#Clinical bacteriology
Text
Week Recap (Nov. 27 - Dec. 3, 2022)
Part 1
Beginning of Microbiology section
Tried to study for the week (Except on thursday siniksik ba naman yung lab sa finals week edi sana nagrereview kami diba)
Crammed the rest of the subjects the night before finals
Didn't finish reading and woke up with a headache during finals
Already on the acceptance stage even if the grades are not out yet
┈┈┈┈․° ☣ °․┈┈┈┈
Part 2
#1st sem#medtech#mls#medical technology#medical laboratory science#studyblr#medblr#uniblr#schoolblr#college#university#final exams#molecular biology and diagnostics#Clinical bacteriology#microbiology#hematology#clinical chemistry#histopathology#dec 2022
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo

local lab rat
#bacteriology#lab#laboratory#campylobacter#candida#ccda#yeast#fungus#microbiology#microbes#technical assistance#diagnostic#medic#ecoli#black and white#clinical#microbiome#pathogen
6 notes
·
View notes
Note
apologies if you've received an ask about this / have made a post about it before (when i tried to search it up on your blog i first accidentally pasted in the entirety of my speech, but the second time i got it right and the only thing that showed up was the ask you answered about why healthcare is the way it is), but i'm very interested in learning about military medicine, specifically about its role in, as you said in the aforementioned ask, the creation of the hospital/clinic system—do you have any specific readings that would be a good introduction to it?
yes, although i should've phrased that more precisely: the first anon was asking about the current US medical system, and my argument is that a lot of what's characteristically "fascist" (as they put it) about it has throughlines to medical knowledge transfer in the 19th-century Atlantic world, & particularly the influence of what is (sort of incorrectly) termed 'Paris medicine'. so, this is not a universal claim about hospitals (eg, there's lots of scholarship on hospital medicine in the Ottoman Empire, which functioned differently and had different relationships to military medicine, &c &c)
anyway i would recommend for some broad introductions to this process:
Medicalizing Blackness: Making Racial Difference in the Atlantic World, 1780-1840, by Rana Hogarth (2017)
The Citizen-Patient in Revolutionary and Imperial Paris, by Dora Wiener (2002)
Maladies of Empire: How Colonialism, Slavery, and War Transformed Medicine, by Jim Downs (2021)
and, jumping a bit to the late 19th century and the origins of 'modern medicine' generally:
The Emergence of Tropical Medicine in France, by Michael Osborne (2014)
Imperial Bodies in London: Empire, Mobility, and the Making of British Medicine, 1880–1914, by Kristin Hussey (2021)
Pasteur's Empire: Bacteriology and Politics in France, Its Colonies, and the World, by Aro Velmet (2020)
Curing the Colonizers: Hydrotherapy, Climatology, and French Colonial Spas, by Eric T. Jennings (2006)
65 notes
·
View notes
Text
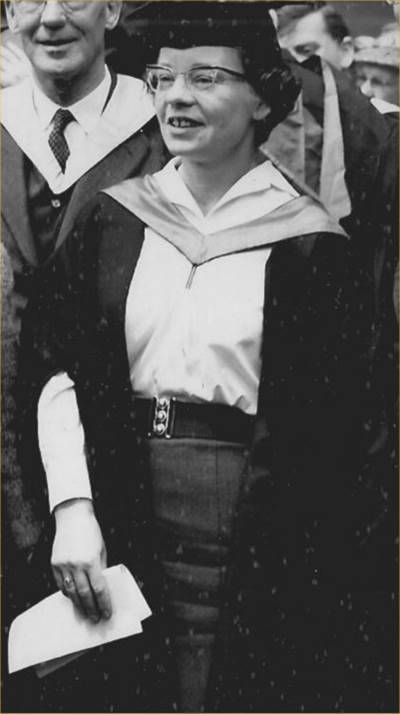


On April 8th 1973 Glasgow University appointed Delphine Parrot as head of the Department of Bacteriology its first female professor in its 522 year history.
Born in London, Parrott graduated in 1949 with an honours BSc degree in Physiology from Bedford College, University of London. She undertook her PhD at King's College Hospital Medical School and graduated in 1952.
From 1952 to 1954 Parrott worked at the MRC Clinical Endocrinology Research Unit in Edinburgh, before returning to London to join the staff of the National Institute for Medical Research in Mill Hill. In 1960, she moved to the Imperial Cancer Research Fund in Mill Hill. She worked on the problems of immune (rejection) reactions to transplants and of the movement of blood cells, especially lymphocytes, involved in inflammation reactions. She also studied the immunology of leukaemia and the effects of the removal of the thymus on immune reactions.
On this day in 1973 Parrott was made Head of Department and later Gardiner Professor of Bacteriology (later known as the Gardiner Chair of Immunology).
Delphine Parrott retired in 1990. She died on 17th January 2016.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is the Bacteriological Incubator?
A bacteriological incubator is an important laboratory tool for growing and propagating bacteria and germs.

working principles of incubator
Anachem Lab Incubators are Operated within specific temperature ranges, typically 5°C to 70°C, bacteriological incubators create optimal conditions for microbial growth and proliferation.
Uses of Bacteriological Incubators:
Microbial Cultivation:
Bacteriological incubators provide controlled environments conducive to the growth of diverse microbial cultures for research and experimentation.
Bacterial Studies:
In microbiology, these incubators support investigations into bacterial morphology, metabolism, and responses to varying environmental conditions.
Drug Development:
In pharmaceutical research, bacteriological incubators aid in assessing the efficacy of antimicrobial agents and antibiotics against specific bacterial strains.
Vaccine Production:
These incubators play a crucial role in vaccine development by facilitating the growth and replication of attenuated or inactivated microorganisms for immunization purposes.
Quality Control:
In industrial settings, bacteriological incubators are utilized for quality control measures, ensuring the sterility and purity of manufactured products, such as food and pharmaceuticals.
Environmental Monitoring:
Bacteriological incubators assist in environmental monitoring programs by incubating samples collected from air, water, or soil for the detection and enumeration of microbial contaminants.
Genetic Engineering:
In biotechnology, these incubators support genetic engineering processes by providing optimal conditions for the growth of genetically modified microorganisms for various applications.
Clinical Diagnostics:
Bacteriological incubators are utilized in clinical laboratories for culturing specimens from patients to identify and characterize pathogenic microorganisms responsible for infectious diseases.
Overall, bacteriological incubators serve as indispensable tools in microbiology and related fields, fostering controlled environments essential for microbial research, experimentation, and applications.
0 notes
Text
Chickens Check-Up: Unparalleled Poultry Diagnostic Technologies
Poultry diagnostics refers to the process of identifying diseases, disorders and health conditions affecting poultry flocks. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for poultry farmers and veterinarians to effectively manage disease outbreaks and maintain bird health. Over the past few decades, there have been significant advancements in diagnostic techniques and technologies used for poultry.
Bacteriological Diagnostics
Bacterial diseases are a major cause of economic losses in poultry production worldwide. Traditional bacteriological diagnostic methods rely on bacterial isolation and identification through culture and biochemical tests. However, these culture-based methods can be time-consuming, taking 2-7 days to identify bacteria. Molecular diagnostic techniques like PCR have revolutionized bacterial diagnostics. PCR allows rapid identification of bacteria directly from clinical samples within hours. Real-time PCR technologies provide quantitative results. Multiplex PCR assays can detect several bacterial pathogens in a single reaction. Advances in sequencing technologies now allow whole genome sequencing of bacterial isolates for epidemiological studies.
Viral Diagnostics
Viral diseases severely impact poultry health and productivity. Serological tests like ELISA, agar gel immunodiffusion and haemagglutination inhibition are most commonly used for viral antibody detection. However, serology only indicates exposure rather than active infection. Molecular tests like PCR and next-generation sequencing play a key role in rapid and sensitive detection of viral pathogens in clinical samples. Quantitative PCR tests allow viral load monitoring during infection and treatment. Microarray technology allows simultaneous detection of multiple viral pathogens. Rapid on-site or pen-side tests are also being developed for prompt diagnosis and decision making.
Avian Influenza and Newcastle Disease Surveillance
Early detection of highly pathogenic notifiable avian influenza (HPAI) and virulent Newcastle disease (ND) viruses in commercial poultry flocks is crucial. In affected regions, poultry diagnostic laboratories conduct active disease surveillance in live birds and post-mortem specimens using real-time PCR and virus isolation following OIE guidelines. Full genome sequencing of positive isolates provides information about virus evolution and spread. Sentinel surveillance programs involve regular sampling from commercial and backyard poultry farms. Such structured surveillance activities aid prompt detection and control of HPAI and ND outbreaks.
Role of AI and Digital Technologies
Artificial intelligence and digital technologies are revolutionizing poultry diagnostics. Computer vision and deep learning enable automatic detection of gross lesions from digital images with high accuracy. Whole genome sequencing data combined with epidemiological metadata aids prediction of outbreak spread using machine learning algorithms. Handheld smartphones and tablets integrated with diagnostic platforms allow remote clinical decision support. Automated laboratory workflows using robotics minimize manual errors and improve turn-around-time. Such advances will make poultry disease diagnosis increasingly rapid, sensitive, accurate and affordable.
Concluding Remarks
Overall, poultry diagnostics has advanced tremendously over the past few decades owing to incorporation of innovative molecular, biochemical and digital technologies. Early and accurate diagnosis remains imperative for effective disease control and optimal poultry production worldwide. Strategy
0 notes
Text
Quiz on bacteriology tomorrow
yey! we’re taking a quiz on 11 BACTERIAS about its:
description,
disease caused by that bacteria, and its description
mode of transmission,
period of incubation,
source of infection,
period of communicability,
clinical symptoms,
common complications,
standard gold test,
treatment modalities, and
common nursing management
#microbiology#nursing school#this will be the death of me#i’m going to be a patient#before i’m going to be a licensed nurse at this point#i’m gonna go cry now#i chose this#i should stfu#and deal with it
0 notes
Text
Medical microbiology


A clinical or medical microbiologist, typically with a Bachelor’s or Master’s degree in Microbiology and sometimes a Ph.D. in life sciences, studies the characteristics of pathogens, their transmission modes, and mechanisms of infection. They play a vital role in providing identification of pathogens, suggesting treatment options, and contributing to the development of health practices.

The historical milestones in medical microbiology include Anton van Leeuwenhoek’s observations of microorganisms in 1676, Edward Jenner’s development of the smallpox vaccine in 1796, and Louis Pasteur’s work on vaccines and pasteurization in 1857. Robert Koch’s germ theory and postulates in the late 19th century were pivotal. The Gram stain, developed by Hans Christian Gram in 1884, revolutionized bacterial identification.

Infectious diseases, including bacterial, viral, parasitic, and fungal, are commonly treated in medical microbiology. Diagnostic tests involve microbial culture, microscopy, biochemical tests, and genotyping. Microbiological culture isolates pathogens in the laboratory, while microscopy provides detailed observations. Biochemical tests and serological methods aid in identifying infectious agents.
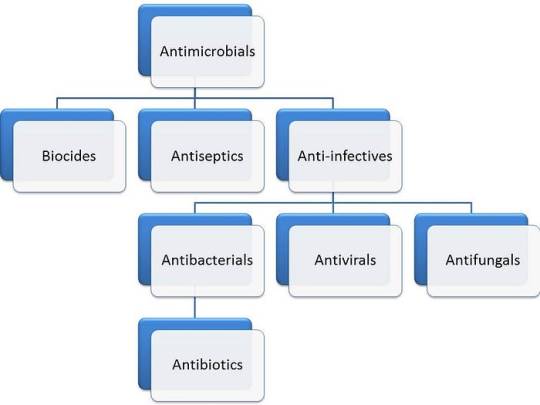
However, the rise of antibiotic resistance poses a significant challenge. Medical microbiologists must consider the specificity and effectiveness of antimicrobial drugs, as well as the presence of resistant strains. Phage therapy, an alternative to antibiotics, is being explored to combat antimicrobial resistance.
In conclusion, medical microbiology is a dynamic field that not only diagnoses and treats diseases but also explores the benefits of microbes for human health. With historical milestones and continuous advancements, this field plays a crucial role in shaping healthcare practices and combating infectious diseases.
Wishing you all the best in pursuing your studies in Medical Bacteriology. It involves a lot of detailed focus on the causative agents of diseases.
In case of any challenges or if you’re looking for guidance during the study period, do not hesitate to;
Email us at;[email protected]
#healthcare#medical students#fullmetal alchemist#aesthetic#assignment help#kittens#puppies#ratblr#medicine#nursing school#nurse#pharmacy#homework help#nursing student#studyblr#student#educate yourself#education#educate yourselves#medical help#bacteriology#bacteria#bacteriophage#medical microbiology
0 notes
Text

My prof be like:
It's Streptococcus payo-genes NOT payo-ge-nes

#medtech#mls#college#university#medical technology#medical laboratory science#schoolblr#school#clinical bacteriology
0 notes
Text
Medical Monday: Dr. Harry Cotton
Dr. Henry Andrews Cotton was once a psychiatrist that worked as the medical director for the New Jersey State Hospital (or now known as Trenton Psychiatric Hospital) starting in 1907 and lasting 26 years til 1930. Here, Dr. Henry Cotton and his staff would perform multiple dangerous and basically inhumane experiments hiding behind the guise of helping patients get better.
In 1902 Cotton would receive a medical degree from John Hopkins School of Medicine where he was a student of Adolf Meyer as well as studied along side German psychiatrists and colleagues Emil Kraepelin and Alois Alzheimer (also a neuropathologist) while in Europe- all of which are prominent figures in the world of psychiatry.
Though the dark cloud that would follow his legacy he did have a few positive practices that he used while working at the hospital- which included removing the use of restraints on patients, promoted the use of occupational therapy and held regular patient evaluations.
But, Cotton had a belief that infections caused mental issues, and in turn- removing the infected part would cure any disorder. Typically teeth were the first to be removed, but when that didn’t resolve the issue, other body parts such as tonsils, spleens, stomaches, colons and other appendages. Cotton believed at this point the infection “spread” causing more extractions needed to “save” the patients.According to Cotton there was an estimated 85% success rate, but unfortunately about one in three would not survive the procedure.
In 1925 an investigation was opened against Cotton and his malpractices, by Dr. Phyllis Greenacre another former student of Dr. Meyer. The investigation did find that results where falsified and patient where not cared for properly, dealing with overcrowding and unable to properly eat and even talk due to the procedure. But, despite this- the New Jersey Senate would also investigate with completely opposite results. Cotton would actually be praised for essentially saving the state money through his practice.
Later, Cotton would open up his own clinic after retiring from the hospital in 1930- performing his odd technique on a more general aspect, and even his wife and children were not immune. Cotton also doing it to himself, saying it did indeed “cure” him. He would pass away on May 8, 1933 from a heart attack.
Sources: The Horrifying “Cures” Of Dr. Henry Cotton — America’s Biggest Quack, The Strange Case of Dr. Henry Cotton: A Look at Surgical Bacteriology, Henry Cotton: Pulling teeth to cure disease
0 notes
Text
Education in Microbiology - Edging into the Future
In the vast landscape of medical education, the discipline of Microbiology plays a pivotal role in unraveling the mysteries of the smallest living entities microorganisms. Aspiring medical professionals seek not only to understand the intricacies of these microscopic organisms but also to leverage this knowledge for advancements in healthcare. This article delves into the realm of Microbiology education, exploring its significance, the evolving landscape, and the educational offerings at GS Medical College, distinguished as one of the Top Private Medical Colleges in Delhi NCR for MBBS.

Microbiology's Dynamic Role in Medicine
Unraveling Microbial Mysteries
Microbiology, a charming area of technological know-how, explores the complex realm of tiny dwelling beings, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. In the clinical context, its importance lies in uncovering the secrets of these microorganisms that impact human health. Microbiologists play an important role in decoding infectious diseases, information immune reactions, and developing interventions based totally on microbiological insights by using analyzing the behaviors and trends of these microorganisms.
A Pillar of Understanding Infectious Diseases
At the coronary heart of clinical science, microbiology stands as a pillar for knowledge infectious illnesses. It offers the framework to discover, represent, and combat pathogens that pose threats to human health. Students navigating the realm of microbiology in their medical education embark on a journey to comprehend the mechanisms of infection, transmission dynamics, and the host's immune responses. This foundational knowledge equips future healthcare professionals to diagnose, treat, and prevent a myriad of infectious diseases.
Immunology: Bridging Microbiology and Medicine
The seamless integration of microbiology and immunology creates a vital symbiotic relationship essential for a thorough understanding of the intricate workings of the human immune system. This integration is a cornerstone in medical education, providing valuable insights into how the body safeguards itself against microbial threats. Exploring immunology within the broader context of microbiology provides medical students with the essential knowledge to unravel the complexities of immune responses, laying the foundation for the advancement of immunotherapies and vaccines.
Microbiological Interventions: Vaccines and Antibiotics
In the sector of medication, microbiology plays a critical position in developing interventions that keep lives. Microbiologists actively interact inside the improvement of vaccines, boosting the body's defenses towards precise dangerous retailers. Moreover, a significant milestone in medical history the discovery and formulation of antibiotics can be attributed to microbiology. Understanding the inner workings of microbes at the physiological and genetic levels has enabled the development of antibiotics that effectively combat bacterial infections, revolutionizing the landscape of healthcare.
Curricular Integration for Holistic Learning
In scientific schooling, microbiology is not taught as a separate entity; alternatively, it is interwoven into the very cloth of the curriculum. The curriculum covers a huge variety of topics, along with bacteriology, virology, mycology, parasitology, and immunology. This all-encompassing method ensures that upcoming doctors acquire a nuanced hold close of microorganisms and their problematic roles in each fitness and ailment.
Microbiology's Renaissance: A Journey through Advancements
Pioneering Diagnostic Frontiers
The landscape of Microbiology education has undergone a profound evolution, particularly in the realm of diagnostic techniques. A paradigm shift is witnessed through the integration of cutting-edge methodologies. Molecular biology techniques, once confined to research laboratories, have seamlessly transitioned into diagnostic applications. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), nucleic acid hybridization, and next-generation sequencing are among the arsenal of tools that have redefined microbial detection. Rapid antigen tests, characterized by their swiftness and accuracy, have emerged as game-changers in the clinical identification of infectious agents. The synergy of these techniques has ushered in an era where the identification of microorganisms is not just accurate but also rapid, significantly impacting patient care and public health.
Genomic Exploration: Microbiology in the Genomic Era
As Microbiology strides into the genomic era, a new chapter unfolds. The microbial genomics stands at the forefront of this evolution, presenting a powerful lens to delve into microbial range, evolution, and the genetic underpinnings of pathogenicity. The creation of excessive-throughput sequencing technology has catapulted genomic exploration, permitting researchers and microbiologists to decode the whole genetic makeup of microorganisms. This comprehensive understanding extends beyond mere identification; it unveils the intricate relationships between microbes, shedding light on their adaptive strategies, evolution over time, and the genomic determinants of their pathogenic potential.
Metagenomics: Illuminating Microbial Dark Matter
In the genomic era, metagenomics emerges as a transformative approach within Microbiology. This technique transcends the study of individual microbial genomes, venturing into the collective genomic landscape of entire microbial communities. Metagenomics becomes a metaphorical flashlight, illuminating the microbial dark matter the vast array of unculturable and previously unknown microorganisms that inhabit diverse environments. This not only expands the horizons of microbial discovery but also underscores the intricacies of microbial ecosystems and their roles in shaping environmental and human health.
Technological Synergy: Integrating Imaging Technologies
Beyond delving into molecular techniques and genomics, Microbiology has tapped into the capabilities of advanced imaging technologies. Sophisticated imaging, including confocal microscopy, super-resolution microscopy, and live-cell imaging, offers extraordinary perspectives into the structures, behaviors, and interactions of microorganisms. These technologies go beyond the limitations of traditional microscopy, providing dynamic, real-time observations that enhance our comprehension of microbial life.
GS Medical College: Microbial Explorations in Excellence
Unveiling the Microcosmic Universe
Within the realm of GS Medical College, the journey into Microbiology excellence begins in cutting-edge laboratories that serve as portals to the microbial universe. These state-of-the-art labs, adorned with advanced instruments, become the playgrounds where students unravel the mysteries of microorganisms. From cultivating bacterial cultures to performing intricate diagnostic tests, lab of the best MBBS college in UP at GS Medical College stands as crucible of discovery, nurturing a generation of microbiologists poised to make meaningful contributions.
Guiding Lights: Faculty Expertise in Microbiology
The faculty at GS Medical College comprises distinguished microbiologists who are esteemed not only for their academic prowess but also for their prolific research contributions. GS Medical College is recognized as the best medical college in UP. Their collective expertise becomes a guiding light, illuminating the path for aspiring microbiologists. In the classrooms and research chambers, students find themselves under the mentorship of seasoned professionals, gaining not just theoretical knowledge but the practical acumen required to navigate the dynamic landscape of Microbiology.
Microbial Odyssey: Clinical Exposure
At GS Medical College, Microbiology education transcends the theoretical boundaries, embracing the practical realities of clinical settings. Rotations in microbiology departments propel students into the heart of healthcare, where they confront real-world scenarios in infectious disease diagnosis and management. This clinical exposure not only hones their diagnostic skills but also instills a profound understanding of the critical role microbiologists play in the broader spectrum of patient care.
Pioneering Paths: Research in Microbiology
GS Medical College is not merely an institution of learning; it is a crucible for innovation and research in Microbiology. The college actively fosters a culture of inquiry, encouraging students to delve into research projects that transcend conventional boundaries. From unraveling the intricacies of microbial pathogenesis to exploring avenues in antibiotic resistance and contributing to the development of cutting-edge diagnostic methods, students engage in pioneering research endeavors that have the potential to reshape the landscape of Microbiology.
Microbiology Education: Forging the Future
Guardians Against Global Threats
In the intricate web of medical education, Microbiology emerges as a stalwart guardian against the looming specter of infectious diseases. GS Medical College, with its comprehensive Microbiology education, plays a pivotal role in shaping professionals capable of standing at the frontline of infectious disease control. The knowledge and skills imparted go beyond textbooks; they become the tools wielded by graduates in the identification, treatment, and prevention of infectious diseases, contributing significantly to global health security.
Sentinels of Resistance: Antimicrobial Stewardship
In an era where antibiotic resistance poses a formidable challenge, Microbiology education at GS Medical College takes on the responsibility of creating stewards of antimicrobials. Graduates emerge not just as diagnosticians but as informed decision-makers, navigating the complex landscape of antibiotics. The emphasis on antimicrobial stewardship becomes a beacon, guiding professionals to wield antibiotics responsibly, ensuring their effectiveness while curbing the rise of resistance.
Frontiers of Exploration: Emerging Microbial Horizons
Beyond the conventional boundaries of medical Microbiology, GS Medical College propels students toward emerging frontiers. Environmental microbiology, industrial microbiology, and microbial biotechnology stand as promising fields that beckon exploration. In these realms, graduates find opportunities to innovate and contribute to diverse sectors, from revolutionizing agricultural practices to advancing biopharmaceuticals. The education at GS Medical College becomes a passport to the future, where microbial sciences become the catalysts for transformative advancements.
Conclusion: Pioneering Microbiology Excellence at GS Medical College
Microcosmic Explorations
In the microscopic realm lies a vast universe of secrets waiting to be unraveled. GS Medical College, with its unwavering commitment to excellence, cutting-edge facilities, and a faculty enriched with experience, stands as the vanguard in pioneering Microbiology education. The journey through the microscopic landscape becomes an odyssey of discovery, a profound exploration of the unseen facets of life.
Beyond Degrees: Crafting Microbiology Maestros
GS Medical College doesn't just confer degrees; it crafts Microbiology maestros. Graduates stepping into the realm of Microbiology from GS Medical College carry with them not merely academic accolades but a holistic understanding of the discipline. They are equipped with the intricate skills essential to navigate the constantly evolving landscape of microbial science. The corridors of Microbiology at GS Medical College become a transformative passage, preparing individuals not just for a career but for a mission to redefine the role of the smallest entities in healthcare and beyond.
Microbial Pioneers: Shaping the Future
As graduates embark on their professional journey, they become microbial pioneers.GS Medical College not only imparts knowledge about microorganisms but also instills in students the vision to apply that knowledge meaningfully. It is considered the best medical colleges in Uttar Pradesh and one of the top medical colleges in the state. The future they step into is one where the smallest entities wield substantial influence over healthcare and beyond. The educational experience at GS Medical College becomes the foundation for innovations that transcend the conventional boundaries of Microbiology, ushering in an era where the microscopic world becomes a catalyst for transformative change.
0 notes
Text
Unlocking the Power of Antibiotics: A Guide to Rational Use
In the realm of healthcare, the judicious use of antibiotics plays a pivotal role in ensuring optimal patient outcomes. This blog explores the key aspects of the rational use of antibiotics, shedding light on the critical considerations that healthcare professionals must keep in mind.
Understanding Rational Medicine Use
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines rational medicine use as the delivery of medications that meet patients' clinical needs, in appropriate doses tailored to individual requirements, for a sufficient duration, and at the lowest cost possible. In the context of antibiotics, this becomes particularly crucial, given the potential negative impacts of their misuse.
Choosing Antibiotics Wisely: Three Key Aspects
Etiological Agent Consideration:
Determining the causative agent is a critical step in prescribing antibiotics. Clinical expertise and laboratory findings guide this decision. However, interpreting bacteriology reports is equally vital, as bacterial isolates may not always be pathogens. Sensitivity results, where available, serve as therapeutic recommendations but should not be the sole determinant.
Patient-Centric Approach:
A) Age:
Vulnerability varies with age. The young and elderly are more susceptible to adverse effects. Factors such as organ development influence antibiotic metabolism in newborns, while older individuals may experience heightened risks of kidney damage and allergic reactions.
B) Pregnancy:
Antibiotic use during pregnancy requires caution. Erythromycin and beta-lactam antibiotics are considered safer options if antibiotic therapy is unavoidable.
C) Infections:
Tailoring antibiotic choices to the severity of the infection is paramount. In critical cases, immediate administration of the most effective antibiotic is crucial, reducing the risk of morbidity and mortality. Conversely, for less severe conditions, targeted antibiotics are sufficient.
Dosage and Pharmacokinetic Considerations:
Understanding the pharmacokinetic properties of antibiotics is essential. Factors such as routes of administration, therapeutic concentrations, and potential drug interactions must be considered. Additionally, healthcare professionals should assess patients' medication compliance.
Responsible Antibiotic Use in Hospitals
In healthcare settings, where antibiotics are indispensable, selecting the right antibiotic is fundamental to minimizing patient risk. The global challenge of antibiotic resistance underscores the importance of using antibiotics responsibly. Engaging in conversations about antibiotic therapy with patients during their hospital stay fosters awareness and contributes to the overall goal of responsible antibiotic use.
As stewards of public health, healthcare professionals must remain vigilant in their approach to antibiotic prescriptions, ensuring that these powerful medications are used judiciously for the benefit of individual patients and the broader community.
More details- https://aissmscop.com/rational-use-of-antibiotics/
0 notes
Text
Bbc Lifestyle Highlights February 2022
It’s the battle of the cheesecakes as full-time pupil Cherish, proud ZCC member Pauline, Formula one fanatic Tumang and meticulous events-planner Masana compete to be topped the winner. With Joe Lycett internet hosting, the remaining home sewers head again in time to the Seventies, making an attempt to revive the glamorous, rebellious and sometimes ridiculous, style of the last decade. Jess Wright is given five menus, every put together by a potential blind date but she’ll only have dinner with three of them. Nadiya Hussain creates dishes for the proper household time out, visits a rapeseed farm in Northampton and meets Gillian, Cornish Pasty Amateur World Champion. It’s chocolate week and the groups should grasp perfection in a surprise problem, earlier than setting up mechanical showpieces, complete with chocolate bons bons and a shifting part. Bobby Norris, reality TV personality has five menus, every put together by a potential blind date but he’ll only have dinner with three of them.
Tonight is the flip of carpenter and country boy Neil Odgers to do his best to land this weeks £1000 prize. Nathan and Amye are building a cathedral-like residence modelled on native Dutch barn houses with a modern twist and a 5000-tile armadillo roof. The culinary comp goes cockney in East London this week, the place five budding cooks are prepping their jellied eels and Ruby Murrays in the hope of scooping the money prize. A group of single farmers take part in one of the liked tv series in Australia.
Medpages provides the contact data of healthcare suppliers as a free public service. The information shown is a small subset of the total content material within the Medpages Database. Gqeberha endocrinologist Dr Gregory Hough has been suspended from practising as a well being care provider for 18 months, reviews HeraldLIVE.
Dr Gregory Hough South Africa
Though the laboratories were giant for their time, extra buildings have been soon required, owing to an increased work load following the formation of the Union of South Africa in 1910. Onderstepoort became one of many leading veterinary research centres in the world and contributed tremendously to the development of inventory farming all over Africa. Theiler and his employees additionally made internationally recognized contributions to fundamental information in bacteriology, protozoology, virology, toxicology, and veterinary pathology.
“The process leads to fast initial weight reduction with a plateau being reached after roughly two years. The upkeep of weight loss has been demonstrated in ongoing 16-year lengthy clinical trials. The process is useful to nearly all of overweight patients who have multiple metabolic complications and appreciable improvements in certain issues of weight problems have been noted. Diseases corresponding to diabetes have shown a resolution or remission in 84% of cases while excessive ldl cholesterol normalised in 97% of circumstances and high-blood strain in 68% of sufferers.
#Dr Gregory Hough South Africa#Dr Greg Hough South Africa#Dr Gregory Hough Port Elizabeth#Dr Greg Hough Port Elizabeth#Dr Greg Hough Eastern Cape#Dr Greg Hough#Greg Hough#Dr Gregory Hough#Dr Greg Hough Images#Dr Greg Hough Facebook
1 note
·
View note
Link
1 note
·
View note
Text
Bbc Lifestyle Highlights February 2022
It’s the battle of the cheesecakes as full-time pupil Cherish, proud ZCC member Pauline, Formula one fanatic Tumang and meticulous events-planner Masana compete to be topped the winner. With Joe Lycett internet hosting, the remaining home sewers head again in time to the Seventies, making an attempt to revive the glamorous, rebellious and sometimes ridiculous, style of the last decade. Jess Wright is given five menus, every put together by a potential blind date but she’ll only have dinner with three of them. Nadiya Hussain creates dishes for the proper household time out, visits a rapeseed farm in Northampton and meets Gillian, Cornish Pasty Amateur World Champion. It’s chocolate week and the groups should grasp perfection in a surprise problem, earlier than setting up mechanical showpieces, complete with chocolate bons bons and a shifting part. Bobby Norris, reality TV personality has five menus, every put together by a potential blind date but he’ll only have dinner with three of them.
Dr Greg Hough
Tonight is the flip of carpenter and country boy Neil Odgers to do his best to land this weeks £1000 prize. Nathan and Amye are building a cathedral-like residence modelled on native Dutch barn houses with a modern twist and a 5000-tile armadillo roof. The culinary comp goes cockney in East London this week, the place five budding cooks are prepping their jellied eels and Ruby Murrays in the hope of scooping the money prize. A group of single farmers take part in one of the liked tv series in Australia.
Medpages provides the contact data of healthcare suppliers as a free public service. The information shown is a small subset of the total content material within the Medpages Database. Gqeberha endocrinologist Dr Gregory Hough has been suspended from practising as a well being care provider for 18 months, reviews HeraldLIVE.
Though the laboratories were giant for their time, extra buildings have been soon required, owing to an increased work load following the formation of the Union of South Africa in 1910. Onderstepoort became one of many leading veterinary research centres in the world and contributed tremendously to the development of inventory farming all over Africa. Theiler and his employees additionally made internationally recognized contributions to fundamental information in bacteriology, protozoology, virology, toxicology, and veterinary pathology.
“The process leads to fast initial weight reduction with a plateau being reached after roughly two years. The upkeep of weight loss has been demonstrated in ongoing 16-year lengthy clinical trials. The process is useful to nearly all of overweight patients who have multiple metabolic complications and appreciable improvements in certain issues of weight problems have been noted. Diseases corresponding to diabetes have shown a resolution or remission in 84% of cases while excessive ldl cholesterol normalised in 97% of circumstances and high-blood strain in 68% of sufferers.
#Dr Gregory Hough South Africa#Dr Greg Hough South Africa#Dr Gregory Hough Port Elizabeth#Dr Greg Hough Port Elizabeth#Dr Greg Hough Eastern Cape#Dr Greg Hough#Greg Hough#Dr Gregory Hough#Dr Greg Hough Images#Dr Greg Hough Facebook
1 note
·
View note
Text
A Career in Microbiology: Degrees, Scope, and Job Opportunities
Want to know what further steps you must take to build a career in microbiology? Here are the details that will help you understand it.
Microbiology studies microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa.
Microbiologists study these organisms' structure, function, and behavior and their interactions with other living things and the environment. They use various techniques, such as microscopy, culturing, and genetic analysis, to study microorganisms and their activities.
Microbiology has many practical applications, such as in developing antibiotics, vaccines, and other medical treatments, as well as in producing food, fuel, and other products.
Degrees you can opt-in for Microbiology after 10th grade:
Pursuing a degree in microbiology after the 10th standard is impossible as it is a field of study requiring a minimum qualification of 10+2 with a science stream. However, after completing 10+2 with a science stream, students can opt for microbiology as an undergraduate course. The degrees that students can opt for in microbiology after 10+2 are:
1. Bachelor of Science in Microbiology:
It is a three-year undergraduate program that covers various aspects of microbiology, such as bacteriology, virology, mycology, immunology, genomics, and more. Graduates in this field can pursue careers in varied fields such as research and development, public health, environmental science, and biotechnology.
2. Bachelor of Science in Microbiology with Biotechnology:
This is a three-year undergraduate program that combines the study of microbiology with biotechnology. It covers genetic engineering, immune technology, fermentation technology, and more. Graduates in this field can pursue careers in varied fields such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, agriculture, and environmental science.
3. Bachelor of Science in Medical Laboratory Technology:
This three-year undergraduate program trains students in medical lab technology with a focus on microbiology. It covers subjects such as clinical microbiology, immunology, serology, and hematology. Graduates in this field can opt for vivid career options such as working in different places such as hospitals, research laboratories, and public health agencies.
4. Bachelor of Science in Microbiology and Biochemistry:
This is a three-year undergraduate program that combines the study of microbiology with biochemistry. It covers subjects such as microbiology, biochemistry, biotechnology, and more. Graduates in this field can pursue careers in varied fields such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, food science, and environmental science.
5. Bachelor of Science in Industrial Microbiology:
It is a three-year undergraduate program that trains students in applying microbiology in industrial settings. It covers industrial microbiology, fermentation technology, bioprocess engineering, and more. Graduates in this field can opt for vivid career options such as biotechnology, food and beverage production, pharmaceuticals, and environmental science.
After completing an undergraduate degree in microbiology, students can opt for postgraduate degrees such as Master of Science in Microbiology, Master of Science in Medical Microbiology, Master of Science in Applied Microbiology, and more. Students who wish to pursue research in microbiology can also opt for a Ph.D. in Microbiology.
Job opportunities and scope in this field:
Microbiology is a vast field that offers many job opportunities after graduation and a Ph.D. Here are some of the job opportunities available for candidates with microbiology degrees:
1. Research Scientist:
Microbiology graduates and Ph.D. holders can work as research scientists in various research institutions, biotech companies, government agencies, and pharmaceutical companies. They can work in vivid areas such as drug discovery, vaccine development, microbiome research, and biotechnology.
2. Quality Control and Quality Assurance Executive:
Microbiology graduates and Ph.D. holders can work as quality control and quality assurance executives in the food and beverage, pharmaceutical, and biotech industries. They can work to ensure that products meet the required safety and quality standards by developing new quality control procedures and compliance with standard quality requirements.
3. Clinical Microbiologist:
Microbiology graduates and Ph.D. holders can work as clinical microbiologists in hospitals, public health laboratories, and research institutions. They can work to identify pathogens and diagnose diseases caused by microorganisms. They also work with the members of the healthcare professionals to develop new treatment plans and monitor their effectiveness.
4. Medical Writer:
Microbiology graduates and Ph.D. holders can work as medical writers for pharmaceutical companies, medical research organizations, and scientific publishers. They can write scientific articles, research papers, and other publications related to microbiology. They also ensure that the documents are accurate, precise, and effective. The essential requirement to become a medical writer is that one must possess excellent writing and communication skills and a practical grasp of scientific terminology.
5. Environmental Microbiologist:
Microbiology graduates and Ph.D. holders can work as environmental microbiologists in government agencies, environmental consulting firms, and research institutions. They can work to monitor and analyze environmental samples for microorganisms and develop strategies for controlling microbial pollution.
6. Food Microbiologist:
Microbiology graduates and Ph.D. holders can work as food microbiologists in the food and beverage industry, regulatory agencies, and research institutions. They can work to ensure the safety and quality of food products by identifying and controlling microbial contamination.
7. Professor:
Microbiology Ph.D. holders can work as professors in universities and research institutions. They can teach and conduct research in microbiology and related fields. They can also publish their research findings in academic journals, present them at scientific conferences, and serve on various committees.
Microbiologist - Statistical data about Salary in India in 2023:
A person working as Microbiologist in India typically earns around 69,800 INR. Salaries range from 36,300 INR (lowest) to 107,000 INR (highest).
How can a Degree affect the salary?
Level 1: Bachelor's Degree
Employees at this education level have an average salary of 53,200 INR.
Level 2: Master's Degree
At this level, the average salary becomes 65,900 INR, 24% more than the previous level.
Level 3: PhD
The average salary becomes 1,05,000 INR at this level, 60% more than the previous level.
List of top colleges and universities providing specialization courses in microbiology:
Many colleges and universities in India offer specialization courses in microbiology. Some of the top colleges and universities include:
1. All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi
2. Jawaharlal Nehru University, New Delhi
3. University of Delhi, New Delhi
4. Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
5. Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
6. University of Calcutta, Kolkata
7. University of Hyderabad, Hyderabad
8. Savitribai Phule Pune University, Pune
9. Bharathidasan University, Tiruchirappalli
10. University of Madras, Chennai
These are just the few best examples available for students. Nowadays, many colleges and universities are providing this course.
How can Career Counseling help you?
Career counseling with CareerNaksha can benefit students considering choosing a career in microbiology. Here are some ways in which career counseling can help in choosing microbiology:
1. Exploration of interests and skills:
A career counselor can help students explore their interests and skills related to microbiology, such as a love of biology, interest in research, or curiosity about microorganisms.
2. Understanding Job Opportunities:
A career counselor can provide insights into the different job opportunities that are available in the field of microbiology.
3. Discussion on Qualifications Required:
A career counselor can discuss the qualifications required to succeed in a career in microbiology, such as the necessary educational background, certifications, and skills.
4. Overview of Industry Trends:
A career counselor can provide an overview of industry trends in microbiology, including emerging technologies, innovations, and opportunities.
5. Guidance on Higher Education:
A career counselor can guide you in choosing the right education program for pursuing a career in microbiology, such as a BSc, MSc, or Ph.D. in microbiology.
Career counseling with CareerNaksha can provide students with valuable insights and guidance on pursuing a career in microbiology.
0 notes