#China's digital influence
Photo

The fog of digital warfare in China is thick and mysterious. Monitors like guardian dragons watch silently from the shadows as data flows through dark networks, controlling the tempo of the cyberbattle. Its web of deception grows ever more intricate as the boundaries of the conflict itself become blurred. The lines between nations sharpen as its impact is felt in the global arena. It's a world where the winners and losers will be determined not in the battlefield, but in the virtual landscape.
#Asia#Cyber Warfare#Security#21st century warfare#China cyber capabilities#China's digital influence#cyber defense strategies#cyber geopolitics#cyber warfare implications#cybersecurity investments#digital warfare#digital warriors#economic impacts of cyber attacks#future of digital battles#global cyber partnerships#global cyber reactions#Headline#interconnected global conflict#modern warfare trends#political implications of digital warfare#technological innovations in warfare#fault#Chinese#warfare#cyberspace#cyberattacks#espionage
0 notes
Text
new oc
he’s gonna pump you with lead and carve your face off <3
bg from unsplash
#art#digital art#i procreate art wow#robot#original character#dark#neon#idk man#he gives me creepy deranged samurai/shogun vibes for some reason#It doesn’t help I have a random pic from unsplash that seems to be in Japan or china or a place of similar origin or influence#procreate#uhhhhh#robot with bloodied toothy mouth#Mm yes tags
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The weird and wonderful history of Kowloon as a digital interactive space - Part I
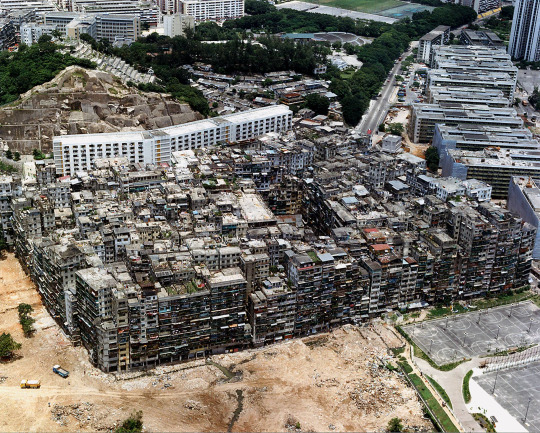

The Kowloon Walled City was one of the most emblematic locations in Hong Kong due to its irregular, fast-paced and largely ungoverned growth within a minute parcel of land. During the occupation of Hong Kong Island by the British in the mid 18th century, the Qing authorities surrounded the area with walls, turning it into a strategic position from where to closely inspect the foreign nation's covert activities. Almost a century later, during World War II, the area was seized by the Japanese, who tore down the walls and repurposed the stone for the construction of a nearby airport.
After the war, China would eventually regain possession of the city, though the disinterest of local authorities in addressing its increasing social disturbances placed it in a downward path to a state of utter degradation. By the 1970s, Kowloon had become the epicentre of Hong Kong's criminal underworld, dominated by a handful of its most vicious Triads.
Towards the last years of its existence, the ancient settlement was as a precarious heap of concrete, sheltering nearly half a million people within less than seven acres of land. Cultural and political changes in China made it increasingly difficult for this urban anomaly to remain unaddressed. In the late 1980s, an action plan was put together aiming to relocate its inhabitants and reconvert the real estate into an inner-city park. Stories about residents refusing to leave their unsafe and unsanitary homes were featured prominently in newspapers, baffling readers all over the world.
Once the single most densely populated area in the world, this enclave was an architectural aberration whose disconcerting aesthetic influenced numerous works of art in different fields of creation; including a small yet consequential number of video games that briefly reference or prominently feature this abominably transfixing space.
九龍島 (Kyu-Ryu-Tou) - Starcraft - 1986

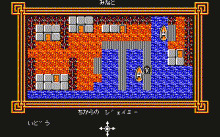
The year is 2025. An arms dealer escalates the tensions between East and West by developing a genetic weapon in a secret base at Kowloon Island. The United Nations react by sending in their best man, Jamie Starr. Unrelated to the Walled City itself, the first game to be located in the Kowloon peninsula - and indeed include the name as a part of its title - is this obscure turn-based RPG, Kyu-Ryu-Tou for the NEC PC88 and FM-77 machines.
The game is a sequel to Shangai, released the year before, featuring the same protagonist. Starcraft would also go on to produce a third instalment in 1987 named TO.KY.O. Clearly there wasn't much regard here from the developers part for geographic accuracy, as Kowloon is depicted here as being an island. While Hong Kong's southern territory is composed of an actual island, all the different areas named Kowloon are located in the mainland.
Riot City - Westone - 1991
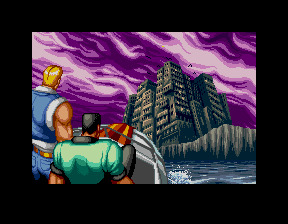
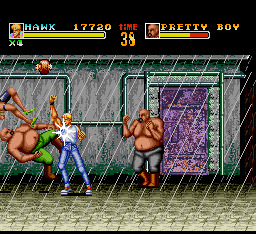
One of the most shameless specimens among a relatively long list of Final Fight clones, Riot City contains subtle references to Kowloon, though never referring to it by name. Two narcotics detectives are assigned with the mission of dismantling a cartel running a crime-ridden located in fictional Riot Island. This recurring yet geographically nonsensical notion of Kowloon as an island comes up here, yet again.
The final moment of the introduction sequence for this minor Sega arcade success shows both protagonists approaching a tight cluster of buildings whose source inspiration is quite unmistakable. Because Westone maintained ownership of most of this production's intellectual property, a later port to the PC Engine entitled Riot Zone was made possible with the help of Hudson soft.
Kowloon's Gate - Zeque - 1997
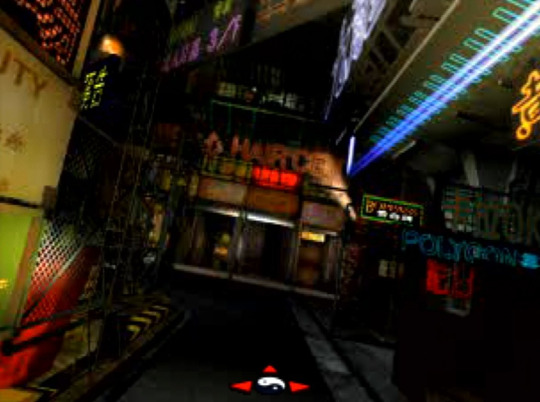



Reviving the Walled City through the lens of cybermystic surrealism, Kowloon's Gate is a dense, daunting adventure masterfully capturing the slum's dark and narrow recesses. This 1997 Japanese Playstation exclusive spans across four discs of unparalleled full motion 3D CGI spectacle, alternating with real-time 3D dungeons brimming with outlandish characters and concepts deeply inspired by Chinese history, geography and cultural traditions.
Ironically, Zeque managed to embed the theme of Feng-Shui, the ancient geomantic art seeking harmony between the individual and their surrounding space, into a story set in the world's most historically untidy district.
SaGa Frontier - Square - 1997
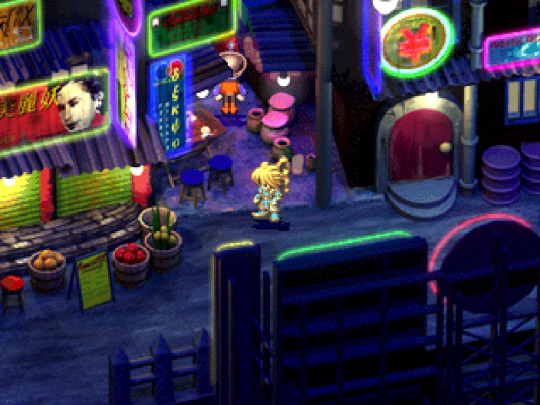


SaGa Frontier takes place in a solar system named The Regions, composed of multiple inhabited worlds for the player to explore, each with its different degree of civilizational development and culture. One of these planets goes by the suggestive name Kūron. Its pervasive neon light signs, food stalls, makeshift cabins and rooftop scaffolding instantly evoke the memory of China’s so-called city of darkness.
Shadow Hearts - Sacnoth - 2001
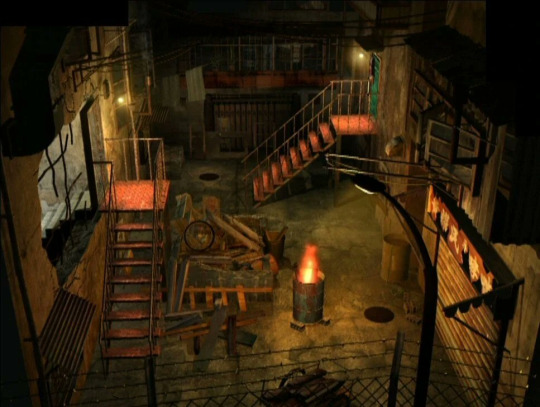
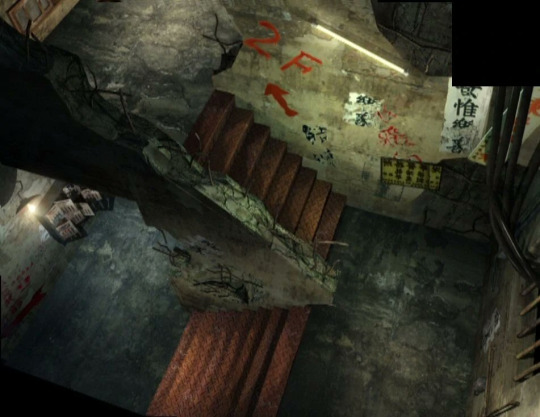



Shortly after the release of Koudelka, Sacnoth's initiated the development of Shadow Hearts, the first episode from a cult RPG trilogy exclusively designed for the Playstation 2. In good Japanese fashion, the game proposes an anachronistic yet visually suggestive depiction of Kowloon, portraying its architectural style and degree of decay as it existed in the late twentieth century, despite the fact that the game's events take place during the nineteen twenties.
Just as noteworthy is the almost complete absence of any inhabitants, which inadvertently make this portrayal of the quarter eerily reminiscent of the state in which it was found circa 1993 or 1994, as local authorities brought the long, arduous eviction project to a close.
Shenmue II - SEGA AM2 - 2001
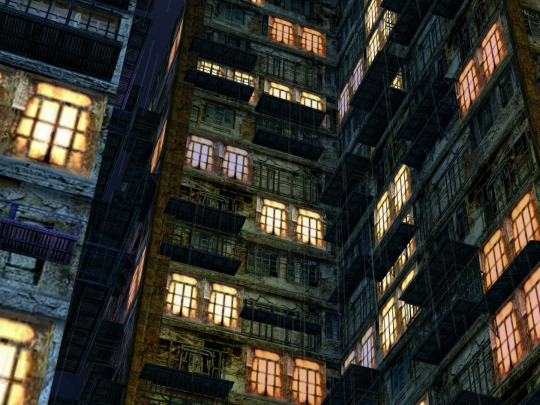
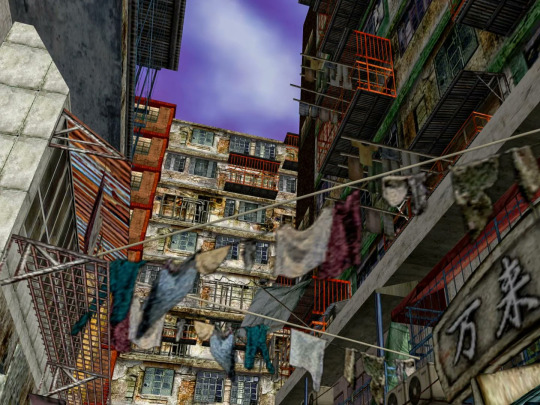



Shenmue II exhibits the most complete and period-accurate video game representation of Kowloon to date. While more recent games featuring this area may represent a number of its aspects with the aid of improved visual fidelity, none features it with such depth as this masterpiece of masterpieces. More than mere background decoration, Kowloon exists in the Shenmue series as a crucial, climacteric element of its modern epic narrative.
It is a well known fact that Yu Suzuki and his team conducted extensive research of the region so as to achieve a result that impresses even to this day. It must be noted, however, that they have similarly taken a fair share of creative liberty when converting the area to best align with the themes they wished to explore. Further reading is required for a more complete context in this regard, namely how this area ties with an early Dreamcast tech demo design which fans lovingly named Tower of Babel.
Ostensively, technical limitations did curtail the degree of precision in which the surrounding area could be replicated. The aerial view from the cutscene in which Ryo Hazuki arrives on location places Kowloon at an imaginary degree of elevation over surrounding vegetation. In the year of 1987, during which the game is set, the actual enclave stood perfectly levelled with a myriad of other modern buildings, undoubtedly more than could be reproduced under the circumstances.
These trifling considerations aside, Shenmue II entirely succeeds in capturing the vibrant life and mesmerizing beauty of the destitute and decayed urban agglomeration, in a way that it was deemed entirely impossible at the time of its release.
For reasons entirely related to per post content limitations imposed by Tumblr, this article will be continued in PART II.
#china#hong kong#kowloon#kowloon walled city#videogames#Kyu-Ryu-Tou#riot city#saga frontier#kowloon's gate#shenmue ii
379 notes
·
View notes
Note
When I get depressed about the numbers of notes and comments on anti-Jewish posts anywhere on social media, I remember this:
https://www.nytimes.com/2023/11/03/technology/israel-hamas-information-war.html
The combined bot farms of China, Russia, and Iran are working against us right now. Just keep it in mind.
Love you guys, we'll get through this too.
The reminder is very appreciated anon! It's important to remember that psyops do exist and actually influence the digital sphere, and vetting out who's an actual person and not just an empty spammer is important. (note: if you do come across a psyop that mostly just spams comments, reporting as spam would be beneficial as it is the only report staff actually look into) -🦦
49 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hey hey! Someone on Anbennar once told me that I should post my art online. I was gonna do it in the past, but I was a bit scared. A year passed and I'm making my first post!
So I just wanted to share some old art I created. I used to have this old worldbuilding setting where Asia industrialized before Europe. It goes a fair bit deeper than that (ie: Zhu Yuanzhang never unites China, the Tay Son dynasty never falls, old historic alliances stay strong, a WW1 equivalent breaks out because of the Ayutthaya-Dai Viet squabble over political influence in what is modern day Cambodia and Laos). To be fair, it never really went anywhere far and I kinda abandoned the project/it got eaten by my favored children.
However, I did get some nice art from it, like this drawing of a Korean soldier from this world's equivalent of WW1. This is at that point where people haven't fully figured out that red uniforms are easy to spot!

I see so much beautiful artwork out there. I swear if I had a tablet and other tools, I'd be a mildly dangerous digital artist. For now, I'll just stick to MS Paint/Paint 3D and mouse.
This was like three years ago. I do think I can do better nowadays, but I haven't done a serious drawing on that program in a very long time. I still think it holds up though!
I think there's a lot of interesting alternate history out there but not enough art of these hypothetical settings.
85 notes
·
View notes
Text
If you're an indie author who has considered working with a printer in China, but hesitated because working with an international printer seems scary, here's how my week went to show you that it absolutely is not scary.
I have a Kickstarter planned for my next book in January. I needed two things for this at the moment: some arc copies to send around to a few book influencers ahead of the campaign, and an actual sample of the fancy version of the book that I'm aiming for with the Kickstarter.
I decided to use IngramSpark for the arc copies because I'd get them a lot quicker, and they'd be cheaper since I only need a few. So I put together all my files, get everything all sorted into the proper templates and file types and everything. Get all the way to the last stage of uploading everything and...error code. Error code #303, specifically. What is error code #303? Who knows! Ingram certainly doesn't tell you. Just says to "contact your credit representative." I figure "credit representative" might mean it's an issue with my credit card, so I put a different one in. Nope, still error #303. Okay, maybe it's a browser issue. Let's try the dreaded Chrome. Nope, still getting #303ed. Website issue? I'll just try again tomorrow. Nope, still #303ed. I found one single old Reddit thread that mentions the error, but it was in relation to using a promo code for the upload fee. But Ingram doesn't HAVE upload fees anymore, so...???
I finally cave and send a ticket to the help desk, dreading how long it will take given Ingram doesn't like to provide customer service unless you pay them these days. Shockingly, they get back to me in about a day, but only to tell me that I have to instead contact this weird other "credit support" email. They don't forward it to them or anything, just tell me to do it myself. So I do, copying over my original email about the mysterious #303 error. Few hours later they reply saying the issue has been fixed. I still have no idea what the issue was, mind you, but I did finally get my book shoved all the way through the process. But! But! Now I have to wait 2-3 days for them to create a digital proof for me to approve before I can actually order the damn thing. And last time I did this, my book got stuck again and I had to email them again to get it fully pushed through which took about an additional week total. So when will I actually be able to order these arcs? Who knows!
Meanwhile, I emailed my printer in China on Sunday night about the sample of the fancy version and my representative got back to me by Monday morning with a fully detailed quote on exactly what I needed, various photos of samples all under the same lighting so I could pick the right colors for everything, and templates ready to go based on my specifications. She did it so fast I actually wasn't ready for her and had to tell her it'd be another 48 hours before I could get her the files.
So yeah. Working with international manufacturers who actually give a shit is a DELIGHT. No need to be intimidated by it.
131 notes
·
View notes
Text
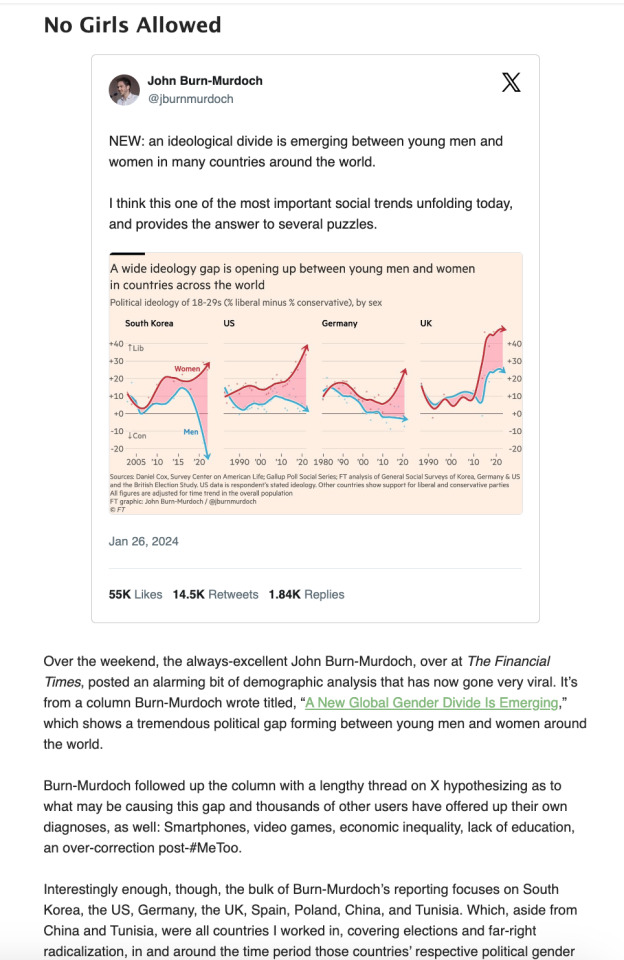
Most mar a garbage day is megirta (egybol ossze is omlott a site)
Over the weekend, the always-excellent John Burn-Murdoch, over at The Financial Times, posted an alarming bit of demographic analysis that has now gone very viral. It’s from a column Burn-Murdoch wrote titled, “A New Global Gender Divide Is Emerging,” which shows a tremendous political gap forming between young men and women around the world.
Burn-Murdoch followed up the column with a lengthy thread on X hypothesizing as to what may be causing this gap and thousands of other users have offered up their own diagnoses, as well: Smartphones, video games, economic inequality, lack of education, an over-correction post-#MeToo.
Interestingly enough, though, the bulk of Burn-Murdoch’s reporting focuses on South Korea, the US, Germany, the UK, Spain, Poland, China, and Tunisia. Which, aside from China and Tunisia, were all countries I worked in, covering elections and far-right radicalization, in and around the time period those countries’ respective political gender gaps began widening. I’m not saying I have a tremendously in-depth understanding of, say, Polish toxic masculinity, but I did spend several days there following around white nationalist rappers and Catholic fundamentalist football fans. And, in South Korea, I worked on a project about radical feminists and their activism against the country’s equivalent of 4chan, Ilbe Storehouse.
In fact, between 2015-2019, I visited over 20 countries, essentially asking the same question: Where do bad men here hangout online? Which has given me a near-encyclopedic directory in my head, unfortunately, of international 4chan knock-offs. In Spain, it’s a car forum that doxxes rape victims called ForoCoches. In France, it’s a gaming forum that organized rallies for Marine Le Pen called Jeux Video. In Japan, it’s 2channel. In Brazil, it’s Dogolachan. And most, if not all, of these spaces pre-date any sort of modern social movement like #MeToo — or even the invention of the smartphone.
But the mainstream acceptance of the culture from these sites is new. Though I don’t actually think the mystery of “why now?” is that much of a mystery. While working in Europe, I came to understand that these sites and their culture war campaigns like Gamergate were a sort of emerging form of digital hooliganism. Nothing they were doing was new, but their understanding how to network online was novel. And in places like the UK, it actually became more and more common in the late-2010s to see Pepe the Frog cosplayers marching alongside far-right football clubs. In the US, we don’t have the same sports culture, but the end result has been the same. The nerds and the jocks eventually aligned in the streets. The anime nazis were simply early adopters and the tough guys with guns and zip ties just needed time to adapt to new technology. And, unlike the pre-internet age, unmoderated large social platforms give them an infinitely-scalable recruitment radius. They don’t have to hide in backrooms anymore.
Much of the digital playbook fueling this recruitment for our new(ish) international masculinist movement was created by ISIS, the true early adopters for this sort of thing. Though it took about a decade for the West to really embrace it. But nowadays, it is not uncommon to see trad accounts sharing memes about “motherhood,” that are pretty much identical to the Disney Princess photoshops ISIS brides would post on Tumblr to advertise their new life in Syria. And, even more darkly, just this week, a Trump supporter in Pennsylvania beheaded his father and uploaded it to YouTube, in a video where he ranted about the woke left and President Biden. Online extremism is a flat circle.
The biggest similarity, though, is in what I can cultural encoding. For ISIS, this was about constantly labeling everything that threatened their influence as a symptom of the decadent, secular West.
(X.com/jeremykauffman)
Taylor Swift, an extremely affluent blonde, blue-eyed white woman who writes country-inflected pop music and is dating a football player headed for the Super Bowl. She should be a resounding victory for these guys. Doesn’t get more American than that. But due to an actually very funny glitch in how they see the world, she’s actually a huge threat.
Pop culture, according to the right wing, should be frivolous. Because before the internet, it was something sold to girls by corporations run by powerful men. Famous pop stars through the ages, like Frank Sinatra, America’s first Justin Bieber, or The Beatles, the One Direction of their time, would be canonized as Great by Serious Men after history had forgotten they rocketed to success as their generation’s Tumblr Sexymen. But from the 2000s onward, thanks to an increasingly powerful digital public square, young women and people of color were able to have more influence in mainstream culture and also accumulate more financial power from it. And after Barack Obama’s 2008 presidential campaign was able to connect this new form of pop influence to both liberal progressive politics and, also, social media, well, conservatives realized they had to catch up and fast. And the fastest way to do that is to try and smash the whole thing by dismissing it as feminine.
Pop music? It’s for girls. Social media? It’s for girls. Democrats? Girls. Taylor Swift? Girls and also a government psyop. But this line of thinking has no limit. It poisons everything. If Swift manages to make it to the Super Bowl, well, that has to become feminine too. And at a certain point, the whole thing falls apart because, honestly, you just sound like an insane loser.
39 notes
·
View notes
Text
[Nikkei is Private Japanese Media]
China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) came at the "right time" for boosting Africa's development, a top African Union (AU) official told Nikkei Asia, as he played down concerns that it was a debt trap for poor countries.
Last week, Beijing said it would ramp up the decade-old infrastructure drive to build ports, roads and railways by pushing into the digital realm, as the multibillion-dollar program becomes China's key foreign policy tool for influence in developing nations.
Chinese President Xi Jinping's renewed focus on industrialization, agriculture and talent development was also just what the continent needs, said Albert Muchanga, head of trade and industry for the African Union Commission, the AU's Ethiopia-based secretariat.
"China will continue BRI, at the same time there is a complementary effort to support us in those three areas. ... Both came at the right time," Muchanga said in an interview on the sidelines of last week's Turkey-Africa Business and Economic Forum in Istanbul. "Africa was making massive investments in developing infrastructure, connectivity, telecommunication systems as well as energy facilities [when BRI launched] and that helped quite a lot."
"We need to start the process of adding value on the continent to push industrialization," added the former Zambian diplomat.[...]
Asked if Western powers were being drawn to Africa in competition with China, Muchanga replied, "Well, they are reacting to it, which is good."
He also questioned growing criticism that the BRI's massive infrastructure loans and an opaque structure have saddled some recipient countries with unsustainable debt.
Some $76.8 billion worth of Chinese overseas loans were renegotiated or written off between 2020 and 2022, according to U.S. research firm Rhodium Group, compared to $17 billion in the preceding three years.
"When you discuss with the scholars from China and other people, I think there's an acknowledgment that if we demonstrate greater transparency, I think some of the allegations that are made may not be well founded," Muchanga said, without elaborating.
AU member nation ministers will gather in November to adopt a critical minerals strategy, the official said, adding that the commission is working on a document for approving its new leaders at a summit scheduled for February.
"We are responding to the issue of green transition by coming up with a critical minerals strategy," he said, "but the message is to come and produce at source to contribute to decarbonization."
16 Oct 23
57 notes
·
View notes
Text
Who knew? Nearly three and a half years after Covid-19 first appeared on the scene, the World Health Organisation has declared the pandemic officially over.
And there we all were thinking it had ended more than a year ago, when the UK and much of the rest of Europe abandoned the last of their Covid restrictions.
Late to recognise Covid as a pandemic, the WHO has also been late to acknowledge that thanks in large measure to Western medicines and vaccines, it is also now essentially part of history.
Perhaps that's because of the continued influence of China, which only very recently abandoned its zero-Covid policy.
As long as a major economy was still imprisoning its citizens at the slightest sign of infection, then I suppose it was indeed hard to declare the disease no longer a public health emergency.
For most of us, the pandemic has nevertheless been over for a long time now.
The grimly dispiriting legacy is, however, still very much with us.
In the UK, the national debt is a fifth of GDP higher than it was, inflation has soared to double digits, economically sub-optimal work from home remains deeply entrenched, labour shortages abide, and many people still complain of long term sickness – much of it unrelated to Covid as such but seemingly triggered by the pandemic's deprivations – with record numbers claiming out of work benefits.
The Government's response to Covid always looked to me like a ruinous over-reaction, and I became something of a lockdown sceptic.
I say “something of” because in the initial stages of the pandemic – call it the “we're all going to die” phase – something fairly dramatic was obviously called for, watching the TV images of emergency hospitals being built in Wuhan and overwhelmed ICU units in Northern Italy.
Politically, it would have been virtually impossible for the UK to have stood alone in remaining open even as virtually the whole of the rest of Europe was closing down.
The Government would have fallen within weeks if it had stood by and done nothing.
Even Sweden, which seems to have got its approach about right, eventually implemented a watered down version of the restrictions imposed elsewhere.
Instinctively, Boris Johnson, then Prime Minister, was against lockdown, preferring instead the idea of “herd immunity”, but then he became seriously ill himself, and ended up fully embracing the made-in-China response.
For some, such as the former Supreme Court judge Lord Sumption – who would regularly warn of police state authoritarianism – the objection was on principled libertarian grounds.
This was, however, very much a minority position. One of the most remarkable things about the whole sorry affair is quite how compliant the country proved, and how quickly we succumbed to instruction.
Somewhat alarmingly, it turned out that supposedly freedom loving societies are remarkably willing to submit to authoritarian rule, especially if paid to stay at home, as was the case with furlough in the UK.
Even the Government was surprised by the obedience.
Yet it was always abundantly clear that these were essentially temporary, wartime measures that would be lifted once the emergency was over, so on those grounds at least, most of us were initially willing to go along with the heavy handed approach imposed.
No, what worried me was not so much the loss of liberty as the economic impact, and once the case mortality rate was confirmed at less than 1 percent for advanced economies, the lack of proportionality and cost benefit consideration.
I could never quite accept the argument that what was being done was similar to putting the economy into a medically induced coma, with the patient reawoken as if nothing had happened once the pandemic was over.
As we can now see, the lasting damage was monumental.
It would no doubt have been disastrous had the health service been overwhelmed, but when the main justification for lockdown becomes the rallying call of “protect the NHS” you have to ask yourself what the whole thing was really all about.
Insulating the health service from a sickness it is there to treat?
You cannot put a price on life, it can be argued, and therefore almost any cost is justified. It is also true that in the fog of war, mistakes are bound to be made; over-reaction is possibly better than under-reaction.
All the same, it now seems abundantly clear that the treatment was in many ways worse than the disease itself. We'll never know the counterfactual, or just how many lives were saved by imposing a strict series of lockdowns.
Most epidemiologists will tell you that it was a lot.
But they are not paid to think about the wider consequences, and it is now patently clear that the lasting damage to education, the economy and to wider public health was off the scale.
What are the lessons? We don't need to wait for the results of the official inquiry, still years away, to know some of the answers.
Let's make a start by examining the death toll, reported on a daily basis during the pandemic as if in some kind of international competition for how effectively each country was dealing with the crisis.
For a long time, Britain seemed to be bottom of the class, which in turn instructed the severity of the counter measures thought necessary.
The worse the numbers looked relative to others, the more draconian and prolonged the restrictions became.
Given differing methodologies and reporting systems, the best way of measuring the impact is not through recorded deaths from Covid, but via the excess death rate over and above what would normally be expected.
On this measure, most major advanced economies ended up in much the same place.
Britain was slightly worse than Germany and France, but not significantly so, and actually quite a bit better than Italy and Spain, according to estimates published in the Lancet.
This was not the impression you got at the time, when the British response was widely viewed as uniquely incompetent.
What is more, Scotland did worse than England, notwithstanding the plaudits the first minister, Nicola Sturgeon, received for outbidding Westminster on the countermeasures needed.
The same is true of Wales, whose first minister, Mark Drakeford, was similarly lauded for a more restrictive and therefore seemingly capable approach.
Well, not according to the numbers.
Culture wars, I'm afraid to say, are as likely to determine your view of the efficacy of lockdown as the underlying facts of the matter.
What we now know, however, is that lockdown is an extraordinarily costly way of dealing with a pandemic.
It is to be hoped that this lesson at least has been learned, and that the response to future pandemics will therefore be better calibrated to the severity of the disease.
A 1pc case mortality rate scarcely seems to justify what was done, even if it was admittedly much higher in older age cohorts.
A more consensual approach that keeps people properly informed but allows them to make their own choices on the degree of risk they are prepared to run must be the way forward.
#nunyas news#who knew?#lots of people did and you censored them#anyone that spoke out was ejected from the room
147 notes
·
View notes
Text
Lai Ching-te will be Taiwan’s next president after winning Saturday’s election, ensuring that the ruling Democratic Progressive Party (DPP) will remain in power and dealing a rebuke to Beijing’s wishes for a more China-friendly administration. In the days before the election, Taiwanese voters were flooded with information. Look up, and they saw posters on buses and buildings declaring the virtues of all three candidates and their running mates. Look down, and they got a stream of news, gossip, and opinions from their phones—not all of it true and much of it likely stirred up by internet trolls in China.
Taiwan is one of the world’s most digitally connected countries, and on social media, false posts and videos are reaching thousands of people before platforms can take them down. TikTok was flooded with disinformation accusing Lai of sex scandals, tax evasion, and conspiring to start a war with China. His vice presidential pick, Hsiao Bi-khim, has been accused of secretly holding U.S. citizenship. So has the running mate of Ko Wen-je, the third-party candidate livestreaming his spoiler campaign on YouTube and TikTok.
Researchers have attributed much of the false information to Chinese actors—and rather than blasting pro-China views to Taiwanese voters, they’ve focused on amplifying negative stories about Taiwan’s domestic politics and wedge issues, such as the role of the United States, with the intent of polarizing Taiwanese society.
“Beijing’s cognitive warfare is evolving,” said Tzu-wei Hung, a scholar at Taiwan’s Academia Sinica. “Negative narratives are effective not because they will change the election result but because they intensify social conflicts and create a vicious cycle of distrust and hate.”
Taiwan faced a similarly toxic disinformation environment before the 2020 presidential election, and at the time, it fought back—hard. Officials frequently accused China of being behind wide-ranging disinformation campaigns. Police summoned private citizens for posting false stories and levied fines in some instances for violating a law preventing public disorder. The National Communications Commission (NCC) issued a series of fines to the pro-China TV station Chung Tien Television (CTi) for broadcasting false information. Eventually, in December 2020, CTi was taken off the air after the NCC declined to renew its broadcast license.
The government learned quickly that none of it worked.
“If you want to curb disinformation by legal measures, it’s difficult and dangerous,” said Yachi Chiang, a professor at National Taiwan Ocean University specializing in intellectual property and tech law. It “opens a pathway for the government to control speech.”
Taiwan has always been a banner holder of free speech in Asia. In 2020, however, DPP legislators were panicked over the prospect of Chinese election-meddling. President Tsai Ing-wen was riding a wave of global popularity by supporting the Hong Kong pro-democracy protests, which had broken out months earlier, giving Beijing every reason to remove her from office or disrupt her legislative majority.
Tsai was reelected in a landslide—but not because her government cracked down on fake news. Many fines levied under the Social Order Maintenance Act, an existing law that was utilized against disinformation peddlers, have since been overturned by the courts.
The NCC’s crusade against CTi hasn’t gone much better. Opposition politicians used its removal from the airwaves to hammer DPP politicians as enemies of free speech. The NCC, at the time, argued that CTi had failed to adhere to basic fact-checking standards and could not ensure impartiality from outside influence—a clear reference to its owner, the domestically unloved Tsai Eng-meng, a snack food tycoon with extensive business interests in China and a track record of pro-unification statements.
In May 2023, a Taipei court ruled against the NCC’s decision to shut down CTi, saying it had failed to provide adequate reasoning for its decision. At present, CTi remains off the air—and its request to have its license renewed by the court was rejected—but the NCC has been ordered to review its own decision and provide stiffer reasoning. “You need something stronger to sustain your ruling,” Chiang said.
Taiwanese authorities have successfully prosecuted citizens who received funding from China to publish fake news. But in general, politicians began to realize that moving through the judicial system “would be slow,” Chiang said. “The decisions might be disappointing. The results might be less effective.”
Just after the 2020 election, however, Taiwan’s government found a better way to combat disinformation when the COVID-19 pandemic swept the globe. Taiwan was the first country to alert the World Health Organization of the presence of a coronavirus in Wuhan and then introduce travel restrictions and quarantine protocols.
Public officials also began releasing accurate, easily digestible information as quickly as possible, before disinformation could reach people’s phone screens. Chen Shih-chung, the health minister at the time, held press conferences each afternoon, earning him the nickname “Minister Clock.” His ministry, along with the social media accounts of Tsai and Premier Su Tseng-chang, posted colorful memes sharing data on the pandemic and extolling the virtues of masking and hand-washing.
It was a triumph of public transparency that paid off handsomely. Taiwan saw just 823 COVID-19 cases in all of 2020, despite its close proximity to the pandemic’s epicenter.
It also helped politicians realize that “you can’t count on laws to tackle disinformation,” Chiang said. “You need to create your own information.”
“Free speech is not the cost but the key to counteract disinformation,” said Hung, who noted that in 2022, Freedom House found that countries that protect free expression and have robust civic society groups do a better job at mitigating false information.
Taiwan has tried other forms of a more open approach. Although it banned the Chinese-owned video platform TikTok from government apps in 2022, Taiwan has not followed countries such as India in issuing a general proscription on the app despite concerns that Beijing can influence content. About one-quarter of Taiwan’s population uses the app, including a host of popular influencers and celebrities.
Taiwan also has a network of strong civic fact-checking organizations that work with social media companies to combat disinformation. One of them, MyGoPen, recently started collaborating directly with TikTok to correct false posts about the 2024 election.
No matter who is in power, politicians seem to acutely understand that the best way to combat false information about them is to push out their own narratives on social media. “If you are popular on the internet, that’s more important than [popularity on] traditional media channels,” Chiang said.
Lai’s win on Saturday is not an outright victory against disinformation itself—both Chinese and domestic actors will surely continue to create confusion and distrust whenever they can. It did, however, show that Taiwanese voters can’t easily be swayed, as long as public officials do their part to communicate rapidly, positively, and honestly.
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
China is joining Russia as part of an axis of misinformation in trying to influence American elections.
Rachel Maddow referenced this article in her report from the nonpartisan Foundation for Defense of Democracies (FDD). It's worth a look.
Much Ado About ‘Somethings’
Being a democracy can be a disadvantage in the digital age. Malefactors can easily manipulate information to attempt to achieve dubious goals.
We need to retaliate against China and Russia. But spamming such populations under totalitarian rule would not have the same impact that it does in democracies. But we could try to punch holes in the firewalls such countries erect around their own information infrastructure. Let the breeze of free information occasionally flow and permit Russians to know about Putin's war crimes in Ukraine and let Chinese see Xi's genocide against the Uygurs in Xinjiang.
What people can do here is get off of Twitter/X and urge others to do the same. Under megalomaniac billionaire Elon Musk, misleading information and hate speech have grown exponentially on the platform.
Old habits die hard and some people have a preternatural attachment to tweeting. But as we see in Rachel Maddow's piece and in the FDD article, Twitter/X is responsible for an inordinate amount of misinformation. It's time to starve the beast one account at a time.
#china#xi jinping#interference in us elections#fake social media accounts#misinformation#state-directed propaganda#rachel maddow#tiffany hsu#spamouflage#social media#twitter#x#elon musk#leave twitter#get off twitter#delete twitter#quit twitter#election 2024#vote blue no matter who#习近平#误传#假新闻#Youtube
13 notes
·
View notes
Photo

The Chinese are on the forefront of a new type of warfare, one that is fought not just on the battlefield, but in cyberspace. They are redefining what it means to wage war, and the rest of the world is scrambling to keep up. The Chinese have always been a formidable foe, but their latest tactics are something else entirely. They have shown that they are willing to use all available tools to gain an advantage, including cyberattacks and espionage. This new type of warfare is a serious threat to the rest of the world, and we need to find a way to counter it. The Chinese are clearly ahead of the curve, but we can't afford to fall too far behind.
#Asia#Cyber Warfare#Security#21st century warfare#China cyber capabilities#China's digital influence#cyber defense strategies#cyber geopolitics#cyber warfare implications#cybersecurity investments#digital warfare#digital warriors#economic impacts of cyber attacks#future of digital battles#global cyber partnerships#global cyber reactions#Headline#interconnected global conflict#modern warfare trends#political implications of digital warfare#technological innovations in warfare#fault#Chinese#warfare#cyberspace#cyberattacks#espionage
0 notes
Text
By: Rob Henderson
Published: Apr 25, 2024
Perhaps counterintuitively, gender equality is leading to greater gender-related differences.
In most wealthy nations, women have been steadily closing the gap with men on several fronts. In the United States, women now earn the majority of the bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral degrees. Women now receive more than half of STEM college degrees, and the proportion of women in the tech sector has risen in recent years, to 35 percent in 2023 from 31 percent in 2019. Among Americans younger than 30, women’s earnings rival or even surpass men’s in many metropolitan areas, including Boston, New York, Los Angeles, and Washington, D.C.
As these gaps have narrowed, we might have expected men and women to become more alike in other ways, including their cultural values and politics. Yet we are seeing the reverse.
This is especially true when it comes to political orientation. Recent polls have highlighted increasing polarization along gender lines on various political issues. Since 2014, women younger than 30 have become steadily more left-leaning each year, while young men have remained relatively static in their political views. In 2021, 44 percent of young women in the United States identified as liberal compared with just 25 percent of young men — the biggest gender gap in 24 years of polling.
In the Financial Times, John Burn-Murdoch recently articulated this stark contrast in a piece titled “A new global gender divide is emerging.” He observes that while older women and men are similar in their political views, young women have veered sharply to the left of young men.
Burn-Murdoch cites the influence of the #MeToo movement, suggesting it empowered young women to address longstanding injustices.
The Washington Post’s editorial board suggested that such polarization is to be expected in the United States, “a large, unwieldy democracy.” The Guardian proposes that digital spaces and social media influencers are luring young people into disparate online platforms that cultivate more extreme political views. No doubt these all play some role.
However, I’d like to propose an idea from my home discipline of academic psychology: the gender-equality paradox. This emerged as one of the most mind-blowing findings that researchers published while I was pursuing my recent doctoral studies at the University of Cambridge.
The paradox is straightforward: Societies with higher levels of wealth, political equality, and women in the workforce show larger personal, social, and political differences between men and women. In other words, the wealthier and more egalitarian the country, the larger the gender differences.
The pattern exists not just for political ideology but also for things like academic preferences, physical aggression, self-esteem, frequency of crying, interest in casual sex, and personality traits such as extraversion. In all these categories, the differences have been largest in societies that have gone the furthest in attempting to treat women and men the same.
Of course, there is an overlap for all of these attributes — aggression, for example, is a trait that both women and men can exhibit.
But there’s less overlap — meaning greater differences — in more-equal societies. In China, which scores low on gender parity, the overlap between men and women in personality traits such as extraversion and openness to experience is actually very high, 84 percent. In the Netherlands, which is among the most gender-equal societies, the overlap is just 61 percent.
More recently, a study of 67 countries found that although women generally tend to hold stricter moral views, gender differences in verdicts in hypothetical court scenarios are largest in wealthier and more equal societies. Specifically, women view misconduct more unfavorably than men in most places, but this difference in judgment is larger in richer and more equal countries.
This gender gap has also been found for physical differences in things like height, BMI, obesity, and blood pressure. Across societies, men tend to be taller, heavier, and have higher blood pressure than women. But in rich and relatively equal societies, gender differences are particularly large.
The gender-equality paradox might also help to explain why the gender gap in political orientation has grown among young people. One natural explanation is that young women are outpacing men in higher education, with men now making up just 40 percent of college students. Some evidence suggests that college tends to cultivate more liberal attitudes.
However, even among college students, women are more left-leaning than men. A Foundation for Individual Rights and Expression survey of 254 colleges and universities found that 55 percent of female students identify as liberal, compared with only 40 percent of male students. Interestingly, at schools ranked below 200 by US News and World Report, 45 percent of women and 33 percent of men identify as liberal. At top 25 schools, though, the difference is more pronounced, with 71 percent of women and 54 percent of men identifying as liberal.
The gender-equality paradox can help to explain why the gender gap is largest at the most selective US colleges, where family income tends to be higher and sociopolitical equality tends to be especially highly prized.
In an interview in The Times of London, the psychologist Steve Stewart-Williams succinctly summarized the paradox: “Treating men and women the same makes them different, and treating them differently makes them the same.”
There are a variety of possible explanations for the gender-equality paradox, but one prevailing view is that as societies become relatively more prosperous and equal, people more fully express their underlying traits and preferences.
Of course, culture matters in explaining gender differences — just not in the way most people think.
In less affluent and less egalitarian societies, gender differences in physical traits are flattened due to scarcity — that is, the absence of food and other resources stunts growth, especially for men, leading to smaller physical disparities. Moreover, gender differences in psychological traits narrow in response to rigid social expectations.
In the most equal nations of the world, it’s not harsh gender socialization by parents and media, strict societal expectations, or institutional forces that widen the differences between men and women. In the absence of dire poverty and strict social expectations, people are in a position to express their intrinsic attributes and preferences.
The freer people are and the more fairly they are treated, the more differences tend to grow rather than shrink. Thus, we shouldn’t be surprised that Gen Z men and women are diverging along political lines to a greater extent than earlier generations did.
Rob Henderson has a PhD in psychology from the University of Cambridge and is the author of “Troubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social Class.”
[ Via: https://archive.today/zzoqm ]
--
Abstract
Men's and women's personalities appear to differ in several respects. Social role theories of development assume gender differences result primarily from perceived gender roles, gender socialization and sociostructural power differentials. As a consequence, social role theorists expect gender differences in personality to be smaller in cultures with more gender egalitarianism. Several large cross-cultural studies have generated sufficient data for evaluating these global personality predictions. Empirically, evidence suggests gender differences in most aspects of personality-Big Five traits, Dark Triad traits, self-esteem, subjective well-being, depression and values-are conspicuously larger in cultures with more egalitarian gender roles, gender socialization and sociopolitical gender equity. Similar patterns are evident when examining objectively measured attributes such as tested cognitive abilities and physical traits such as height and blood pressure. Social role theory appears inadequate for explaining some of the observed cultural variations in men's and women's personalities. Evolutionary theories regarding ecologically-evoked gender differences are described that may prove more useful in explaining global variation in human personality.
==
For reference, "liberal" is used here in the American sense of "left-wing," rather than the sense of classical liberalism.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liberalism
Liberalism is a political and moral philosophy based on the rights of the individual, liberty, consent of the governed, political equality, right to private property and equality before the law. Liberals espouse various and often mutually warring views depending on their understanding of these principles but generally support private property, market economies, individual rights (including civil rights and human rights), liberal democracy, secularism, rule of law, economic and political freedom, freedom of speech, freedom of the press, freedom of assembly, and freedom of religion, constitutional government and privacy rights. Liberalism is frequently cited as the dominant ideology of modern history.
Much of what constitutes modern day "leftism," such as Critical Theory, modern "color conscious" conceptions of "antiracism," and gender ideology is extraordinarily illiberal.
#Rob Henderson#gender differences#left wing#right wing#conservative#progressive#the left#the right#gender polarization#political polarization#religion is a mental illness
10 notes
·
View notes
Text

(CNN) — Jack Latham was on a mission to photograph farms in Vietnam — not the country’s sprawling plantations or rice terraces but its “click farms.”
Last year, the British photographer spent a month in the capital Hanoi documenting some of the shadowy enterprises that help clients artificially boost online traffic and social media engagement in the hope of manipulating algorithms and user perceptions.
The resulting images, which feature in his new book “Beggar’s Honey,” provide rare insight into the workshops that hire low-paid workers to cultivate likes, comments and shares for businesses and individuals globally.
“When most people are on social media, they want nothing but attention — they’re begging for it,” Latham said in a phone interview, explaining his book’s title.
“With social media, our attention is a product for advertisers and marketers.”

In the 2000s, the growing popularity of social media sites — including Facebook and Twitter, now called X — created a new market for well-curated digital profiles, with companies and brands vying to maximize visibility and influence.
Though it is unclear when click farms began proliferating, tech experts warned about “virtual gang masters” operating them from low-income countries as early as 2007.
In the following decades, click farms exploded in number — particularly in Asia, where they can be found across India, Bangladesh, Indonesia, the Philippines, and beyond.
Regulations have often failed to keep pace: While some countries, like China, have attempted to crack down on operations (the China Advertising Association banned the use of click farms for commercial gain in 2020), they continue to flourish around the continent, especially in places where low labor and electricity costs make it affordable to power hundreds of devices simultaneously.
‘Like Silicon Valley startups’
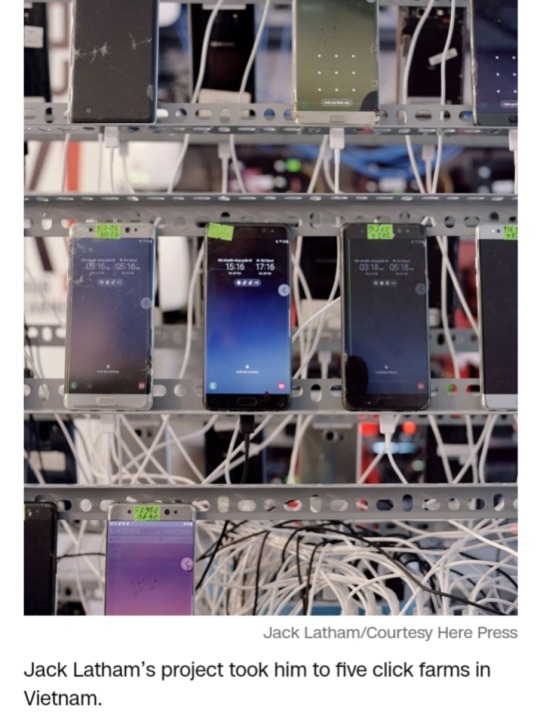
Latham’s project took him to five click farms in Vietnam.
(The click farmers he hoped to photograph in Hong Kong “got cold feet,” he said, and pandemic-related travel restrictions dashed his plans to document the practice in mainland China).
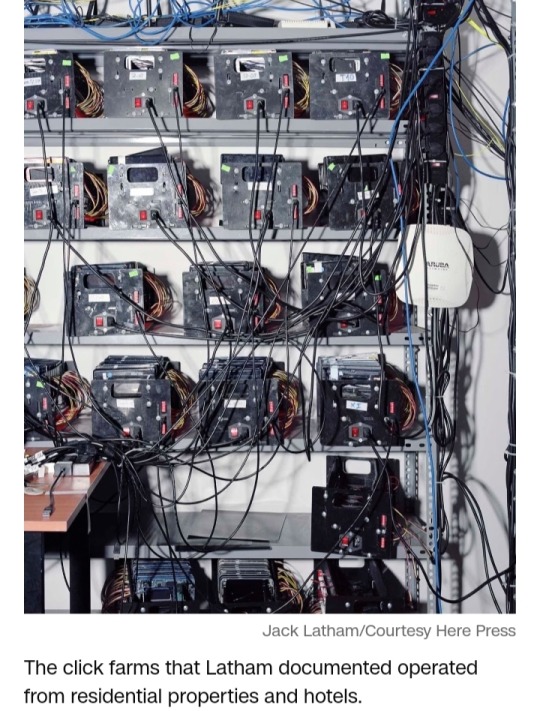
On the outskirts of Hanoi, Latham visited workshops operating from residential properties and hotels.
Some had a traditional setup with hundreds of manually operated phones, while others used a newer, compact method called “box farming” — a phrase used by the click farmers Latham visited — where several phones, without screens and batteries, are wired together and linked to a computer interface.

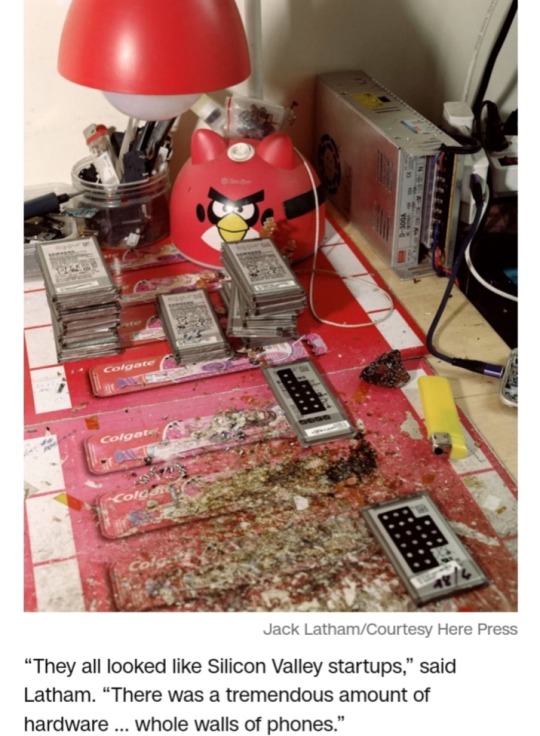
Latham said one of the click farms he visited was a family-run business, though the others appeared more like a tech companies.
Most workers were in their 20s and 30s, he added.
“They all looked like Silicon Valley startups,” he said. “There was a tremendous amount of hardware … whole walls of phones.”
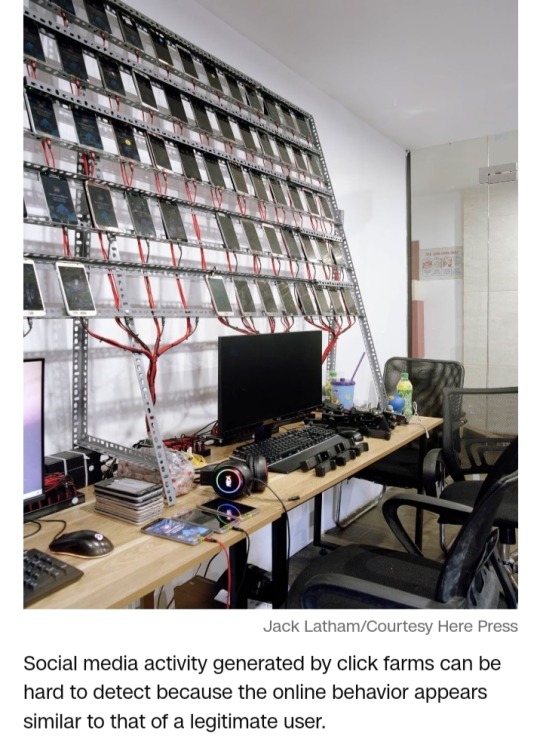
Some of Latham’s photos depict — albeit anonymously — workers tasked with harvesting clicks.
In one image, a man is seen stationed amid a sea of gadgets in what appears to be a lonely and monotonous task.
“It only takes one person to control large amounts of phones,” Latham said. “One person can very quickly (do the work of) 10,000. It’s both solitary and crowded.”
At the farms Lathan visited, individuals were usually in charge of a particular social media platforms.
For instance, one “farmer” would be responsible for mass posting and commenting on Facebook accounts, or setting up YouTube platforms where they post and watch videos on loop.
The photographer added that TikTok is now the most popular platform at the click farms he visited.

The click farmers Latham spoke to mostly advertised their services online for less than one cent per click, view or interaction.
And despite the fraudulent nature of their tasks, they seemed to treat it like just another job, the photographer said.
‘There was an understanding they were just providing a service,” he added. “There wasn’t a shadiness. What they’re offering is shortcuts.”
Deceptive perception
Across its 134 pages, “Beggar’s Honey” includes a collection of abstract photographs — some seductive, others contemplative — depicting videos that appeared on Latham’s TikTok feed.
He included them in the book to represent the kind of content he saw being boosted by click farms.
But many of his photos focus on the hardware used to manipulate social media —webs of wires, phones and computers.
“A lot of my work is about conspiracies,” Latham said. ” Trying to ‘document the machines used to spread disinformation’ is the tagline of the project. The bigger picture is often the thing we don’t see.”

Click farms around the world are also used to amplify political messages and spread disinformation during elections.
In 2016, Cambodia’s then-prime minister Hun Sen was accused of buying Facebook friends and likes, which according to the BBC he denied, while shadowy operations in North Macedonia were found to have spread pro-Donald Trump posts and articles during that year’s US presidential election.
While researching, Latham said he found that algorithms — a topic of his previous book, “Latent Bloom” — often recommended videos that he said got increasingly “extreme” with each click.
“If you only digest a diet of that, it’s a matter of time you become diabetically conspiratorial,” he said.
“The spreading of disinformation is the worst thing. It happens in your pocket, not newspapers, and it’s terrifying that it’s tailored to your kind of neurosis.”
Hoping to raise awareness of the phenomenon and its dangers, Latham is planning to exhibit his own home version of a click farm — a small box with several phones attached to a computer interface — at the 2024 Images Vevey Festival in Switzerland.
He bought the gadget in Vietnam for the equivalent of about $1,000 and has occasionally experimented with it on his social media accounts.
On Instagram, Latham’s photos usually attract anywhere from a few dozen to couple hundred likes.
But when he deployed his personal click farm to announce his latest book, the post generated more than 6,600 likes.
The photographer wants people to realize that there’s more to what they see on social media — and that metrics aren’t a measurement of authenticity.
“When people are better equipped with knowledge of how things work, they can make more informed decisions,” he said.

“Beggar’s Honey,” co-published by Here Press and Images Vevey, is available now.
#Jack Latham#click farms#box farms#Hanoi#Vietnam#Beggar’s Honey#box farming#social media#algorithms#user perception#trolls#PR#marketing#advertising#likes#comments#shares#digital profiles#virtual gang masters#bots#spam#China Advertising Association#click farmers#mass post#disinformation#misinformation#fake news#metrics
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
"From populist politicians to holistic wellness influencers, anyone interested in power is able to weaponise thought-terminating cliches to dismiss followers’ dissent or rationalise flawed arguments. In his book Thought Reform and the Psychology of Totalism, Lifton wrote that these semantic stop signs compress “the most far-reaching and complex of human problems … into brief, highly selective, definitive-sounding phrases, easily memorized and easily expressed. They become the start and finish of any ideological analysis.”
Such zingy stock phrases are enjoying something of a golden age in the digital era, propagated by way of aesthetically pleasing quotegrams and viral social media posts. During Covid lockdowns, dogmatic maxims such as “Reality is subjective”, “Don’t let yourself be ruled by fear” and “Truth is a construct” exploded among online conspiracy theorists.
Thought-terminating cliches exist, of course, in every language. In China, some government officials are known to exploit the phrase “Mei banfa”, meaning “No solution”, or “There’s nothing to be done” to justify inaction. The saying “Shouganai”, a linguistic shrug of resignation similar to “It is what it is”, is similarly weaponised in Japan. The Polish idiom “Co wolno wojewodzie, to nie tobie, smrodzie” roughly means “People in positions of power can get away with anything” (hence, don’t bother putting up a fight). According to Walter Scheirer, author of A History of Fake Things on the Internet, thought-terminating cliches commonly carry a defeatist flavour. It’s hard work, involving psychological friction, to figure out the best way to think about complex subjects such as climate policy or geopolitics. Any licence to give up the struggle is going to be appealing."
Példáim magyarul:
-ez egy következmények nélküli ország (mennyivel jobb ez a lengyelnél)
-a pénz beszél, a kutya ugat
-és, drágább lesz ettől a kenyér?
-ha balról is és jobbról is támadják, valamit csak jól csinál
Biztos van még egy csomó ilyen, össze kéne hozni egy gyűjtést.
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tik Tok on the Chopping Block - 04/25/2024
Yesterday, Joe Biden signed the Tik Tok Divest-or-Ban bill into law. I covered this bill extensively in my post, "Tik Tok Bill/HR 7521" back on March 16th of this year. This bill forces ByteDance to sell Tik Tok within one year. It's clear to me that this Chinese owned company is controlled by the CCP and is using it to gather information on US citizens and influence children toward committing self-harm and suicide.
Tik Tok's CEO, Shou Zi Chew released the following video statement yesterday. "Make no mistake, this is a ban, a ban on you and your voice. We are confident, and we will keep fighting for your rights in the courts. The facts and the Constitution are on our side, and we expect to prevail again." He was referring to how they circumvented Trump's executive order to ban the app in the U.S. back in 2020. Tik Tok's position is that through China's Counterespionage Law, its customer data is stored in Virginia and backed up in Singapore. They claim that they have never or ever will share U.S. data with the CCP. Yet the owner of ByteDance previously issued a letter of apology to the CCP about failing to follow the CCP's directives. It's obvious to me that they are more of an arm of the CCP than a private company and we should not trust them. At the same time, I'm also conflicted about trusting our own government. Regardless it's now signed into law, like it or not.
Tik Tok and ByteDance together spent over $7 million since the beginning of this year on TV and digital ads in an effort to stop legislation from passing the bill. A Tik Tok spokesperson said this, "This expenditure reflects work we do to educate policy makers about how legislation could affect our community of 170 million American users." Tik Tok officials lobbied Congress and Biden's executive office last quarter. Biden's executive office contains the National Security Council, the Office Management and Budget, the Office of the U.S. Trade Representative, and other divisions.
As I mentioned in my previous post on this bill last March, Donald Trump and Elon Musk both came out against it. Trump is concerned that it could expand government powers on other platforms, and Musk is concerned about censorship. The bill is intended to remove any foreign influence and investment in social media platforms and websites here in the U.S. The government would have to prove that a foreign entity is directly involved and then initially force divestment, and then later if necessary deplatform the app and shut down their operating websites.
I'm all for private companies operating platforms that allow freedom of expression, but not if they're being operated by a foreign adversary like China's CCP. Yet I'm always very skeptical of our government and their tendencies to over-reach in order to go after their political opposition. Especially with this current bunch in charge. All we can do is to stay informed and hopefully for the sake of our freedom and security vote in Republican majorities in both the house and senate, and get Donald Trump back into office, in my opinion.
#donald trump#trump#joe biden#biden#tiktok#tik tok#tik tok bill#us#censorship#social media#platforms#platform#ccp#china#chinas ccp#divestment#foreign adversaries#foreign adversary#office#republican#websites#elon musk#musk#app#government#national security#national security council#office management and budget#us trade council#bytedance
7 notes
·
View notes