#dct decentralized clinical trial
Text
Decentralized Clinical Trials and Contract Research Organizations in 2023
Decentralized Clinical Trials for the CRO
Decentralized clinical trials (DCTs) are a relatively new concept in the world of clinical research, but they are quickly becoming more popular. In 2023, DCTs are expected to become even more widely used as the technology and infrastructure needed to support them continues to develop.
A decentralized clinical trial is one that is centered around patient needs and improves the patient experience by allowing them to participate from their own homes or local healthcare providers. This type of trial eliminates the need for patients to physically access hospital-based trial sites, which can be difficult for some people due to distance or other factors. It also allows for greater flexibility in terms of scheduling and data collection, as well as improved accuracy of results due to fewer potential sources of error.
In addition to these guidelines from the FDA, there are several ethical considerations that must be taken into account when conducting a decentralized clinical trial. These include ensuring patient privacy and confidentiality, providing informed consent forms that clearly explain the risks associated with participating in a DCT, and ensuring that all participants have access to appropriate medical care if needed during the course of the study.
How CROS can Implement DCTs
Contract research organizations (CROs) can implement decentralized clinical trials by modifying their protocol to incorporate remote data collection, patient-centric protocols, and virtual engagement between trial participants and CRO personnel. Remote data collection allows for the capture of participant-generated data outside of a traditional clinical setting via digital devices. Patient-centric protocols allow for a more personal approach to clinical trials by allowing patients to participate in activities such as self-reporting on symptom severity, digitally submitting medical images and lab results, and engaging with physicians from the comfort of their own home. Virtual engagement between trial participants and CRO personnel can be facilitated through secure video conferencing tools that enable real-time interactions.
Further modifications to the CRO protocols could also include integrating artificial intelligence technology into the trial process such as automated monitoring of patient behavior, prioritizations of interventions based on individual risk profiles, and remote health guidance by virtual nurses or other healthcare professionals. Mobile applications could also be used to remind participants about upcoming appointments or events related to the study as well as remind them about taking medication or completing questionnaires. Incorporating these types of technologies would ensure that decentralized clinical trials are conducted efficiently while providing participants with an enhanced user experience throughout every step of the trial process.
Five Steps to Implementing Decentralized Clinical Trials
1.Educate Project Managers: Contract research organizations (CROs) should ensure that their project managers are educated about the benefits of decentralized clinical trials and how to go about implementing them. This could include learning about the technology, regulations, data privacy, and other important elements related to this type of trial design.
2. Establish Data Security Measures: Before conducting a decentralized clinical trial, CROs should have strong data security measures in place to protect participants’ information and ensure that it is secure throughout the study duration. This includes accessing participant data only with permission and using encryption protocols when transmitting or storing any sensitive information.
3.Evaluate eClinical Platforms: A key part of implementing decentralized clinical trials is choosing the right eClinical platform for your study design. CROs should evaluate the various eClinical platforms available to them and select one that meets their needs for a successful trial, such as being user friendly for participants, having features such as remote monitoring capabilities, offering robust reporting capabilities, and providing easy access to data from multiple sites.
4.Utilize Mobile Technologies: To make a decentralized clinical trial successful, leveraging mobile technologies can be extremely helpful for CROs to communicate with volunteers remotely, manage participant engagement in real-time, collect patient-reported outcomes quickly and accurately from anywhere, track compliance with protocols on site visits or assessments done remotely, etc., reducing the need for face-to-face visits whenever possible.
5. Create Protocols: Having clear protocols in place is essential if a CRO wants to successfully implement decentralized clinical trials as they help ensure consistency across different sites by setting expectations around communication between sites and central teams; supervision of staff; quality control procedures; safety reporting; use of investigational drugs; collection of patient data; follow up on withdrawals or lost patients; etc., throughout the duration of the trial
How do DCTs Work?
Decentralized clinical trials offer a variety of benefits to CROs, such as reduced costs associated with traditional on-site trials, improved patient recruitment, faster data collection and analysis, and greater efficiency.
Decentralized clinical trials (DCTs) offer a promising new model for contract research organizations (CROs). By leveraging decentralized technologies such as blockchain and distributed ledger technology, DCTs provide a secure, efficient, and cost-effective alternative to traditional CRO models.
The key advantages of DCTs for CROs include enhanced security and data integrity, improved consent management, faster and more secure patient recruitment, and greater visibility into the trial process. With DCTs, CROs can leverage existing research infrastructure while streamlining processes such as data management and quality control.
To further explore the potential of DCTs, it's helpful to look at some recent developments in the industry. In 2018, Decentralized Clinical Trials LLC partnered with Johnson & Johnson to create JLABS@TMCx to develop innovative digital health solutions for clinical trials. This collaboration unveiled two major projects that leverage decentralized technologies: Project Catalyst and Project Ovenbird.
Project Catalyst seeks to develop a system of protocols that will allow researchers to securely exchange information in real-time. The project is currently focused on developing decentralized application (dApp) versions of standard protocols and applications used in clinical trials. Meanwhile, Project Ovenbird seeks to create an enterprise-grade distributed data platform that will enable researchers to collect structured data from decentralized sources while maintaining privacy standards comparable to those set by HIPAA.
In addition to these projects with J&J, Decentralized Clinical Trials LLC has also partnered with Microsoft Corporation on a pilot program called "Verified Credentials." This program leverages blockchain technology to ensure accurate identity verification during patient recruitment processes for clinical trials.
For CROs interested in exploring DCTs further, there are several resources available online that can help provide a better understanding of their benefits, applications, and potential challenges. The National Institutes of Health recently launched the Decentralized Clinical Trials Hub (DCThub), which provides educational materials about DCTs for research professionals. Additionally, several companies offer products tailored specifically for DCTs such as TrialX from OptumIQ or Oneyield from Castor EDC Solutions Ltd., both of which are designed to support decentralized clinical trial design and implementation workflows.
Types of Remote Monitoring in DCTs
Decentralized clinical trials are conducted using remote monitoring technology to capture data from patients rather than requiring them to come into a physical research site. This allows for more flexible trial designs that can be tailored to specific patient populations and geographic locations. In addition, patients can more easily participate in a trial without having to travel or take time off from their daily lives. For example, virtual visits through telemedicine can be used for initial screening and assessments, reducing the number of visits required at an on-site research facility.
Data collected from decentralized clinical trials is often more accurate than what is typically collected in traditional on-site trials due to the use of continuous wearables, mobile devices and other innovative digital technologies that provide real-time monitoring of health parameters such as blood pressure or glucose levels. This increases the quality and granularity of information available to researchers while decreasing the amount of labor required for data collection. Additionally, electronic health records (EHRs) can be integrated with decentralized trial platforms allowing for rich longitudinal datasets that enable deeper insights into patient outcomes over time.
One example of a decentralized clinical trial is the use of telemedicine to support remote monitoring. This could involve providing video conferencing for patient-physician visits and using smartphones for tracking vital signs. In addition, telemedicine can enable doctors to monitor patients with chronic conditions remotely, by collecting medical data from sensors that have been placed on the patient’s body. This type of monitoring allows doctors to keep track of changes in health parameters without requiring an in-person visit, significantly reducing both costs and risks associated with traveling for treatment.
Another example is direct-to-patient (DTP) trials, in which medication is shipped directly to a patient's home instead of them having to travel to a clinic. In this case, study coordinators can monitor the progress remotely via phone calls or text messages while also providing support when needed. This approach has enabled researchers to conduct studies involving large numbers of participants located around the world who would otherwise not have been able to participate due to geographic distance or lack of transportation resources.
Finally, wearable devices are also being used increasingly in decentralized clinical trials as they allow researchers to collect more accurate data about activity levels and other health metrics over long periods of time without needing frequent interventions from healthcare personnel. It is possible for these devices to be connected directly with electronic data capture systems so that the collected information can be analyzed quickly and accurately by researchers.
Larger Patient Engagement
The decentralization of clinical research also opens up new opportunities for CROs to reach larger populations by enabling simultaneous studies across multiple sites around the world and removing many logistical barriers related to travel or geographical distance between participants and study sites. Additionally, leveraging social media platforms for recruiting further expands access potential outside of traditional recruitment networks and offers ways to engage with potential participants more directly than before.
Decentralized clinical trials, also called virtual studies or remote research, have the potential to revolutionize the way clinical studies are conducted. A decentralized clinical trial is a type of clinical study where participants are distributed across geographical and other boundaries, allowing them to participate from their own homes or from one of many remote sites.
To explore further options regarding DCTs and related technologies, interested parties may consult companies such as Medidata Solutions (www.medidatasolutionsinc.com), IMS Health (www.imshealth.com), HRA Pharma (www.hrapharma) or IQVIA (www.iqvia). These firms specialize in providing comprehensive services related to DCT implementation, ranging from development and customization of software solutions through full project management services that cover all aspects of a clinical trial operation from start-up through completion – including training protocols for implementing these new technologies at each site visited during study duration and beyond..
Overall, decentralized clinical trials represent a significant opportunity for CROs looking to move away from costly on-site studies in favor of more cost effective approaches that offer equally robust data sets but require fewer resources from both researchers and participants alike. As technology continues to advance so too will our collective ability to take advantage of decentralized trial designs for bigger impact studies without sacrificing quality or rigor.
Decentralized clinical trials offer many advantages over traditional site-based studies. They provide greater convenience for patients while still maintaining high levels of safety and efficacy standards. As technology continues to advance in 2023, we can expect even more opportunities for DCTs to become available.
More Examples on Decentralized Clinical Trials:
In the past decade, the advent of blockchain and other technologies have made it possible for clinical trials to be conducted in a decentralized manner. Here are five examples of decentralized clinical trials currently taking place across the world.
1. Mediledger Clinical Trial Supply Chain: This trial is being managed by MediLedger, a healthcare-focused blockchain consortium. The goal of this trial is to use blockchain technology to streamline and secure the global movement and tracking of drugs within the supply chain. The solution will enable parties to share data about patient safety, drug expiration dates, and more in real-time – all while remaining compliant with regulatory standards.
2. CardiLynx Smart Phone ECG Readings: This study is being conducted by CardiLynx, a healthcare technology company that specializes in mobile health applications that measure electrocardiograms (ECGs). The aim of this trial is to use an app on a smartphone to accurately detect heart arrhythmias in patients over time, as well as identify early symptoms and risk factors associated with cardiovascular diseases like stroke and heart attack.
3. Cogstate Cognitive Testing Trial: This study is sponsored by Cogstate, an AI-powered cognitive assessment platform that uses computer games to measure cognitive performance across multiple disciplines such as memory, attention and executive functioning. The purpose of this trial is to evaluate how well Cogstate’s technology can accurately detect changes in cognition over time in various patient populations and disease states.
4. Takeda Whole Genome Sequencing Study: This research project is sponsored by Takeda Pharmaceuticals, one of the world’s largest pharmaceutical companies. In this project, researchers are using whole genome sequencing technology to increase our knowledge about genetic mutations related to certain diseases such as hemoglobinopathies or rare blood disorders. They are also trying to identify new treatment options based on these mutations that could help improve patient outcomes overall.
5. Verily Life Sciences Patient Health Monitoring Project: This project involves Verily Life Sciences working with healthcare providers, payers and employers on an initiative called “Project Baseline” which uses wearables and other devices such as Fitbits or Apple watches to monitor patients’ health data in real-time while they go about their daily lives outside of a clinical setting. Through this project, Verily aims to understand how different lifestyle behaviors can influence health outcomes; enhance patient engagement; reduce healthcare costs; and ultimately improve population health management globally
6. GlaxoSmithKline’s digital platform trial: GlaxoSmithKline developed an innovative digital platform to conduct a clinical trial of its new asthma drug, mepolizumab, in the United States. The trial involved recruiting participants through a web-based interface, using secure electronic data capture (EDC) tools to collect and store data in real time, and utilizing mobile devices for remote patient monitoring. This decentralized clinical trial was able to reduce the traditional costs associated with running a large-scale clinical trial because it eliminated many of the steps required for enrollment and data collection. Additionally, it enabled GSK to recruit more geographically diverse participants who would not have been able to take part in a conventional trial setting.
7. Merck's MyEHRConnected study: Merck conducted the MyEHRConnected study, which sought to evaluate the efficacy and safety of its diabetes medication Januvia (sitagliptin). This was an international phase III study that utilized electronic health records (EHRs) from more than 60 sites located throughout Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America and Canada in order to identify eligible patients with type 2 diabetes. The EHRs enabled Merck to recruit participants quickly without requiring physical visits or extensive paperwork. Furthermore, researchers could securely access patient data stored within the EHR system during the duration of the study for analysis and evaluation purposes—a process that would have been impossible with paper-based records.
8. Sanofi's Telcare Diabetes Trial: Sanofi conducted a revolutionary telephone-based randomized control trial known as the Telcare Diabetes Trial (TDCAT), which aimed to assess the impact of telemedicine on diabetes care management among patients at risk for complications due to uncontrolled blood sugar levels. Patients were randomly divided into two groups—one group received standard care while another group received a combination of traditional care plus remote support provided by nurses through weekly phone calls over a period of six months. Results showed that those participants receiving telemedicine services had significantly better glycemic control than those who did not receive any telemedicine services at all—highlighting one powerful benefit of decentralizing clinical trials using technology such as telephone communication services.
9. Novartis’wearable device clinical trial: Novartis launched an ambitious clinical trial involving 20,000 individuals across nine countries in order to evaluate whether wearable devices such as smart watches can detect early signs of heart failure before medical symptoms appear. The decentralized nature of this study offered numerous advantages over traditional studies in terms of cost savings as well as recruitment speed; enabling Novartis to rapidly reach out potential participants worldwide instead of relying solely on localized recruitment methods used previously by other companies conducting similar trials with much smaller sample sizes due to limited resources or geographic restrictions
10. Eli Lilly & Company's eCOA Study: Eli Lilly & Company recently completed an innovative eCOA (electronic Clinical Outcomes Assessment) study that leveraged mobile applications and internet-connected devices in order to record patient outcomes over longer periods of time compared with traditional studies involving paper forms or periodic clinic visits alone. By using this decentralized approach, Lilly was able to gather more accurate data while reducing costs associated with running conventional trials; making it possible for them to enroll larger numbers of patients in shorter periods than ever before.
11. The IQVIA-sponsored study by the Alzheimer's Prevention Initiative (API). This study was designed to evaluate the effects of an investigational oral form of the drug solanezumab on the cognitive decline associated with early stage Alzheimer's disease. It was a decentralized trial conducted using remote monitoring, which allowed participants and clinical sites to interact online via web-based video visits, digital questionnaires and remote diagnostic testing. The trial collected data from over 800 participants at over 30 clinical sites in 12 countries.
12. A decentralized clinical trial launched by Durect Corporation to assess its investigational drug DUR-928 for the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). The Durect NASH study was conducted across 16 countries and used innovative telemedicine technologies for patient monitoring and data collection. In addition to traditional site visits, remote video visits were performed with patients and caregivers to observe adverse events, review patient-reported outcomes, analyze lab results remotely and monitor compliance with the protocol.
13. The Institute for Qualitative Medicine’s (IQM) pilot study that evaluated an innovative approach to decentralizing clinical trials using mobile health technology (mHealth). The mHealth platform was used to connect participants remotely with healthcare professionals who monitored vital signs such as blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, oxygen saturation level and body temperature using wireless medical devices connected directly to smartphones or computers. In addition, the platform included a chatbot that trained participants on how to use their medical device correctly or send real-time reminders when it was time for follow-up appointments or tests.
14. An analysis conducted by PPD Incorporated comparing decentralized vs centralised clinical trials for a Phase IIb study evaluating an investigational vaccine for malaria prevention in children aged 1–6 years old. They found that decentralizing the trial saved approximately 25% in total resources spent compared to a centralized approach and resulted in shorter recruitment times due to increased convenience for both investigators and participants alike compared with centralised approaches where people had to travel long distances for appointments or procedures.
15. A global Phase IIIa research program sponsored by GSK which evaluated an experimental shingles vaccine involving over 17000 elderly individuals across 11 countries in Europe and Latin America including Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Germany Spain France Italy Netherlands Poland Portugal UK..The study incorporated various decentralized models such as virtual/remote clinic visits with self-administered questionnaires through smartphones/tablets; home delivery of intervention product; remote diagnostics; online physician/patient communication through video calls; collection of sample storage through kits sent remotely from local courier companies etc., thus enabling a truly distributed model of conducting clinical trials without relying solely on physical presence at site locations
Want to train your staff to run decentralized clinical trials? Enroll them in our in-depth clinical trial certification courses with hours of lectures focuses on remote monitoring alone.
#decentralised clinical trials#decentralized clinical trial#decentralized trials#decentralization of clinical trials#decentralized trial#dct clinical trials#decentralized studies#what are decentralized trials#what is a decentralized trial#dct trials#decentralized clinical trial model#decentralized clinical trials meaning#decentralized research#decentralized research organization#decentralized study#examples of decentralized clinical trials#what are decentralized clinical trials#what is a decentralized clinical trial#what is decentralized clinical trials#dct decentralized clinical trial#decentralized clinical trial definition#decentralized clinical trials definition#decentralized trials meaning#what does decentralized clinical trials mean#what is decentralized trials#distributed clinical trials#fda definition of decentralized clinical trials#dct clinical trial#decentralized clinical trial platform#what is dct in clinical trials
0 notes
Link
Explore the potential of DCT decentralized clinical trials and how they are addressing the challenges of traditional clinical trials, improving patient engagement, and enhancing research outcomes
0 notes
Text
Global Decentralized Clinical Trials (DCTs) Market valued at US$ 8.8 billion in 2021 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 10% to reach ~US$ 14.2 billion by 2026
Decentralized clinical trials (DCT) employ a method of conducting clinical trials where parts or all of the trial happen outside a traditional physical clinic or trial site. Telemedicine, local/mobile healthcare providers, and digital/mobile technology are used to perform clinical trial studies.
The Global Decentralized Clinical Trials (DCTs) Market valued at US$ 8.8 billion (2021) is set to witness a healthy growth rate of 10% to reach ~US$ 14.2 billion by 2026.
Some of the main factors propelling the global decentralized clinical trials (DCTs) market include the advantages of DCTs, Covid-19, growing adoption by pharmaceutical, medical device companies, and research organizations (CROs), formation of industry stakeholder groups like the Decentralized Trials & Research Alliance (DTRA) to facilitate collaboration and research, favourable funding & regulatory outlook, and surge in M&A activities. However, concerns around patient data privacy are likely to hamper the growth of the decentralized clinical trials (DCTs) market.
Covid-19 Spurs Adoption of Decentralized Clinical Trials (DCTs) Market
Internationally, Covid-19 had a negative influence on health care, and the clinical industry was not an exception. The challenges of doing clinical research during the Covid-19 pandemic resulted to the termination of more than 2000 trials that were registered on ClinicalTrials.gov. Covid-19 harmfully impacted participant recruitment, retention, the safety of trial subjects, protocol compliance, and highlighted the need for safe, reliable, and secure remote capabilities, which in turn led to a renewed focus on digitization.
Decentralized clinical trials (DCT) have become a vital tool in the wake of the Covid-19 pandemic, providing for the remote recruitment of patients, physician visits/patient consent can take place via telemedicine, and mobile technology can be used for remote data collection.
“The Covid-19 pandemic compelled several sponsors to incorporate virtual elements such as telemedicine, remote electronic medical record access for monitors, and virtual monitoring of data & study documentation into their trials.” - Senior Director, Leading DCT Solution Provider, United States
Explore Premium Report on Decentralized Clinical Trials (DCTs) Market @ https://meditechinsights.com/decentralized-clinical-trials-market/
Regulatory Hurdles Likely to Hamper Adoption of Decentralized Clinical Trials (DCTs) Market
The digital tools utilized for decentralized trials have not kept up with the market's clinical trial regulations. For instance, for wearable devices, there is a need to create an ecosystem where data from different devices and technologies are standardized, validated, and exchanged without data integrity issues.
Regulatory agencies follow a variety of approaches to DCTs, but currently, there is no international standard. The DCT regulatory landscape is continuously changing, and hence clinical-trial sponsors need to align their studies with the most up-to-date guidelines. For multi-regional clinical trials, there is a need to recognize the increased regulations and limited possibilities for variation in research methods. A customized strategy and consideration for complexity in the clinical trial design are required for all global clinical trials that implement decentralization.
Growing Adoption and Financial Backing of DCTs by Pharmaceutical, Medical Device Companies, and Contract Research Organizations (CROs)
Due to Covid-19, pharmaceutical, medical device companies and contract research organizations (CROs) have all increased their usage of the DCT model in recent years:
To reduce contact, improve the patient experience and keep studies on track during the Covid-19 pandemic
Due to the growing trend toward more patient-centric trials
The formation of industry stakeholder groups to facilitate collaboration and research
The possibility of reducing trial time and costs. Cost savings arising from diverse sources, including fewer sites (i.e., less investigator fees and costs for patient visits, and other site costs), less patient travel costs, and less site monitoring and management fees
Additionally, funding from large pharmaceutical companies to specialists in virtual clinical trials is probably going to expand the market.
For instance,
In August 2020, Science 37, an American clinical research company that specializes in decentralized clinical trials, secured $40 million in funding from Novartis, Amgen, Sanofi, PPD, and Google’s VC arm.
The decentralized clinical trials (DCTs) market is a booming market that is expected to gain further momentum in the coming years due to its ability to harness technological developments to improve the efficiency, participant experience, and generalizability of clinical studies.
Competitive Landscape Analysis of Decentralized Clinical Trials (DCTs) Market
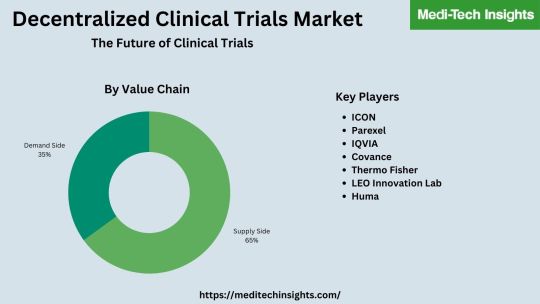
The global decentralized clinical trials (DCTs) market is marked by the presence of players such as ICON, Parexel, IQVIA, Covance, Thermo Fisher, LEO Innovation Lab, Huma, Medidata (part of Dassault), Oracle, CRF Health, Medable, Signant Health, and Clinical Ink, among others.
For More Detailed Insights, Contact Us @ https://meditechinsights.com/contact-us/
About Medi-Tech Insights
Medi-Tech Insights is a healthcare-focused business research & insights firm. Our clients include Fortune 500 companies, blue-chip investors & hyper-growth start-ups. We have completed 100+ projects in Digital Health, Healthcare IT, Medical Technology, Medical Devices & Pharma Services.
Contact:
Ruta Halde
Associate, Medi-Tech Insights
+32 498 86 80 79
0 notes
Text
Decentralized Clinical Trials (DCTs) Market Size, Share, Growth Analysis, Trends and Forecast 2031
This Market Research report 2024-2031 is a valuable source of insightful data for business strategists, describes industrial study, driving features and current market trends, which often benefit to the newly entering key players in the market. This market report is vital for them as it covers the profit-making related features that play a vital role in driving the development of the market. Research analysts offers an whole description of the technological progressions, confronts, SWOT study, Porter’s five forces study, and feasibility studies, to better understand the depth of competition, opportunities for the players and modern inclinations. Your business will produce much faster with the help of an authentic source of statistical surveying from the Report. One can get an entire review of the market and also a brief insight of the market evolution.
0 notes
Text
Decentralized Clinical Trials for Drugs, Biological Products, and Devices Guidance Free download PDF
This draft guidance provides recommendations for sponsors, investigators, and other stakeholders regarding the implementation of decentralized clinical trials (DCTs) for drugs, biological products, and devices. In this guidance, a DCT refers to a clinical trial where some or all of the trial-related activities occur at locations other than traditional clinical trial sites. In fully…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Octalsoft: 5 Decentralized Clinical Trial Myths
Conventional clinical trial models revolve around a study site with participants being required to travel to the clinic to give data. Decentralized clinical trials (DCTs) are a modern research paradigm that employs digital technology to improve all stages of a trial, from recruiting and enrollment to engagement, retention, and data collecting, with capabilities achievable outside of a clinic.
According to a recent report, the global Decentralized Clinical Trials market size was valued at USD 4476.49 million in 2022 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 15.42% during the forecast period, reaching USD 10582.65 million by 2028. While these numbers are promising, they still cannot be compared to a traditional clinical trial.
A decentralized clinical trial has several advantages, including a better participant experience, but clinical trial sponsors and researchers have been sluggish in adopting it. Here, we address five of the most pertinent myths about DCTs that have contributed to their relatively low acceptance.

Myth 1: All components of the study are decentralized
The phrase "decentralized clinical trial" might mean that the entire research protocol is digitized and relocated away from the clinic. DCTs, on the other hand, are simply described as studies including digital data gathering outside of a study location, as opposed to studies that collect all data online. Several trials that now use DCT technology use a hybrid trial approach, which gives participants additional options, potentially increasing interest and compliance.
Decentralized clinical trials software and digitization enable different components of a protocol to be improved to best meet the research purposes and boost possible pools for recruitment while sustaining engagement. This gives researchers additional possibilities for meeting participants in ways that are both effective for the study and efficient for the participant. This allows the study team to explore solutions that would not have been viable owing to geographic or physical constraints.
With the optionality allowed by DCT technology and digitalization, in-person data collection may be supplemented with research activities that the participants can perform in the way that they desire. Surveys or participant-reported outcomes, for example, might be completed remotely, at the participant's convenience, or during an in-person visit in the presence of a research coordinator.
Similarly, blood or saliva samples may be obtained at the clinic, at a Quest site, or at home using an at-home kit. These alternatives allow individuals from a far broader range of conditions and restrictions to engage. Finally, DCT technology allows for more engagement and more reliable data collecting while keeping the participant experience in mind.
Myth 2: Virtual recruitment is ineffective
A prevalent misperception regarding DCTs is that recruiting patients is too difficult without an established in-person connection. Alternatively, by reducing geographic obstacles to participation, recruitment may be improved by allowing a greater population to interact for possible enrolment. This recruiting is further aided by the addition of new recruitment channels such as social media, QR codes, websites, emails, and others.
Participants may find clinical trials on their own by permitting in-person and remote interaction, rather than depending entirely on doctors to recommend patients to appropriate forthcoming studies. This improves studies by broadening the scope of outreach, allowing for a more diversified participant base. Finally, DCT technology can reach more people and produce more detailed research results by utilizing the finest in-person and remote ways to locate and engage with participants.
Myth 3: DCTs worsen the digital divide
When contemplating implementing DCT technology in a clinical research context, one prevalent issue is the introduction of biases caused by necessitating the use of a mobile phone or other internet-connected devices. Recent studies, however, show that the digital divide in the United States has narrowed, and underrepresented populations—sexual and gender minorities (SGM), ethnic/racial minorities, females, and other underrepresented or underserved populations—make good candidates for participation in digital clinical studies.
For example, 85% of persons with SGM use social media in some capacity, and 91% of those with a physical or mental handicap own a smartphone or tablet.
For people who do not have access to technology or have minimal digital literacy, data gathering can still be done in person. DCT technology broadens the methods for any participant to contribute data and properly participate in a study.
Myth 4: Electronic consent models impede study understanding
Using typical long-form permission agreements, participants are often able to grasp common components of clinical trials (e.g., voluntary participation, the ability to withdraw at any time, etc. ). Many participants, however, continue to struggle with the concepts of a placebo, randomization, dangers, and potential adverse effects. This misunderstanding can have an influence on recruitment, study adherence, and retention rates.
A prevalent myth about DCTs is that digital, eConsent models, in which a research coordinator does not take the participant through the permission process in person, will further reduce participants' knowledge of the study. In reality, DCT technology can potentially boost study understanding by improving consent forms.
Clinical trial consent can be improved with technology by using multimedia material and delivering information in the participant's chosen language. It has been demonstrated that multimedia material improves participant comprehension of trial details. Because participant learning methods differ, this multimedia content can be used to complement long-form consents.
Technology also makes it possible to offer consent information in a language that the person understands. Moreover, tailored quizzes that validate understanding and offer further resources to address identified gaps can be used to test and enhance comprehension. Finally, if certain populations or groups of participants require one-on-one discussions with a research coordinator, it may be better tailored to the individual's requirements.
Myth 5: DCTs impose additional burdens on research locations and participants
DCT technology introduces change to study locations, which naturally raises concerns about increased responsibilities and complexity. A well-implemented DCT focuses on removing the difficulties associated with necessary on-premise activities for both participants and coordinators while enhancing the manageability of these tasks in a virtual context.
DCT technology transfers work from the clinic to a suitable time in the participant's day for research locations, making interactions more comfortable for the participant. Not only is this more convenient, but information is frequently asked closer to an important event, reducing the strain associated with recollection. Participants often prefer this style of contact as long as the additional convenience is not outweighed by the demand for more data.
DCTs generally demand less time from research coordinators, in addition to enhanced participant convenience, because a lot of tests no longer require direct interaction.
The time saved in scheduling assessments and reminding participants of impending assignments and visits to ensure compliance can be spent to focus on high-impact engagement for selected participants with special needs. With automated notifications and reminders, as well as participant dashboards and reward systems, research teams may achieve improved compliance and adherence rates with less time and effort during clinical investigations.
In Summation
Now that we've broached the five most common myths about DCTs, it's time to embrace the fact that decentralized and hybrid trials are here to stay. Apart from the patient's convenience and the increased level of continuous monitoring, DCTs aid the investigators and overall clinic operations. Doctors have more "chair time" to meet with patients (virtually or in-person), waiting times are lowered for everyone - not just the study participants, but all patients - and physicians can be more productive with their time. But how does one go about conducting a DCT, especially APAC decentralized clinical trials?
Octalsoft, a long-standing leader in the DCT field, is here to assist. We provide specialized, qualified advice and a comprehensive eClinical suite for end-to-end DCT trial design and implementation. Our industry specialists can lead a complete, multifaceted strategy to ensure organizational success and end-user uptake while our eClinical suite sports all the tools and software systems that a modern clinical trial requires.
To learn more about how Octalsoft can assist you in developing and implementing a decentralized clinical trial system that links trial experiences for patients, sites, and sponsors,
schedule a Free Demo NOW!
0 notes
Text
Mobile healthcare dominates as most commonly used component in decentralized clinical trials, reveals GlobalData

Mobile healthcare dominates as most commonly used component in decentralized clinical trials, according to GlobalData.
The COVID-19 pandemic catalyzed the adoption of decentralized clinical trials (DCTs) even though they have been in use for decades. DCTs offer the advantage of enabling patients to take part in clinical studies from the convenience of their homes, eliminating the need for them to travel to clinical sites. This not only reduces the burden on patients but also leads to higher participation rates. Against this backdrop, out of the virtual components used in clinical trials, mobile healthcare is the most commonly used component, with 47% of DCTs using this element, reveals GlobalData, a leading data and analytics company.
GlobalData’s latest report “Thematic Intelligence: Digital Transformation and Emerging Technologies in the Healthcare Industry,” reveals that web-based technology is the second most commonly used virtual component, with 23% of DCTs using it for activities such as electronic data collection (eCOA, eConsent, eDiary, ePRO, and questionnaire). Mobile healthcare consists of activities such as remote patient monitoring, remote drug delivery, telemedicine, and home nursing.
“As technologies continue to improve, it has become easier to collect, transfer, and store data electronically. After the COVID-19 pandemic, there has been a drastic increase in patients becoming more comfortable with using gadgets. As people were forced to adapt to social distancing measures and lockdowns, many became more comfortable with using technologies for various purposes, including healthcare.”
Shiva Narayana, Associate Project Manager, Pharma at GlobalData, comments:
Progress in network technologies, connected gadgets, medical wearables, sensors, data analytics algorithms, and software is reshaping the healthcare and clinical trial environments. These breakthroughs are facilitating the more effective gathering of data and the provision of advanced healthcare through a variety of means.
With more patients using technologies such as wearable devices, smartphone apps, or other remote monitoring tools to collect and transmit data such as vital signs, medication adherence, and symptoms, clinicians have an opportunity to access real-world data and gain timely insights.
“By introducing virtual components, the study sponsors or clinical research organizations (CROs) can drive more cost-effective and efficient clinical trials. With fewer geographical constraints and increased patient engagement, decentralized trials can potentially be completed more quickly. However, there are also challenges and considerations in implementing decentralization in clinical trials, such as ensuring data privacy and security, addressing the digital divide, and maintaining the integrity of the study.”
Shiva Narayana concludes
Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Recent Trends in Clinical Research: What's New in 2023
Clinical research is a dynamic field that continually evolves to meet the demands of advancing healthcare, technological innovations, and regulatory changes. As we step into 2023, the landscape of clinical research is marked by a series of transformative trends that promise to shape the future of healthcare. In this article, we'll explore the latest developments in clinical research and shed light on the growing prominence of clinical research companies in Bangalore, India.
1. Decentralized Clinical Trials (DCTs)
One of the most significant shifts in clinical research is the increasing adoption of decentralized clinical trials. Traditional clinical trials often require patients to visit physical research sites, which can be challenging for some participants. DCTs leverage technology to facilitate remote data collection, patient monitoring, and even medication delivery. These trials improve patient access, reduce dropout rates, and provide more comprehensive and real-world data.
Clinical research companies in Bangalore are actively embracing DCTs, harnessing the city's reputation as a hub for technological innovation. With a thriving IT ecosystem and a strong focus on healthcare, Bangalore is poised to lead the way in implementing decentralized clinical trials.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are revolutionizing clinical research. These technologies are streamlining various aspects of the research process, from patient recruitment and data analysis to drug discovery. AI-driven algorithms can analyze vast datasets, identify patterns, and accelerate the identification of potential drug candidates.
In Bangalore, renowned for its vibrant tech industry, numerous clinical research companies are at the forefront of AI and machine learning applications in healthcare. They are developing innovative solutions to optimize clinical trial design, predict patient outcomes, and personalize treatment regimens.
3. Real-World Evidence (RWE)
Real-world evidence is gaining prominence as a valuable complement to traditional clinical trial data. RWE leverages data from electronic health records, wearables, and other sources to provide insights into a drug's effectiveness and safety in real-world scenarios. This trend is crucial in facilitating faster drug approvals and more precise treatment recommendations.
Clinical research companies in Bangalore are actively working on RWE initiatives, collaborating with healthcare providers and technology companies to harness the vast troves of data generated in the region's healthcare ecosystem.
4. Patient-Centric Approaches
A growing emphasis on patient-centricity is reshaping the clinical research landscape. Researchers are recognizing the importance of involving patients in study design, recruitment strategies, and decision-making processes. This approach not only enhances patient engagement but also leads to more meaningful and relevant research outcomes.
Bangalore-based clinical research companies are aligning with this trend by implementing patient-centric practices. They are employing innovative communication tools and platforms to ensure patients are active participants in the research journey.
5. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
Virtual reality and augmented reality are finding applications in clinical research, particularly in patient education, training, and data visualization. These immersive technologies enhance the understanding of complex medical concepts, improve training for healthcare professionals, and enable researchers to visualize and interact with data in novel ways.
In Bangalore, a burgeoning tech startup scene is driving the development of VR and AR solutions for clinical research. These innovations hold the potential to revolutionize medical education, clinical trial design, and patient engagement.
6. Regulatory Advances
Regulatory agencies are increasingly open to innovative trial designs and data sources. The use of digital endpoints, such as smartphone apps and wearable devices, is gaining acceptance. This flexibility is accelerating the drug development process and allowing for more efficient and patient-friendly trials.
Clinical research companies in Bangalore are navigating these regulatory changes adeptly, leveraging their expertise to design and execute trials that meet both global and local regulatory requirements.
7. Sustainability in Clinical Trials
Sustainability is a growing concern in clinical research. The pharmaceutical industry is exploring ways to reduce the environmental impact of clinical trials by minimizing paper usage, optimizing supply chains, and reducing travel-related carbon emissions.
Bangalore, often referred to as the Silicon Valley of India, is home to a cluster of environmentally conscious companies. Clinical research firms in the region are aligning with sustainability trends by adopting eco-friendly practices in their operations and trial execution.
8. Gene and Cell Therapies
The field of gene and cell therapies is experiencing remarkable growth. These therapies hold the potential to treat previously incurable diseases by targeting the root causes at the genetic level. Clinical research in this area is expanding rapidly, with numerous trials underway to assess the safety and efficacy of these innovative treatments.
Clinical research companies in Bangalore are actively involved in gene and cell therapy research, leveraging their expertise in biotechnology and genomics to advance these groundbreaking therapies.
9. Global Collaborations
The globalization of clinical research continues to be a dominant trend. Collaboration among research organizations, pharmaceutical companies, and academic institutions across borders is essential for conducting large-scale trials and accessing diverse patient populations.
Bangalore's international connectivity and reputation as a healthcare and technology hub make it an attractive destination for global collaborations in clinical research.
10. Data Security and Privacy
As clinical research becomes increasingly data-driven, ensuring the security and privacy of sensitive patient information is paramount. Stringent data protection measures and adherence to regulatory guidelines are essential to maintaining trust and compliance in clinical research.
Clinical research companies in Bangalore, known for their robust data security infrastructure, are playing a crucial role in developing and implementing data protection strategies to safeguard patient information.
Conclusion
The field of clinical research is undergoing a profound transformation in 2023, driven by advancements in technology, changing regulatory landscapes, and a growing emphasis on patient-centricity. Bangalore, with its vibrant ecosystem of clinical research companies and its alignment with emerging trends, is poised to lead the way in shaping the future of healthcare through innovative research and development. As these trends continue to unfold, the promise of improved treatments, enhanced patient experiences, and a healthier future becomes increasingly tangible.
If you are searching for a clinical research course in Bangalore then CRBtech is the best corporate training institute in Pune. It has focused on training candidates in IT, Mechanical, Electrical,Civil and Clinical Research. It helps students to start their career journey with a good beginning in the industry.
0 notes
Text
DCTs are not a fad, but a trend that is transforming clinical research and patient care. By leveraging technology to make trials more accessible, engaging, and efficient, DCTs can enable faster and better development and delivery of new therapies that can improve the lives of millions of people.
Full Article Link:
https://lnkd.in/g2aH3zJy
#ClinicalTrials#DecentralizedClinicalTrials#DCTs#PatientCentricTrials#RemoteClinicalTrials#DigitalHealth#HealthTech#ClinicalInnovation#PatientEngagement#ResearchRevolution#ClinicalDevelopment#InclusiveTrials#HealthcareTechnology#RegulatoryGuidelines#PatientOutcomes#MedicalResearch#DCTBenefits#HealthcareInnovation#ClinicalResearchTrends#RemoteMonitoring#DigitalTherapeutics#DTx#RegulatoryCompliance#DCTChallenges#MedicalAdvancements#FutureOfMedicine#RealWorldEvidence#FDAGuidance#EMAGuidance#TransformingResearch
1 note
·
View note
Text
Healthcare Outsourcing Industry—an Exposition of Top 10 Trends Reshaping the Global Dynamics
The rising applications of CROs, including augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR) and mixed reality (MR) have fueled the demand for healthcare outsourcing. The adoption of ML and AI has become pronounced in the wake of increasing scrutiny to adhere to regulatory compliance of healthcare products. For instance, AI can propel transparency with accurate results and enhance the efficiency and pace of product development. Since AI is less prone to human error, it enables better quality control to bolster decision-making.
An uptick in the number of decentralized clinical trials (DCTs) in 2021 leveraged forward-looking companies to penetrate the pharmaceutical industry. The number of DCTs was forecast to be pegged at 1300 trials by 2022-end.
The report will offer a bird’s eye view of qualitative development/s in the healthcare outsourcing landscape. The final report, coupled with the database, will offer insights into the following dynamics:
• Capacity expansion in niche markets; decoupling of service offerings; rise in safety assessment; and extended reality.
• Diversifying geographical footprints and mergers & acquisitions. In 2021, over 132 M&As were completed.
• The expanding footprint of personalized medication, genomics and biosimilars.
• IoT implementation and innovations.
Get your copy or request for a free sample of the report “Healthcare Outsourcing Industry - Analysis of Top 10 Trends,” compiled and published by Grand View Research.
Healthcare Outsourcing Industry Report Scope
Divestiture/Consolidation Activities
List of mergers, by CROs/CMOs
List of acquisitions, by CROs/CMOs
List of divestitures, by CROs/CMOs
List of partnerships, by CROs/CMOs
Innovation
New product launches, by Industry
Introduction of generics (for pharmaceutical drugs only)
Globalization
Analysis of level of globalization
Regional presence of top 50 CROs & CMOs
Political pacts/policies impacting international business
Virtual Augmentation
Virtualization in R&D
Virtualization in Business operations implementation
Service Portfolio Modification
Study of the business organization restructuringsOwing to M&A activities
Owing to modernization/revolution
Capacity Expansion in Niche Markets
Analysis of current demand and supply
Focused capacity expansions from 2020 till 2023
Related Reports:
• Digital Health Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Technology (Healthcare Analytics, mHealth, Tele-healthcare, Digital Health Systems), By Component (Software, Hardware, Services), By Region, And Segment Forecasts, 2023 - 2030
• Digital Therapeutics Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Application (Diabetes, Obesity, CVD), By End User (Patients, Providers, Payers, Employers), By Region, And Segment Forecasts, 2022 - 2030
About Us
Grand View Research, Inc. is a market research and consulting comp make informed business decisions, we offer market intelligence studies ensuring relevant and fact-based research across a range of industries, from technology to chemicals, materials and energy. With a deep-seated understanding of varied business environments, Grand View Research provides strategic objective insights.
Find More information @ https://www.grandviewresearch.com/info/trend-reports
#Healthcare Outsourcing Industry#Healthcare outsourcing market#Healthcare Outsourcing#Healthcare Outsourcing Industry Trends
0 notes
Text
Issues with Decentralized Clinical Trial Translation | SYSTRAN
Issues with Decentralized Clinical Trial Translation | SYSTRAN
https://blog.systran.us/issues-with-decentralized-clinical-trial-translation
Decentralized clinical trials (DCTs) include a broad range of patients, helping studies achieve more comprehensive findings. However, as beneficial as DCTs can be, they face unique challenges other studies may not experience.
via https://blog.systran.us/issues-with-decentralized-clinical-trial-translation https://blog.systran.us
May 17, 2023 at 04:03PM
0 notes
Text
FDA’s Landmark Guidance On Decentralized Clinical Trials (DCTs) Signals A New Era Of Patient-Centered Research https://t.co/1BaQ0jTd7Y
FDA’s Landmark Guidance On Decentralized Clinical Trials (DCTs) Signals A New Era Of Patient-Centered Research https://t.co/1BaQ0jTd7Y
— Christie Law Office (@ChristieLawOfc) May 16, 2023
via https://twitter.com/ChristieLawOfc/status/1658502062685007872
0 notes
Text
Decentralized Clinical Trials (DCTs) Market Global Industry Analysis and Opportunity Valuation and Forecast to 2031
The research report delivers a comprehensive analysis of the market structure along with a forecast of the various segments and sub-segments of the market. The report covers a strategic profiling of key players in the market, comprehensively analyzing their core competencies, and drawing a competitive landscape for the market. Key players in the market have been identified through secondary research, and their market shares have been determined through primary and secondary research. All percentage shares, splits, and breakdowns have been determined using secondary and verified primary sources. This report includes the estimation of market size for value and volume. Top-down and bottom-up approaches have been used to estimate and validate the market size of the market, and to estimate the size of various other dependent submarkets in the overall market.
Get the complete sample, please click:
0 notes
Text
FDA Advances Decentralized Trials: Boosting Diversity & Efficiency in Research
📢 FDA embraces Decentralized Clinical Trials, revolutionizing medical research with enhanced accessibility, diversity & efficiency. 🏥💡 #FDA #DCTs #HealthTech
Overall, the FDA’s latest draft guidance on the implementation of decentralized clinical trials is a significant step forward in advancing medical product development and research. By leveraging digital health technologies and reducing barriers to participation, DCTs are expected to increase inclusivity, improve trial efficiency, and accelerate the development of much-needed treatments for…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Navigating the Complexities: Challenges of Site-Centricity in Medical Trials
The landscape of medical trials is evolving rapidly, with a profound shift towards enhanced levels of patient centricity in clinical trials. However, despite this progression, challenges persist, particularly in the realm of site-centricity.
Site-centricity refers to the traditional model where clinical trials are primarily conducted at physical sites such as hospitals, clinics, or research centers. While this approach has its advantages, it also presents a myriad of challenges that can impede the efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and inclusivity of medical trials.

The Significance of Site-Centricity
The question of what is patient centricity in clinical trials has long since been answered but Site-centric trials are now increasingly gaining gravitas. They offer a controlled environment, access to specialized equipment, and oversight by trained professionals, ensuring data accuracy and patient safety.
Moreover, they foster collaboration among investigators and provide a structured framework for trial execution. However, the dependence on physical sites brings forth a set of formidable challenges that cannot be overlooked.
Geographical Limitations
One of the most evident challenges of site-centric trials is the geographical limitations they impose. Patients participating in these trials must often travel long distances to access specific sites, causing inconvenience and financial strain. This limitation hampers recruitment rates and results in a lack of diversity among participants, potentially affecting the generalizability of trial outcomes.
Furthermore, rural or remote populations face heightened barriers, often lacking access to trial sites altogether. This disparity contributes to underrepresentation, affecting the applicability of research findings to these communities.
2. Patient Recruitment and Retention
Recruiting and retaining participants in site-centric trials pose substantial hurdles. Limited awareness about trials, coupled with the inconvenience of frequent site visits, deters many potential candidates from enrolling or completing the trial. This challenge is exacerbated by strict eligibility criteria, further narrowing the pool of eligible participants.
Moreover, maintaining patient engagement and adherence to the trial protocol becomes challenging over extended periods. Patients may face difficulties in balancing trial commitments with their daily lives, leading to dropouts and compromising the integrity of trial results.
3. Cost and Time Inefficiencies
Site-centric trials often incur substantial costs associated with site setup, infrastructure, and personnel. The need for physical space, equipment, and staff can significantly inflate the overall expenses.
Additionally, prolonged timelines due to recruitment delays, administrative processes, and logistical issues escalate the costs further, leading to budget overruns and delayed drug approvals.
4. Regulatory Compliance and Data Quality
Compliance with stringent regulations and ensuring data integrity are pivotal in clinical trials. However, site-centric trials encounter difficulties in maintaining consistent protocol adherence across multiple sites.
Variability in data collection methods, documentation practices, and adherence to protocols among different sites can compromise the reliability and quality of the collected data.
5. The Emergence of Decentralized Clinical Trials
Recognizing the limitations of site-centric trials, the concept of decentralized clinical trials (DCTs) has gained traction.
DCTs leverage technology to decentralize various trial components, minimizing the reliance on physical sites. These trials offer a promising solution to many challenges posed by site-centricity.
6. Virtual Engagement and Remote Monitoring
DCTs leverage telemedicine, wearable devices, and digital platforms to facilitate remote patient monitoring and data collection.
This approach allows patients to participate from the comfort of their homes, eliminating the need for frequent site visits. Virtual engagement enhances convenience for participants, potentially improving recruitment rates and retention while reducing geographical barriers.
7. Enhanced Diversity and Inclusivity
By transcending geographical constraints, DCTs have the potential to achieve greater diversity among participants.
Remote participation enables the inclusion of individuals from various geographic locations and demographic backgrounds, enhancing the representativeness of trial populations and the generalizability of findings.
8. Data Integrity and Real-Time Insights
The integration of digital tools in DCTs enables real-time data collection and analysis. Continuous monitoring and instant data feedback enhance the quality and timeliness of information, allowing for early identification of trends or adverse events. Moreover, centralized data collection minimizes discrepancies and ensures consistency across the trial, enhancing data integrity.
9. Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
While DCTs offer numerous advantages, they also present unique regulatory and ethical challenges. Issues related to data privacy, patient consent, and the validation of remote data collection methods necessitate careful consideration and adaptation of regulatory frameworks to accommodate these innovative trial designs.
Conclusion
The evolution from traditional site-centric trials to decentralized approaches represents a paradigm shift in medical research. While site-centricity has been foundational, its limitations in terms of geographical constraints, patient recruitment, cost inefficiencies, and data quality necessitate a transformation in trial methodologies.
Decentralized clinical trials offer a promising avenue to overcome these challenges, fostering inclusivity, enhancing data quality, and revolutionizing the landscape of medical research by incorporating some of the best site-centricity platforms
Embracing innovation while addressing regulatory and ethical considerations will be pivotal in harnessing the full potential of decentralized trials and advancing medical knowledge for the benefit of patients worldwide. Want to know more about how Octalsoft’s eClinical suite can help you overcome the challenges of site-centricity? Book a demo with us now!
#patient centricity in clinical trials#patient centricity clinical trials#challenges of site centricity
0 notes