#religion is a mental illness
Text

By: Andy L.
Published: Apr 14, 2024
It has now been just little under a week since the publication of the long anticipated NHS independent review of gender identity services for children and young people, the Cass Review.
The review recommends sweeping changes to child services in the NHS, not least the abandonment of what is known as the “affirmation model” and the associated use of puberty blockers and, later, cross-sex hormones. The evidence base could not support the use of such drastic treatments, and this approach was failing to address the complexities of health problems in such children.
Many trans advocacy groups appear to be cautiously welcoming these recommendations. However, there are many who are not and have quickly tried to condemn the review. Within almost hours, “press releases“, tweets and commentaries tried to rubbish the report and included statements that were simply not true. An angry letter from many “academics”, including Andrew Wakefield, has been published. These myths have been subsequently spreading like wildfire.
Here I wish to tackle some of those myths and misrepresentations.
-
Myth 1: 98% of all studies in this area were ignored

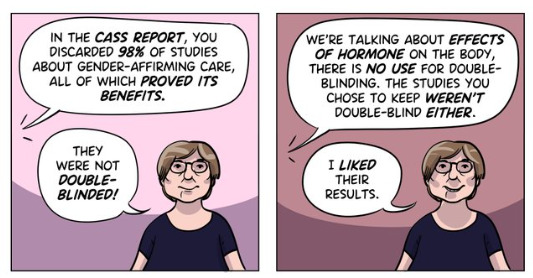
Fact
A comprehensive search was performed for all studies addressing the clinical questions under investigation, and over 100 were discovered. All these studies were evaluated for their quality and risk of bias. Only 2% of the studies met the criteria for the highest quality rating, but all high and medium quality (50%+) studies were further analysed to synthesise overall conclusions.
Explanation
The Cass Review aimed to base its recommendations on the comprehensive body of evidence available. While individual studies may demonstrate positive outcomes for the use of puberty blockers and cross-sex hormones in children, the quality of these studies may vary. Therefore, the review sought to assess not only the findings of each study but also the reliability of those findings.
Studies exhibit variability in quality. Quality impacts the reliability of any conclusions that can be drawn. Some may have small sample sizes, while others may involve cohorts that differ from the target patient population. For instance, if a study primarily involves men in their 30s, their experiences may differ significantly from those of teenage girls, who constitute the a primary patient group of interest. Numerous factors can contribute to poor study quality.
Bias is also a big factor. Many people view claims of a biased study as meaning the researchers had ideological or predetermined goals and so might misrepresent their work. That may be true. But that is not what bias means when we evaluate medical trials.
In this case we are interested in statistical bias. This is where the numbers can mislead us in some way. For example, if your study started with lots of patients but many dropped out then statistical bias may creep in as your drop-outs might be the ones with the worst experiences. Your study patients are not on average like all the possible patients.
If then we want to look at a lot papers to find out if a treatment works, we want to be sure that we pay much more attention to those papers that look like they may have less risk of bias or quality issues. The poor quality papers may have positive results that are due to poor study design or execution and not because the treatment works.
The Cass Review team commissioned researchers at York University to search for all relevant papers on childhood use of puberty blockers and cross-sex hormones for treating “gender dysphoria”. The researchers then graded each paper by established methods to determine quality, and then disregarded all low quality papers to help ensure they did not mislead.
The Review states,
The systematic review on interventions to suppress puberty (Taylor et al: Puberty suppression) provides an update to the NICE review (2020a). It identified 50 studies looking at different aspects of gender-related, psychosocial, physiological and cognitive outcomes of puberty suppression. Quality was assessed on a standardised scale. There was one high quality study, 25 moderate quality studies and 24 low quality studies. The low quality studies were excluded from the synthesis of results.
As can be seen, the conclusions that were based on the synthesis of studies only rejected 24 out of 50 studies – less than half. The myth has arisen that the synthesis only included the one high quality study. That is simply untrue.
There were two such literature reviews: the other was for cross-sex hormones. This study found 19 out of 53 studies were low quality and so were not used in synthesis. Only one study was classed as high quality – the rest medium quality and so were used in the analysis.
12 cohort, 9 cross-sectional and 32 pre–post studies were included (n=53). One cohort study was high-quality. Other studies were moderate (n=33) and low-quality (n=19). Synthesis of high and moderate-quality studies showed consistent evidence demonstrating induction of puberty, although with varying feminising/masculinising effects. There was limited evidence regarding gender dysphoria, body satisfaction, psychosocial and cognitive outcomes, and fertility.
Again, it is myth that 98% of studies were discarded. The truth is that over a hundred studies were read and appraised. About half of them were graded to be of too poor quality to reliably include in a synthesis of all the evidence. if you include low quality evidence, your over-all conclusions can be at risk from results that are very unreliable. As they say – GIGO – Garbage In Garbage Out.
Nonetheless, despite analysing the higher quality studies, there was no clear evidence that emerged that puberty blockers and cross-sex hormones were safe and effective. The BMJ editorial summed this up perfectly,
One emerging criticism of the Cass review is that it set the methodological bar too high for research to be included in its analysis and discarded too many studies on the basis of quality. In fact, the reality is different: studies in gender medicine fall woefully short in terms of methodological rigour; the methodological bar for gender medicine studies was set too low, generating research findings that are therefore hard to interpret. The methodological quality of research matters because a drug efficacy study in humans with an inappropriate or no control group is a potential breach of research ethics. Offering treatments without an adequate understanding of benefits and harms is unethical. All of this matters even more when the treatments are not trivial; puberty blockers and hormone therapies are major, life altering interventions. Yet this inconclusive and unacceptable evidence base was used to inform influential clinical guidelines, such as those of the World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH), which themselves were cascaded into the development of subsequent guidelines internationally.
-
Myth 2: Cass recommended no Trans Healthcare for Under 25s
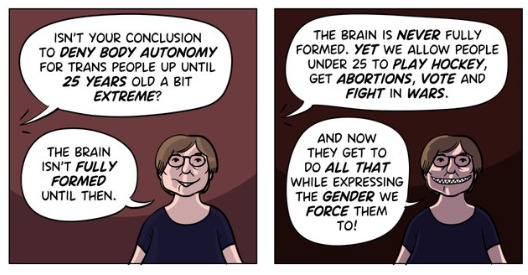
Fact
The Cass Review does not contain any recommendation or suggestion advocating for the withholding of transgender healthcare until the age of 25, nor does it propose a prohibition on individuals transitioning.
Explanation
This myth appears to be a misreading of one of the recommendations.
The Cass Review expressed concerns regarding the necessity for children to transition to adult service provision at the age of 18, a critical phase in their development and potential treatment. Children were deemed particularly vulnerable during this period, facing potential discontinuity of care as they transitioned to other clinics and care providers. Furthermore, the transition made follow-up of patients more challenging.
Cass then says,
Taking account of all the above issues, a follow-through service continuing up to age 25 would remove the need for transition at this vulnerable time and benefit both this younger population and the adult population. This will have the added benefit in the longer-term of also increasing the capacity of adult provision across the country as more gender services are established.
Cass want to set up continuity of service provision by ensure they remain within the same clinical setting and with the same care providers until they are 25. This says nothing about withdrawing any form of treatment that may be appropriate in the adult care pathway. Cass is explicit in saying her report is making no recommendations as to what that care should look like for over 18s.
It looks the myth has arisen from a bizarre misreading of the phrase “remove the need for transition”. Activists appear to think this means that there should be no “gender transition” whereas it is obvious this is referring to “care transition”.
-
Myth 3: Cass is demanding only Double Blind Randomised Controlled Trials be used as evidence in “Trans Healthcare”
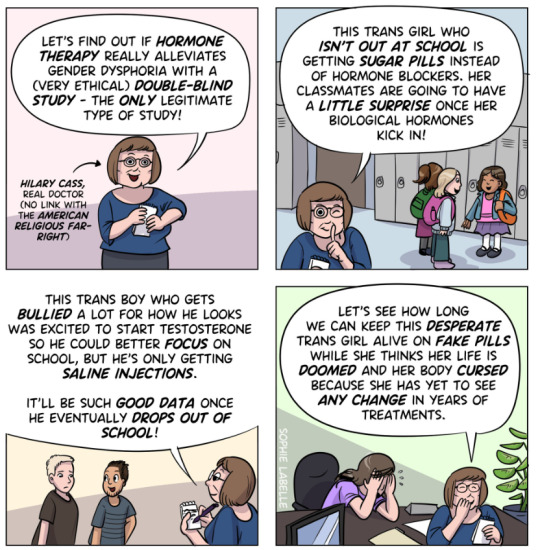
Fact
While it is acknowledged that conducting double-blind randomized controlled trials (DBRCT) for puberty blockers in children would present significant ethical and practical challenges, the Cass Review does not advocate solely for the use of DBRCT trials in making treatment recommendations, nor does it mandate that future trials adhere strictly to such protocols. Rather, the review extensively discusses the necessity for appropriate trial designs that are both ethical and practical, emphasizing the importance of maintaining high methodological quality.
Explanation
Cass goes into great detail explaining the nature of clinical evidence and how that can vary in quality depending on the trial design and how it is implemented and analysed. She sets out why Double Blind Randomised Controlled Trials are the ‘gold standard’ as they minimise the risks of confounding factors misleading you and helping to understand cause and effect, for example. (See Explanatory Box 1 in the Report).
Doctors rely on evidence to guide treatment decisions, which can be discussed with patients to facilitate informed choices considering the known benefits and risks of proposed treatments.
Evidence can range from a doctor’s personal experience to more formal sources. For instance, a doctor may draw on their own extensive experience treating patients, known as ‘Expert Opinion.’ While valuable, this method isn’t foolproof, as historical inaccuracies in medical beliefs have shown.
Consulting other doctors’ experiences, especially if documented in published case reports, can offer additional insight. However, these reports have limitations, such as their inability to establish causality between treatment and outcome. For example, if a patient with a bad back improves after swimming, it’s uncertain whether swimming directly caused the improvement or if the back would have healed naturally.
Further up the hierarchy of clinical evidence are papers that examine cohorts of patients, typically involving multiple case studies with statistical analysis. While offering better evidence, they still have potential biases and limitations.
This illustrates the ‘pyramid of clinical evidence,’ which categorises different types of evidence based on their quality and reliability in informing treatment decisions

The above diagram is published in the Cass Review as part of Explanatory Box 1.
We can see from the report and papers that Cass did not insist that only randomised controlled trials were used to assess the evidence. The York team that conducted the analyses chose a method to asses the quality of studies called the Newcastle Ottawa Scale. This is a method best suited for non RCT trials. Cass has selected an assessment method best suited for the nature of the available evidence rather than taken a dogmatic approach on the need for DBRCTs. The results of this method were discussed about countering Myth 1.
Explainer on the Newcastle Ottawa Scale
The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) is a tool designed to assess the quality of non-randomized studies, particularly observational studies such as cohort and case-control studies. It provides a structured method for evaluating the risk of bias in these types of studies and has become widely used in systematic reviews and meta-analyses.
The NOS consists of a set of criteria grouped into three main categories: selection of study groups, comparability of groups, and ascertainment of either the exposure or outcome of interest. Each category contains several items, and each item is scored based on predefined criteria. The total score indicates the overall quality of the study, with higher scores indicating lower risk of bias.
This scale is best applied when conducting systematic reviews or meta-analyses that include non-randomized studies. By using the NOS, researchers can objectively assess the quality of each study included in their review, allowing them to weigh the evidence appropriately and draw more reliable conclusions.
One of the strengths of the NOS is its flexibility and simplicity. It provides a standardized framework for evaluating study quality, yet it can be adapted to different study designs and research questions. Additionally, the NOS emphasizes key methodological aspects that are crucial for reducing bias in observational studies, such as appropriate selection of study participants and controlling for confounding factors.
Another advantage of the NOS is its widespread use and acceptance in the research community. Many systematic reviews and meta-analyses rely on the NOS to assess the quality of included studies, making it easier for researchers to compare and interpret findings across different studies.
As for future studies, Cass makes no demand only DBRCTs are conducted. What is highlighted is at the very least that service providers build a research capacity to fill in the evidence gaps.
The national infrastructure should be put in place to manage data collection and audit and this should be used to drive continuous quality improvement and research in an active learning environment.
-
Myth 4: There were less than 10 detransitioners out of 3499 patients in the Cass study.


Fact
Cass was unable to determine the detransition rate. Although the GIDS audit study recorded fewer than 10 detransitioners, clinics declined to provide information to the review that would have enabled linking a child’s treatment to their adult outcome. The low recorded rates must be due in part to insufficient data availability.
Explanation
Cass says, “The percentage of people treated with hormones who subsequently detransition remains unknown due to the lack of long-term follow-up studies, although there is suggestion that numbers are increasing.”
The reported number are going to be low for a number of reasons, as Cass describes:
Estimates of the percentage of individuals who embark on a medical pathway and subsequently have regrets or detransition are hard to determine from GDC clinic data alone.
There are several reasons for this:
Damningly, Cass describes the attempt by the review to establish “data linkage’ between records at the childhood gender clinics and adult services to look at longer term detransition and the clinics refused to cooperate with the Independent Review. The report notes the “…attempts to improve the evidence base have been thwarted by a lack of cooperation from the adult gender services”.
We know from other analyses of the data on detransitioning that the quality of data is exceptionally poor and the actual rates of detransition and regret are unknown. This is especially worrying when older data, such as reported in WPATH 7, suggest natural rates of decrease in dysphoria without treatment are very high.
Gender dysphoria during childhood does not inevitably continue into adulthood. Rather, in follow-up studies of prepubertal children (mainly boys) who were referred to clinics for assessment of gender dysphoria, the dysphoria persisted into adulthood for only 6–23% of children.
This suggests that active affirmative treatment may be locking in a trans identity into the majority of children who would otherwise desist with trans ideation and live unmedicated lives.
I shall add more myths as they become spread.
==
It's not so much "myths and misconceptions" as deliberate misinformation. Genderists are scrambling to prop up their faith-based beliefs the same way homeopaths do. Both are fraudulent.
#Andy L.#Cass Review#Cass Report#Dr. Hilary Cass#Hilary Cass#misinformation#myths#misconceptions#detrans#detransition#gender affirming healthcare#gender affirming care#gender affirmation#affirmation model#medical corruption#medical malpractice#medical scandal#systematic review#religion is a mental illness
146 notes
·
View notes
Text

#religion#dogma#atheist#science#bible nonsense#sun#universe#earth#ausgov#politas#auspol#tasgov#taspol#australia#fuck neoliberals#neoliberal capitalism#anthony albanese#albanese government#religion is a mental illness#religion is bullshit#religion is toxic#religion is a scam#religion is stupid#class war#bible scripture#bible quote#bible study#bible verse#bible#eat the rich
95K notes
·
View notes
Text

#religion is a mental illness#womens rights#health care#separation of church and state#USA#Christo-fascism
244 notes
·
View notes
Text

#religion and reason#bible#translation#william tyndale#1536#catholics#religion is a mental illness#religion is toxic#think for yourself#question everything#sunday sermon
366 notes
·
View notes
Text

87 notes
·
View notes
Text
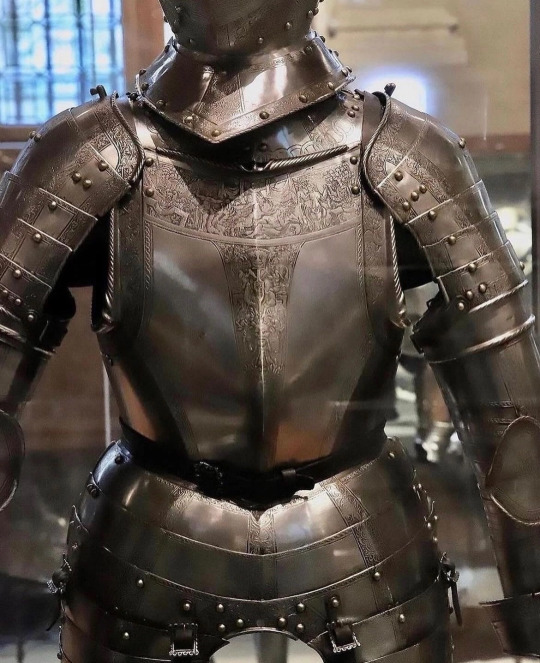
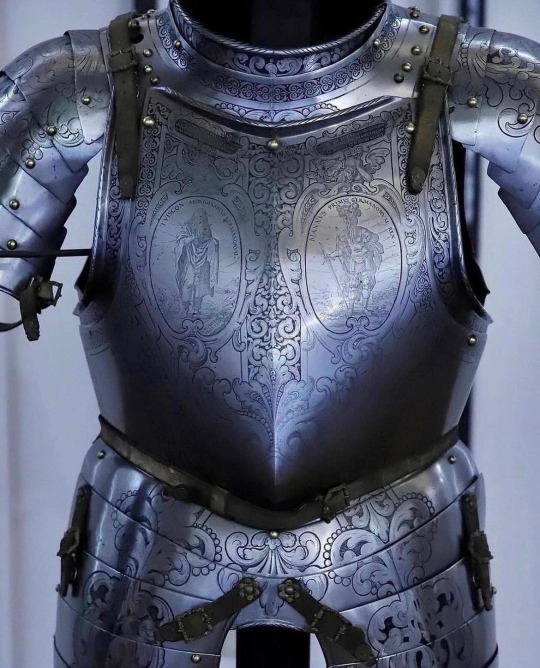
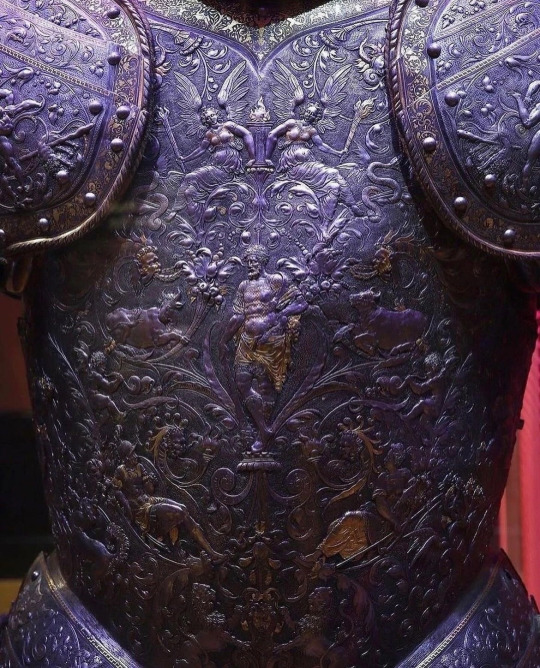
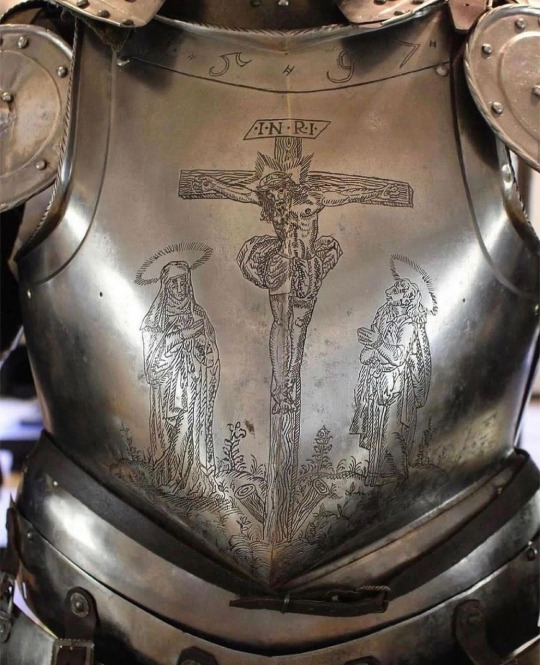






𝙱𝚎 𝚙𝚛𝚎𝚙𝚊𝚛𝚎𝚍:
16𝚝𝚑 𝚌𝚎𝚗𝚝𝚞𝚛𝚢 𝚔𝚗𝚒𝚐𝚑𝚝𝚜 𝚊𝚛𝚖𝚘𝚛 ⚔️ 🗡️ ✝️ ☮️
20202020 𝚋𝚢 𝚄𝚗𝚑𝚘𝚕𝚢
@bigbonzo
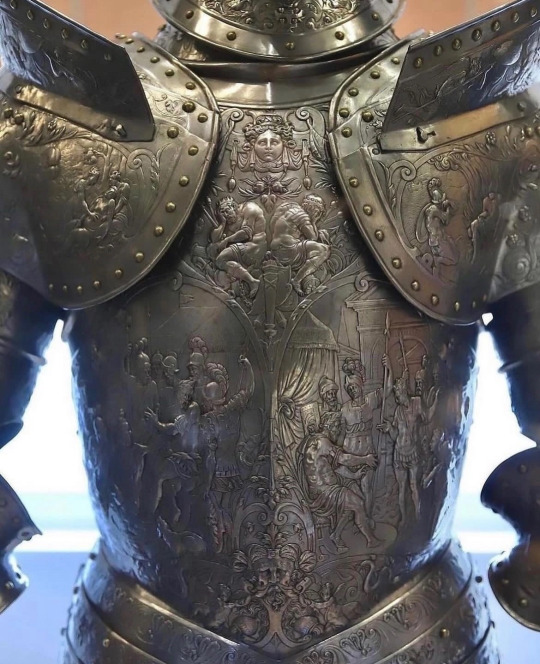

#fucking favorite#16th century#knights armor#knights#armor#be prepared#3/2024#history#historialex#fashion#Metal#im already against next war#vintage#Museum#kreuzzug#crusade#x-heesy#now playing#music and art#Metal armor#⚔️#🗡️#☮️#✝️#✝️umblr#religion is a mental illness
51 notes
·
View notes
Text
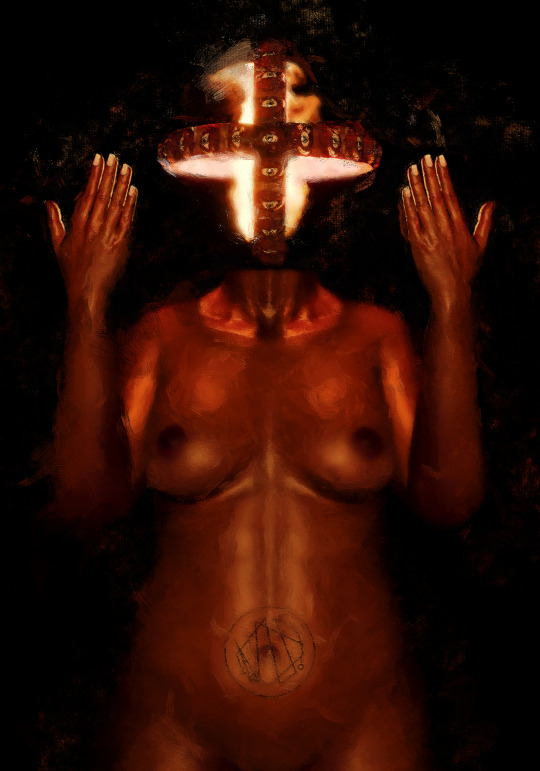
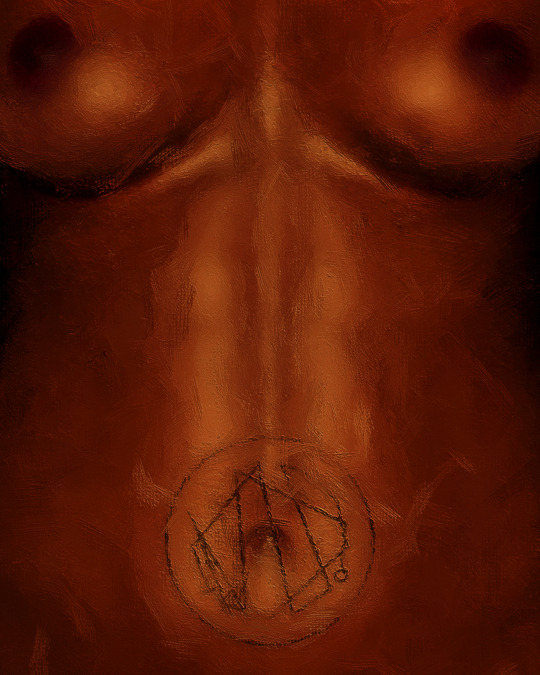





FLAMMA FURORIS
A portrait exploring rage, anger, and the struggle to control one's impulses.
Check the links in my bio for more 🔗 @artmajeur
#art#artists on tumblr#digital illustration#illustration#artwork#drawing#digital painting#digital art#darksurrealism#dark art#dark aesthetic#darkness#mysterious#dark urge#obsession#religion#religion is a mental illness#childhood trauma#mental health#mental illness#mentally fucked#struggle#life#experience#therapy#catharsis#black women#black beauty#female rage#demon
45 notes
·
View notes
Text
okay happy easter to her too
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
I am incredibly suspicious of progressives that don't think it is possible to separate a criticism of a religion from the people of that group. Because we do that everyday with white supremacy and patriarchy, RIGHT? We aren't anti-white for hating the concept of whiteness, nor are we man haters, RIGHT?. Just like we are against white supremacy and patriarchy partially because they are used to justify bigotries, we should be anti religion. Religion often reinforces those same bigotries and then adds more on top.
#atheism#anti theism#antitheistic#religion is a mental illness#anti religion#progressive politics#vaush#anti racism
32 notes
·
View notes
Text

"God either doesn't exist, is powerless, or is a huge asshole."
No matter which way you cut it, he's not worth worshipping.
His best defence for baby cancer would be not existing.
36 notes
·
View notes
Text

These pro-Hamas terrorist supporters claim to be "anti-war" and want a "ceasefire," while celebrating a (failed) attempt to eradicate Israel from the face of the Earth. Meaning, they're as "anti-war" as Antifa is "anti-fascist"; they're in favor of war/fascism when they do it.
These crazed fanatics support the brutal Islamic regime of Iran. You remember, the one that the citizens had an uprising against when Mahsa Amini was murdered. At the time, even the most left-wing ideologues finally got around to condemning the regime, albeit with the caveat that the fault lies with the regime, not with Islam, and scolded us not to be "Islamophobic" about it.
Now, far-left western terrorists are shouting "Allahu Akbar" and cheering for the same regime, having decided their goals line up with those of a far-right fundamentalist theocracy.
Given they're chanting "Allahu Akbar," any claim that this isn't about Islamic supremacy is completely dishonest. These people need to be removed from our societies before they destroy them and turn them into Islamic hellholes.
#ceasefire#antisemitism#Iran#israel#iran vs israel#anti war#islam#islamic regime#islamic republic of iran#iranian regime#islamic supremacy#religion#religion is a mental illness
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
By: Julian Adorney, Mark Johnson and Geoff Laughton
Published: Mar 23, 2024
In The Divine Conspiracy, Dallas Willard tells the story of a jet fighter pilot who was practicing high-speed maneuvers. As Willard puts it, “She turned the controls for what she thought was a steep ascent—and flew straight into the ground. She was unaware that she had been flying upside down.”
What if we were flying upside down? But let’s go further. What if an entire generation was flying upside down–flying through fog and danger, unable to see either ground or sky, and the well-intended adjustments pushed on them by “experts” were just bringing them closer to catastrophe?
That’s the lens through which we interpret Abigail Shrier’s New York Times bestseller Bad Therapy.
There’s no denying that the youngest generation is in crisis. As the Addiction Center notes, members of Generation Z “run a higher risk of developing a substance abuse problem than previous age groups.” A 2015 report found that 23.6 percent of 12th graders use illicit drugs. The American Psychological Association reports that just 45 percent of Gen Zers report that their mental health is “very good” or “excellent,” compared with 51 percent of Gen Xers and 70 percent of Boomers. A concerning 42 percent of Gen Zers have been diagnosed with a mental health condition, and an astounding 60 percent take medication to manage their mental health.
It gets worse. The rate of self-harm for girls age 10-14 increased over 300 percent from 2001 to 2019 (before the pandemic). According to a 2021 CDC survey, 1 in 3 teenage girls have seriously considered killing themselves.
Well-meaning therapists, teachers, and school counselors are trying to help the next generation to rise up. But what if everyone involved is upside down? What if, like the fighter pilot that Willard describes, what they think is rising up is actually bringing them into deeper danger? Shrier makes a strong case that that’s exactly what’s happening.
Lots of educators encourage kids to spend more time checking in with their feelings. In the 2021-2022 school year, 76 percent of principals said that their school had adopted a Social and Emotional Learning (SEL) curriculum. Common SEL practices include: asking students how they’re feeling at the start of each day, teaching that students should be more aware of how they’re feeling in any given moment, and encouraging students to use activities like writing and art to express their feelings.
The problem is that all of this obsession with feelings can actually make students feel worse. As Yulia Chentsova Dutton, head of the the Culture and Emotions Lab at Georgetown University, says, “Emotions are highly reactive to our attention to them.” “Certain kinds of attention to emotions, focus on emotions,” she explains, “can increase emotional distress. And I’m worried that when we try to help our young adults, help our children, what we do is throw oil into the fire.” Or to put it another way: when we ask kids over and over again how they’re feeling, we’re subtly and accidentally encouraging them to feel bad.
The reason is that, as psychiatry professor Michael Linden explains, most of us don’t feel happy all the time. Dealing with life involves ignoring a certain amount of moment-by-moment discomfort: I’m tired, my feet hurt, I’m sore from sitting down all day, I’m a little worried about my mom. When we encourage kids to check in many times per day on how they’re feeling, we’re tacitly encouraging them to bring to the surface–and then dwell on–all the things going on in their minds that are not “happiness.” That’s why, as Linden puts it, “Asking somebody ‘how are you feeling?’ is inducing negative feelings. You shouldn’t do that.”
But it gets worse.
Obsessing over our emotions can actually prevent us from doing the things that might make us feel better. Anyone who’s spent too long wallowing after a bad break-up knows this; at a certain point, you have to shelve your unpleasant emotions so that you can get on with your life. Psychologists describe two mental states that we can occupy at any given time: “action orientation” and “state orientation.” “State orientation” is where you focus primarily on yourself (e.g., how you feel about doing the task at hand, whether your wrist hurts or you’re starting to get sick, etc.). “Action orientation” is where you primarily focus on the task at hand. As a study published by Cambridge University Press notes, only the latter is actually conducive to pursuing and accomplishing goals. “State orientation is a personality that has difficulty in taking action toward goal fulfillment,” the authors warn. By encouraging young people to focus so much on their feelings, we might be hurting their ability to adopt the mindset necessary to accomplish goals in life. If so, that would make them even more unhappy.
But the dangers posed by well-meaning “experts” telling students to fly in the wrong direction–towards the ground instead of towards the sky–go well beyond encouraging unhappiness and depression. Rates of suicide and self-harm for young people are skyrocketing. But in their attempts to cope with the spike, well-meaning administrators might be making the problem worse. Here are questions from the 2021 Florida High School Youth Risk Behavior Survey, administered to students age 14 and up:
During the past 12 months, did you ever feel so sad or hopeless almost every day for two weeks or more in a row that you stopped doing your usual activities?
During the past 12 months, did you ever seriously consider attempting suicide?
During the past 12 months, did you make a plan about how you would attempt suicide?
During the past 12 months, how many times did you actually attempt suicide?
If you attempted suicide during the past 12 months, did any attempt result in an injury, poisoning, or overdose that had to be treated by a doctor or nurse?
A survey authored by the CDC asked students “During the past year, did you do something to purposely hurt yourself without wanting to die, such as cutting or burning yourself on purpose?” Another survey offered this question to Delaware middle schoolers: “Sometimes people feel so depressed about the future that they may consider attempting suicide or killing themselves. Have you ever seriously thought about killing yourself?”
Administrators may be asking these questions with the best of intentions, but the end result is to normalize suicide in young peoples’ minds. If you were 12 years old and taking a survey like this along with all of your classmates, you might reasonably conclude that suicide, or at least suicidal ideation and/or self harm, were pretty common at your school. Otherwise, why would everyone your age have to take such an exhaustive assessment about it?
One reason this is so dangerous is that, as Shrier writes, “The virality of suicide and self-harm among adolescents is extremely well-established.” Following the release of Netflix’s TV show 13 Reasons Why, which some said valorized a fictional girl who killed herself, several studies found a spike in teen suicide rates. The CDC agrees. In a post warning about the dangers of “suicide contagion,” the CDC said that journalists should avoid things like:
“Engaging in repetitive, ongoing, or excessive reporting of suicide in the news.”
“Reporting ‘how-to’ descriptions of suicide.”
“Presenting suicide as a tool for accomplishing certain ends” (i.e., as a “means of coping with personal problems”).
But this is most of what the surveys described above are doing. They are deluging students with repetitive and excessive discussion of suicide. They are describing different methods for killing yourself (e.g., cutting or burning yourself). One survey, which asks students who have considered killing themselves why they did so (possible answers include “demands of schoolwork,” “problems with peers or friends,” and “being bullied”) is a textbook example of presenting suicide as a “means of coping with personal problems.”
The authors of these surveys seem to at least recognize the risk that students are flying upside down, and that these surveys might take them closer to the ground. One survey concludes by telling students, “If any survey questions or your responses have caused you to feel uncomfortable or concerned and you would like to talk to someone about your feelings, talk to your school’s counselor, to a teacher, or to another adult you trust.” The survey also includes links to different hotlines.
Communicating to kids that suicide is normal and a possible solution to their problems might be the worst way that some schools are failing kids, but it’s also far from the only way.
Schools are increasingly lax about standards, willing to let almost anyone get away with almost anything. Some accommodations do make sense: for example, it makes sense to give a kid with dyslexia more time to complete the verbal component of the SAT. But Shrier argues that standards are falling for perfectly healthy students too. “School counselors—students’ in-school ‘advocates,’” Shrier writes, now “lobby teachers to excuse lateness or absence, forgive missed classwork, allow a student to take walks around the school in the middle of class, ratchet grades upward, reduce or eliminate homework requirements, offer oral exams in place of written ones, and provide preferential seating to students who lack even an official diagnosis.”
Shrier documents stories of students who have been allowed to turn in work late because they were having a “tough Mental Health Day” or because “I was having a rough day and dealing with my gender identity.”
The problem with this is that one of the primary things that children and teenagers do is try to figure out the boundaries of the world. When a child throws a tantrum, it’s not malicious–they’re trying to understand this new world and figure out what they can get away with. As Jordan Peterson writes in Twelve Rules for Life, young children are “like blind people, searching for a wall.” “They have to push forward, and test,” he writes, “to see where the actual boundaries lie.” What’s true of young children is also true of older children and even (to a lesser extent) adults. All of us are trying to figure out the rules of life–that is, what we can get away with. If well-meaning teachers and counselors tell students that one of the rules is that you don’t have to do your homework on time if you say that you’re having a rough day, then we shouldn’t be surprised when more young people seem to manifest rough days.
But this is the opposite of what students need–especially the truly disadvantaged students who so many of these efforts seem to be aimed at helping. In his memoir Troubled, clinical psychologist Rob Henderson writes that, “People think that if a young guy comes from a disorderly or deprived environment, he should be held to low standards.” But, he warns, “this is misguided. He should be held to high standards. Otherwise, he will sink to the level of his environment.”
So kids are depressed, anxious, and poorly behaved. Educators are trying to help them by encouraging them to tap in more to their feelings, by asking them more questions about suicide, and by trying to accommodate their difficulties even more. But all of this is backwards. Educators are encouraging students to do what they think will take them higher–away from the ground and back to the safety of the sky. But both kids and educators are upside down. And every adjustment that the “experts” are telling kids to make just brings them closer to the ground–and a catastrophic collision.
Now’s a good time to emphasize that this isn’t all schools, all teachers, or all administrators–not by a long shot. There are heroic educators working every day to help students to rein in their problems, stop taking advantage of accommodations that they don’t need, and develop the emotional resilience to deal with the problems of adolescence. But the problems documented above do represent a trend. And while it’s not every school, the trend is too big to ignore.
What will happen if this trend continues–if an entire generation keeps going “up” until they crash into the ground? Most severe and most damaging is the harm to the generation itself. Shrier tells the story of Nora, a 16-year-old girl who helps put a human face on all of the brutal statistics described in the introduction to this piece. Nora describes her friends as going through a litany of serious mental health problems: “anxiety,” “depression”; “self-harm” (as Shrier notes, “lots of self-harm”) including “Scratching, cutting, anorexia,” “Trichotillomania” (pulling your hair out by the roots); and more. As Shrier writes, “Dissociative identity disorder, gender dysphoria, autism spectrum disorder, and Tourette’s belong on her list of once-rare disorders that are, among this rising generation, suddenly not so rare at all.”
But the dangers can also ripple out beyond just one generation. The full danger may be nothing less than an imperiling of our democracy.
As Shrier notes, many kids in school are almost constantly monitored. Her own kids have “recess monitors” at their school–“teachers who involve themselves in every disagreement at playtime and warn kids whenever the monkey bars might be slick with rain.” On the bus home, they have “bus monitors.” Better that kids know they’re being observed by an adult at all times than that one kid push another to give him his lunch money.
One of the most pervasive forms of monitoring is what are called “shadows”—ed techs or paraeducators whose job is to cling closely to one particular student so that they don’t have any issues. The original intention certainly made sense. If a child had autism, a shadow could help the kid to integrate into the main classroom rather than being sent to Special Ed. But, as Shrier notes, scope creep has been substantial. “Today,” she writes, “public schools assign shadows to follow kids with problems ranging from mild learning disabilities to violent tendencies.” Nor is the problem restricted to public schools: “private schools advise affluent parents to hire shadows to trail neurotypical kids for almost any reason.” Shadows monitor and guide almost every interaction with their chosen student, from when to raise her hand to how long to hug a fellow student.
As Peter Gray, professor of psychology at Boston College and an expert on child development, puts it, “Kids today are always under the situation of an observer. At home, the parents are watching them. At school, they’re being observed by teachers. Out of school, they’re in adult-directed activities. They have almost no privacy.”
But when kids spend their entire waking lives being monitored by an adult, they start to think that kind of monitoring is normal. Worse, they start to think that they need it. If a child gets constant guidance from an adult, what are the odds that she’s going to cultivate her own independence? If she expects authoritarian adults to monitor and run every aspect of her life already, what is she going to think of a liberal democracy that more-or-less leaves people free to handle their own affairs?
No wonder just 27 percent of Americans age 18-25 strongly agree with the statement that “Democracy may have problems, but it is the best system of government” (compared to 48 percent of Americans as a whole).
So what’s the solution? If our kids are upside down and getting lower to the ground, then the only thing that makes sense is to help them reverse course. Is there something that’s the opposite of always asking them about their feelings, telling them that life is too much for them or their peers to cope with, and constantly telling them that they’re too fragile to do their homework if they’re having a rough day? Yes. That something is called antifragility.
Antifragility is the idea that whatever doesn’t kill you makes you stronger. As social psychologist Jonathan Haidt and president of the Foundation for Individual Rights and Expression Greg Lukianoff note in The Coddling of the American Mind, kids are naturally antifragile. That doesn’t just mean that they’re tough. It means that “they require stressors and challenges in order to learn, adapt, and grow.” Not letting a kid hand in homework late doesn’t just teach them to do their homework on time; it also teaches them that they can deal with a 0 in class and not die. They can pick themselves up, brush themselves off, and even earn an A in the class overall if they bust a sweat for the rest of the semester. Telling a kid who’s having a “tough mental health day” that you’re sorry to hear it but they still need to take today’s test doesn’t just teach the kid that low-level excuses don’t fly; it also teaches them that a hard day isn’t enough to stop them. It teaches them that they’re stronger than whatever negative emotions they’re currently experiencing.
It’s time to remind kids that they are strong–before it’s too late.
All quotes not otherwise attributed come from Abigail Shrier’s book Bad Therapy.
-
About the Authors
Julian Adorney is a Contributing Writer to FAIR’s Substack and the founder of Heal the West, a Substack movement dedicated to preserving and protecting Western civilization. You can find him on X at @Julian_Liberty.
Mark Johnson is a trusted advisor and executive coach at Pioneer Performance Partners and a facilitator and coach at The Undaunted Man. He has more than 25 years of experience optimizing people and companies. He blogs at The Undaunted Man’s Substack.
Geoff Laughton is a Relationship Architect/Coach, multiple-International Best-Selling Author, Speaker, and Workshop Leader. He is the founder of The Undaunted Man. He has spent the last twenty-six years coaching people world-wide, with a particular passion for supporting those in relationship, and helping men from all walks of life step up to their true potential.
#Julian Adorney#Mark Johnson#Geoff Laughton#Abigail Shrier#Bad Therapy#human psychology#psychology#emotions#emotional distress#feelings#antifragility#coddling#emotional fragility#religion is a mental illness
19 notes
·
View notes
Text

An interesting demonstration of how the human brain works.
But also something of a lesson regarding perception, and the unreliability of subjective perspective versus objective reality.
You can be extremely certain about how you perceive the world, your "lived experience," that which you "feel it in my heart." But that doesn't mean it's actually true. And it doesn't mean we have to endorse it, or ignore or outright deny objective reality.
That's a "you" thing, not a "we" thing.
#Adelbert Ames#Ames Window#perception#perspective#objective reality#lived experience#i feel it in my heart#subjective experience#The Curiosity Show#science#optical illusion#religion is a mental illness
31K notes
·
View notes
Text

7K notes
·
View notes
Text



2K notes
·
View notes