#S gene target failure
Text
Cells, Vol. 12, Pages 2853: MiR-630 Promotes Radioresistance by Induction of Anti-Apoptotic Effect via Nrf2–GPX2 Molecular Axis in Head–Neck #cancer
Head and neck #cancer (HNC) ranks among the top ten prevalent #cancers worldwide. Radiotherapy stands as a pivotal treatment component for HNC; however, radioresistance in #cancerous cells often leads to local recurrence, becoming a substantial factor in treatment failure. Micro#RNAs (#miRNAs) are compact, non-coding #RNAs that regulate gene expression by targeting #mRNAs to inhibit protein translation. Although several studies have indicated that the dysregulation of #miRNAs is intricately linked with malignant transformation, understanding this molecular family’s role in radioresistance remains limited. This study determined the role of miR-630 in regulating radiosensitivity in HNC. We discovered that miR-630 functions as an oncomiR, marked by its overexpression in HNC patients, correlating with a poorer prognosis. We further delineated the malignant function of miR-630 in HNC cells. While it had a minimal impact on cell growth, the miR-630 contributed to radioresistance in HNC cells. This result was supported by decreased cellular apoptosis and caspase enzyme activities. Moreover, miR-630 overexpression mitigated irradiation-induced DNA damage, evidenced by the reduced levels of the γ-H2AX histone protein, a marker for double-strand DNA breaks. Mechanistically, the overexpression of miR-630 decreased the cellular ROS levels and initiated Nrf2 transcriptional activity, resulting in the upregulation of the antioxidant enzyme GPX2. Thus, this study elucidates that miR-630 augments radioresistance by inducing an anti-apoptotic effect via the Nrf2–GPX2 molecular axis in HNC. The modulation of miR-630 may serve as a novel radiosensitizing target for HNC. https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4409/12/24/2853?utm_source=dlvr.it&utm_medium=tumblr
0 notes
Text
Machine Learning's Influence on the Pharma Industry
The pharmaceutical industry has long been a cornerstone of global healthcare, consistently pushing the boundaries of innovation and research. In recent years, it has witnessed a dramatic transformation, largely driven by the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into various facets of drug discovery, development, and patient care. With the sector poised to reach a staggering $1.5 trillion economy by 2023, the adoption of more efficient and automated processes is not only a choice but a necessity.

AI in Pharma: A Paradigm Shift
The integration of AI in the pharmaceutical industry has been a game-changer, revolutionizing the landscape of drug discovery and development. AI empowers pharmaceutical companies to advance precision medicine, ensuring that healthcare treatments reach the right patients at the right time. This transformative influence of AI extends from the early stages of drug discovery to the improved understanding and utilization of clinical trial data, marking a consistent and progressive integration of AI technologies.
Here Are Four AI & ML Trends in the Pharma Industry
Drug Discovery and Development using AI in Pharma
The journey from conceptualizing a new drug to bringing it to market is arduous, taking 7-10 years and costing a staggering $2 billion. Furthermore, the process is fraught with high failure rates at various stages. Companies like Cyclica and Bayer are leading the charge in this sector, collaborating to expedite drug discovery. Cyclica, a biotechnology firm, has harnessed AI and computational biophysics to screen small molecule drugs against existing repositories of proteins, dramatically reducing discovery time. Their algorithms predict ADMET (Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion, and Toxicity) to enhance drug efficacy.
Verge Genomics, a neuroscience firm, is partnering with pharmaceutical companies and tissue banks to leverage AI in bringing AI-generated compounds to market for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Through large databases of patient tissues and AI-driven analysis, they discover novel gene targets.
Rare Diseases & Personalized Medicine
Historically, pharma companies focused on diseases affecting large populations, driven by regulatory requirements and the need for affordable drugs. However, AI has opened doors to drug development for rare diseases. The partnership between Tencent Holdings and Huma exemplifies the power of AI in detecting and diagnosing rare neurological diseases. AI algorithms are also used to create personalized drug treatments based on an individual’s genes, environment, and lifestyle. This shift towards personalized medicine is epitomized by the collaboration between Aprecia and Cycle Pharmaceuticals in the development of orphan drugs.
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are a critical phase in drug development, but they face significant challenges. According to a study, 80% of clinical trials fail to meet enrollment timelines, and 1/3 of phase 3 trials terminate due to enrollment difficulties. Start-ups like Deep and Antidote are addressing these challenges using machine learning algorithms. Deep6's AI software analyzes a wide range of clinical data to streamline patient selection for pharmaceutical firms, while Antidote's AI platform matches patients with suitable trials based on their health conditions.
Drug Adherence and Dosage
Maintaining patient adherence and precise dosage during clinical trials is essential. AbbVie and AiCure use smartphone technology with machine learning algorithms to monitor drug adherence, particularly in diseases like schizophrenia. Curate.Ai, on the other hand, assists clinicians in identifying the right drug combination and dosing strategy based on individual patient data, especially relevant in complex diseases like cancer.
AI in Pharmaceuticals: A Healthcare Revolution
The integration of AI in the pharmaceutical industry is drastically altering how medicines are formulated and brought to market. The traditionally prolonged and costly process has evolved into an efficient and collaborative endeavor, thanks to AI. Pharmaceutical companies are partnering with technology firms, resulting in the development of groundbreaking products. AI's influence extends throughout the industry, making it an intelligent assistant for scientists and doctors, enabling the faster and more cost-effective development of superior medicines.
The expedited introduction of new treatments enhances healthcare for all. BirdzAI, a data management solution that combines AI and ML, empowers the industry with insights and predictions to make data-driven decisions. Data360, another solution, leverages machine learning to predict outcomes more accurately than humans using a multitude of variables.
The pharmaceutical industry is at the cusp of a transformative era, driven by the power of AI and ML. From drug discovery and development to clinical trials, rare diseases, and drug adherence, AI is changing the game. It's not just about making processes more efficient; it's about improving patient care, enhancing the quality of medicines, and ushering in a new era of healthcare. The integration of AI is not just a trend; it's a revolution that's here to stay. As we move forward, the pharmaceutical industry, in partnership with AI, will continue to unlock new possibilities and reach even greater heights.
To learn more about all of P360’s innovative products, visit P360.com
0 notes
Text
Precision Medicine Market Size, Insights, Application & Growth Drivers
Overview:
The global precision medicine market size is witnessing unprecedented growth due to people turning their focus more on personal healthcare. It could attain an astonishing CAGR of 12.5% during the forecast period (2023-2032). Precision medicine evolved from the concept that same medicine cannot function equally for two different individuals with the same disease as they have different gene structure. At the same time, medication depends on how well patients can respond to its dosage. Hence, the need for precision medicine. Market Research Future (MRFR), in their report, has included various drivers and segments that can produce a reliable prediction for the future market. Prevalent diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and others are boosting the precision medicine market as treatment of such diseases gets a better result with personalized medicine structure. Furthermore, its impact can significantly lower the cost of treatment.
However, a personal data breach can be seen as a major precision medicine market growth prohibition. The diagnostic cost can incur a high cost, stringent government policies, the risk with hardware and software failure, and lack of medical framework can hold back the market during the forecast period.
Market Insights:
Mergers, acquisitions, collaborations and other strategies dominate the market substantially when it comes to strategic decisions. For instance, Roche purchased Foundation Machine to better their portfolio. On the other hand, New Medicine Partners is trying to increase their market reach by proposing a plan based on personalized medicines to Kazakhstan officials to develop a plant there.
Prominent players in the global precision medicine market include Abbott Laboratories (USA), Ab-Biotics SA (USA), Almac Group Ltd. (UK), Asuragen Inc (USA), Biobase GmbH (Germany), Biomérieux SA (France), Caris Life Sciences (USA), Cepheid Inc. (USA), Cetics Healthcare Technologies Gmbh (Germany), GE Healthcare (USA), GlaxoSmithKline PLC (UK), Healthcore Inc. (USA), IBM (USA), Innventis (Israel), Intel Corporation (USA), Johnson & Johnson (USA), Laboratory Corporation Of America Holdings (USA), Medtronic (USA), Molecular Health GmbH (Germany), Novartis (Switzerland), Pfizer Inc. (USA), Qiagen (Germany), Quest Diagnostics Inc (USA), Randox Laboratories Ltd. (UK), Sanofi Pharma (France), Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited (Japan), Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. (Israel), and others.
Industry Trends:
Precision medicine is showing great promise for the cure of the Alzheimer’s disease. Two new drugs are waiting on the sideline for final approval; one called BAN2401 and the other Anavex 2-73. BAN2401’s use on patients shows a reduction in generation of proteins called amyloid plaques that cause memory loss.
Recently, an article published in SLAS Technology (Society for Laboratory Automation and Screening) revealed that artificial intelligence (AI) is all set to impact precision medicine industry significantly as it can efficiently analyze small datasets and assist in the optimal design of drug combinations.
Segmentation:
The global precision medicine market can be segmented by ecosystem, sub-market, and therapeutics.
Based on the ecosystem, the precision medicine market can be segmented into clinical laboratories, diagnostic tool companies, healthcare IT/ big data companies, and pharma & biotech companies. Diagnostic tools segment has the largest market volume.
Sub-market segment of the precision medicine can be segmented by biomarker-based test, companion diagnostics, molecular diagnostics, pharmacogenomics, targeted therapeutics, and others. Company diagnostics is leading the segment.
Therapeutics-based segmentation of the precision medicine market includes cancer/oncology, cardiovascular disease, central nervous system, infectious diseases, and others.
Regional Analysis:
Region-specific analysis of the precision medicine market encompasses North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), and the Middle East & Africa (MEA).
North America is the largest market for global precision medicine. The region has superior infrastructure, both in healthcare and biotechnology. It sets up the zone perfectly for research and developments assisting further in new product development.
Europe is the second-largest market for global precision medicine. Various investors are taking an interest in the sector and is helping in the development of new drugs. However, the developing regions market particularly, the APAC will be the fastest growing and is likely to be the key to the future. But the MEA region may not find much thrust due to but can expect steady growth.
About US:
Market Research Future (MRFR), enable customers to unravel the complexity of various industries through Cooked Research Report (CRR), Half-Cooked Research Reports (HCRR), Raw Research Reports (3R), Continuous-Feed Research (CFR), and Market Research & Consulting Services.
Contact us:
Market Research Future (part of Wantstats Research and Media Private Limited),
99 Hudson Street,5Th Floor, New York,
New York 10013
United States of America
#Medical Devices#Health#Science#Medical#Healthcare#Precision Medicine Market#Precision Medicine Market Share#Precision Medicine Market Size
0 notes
Text
A Comparison of Lenvatinib as opposed to gelatin within the First-Line Treatment of Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Selection Criteria to steer Physician's Selection inside a New Therapeutic Predicament
Pearson connection make certain you Mann-Whitney U-test with regard to unpaired biological materials were helpful to get the affect of various settings. RESULTS. Using the A hundred and forty mu mirielle chopping go, best precision in the flap breadth had been attained using a go move forward charge of merely one.5 mm/s and an oscillation charge regarding Ten,1000 revoltions per minute (suggest 132.One +/- Ten.2 mu meters; range One hundred twenty.2-147.Two mu meters). Recycling your knife, best accuracy (suggest 130 +/- Six.Being unfaithful mu meters; array 118.5-135 mu meters) had been accomplished along with Eight thousand revolutions per minute. While using the One hundred sixty mu mirielle reducing go, the best possible flap thickness ended up being achieved having a go progress fee of three.Your five mm/s and an oscillation price regarding Tough luck,Thousand rpm (suggest 162.4 +/- Several.Seven mu meters; assortment 151.9-169.8 mu michael). Use the particular edge using the A hundred and sixty mu m chopping go, an adjustment to three.5 mm/s as well as Ten,1000 revolutions per minute was needed (mean 157.Four +/- Several.6 mu michael; array 153.7-161.8-10 mu m). CONCLUSIONS. Seo'ed microkeratome options cause reduced change from your designed flap thickness and so are necessary to enhance flap accuracy. OLCR is a perfect method to proof individualized settings. (Eur T Ophthalmol 2010; Something like 20: 41-7)Toll-like receptors (TLR) certainly are a group of receptors in which participate in a crucial role throughout natural resistant result. Their particular profile is proven throughout macrophages, dendritic tissues, neutrophils as well as mast cells. Toll-like receptors receptors recognize bacterial products and their service sparks the particular inbuilt immune system reply procedure. They may also get involved not directly in the adaptive immune reaction. Sensitive symptoms of asthma #Link# is often a long-term -inflammatory condition together with trait clinical symptoms which includes air passage hypersensitivity, throat impediment and also wheezing. Airway inflammation relates to eosinophilia, elevated amounts of inflammatory mediators and also too much mucous secretion. In animal versions it has been revealed that Toll-like receptors, due to their role within immunological techniques, might be an essential beneficial target in bronchial asthma.Shwachman-Diamond symptoms (SDS), an uncommon autosomal- recessive disorder seen as an exocrine pancreatic deficiency as well as hematopoietic problems, is because versions within the Shwachman-Bodian- Stone syndrome (SBDS) gene. Many of us made human being pluripotent come cell styles of SDS via knockdown regarding SBDS in human being embryonic originate tissues (hESCs) along with age group associated with caused pluripotent originate mobile (iPSC) collections via a pair of individuals using SDS. SBDS-deficient hESCs along with iPSCs manifest failures in exocrine pancreatic as well as hematopoietic difference in vitro, superior apoptosis, and also increased protease amounts in culture supernatants, that may #Link# be reversed simply by restoring SBDS necessary protein phrase by way of transgene recovery as well as simply by adding to lifestyle advertising together with protease inhibitors. Protease-mediated autodigestion provides a mechanistic eating habits study the pancreatic and also hematopoietic phenotypes inside SDS, showcasing the actual electricity regarding hESCs along with #Link# iPSCs inside obtaining book observations straight into human ailment.
0 notes
Text
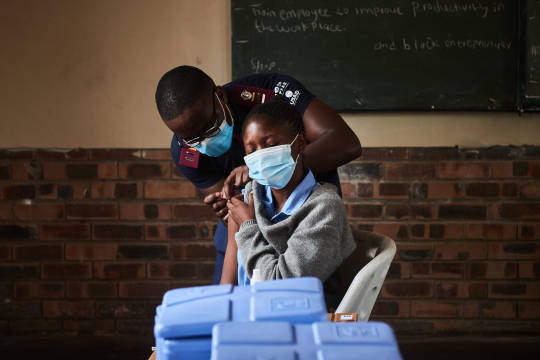
BA.4 and BA.5, two new Omicron variants sweeping South Africa, detected in U.S.
BA.4 and BA.5, two new Omicron variants sweeping South Africa, detected in U.S.
BA.4 and BA.5, two new Omicron variants sweeping South Africa, detected in U.S. | Fortune
You need to enable JavaScript to view this site.
Source link
View On WordPress
#Alpha#Beta#Coronavirus#covid-19#delta#is ba.4 in the u.s.#is ba.5 in the u.s.#morbidity#Mortality#omicron#PCR test#Public health#S dropout signal#S gene target failure#SARS-CoV2#South Africa#U.S.#United States#wild type
0 notes
Text
When identifying the original Omicron variant, labs have indicated that when using PCR tests, one of three target genes is not detected, the World Health Organization says.
This is known as S-gene dropout, which the new sub-lineage in Queensland does not have, the state’s acting chief health officer Peter Aitken said.
“Normal” Omicron has about 30 different gene changes, while the new sub-lineage has about 14.
“So it’s got enough to be able to classify it as Omicron, but we don’t know enough about it as to what that means as far as … clinical severity [and] vaccine effectiveness,” Aitken said.
“What we do know is that it’s looking like Omicron is more infectious and more transmissible.”

Catherine Bennett, chair of epidemiology at Deakin University, said it was important to understand that this “was not new”, in fact, every variant had different genes.
“70% or so of Omicron variants don’t have the S-gene dropout. We have variation within strains,” Bennett said.
The S-gene was interesting because “it allowed the PCR test to differentiate it”, she said.
“The pity is, we miss out on the PCR screening when it would have been nice to distinguish it,” Bennett said.
“It just takes longer to do, instead of having a result in six hours, it means you have to wait the extra day.”
In the strains Australia has already had – such as Alpha and Delta, there are differences in genes, she said.
“Every Delta variant isn’t quite the same. The one we had in Victoria behaved differently to the one that came into NSW – that took off in a very different way.
“There’s a bit of variation within strains, even in the early days. It’s a characteristic mutation but it is not what defines it as Omicron.”
#coronavirus#covid19#pandemic#omicron#omicron variant#covid#coronavirus pandemic#delta variant#S gene dropout#S gene target failure
0 notes
Text
Omicron News Roundup
Reposting links from Naked Capitalism, a great blog that I can't recommend enough.
Link to the study itself:
To estimate the growth of the Omicron variant of concern (1) and its immune escape (2–9) characteristics, we analysed data from all PCR-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 cases in England excluding those with a history of recent international travel. We undertook separate analyses according to two case definitions. For the first definition, we included all cases with a definitive negative S-gene Target Failure (SGTF) result and specimen dates between 29/11/2021 and 11/12/2021 inclusive. For the second definition, we included cases with a positive genotype result and specimen date between 23/11/2021 and 11/12/2021 inclusive. We chose a later start date for the SGTF definition to ensure greater specificity of SGTF for Omicron.
We used logistic and Poisson regression to identify factors associated with testing positive for Omicron compared to non-Omicron (mostly Delta) cases. We explored the following predictors: day, region, symptomatic status, sex, ethnicity, age band and vaccination status. Our results suggest rapid growth of the frequency of the Omicron variant relative to Delta, with the exponential growth rate of its frequency estimated to be 0.34/day (95% CI: 0.33-0.35) [2.0 day doubling time] over the study period from both SGTF and genotype data. The distribution of Omicron by age, region and ethnicity currently differs markedly from Delta, with 18–29-year-olds, residents in the London region, and those of African ethnicity having significantly higher rates of infection with Omicron relative to Delta.
Hospitalisation and asymptomatic infection indicators were not significantly associated with Omicron infection, suggesting at most limited changes in severity compared with Delta.
To estimate the impact of Omicron on vaccine effectiveness (VE) for symptomatic infection we used conditional Poisson regression to estimate the hazard ratio of being an Omicron case (using SGTF definition) compared with Delta, restricting our analysis to symptomatic cases and matching by day, region, 10-year age band, sex and ethnicity. We found a significant increased risk of an Omicron case compared to Delta for those with vaccine status AZ 2+weeks post-dose 2 (PD2) , Pfizer 2+w PD2, AZ 2+w post-dose 3 (PD3) and PF 2+w PD3 vaccine states with hazard ratios of 1.86 (95%CI: 1.67-2.08), 2.68 (95%CI: 2.54-2.83), 4.32 (95%CI: 3.84-4.85) and 4.07 (95%CI: 3.66-4.51), respectively, where PD3 states are categorised by the dose 1/2 vaccine used. Depending on the Delta VE estimates used (10), these estimates translate into Omicron VE estimates of between 0% and 20% PD2 and between 55% and 80% PD3 against Omicron, consistent with other estimates (11). Similar estimates were obtained using genotype data, albeit with greater uncertainty.
To assess the impact of Omicron on reinfection rates we relied on genotype data, since SGTF is associated with a higher observed rate of reinfection, likely due to reinfections typically having higher Ct values than primary infections and therefore being subject to a higher rate of random PCR target failure. Controlling for vaccine status, age, sex, ethnicity, asymptomatic status, region and specimen date and using conditional Poisson regression to predict reinfection status, Omicron was associated with a 5.41 (95% CI: 4.87-6.00) fold higher risk of reinfection compared with Delta. This suggests relatively low remaining levels of immunity from prior infection.
The N501Y mutation in Omicron is universally observed to increase affinity roughly 6-fold, yet other mutations in key sites like K417N, Q493R, and G496S were shown by deep mutational scanning to decrease affinity. Increased affinity for the receptor may account, in part, for increased transmissibility, but that is clearly not the whole story as Omicron is much more transmissible than any previously isolates, including Alpha, Beta, Gamma, and Delta.
In the following weeks, an estimated 29,812 people would be hospitalized with COVID-19 and 3,876 would die every day on average, according to this projection.
"The most pessimistic scenarios are scary. And we need to sort of equip ourselves to make changes — change policies, encourage more cautionary behavior — if and when we start to see hospitalizations tick up in this country," Meyers says.
But Meyers stresses that the most dire scenarios assume the very worst, including that the U.S. takes no additional measures or behavior changes to slow the spread of the virus, such as more masking and social distancing.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is stealth Omicron variant?
In some countries, like Denmark, BA.2 has already surpassed the original Omicron (BA.1) as the dominant variant. Because it doesn't cause a certain signature on lab tests called an s-gene target failure, it can look like other coronavirus variants on a first screen. That has some calling it “the stealth variant.”Feb 3, 2022
2 notes
·
View notes
Link
2020 Yale-G’s Monthly Clinical Updates According to www.uptodate.com
(As of 2020-11-12, updated in Yale-G’s 6th-Ed Kindle Version; will be emailed to buyers of Ed6 paper books)
Chapter 1: Infectious Diseases
Special Viruses: Coronaviruses
Coronaviruses are important human and animal pathogens, accounting for 5-10% community-acquired URIs in adults and probably also playing a role in severe LRIs, particularly in immunocompromised patients and primarily in the winter. Virology: Medium-sized enveloped positive-stranded RNA viruses as a family within the Nidovirales order, further classified into four genera (alpha, beta, gamma, delta), encoding 4-5 structural proteins, S, M, N, HE, and E; severe types: severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV), and novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV, which causes COVID-19). Routes of transmission: Similar to that of rhinoviruses, via direct contact with infected secretions or large aerosol droplets. Immunity develops soon after infection but wanes gradually over time. Reinfection is common. Clinical manifestations: 1. Coronaviruses mostly cause respiratory symptoms (nasal congestion, rhinorrhea, and cough) and influenza-like symptoms (fever, headache). 2. Severe types (2019-nCoV, MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV): Typically with pneumonia–fever, cough, dyspnea, and bilateral infiltrates on chest imaging, and sometimes enterocolitis (diarrhea), particularly in immunocompromised hosts (HIV+, elders, children). 3. Most community-acquired coronavirus infections are diagnosed clinically, although RT-PCR applied to respiratory secretions is the diagnostic test of choice.
Treatment: 1. Mainly consists of ensuring appropriate infection control and supportive care for sepsis and acute respiratory distress syndrome. 2. In study: Chloroquine showed activity against the SARS-CoV, HCoV-229E, and HCoV-OC43 and remdesivir against 2019-nCoV. Dexamethasone may have clinical benefit.
Prevention: 1. For most coronaviruses: The same as for rhinovirus infections, which consist of handwashing and the careful disposal of materials infected with nasal sec retions. 2. For novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV: (1) Preventing exposure by diligent hand washing, respiratory hygiene, and avoiding close contact with live or dead animals and ill individuals. (2) Infection control for suspected or confirmed cases: Wear a medical mask to contain their respiratory secretions and seek medical attention; standard contact and airborne precautions, with eye protection.
Hepatitis A: HAV vaccine is newly recommended to adults at increased risk for HAV infection (substance use treatment centers, group homes, and day care facilities for disabled persons), and to all children and adolescents aged 2 to 18 years who have not previously received HAV vaccine.
Hepatitis C: 8-week glecaprevir-pibrentasvir is recommended for chronic HCV infection in treatment-naive patients. In addition to the new broad one-time HCV screening (17-79 y/a), a repeated screening in individuals with ongoing risk factors is suggested.
New: Lefamulin is active against many common community-acquired pneumonia pathogens, including S. pneumoniae, Hib, M. catarrhalis, S. aureus, and atypical pathogens.
New: Cefiderocol is a novel parenteral cephalosporin that has activity against multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacteria, including carbapenemase-producing organisms and Pseudomonas aeruginosa resistant to other beta-lactams. It’s reserved for infections for which there are no alternative options.
New: Novel macrolide fidaxomicin is reserved for treating the second or greater recurrence of C. difficile infection in children.
Vitamin C is not beneficial in adults with sepsis and ARDS.
Chapter 2: CVD
AF: Catheter ablation is recommended to some drug-refractory, paroxysmal AF to decrease symptom burden. In study: Renal nerve denervation has been proposed as an adjunctive therapy to catheter ablation in hypertensive patients with AF. Alcohol abstinence lowers the risk of recurrent atrial fibrillation among regular drinkers.
VF: For nonshockable rhythms, epinephrine is given as soon as feasible during CPR, while for shockable rhythms epinephrine is given after initial defibrillation attempts are unsuccessful. Avoid vasopressin use.
All patients with an acute coronary syndrome (ACS) should receive a P2Y12 inhibitor. For patients undergoing an invasive approach, either prasugrel or ticagrelor
has been preferred to clopidogrel. Long-term antithrombotic therapy in patients with stable CAD and AF has newly been modified as either anticoagulant (AC)
monotherapy or AC plus a single antiplatelet agent.
Long-term antithrombotic therapy (rivaroxaban +/- aspirin) is recommended for patients with AF and stable CAD. Ticagrelor plus aspirin is recommended for some patients with CAD and diabetes.
VTE (venous thromboembolism): LMW heparin or oral anticoagulant edoxaban is the first-line anticoagulants in patients with cancer-associated VTE.
Dosing of warfarin for VTE prophylaxis in patients undergoing total hip or total knee arthroplasty should continue to target an INR of 2.5.
Chapter 3: Resp. Disorders
Asthma: Benralizumab is an IL-5 receptor antibody that is used as add-on therapy for patients with severe asthma and high blood eosinophil counts.
Recombinant GM-CSF is still reserved for patients who cannot undergo, or who have failed, whole lung lavage.
Pulmonary embolism (PE): PE response teams (PERT, with specialists from vascular surgery, critical care, interventional radiology, emergency medicine, cardiac surgery, and cardiology) are being increasingly used in management of patients with intermediate and high-risk PE.
Although high-sensitivity D-dimer testing is preferred, protocols that use D-dimer levels adjusted for pretest probability may be an alternative to unadjusted D-dimer in patients with a low pretest probability for PE.
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Newly approved capmatinib is for advanced NSCLC associated with a MET mutation, and selpercatinib for those with advanced RET fusion-positive. Atezolizumab was newly approved for PD-L1 high NSCLC.
Circulating tumor DNA tests for cancers such as NSCLC are increasingly used as “liquid biopsy”. Due to its limited sensitivity, NSCLC patients who test (-) for the biomarkers should undergo tissue biopsy.
Cystic Fibrosis (CF): Tx: CFTR modulator therapy (elexacaftor-tezacaftor-ivacaftor) is recommended for patients ≥12 years with the F508del variant.
Vitamin E acetate has been implicated in the development of electronic-cigarette, or vaping, product use associated lung injury.
Chapter 4: Digestive and Nutritional Disorders
Comparison of Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC) and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC):
Common: They are two major types of chronic cholestatic liver disease, with fatigue, pruritus, obstructive jaundice, similar biochemical tests of copper metabolism, overlapped histology (which is not diagnostic), destructive cholangitis, and both ultimately result in cirrhosis and hepatic failure. (1) PBC: Mainly in middle-aged women, with keratoconjunctivitis sicca, hyperpigmentation, and high titer of antimitochondrial Ab (which is negative for PSC). (2) PSC: Primarily in middle-aged men, with chronic ulcerative colitis (80%), irregular intra- and extra-hepatic bile ducts, and anti-centromere Ab (+).
CRC: Patients with colorectal adenomas at high risk for subsequent colorectal cancer (CRC) (≥3 adenomas, villous type with high-grade dysplasia, or ≥10 mm in diameter) are advised short follow-up intervals for CRC surveillance. Pembrolizumab was approved for the first-line treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic DNA mismatch repair (dMMR) CRC.
UC and CRC: Patients with extensive colitis (not proctitis or left-sided colitis) have increased CRC risk.
Eradication of H. pylori: adding bismuth to clarithromycin-based triple therapy for patients with risk factors for macrolide resistance.
Thromboelastography and rotational thromboelastometry are bedside tests recommended for patients with cirrhosis and bleeding.
Pancreatic cancer: Screening for patients at risk for hereditary pancreatic cancer (PC): Individuals with mutations in the ataxia-telangiectasia mutated gene and one first-degree relative with PC can be screened with endoscopic ultrasound and/or MRI/magnetic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
Olaparib is recommended for BRCA-mutated advanced pancreatic cancer after 16 weeks of initial platinum-containing therapy.
HCC (unresectable): New first-line therapy is a TKI (sorafenib or sunitinib) or immune checkpoint inhibitor atezolizumab plus bevacizumab, +/- doxorubicin. Monitor kidney toxicity for these drugs.
UC: Ustekinumab (-umab) anti-interleukin 12/23 antibody, is newly approved for the treatment of UC.
Crohn disease: The combination of partial enteral nutrition with the specific Crohn disease exclusion diet is a valuable alternative to exclusive enteral nutrition for induction of remission.
Obesity: Lorcaserin, a 5HT2C agonist that can reduce food intake, has been discontinued in the treatment of obesity due to increased malignancies (including colorectal, pancreatic, and lung cancers).
Diet and cancer deaths: A low-fat diet rich in vegetables, fruits, and grains experienced fewer deaths resulted from many types of cancer.
Note that H2-blockers (-tidines) are no longer recommended due to the associated carcinogenic N-nitrosodimethylamine.
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST):
GIST is a rare type of tumor that occurs in the GI tract, mostly in the stomach (50%) or small intestine. As a sarcoma, it’s the #1 common in the GI tract. It is considered to grow from specialized cells in the GI tract called interstitial cells of Cajal, associated with high rates of malignant transformation.
Clinical features and diagnosis: Most GISTs are asymptomatic. Nausea, early satiety, bloating, weight loss, and signs of anemia may develop, depending on the location, size, and pattern of growth of the tumor. They are best diagnosed by CT scan and mostly positive staining for CD117 (C-Kit), CD34, and/or DOG-1.
Treatment: Approaches include resection of primary low-risk tumors, resection of high-risk primary or metastatic tumors with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) imatinib for 12 months, or if the tumor is unresectable, neoadjuvant imatinib followed by resection. Radiofrequency ablation has shown to be effective when surgery is not suitable. Newer therapies of ipilimumab, nivolumab, and endoscopic ultrasound alcohol ablation have shown promising results. Avapritinib or ripretinib (new TKI) is recommended for advanced unresectable or metastatic GIST with PDGFRA mutations.
Anal Cancer:
Anal cancer is uncommon and more similar to a genital cancer than it is to a GI malignancy by etiology. By histology, it is divided into SCC (#1 common) and adenocarcinoma. Anal cancer (particularly SCC among women) has increased fast over the last 30 years and may surpass cervical cancer to become the leading HPV-linked cancer in older women. A higher incidence has been associated with HPV/HIV infection, multiple sexual partners, genital warts, receptive anal intercourse, and cigarette smoking. SCCs that arise in the rectum are treated as anal canal SCCs.
Clinical features and diagnosis: 1. Bleeding (#1) and itching (often mistaken as hemorrhoids). Later on, patients may develop focal pain or pressure, unusual discharges, and lump near the anus, and changes in bowel habits. 2. Diagnosis is made by a routine digital rectal exam, anoscopy/proctoscopy plus biopsy, +/- endorectal ultrasound.
Treatment: Anal cancer is primarily treated with a combination of radiation, chemotherapy, and surgery—especially for patients failing the above therapy or for true perianal skin cancers.
Chapter 5: Endocrinology
Diabetes (DM):
Liraglutide can be added as a second agent for type-2 DM patients who fail monotherapy with metformin or as a third agent for those who fail combination therapy with metformin and insulin.
Metformin is suggested to prevent type 2 DM in high-risk patients in whom lifestyle interventions fail to improve glycemic indices.
Metabolic (bariatric) surgery improves glucose control in obese patients with type 2 DM and also reduce diabetes-related complications, such as CVD.
Teprotumumab, an insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor inhibitor, can be used for Graves’ orbitopathy if corticosteroids are not effective. Subclinical hypothyroidism should not be routinely treated (with T4) in older adults with TSH <10 mU/L.
Chapter 6: Hematology & Immunology
Anticoagulants: Apixaban is preferred to warfarin for atrial fibrillation with osteoporosis because it lowers the risk of fracture. Rivaroxaban is inferior to warfarin for antiphospholipid syndrome.
Cancer-associated VTE: LMW heparin or oral edoxaban is the first-line anticoagulant prophylaxis.
NH-Lymphoma Tx: New suggestion is four cycles of R(rituximab)-CHOP for limited stage (stage I or II) diffuse large B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (DLBCL) without adverse features. New suggestions: selinexor is for patients with ≥2 relapses of DLBCL, and tafasitamab plus lenalidomide is for patients with r/r DLBCL who are not eligible for autologous HCT.
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T (NK) immunotherapy is newly suggested for refractory lymphoid malignancies, with less toxicity than CAR-T therapy. Polatuzumab + bendamustine + rituximab (PBR) is an alternative to CAR-T, allogeneic HCT, etc. for multiply relapsed diffuse large B-C NHL.
Refractory classic Hodgkin lymphoma (r/r cHL) is responsive to immune checkpoint inhibition with pembrolizumab or nivolumab, including those previously treated with brentuximab vedotin or autologous transplantation.
Mantle cell lymphoma: Induction therapy is bendamustine + rituximab or other conventional chemoimmunotherapy rather than more intensive approaches. CAR-T cell therapy is for refractory mantle cell lymphoma.
AML: Gilteritinib is a new alternative to intensive chemotherapy for patients with FLT3-mutated r/r AML.
Oral decitabine plus cedazuridine is suggested for MDS and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia.
Multiple myeloma (MM): Levofloxacin prophylaxis is suggested for patients with newly diagnosed MM during the first three months of treatment. For relapsed MM: Three-drug regimens (daratumumab, carfilzomib, and dexamethasone) are newly recommended.
Transplantation: As the transplant waitlist continues to grow, there may be an increasing need of HIV-positive to HIV-positive transplants.
Porphyria:
Porphyria is a group of disorders (mostly inherited) caused by an overaccumulation of porphyrin, which results in hemoglobin and neurovisceral dysfunctions, and skin lesions.
Clinical types, features, and diagnosis: I. Acute porphyrias: 1. Acute intermittent porphyria: Increased porphobilinogen (PBG) causes attacks of abdominal pain (90%), neurologic dysfunction (tetraparesis, limb pain and weakness), psychosis, and constipation, but no rash. Discolored urine is common. 2. ALA (aminolevulinic acid) dehydratase deficiency porphyria (Doss porphyria): Sensorimotor neuropathy and cutaneous photosensitivity. 3. Hereditary coproporphyria: Abdominal pain, constipation, neuropathies, and skin rash. 4. Variegate porphyria: Cutaneous photosensitivity and neuropathies. II. Chronic porphyrias: 1. Erythropoietic porphyria: Deficient uroporphyrinogen III synthase leads to cutaneous photosensitivity characterized by blisters, erosions, and scarring of light-exposed skin. Hemolytic anemia, splenomegaly, and osseous fragility may occur. 2. Cutaneous porphyrias–porphyria cutanea tarda: Skin fragility, photosensitivity, and blistering; the liver and nervous system may or may not be involved. III. Lab diagnosis: Significantly increased ALA and PBG levels in urine have 100% specificity for most acute porphyrias. Normal PBG levels in urine can exclude acute porphyria.
Treatment: 1. Acute episodes: Parenteral narcotics are indicated for pain relief. Hemin (plasma-derived intravenous heme) is the definitive treatment and mainstay of management. 2. Avoidance of sunlight is the key in treating cutaneous porphyrias. Afamelanotide may permit increased duration of sun exposure in patients with erythropoietic protoporphyria.
Chapter 7: Renal & UG
Membranous nephropathy (MN): Rituximab is a first-line therapy in patients with high or moderate risk of progressive disease and requiring immunosuppressive therapy.
Diabetes Insipidus (DI): Arginine-stimulated plasma copeptin assays are newly used to diagnose central DI and primary polydipsia, often alleviating the need for water restriction, hypertonic saline, and exogenous desmopressin.
Prostate cancer: Enzalutamide (new androgen blocker) is available for metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer. Cabazitaxel, despite its great toxicity, is suggested as third-line agent for metastatic prostate cancer. Either early salvage RT or adjuvant RT is acceptable after radical prostatectomy for high-risk disease.
UG cancers: Nivolumab plus ipilimumab is suggested in metastatic renal cell carcinoma for long-term survival.
Enfortumab vedotin is suggested in locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma. Maintenance avelumab is recommended with other chemotherapy in advanced urothelial bladder cancer. Pyelocalyceal mitomycin is suggested for low-grade upper tract urothelial carcinomas.
Chapter 8: Rheumatology
Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors (upadacitinib, filgotinib) are new options for active, resistant RA and ankylosing spondylitis.
Graves’ orbitopathy: new therapy–teprotumumab, an insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor inhibitor.
Chapter 9: Neurology & Special Senses
Epilepsy: Cenobamate, a novel tetrazole alkyl carbamate derivative that inhibits Na-channels, provides a new treatment option for patients with drug-resistant focal epilepsy. A benzodiazepine plus either fosphenytoin, valproate, or levetiracetam is recommended as the initial treatment of generalized convulsive status epilepticus.
Migraine: Lasmiditan is a selective 5H1F receptor agonist that lacks vasoconstrictor activity, new therapy for patients with relative contraindications to triptans due to cardiovascular risk factors.
Stroke: New recommendation for cerebellar hemorrhages >3 cm in diameter is surgical evacuation.
TBI: Antifibrolytic agent tranexamic acid is newly recommended for moderate and severe acute traumatic brain injury (TBI).
Ofatumumab is a new agent that may delay progression of MS.
Chapter 10: Dermatology
Minocycline foam is a new topical drug option for moderate to severe acne vulgaris.
Melanloma: Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in metastatic melanoma has confirmed long-term survival. With sun-protective behavior, melanoma incidence is decreasing.
New: Tazemetostat is suggested in patients with locally advanced or metastatic epithelioid sarcoma (rare and aggressive) ineligible for complete surgical resection.
Psoriasis: New therapies for severe psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: a TNF-alpha inhibitor (infliximab or adalimumab, golimumab) or IL-inhibitor (etanercept or ustekinumab) is effective. Ixekizumab is a newly approved monoclonal antibody against IL-17A. Clinical data support vigilance for signs of symptoms of malignancy in patients with psoriasis.
Chapter 11: GYH
Breast cancer:
Although combined CDK 4/6 and aromatase inhibition is an effective strategy in older adults with advanced receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer, toxicities (myelosuppression, diarrhea, and increased creatinine) should be carefully monitored. SC trastuzumab and pertuzumab is newly recommended for HER2-positive breast cancer.
Whole breast irradiation is suggested for most early-stage breast cancers treated with lumpectomy. Accelerated partial breast irradiation can be an alternative for women ≥50 years old with small (≤2 cm), hormone receptor-positive, node-negative tumors.
Endocrine therapy is recommended for breast cancer prevention in high-risk postmenopausal women.
Uterine fibroids: Elagolix (oral gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist) in combination with estradiol and norethindrone is for treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB) due to uterine fibroids.
Chapter 12: OB
Table 12-6: Active labor can start after OS > 4cm, and 6cm is relatively more acceptable but not a strict number.
Table 12-7: Preeclampsia is a multisystem progressive disorder characterized by the new onset of hypertension and proteinuria, or of hypertension and significant end-organ dysfunction with or without proteinuria, in the last half of pregnancy or postpartum. Once a diagnosis of preeclampsia is established, testing for proteinuria is no longerdiagnostic or prognostic. “proteinuria>5g/24hours” may only indicate the severity.
Mole: For partial moles, obtain a confirmatory hCG level one month after normalization; for complete moles, reduce monitoring from 6 to 3 months post-normalization.
Chapter 14: EM
SHOCK RESUSCITATION
Emergency treatment—critical care!
“A-B-C”: Breathing: …In mechanically ventilated adults with critical illness in ICU, intermittent sedative-analgesic medications (morphine, propofol, midazolam) are
recommended.
Chapter 15: Surgery
Surgery and Geriatrics: Hemiarthroplasty is a suitable option for patients who sustain a displaced femoral neck fracture.
Chapter 16: Psychiatry
Depression: Both short-term and maintenance therapies with esketamine are beneficial for treatment-resistant depression.
Schizophrenia: Long-term antipsychotics may decrease long-term suicide mortality.
Narcolepsy: Pitolisant is a novel oral histamine H3 receptor inverse agonist used in narcolepsy patients with poor response or tolerate to other medications. Oxybate salts, a lower sodium mixed-salt formulation of gamma hydroxybutyrate is for treatment of narcolepsy with cataplexy.
Chapter 17: Last Chapter
PEARLS—Table 17-9: Important Immunization Schedules for All (2020, USA)
Vaccine Birth 2M 4M 6M 12-15M 2Y 4-6Y 11-12Y Sum
HAV 1st 2nd (2-18Y) 2 doses
HBV 1st 2nd 3rd (6-12M) 3 doses
DTaP 1st 2nd 3rd 4th (15-18M) 5th + Td per 10Y
IPV 1st 2nd 3rd (6-18M) 4th 4 doses
Rotavirus 1st 2nd 2 doses
Hib 1st 2nd (3rd) (3-4th) 3-4 doses
MMR 1st 2nd 2 doses
Varicella 1st 2nd + Shingles at 60Y
Influenza 1st (IIV: 6-12Y; LAIV: >2Y (2nd dose) 1-2 doses annually
PCV 1st 2nd 3rd 4th PCV13+PPSV at 65Y
MCV (Men A, B) 1st Booster at 16Y
HPV 9-12Y starting: <15Y: 2 doses (0, 6-12M); >15Y or immunosuppression: 3 doses (0, 2, 6M).
Chapter 17 HYQ answer 22: No routine prostate cancer screening (including PSA) is recommended and answer “G” is still correct–PSA
screening among healthy men is not routinely done but should be indicated in a patient with two risk factors.
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Diagnostics, Vol. 12, Pages 2252: A Novel Rolling Circle Amplification-Based Detection of SARS-CoV-2 with Multi-Region Padlock Hybridization
SARS-CoV-2 has remained a global health burden, primarily due to the continuous #evolution of different mutant strains. These mutations present challenges to the detection of the virus, as the target genes of qPCR, the standard diagnostic method, may possess sequence alterations. In this study, we develop an isothermal one-step detection method using rolling circle amplification (RCA) for SARS-CoV-2. This novel strategy utilizes a multi-padlock (MP-RCA) approach to detect viral-#RNA via a simplified procedure with the reliable detection of mutated strains over other procedures. We designed 40 padlock-based probes to target different sequences across the SARS-CoV-2 genome. We established an optimal one-step isothermal reaction protocol utilizing a fluorescent output detected via a plate reader to test a variety of padlock combinations. This method was tested on #RNA samples collected from nasal swabs and validated via PCR. S-gene target failure (SGTF)-mutated strains of SARS-CoV-2 were included. We demonstrated that the sensitivity of our assay was linearly proportional to the number of padlock probes used. With the 40-padlock combination the MP-RCA assay was able to correctly detect 45 out 55 positive samples (81.8% efficiency). This included 10 samples with SGTF mutations which we were able to detect as positive with 100% efficiency. We found that the MP-RCA approach improves the sensitivity of the MP-RCA assay, and critically, allows for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 variants with SGTF. Our method offers the simplicity of the reaction and requires basic equipment compared to standard qPCR. This method provides an alternative approach to overcome the challenges of detecting SARS-CoV-2 and other rapidly mutating viruses. https://www.mdpi.com/2075-4418/12/9/2252?utm_source=dlvr.it&utm_medium=tumblr
0 notes
Text
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2019: What Cells Do When the Air Gets Thin
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2019 was awarded jointly to William G. Kaelin Jr, Sir Peter J. Ratcliffe and Gregg L. Semenza "for their discoveries of how cells sense and adapt to oxygen availability."

Life on this earth would just about be unimaginable without oxygen – even a few minutes without this vital element can be fatal for many organisms. However, oxygen levels fluctuate, and therefore a mechanism to ensure that cells can appropriately respond when oxygen levels are low, a condition known as hypoxia, is needed. To ensure that this is possible, multicellular organisms have evolved highly effective signalling molecules and pathways that sense when oxygen is scarce and trigger mechanisms that seek to redress the problem. For the discovery of these molecules and mechanisms, William G. Kaelin, Sir Peter J. Ratcliffe and Gregg L. Semenza, have been awarded the 2019 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
All three of this year’s laureates come from medical backgrounds and all three approached the theme of oxygen sensing from a distinct physiological context. The American Greg Semenza found his way to oxygen sensing by way of an initial interest in thalassemia, a blood condition in which the production of haemoglobin is faulty. At the suggestion of colleagues, he decided to also focus on a gene called erythropoietin (EPO), which encodes a hormone that regulates red blood cell production. It was to be a faithful decision, because it would lead him to unravel how cells deal with hypoxia. It was known that some cells produced more EPO when oxygen was scarce, suggesting that cells could both actively sense – and respond – to oxygen levels. Semenza set out to discover the genetic mechanism behind this.
Ratcliffe, meanwhile, who hails from the UK, is a kidney expert and was curious about how specifically that organ was able to sense oxygen. Semenza’s and Ratcliffe’s approaches converged on identifying the DNA regions in EPO and other genes that rendered these cells oxygen-sensitive. After defining these regulatory sequences in DNA that allowed some genes to respond to oxygen, the next challenge was to discover the special protein or transcription factor that bound such sequences, termed hypoxia response elements (HRE), and activated the expression of these genes.
Semenza and his group succeeded in identifying the protein, which they termed hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) and determined that it was active in a range of different mammalian cells. It was also found to regulate the expression of many other genes rather than just EPO – it is now thought that as much as 5% of the human genome is regulated by the HIF-1 protein. This widespread role for HIF-1 suggests that it is performing some crucial function inside cells, and, indeed, embryos lacking the protein fail to develop normally and die before birth because of a failure to properly develop a circulatory system – a process known as angiogenesis.

William Kaelins Jr. comes from the US and his background is in oncology. Kaelin Jr.’s interest in oxygen sensing arose from his focus on a particular type of tumour called von Hippel–Lindau (VHL) disease, named after the German Eugen von Hippel and the Swede Arvid Lindau. These tumours are defined by mutations in the VHL gene and act as if oxygen is scarce – even when it is plentiful. Putting two and two together, Kaelin hypothesised that studying this disease would tell him something interesting about how cells normally respond to low oxygen levels. In a major breakthrough, Kaelin and his collaborators could show that several genes that were already known to be regulated by HIF-1 were produced in high amounts even when oxygen levels were high in cancer cells lacking VHL. Thus, in short, VHL acts to ensure that oxygen-sensitive genes are activated only when oxygen levels are low. How does it do this? It turns out that VHL directly regulates the HIF-1 protein itself. In the presence of normal oxygen levels, the HIF-1 protein is chemically modified. This promotes interaction with VHL which leads to subsequent breakdown of HIF-1.
VHL was originally discovered in the context of cancer, and it is probably true to say that a large part of HIF-1’s fame also rests on its reputation as a ‘good guy gone bad’: many cancers express the protein at very high levels and it is important for cancer development. What is it about oxygen sensing that is so important for cancer? As they grow erratically and evade checkpoints that block uncontrolled cell division, many solid tumours especially often move into areas not serviced by the body’s own blood supply and which are therefore oxygen-poor; thus, they require the blood system to grow in order to make sure that all areas of the tumour receive adequate oxygen. Strategies that target angiogenesis in general and HIF-1 in particular seem to be a promising way of stopping cancer in its tracks, because they block the cancer cell’s oxygen supply.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Genome of girl with severe lupus pins down genetic target for treatments | Science

There is no cure for lupus, a disease that causes the body’s immune system to attack itself. But researchers are now closer to a genetic explanation for the puzzling condition, thanks to the genome of a child with a rare inherited form of the disease.
A new study fingers a gene called TLR7 that helps fight off viruses; when overactive, it unleashes the immune system on the body’s organs and tissues. Although TLR7 is not the only gene implicated in lupus, targeting its activity or protein could help many patients. “TLR7 is likely to be a central hub, if not the central signaling pathway in lupus,” says Carola Vinuesa, an immunogeneticist at the Francis Crick Institute who led the work, published today in Nature.
“It’s a great paper,” says Betty Tsao of the Medical University of South Carolina, who studies lupus genetics but was not involved with the research.
At least 200,000 people in the United States have systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), the most common form of the autoimmune disease. Patients can develop skin rashes, joint pain, fatigue, blood clots, kidney failure, heart disease, and psychiatric problems. Lupus is thought to involve both genetics—it runs in families—along with environmental triggers. Patients usually receive immune-suppressing drugs, but these can make them vulnerable to infections.
In 2016, Vinuesa, then at Australian National University, and collaborators came across a 7-year-old Spanish girl named Gabriela who had symptoms of SLE, which is unusual in children. Sequencing Gabriela’s genome revealed a single-base change in the gene for TLR7, which encodes a pathogen-detecting protein called toll-like receptor 7 on the surface of multiple types of immune cells, including antibodymaking B cells. A TLR7 mutation had never been implicated in lupus before, but the researchers subsequently found several other lupus patients with similar mutations. Mice that were gene edited to carry Gabriela’s TLR7 mutation developed lupus symptoms such as low platelets and kidney damage.
The TLR7 protein’s job is to spot RNA viruses. When the receptor is triggered, cells carrying it produce biochemicals called interferons that block the virus from replicating in other, infected cells; TLR7 also tells B cells to produce antibodies to the virus. (People who lack a functioning TLR7 are prone to severe COVID-19 from SARS-CoV-2, an RNA virus.)
But Gabriela’s TLR7 mutation makes the receptor it encodes much more sensitive, Vinuesa’s team found. Studies of the gene-edited mice showed their TLR7 protein is activated simply by encountering the molecule guanosine, which is present in the DNA and RNA of healthy human cells, her team reports today. “Basically, any nucleic acid component triggers a signal,” Vinuesa says.
The resulting overproduction of interferon leads to an immune attack on normal cells. But an even more important effect was that the mutant TLR7 protein promotes the survival of B cells that recognize normal cell proteins, leading to the production of self-reactive antibodies to those proteins that harm human tissues. Normally those traitorous B cells are weeded out by the immune system.
Researchers already knew mice with extra copies of TLR7 develop a mild lupuslike disorder, and that lupus patients often carry mutations near the gene that slightly alter its activity. But “this is definitive proof” of TLR7’s role, Vinuesa says. Because the TLR7 pathway is often overactivated in people with lupus, even if they don’t have mutations in the gene, her team thinks blocking this pathway with drugs—either targeting the receptor or downstream signals, “is a reasonable therapeutic strategy.”
A role for TLR7 also helps explain why most people with lupus are women: The gene is on the X chromosome in a section where, unlike with most genes, both copies of a gene are often expressed. Men, with their X and Y chromosome pair, have just one copy so they make less of the immune receptor overall, even if they carry the TLR7 mutation.
Tsao says the team makes “a very convincing” case that TLR7 is “a pivotal pathway” in lupus. Rheumatologist Amr Sawalha of the University of Pittsburgh notes that an interferon-blocking drug approved last year called anifrolumab has already been used to treat lupus. The new study, he says, “reinforces targeting TLR7 as a potential treatment.”
Gabriela, now a teenager, takes a cocktail of immunosuppressants to control her disease; the drugs have had the side effect of stunting her growth. She said in a press release that she hopes the new research will lead to better treatments for “so many lupus warriors who suffer from this disease.”
New post published on: https://livescience.tech/2022/04/27/genome-of-girl-with-severe-lupus-pins-down-genetic-target-for-treatments-science/
0 notes
Photo

孔雀大師 • 23m 最新研究發現,COVID-19(2019冠狀病毒疾病)Omicron亞型變異株BA.2不僅傳播更快速,可能引發更嚴重的重症,甚至可以阻撓人類對抗冠狀病毒的某些重要武器。 美國有線電視新聞網(CNN)報導,根據日本實驗室研究發現,BA.2可能與Delta等舊變異株一樣,能夠引發重症,而且就像Omicron,它也可能對疫苗產生的免疫力有部分免疫逃逸能力。但施打追加劑可以重新取得防護力,讓感染後的重症機率減少約74%。 研究也發現,BA.2似乎對於某些治療具有抗藥性,包括目前被廣用於治療Omicron的Sotrovimab單株抗體療法。 這項研究16日發表在醫學期刊預印本伺服器bioRxiv,尚未經過同行評審。 俄亥俄州克里夫蘭醫院(Cleveland Clinic)微生物學部門負責人羅德斯 (Daniel Rhoads)表示:「從人類角度來看,它可能是一種比BA.1更嚴重的病毒,可能更快速傳播並導致更嚴重疾病。」羅德斯審閱了研究報告,但並未參與研究。 BA.2相較於源自中國武漢的原始病毒株,具有高度突變,與Omicron病毒株也有數十種基因變異,使得它與近來的變異株如Alpha、Beta、Gamma和Delta之間有很大差異。 研究作者、東京大學醫科學研究所副教授佐藤佳(Kei Sato)認為,這些發現證明BA.2不應被視為Omicron的亞型變異株,需要對它進行更密切監視。 佐藤告訴CNN,BA.2被稱為「匿蹤Omicron」,因為它在PCR測試中檢測不到S基因靶標(S-gene target failure, SGTF),這點與Omicron不同。因此實驗室必須採取額外步驟,對病毒進行定序,以找到這種變異株。 他表示,許多國家首先需要做的「就是建立一種檢測BA.2的特定方法」。 華盛頓大學醫學院病毒學家傅勒(Deborah Fuller)表示,「看來我們必須替這個變異株找一個新的希臘字母。」她同樣審閱了研究報告,但並未參與研究。 BA.2的傳染力比Omicron高約30%至50%,目前已在74個國家以及全美47個州現蹤。 根據美國疾病管制暨預防中心(CDC)估計,美國目前約有4%確診病患感染的是BA.2變異株。 其他國家則更有經驗,根據世界衛生組織(WHO)每週流行病學報告,這種變異株已在至少10個國家地區成為主流病毒株,包括孟加拉、汶萊、中國、丹麥、關島、印度、蒙特內哥羅、尼泊爾、巴基斯坦和菲律賓。 https://www.nownews.com/news/5720650 https://www.instagram.com/p/CaJApksvyJ5/?utm_medium=tumblr
0 notes