Text
#Uterine Artery Embolisation (UAE) And Ablation#interventionalradiologistindelhi#uterinefibroidtreatmentindelhi#pinholesurgeryindelhi#uterinearteryembolizationtreatmentdelhi#lymphangiographytreatmentindelhi#thyroidablationtreatmentindelhi#health & fitness#paetreatmentindelhi#taretreatmentindelhi#bphtreatmentindelhi
0 notes
Text
#interventionalradiologistindelhi#uterinefibroidtreatmentindelhi#uterinearteryembolizationtreatmentdelhi#bphtreatmentindelhi#pinholesurgeryindelhi#thyroidablationtreatmentindelhi#paetreatmentindelhi#lymphangiographytreatmentindelhi#taretreatmentindelhi
0 notes
Text
Liver Tumor Treatment, Transarterial chemoembolization, Transarterial Radioembolization
Liver Tumor Treatment
Explore this section to learn more about liver cancer, including a description of the disease and how it's diagnosed.
Liver cancer Liver cancer
Why is the liver important?
What is liver cancer?
What causes liver cancer?
What are the symptoms of liver cancer?
How is liver cancer diagnosed?
How is liver cancer treated?
What is the outlook for patients with liver cancer?
What is the best way to reduce the risk of liver cancer?
Related Terms
Why is the liver important?
The liver is the second most important organ in your body and is located on the right side. The liver performs many jobs in your body. It processes what you eat and drink into energy and nutrients that it stores for your body to use. The liver also removes harmful substances from your blood.
What is liver cancer?
Liver cancer is the growth and spread of unhealthy cells in the liver. Cancer that starts in the liver is called primary liver cancer. Cancer that spreads to the liver from another organ is called metastatic liver cancer.
What causes liver cancer?
There are several risk factors for liver cancer:
Long-term hepatitis B and hepatitis C infection are linked to liver cancer because they often lead to cirrhosis. Hepatitis B can lead to liver cancer without cirrhosis.
Excessive alcohol use.
Obesity and diabetes are closely associated with a type of liver abnormality called nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) that may increase the risk of liver cancer, especially in those who drink heavily or have viral hepatitis.
Certain inherited metabolic diseases.
Environmental exposure to aflatoxins.
What are the symptoms of liver cancer?
Symptoms may include fatigue, bloating, pain on the right side of the upper abdomen or back and shoulder, nausea, loss of appetite, feelings of fullness, weight loss, weakness, fever, and jaundice (yellowing of the eyes and the skin).
How is liver cancer diagnosed?
A physical examination or imaging tests may suggest liver cancer. To confirm a diagnosis, blood tests, ultrasound tests, computed tomography (CT) scans, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and angiogram needed. Sometimes when picture remains unclear you may also need to get a liver biopsy. During a biopsy, a small piece of liver tissue is removed and studied in the lab.
How is liver cancer treated?
Liver cancerLiver cancer
Liver cancer treatment depends on:
If the cancer has spread outside the liver
The person's age and overall health
Treatment options if the cancer has not spread and the rest of the liver is healthy are:
Transplant: If the cancer has not spread, for some patients a liver transplant (replacement of the liver) may be an option.
Surgery: If the cancer has been found early and the rest of the liver is healthy, doctors may perform surgery to remove the tumor from the liver (partial hepatectomy).
Radiofrequency/Microwave Ablation: Radiofrequency ablation uses a special probe to destroy cancer cells with heat.
Other treatment options if surgery and transplant are not possible include:
For cancer that has not spread outside the liver:
Bland embolization or chemoembolization are procedures in which the blood supply to the tumor is blocked, after giving anticancer drugs (chemoembolization) and one without (bland embolization). Both are given in blood vessels near the tumor.
Internal Radiation therapy (TARE) uses Y-90 particles that emits beta radiation to destroy cancer cells.
For cancer that has spread outside the liver:
Oral medication is available for use in some cases of hepatocellular carcinoma(the most common type of primary liver cancer).
Clinical trials may be an option for some patients.
Talk to your doctor about other options that may be available.
What is the outlook for patients with liver cancer?
A successful liver transplant will effectively cure liver cancer, but it is an option for only a small percentage of patients. Surgical resections are successful in only about one out of three cases. However, scientists are experimenting with several promising new drugs and therapies that could help prolong the lives of people with liver cancer.
What is the best way to reduce the risk of liver cancer?
Steps to reduce the risk of liver cancer include:
Regularly see a doctor who specializes in liver disease
Talk to your doctor about viral hepatitis prevention, including hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccinations
Take steps to prevent exposure to hepatitis B and hepatitis C.
If you have cirrhosis or chronic liver disease, follow your doctor's recommendations for treatment and be screened regularly for liver cancer
If you are overweight or obese, diabetic, or drink heavily, talk to your doctor
For more information-http://www.interventionalradiologyindia.com/
Tag- Liver Tumor Treatment, Transarterial chemoembolization, Transarterial Radioembolization, Tare Treatment in Delhi"
#Liver Tumor Treatment#Transarterial chemoembolization#Transarterial Radioembolization#Tare Treatment in Delhi"
0 notes
Text
#Interventional Radiologist in Delhi#pinholesurgeryindelhi#lymphangiographytreatmentindelhi#interventionalradiologistindelhi#bphtreatmentindelhi#taretreatmentindelhi#uterinearteryembolizationtreatmentdelhi
0 notes
Text
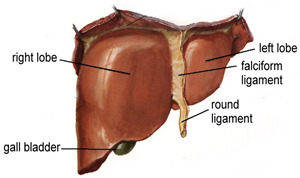
Liver Cancer
Get more information about Liver Tumour Treatment, Transarterial chemoembolization, Transarterial Radioembolization ( Tare ). Book an Appointment online now with Interventional Radiologist
0 notes
Text
Interventional radiologists perform a wide range of procedures, including: Laser Treatment of Varicose Veins, Uterine Artery Embolization, Biliary Stenting, Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization, Pre and post liver transplant, Renal Procedures, Portal Hypertension, GI bleed etc.
0 notes
Text
Uterine Artery Embolization For Fibroids | Uterine fibroid treatment in Delhi
Uterine Artery Embolisation (UAE) And Ablation
It is a minimally invasive treatment for uterine fibroids, noncancerous growths in the uterus. It uses a common femoral artery puncture. Super selective embolisation of Uterine arteries is done to block the fibroid blood vessels, starving the fibroids and causing them to shrink and die.
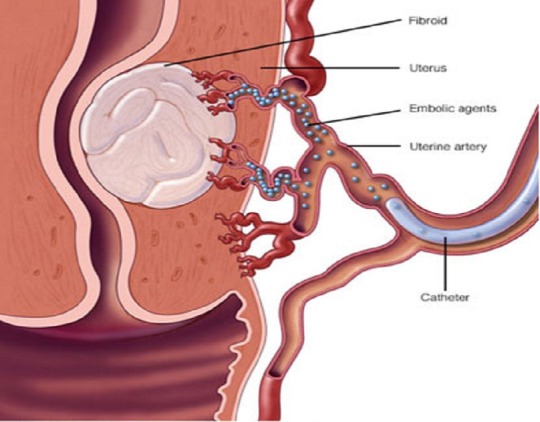
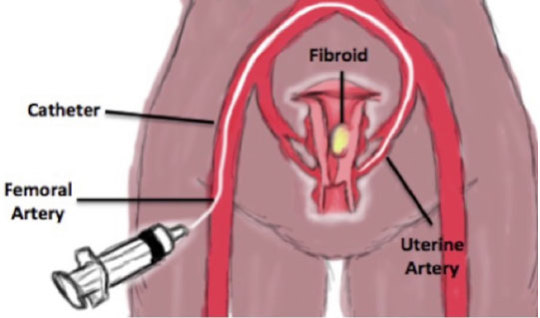
Why (Indications)?
Large fibroids with bulky uterus causing increased frequency of urine, pain , increased and heavy menstruation.
Adenomyosis
Uterine AVM
RPOC (retained products of conception)
Why Not (Contraindications)?
Avoid uterine artery embolization if you:
Are pregnant
Have possible pelvic cancer
Have an active, recent or chronic pelvic infection
Are allergic to contrast material containing iodine
What you are to do before procedure (Preparation)?
Book prior appointment if elective or get admission in causality if emergency
Lab investigation (*PT/INR, CBC, Serum Creatinine, Viral markers) and previous records. An MRI or ultrasound of the prostate gland.
Urine test (urinalysis)
4-6 Hours fasting.
If you are on blood thinner like Aspirin inform during appointment.
One accompanying person
Need to sign a consent form for procedure
Approx. Stay in hospital?
We have very fast and competent working team (Consultant, fellow, clinical assistant, technician and ward assistant) which provide you comfortable atmosphere and ease your nerves. Usual time of stay is around 1 day.
Complications
Mild Pain (usually ends within a day or two). In some patients pain may last for few weeks.
Vaginal discharge.
Post-embolization syndrome — characterized by low-grade fever, pain, fatigue, nausea and vomiting — about 48 hours after the procedure and usually resolve on its own within a week.
Resume to work?
You can resume your work after 2-3 days if existing disease allows.
Results?
Symptoms such as heavy bleeding, urinary incontinence and abdominal enlargement are relieved in the first three months after treatment. These results appear to be comparable to that of myomectomy, in which the fibroids are surgically removed and the uterus repaired.
Your menstrual period may continue on its normal schedule. If you miss any periods, they will probably resume within a few months.
There is low risk of subtle ovarian damage which may make getting pregnant more difficult. Despite these risks, many women have had successful pregnancies after uterine artery embolization.
Ablation
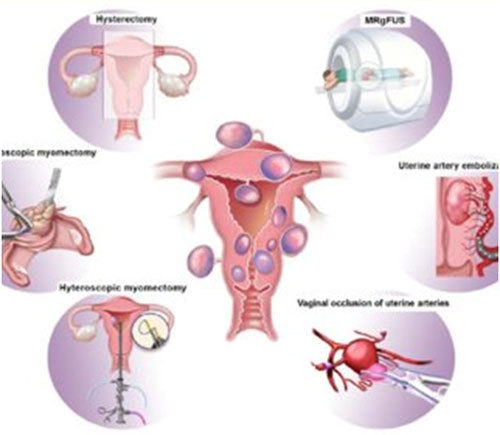
What is it?
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and microwave ablation (MWA) are treatments that use image guidance to place a needle through the skin into fibroid
In RFA, high-frequency electrical currents are passed through an electrode in the needle, creating a small region of heat.
In MWA, microwaves are created from the needle to create a small region of heat. The heat destroys the liver cancer cells.
RFA and MWA are effective treatment options for patients who might have difficulty with surgery
The success rate is greater than 85 percent.
For more information- http://www.interventionalradiologyindia.com/
Tag- Uterine fibroid treatment in Delhi, Uterine Artery Embolization For Fibroids, Interventional Radiologist in Delhi, Uterine artery embolization treatment Delhi
#UterinefibroidtreatmentinDelhi#UterinearteryembolizationtreatmentDelhi#uterinefibroidtreatmentindelhi#uterinearteryembolizationtreatmentdelhi#interventionalradiologistindelhi
0 notes
Text

Dr. Arun Gupta
(Chairperson Department of Interventional Radiologist)
Dr Arun Gupta did his Masters in Radio Diagnosis from Ganesh Shanker Vidyarthi Medical (GSVM) College, Kanpur in 2002. He pursued super-specialization training during his Senior Residency (SR) in Interventional Radiology from Sanjay Gandhi Post Graduate Institute (SGPGI), Lucknow till 2005.
#BPH Treatment in Delhi#InterventionalRadiologistinDelhi#ThyroidablationtreatmentinDelhi#ProstateEmbolizationtreatmentinDelhi#UterinefibroidtreatmentinDelhi#PinholesurgeryinDelhi
0 notes
Text

#ProstateEmbolizationtreatmentinDelhi#UterinefibroidtreatmentinDelhi#UterinearteryembolizationtreatmentDelhi#ThyroidablationtreatmentinDelhi#InterventionalRadiologistinDelhi#PinholesurgeryinDelhi#BPHTreatmentinDelhi#TARETreatmentinDelhi#LymphangiographyTreatmentinDelhi#PAETreatmentinDelhi
0 notes
Text
#ProstateEmbolizationtreatmentinDelhi#UterinefibroidtreatmentinDelhi#UterinearteryembolizationtreatmentDelhi#ThyroidablationtreatmentinDelhi#InterventionalRadiologistinDelhi#PinholesurgeryinDelhi#BPHTreatmentinDelhi#TARETreatmentinDelhi#LymphangiographyTreatmentinDelhi#PAETreatmentinDelhi
0 notes
Text
Arun Gupta - Interventional Radiologist in Delhi

Dr. Arun Gupta (Chairperson Department of Interventional Radiologist)
Dr Arun Gupta did his Masters in Radio Diagnosis from Ganesh Shanker Vidyarthi Medical (GSVM) College, Kanpur in 2002. He pursued super-specialization training during his Senior Residency (SR) in Interventional Radiology from Sanjay Gandhi Post Graduate Institute (SGPGI), Lucknow till 2005.
In 2006, he joined Sir Ganga Ram Hospital as a Consultant and established Department of Interventional Radiology and presently is the Chairperson of the Department at the hospital. Under the capable leadership of Dr. Arun Gupta, the Department of Interventional Radiology, Sir Ganga Ram Hospital has reached new heights and continuously working for advancement and meteoric rise of the department.
Dr. Gupta is an international figure and a key opinion leader in the country in field of Interventional Radiology with numerous International and National paper publications, paper presentations and has taken national as well as international guest lectures. He is the Vice-President of the Indian Society of Vascular and Interventional Radiology and Member of Asia Pacific Society of Cardio-Vascular Interventional Radiology.
Dr. Arun Gupta has special academic interest in the Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and has one of the largest experiences in the country on Trans-arterial Chemo Embolization and has done a lot of research in this field. He also has one of the largest series of embolization for management of Hepatic Artery Pseudo-aneurysms. He is the First to perform Percutaneous Hepatico-gastrostomy in case of Portal Biliopathy all over the world.
He has excellent organisational skills and is involved in all academic and clinical activities of the department. He is a vision oriented person with the highest professional standards and has contributed largely to the development and recognition of Interventional Radiology in India. He also has established a comprehensive training program for Interventional Radiologists which can be implemented across the country to enhance patient care. He also wants to create an environment where healthcare costs can be reduced and treatment for diseases can be made more affordable to the masses.
For more information-www.interventionalradiologyindia.com
Tag-Interventional Radiologist in Delhi, Interventional Radiologist Near Me, Interventional Radiologist Near By
#InterventionalRadiologistinDelhi#ProstateEmbolizationtreatmentinDelhi#UterinefibroidtreatmentinDelhi#UterinearteryembolizationtreatmentDelhi#PinholesurgeryinDelhi#BPHTreatmentinDelhi#TARETreatmentinDelhi#LymphangiographyTreatmentinDelhi#PAETreatmentinDelhi
0 notes
Text
Dr. Ajit Yadav, MBBS,DNB (Radiodiagnosis) - Interventional Radiologist in Delhi

Dr. Ajit Yadav MBBS,DNB (Radiodiagnosis)
Dr. Ajit K Yadav is consultant at Department of Interventional radiology, Sir Gangaram Hospital, New Delhi. After receiving a medical degree at the Pt BDS PGIMS, Rohtak, he served as medical officer at rural government hospital for 6 months. He completed residency training in radiodiagnosis at Sir Gangaram Hospital. He was national board certified in 2011, and went on to complete a fellowship in Interventional Radiology at GRIPMER, Delhi. He also visited MD Anderson cancer center, Houston, Texas, USA for short term fellowship in 2013. He attended short training programme on TACE at Seoul National University Hospital, South Korea in 2014. Dr. Yadav’s clinical interests include uterine artery embolization for minimally invasive treatment of uterine fibroids and post-partum hemorrhage, Bronchial artery embolization for hemoptysis, minimally invasive oncologic interventions (including transarterial chemoembolization, radioembolization and radiofrequency tumor ablation), and percutaneous interventions. In addition, he offers minimal invasive procedures for various diseases like Benign prostatic hyperplasia, Varicose veins, Liver diseases and traumatic bleeding.
His research interests include interventional treatment of liver malignancy, a topic in which he has written peer reviewed publications. He has authored more than 15 papers in the field of interventional radiology. He has also presented his work in numerous national and International meetings. In addition to clinical activities, he is an active teacher of residents including Interventional Radiology fellows.
He is a member of several professional organizations, Indian Radiological and Imaging Association (IRIA), Indian Society of Vascular and Interventional Radiology (ISVIR), and the Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe (CIRSE). He is actively involved in Delhi chapter of ISVIR.
For more information- http://www.interventionalradiologyindia.com/
Tag- Interventional Radiologist in Delhi, Uterine fibroid treatment in Delhi, Pin hole surgery in Delhi
#Dr. AjitYadav#InterventionalRadiologistinDelhi#UterinefibroidtreatmentinDelhi#PinholesurgeryinDelhi#ProstateEmbolizationtreatmentinDelhi#UterinearteryembolizationtreatmentDelhi
2 notes
·
View notes