#Transarterial Radioembolization
Text
What is Transarterial Radioembolization (TARE)
Transarterial Radioembolization (TARE) is also simply known as Radioembolization is a combination of Radiation Therapy and a procedure known as Embolization – a minimally invasive treatment in which blood vessels are blocked off to prevent blood flow.
Know more at:
0 notes
Text
Liver Tumor Treatment, Transarterial chemoembolization, Transarterial Radioembolization
Liver Tumor Treatment
Explore this section to learn more about liver cancer, including a description of the disease and how it's diagnosed.
Liver cancer Liver cancer
Why is the liver important?
What is liver cancer?
What causes liver cancer?
What are the symptoms of liver cancer?
How is liver cancer diagnosed?
How is liver cancer treated?
What is the outlook for patients with liver cancer?
What is the best way to reduce the risk of liver cancer?
Related Terms
Why is the liver important?
The liver is the second most important organ in your body and is located on the right side. The liver performs many jobs in your body. It processes what you eat and drink into energy and nutrients that it stores for your body to use. The liver also removes harmful substances from your blood.
What is liver cancer?
Liver cancer is the growth and spread of unhealthy cells in the liver. Cancer that starts in the liver is called primary liver cancer. Cancer that spreads to the liver from another organ is called metastatic liver cancer.
What causes liver cancer?
There are several risk factors for liver cancer:
Long-term hepatitis B and hepatitis C infection are linked to liver cancer because they often lead to cirrhosis. Hepatitis B can lead to liver cancer without cirrhosis.
Excessive alcohol use.
Obesity and diabetes are closely associated with a type of liver abnormality called nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) that may increase the risk of liver cancer, especially in those who drink heavily or have viral hepatitis.
Certain inherited metabolic diseases.
Environmental exposure to aflatoxins.
What are the symptoms of liver cancer?
Symptoms may include fatigue, bloating, pain on the right side of the upper abdomen or back and shoulder, nausea, loss of appetite, feelings of fullness, weight loss, weakness, fever, and jaundice (yellowing of the eyes and the skin).
How is liver cancer diagnosed?
A physical examination or imaging tests may suggest liver cancer. To confirm a diagnosis, blood tests, ultrasound tests, computed tomography (CT) scans, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and angiogram needed. Sometimes when picture remains unclear you may also need to get a liver biopsy. During a biopsy, a small piece of liver tissue is removed and studied in the lab.
How is liver cancer treated?
Liver cancerLiver cancer
Liver cancer treatment depends on:
If the cancer has spread outside the liver
The person's age and overall health
Treatment options if the cancer has not spread and the rest of the liver is healthy are:
Transplant: If the cancer has not spread, for some patients a liver transplant (replacement of the liver) may be an option.
Surgery: If the cancer has been found early and the rest of the liver is healthy, doctors may perform surgery to remove the tumor from the liver (partial hepatectomy).
Radiofrequency/Microwave Ablation: Radiofrequency ablation uses a special probe to destroy cancer cells with heat.
Other treatment options if surgery and transplant are not possible include:
For cancer that has not spread outside the liver:
Bland embolization or chemoembolization are procedures in which the blood supply to the tumor is blocked, after giving anticancer drugs (chemoembolization) and one without (bland embolization). Both are given in blood vessels near the tumor.
Internal Radiation therapy (TARE) uses Y-90 particles that emits beta radiation to destroy cancer cells.
For cancer that has spread outside the liver:
Oral medication is available for use in some cases of hepatocellular carcinoma(the most common type of primary liver cancer).
Clinical trials may be an option for some patients.
Talk to your doctor about other options that may be available.
What is the outlook for patients with liver cancer?
A successful liver transplant will effectively cure liver cancer, but it is an option for only a small percentage of patients. Surgical resections are successful in only about one out of three cases. However, scientists are experimenting with several promising new drugs and therapies that could help prolong the lives of people with liver cancer.
What is the best way to reduce the risk of liver cancer?
Steps to reduce the risk of liver cancer include:
Regularly see a doctor who specializes in liver disease
Talk to your doctor about viral hepatitis prevention, including hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccinations
Take steps to prevent exposure to hepatitis B and hepatitis C.
If you have cirrhosis or chronic liver disease, follow your doctor's recommendations for treatment and be screened regularly for liver cancer
If you are overweight or obese, diabetic, or drink heavily, talk to your doctor
For more information-http://www.interventionalradiologyindia.com/
Tag- Liver Tumor Treatment, Transarterial chemoembolization, Transarterial Radioembolization, Tare Treatment in Delhi"
#Liver Tumor Treatment#Transarterial chemoembolization#Transarterial Radioembolization#Tare Treatment in Delhi"
0 notes
Text
Dr. Jeff Geschwind Pioneering Advances in Vascular and Interventional Radiology
Dr. Jeff Geschwind stands at the forefront of medical innovation, renowned for his groundbreaking contributions to vascular and interventional radiology. With a distinguished career spanning decades, Dr. Geschwind has revolutionized patient care through his expertise, research, and leadership in the field. From his formative years at Boston University School of Medicine to his residency at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), and fellowship at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Dr. Geschwind's journey has been marked by a relentless pursuit of excellence and a commitment to advancing medical science.
Early Years and Education:
Born with a natural curiosity and passion for medicine, Dr. Jeff Geschwind embarked on his academic journey at Boston University School of Medicine, where he earned his Medical Degree. It was during these formative years that he developed a keen interest in diagnostic radiology, recognizing its potential to transform patient care through minimally invasive procedures.
Residency Training at UCSF:
Dr. Geschwind's quest for excellence led him to the University of California, San Francisco, where he completed his residency training in Diagnostic Radiology. His exceptional skills and dedication were soon recognized, earning him the prestigious position of Resident-Scholar sponsored by the National Institutes of Health (NIH). This unique opportunity allowed Dr. Geschwind to immerse himself in cutting-edge research while honing his clinical expertise under the guidance of world-renowned experts.
Fellowship in Vascular and Interventional Radiology at Johns Hopkins:
Driven by a desire to push the boundaries of medical innovation, Dr. Geschwind pursued fellowship training in Vascular and Interventional Radiology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. Here, he had the privilege of learning from pioneers in the field and gaining hands-on experience in performing complex procedures that would shape the future of interventional radiology.
Contributions to Medical Science:
Throughout his career, Dr. Jeff Geschwind has been a trailblazer in vascular and interventional radiology, spearheading numerous advancements that have transformed patient care. His research has encompassed a wide range of topics, from the development of novel imaging techniques to the refinement of minimally invasive procedures for the treatment of vascular diseases, liver cancer, and beyond.
One of Dr. Geschwind's most significant contributions lies in the field of interventional oncology, where he has pioneered innovative approaches for the treatment of liver cancer. His groundbreaking work on transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and radioembolization has revolutionized the management of hepatocellular carcinoma, offering patients new hope and improved outcomes.
In addition to his research endeavors, Dr. Geschwind is widely recognized for his leadership in academic medicine. He has served in various leadership roles, including as the Director of Interventional Radiology at Johns Hopkins Hospital and as the President of the Society of Interventional Radiology (SIR). Through his visionary leadership, Dr. Geschwind has inspired countless colleagues and trainees to pursue excellence in patient care, research, and education.
Legacy and Future Directions:
As Dr. Jeff Geschwind continues to push the boundaries of medical science, his legacy looms large in the field of vascular and interventional radiology. His relentless pursuit of innovation and his unwavering commitment to improving patient outcomes serve as a beacon of inspiration for future generations of medical professionals.
Looking ahead, Dr. Geschwind remains dedicated to advancing the frontiers of medical knowledge, with a particular focus on harnessing the power of precision medicine and personalized therapies. Through ongoing research and collaboration, he seeks to usher in a new era of patient-centered care, where every individual receives tailored treatments based on their unique genetic makeup and disease characteristics.
In conclusion, Dr. Jeff Geschwind's remarkable career embodies the spirit of innovation and excellence that defines modern medicine. From his early days as a medical student to his current role as a leader in the field of vascular and interventional radiology, Dr. Geschwind has left an indelible mark on the medical community and continues to shape the future of healthcare through his pioneering work.
0 notes
Text
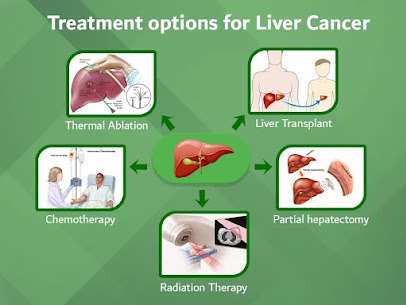
Treatment options for liver cancer
Surgery: Surgical options for liver cancer depend on the stage and location of the tumor. In early stages, surgical resection, where the tumor and surrounding tissue are removed, may be an option. For more advanced cases, liver transplantation might be considered for select patients.
Ablation Therapy: This minimally invasive technique involves destroying cancerous cells using heat (radiofrequency ablation) or cold (cryoablation). It's suitable for small tumors and for patients who are not good candidates for surgery.
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy involves using drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing. For liver cancer, chemotherapy can be given orally or through intravenous infusion. It may be used as a primary treatment, particularly for advanced cases, or in combination with other therapies.
Targeted Therapy: Targeted therapy drugs work by targeting specific abnormalities within cancer cells that allow them to grow and survive. These drugs may be used alone or in combination with other treatments for liver cancer, particularly for cases where surgery is not an option.
Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy helps the body's immune system fight cancer. This treatment option is relatively new for liver cancer but shows promise, especially for cases where other treatments haven't been effective.
Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to kill cancer cells. It can be used externally, where a machine outside the body directs radiation toward the cancer, or internally (brachytherapy), where radioactive material is placed directly into or near the tumor.
Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE): TACE is a procedure where chemotherapy drugs are directly delivered into the blood vessels feeding the tumor, followed by blocking the vessels to cut off the tumor's blood supply. It's commonly used for liver cancer that can't be surgically removed.
Radioembolization: In this procedure, tiny radioactive beads are injected directly into the blood vessels supplying the tumor. These beads emit radiation, targeting the cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue. It's often used for patients with advanced liver cancer.
Clinical Trials: Participation in clinical trials may offer access to experimental treatments that are not yet widely available. These trials aim to test new therapies or combinations of therapies to improve outcomes for liver cancer patients.
Palliative Care: Palliative care focuses on improving the quality of life for patients with advanced liver cancer by managing symptoms and providing support. It can be integrated with other treatments or used alone for patients who are not candidates for aggressive therapies.
Book an appointment with Dr. Sushil Kumar Jain, He is one of the most experienced Gastroenterologists in Jaipur, having more than 16+ years of experience in this field. provide world-class treatment for gastro and liver diseases at ACE Gastro Super-Speciality Clinic. You can directly book an appointment at 94620 67445.
#gastroenterologist#drsushilkumarjain#gastroenterologistindia#liver specialist in jaipur#gastroenterologist in jaipur
0 notes
Text
Leading the Way: Trusted Primary Liver Cancer Treatment Centers
Advanced Therapies:
Trusted primary liver cancer treatment center are at the forefront of innovation, continuously exploring and implementing advanced therapies to combat the disease. These therapies may include:
Surgical Interventions:
Skilled surgical teams proficient in liver resections, liver transplants, and minimally invasive procedures like radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and microwave ablation.
Locoregional Therapies:
Expertise in locoregional therapies such as transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), radioembolization (TARE), and percutaneous ethanol injection (PEI), aimed at targeting cancerous cells directly within the liver.
Systemic Treatments:
Access to systemic treatments including chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and emerging molecularly targeted agents, tailored to individual patient profiles.
Multidisciplinary Approach:
Trusted primary liver cancer treatment centers adopt a multidisciplinary approach, bringing together a diverse team of specialists to develop personalized treatment plans. These teams typically consist of hepatologists, surgical oncologists, interventional radiologists, medical oncologists, pathologists, and supportive care professionals. Collaboration among these experts ensures comprehensive evaluation, accurate staging, and optimal treatment selection, considering factors such as tumor size, location, and overall patient health.
Cutting-Edge Technology:
Equipped with cutting-edge technology, these centers utilize state-of-the-art imaging modalities for accurate diagnosis and precise treatment delivery. Advanced imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), positron emission tomography (PET), and angiography enable detailed assessment of liver tumors, facilitating personalized treatment strategies. Additionally, innovative radiation therapy platforms like stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) offer precise tumor targeting while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
Clinical Trials and Research:
Trusted primary liver cancer treatment centers actively engage in clinical trials and research endeavors, striving to advance treatment options and improve patient outcomes. Participation in clinical trials allows patients access to novel therapies and investigational drugs not yet available to the general public. Additionally, ongoing research initiatives contribute to a deeper understanding of liver cancer biology, leading to the development of more effective treatment strategies in the future.
Comprehensive Support Services:
Recognizing the holistic needs of patients and their families, trusted primary liver cancer treatment centers offer comprehensive support services. These services may include nutritional counseling, pain management, psychosocial support, palliative care, and survivorship programs. Patient navigators and care coordinators assist individuals throughout their treatment journey, ensuring seamless coordination of care and addressing any concerns or questions that may arise.
Empowering Patients:
Central to the mission of trusted primary liver cancer treatment centers is the empowerment of patients through education and support. integrative cancer treatment california Patients are actively involved in decision-making processes, equipped with the knowledge needed to understand their diagnosis, treatment options, and potential side effects. Educational resources, support groups, and survivorship programs foster a sense of community and resilience among patients, empowering them to navigate their cancer journey with confidence and hope.

0 notes
Text
7 Major Risk Factors of liver cancer in India
In India October month is celebrated as liver cancer awareness month and the cases of liver cancer is rising in India in the last few years rapidly. A study published in the Journal of Hepatology in October last year warned that by 2040, the annual number of new cases and deaths is predicted to increase by more than 55 per cent. In India, the primary reason for the prevalence of liver cancer in India is the increase in Hepatitis B & C infected population. Due to we need to raising awareness about liver health and working towards a world where liver disease is no longer a leading cause of death. Dr. Pratik Patil Medical oncologist in Pune share some Major risk factors of Liver Cancer and its’ treatment option.
let’s see:
7 Major Risk Factors of liver cancer in India:
Chronic Liver Conditions: If your liver experiences ongoing problems like cirrhosis, which results from the scarring of liver tissue, it significantly increases the risk of liver cancer. Cirrhosis can develop due to chronic alcohol abuse, persistent infections such as hepatitis B or C, or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Viral Infections: Chronic infections with hepatitis B or C viruses pose a significant risk for liver cancer. These infections can cause continuous inflammation and harm to the liver, which raises the chances of developing cancer.
Heavy Alcohol Consumption: Drinking alcohol excessively and over an extended period can damage the liver, potentially leading to cirrhosis and ultimately increasing the risk of liver cancer.
Diabetes: Individuals with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing liver cancer, especially when they have additional risk factors like obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Obesity: Being overweight increases your risk of developing liver cancer, especially your possess diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Age and Gender: Men is more likely than women to get liver cancer. In addition, the risk of liver cancer increases with age, with 90% of cases occurring among individuals over 60.
Certain inherited liver diseases: Liver diseases that can increase the risk of liver cancer include hemochromatosis and Wilson’s disease.
Treatment Options for Liver Cancer:
Surgery: Surgical procedures are often the preferred approach when liver cancer is detected early and the tumor is localized within the liver. There are two main surgical options:
Partial Liver Removal (Hepatectomy): This procedure involves removing the portion of the liver containing the tumor. In some cases, when the entire liver is affected or the tumor is large, a liver transplant may be considered.
Liver Transplant: In certain situations, individuals with early-stage liver cancer and cirrhosis may be candidates for a liver transplant. This complex procedure entails replacing the diseased liver with a healthy one from a compatible donor
Ablation Therapy: Ablation methods utilise either heat or cold to eliminate cancerous cells. Common techniques include radiofrequency ablation (RFA), microwave ablation, and cryoablation. These treatments are suitable for smaller tumours or when surgery is not feasible.
Embolization: Embolization encompasses procedures like transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and radioembolization (Yttrium-90). These techniques are employed to block the blood supply to the tumor while delivering chemotherapy or radiation directly to the cancer cells.
Immunotherapy: Certain individuals with liver cancer may find value in immunotherapy medications that activate the body’s immune system to combat cancer.
Liver cancer is a formidable health challenge in India, but many cases can be prevented or detected early through awareness and risk factor management. Regular screenings, vaccination against Hepatitis B, responsible alcohol consumption, healthy lifestyle choices, and food safety measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing liver cancer. Understanding these major risk factors is the first step in combating this disease and promoting liver health across the nation. For more information & treatment Book An Appointment Or call on 096374 39163
0 notes
Link
Symptoms may include fatigue, bloating, pain on the right side of the upper abdomen or back and shoulder, nausea, loss of appetite, feelings of fullness, weight loss, weakness, fever, and jaundice (yellowing of the eyes and the skin).
0 notes
Text
Global Embolotherapy Market Size, Share, and Demand Forecast to 2027
The Global Embolotherapy Market size was valued at USD 3,600.0 million by 2020 and is expected to develop at a CAGR of 6.8% during the forecast period (2021-2027), according to VynZ Research. For the forecast year 2021-2027, as well as the historical period 2015-2019, the Global Embolotherapy Market has been studied.
The research report provides a comprehensive and insightful examination of the Global Embolotherapy Market and includes market analysis on segmentation, dynamics, competition, and regional development. It considers the Global Embolotherapy Market's CAGR, value, volume, revenue, production, consumption, sales, manufacturing cost, pricing, and other significant parameters. The forecasts in the report are based on well-established research methodology and assumptions.
Get the sample copy of the Market Research @ https://www.vynzresearch.com/healthcare/embolotherapy-market/request-sample
Individual strategies were examined in the Global Embolotherapy Market study, followed by business profiles of Global Embolotherapy Market providers. The study includes an 'Industry Landscape' section that provides readers with a comprehensive view and firms’ market share analysis of major industry players in the Global Industry.
Most of the major players in the Global Embolotherapy Market are profiled in the report. The strengths and weaknesses, business developments, recent innovations, mergers and acquisitions, expansion plans, global footprint, market presence, and product portfolios of key market competitors are all covered in the company profiling section.
The following are some of the major and developing players in the Global Market:
Merit Medical Systems
Acandis GmbH
Medtronic plc
Abbott Laboratories
Boston Scientific Corporation
Cook Medical
Terumo Corporation
Stryker Corporation
Johnson & Johnson
BALT Extrusion
Sirtex Medical Limited
Kaneka Corporation
Meril Life Sciences Pvt. Ltd.
Penumbra, Inc.
BTG Plc.
Breakdown of The Segments:
The Global Embolotherapy Market is segmented by Product, Procedure, Indication, End-User and Geography in this study. This segmentation aids executives in planning their products and budgets depending on each segment's expected growth rates.
By Product
Embolic Agents
Support Devices
Microspheres
Embolic Coils
Liquid Embolic Agents
Embolic Plug Systems
Detachable Balloons
Microcatheters
Guidewires
By Procedure
Transcatheter Arterial Embolization (TAE)
Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE)
Transarterial Radioembolization (TARE)/Selective Internal Radiation Therapy (SIRT)
By Indication
Cancer
Neurological Diseases
Peripheral Vascular Diseases
Urological and Nephrological Disorders
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Liver
Kidney
Others
Cerebral Aneurysm
Arteriovenous Malformation And Fistulas
By End User
Hospitals and Clinics
Ambulatory Surgical Centers (ASCs)
Others
Geographical Viewpoint:
The research overview provides the major industry trend and the global market's predicted volume based on the regional analysis. The elements that have driven and hampered the market's expansion are also mentioned in this market research analysis. The study is also equipped with the most advanced and effective techniques for gathering, recording, estimating, and evaluating market data.
FAQ
Who are the most dominant players in the global market, and what elements are assisting them in gaining a competitive advantage?
What are the strategies adopted by the key industry players to gain traction in the industry?
By the end of the forecast period, what will the market size and growth rate?
What are the biggest Global Embolotherapy Market trends that are influencing market growth?
In the global market, which segment had the biggest revenue share?
Explore More Reports by VynZ Research:
Global Floating Farms Market – Analysis and Forecast (2022-2030)
Global Residential Energy Storage Market - Analysis and Forecast (2022-2030)
Global Photovoltaic Market – Analysis and Forecast (2022-2030)
About VynZ Research
VynZ Research is a global market research firm offering research, analytics, and consulting services on business strategies. VynZ have a recognized trajectory record and our research database is used by many renowned companies and institutions in the world to strategize and revolutionize business opportunities. The company focuses on providing valuable insights on various technology verticals such as Chemicals, Automotive, Transportation, Energy, Consumer Durables, Healthcare, ICT and other emerging technologies.
#Global Embolotherapy Market#Global Embolotherapy Market size#Global Embolotherapy Market share#Global Embolotherapy Market demand#Global Embolotherapy Market growth
0 notes
Text
Interventional Radiologist in Delhi - Dr. Ajit Yadav
Dr. Ajit Yadav
MBBS,DNB (Radiodiagnosis)

Dr. Ajit K Yadav is consultant at Department of Interventional radiology, Sir Gangaram Hospital, New Delhi. After receiving a medical degree at the Pt BDS PGIMS, Rohtak, he served as medical officer at rural government hospital for 6 months. He completed residency training in radiodiagnosis at Sir Gangaram Hospital. He was national board certified in 2011, and went on to complete a fellowship in Interventional Radiology at GRIPMER, Delhi. He also visited MD Anderson cancer center, Houston, Texas, USA for short term fellowship in 2013. He attended short training programme on TACE at Seoul National University Hospital, South Korea in 2014. Dr. Yadav’s clinical interests include uterine artery embolization for minimally invasive treatment of uterine fibroids and post-partum hemorrhage, Bronchial artery embolization for hemoptysis, minimally invasive oncologic interventions (including transarterial chemoembolization, radioembolization and radiofrequency tumor ablation), and percutaneous interventions. In addition, he offers minimal invasive procedures for various diseases like Benign prostatic hyperplasia, Varicose veins, Liver diseases and traumatic bleeding.
His research interests include interventional treatment of liver malignancy, a topic in which he has written peer reviewed publications. He has authored more than 15 papers in the field of interventional radiology. He has also presented his work in numerous national and International meetings. In addition to clinical activities, he is an active teacher of residents including Interventional Radiology fellows.
He is a member of several professional organizations, Indian Radiological and Imaging Association (IRIA), Indian Society of Vascular and Interventional Radiology (ISVIR), and the Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe (CIRSE). He is actively involved in Delhi chapter of ISVIR.
Tags - Interventional Radiologist in Delhi
For more information link - www.interventionalradiologyindia.com
0 notes
Link
Yttrium-90 or Y-90 is a commonly used isotope in the medical field specially in departments like nuclear medicine and radiation oncology for radiation therapy. This radioisotope is relied upon to provide a prescribed amount of radiation to a targeted area , such as a tumor.
#PRRT Treatment#PRRT Therapy#PRRT in Neuroendocrine Tumors#Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy#Nuclear Medicine Therapy#Lutetium Treatment#Lutetium Therapy#Y90 PRRT#hepatocellular carcinoma#Transarterial Radioembolization#Yttrium-90 radioembolization
0 notes
Text
TARE is the short form of Transarterial Radioembolization. Transarterial Radioembolization is a technique by which we inject radioisotope directly into a liver tumor by cannulating the hepatic artery and then delivering the radioisotope directly into the tumor.
know more at:
#Transarterial Radioembolization#Transarterial Radioembolisation in India#Side Effects of TARE#Dr Ishita B Sen#TACE vs TARE#Nuclear Medicine Therapy#Nuclear Medicine Expert in India#Ishita Sen#Tare Procedure#TARE Procedure Side Effects#TARE Treatment
0 notes
Text
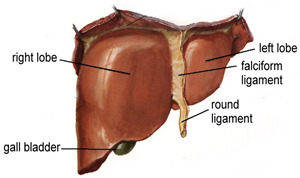
Liver Cancer
Get more information about Liver Tumour Treatment, Transarterial chemoembolization, Transarterial Radioembolization ( Tare ). Book an Appointment online now with Interventional Radiologist
0 notes
Text
Advancing Medical Innovation A Profile of Dr. Jeff Geschwind's Pioneering Work in Interventional Radiology
Dr. Jeff Geschwind stands as a luminary in the field of Interventional Radiology (IR), recognized for his groundbreaking contributions to medical innovation. As Professor of Radiology, Surgery, and Oncology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, he has spearheaded transformative research and clinical practice in minimally invasive procedures. Additionally, as the Director of the Division of Vascular and Interventional Radiology and the Interventional Radiology Center at the Johns Hopkins Hospital, Dr. Geschwind continues to drive advancements that redefine patient care paradigms.
Pioneering Research in Interventional Oncology: At the forefront of Dr. Geschwind's endeavors is his pioneering work in Interventional Oncology (IO), a burgeoning field focusing on minimally invasive treatments for cancer. His research has profoundly influenced the development of novel techniques such as transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and radioembolization, which deliver targeted therapies directly to tumors while minimizing systemic side effects. Through innovative approaches like these, Dr. Geschwind has revolutionized the landscape of cancer treatment, offering new hope to patients with previously untreatable malignancies.
Innovations in Image-Guided Therapies: Central to Dr. Geschwind's achievements is his expertise in leveraging advanced imaging technologies to guide minimally invasive procedures with unparalleled precision. Whether utilizing angiography, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or other modalities, he harnesses the power of imaging to navigate complex anatomies and deliver therapeutic agents with pinpoint accuracy. This fusion of imaging and intervention has opened new frontiers in patient care, enabling tailored treatments that maximize efficacy while minimizing risks.
Collaborative Approach to Patient Care: Beyond his research and clinical endeavors, Dr. Geschwind is renowned for his collaborative approach to patient care. Recognizing the multidisciplinary nature of modern medicine, he works closely with colleagues from diverse specialties, including oncology, surgery, and radiology, to develop comprehensive treatment plans tailored to each patient's unique needs. This collaborative ethos not only ensures the delivery of high-quality care but also fosters innovation through the cross-pollination of ideas and expertise.
Educator and Mentor: As a dedicated educator and mentor, Dr. Geschwind plays a pivotal role in shaping the future of interventional radiology. Through his mentorship, he cultivates the next generation of physicians and researchers, instilling in them a passion for innovation and a commitment to excellence. His contributions to medical education extend beyond the classroom, encompassing the dissemination of knowledge through lectures, publications, and professional societies, thereby perpetuating a culture of continuous learning and advancement.
Dr. Jeff Geschwind's transformative work in Interventional Radiology epitomizes the ethos of medical innovation and compassionate patient care. Through his pioneering research, innovative therapies, and collaborative approach, he has redefined the treatment landscape for patients with complex medical conditions, offering new hope where previously there was none. As he continues to push the boundaries of medical science, Dr. Geschwind's legacy will endure as a beacon of inspiration for generations to come.
0 notes
Text
A Case Report of Chemical Pneumonia after Trans-Arterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma during Covid-19 Outbrea by Rimondi
Abstract
Due to the dramatic outbreak of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection in Italy, management of patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) has become challenging. Palliative treatments, such as transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and radioembolization (TARE) have been maintained in selected patients, in order to optimize the risk-benefit ratio, by minimizing risks related to hospitalization.
Although considered safe procedures, these palliative treatments are associated with generally underestimated complications.
Here we report the case of a 78-year-old patient who developed respiratory failure after TACE procedure while being hospitalized during Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID19) outbreak. Clinical decisions and outcomes are therefore described.
Keywords: TACE; Chemical Pneumonia; Hepatocellular Carcinoma; COVID 19; Respiratory Failure
Abbreviations: SARS-CoV-2: Severe Acute Respiratory Coronavirus-2; HCC: Hepatocellular Carcinoma; TACE: Transarterial Chemoembolization; TARE: Transarterial Radioembolization; CPT: Child-Pugh Turcotte; HCV: Hepatitis C Virus; LUF: Lipiodol Ultrafluid; EPI: Epirubicin; CT: Computed Tomography; AFP: Alpha-fetoprotein; S: Segment; Sat: Saturation; COVID-19: Coronavirus Disease
Introduction
A 78-year-old woman was diagnosed with multifocal recurrence of a previously resected HCC on compensated (CPT-A) cirrhosis due to untreated Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) infection. She could not benefit from Direct-Acting Antivirals (DAA), since in Italy treatment is currently not reimbursed in patients with active HCC outside liver transplant waiting list. She had no comorbidities, and TACE was planned by our multidisciplinary team. After the first c-TACE [Lipiodol ultrafluid (LUF) plus Epirubicin (EPI)], abdomen CT-scan showed three residual nodules [11 mm in liver segment (S) 7, 10 mm in S5 and 10 mm in S6] with typical HCC pattern and Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP) lowering from 260 to 85 ng/mL. The next TACE procedure occurred to be planned during peaking Italian SARS-CoV-2 outbreak at the very beginning of April 2020. The patient was still motivated to undertake HCC treatment, aware of the risks associated with current pandemic, albeit mitigated by protocols implemented in our Coronavirus disease (COVID-19)-free department. She underwent two SARS-CoV-2 nasopharyngeal swabs, 5 and 3 days before hospital admission, which both tested negative. At admission, blood tests showed mildly increased liver enzymes, however with normal bilirubin and liver function tests.
Case Report
After checking S7, S6 and S5 lesions vascular supply, the hypertrophic right inferior phrenic artery was selectively catheterized, and LUF 2 mg emulsified with EPI 5 mg was injected (Figures 1a,1b). TACE procedure was immediately interrupted due to appearance of not previously described pulmonary shunts (Figure 1c).
Thereafter, HCCs were treated with standard doses of LUF and EPI through the right hepatic artery. No adverse events related to TACE were recorded, during and immediately after the procedure. Twenty hours later, the patient presented with fever (38.0°C) and desaturation (SatO2 78%), in absence of pronounced dyspnea. Arterial blood gas analysis showed respiratory failure with pH 7.40, pO2 34, pCO2 49, SpO2 65%, lactates 1.2, P/F 161. Differential diagnosis was made. Acute Respiratory Failure should prompt a rapid evaluation and physicians are required to quickly rule out the most common acute pulmonary pathologies. Acquired infectious pneumonia is quite a common cause of rapid deteriorating respiratory function and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Among infectious pneumonia, due to current high incidence scenario with rapidly spreading intra-hospital potential outbreaks, COVID-19 should be the first pathology to be excluded in order to keep infected patients out of SARS-CoV-2 free departments and, on the other hand, to prevent SARS-CoV-2 negative patients to become ill. Although our patient had been tested for COVID-19 before hospital admission, high rates of false negative RT-PCR tests should suggest to keep a low threshold for re-testing, especially if we take into consideration our subject’s clinical presentation with fever, acute respiratory failure and the absence of frank dyspnea which are all clinical characteristics of acute SARS-CoV-2 infection.Also, in this specific case, pulmonary venous thromboembolism should be suspected given the sudden desaturation and considering the hypercoagulable state due to active cancer, the post-procedural bed confinement and the recent vascular maneuvers.
Furthermore, the accidental injection of LUF + EPI into not previously known pulmonary shunt should raise the suspicion of possible adverse events related to the injection of relatively high doses of iodinated contrast agents into pulmonary parenchyma thus provoking chemical pneumonia. Oxygen support was then delivered (VM 50% 12 l/min), with benefit. Blood tests were repeated and they revealed unchanged white blood cells count (3,780/mm3), with relatively low lymphocytes (10%); hemoglobin, C-Reactive Protein, D-Dimer and ferritin were normal.
Chest X-ray showed an interstitial lung reinforcement and a possible basal right pneumonia. Due to parallel high incidence clinical scenario and the radiologic findings, a third SARS-CoV-2 nasopharyngeal swab was obtained, which still tested negative. To rule out the other possible complications, the patient underwent chest CT-scan which revealed the presence of radio-opaque material within the apical and posterior segment of the lower right lobe, that was suggestive for lipiodol accumulation (Figures 2a,2b). Liver accumulation were as well noted (Figure 2c). Right basal pneumonia was not confirmed, despite the presence of mild pleural effusion and lobar dystelectasia. Both antibiotics and low-molecular-weight heparin prophylaxis were started, and patient’s respiratory function was closely monitored. The patient experienced a progressive improvement in respiratory function with oxygen weaning after 7 days, and was discharged without sequelae.
Figure 1: Angiographic study of the celiac trunk showing the hypertrophic right inferior phrenic artery (a), which appear to supply the upper liver segments on the selective study, and two lesions (b); note the pulmonary shunts after LUF injection (c).
Figure 2: Chest CT-scan showing the presence of parenchymal dystelectasia (a) and radio-opaque material within the apical and posterior segment of the lower right lobe (b), as well as liver accumulation (c).
Discussion
Here, we described a case of chemical pneumonia in a patient affected by HCC undergoing loco-regional treatment with TACE. Due to her high motivation, the absence of major comorbidities, as well as the decrease in AFP values following previous HCC treatments, the patient was hospitalized despite several difficulties related to the concomitant peak of SARS-CoV-2 spread in Milan, Italy [1]. In order to minimize the risk of nosocomial infection, she had previously undergone two SARS-CoV-2 nasopharyngeal swabs, which tested negative. However, the onset of desaturation in absence of respiratory symptoms led physicians to reconsider COVID-19, due to the current high-risk clinical scenario. In fact, it has been recognized that several factors may limit molecular assays accuracy [2], with false negative rates of nearly 30%. Moreover, SARS-CoV-2 incubation period is crucial when interpreting swab results, thus making patient history collection essential, especially in the current “COVID-19 era” [3]. Also, the presence of liver diseases may increase the risk of unfavorable SARS-CoV-2 infection [4].
Our patient reported a rare complication of TACE, ranging between 0.05%-4.5% [5]. In fact, patients undergoing multiple TACE can develop collateral vessels, arising from non-hepatic arteries. Interestingly, S7 and S8 can be supplied by the right inferior phrenic artery, which accounts for 62-83% of extrahepatic collaterals. Moreover, naturally present pulmonary shunts could significantly increase. Although demonstrated that in these cases TACE remains a safe procedure, infused ethiodized oils or chemotherapeutic agents could shunt into lung vessels, with chemical injury being further worsened by the consequent inflammatory response. Despite both LUF and EPI had been injected at lower than standard doses following the identification of previously unrecognized pulmonary shunts, their quantity was probably enough to cause subsequent pulmonary inflammation and respiratory failure.
Although is strongly advisable to “think of horses not zebras, when you hear hoof beats”, this case reminds us to keep an open-minded approach even in specific pandemic high incidence scenarios.
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Ethical Approval
Approval was obtained from the local ethics committee.
Consent for Publication
The Author transfers to Springer the non-exclusive publication rights and he/she warrants that his/her contribution is original and that he/she has full power to make this grant. The author signs for and accepts responsibility for releasing this material on behalf of any and all co-authors.
Contributors
We were all involved in caring, treating, diagnosing and providing follow-up for the patient. RDA and AR wrote the manuscript; AR, IB and MI collected data; SC was responsible for Radiology; PL revised the paper. Written consent for publication was obtained from the patient.
For more information about Article : https://ijclinmedcasereports.com/
https://ijclinmedcasereports.com/ijcmcr-cr-id-00107/
https://ijclinmedcasereports.com/pdf/IJCMCR-CR-00107.pdf
#TACE#Chemical Pneumonia#Hepatocellular Carcinoma#COVID 19#Respiratory Failure#Rimondi#IJCMCR#clinical studies
0 notes
Text
Embolotherapy Market Astonishing Growth with Top Influencing Key players- Merit Medical Systems.
Embolotherapy Market Embolotherapy is a procedure in which the artery is blocked intentionally by inserting coils, balloons and other with the help of an angiographic catheter so that hemorrhaging can be prevented or controlled. Different procedures such as transcatheter arterial embolization, selective internal arterial therapy, transarterial chemoembolization and other are used. It is also used to treat bleeding ulcers and blood vessel defects and also block the blood to flow to a tumor during surgery. They are widely used in the diseases such as cancer, neurological diseases, gastrointestinal disorders, peripheral vascular disease and others.
Market Drivers
Increasing patient preference for minimally invasive procedures will drive the market growth
Rising funding by government and private organizations will also accelerate the growth of this market
Technological advancement and development in embolotherapy devices will also propel the market growth
Favorable repayment policies for the minimally invasive surgeries is also contributing as a factor for the market growth
Increasing cases of heptocellular cancer and liver cancer will also accelerate the market growth Get Exclusive Sample Report: @ https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/request-a-sample/?dbmr=global-embolotherapy-market
Scope of the Embolotherapy Market
Current and future of Embolotherapy Market outlook in the developed and emerging markets
The segment that is expected to dominate the market as well as the segment which holds highest CAGR in the forecast period
Regions/Countries that are expected to witness the fastest growth rates during the forecast period
The latest developments, market shares, and strategies that are employed by the major market players
Global Embolotherapy Market By Product (Embolic Agents, Support Devices), Disease Indication (Cancer, Peripheral Vascular Disease, Neurological Diseases, Urological & Nephrological Disorders, Gastrointestinal Disorders), Procedure (Transcatheter Arterial Embolization (TAE), Transcatheter Arterial Radioembolization (TARE)/Selective Internal Radiation Therapy (SIRT), Transarterial Chemoembolization), End- User (Hospitals and Clinics, Ambulatory Surgery Centers, Other End Users), Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, Middle East and Africa) – Industry Trends and Forecast to 2026
Browse Related Report Here:
Skin Closure Devices Market
Microneedle Drug Delivery Systems Market
Some of the leading key players profiled in this study:
Few of the major competitors currently working in the global embolotherapy market are Terumo Medical Corporation, Merit Medical Systems, Simbionix USA Corporation, Cook, Boston Scientific Corporation, Penumbra, Inc., Meril Life Sciences Pvt. Ltd., Medtronic, BTG International Ltd, ABK Biomedical Inc., Abbott., AngioDynamics., IMBIOTECHNOLOGIES LTD., Debakey Medlife Private Limited, Heraeus Holding, Guerbet, and others.
Get Detailed Toc and Charts & Tables @ https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/toc/?dbmr=global-embolotherapy-market
Key Pointers Covered in the Embolotherapy Market Trends and Forecast to 2026
Embolotherapy Market New Sales Volumes
Embolotherapy Market Replacement Sales Volumes
Embolotherapy Market Installed Base
Embolotherapy Market By Brands
Embolotherapy Market Size
Embolotherapy Market Procedure Volumes
Embolotherapy Market Product Price Analysis
Embolotherapy Market Healthcare Outcomes
Embolotherapy Market Cost of Care Analysis
Embolotherapy Market Regulatory Framework and Changes
Embolotherapy Market Prices and Reimbursement Analysis
Embolotherapy Market Shares in Different Regions
Recent Developments for Embolotherapy Market Competitors
Embolotherapy Market Upcoming Applications
Embolotherapy Market Innovators Study
Inquiry before Buying @ https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/inquire-before-buying/?dbmr=global-embolotherapy-market
About Us:
Data Bridge Market Research set forth itself as an unconventional and neoteric Market research and consulting firm with unparalleled level of resilience and integrated approaches. We are determined to unearth the best market opportunities and foster efficient information for your business to thrive in the market
Contact:
Data Bridge Market Research
Tel: +1-888-387-2818
Email: [email protected]
0 notes
Text
Lupine Publishers | The Current Approach to the Hepatocellular Carcinoma; A Mini Review of Etiology, Prognosis and Treatment
Lupine Publishers |Current Trends in Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common liver malignancy worldwide and is one of the major causes of cancerrelated deaths. HCC is reported to be the second most fatal malignancy. The major risk factors for HCC are well known; the known risk factors include hepatitis C virus (HCV) and hepatitis B virus (HBV). Major advances have been reported in the treatment of HCC. Success of early diagnosis increases when these risk factors are identified, and the cases are followed up. It is reported that in the treatment of early-diagnosed HCC cases, ethanol injection or radiofrequency ablation methods as well as surgical resection should be preferred, particularly in cases without liver cirrhosis and in cases where the tumor is restricted. Similarly, liver transplantation may be an option for patients that meet specific criteria.
Keywords: Hepatocellular Carcinoma; Liver Carcinoma; Liver; Cirrhosis
Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths in the world. HCC is reported to be the second most fatal malignancy after pancreatic carcinoma [1-3]. In the United States of America, 5-year survival of patients with HCC is reported to be approximately 9% [4]. In contrast to several other malignancies, the major risk factors for HCC are well known. These risk factors include hepatitis C (HCV) and hepatitis B virus (HBV). Major advances have been reported in the treatment of HCC. Success of early diagnosis increases when these risk factors are identified, and the cases are followed up [1]. A glance at the epidemiology of HCC reveals that it is more common in developing regions [5,6]. A 2008 study reported extremely high mortality rates for HCC [7]. Owing to the high mortality rate, HCC is one of the most common causes of cancer-related deaths. There are several predisposing factors in the etiology and pathogenesis of HCC. Following are the few examples of these factors: Hepatotropic viruses, HBV and HCV, are the most common cause [8]. Cirrhosis: Considering its annual incidence, approximately 3% of the patients with cirrhosis are expected to develop HCC [9]. Liver cell dysplasia (Large cell dysplasia and small cell dysplasia): Although both large and small cell dysplasia’s are risk factors for HCC, some authors argue that the presence of small cell dysplasia is a more important risk factor for HCC [10,11]. Thorotrast: It has been reported to play a role in HCC development [12]. Alpha1 antitrypsin deficiency: It is reported that individuals born with this metabolic disorder have a predisposition for HCC [13]. Tyrosinemia: There is a high risk of HCC in individuals born with this metabolic problem [14]. Aflatoxin: Aflatoxin, derived from the metabolic wastes of the fungus Aspergillus flavus, is associated with HCC [15].
HCC can be radiographically diagnosed by computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Moreover, dynamic imaging maintains contrast in the early arterial phase, which is then washed or released in the next portal phase. This imaging approach is 90% sensitive and 95% specific for HCC [16]. Ultrasound (US) findings are similar to those of CT and MRI. However, in recent years, contrast-enhanced US is no longer accepted as a diagnostic tool owing to the fact that cholangiocarcinoma cases cannot be distinguished from HCC and further investigation methods are recommended. In terms of laboratory findings, alpha fetoprotein (AFP) elevation in patients with HCC has been known for more than 40 years. AFP elevation can also be detected in pregnancy, normal fetal yolk sac, and fetal liver tissues. Other than HCC, it is also detected in the malignancies of the biliary tract, pancreas, and gastrointestinal system, as well as in nonseminamatous tumors. AFP level is expected to decrease in infants at 300 days after birth, and any AFP elevation detected after this period is a cause to suspect malignancy [17]. However, it has been reported that approximately one-third of the diagnosed cases may have normal AFP levels at the time of diagnosis [18]. Despite the advances in imaging systems and the support provided by laboratory findings, final diagnosis of HCC is still made on the basis of histopathological examination. US or CT-guided cytological fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) or histological tru-cut biopsy might be preferred in cases suspected with HCC. It has been reported that the diagnostic accuracy of concurrent FNAB and tru-cut biopsy is higher than that of either procedure on its own, with a sensitivity of 96% and specificity of 95% [19]. In microscopic examination of HCC, neoplastic hepatocytes mimic normal liver tissue depending on the degree of differentiation. Well-differentiated tumors that are almost similar to normal tissue are generally difficult to histopathologically distinguish from differentiated liver adenoma tissues. Less differentiated anaplastic tumors can be identified using certain additional immunohistochemical or histochemical analyses because their similarity with normal tissue is reduced.
The most common histological patterns in microscopy are trabecular (sinusoidal), solid, and pseudoglandular (acinar) patterns [20]. Most HCC cases are immunohistochemically positive for AFP, epithelial membrane antigen, alpha1 antitrypsin, fibrinogen, IgG, ferritin, Heppar 1, MOC 31, glypican-3, and polyclonal CEA [21]. HCC staging is generally dependent on many criteria such as tumor size, number of tumor nodules, and the presence/absence of vascular invasion [21]. There are various treatment approaches available for HCC cases. Considering the HCC stage, the functional status of liver and the accompanying medical problems, the treatment decision for HCC should be made with a multidisciplinary team comprising a surgeon, oncologist, pathologist, radiologist, and hepatologist [1]. The most effective treatment in HCC cases is surgical resection and liver transplantation (Figures 1 & 2) [22]. Ablative therapies such as radiofrequency ablation (RF), microwave ablation, or percutaneous ethanol injection are among the treatments that should be primarily used for masses smaller than 2 cm. However, ablative therapies are also preferred in patients with advanced age and poor clinical condition, and in whom surgical resection or transplantation cannot be employed [23]. In cases of HCC, many factors such as the number of tumors, tumor size, presence of cirrhosis, and surgical experience should be taken into account before performing resection and transplantation procedures. In case of partial resection of cirrhotic livers, patient’s condition may deteriorate owing to impaired function and low regeneration capacity. For this reason, liver functions should be comprehensively evaluated in patients with cirrhosis, and then decision regarding surgery should be taken [22]. In patients in whom surgery cannot be performed, neoadjuvant therapies such as transarterial embolization (TAE), transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), RF ablation, and percutaneous acid injection can be employed. In addition to these techniques, the use of microwave therapy, transarterial radioembolization, and cryotherapy applications has also been reported. Furthermore, sorafenib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor used for molecular therapy, can be preferred in patients with advanced stage HCC [24].
Figure 1: Right Hepatectomy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.
Figure 2: Liver Hiler dissection.
0 notes