyright claim.”
The decision, issued by Judge Beryl Howell, stemmed from computer scientist Stephen Thaler’s efforts to copyright an image he said was created by an AI model, identified as Creativity Machine. Thaler claimed that as the owner of Creativity Machine, he was entitled to the copyright. The Copyright Office rejected that application on the grounds that human authorship is necessary to secure a copyright, prompting Thaler to sue.
Howell ultimately upheld the Copyright Office’s decision, citing long-standing precedent about human authorship. “The act of human creation — and how to best encourage human individuals to engage in that creation, and thereby promote science and the useful arts — was thus central to American copyright from its very inception,” Howell wrote. “Non-human actors need no incentivization with the promise of exclusive rights under United States law, and copyright was therefore not designed to reach them.” ...
Howell’s opinion did nod to the drastically shifting landscape of copyright law in the AI era. She even acknowledged Thaller’s own argument about the malleability of copyright law to account for changes in technology. But again, Howell noted that human authorship remained key."
-via Rolling Stone, August 18, 2023
665 notes
·
View notes
Text
'Unless you’ve been hiding under a rock for the past few months, you’re undoubtedly aware that award-winning director Christopher Nolan has released a new film about Robert Oppenheimer, known as the “father of the atomic bomb” for leading the group of scientists who created that deadly weapon as part of America’s World War II-era Manhattan Project. The film has earned widespread attention, with large numbers of people participating in what’s already become known as “Barbieheimer” by seeing Greta Gerwig’s hit film Barbie and Nolan’s three-hour-long Oppenheimer on the same day.
Nolan’s film is a distinctive pop cultural phenomenon because it deals with the American use of nuclear weapons, a genuine rarity since ABC’s 1983 airing of The Day After about the consequences of nuclear war. (An earlier exception was Stanley Kubrick’s Dr. Strangelove, his satirical portrayal of the insanity of the Cold War nuclear arms race.)
The film is based on American Prometheus, the Pulitzer Prize-winning 2005 biography of Oppenheimer by Kai Bird and Martin Sherwin. Nolan made it in part to break through the shield of antiseptic rhetoric, bloodless philosophizing, and public complacency that has allowed such world-ending weaponry to persist so long after Trinity, the first nuclear bomb test, was conducted in the New Mexico desert 78 years ago this month.
Nolan’s impetus was rooted in his early exposure to the nuclear disarmament movement in Europe. As he said recently:
“It’s something that’s been on my radar for a number of years. I was a teenager in the ‘80s, the early ‘80s in England. It was the peak of CND, Campaign for Nuclear Disarmament, the Greenham Common [protest]; the threat of nuclear war was when I was 12, 13, 14 — it was the biggest fear we all had. I think I first encountered Oppenheimer in… Sting’s song about the Russians that came out then and talks about Oppenheimer’s ‘deadly toys.’”
A feature film on the genesis of nuclear weapons may not strike you as an obvious candidate for box-office blockbuster status. As Nolan’s teenage son said when his father told him he was thinking about making such a film, “Well, nobody really worries about nuclear weapons anymore. Are people going to be interested in that?” Nolan responded that, given what’s at stake, he worries about complacency and even denial when it comes to the global risks posed by the nuclear arsenals on this planet. “You’re normalizing killing tens of thousands of people. You’re creating moral equivalences, false equivalences with other types of conflict… [and so] accepting, normalizing… the danger.”
These days, unfortunately, you’re talking about anything but just tens of thousands of people dying in a nuclear face-off. A 2022 report by Ira Helfand and International Physicians for the Prevention of Nuclear War estimated that a “limited” nuclear war between India and Pakistan that used roughly 3% of the world’s 12,000-plus nuclear warheads would kill “hundreds of millions, perhaps even billions” of us. A full-scale nuclear war between the United States and Russia, the study suggests, could kill up to five (yes, five!) billion people within two years, essentially ending life as we know it on this planet in a “nuclear winter.”
Obviously, all too many of us don’t grasp the stakes involved in a nuclear conflict, thanks in part to “psychic numbing,” a concept regularly invoked by Robert Jay Lifton, author of Hiroshima in America: A History of Denial (co-authored with Greg Mitchell), among many other books. Lifton describes psychic numbing as “a diminished capacity or inclination to feel” prompted by “the completely unprecedented dimension of this revolution in technological destructiveness.”
Given the Nolan film’s focus on Oppenheimer’s story, some crucial issues related to the world’s nuclear dilemma are either dealt with only briefly or omitted altogether.
The staggering devastation caused by the bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki is suggested only indirectly without any striking visual evidence of the devastating human consequences of the use of those two weapons. Also largely ignored are the critical voices who then argued that there was no need to drop a bomb, no less two of them, on a Japan most of whose cities had already been devastated by U.S. fire-bombing to end the war. General (and later President) Dwight D. Eisenhower wrote that when he was told by Secretary of War Henry Stimson of the plan to drop atomic bombs on populated areas in Japan, “I voiced to him my grave misgivings, first on the basis of my belief that Japan was already defeated and that dropping the bomb was completely unnecessary.”
The film also fails to address the health impacts of the research, testing, and production of such weaponry, which to this day is still causing disease and death, even without another nuclear weapon ever being used in war. Victims of nuclear weapons development include people who were impacted by the fallout from U.S. nuclear testing in the Western United States and the Marshall Islands in the Western Pacific, uranium miners on Navajo lands, and many others. Speaking of the first nuclear test in Los Alamos, New Mexico, Tina Cordova of the Tularosa Basin Downwinders Consortium, which represents that state’s residents who suffered widespread cancers and high rates of infant mortality caused by radiation from that explosion, said “It’s an inconvenient truth… People just don’t want to reflect on the fact that American citizens were bombed at Trinity.”
Another crucially important issue has received almost no attention. Neither the film nor the discussion sparked by it has explored one of the most important reasons for the continued existence of nuclear weapons — the profits it yields the participants in America’s massive nuclear-industrial complex.
Once Oppenheimer and other concerned scientists and policymakers failed to convince the Truman administration to simply close Los Alamos and place nuclear weapons and the materials needed to develop them under international control — the only way, as they saw it, to head off a nuclear arms race with the Soviet Union — the drive to expand the nuclear weapons complex was on. Research and production of nuclear warheads and nuclear-armed bombers, missiles, and submarines quickly became a big business, whose beneficiaries have worked doggedly to limit any efforts at the reduction or elimination of nuclear arms.
The Manhattan Project and the Birth of the Nuclear-Industrial Complex
The Manhattan Project Oppenheimer directed was one of the largest public works efforts ever undertaken in American history. Though the Oppenheimer film focuses on Los Alamos, it quickly came to include far-flung facilities across the United States. At its peak, the project would employ 130,000 workers — as many as in the entire U.S. auto industry at the time.
According to nuclear expert Stephen Schwartz, author of Atomic Audit, the seminal work on the financing of U.S. nuclear weapons programs, through the end of 1945 the Manhattan Project cost nearly $38 billion in today’s dollars, while helping spawn an enterprise that has since cost taxpayers an almost unimaginable $12 trillion for nuclear weapons and related programs. And the costs never end. The Nobel prize-winning International Campaign to Abolish Nuclear Weapons (ICAN) reports that the U.S. spent $43.7 billion on nuclear weapons last year alone, and a new Congressional Budget Office report suggests that another $756 billion will go into those deadly armaments in the next decade.
Private contractors now run the nuclear warhead complex and build nuclear delivery vehicles. They range from Raytheon, General Dynamics, and Lockheed Martin to lesser-known firms like BWX Technologies and Jacobs Engineering, all of which split billions of dollars in contracts from the Pentagon (for the production of nuclear delivery vehicles) and the Department of Energy (for nuclear warheads). To keep the gravy train running — ideally, in perpetuity — those contractors also spend millions lobbying decision-makers. Even universities have gotten into the act. Both the University of California and Texas A&M are part of the consortium that runs the Los Alamos nuclear weapons laboratory.
The American warhead complex is a vast enterprise with major facilities in California, Missouri, Nevada, New Mexico, South Carolina, Tennessee, and Texas. And nuclear-armed submarines, bombers, and missiles are produced or based in California, Connecticut, Georgia, Louisiana, North Dakota, Montana, Virginia, Washington state, and Wyoming. Add in nuclear subcontractors and most states host at least some nuclear-weapons-related activities.
And such beneficiaries of the nuclear weapons industry are far from silent when it comes to debating the future of nuclear spending and policy-making.
Profiteers of Armageddon: The Nuclear Weapons Lobby
The institutions and companies that build nuclear bombs, missiles, aircraft, and submarines, along with their allies in Congress, have played a disproportionate role in shaping U.S. nuclear policy and spending. They have typically opposed the U.S. ratification of a Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban treaty; put strict limits on the ability of Congress to reduce either funding for or the deployment of intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs); and pushed for weaponry like a proposed nuclear-armed, sea-launched cruise missile that even the Pentagon hasn’t requested, while funding think tanks that promote an ever more robust nuclear weapons force.
A case in point is the Senate ICBM Coalition (dubbed part of the “Dr. Strangelove Caucus” by Arms Control Association Director Daryl Kimball and other critics of nuclear arms). The ICBM Coalition consists of senators from states with major ICBM bases or ICBM research, maintenance, and production sites: Montana, North Dakota, Utah, and Wyoming. The sole Democrat in the group, Jon Tester (D-MT), is the chair of the powerful appropriations subcommittee of the Senate Appropriations Committee, where he can keep an eye on ICBM spending and advocate for it as needed.
The Senate ICBM Coalition is responsible for numerous measures aimed at protecting both the funding and deployment of such deadly missiles. According to former Secretary of Defense William Perry, they are among “the most dangerous weapons we have” because a president, if warned of a possible nuclear attack on this country, would have just minutes to decide to launch them, risking a nuclear conflict based on a false alarm. That Coalition’s efforts are supplemented by persistent lobbying from a series of local coalitions of business and political leaders in those ICBM states. Most of them work closely with Northrop Grumman, the prime contractor for the new ICBM, dubbed the Sentinel and expected to cost at least $264 billion to develop, build, and maintain over its life span that is expected to exceed 60 years.
Of course, Northrop Grumman and its 12 major ICBM subcontractors have been busy pushing the Sentinel as well. They spend tens of millions of dollars on campaign contributions and lobbying annually, while employing former members of the government’s nuclear establishment to make their case to Congress and the executive branch. And those are hardly the only organizations or networks devoted to sustaining the nuclear arms race. You would have to include the Air Force Association and the obscurely named Submarine Industrial Base Council, among others.
The biggest point of leverage the nuclear weapons industry and the arms sector more broadly have over Congress is jobs. How strange then that the arms industry has generated diminishing job returns since the end of the Cold War. According to the National Defense Industrial Association, direct employment in the weapons industry has dropped from 3.2 million in the mid-1980s to about 1.1 million today.
Even a relatively small slice of the Pentagon and Department of Energy nuclear budgets could create many more jobs if invested in green energy, sustainable infrastructure, education, or public health – anywhere from 9% to 250% more jobs, depending on the amount spent. Given that the climate crisis is already well underway, such a shift would not only make this country more prosperous but the world safer by slowing the pace of climate-driven catastrophes and offering at least some protection against its worst manifestations.
A New Nuclear Reckoning?
Count on one thing: by itself, a movie focused on the origin of nuclear weapons, no matter how powerful, won’t force a new reckoning with the costs and consequences of America’s continued addiction to them. But a wide variety of peace, arms-control, health, and public-policy-focused groups are already building on the attention garnered by the film to engage in a public education campaign aimed at reviving a movement to control and eventually eliminate the nuclear danger.
Past experience — from the Campaign for Nuclear Disarmament that helped persuade Christopher Nolan to make Oppenheimer to the “Ban the Bomb” and Nuclear Freeze campaigns that stopped above-ground nuclear testing and helped turn President Ronald Reagan around on the nuclear issue — suggests that, given concerted public pressure, progress can be made on reining in the nuclear threat. The public education effort surrounding the Oppenheimer film is being taken up by groups like The Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists, the Federation of American Scientists, and the Council for a Livable World that were founded, at least in part, by Manhattan Project scientists who devoted their lives to trying to roll back the nuclear arms race; professional groups like the Union of Concerned Scientists and Physicians for Social Responsibility; anti-war groups like Peace Action and Win Without War; the Nobel Peace prize-winning International Campaign to Abolish Nuclear Weapons; nuclear policy groups like Global Zero and the Arms Control Association; advocates for Marshall Islanders, “downwinders,” and other victims of the nuclear complex; and faith-based groups like the Friends Committee on National Legislation. The Native American–led organization Tewa Women United has even created a website, “Oppenheimer — and the Other Side of the Story,” that focuses on “the Indigenous and land-based peoples who were displaced from our homelands, the poisoning and contamination of sacred lands and waters that continues to this day, and the ongoing devastating impact of nuclear colonization on our lives and livelihoods.”
On the global level, the 2021 entry into force of a nuclear ban treaty — officially known as the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons — is a sign of hope, even if the nuclear weapons states have yet to join. The very existence of such a treaty does at least help delegitimize nuclear weaponry. It has even prompted dozens of major financial institutions to stop investing in the nuclear weapons industry, under pressure from campaigns like Don’t Bank on the Bomb.
In truth, the situation couldn’t be simpler: we need to abolish nuclear weapons before they abolish us. Hopefully, Oppenheimer will help prepare the ground for progress in that all too essential undertaking, beginning with a frank discussion of what’s now at stake.'
#Christopher Nolan#Oppenheimer#The Manhattan Project#Barbie#Barbenheimer#Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons#Greta Gerwig#Dr. Strangelove#The Day After#American Prometheus#Kai Bird#Martin J. Sherwin#Robert Jay Lifton#Hiroshima in America: A History of Denial#Los Alamos#Stephen Schwartz#Atomic Audit#The Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists#Federation of American Scientists#Council for a Livable World#International Campaign to Abolish Nuclear Weapons
0 notes
Text
Are you an American? Frustrated by the political process? Do you feel like you have no voice in our government? Let me introduce you to the wonderful world of public comments.
This is where federal agencies propose new regulations asking for public feedback:
Regulations.gov
Here's a step by step on how to navigate this:
Look through the proposals on the explore tab and filter by "Proposed Rule". These are the regulations that have been proposed, but not finalized.

If you click on these, they are pretty dense, text heavy explanations of the proposed rule changes. I definitely do a lot of googling when trying to understand what I'm reading. Also there are a lot of different topics here and I definitely don't comment on everything.
This is how you make a public comment. For example, for this proposed rule:

Start a new document and write the subject and docket number. Your comment NEEDS to have the docket number for them to count it most of the time, and the correct subject some of the time.

^^ this is ambiguous, but add the docket ID and subject just to be safe, it should look like this:
Ref: Docket ID No. NSD 104
Provisions Pertaining to Preventing Access to Americans' Bulk Sensitive Personal Data and U.S. Government-Related Data by Countries of Concern
Then address to the person at the very very end of the page.
Scroll all the way to the end:

^^this is the person you address to.
Then introduce yourself. If you have experience related to the proposed rule, talk about that. For rules related to the environment and public health I say that I'm a geologist with a master's degree and I work in environmental remediation. Otherwise, I just say I'm a concerned citizen.
Then I say hey I agree/ disagree with this proposed rule and here's why. Oftentimes there will be lists that the federal agency is asking for specific feedback on.

Commenting on these will have a lot of impact.
Here's an example comment I forgot to post for a rule regarding methane emissions in the oil and gas industry:
Administrator Michael Regan
The United States Environmental Protection Agency
1200 Pennsylvania Avenue, N.W.
Washington, DC 20460
Ref: Docket ID No. __
Waste Emissions Charge for Petroleum and Natural Gas Systems
Dear Administrator Regan,
My name is __ and I am writing to you as a geologist and graduate of ___. I currently work in ____. Thank you for your interest in reducing methane pollution, which I believe to be one of the most important aspects in reducing the harm caused by the climate crisis.
Within the short term, methane is a much more powerful force of global warming than carbon dioxide. It breaks down faster than carbon dioxide— but it traps significantly more heat that should be bouncing back into space. When scientists talk about taking our foot off the gas pedal in regards to the climate crisis, methane is at the forefront of our minds. Natural gas is often proposed as a solution to reducing our greenhouse gas emissions (since it produces less carbon dioxide than coal plants), but these methane leaks are a serious threat to public health. Not only is methane hazardous, it’s ability to cause short-term superheating is contributing to the rapid increase in wildfires within the U.S. and globally, further degrading air quality.
Last summer in NYC skies were orange, caused by ash from Canadian wildfires. As someone who sets up air monitoring equipment every day to ensure the surrounding community is not impacted from the disposal of hazardous waste, I have a unique opportunity to see on a day-to-day basis how air quality is degrading. I strongly support the Environmental Protection Agency's proposed waste emissions charge.
For EPA’s implementation of the fee to fulfill Congress’s goals, the final regulation must continue to include key requirements including:
· Regulatory compliance exemptions must only become available after final standards and plans are in effect in all states and that these plans are at least as strong as the EPA's 202 methane emissions proposal. Operators filing for exemption must also demonstrate full compliance across their facilities;
· Strong and clear criteria must remain in place for operators seeking an exemption based on unreasonable permitting delays;
· When operators seek an exemption for plugged wells, they must clearly demonstrate that their wells have been properly plugged and are no longer polluting;
· Transparent calculations and methodologies to accurately determine an owner or operator’s net emissions; and
· Strong verification protocols so that fee obligations accurately reflect reported emissions and that exemptions are only available once the conditions Congress set forth are met.
I urge the EPA to quickly finalize this proposal with limited flaring, strengthened emissions standards for storage tanks, and a pathway for enhanced community monitoring.
Thank you,
___________
And then paste your comment in or upload a document and submit! You will be asked to provide your name and address. Also the FCC will only take comments on their website, but the proposed rule will be posted on the federal regulations website I put above and they should have a link to the FCC website within that post.
#this is one of those things like jury nullification that nobody knows about but should#i like this because it's a written format that actually gets taken into account#I feel like emailing representatives gets lost in the sauce#resource#us politics#american politics#geolife
263 notes
·
View notes
Text
A 32-year-old man in Pennsylvania posted a video on YouTube this week where he picked up a clear plastic bag containing the severed head of his father and held it in front of the camera.
“This is the head of Mike Mohn, a federal employee of over 20 years, and my father,” Justin Mohn said in the now-deleted video reviewed by WIRED. “He is now in hell for eternity as a traitor to his country.”
Over the course of the next 14 minutes, he ranted about a myriad of far-right talking points and conspiracies including Black Lives Matter, taxes, the LGBTQ community, and the Biden administration. He also urged viewers to kill all federal employees and seize federal offices, while railing against “far-left woke mobs.” He claimed to be the head of an American militia network known as Mohn’s Militia. “I am now officially the acting president of America under martial law,” he said.
But there was one issue that he focused on more than any other: migrants along the southern US border.
“The federal government of America has declared war on the American citizens and the American states,” the man says. “America will be less protected when the fifth column of illegal immigrants strikes Americans on our own soil.”
He also made demands that the US close its borders to immigrants and for “the mass deportation of the millions of illegal immigrants who have entered the country under the Biden regime, which has put Americans in direct harm.”
Over the past few weeks, right-wing rhetoric around a so-called migrant invasion reached new heights as the standoff between Texas governor Greg Abbott and President Joe Biden’s administration over the removal of razor wire on the Texas-Mexico border has continued. A convoy of far-right extremists is driving to the border and Republican politicians around the country have come out in support of Abbott.
Multiple researchers tell WIRED that the events and rhetoric surrounding the Texas-Mexico border could be linked to the violent video Mohn posted this week. This border controversy and the incendiary rhetoric surrounding it appeared to be something that deeply angered Mohn, highlighted by his YouTube video and the rest of his extensive online footprint of books, pamphlets, music and social media posts, many of which are steeped in far-right conspiracies. In a 2020 essay entitled “America’s Coming Bloody Revolution,” Mohn claims a violent revolution against the government is not only necessary but will succeed.
“For individuals in this conspiratorial mindset who have been subjected to countless hours of extremist narratives and grievances, every new flashpoint—from the Texas border crisis to the Israel/Hamas war to Taylor Swift—is evidence that their worldview is the reality,” Jon Lewis, a research fellow with the Program on Extremism at George Washington University, tells WIRED. “This act of violence represents the threat posed by mainstreaming hateful and dehumanizing rhetoric.”
“I listened to his diatribe about 20 times to write it all out and there is zero doubt in my mind that he was influenced by the recent events involving Texas,” Caroline Orr, a behavioral scientist and postdoctoral researcher at the University of Maryland who tracks extremism online, wrote on X. “This was expected and there will be others.”
Investigators have not mentioned a motive for the alleged decapitation, but Mohn was formally charged early Wednesday morning with first-degree murder, abuse of a corpse, and possession of an instrument of crime with intent. Police said in a statement posted to Facebook that they were alerted to the incident when Mohn’s mother called 911 and said she had come home to find her husband’s decapitated body on the floor of their bathroom. Mohn was arrested 100 miles away on Tuesday evening when he was discovered armed and wandering around a Pennsylvania National Guard training center at Fort Indiantown Gap, AP reported.
Multiple experts believe that extremism and conspiracy theories could still be at the root of what happened. “Some have been quick to write Mohn off as mentally unwell and while this may be accurate, this incident illustrates the threat of anti-government extremism and conspiracy theories, which have become all too common since the 2020 election,” Katherine Kenealy, the head of threat analysis at the Institute for Strategic Dialogue, tells WIRED. “He was so steeped in anti-government beliefs that he not only viewed his father as a ‘traitor’ because of his purported job, but selected him as a target because of it.”
Following the alleged murder, far-right figures immediately began boosting conspiracies about the beheading being a false flag in favor of the Democrats—something that has virtually become a reflex action among far-right figures following major news.
One of the main narratives shared was a claim that the Democrats were behind the incident as a way of boosting support for the Preventing Private Paramilitary Activity bill currently making its way through Congress. One of those pushing this narrative was Laura Loomer, a close ally of former president Donald Trump.
“Justin Mohn sure looks like the perfect Democrat Patsy for the sake of demonizing people who call out the invasion on the border, and for the sake of getting support to ban militia,” Loomer wrote on X, adding: “Just another ‘coincidence.’”
“False flag and ‘psyop’ conspiracy theories have rapidly spread online since the incident,” Kenealy tells WIRED. “These narratives detract from the severity of the incident and attempt to minimize the threat posed by anti-government ideologies.”
But despite a long history of Mohn expressing his disturbing views on platforms like Reddit, Facebook, Twitter, as well as publishing music on YouTube, Spotify, and Deezer, experts say that it would have been virtually impossible to identify him as a threat before his alleged beheading of this father this week.
“It’s more or less impossible to track this stuff in advance most of the time,” Orr tells WIRED. “We can make an educated guess about what will happen when politicians are putting out inflammatory rhetoric that has incited violence previously, but it’s extremely hard to identify who is going to be the one who responds to the ‘call.’”
As the convoy heads toward the border and rallies are organized in Eagle Pass, Texas, Republican lawmakers, including former president Donald Trump, continue to push violent rhetoric. These kinds of actions, experts say, could lead to potential violence.
“It's hard to determine when acts of violence like this will occur, but given the panic being spread about the border, it's highly likely that more will act on these narratives,” Samantha Kutner, an extremism researcher and CEO of counter-terrorism company GlitterPill, tells WIRED. “Not everyone who gets exposed to conspiratorial worldviews and beliefs and theories about the border wall engages in violence, but the proliferation of disinformation and conspiracy theories does impact certain subsets of the population who are perhaps more vulnerable to that messaging than others.”
60 notes
·
View notes
Text
Scientists have discovered cannabidiol, a compound in cannabis known as CBD, in a common Brazilian plant, opening potential new avenues to produce the increasingly popular substance.
The team found CBD in the fruits and flowers of a plant known as Trema micrantha blume, a shrub which grows across much of the South American country and is often considered a weed, molecular biologist Rodrigo Moura Neto of the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro told AFP in June.
CBD, increasingly used by some to treat conditions including epilepsy, chronic pain and anxiety, is one of the main active compounds in cannabis, along with tetrahydrocannabinol, or THC – the substance that makes users feel high.
Continue Reading.
119 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Clear Lake hitch (Lavinia exilicauda chi) is a rare endemic species of minnow living only in the Clear Lake watershed of northern California, a fish that was once a “symbol of abundance” for Indigenous people. In December 2022, the Big Valley Band of Pomo Indians, Robinson Rancheria Band of Pomo Indians, Scotts Valley Band of Pomo Indians and the Habematolel Pomo of Upper Lake ask for immediate emergency protection of the hitch. The fish is in danger of extinction as the last observed successful breeding for the species was in 2017, and the creatures only have a six-year-long lifespan. US land management agencies say hitch numbers have “fallen to near zero.” However, in the past, there were millions of hitch in the watershed each year, and the fish was important to Indigenous food systems. Local “entrepreneurs” prefer to protect the introduced non-native bass, which voraciously preys on the endangered hitch. Clear Lake hosts dozens of bass tournaments each year, events large enough to attract international visitors. There is a past-time tradition (”hitching”) of children beating the hitch to death with baseball bats in the springtime as the hitch gather in streams to try to spawn. The hitch is also threatened by pesticides, runoff, and overuse of water for the region’s prominent local vineyards. The hitch is referred to as a “trash fish,” and some feel that this insults the importance of the fish to Pomo people.
Excerpts below from: Louis Sahagun of Los Angeles Times. “As a sacred minnow nears extinction, Native Americans of Clear Lake call for bold plan.” As published at Phys.org. 6 December 2022.
---

Spring runs of a large minnow numbering in the millions have nourished Pomo Indians since they first made their home alongside Northern California’s Clear Lake more than 400 generations ago. The Clear Lake hitch glinted like silver dollars as they headed up the lake’s tributaries to spawn, a reliable squirming crop of plenty, steeped in history [...].
In all that time, the hitch’s domain, about 110 miles northwest of Sacramento, had never suffered the degradation of recent years.
Now, with a growing sense of sorrow, if not anger, the Pomo Indian tribes of Clear Lake are watching the symbol of abundance and security they call chi dwindle into extinction.
---
On Monday [December 2022], they took the rare and drastic step of urging Interior Secretary Deb Haaland to use her emergency powers and invoke the federal Endangered Species Act on behalf of the Clear Lake hitch. “Bringing the chi back will require a bold plan of action devised by people with the power to move mountains,” said Ron Montez, tribal historic preservation officer for the Big Valley Band of Pomo Indians.
“I have almost zero confidence in state or federal officials to save the chi and our way of life,” Montez, 72, said. [...]
The Clear Lake hitch was designated as a threatened species under California’s Endangered Species Act in 2014. Since then, however, its numbers have fallen to near zero, according to recent surveys.
Some causes of the hitch’s decline, however, seem extraordinarily difficult to fix: prolonged drought, mercury contamination, gravel mining, an overtaxed water distribution system, pesticides and runoff from vineyards [...], and predatory nonnative game fish. [...]
---
The 2023 spring spawning season is crucial for the continued survival of the Clear Lake hitch, scientists say. That’s because the last observed successful spawning was in 2017. “Hitch have a six-year life span,” said Meg Townsend, an attorney with the Center for Biological Diversity. [...]
---
But until its fate is known for certain, Michael Fris, a field supervisor at the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, said his agency is unlikely to list the hitch on an emergency basis. [...] That kind of talk prompted the Center for Biological Diversity, together with the Big Valley Band of Pomo Indians, Robinson Rancheria Band of Pomo Indians, Scotts Valley Band of Pomo Indians and the Habematolel Pomo of Upper Lake to take their request for emergency listing to Haaland.
All involved agree that seeking intervention under the federal Endangered Species Act is an act of desperation. Only two species have been emergency-listed as federally endangered over the last 20 years: the Miami blue butterfly in 2011 and Nevada’s Dixie Valley toad earlier this year. [...]
---
The hitch is a 12-inch-long minnow found only in and around the oldest, largest and perhaps most polluted and wildfire-prone watershed in California. In 2020, the Lake County region was charred by six of the 20 largest wildfires in state history. [...]
It’s been the poor luck of the hitch to require adequate stream flows in February, March and April to trek from the lake to spawning beds at the same time agricultural interests need water to defrost their vineyards.
---
“An emergency listing would force people to consider alternatives to the way water is used in this region,” said Sarah Ryan, environmental director for the Big Valley Band of Pomo Indians.
Beyond water flows, the prospect of emergency-listing the hitch raises other economically significant issues connected to the lake’s food chain: Zooplankton are eaten by shad, crayfish and hitch, which are favored by monster catfish and largemouth bass.
Clear Lake entrepreneurs host dozens of professional bass tournaments each year that are supported by contestants from around the world.
The most popular lures in local tackle shops are hitch replicas that cost up to $180 each. Other lures are made to resemble juvenile hitch and sold under a slogan that some people feel mocks the creature’s cultural importance to Pomo people: “The All-American Trash Fish.”
Over at [C.O.], a sporting goods store on the southern end of the lake, old-timers still talk about how local kids had a tradition of “hitching,” beating hitch to death with baseball bats for fun as they ascended streams to spawn in spring.
They also grumble over the thought of new special protections for a nongame fish disrupting human pastimes for any reason [...].
"The reason our bass grow so big is that they love to eat hitch," mused [D.B.], owner of [C.O.]. "So, when customers ask me, 'Where can I catch the biggest bass of my life?' " he added, "I send them to places hitch hang out in."
---
That kind of banter and lore suggests that unless government agencies yield to Native American concerns, they are headed for a showdown of complicated and competing values.
“The way some people ridicule hitch makes me wonder what they think about the folks who eat them,” lamented Robert Geary, cultural resources director for the Habematolel Pomo of Upper Lake. [...]
---
At the heart of the matter is that Pomo people [...] did not consider their native attitudes and lifestyles to be an expendable price of living in America.
Yet, their modern history is told mostly through economic hardship, rip-offs, massacres and environmental destruction.
---
Headline, image, caption, and text by: Louis Sahagun of Los Angeles Times. “As a sacred minnow nears extinction, Native Americans of Clear Lake call for bold plan.” As published at Phys.org. 6 December 2022. [First paragraph in this post added by me.]
579 notes
·
View notes