#PDS(PUBLIC DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM)
Text
AMS’s second new life
AMS’s second new life
In 2011, the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS) was installed on the International Space Station (ISS). Since then, it has recorded more than 200 billion cosmic ray events and, while most of their sources are known, a few signatures in the data could point to dark matter. The detector’s latest upgrade will enable scientists to investigate this further.
AMS collects cosmic ray particles that reach Earth coming either directly from the Sun or from far-away sources such as stars ending in supernovae or black holes. Most of the cosmic rays that AMS detects are protons, but heavy nuclei like iron or silicon also reach the detector. However, one signature is particularly intriguing. AMS has detected an unusually high flux of positrons – the antimatter partners of electrons. Positrons and other antimatter particles are rare in the Universe and hence not expected to be seen in the observed data at the strength found by AMS. Their origin is not yet confirmed; they could come from pulsars (fast rotating remnants of stars that emit regular signals), a yet-unknown astrophysical source or dark matter. The observed positron flux fits very well with dark matter models. But in order to investigate this more accurately, the AMS collaboration is now working on refurbishing the detector.
The main upgrade will be a new detector layer with a higher number of silicon strips that will increase the acceptance of recording infalling particles by 300%. “By 2030, AMS will extend the energy range of the positron flux and reduce the error by a factor of two compared with current data,” says AMS spokesperson Sam Ting (MIT). This will allow the detector to investigate the positron signature even further.
A second important addition will be three new radiative surfaces. Because AMS is exposed to direct sunlight, it was painted white to reflect excess heat and remain at operational temperatures. After 13 years in the demanding conditions of space, the paint has degraded and, to compensate for this, the new radiators will keep AMS cool again.
Astronauts training at NASA’s “Neutral Buoyancy Lab” on a full-scale ISS model submerged under water where they learn to mount the new AMS upgrade parts (Image: Corrado Gargiulo/NASA)
Currently, all the parts of the new upgrade, including electronics and hardware, are being built as “validation” and “qualification” models. If they pass all the tests happening at CERN, INFN Perugia and IABG in Germany, the final flight model will go into production. Astronauts are already training with the prototypes in space-like environments on Earth. In 2026, when the upgrade is launched, the astronauts will mount the new detector parts onto AMS during spacewalks. “Everything is going very, very fast,” says chief engineer Corrado Gargiulo (CERN). “This is a requirement, otherwise we arrive too late at the ISS for the upgrade to make sense.” Indeed, the mission now has an end date. NASA has scheduled the deorbiting of the ISS for 2030 and, until then, AMS will have plenty of cosmic ray events to record to explore the positron signature.
A mock-up detector for the next AMS upgrade, which will be installed during the next anticipated spacewalk for AMS. Another part of the upgrade includes a large power distribution system (PDS) radiator to restore AMS’s optimal thermal performance. (Image: Chetna Krishna/CERN)
ckrishna
Tue, 03/26/2024 - 13:40
Byline
Sanje Fenkart
Publication Date
Tue, 04/02/2024 - 10:00 https://home.web.cern.ch/news/news/experiments/amss-second-new-life (Source of the original content)
0 notes
Text
Streamlining Public Distribution Systems: The Aadhaar and Ration Card Link
Introduction:
In recent years, the integration of technology with essential public services has become a hallmark of efficient governance. One such initiative in India that exemplifies this trend is the link Aadhaar with ration cards. Aadhaar, a unique identification number issued to residents of India, and ration cards, a critical document for accessing subsidized food through the Public Distribution System (PDS), have been linked to enhance transparency, eliminate duplication, and streamline the distribution of essential commodities.
Background:
Aadhaar, a biometric-based identification system, was introduced in 2009 with the aim of providing a unique identity to every resident of India. Simultaneously, the PDS has been a crucial mechanism for delivering food grains, sugar, and kerosene at subsidized rates to the economically disadvantaged sections of society. However, over the years, issues such as leakages, ghost beneficiaries, and duplicate ration cards have plagued the system, leading to inefficiencies and corruption.
The Aadhaar and Ration Card Link:
To address these challenges, the Indian government initiated the process of linking Aadhaar with ration cards. The objective was to create a more robust and foolproof system that ensures the targeted delivery of benefits to the intended recipients. The linking process involves associating the unique Aadhaar number with the ration card, enabling authorities to authenticate the identity of individuals through biometric verification.
Benefits of Aadhaar-Ration Card Linkage:
Elimination of Duplicate and Ghost Beneficiaries:
By linking Aadhaar with ration cards, the government aims to eliminate duplicate and ghost beneficiaries from the PDS system. Aadhaar's biometric authentication ensures that only genuine individuals receive the subsidized food items, reducing leakages and corruption.
Transparent and Efficient Distribution:
The linkage enhances transparency in the distribution process by creating a digital trail of transactions. This transparency helps in monitoring the movement of food grains and other commodities, reducing the chances of diversion and ensuring that the intended beneficiaries receive their entitlements promptly.
Financial Savings:
The elimination of duplicate beneficiaries and reduction in leakages result in significant financial savings for the government. These savings can be redirected towards improving the quality and quantity of subsidies, ultimately benefiting the vulnerable sections of society.
Improved Targeting of Welfare Schemes:
The Aadhaar-linked ration card system enables the government to better target welfare schemes and subsidies. With accurate data on the socio-economic status of individuals, authorities can design and implement policies that address the specific needs of different segments of the population.
Digital Empowerment:
The integration of Aadhaar with ration cards contributes to the digital empowerment of citizens. It encourages the use of technology for accessing essential services, paving the way for a more inclusive and digitally literate society.
Challenges and Concerns:
While the Aadhaar-ration card linkage offers numerous benefits, it has not been without challenges. Concerns regarding privacy, data security, and exclusion errors have been raised. Addressing these concerns is crucial to ensure that the benefits of the system are maximized without compromising individual rights and inclusivity.
Conclusion:
The Aadhaar and ration card linkage represents a significant step towards modernizing and improving the efficiency of public distribution systems. By leveraging technology to authenticate identities and streamline processes, the Indian government aims to create a more accountable and responsive system that prioritizes the welfare of its citizens. As the implementation progresses, addressing challenges and incorporating feedback from stakeholders will be essential to realizing the full potential of this transformative initiative.
0 notes
Text
VILLAGE OFFICE KALPETTA
Kalpetta Village Office is among Wayanad District's top Village Offices. The employs are trained professionals. The Kalpetta Village Office interacts with clients more peacefully. The services providing by village office are, Civil Registration Services: Birth registration, Death registration, Marriage registration. Land Records and Property Services: Land ownership records, Property tax assessment, Land surveys and demarcation. Welfare and Social Services: Issuing certificates for various welfare programs, Distribution of social security benefits, Assistance for vulnerable populations. Local Governance Support: Conducting local elections, Supporting local government functions, Handling local disputes and conflicts. Public Distribution System (PDS): Distribution of essential commodities at subsidized rates. Issuance of Certificates: Income certificates, Caste certificates, Residence certificates, OBC (Other Backward Classes) certificates. Permits and Licenses: Small business licenses, Fishing permits (in coastal areas), Agriculture-related licenses. Education Services: School enrollment and attendance monitoring, Scholarships and educational support. Health Services: Basic health information and assistance, Immunization programs, Distribution of health-related information. Public Grievance Redressal: Handling and resolving local issues and complaints. Agricultural Services: Agricultural extension services, Information on government schemes for farmers. Infrastructure Development: Local road maintenance, Basic infrastructure projects. etc.
0 notes
Text
=Professional Development=
This is my blog by Oleksandr Sodol, for assignment: Professional Development by: Rob Murphy
LO1 Investigate the range and accessibility of employment opportunities that relate to your specialism
For first i wish highlight the specialty relate with my accessibility way in Music Industry.
So, on my opinion an better specialty for could be:
Producer(PD)

or Promoter(PM)

(PD)Opportunities for Music Producer:
Opportunities for music producers are diverse and can be found across various sectors of the music industry:
Recording Studios:
Studio Producer/Engineer: Working in recording studios, overseeing recording sessions, mixing, and mastering music for artists across genres.
Music Labels and Publishing Companies:
In-House Producer: Employed by a record label or publishing company to work with their roster of artists, assisting in music production and development.
Freelance and Independent Work:
Freelance Producer: Offering services independently to artists, bands, or labels, working on individual projects or album productions.
Live Music and Performance:
Live Sound Producer: Working in live music settings, managing sound systems and ensuring quality during live performances or events.
Film, TV, and Gaming:
Film/TV/Game Music Producer: Creating or overseeing the production of music for movies, TV shows, commercials, or video games.
Educational Institutions:
Educational Producer/Instructor: Teaching music production in schools, colleges, or through online courses and tutorials.
Online Platforms and Streaming Services:
Digital Content Producer: Creating music content for online platforms, streaming services, or social media, including tutorials, reviews, and original compositions.
(PD)Access to Opportunities:
Networking and Collaboration: Building relationships with artists, industry professionals, and studios through networking events, online platforms, and collaboration opportunities.
Portfolio and Reputation: Showcasing a strong portfolio of work, having credits on successful projects, and building a reputation for quality production work.
Skill Development: Continuously honing music production skills, staying updated with industry-standard software and techniques.
Internships and Entry-Level Positions: Gaining experience through internships, assisting established producers, or starting in entry-level roles within studios or production houses.
The music industry is dynamic, and opportunities for music producers can come from various sources. Building a diverse skill set, being adaptable, and staying connected within the industry are key factors in accessing and succeeding in music production roles.
(PM)Opportunities for Music Promoter:
Music promoters play a vital role in the music industry by promoting artists, events, and music releases. Opportunities for music promoters exist in various sectors:
Concert Promotion and Event Management:
Concert Promoter: Organizing and promoting live music events, concerts, and festivals. This involves booking artists, securing venues, and marketing the events to the public.
Event Management: Working with venues or event companies to organize and promote music-related events, including showcases, tours, and music conferences.
Music Marketing and Public Relations:
Music Marketing Specialist: Developing and implementing marketing strategies to promote artists, albums, and music releases. This includes digital marketing, social media campaigns, and collaborations with brands.
Public Relations (PR) Manager: Managing public relations for artists or music-related companies, handling media relations, press releases, and reputation management.
Artist Management and Booking Agencies:
Artist Manager: Working closely with artists to plan their careers, oversee their schedules, and promote their music to a wider audience.
Booking Agent: Connecting artists with venues, negotiating performance contracts, and promoting live shows for musicians.
Record Labels and Music Distribution:
Label Promoter: Working within a record label to promote the label's artists and releases to the public, media, and industry professionals.
Music Distribution Promotion: Promoting music releases through distribution channels, ensuring visibility on streaming platforms, radio, and digital stores.
Digital Platforms and Streaming Services:
Streaming Service Promotion: Working with streaming platforms to promote artists' music through playlists, featured content, and marketing initiatives.
Social Media Promotion: Managing social media accounts, creating engaging content, and leveraging online platforms to promote artists and music releases.
(PM)Access to Opportunities:
Networking: Building relationships within the music industry, connecting with artists, labels, venues, and other industry professionals.
Marketing Skills: Developing strong marketing skills, understanding trends, and being able to create effective promotional campaigns.
Industry Knowledge: Staying informed about the music industry's trends, changes, and emerging technologies to adapt promotional strategies.
Internships and Entry-Level Positions: Gaining experience through internships or starting in entry-level roles within music promotion companies or agencies.
Success in music promotion often requires a combination of creativity, strategic thinking, networking, and a deep understanding of the music market to effectively promote artists and their music to a wider audience.
LO2Design a personal professional development strategy that will outline targets for pro-active skills development
Identify the key professional attributes that relate to your specialism
(PD)As a music producer, several key professional attributes are crucial for success within the field:
Technical Skills:
Audio Engineering Expertise: Proficiency in recording, mixing, and mastering audio using industry-standard software and hardware.
Instrumentation Knowledge: Understanding various musical instruments and their sonic characteristics to guide musicians during recording sessions.
Sound Design and Synthesis: Ability to create and manipulate sounds using synthesis techniques and virtual instruments.
Musical Proficiency:
Music Theory Knowledge: Understanding musical concepts, harmony, rhythm, and song structures to contribute creatively to music production.
Instrumentation Proficiency: Proficiency in playing musical instruments can aid in composing, arranging, and communicating musical ideas effectively.
Creativity and Innovation:
Creative Vision: Having a unique creative vision and the ability to bring that vision to life through music production.
Innovative Approach: Embracing new techniques, technologies, and trends to innovate and evolve in music production.
Communication and Collaboration:
Effective Communication: Strong communication skills to effectively convey ideas, provide feedback, and collaborate with artists, engineers, and other team members.
Collaborative Approach: Working collaboratively with artists and other industry professionals while respecting their creative input.
Time Management and Organisation:
Project Management Skills: Organizing and managing recording sessions, timelines, and multiple projects simultaneously.
Attention to Detail: Having a meticulous approach to ensure high-quality production and meticulous sound quality.
Business Acumen:
Networking Skills: Building and maintaining relationships within the music industry, establishing connections with artists, labels, studios, and other professionals.
Understanding Industry Trends: Keeping abreast of industry trends, market demands, and technological advancements to stay competitive.
Adaptability and Resilience:
Adaptability: Being adaptable to different music genres, artists' preferences, and changing production environments.
Resilience: Handling setbacks, challenges, and rejections, while maintaining motivation and dedication to the craft.
Continuous Learning and Improvement:
Curiosity and Growth Mindset: Being open to learning new techniques, exploring new genres, and continuously improving one's craft.
Professional Development: Attending workshops, courses, or seeking mentorship to stay updated with evolving industry standards.
Developing and honing these professional attributes is essential for a music producer to excel in the ever-evolving and competitive landscape of music production.
(PM)Here is some key professional attributes for a music promoter:
Networking and Relationship Building:
Networking Skills: Building and maintaining relationships within the music industry, connecting with artists, venues, media, and other industry professionals.
Effective Communication: Strong communication skills to negotiate deals, convey promotional messages, and build rapport with various stakeholders.
Marketing and Promotion:
Marketing Expertise: Knowledge of marketing strategies, including digital marketing, social media, PR campaigns, and traditional marketing avenues.
Promotional Creativity: Ability to devise innovative and engaging promotional campaigns to effectively market artists and their music.
Industry Knowledge and Trends:
Understanding the Music Industry: Knowledge of industry trends, market demands, and an understanding of the dynamics of the music business.
Trend Awareness: Staying updated with the latest trends in music, marketing, and technology to adapt promotional strategies accordingly.
Strategic Thinking and Planning:
Strategic Planning: Developing comprehensive marketing plans, setting achievable goals, and executing strategies to promote artists effectively.
Adaptability: Being adaptable to different genres, target audiences, and the evolving landscape of the music industry.
Negotiation and Business Skills:
Negotiation Skills: Negotiating contracts, deals, and partnerships beneficial to the artists and their careers.
Business Acumen: Understanding the business side of music, including revenue streams, royalties, and copyright laws.
Organisation and Time Management:
Project Management: Organizing promotional campaigns, coordinating events, and managing multiple projects concurrently.
Time Management: Handling deadlines, schedules, and ensuring timely execution of promotional activities.
Resilience and Problem-Solving:
Resilience: Handling setbacks, adapting to challenges, and persistently pursuing promotional efforts amidst rejections or obstacles.
Problem-Solving Skills: Ability to troubleshoot issues, find creative solutions, and think on one's feet during promotional campaigns.
Passion and Commitment:
Passion for Music: A genuine love for music and a commitment to supporting and promoting artists' careers.
Dedication: Being dedicated to promoting artists' work and contributing positively to the music industry.
Cultivating these attributes can empower a music promoter to effectively market and promote artists, create impactful campaigns, and contribute significantly to the success and visibility of musicians within the industry.
(PD)Identify experiential activity that will address the development of relevant professional attributes for music producer:
Experiential activities play a crucial role in developing professional attributes for a music producer. Here are some activities tailored to foster growth in key areas:
Technical Skills Development:
Studio Internship or Shadowing: Assisting experienced producers/engineers in a studio setting to learn recording, mixing, and mastering techniques hands-on.
Hands-On Software Training: Workshops or online courses focusing on mastering industry-standard software used in music production.
Musical Proficiency Enhancement:
Music Theory Workshops/Classes: Deepening understanding of musical concepts, harmony, and song structures to improve compositional skills.
Instrument Proficiency Practice: Regular practice with musical instruments to gain fluency and enhance the ability to guide musicians effectively during recording sessions.
Creativity and Innovation:
Music Production Challenges: Participating in online production challenges or hackathons to spark creativity and experiment with innovative techniques.
Collaborative Projects: Working on collaborative projects with artists or peers to explore diverse genres and develop a unique creative vision.
Communication and Collaboration:
Live Recording Sessions: Organizing or participating in live recording sessions to practice effective communication with musicians, engineers, and other team members.
Collaborative Workshops: Engaging in workshops or seminars focusing on communication skills, providing constructive feedback, and fostering teamwork.
Time Management and Organization:
Project-Based Learning: Managing personal or group projects from start to finish, including setting timelines, tracking progress, and meeting deadlines.
Studio Simulation Exercises: Simulating studio scenarios to practice handling multiple tasks concurrently and managing time effectively.
Business Acumen Development:
Industry Networking Events: Attending music industry events, conferences, or seminars to network with professionals and understand market trends.
Case Studies and Analysis: Reviewing case studies of successful productions, analyzing industry trends, and understanding the business side of music production.
Adaptability and Resilience Building:
Diverse Genre Exploration: Experimenting with producing different music genres to adapt to varied artistic demands and styles.
Feedback Incorporation: Seeking and integrating constructive feedback from mentors, peers, or professionals to adapt and improve continually.
Continuous Learning and Improvement:
Continual Skill Development: Participating in ongoing workshops, online courses, or mentorship programs to stay updated with industry advancements.
Self-Initiated Projects: Undertaking personal projects or challenges to explore new techniques and consistently improve skills.
Engaging in these experiential activities provides invaluable hands-on learning, allowing music producers to cultivate and enhance their professional attributes crucial for success in the dynamic field of music production.
(PM)Identify experiential activity that will address the development of relevant professional attributes for music promoter:
Experiential activities are instrumental in developing skills essential for a music promoter. Here are activities tailored to enhance relevant professional attributes:
Networking and Relationship Building:
Industry Events and Conferences: Attending music industry events, seminars, and conferences to network with professionals, artists, and potential collaborators.
Artist Showcases/Networking Mixers: Organizing or attending showcases and mixers to establish connections and build relationships within the industry.
Marketing and Promotion:
Mock Campaign Creation: Formulating mock promotional campaigns for hypothetical artists or projects to practice marketing strategies and promotional creativity.
Social Media Management: Managing social media profiles or campaigns for emerging artists or personal projects to gain hands-on marketing experience.
Industry Knowledge and Trends:
Market Research and Analysis: Conducting research on industry trends, analyzing market demands, and preparing reports or case studies on successful promotional strategies.
Artist Discovery Workshops: Hosting workshops or events to discover and understand emerging talent, staying abreast of new music trends.
Strategic Planning and Negotiation:
Mock Contract Negotiations: Simulating contract negotiations for artist representation or event planning to practice negotiation skills.
Event Planning and Execution: Organizing small-scale music events, handling logistics, marketing, and execution to hone organizational skills.
Communication and Collaboration:
Artist/Label Collaboration Workshops: Organizing collaborative workshops between artists and labels to practice effective communication and foster collaborations.
PR Campaign Simulation: Simulating PR campaigns, drafting press releases, and media outreach exercises to enhance communication skills.
Time Management and Adaptability:
Promotional Campaign Simulation: Planning and executing mock promotional campaigns within limited timeframes to practice time management and adaptability.
Crisis Management Scenarios: Simulating crisis scenarios and developing strategies to manage unforeseen challenges in promotional campaigns or events.
Continuous Learning and Networking:
Mentorship Programs: Engaging in mentorship programs with experienced promoters or industry professionals to gain insights and guidance.
Online Courses and Webinars: Participating in online courses, webinars, or workshops focused on music marketing, PR, and industry advancements.
Passion Projects and Real-Life Applications:
Personal Promotion Projects: Undertaking personal promotion projects for local artists or community events to apply learned promotional strategies in real-life scenarios.
Music Blog/Content Creation: Creating a music blog, podcast, or content platform to promote emerging talent and develop promotional content creation skills.
Engaging in these experiential activities allows music promoters to acquire, refine, and apply critical skills in networking, marketing, strategic planning, and communication within the music industry, fostering professional growth and effectiveness in promoting artists and their work.

Illustrate short, medium and long-term career targets
(PD)Here's a plan outlining short, medium, and long-term career targets for a music producer:
Short-Term (0-2 years):
Skill Enhancement:
Improve proficiency with a specific music production software/tool.
Attend workshops or online courses focusing on advanced mixing and mastering techniques.
Portfolio Development:
Produce at least 3-5 high-quality tracks across different genres.
Collaborate with emerging artists or friends to diversify the portfolio.
Networking and Exposure:
Attend local industry events, open mic nights, or producer meet-ups to network.
Secure an internship or assistant role in a reputable studio to gain hands-on experience.
Medium-Term (2-5 years):
Project Expansion:
Produce an EP or album for an emerging artist, aiming for a commercial release.
Collaborate with established artists or secure placements in films/TV/games.
Career Advancement:
Pursue a specialized certification or degree in audio engineering or music production.
Consider joining a production company or label to gain broader industry exposure.
Brand Building and Marketing:
Create an online presence with a professional website and active social media profiles.
Start a production label or brand to establish a recognizable identity.
Long-Term (5+ years):
Professional Recognition:
Establish oneself as a sought-after producer with a solid track record of successful projects.
Aim for industry awards, nominations, or recognition for notable productions.
Business Expansion:
Expand the production studio, hire additional staff, and collaborate with top-tier artists.
Diversify income streams by exploring music publishing, licensing, or production education.
Mentorship and Contribution:
Mentor aspiring producers through workshops, tutorials, or speaking engagements.
Contribute expertise to industry panels, educational institutions, or music organizations.
Global Reach and Impact:
Collaborate with international artists, tapping into diverse markets and audiences.
Engage in humanitarian or social projects, using music for positive social impact.
This career plan serves as a roadmap, setting achievable milestones and targets for continuous growth and advancement in the field of music production. Adjustments and refinements to this plan can be made based on evolving industry trends, personal aspirations, and feedback from mentors or peers along the journey.
(PM)Here's a plan outlining short, medium, and long-term career targets for a music promoter:
Short-Term (0-2 years):
Networking and Learning:
Attend industry events, seminars, and workshops to build connections.
Engage in online forums, groups, or communities to learn about current trends.
Artist Discovery and Support:
Discover and promote emerging artists through local showcases or online platforms.
Assist in organizing small-scale events or gigs to gain hands-on experience.
Skill Development:
Enhance marketing skills by creating promotional content for local artists.
Learn about social media advertising, PR strategies, and basic event planning.
Medium-Term (2-5 years):
Establishing Presence:
Develop a strong online presence via social media, blogs, or a dedicated website.
Secure partnerships with local venues, artists, and media outlets for wider reach.
Event Management and Promotion:
Organize larger-scale events, concerts, or showcases to showcase multiple artists.
Collaborate with sponsors or brands to enhance event visibility and funding.
Industry Recognition:
Aim for nominations or recognition in local music awards or industry publications.
Build a reputation for promoting successful, well-attended events with positive feedback.
Long-Term (5+ years):
Expanded Roster and Global Reach:
Expand the artist roster, working with diverse talents across genres.
Collaborate with international artists, aiming for cross-border promotions.
Business Growth and Specialization:
Consider starting a promotion company or label specializing in a particular genre.
Diversify services into artist management, tour planning, or music consulting.
Industry Leadership and Mentorship:
Act as a mentor or advisor for aspiring promoters, sharing expertise and insights.
Participate in industry panels, workshops, or educational initiatives.
Impact and Legacy:
Use promotional events or campaigns to support social causes or community initiatives.
Leave a lasting impact on the industry by fostering emerging talent and innovation.
This career plan aims to guide a music promoter toward establishing a strong foothold in the industry, expanding their network, honing promotional skills, and making a lasting impact within the music promotion sphere over time. Adjustments and adaptations can be made based on individual aspirations, industry shifts, and evolving market dynamics.
So, now ima wish to show: development plan for a music promoter across different timeframes.
Short-Term (0-6 months):
Networking and Skill Enhancement:
Attend at least three industry events or workshops to expand the professional network.
Enroll in an online course or workshop focusing on social media marketing for music promotion.
Volunteer to assist in organizing local music events or showcases for hands-on experience.
Online Presence and Content Creation:
Establish a professional online presence through a dedicated website or social media profiles.
Regularly create engaging content (interviews, behind-the-scenes content) for social media promotion.
Artist Discovery and Partnership:
Discover and collaborate with two local emerging artists, promoting their music through online channels.
Initiate partnerships with two local venues or event organizers for future collaborations.
Medium-Term (6 months - 2 years):
Event Management and Brand Building:
Organize a mid-sized local music event or showcase, handling marketing and logistics.
Aim for regular participation in industry-relevant panels or discussions for exposure.
Marketing and Strategic Planning:
Develop and implement two comprehensive marketing plans for different artists or events.
Enroll in a marketing strategy course to deepen knowledge and skills in promotional planning.
Expansion and Collaboration:
Expand promotional efforts to neighboring cities or regions, collaborating with artists and venues.
Establish collaborations with at least three local businesses or brands for event sponsorships.
Long-Term (2 years+):
Business Growth and Specialization:
Evaluate the feasibility of starting a specialized promotion company focusing on specific music genres or events.
Diversify services by offering artist management or consulting services to emerging talents.
Global Reach and Industry Influence:
Develop strategies to expand promotional efforts to international markets or collaborations with overseas artists.
Initiate mentorship programs or workshops for aspiring promoters, contributing to industry growth.
Social Impact and Legacy:
Incorporate social responsibility into promotional campaigns by supporting local charities or causes.
Aim to leave a positive mark on the industry by fostering new talents and innovative promotional approaches.
Continuous Development:
Continuous Learning:
Regularly attend industry events, workshops, or webinars to stay updated with trends and strategies.
Seek feedback from peers or mentors to continually refine promotional approaches and strategies.
Professional Networking:
Actively engage in networking events, maintaining connections, and nurturing industry relationships.
Collaborate with other promoters or professionals to exchange ideas and explore new opportunities.
Evaluation and Adaptation:
Regularly assess the effectiveness of promotional campaigns and strategies, adapting to changing market dynamics.
Set aside time for self-reflection and goal-setting to ensure continual growth and improvement.
This personal development plan outlines a trajectory for growth, focusing on skill enhancement, networking, strategic planning, and long-term impact within the music promotion industry. Adjustments can be made based on personal aspirations, market changes, and evolving career objectives.
0 notes
Text
Navigating 'The Arduous March': Analyzing Jihyun Ah's Perspective
"The Arduous March" is a memoir by Ji Hyun Ah that reflects on her childhood in North Korea during the famine of the 1990s. The famine, also known as the "Arduous March" or the "March of Suffering," was a period of mass starvation and economic crisis that lasted from 1994 to 1998. During this time, an estimated 240,000 to 3.5 million people died from starvation and related causes. Ji Hyun Ah's memoir provides a personal account of the hardships and propaganda she experienced during this time. In the case of "The Arduous March," a thematic analysis could involve identifying recurring themes in Ji Hyun Ah's memoir, such as survival, nationality, economic crisis and poverty.

Theme 1: Self Reliance and Identity Crisis
Ji Hyun Ah's memoir highlights the importance of self-reliance in the face of extreme adversity. She describes how malnutrition was a common condition in North Korea, and how the people did not have access to medical support or even medicine for a cold. In this environment, it was essential to rely on oneself to survive. Ji Hyun Ah's family had to find ways to obtain food and other necessities, such as by trading goods on the black market. The memoir also describes how the North Korean government's public distribution system (PDS) collapsed during the famine, forcing people to fend for themselves. Ji Hyun Ah's experiences demonstrate the resilience and resourcefulness required to survive in such a challenging environment.
The famine in North Korea also led to an identity crisis for many of its citizens. The collapse of the PDS and the resulting migration and corruption undermined the government's legitimacy. Ji Hyun Ah describes how the propaganda she was exposed to as a child portrayed North Korea as a utopia, but the reality was far from it.

The famine shattered the illusion of a perfect society and forced people to confront the harsh realities of their situation. The decisions that heads of households had to make about who would and would not eat were demoralizing and traumatic. The memoir highlights the struggle to reconcile the idealized image of North Korea with the harsh reality of the famine. "The Arduous March" by Ji Hyun Ah provides a firsthand account of the famine that occurred in North Korea during the 1990s. The memoir highlights the themes of self-reliance and identity crisis, demonstrating the resilience and resourcefulness required to survive in a challenging environment, as well as the struggle to reconcile the idealized image of North Korea with the harsh reality of the famine.

Theme 2: Poverty and dreams of an individual
Poverty is a harsh reality for a significant portion of the world's population. It is not just the lack of material possessions, but also the absence of basic needs such as food, shelter, education, and healthcare. For those trapped in the vicious cycle of poverty, dreams often seem like an unattainable luxury.
In the text, there are many instances of poverty depicted.The narrator’s family had to be dependent on their relatives in China for even basic necessities like education, food and clothes. At the mere age of seventeen, the narrator had to take up the responsibility of supporting her family. She used to make songgi tteok to feed her family. She also used to chop firewood and drag it with a rope to her house.It was an extremely difficult task for such a young girl .In their house ,when the smoke started to come out of the chimney, she had to fix it all by herself. Along with this , she also had to take care of her ill mother and younger siblings.In order to get out of numerous debts her father had to sell their own belongings.When their debts increased and their living conditions deteriorated, they finally decided to leave North Korea.
During the famine in North Korea, poverty reached severe levels. The country faced food shortages, economic collapse, and a lack of resources, leading to widespread malnutrition and suffering among the population. Poverty in North Korea has also been attributed to poor governance by the totalitarian regime. It is estimated that 60% of the total population of North Korea live below the poverty line in 2020.

Dreams have the power to inspire, ignite passion, and propel individuals forward.They serve as a beacon of hope, motivating people to overcome obstacles and strive for a better life.
However, when poverty enters the scene, dreams are often pushed aside, overshadowed by the daily struggle for survival. Financial constraints can limit access to education, obstructing the pursuit of knowledge and skills necessary to achieve desired goals. Lacking basic necessities, individuals may be forced into early marriages or child labor, sacrificing their dreams for immediate survival.Living in a constant state of scarcity and uncertainty can erode one's belief in the possibility of a brighter future.
Instead of enjoying her teenage years , the narrator had to bear the burden of running her household.While the wealthy kids went to schools, took part in sports and other extra curricular activities, she had to help her father in supporting their family.She talks about how her dream of becoming a musician changed to a writer due to the harsh reality they lived in. Despite of having a passion for music and encouragement by her father, after the Arduous March, she had the desire to become a writer to record her experiences for people to read and become aware of the dire situation in North Korea.

Poverty may cast a shadow of despair and uncertainty over the dreams of individuals, but it doesn't mean those dreams are lost forever. With the right support, opportunities, and a resilient spirit, people living in poverty can still fight against the odds and pursue their dreams.
Theme 3: Economic Crisis
The theme of economic crisis is central to the text, as it describes the struggles of North Koreans during this time. The following is a thematic analysis of the theme of economic crisis in The Arduous March by Ji Hyun Ah:
Economic Mismanagement: The economic crisis in North Korea was caused by a combination of factors, including economic mismanagement by the government. The text describes how the North Korean people did not have any standard when it came to malnutrition, as it was such a common condition. Scarcity of Resources: During the Arduous March, resources such as food and medicine were scarce, and people had to resort to extreme measures to survive. The text describes how Ji Hyun Ah's family ate tree bark and rice roots to survive.

Militarization of the Economy: As a result of the economic crisis, the North Korean government began to prioritize the military over other sectors of the economy. This led to the spread of limited market activity and the militarization of the economy
International Sanctions: The economic crisis in North Korea was also exacerbated by international sanctions. The text mentions how North Koreans could not get any medical support, even medicine for a cold. Defection: The economic crisis in North Korea led to an increase in defection from the country. The text mentions how Ji Hyun Ah's family considered defecting to China, but ultimately decided against it.
Theme 4: Nationality and Patriotism
In "The Arduous March," the theme of nationality and borders is explored through the experiences of the North Korean people during a time of political and economic turmoil. As the country faced a severe famine and economic collapse in the 1990s, the government enforced strict control over the movement of people across borders. This led to a sense of isolation and desperation among the North Korean people, who were unable to seek help or resources from neighboring countries.Throughout the text, we see how the North Korean government emphasises the importance of national identity and loyalty, even as its policies lead to the suffering of its citizens. The government's prioritization of national security and pride over the well-being of its people is reflected in the strict border controls and propaganda that seek to maintain a sense of unity among the population.However, the author also highlights the ways in which nationality and borders can be arbitrary and harmful. As the North Korean people struggle to survive, they are forced to cross into China in search of food and resources. Here, they face discrimination and exploitation from Chinese citizens and authorities, who view them as illegal immigrants. This demonstrates how borders can create divisions between people and perpetuate inequality and suffering.

Overall, "The Arduous March" shows how the theme of nationality and borders can have both positive and negative effects on individuals and societies. While borders can provide security and a sense of identity, they can also lead to harm and injustice when used to enforce strict control and division.
Conclusion
The Arduous March was a period of famine in North Korea that lasted from 1994 to 1998. The famine was caused by a combination of factors, including economic mismanagement, natural disasters, international sanctions, and the collapse of the Soviet block. The North Korean government's propaganda campaign referred to the famine as the "Arduous March" or "March of Suffering". The famine resulted in the deaths of an estimated 240,000 to 3.5 million people. The famine was so severe that people were forced to eat grass, tree bark, and even insects to survive. Many people were also forced to flee the country in search of food and a better life.

JiHyun Ah, who grew up in North Korea during the famine, shared her experience of the Arduous March in an article published in The Guardian. She described how people were forced to eat fern, bracken fiddlehead, bonnet bellflower, Solomon’s seal, mountain wormwood, victory onion, clavaria, naematoloma, and other wild plants to survive. She also shared how weak and malnourished she was when she left North Korea, and how her mother sobbed when she saw her.
The North Korean government's response to the famine was inadequate, and it took until July 11, 1997, for the State Department to first make a large food donation and use the word "famine" in describing the situation. The regime's cruel policies and defensiveness led to the crisis. The famine had long-lasting consequences, including the militarization of the economy, the spread of limited market activity, and food aid from various countries.
In conclusion, the Arduous March was a period of famine in North Korea that lasted from 1994 to 1998. The famine was caused by a combination of factors, including economic mismanagement, natural disasters, international sanctions, and the collapse of the Soviet bloc. The famine resulted in the deaths of an estimated 240,000 to 3.5 million people. The North Korean government's response to the famine was inadequate, and it had long-lasting consequences. JiHyun Ah's experience of the Arduous March highlights the suffering that many North Koreans endured during this period.
Citations:
[1] https://www.theguardian.com/world/2014/jun/13/arduous-march-north-korea-famine
[2] https://www.123helpme.com/essay/The-Arduous-March-Summary-743467
[3] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/North_Korean_famine
[4] https://www.wilsoncenter.org/article/how-did-the-north-korean-famine-happen
[5] http://www.workday.upenn.edu/http%3A%2F%2Fd53.org/m0gi1vl.htm
[6] http://www.workday.upenn.edu/http%3A%2F%2Fmestslidsu.cf/3lhidad13wwwworkdayupennedugo4
Ariktha Sunil Naidu MB227009
Aviva Raula MB227012
Mitali Subhash MB227067
Eshika Jain MB227030
Khushi Seth MB227055
Deeksha V MB227018
0 notes
Text
Evolution of Retail in India
Written by: Jagriti Shahi, Business Analyst at Global Launch Base

The retail industry in India has undergone significant evolution over the years, driven by factors such as economic growth, urbanization, changing consumer preferences, technological advancements, and government policies. The retail industry in India has evolved significantly over the years. The early days of retailing in India were dominated by small, independent mom-and-pop stores and Kirana stores. These stores catered to the needs of the local community and offered a limited range of products.
In the 1990s, the Indian economy liberalized, which led to the entry of foreign retailers into the Indian market. These retailers brought with them new concepts and practices, such as large format stores, supermarkets, and hypermarkets. This led to the growth of the organized retail sector in India.
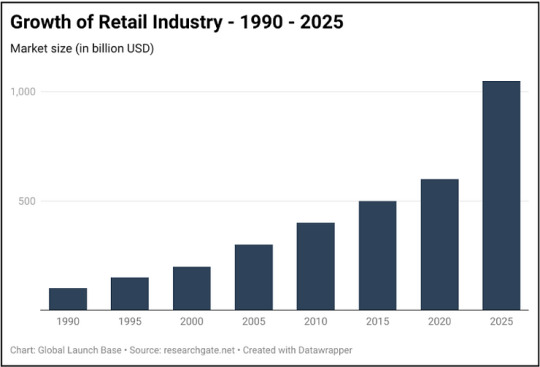
Figure 1: Expected Growth of Retail Industry till 2025
The market size of the Indian retail market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10% from 2022 to 2025. This growth is being driven by a number of factors, including the growing population, rising incomes, and increasing urbanization.
The Indian retail industry is expected to continue to grow in the coming years. The factors driving this growth include increasing urbanization, rising disposable incomes, and growing consumer demand for convenience.
Here's an overview of the evolution of retail in India:
Traditional Retail (Pre-1990s)

Figure 2: Traditional Retail Store
Traditional retail in India refers to the practice of selling products or services through physical stores, such as mom-and-pop stores, Kirana stores, bazaars, and weekly markets. These stores are typically small and family-owned, and they offer a limited range of products. They are often located in residential areas and cater to the needs of the local community.

Figure 3: Kirana Stores
Kirana stores: Kirana stores are small, neighborhood grocery stores that sell a variety of food items, household goods, and other necessities. They are often family-owned and operated, and they play an important role in the daily lives of many Indians.

Figure 4: Weekly Markets
Weekly markets: Weekly markets are held in different parts of the city on a weekly basis. They sell a variety of goods, including fresh produce, meat, fish, and other food items. Weekly markets are a popular place for people to buy their groceries and other household items.

Figure 5: Street Shops
Street shops: Street shops are small, open-air shops that line the streets of many Indian cities. They sell a variety of goods, including clothing, jewellery, souvenirs, and other items. Street shops are a popular place for tourists to buy souvenirs and other items.
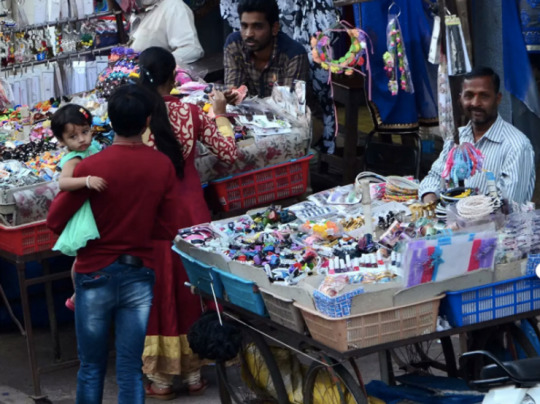

Figure 6: Hawkers
Hawkers: Hawkers are street vendors who sell a variety of goods, including food, drinks, and other items. They often move around from place to place, and they are a common sight in many Indian cities.

Figure 7: Public Distribution System
Public distribution system: The public distribution system (PDS) is a government-run program that provides essential food items to low-income households. The PDS operates through a network of ration shops, which are small, government-run stores that sell subsidized food items.
Economic Liberalization (1990s)
India's economic reforms in the 1990s opened the doors for foreign direct investment (FDI) and led to the emergence of modern retail formats. Brands like McDonald's and Pizza Hut entered the Indian market during this time. However, organized retail remained limited due to challenges such as infrastructure constraints, regulatory hurdles, and consumer preferences for familiar traditional shopping experiences.

Figure 8: Shopping Malls in India
The 2000s witnessed the growth of shopping malls in major cities. These malls housed a mix of international and domestic brands, along with entertainment and dining options. The mall culture changed the way Indians shopped, providing a one-stop destination for shopping and leisure.
The rise of shopping malls in the 2000s was driven by a number of factors, including:
The growth of the middle class in developing countries, such as India and China, led to an increase in demand for Western-style shopping experiences.
The rise of e-commerce had a limited impact on the mall industry in the early 2000s, as many consumers still preferred to shop in person.
Malls were seen as a safe and convenient place to shop, especially for families.
Malls offered a variety of entertainment options, such as movie theaters, food courts, and arcades, which made them a popular destination for people of all ages.
As a result of these factors, the number of shopping malls in the world grew rapidly in the 2000s. In India, for example, the number of malls increased from 3 in 2000 to over 650 in 2022.
However, the rise of e-commerce in the late 2000s and early 2010s began to have a negative impact on the mall industry. As more and more people started shopping online, mall traffic declined. This trend was exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic, which forced many malls to close temporarily.
As a result, the mall industry is facing a number of challenges in the 2020s. Malls are having to adapt to the changing retail landscape by offering more experiential and interactive experiences, such as food halls, art installations, and fitness centers. They are also trying to attract more foot traffic by partnering with non-retail businesses, such as healthcare providers and coworking spaces.
Only time will tell whether the mall industry will be able to survive the challenges of the 2020s. However, the rise of shopping malls in the 2000s is a testament to their ability to adapt to changing consumer trends.
Modern Retail Formats (2000s-2010s): Large-format retail stores like Big Bazaar, Reliance Retail, and others introduced modern retail concepts, offering a variety of products under one roof. These stores aimed to provide convenience, value, and a wide range of options to consumers.
Here are some of the modern retail formats that emerged in the 2000s and 2010s:
E-commerce: This is the sale of goods and services over the Internet. E-commerce has grown rapidly in recent years and is now a major force in the retail industry.
Omnichannel retailing: This refers to the integration of online and offline retail channels. Omnichannel retailers offer customers the ability to shop online, in-store, or through a combination of both channels.
Pop-up stores: These are temporary retail stores that are typically open for a short period of time, such as a few weeks or months. Pop-up stores are often used by brands to test new products or concepts or to reach a specific target audience.
Warehouse clubs: These are large-scale retailers that offer members discounted prices on a variety of goods. Warehouse clubs typically require an annual membership fee.
Factory outlets: These are stores that sell discounted merchandise, such as overstock, discontinued items, and seconds. Factory outlets are often located in outlet malls.
Membership-based retailers: These are retailers that require customers to pay a membership fee in order to shop. Membership-based retailers typically offer exclusive benefits to members, such as discounts, free shipping, and early access to new products.
Social commerce: This is the use of social media platforms to sell goods and services. Social commerce has grown in popularity in recent years, as more and more people use social media to shop.
Blurring of the lines between retail and entertainment: Retailers are increasingly incorporating entertainment elements into their stores, such as arcades, game rooms, and food courts. This is done in an effort to make shopping more fun and engaging for customers.
E-commerce Boom (2010s): The advent of the internet and the rise of e-commerce platforms like Flipkart, Amazon, and Snapdeal brought a transformative change to the retail landscape. E-commerce offers consumers the convenience of shopping from home, a vast array of products, and attractive discounts. The growth of smartphones and improved internet connectivity further accelerated the adoption of online shopping.
The e-commerce boom in India began in the early 2010s, driven by a number of factors, including:
The increasing availability of high-speed internet
The growth of the Indian middle class
The rise of smartphones
The government's pro-business policies
In 2010, the Indian e-commerce market was worth just $3.9 billion. By 2022, it had grown to $84.5 billion, making India the second-largest e-commerce market in the world after China.
The growth of e-commerce in India has had a major impact on the economy. It has created jobs, boosted exports, and helped to bring down prices for consumers. It has also helped to connect rural areas with the rest of the country.
Some of the major players in the Indian e-commerce market include:
Flipkart
Amazon
Paytm Mall
Snapdeal
Myntra
Nykaa
BigBasket
Grofers
Udaan
Zilingo
These companies offer a wide range of products and services, including electronics, fashion, groceries, home goods, and travel. They have also expanded into new areas, such as food delivery and online payments.
The e-commerce boom in India is still in its early stages. It is expected to continue to grow in the coming years, driven by the factors mentioned above. This growth will have a positive impact on the Indian economy and society.
Here are some of the key impacts of the e-commerce boom in India:
Increased access to goods and services: E-commerce has made it possible for people in rural areas and smaller towns to access a wider range of goods and services than ever before.
Increased competition: The entry of new players into the e-commerce market has led to increased competition, which has benefited consumers in the form of lower prices and better-quality products.
Job creation: The e-commerce sector has created millions of jobs in India, both directly and indirectly.
Increased tax revenue: The government has been able to collect more tax revenue from the e-commerce sector.
Improved logistics: The e-commerce boom has led to the development of better logistics infrastructure in India, which has benefited other sectors of the economy as well.
Overall, the e-commerce boom has been a positive force for the Indian economy and society. It has helped to improve the lives of millions of people and has boosted the country's economic growth.
Omni-Channel Retailing: Retailers started adopting omni-channel strategies, integrating physical stores with online platforms. This approach allowed consumers to research products online and make purchases either online or in-store. Retailers like Tata Group's Croma and fashion brands implemented these strategies to provide a seamless shopping experience.
Omni-channel retailing has gained significant traction in India as the country's retail landscape continues to evolve and adapt to changing consumer preferences and technological advancements. Indian retailers have embraced omni-channel strategies to provide customers with seamless and personalized shopping experiences across various channels. Here's how omni-channel retailing is shaping up in India:
E-commerce Pioneers: India's booming e-commerce sector has been at the forefront of omni-channel adoption. Leading e-commerce platforms like Flipkart, Amazon India, and Snapdeal have expanded their offerings to include not only online marketplaces but also BOPIS (Buy Online, Pick Up In-Store) options and partnerships with brick-and-mortar stores for faster deliveries.
Traditional Retailers Going Digital: Traditional retailers have recognized the importance of digital transformation. Many established brick-and-mortar brands have launched their own e-commerce websites and mobile apps to cater to the growing online shopper base. For instance, retail chains like Shoppers Stop, Reliance Retail, and Tata-owned Croma have developed omni-channel strategies to bridge the gap between offline and online shopping.
Click-and-Mortar Stores: Some Indian retailers have adopted the "click-and-mortar" approach, wherein they maintain both physical stores and robust online platforms. This approach allows customers to seamlessly move between online and offline channels. Brands like Nykaa, a cosmetics and beauty retailer, have successfully combined their e-commerce presence with offline stores to offer customers a comprehensive shopping experience.
Fashion and Lifestyle Industry: The fashion and lifestyle sector in India has been a key driver of omni-channel strategies. Leading fashion brands like Myntra, Lifestyle, and FabIndia have integrated their online and offline operations, offering customers options like trying on clothes in-store before ordering online or making online purchases and returning items to physical stores.
Mobile-First Approach: With the increasing penetration of smartphones in India, mobile apps have become a crucial aspect of omni-channel strategies. Retailers focus on creating user-friendly and responsive apps that allow customers to browse, shop, and track orders on their mobile devices.
Personalization and Loyalty Programs: Indian retailers are leveraging customer data to offer personalized recommendations, discounts, and promotions. Loyalty programs that span across online and offline channels encourage repeat business and brand loyalty.
Challenges: While omni-channel retailing is on the rise in India, challenges such as inadequate technology infrastructure, supply chain complexities, and varying levels of digital literacy in different regions still exist. Retailers need to tailor their omni-channel strategies to suit the diverse Indian market.
Government Regulations: Indian regulations around e-commerce and foreign direct investment (FDI) have influenced how some companies implement omni-channel strategies, particularly in the multi-brand retail segment. Regulations may impact how international brands and retailers establish their presence in India.
Future Outlook: As technology continues to advance and consumer expectations evolve, omni-channel retailing is expected to play an increasingly vital role in the Indian retail sector. Retailers will likely continue to invest in technology, data analytics, and personalized experiences to create a seamless and convenient shopping journey for customers across various channels.
Rural Retail Expansion

Figure 9: Rural Retail
Here are some key points to consider in the context of rural retail expansion:
Rationale for Rural Retail Expansion:
Untapped Market Potential: Rural areas often have a large population that can be a significant consumer base. As rural incomes rise and lifestyles change, there is a growing demand for a wide range of products.
Increased Purchasing Power: With the expansion of agriculture, government schemes, and remittances from urban areas, rural consumers have more disposable income to spend on goods and services.
Market Saturation in Urban Areas: In many cases, urban markets may have become saturated or highly competitive, prompting retailers to explore new growth opportunities in rural regions.
Government Initiatives: Various government initiatives aimed at rural development and financial inclusion can boost rural purchasing power and create an enabling environment for retail expansion.
Strategies for Successful Rural Retail Expansion:
Local Understanding: Successful expansion requires a deep understanding of the local culture, preferences, and consumer behavior in rural areas. What works in urban markets may not necessarily work in rural regions.
Product Localization: Tailoring product offerings to suit local tastes and needs is crucial. This may involve introducing smaller pack sizes, adapting to local preferences, and offering products that are relevant to rural lifestyles.
Distribution Networks: Establishing efficient and cost-effective distribution networks is essential. This might involve partnerships with local distributors, leveraging existing local retailers, or using innovative delivery methods.
Affordability: Rural consumers are often more price-sensitive than their urban counterparts. Offering affordable options and value for money is critical to gaining their trust and loyalty.
Education and Awareness: Rural consumers might not be familiar with certain products or brands. Providing information and education about the benefits and usage of products can drive adoption.
Localized Marketing: Customizing marketing campaigns to resonate with rural consumers' aspirations, values, and cultural nuances can help build a strong brand presence.
Technology Adoption: Leveraging technology, especially mobile phones, can be a powerful tool for reaching rural consumers. Mobile apps, SMS campaigns, and digital platforms can facilitate engagement.
Financial Inclusion: Introducing payment options that align with rural consumers' financial cycles and offering credit or installment payment plans can enhance affordability.
Challenges of Rural Retail Expansion:
Infrastructure: Poor roads, inadequate transportation, and lack of basic amenities can pose logistical challenges.
Lack of Awareness: Rural consumers might not be aware of new products or brands, necessitating efforts to build awareness and educate them.
Distribution Challenges: Reaching remote areas with limited connectivity can be challenging, impacting the efficiency of distribution networks.
Cultural Sensitivity: Diverse cultures and languages in different rural regions require a sensitive and localized approach to marketing and communication.
Grocery and Fresh Retail: The grocery segment saw significant transformation with players like BigBasket and Grofers offering online grocery delivery services. Additionally, numerous hypermarkets and supermarkets entered the scene, catering to consumers' demand for fresh produce and convenience.
Key Characteristics:
Essential Goods: Grocery and fresh retail primarily deals with essential food items and household consumables that people need on a regular basis.
Perishable Items: A significant portion of the products sold in this segment are perishable, which requires careful management of inventory, supply chain, and storage to maintain product quality and reduce wastage.
Wide Product Range: Grocery and fresh retail encompasses a wide range of products, from staples like rice, flour, and lentils to fresh produce, dairy products, bakery items, frozen foods, and packaged goods.
Frequent Purchases: Consumers tend to visit grocery stores regularly for their daily or weekly needs, making it an integral part of their routine.
Customer Loyalty: Successful grocery retailers often build strong customer loyalty due to their consistent and reliable supply of essentials.
Challenges:
Quality Maintenance: Maintaining the quality and freshness of perishable items is a significant challenge, requiring proper storage, transportation, and inventory management.
Wastage Management: Reducing food wastage due to spoilage or expiration is a top concern in this sector.
Price Sensitivity: Grocery shoppers are often price-sensitive and seek the best value for their money. Retailers need to strike a balance between quality and affordability.
Competition: The grocery sector is highly competitive, with multiple retailers vying for consumers' attention. This can lead to slim profit margins.
Supply Chain Complexity: Managing the supply chain for perishable products requires a robust distribution network and efficient transportation to ensure timely deliveries.
Modern Trends and Innovations:
Online Grocery Shopping: The rise of e-commerce has led to the growth of online grocery platforms that allow customers to order essentials and have them delivered to their doorstep.
Contactless Shopping: The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of contactless shopping methods, such as curbside pickup and home delivery.
Smart Inventory Management: Retailers are using technology and data analytics to optimize inventory, reduce wastage, and streamline the supply chain.
Private Labels: Many retailers are introducing their own private-label brands for grocery items, offering quality products at competitive prices.
Fresh Formats: Some retailers are focusing on "fresh" formats, offering a wide selection of high-quality produce and perishables.
Key Players:
In India, the grocery and fresh retail sector is served by various players:
Kirana Stores: Small neighborhood stores that play a crucial role in serving local communities with everyday essentials.
Supermarkets: Larger stores that offer a broader range of products and are known for organized displays and air-conditioned shopping environments.
Hypermarkets: Larger than supermarkets, hypermarkets provide an extensive range of products, including groceries, electronics, clothing, and more.
Online Grocers: E-commerce platforms like BigBasket, Grofers, and Amazon Pantry offer online grocery shopping and home delivery.
Specialty Stores: These focus on specific categories, such as organic foods, gourmet products, or health-conscious items.
The grocery and fresh retail segment is an essential and dynamic part of the retail industry, continually adapting to consumer preferences, technological advancements, and changing market dynamics.

Figure 10: Luxury Retails Stores
The luxury retail sector also experienced growth, with international luxury brands setting up stores in premium malls and high-street locations in major cities. This shift reflected changing consumer aspirations and increased disposable incomes.
Key Characteristics:
Premium Products: Luxury goods are characterized by their exceptional quality, craftsmanship, and attention to detail. These products often use the finest materials and are crafted with precision.
Exclusivity: Luxury brands often limit the availability of their products to maintain a sense of exclusivity and rarity.
Brand Image and Status: Luxury brands are built around a strong brand identity and aspirational image. Owning luxury items can signal a certain social status and lifestyle.
Innovation and Design: Luxury brands focus on innovation in design, technology, and aesthetics to create unique and desirable products.
Retail Experience: Luxury retail emphasizes providing a superior shopping experience, with well-designed stores, personalized customer service, and immersive brand environments.
Factors Driving Luxury Retail Growth:
Rising Affluence: The growth of high-net-worth individuals and the middle class in various regions, including Asia, has expanded the customer base for luxury products.
Globalization: Luxury brands have expanded their presence beyond traditional markets, tapping into emerging economies and new consumer segments.
E-commerce: The growth of online luxury retail has allowed brands to reach a wider audience and provide a convenient shopping experience for consumers.
Millennial and Gen Z Influence: Younger consumers are showing an affinity for luxury brands and experiences, pushing the industry to evolve and adapt to changing tastes.
Experiential Retail: Luxury brands are focusing on creating memorable and immersive retail experiences, combining art, culture, and technology to engage customers.
Challenges and Trends:
Counterfeit Concerns: Luxury brands often face challenges related to counterfeit products and protecting their brand's authenticity.
Sustainability: Consumers are increasingly seeking sustainable and ethical luxury products, prompting brands to adopt more environmentally friendly practices.
Digital Transformation: Luxury brands are adopting digital strategies to engage consumers, whether through social media, e-commerce, or augmented reality experiences.
Inclusivity and Diversity: Brands are working towards greater inclusivity and diversity to cater to a wider range of consumers and reflect changing societal values.
Personalization: Customization and personalization are becoming more important in luxury retail, allowing customers to create unique products that resonate with their individual preferences.
Technology Integration
Retailers embraced technology with features like digital payment options, personalized recommendations, and augmented reality (AR) for virtual try-ons. Data analytics and AI-driven insights were also employed to understand consumer behavior and optimize inventory management.
Technology integration in the Indian retail industry has undergone a significant transformation, driven by the nation's expanding digital infrastructure and the changing behaviors of consumers. E-commerce platforms like Flipkart, Amazon India, and Snapdeal have established a dominant presence, offering a wide spectrum of products and streamlining order fulfillment and delivery processes. With the surge in smartphone usage, mobile commerce (m-commerce) has taken center stage, facilitated by mobile apps and optimized websites that provide convenient shopping experiences. The rise of digital payment methods such as mobile wallets (Paytm, Google Pay, PhonePe) and the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) has revolutionized the way Indians transact, fostering a cashless ecosystem both online and offline.
Moreover, data analytics and personalization have become integral to retail strategies, empowering businesses to tailor product recommendations and marketing efforts based on consumer insights. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has expedited the adoption of contactless technologies, including digital payments, QR code menus, and touchless checkout solutions, ensuring the safety of customers. As part of omni-channel initiatives, retailers are endeavoring to create cohesive shopping experiences across physical and digital channels.
This technological transformation is not only visible in urban areas; it has also reached rural regions where retailers are introducing technology solutions to meet the growing demand for digital shopping experiences. Ultimately, the fusion of technology and retail in India is reshaping the consumer landscape, altering brand-customer interactions, and reshaping the dynamics of business operations. With technology continuing to evolve and consumer preferences shifting, the Indian retail sector is poised for further innovation and growth.
Emerging Technologies: Emerging technologies are shaping the future of the retail industry, transforming the way businesses operate and engage with customers. These technologies offer innovative solutions to enhance customer experiences, optimize operations, and drive business growth.
Here are some of the key emerging technologies in the retail sector:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning:
Personalization: AI analyzes customer data to provide personalized product recommendations, offers, and marketing messages.
Inventory Optimization: Machine learning predicts demand, helping retailers optimize inventory levels and reduce stockouts.
Chatbots: AI-powered chatbots provide instant customer support and assist in product inquiries and purchases.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR):
Virtual Try-Ons: AR allows customers to virtually try on clothing, accessories, and cosmetics before making a purchase.
Virtual Showrooms: VR creates immersive shopping environments where customers can explore products and make selections.
Internet of Things (IoT):
Smart Shelves: IoT-enabled shelves track inventory levels and trigger restocking orders when products are running low.
Beacon Technology: Beacons send location-based notifications to customers' smartphones, offering personalized promotions and recommendations.
Contactless and Cashless Solutions:
Contactless Payments: NFC-enabled payments, QR code scans, and mobile wallets provide convenient and hygienic payment options.
Touchless Checkout: Self-checkout kiosks and mobile apps enable customers to complete transactions without physical contact.
Robotics and Automation:
Inventory Management: Robots automate stock counting and shelf restocking, improving inventory accuracy and reducing manual labor.
Fulfillment Centers: Automated warehouses and fulfillment centers streamline order processing and reduce delivery times.
5G Technology:
Enhanced Connectivity: 5G offers faster and more reliable internet connectivity, enabling real-time interactions, immersive experiences, and IoT applications.
Voice Commerce:
Voice Assistants: Voice-activated devices like Amazon Echo and Google Home allow customers to shop and make purchases using voice commands.
Blockchain Technology:
Supply Chain Transparency: Blockchain enhances supply chain transparency by providing an immutable and verifiable record of product origins, transactions, and authenticity.
Biometric Technology:
Facial Recognition: Biometrics enable personalized experiences, including fast and secure payments through facial recognition.
Customer Identification: Biometric authentication helps retailers identify and serve customers more efficiently.
Sustainable Technologies:
Green Retail: Technologies that focus on reducing carbon footprints and minimizing waste are gaining traction as consumers prioritize sustainability.
Sustainable Packaging Solutions: Biodegradable and compostable packaging materials reduce the environmental impact of packaging waste. Retailers can explore alternatives to traditional single-use plastics.
Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs): Retailers can purchase RECs to offset their carbon footprint by supporting renewable energy projects elsewhere.
Digital Receipts and Paperless Transactions: By offering digital receipts and reducing paper usage, retailers can minimize their environmental impact.
Data Analytics and Predictive Insights:
Predictive Analytics: Advanced analytics tools use historical data to forecast consumer trends, allowing retailers to make informed decisions.
Demand Forecasting: Retailers use historical sales data, seasonal trends, and external factors like holidays to predict future demand for products. This helps in optimizing inventory levels, reducing stockouts, and minimizing overstock situations.
Price Optimization: Analytics help retailers determine the optimal pricing strategy by analyzing customer behavior, competitor pricing, and market dynamics. Dynamic pricing adjusts prices in real-time based on factors like demand and competition.
Customer Segmentation: Data analytics group customers based on purchasing behavior, demographics, and preferences. Retailers can then tailor marketing campaigns and product offerings to specific segments.
Personalized Recommendations: Retailers use customer data to provide personalized product recommendations, improving cross-selling and upselling opportunities.
Inventory Management: Advanced analytics help retailers optimize stock levels by analyzing sales patterns, product turnover rates, and seasonal trends.
Social Commerce:
Shopping on Social Media: Retailers are leveraging social media platforms to showcase products and enable shopping directly from posts.
These emerging technologies are driving innovation across the retail sector, enabling retailers to provide seamless, personalized, and convenient experiences for customers while optimizing business operations for improved efficiency and competitiveness.
Tier Cities in the Retail Industry
Tier cities, also known as tier 2, tier 3, or tier 4 cities, are a classification system used in India to categorize cities based on their population size, economic development, infrastructure, and overall urbanization. The concept of tier cities is significant in the context of the retail industry as it plays a crucial role in shaping retail strategies and market expansion.
Let's explore how tier cities work in the retail industry:
Classification of Tier Cities:
The classification of tier cities is not standardized, and the specific criteria used to determine which city falls into which tier can vary. However, the general classification is as follows:
Tier 1 Cities: These are the largest and most economically developed cities in India, including metropolitan areas like Mumbai, Delhi, Chennai, and Kolkata.
Tier 2 Cities: These are smaller cities with moderate economic development and infrastructure, such as Jaipur, Ahmedabad, and Pune.
Tier 3 Cities: These cities are smaller and less developed than tier 2 cities, often serving as district or regional centers.
Tier 4 Cities: These cities are typically smaller towns and municipalities with limited economic activity and infrastructure.
Role of Tier Cities in the Retail Industry:
Market Potential: Tier cities collectively represent a substantial portion of the Indian population. As urbanization and disposable incomes increase, these cities become important markets for retail expansion.
Untapped Consumer Base: Retailers recognize the growth potential in tier cities due to the rising purchasing power of residents who are looking for better quality products and improved shopping experiences.
Reduced Competition: Tier cities often have lower levels of retail saturation compared to tier 1 cities. This provides opportunities for retailers to establish a presence with potentially less competition.
Diverse Consumer Behavior: Consumer preferences and behaviors can vary significantly between tier cities and tier 1 cities. Retailers need to understand these nuances to tailor their offerings effectively.
Digital Adoption: As digital connectivity increases across India, including tier cities, e-commerce platforms and online shopping are becoming popular. Retailers can tap into this trend by offering online options.
Hyperlocal Strategies: Tier cities may require more localized strategies, considering regional tastes, preferences, and cultural factors that influence shopping decisions.
Offline and Online Mix: A hybrid approach that combines both physical stores and online platforms can be effective in tier cities. Consumers may prefer exploring products in-store before making purchases.
Logistics and Distribution: Efficient supply chain management becomes crucial in tier cities, ensuring timely deliveries of products to meet customer demands.
Challenges in Tier Cities:
Infrastructure: Some tier cities might have limited infrastructure, posing challenges for setting up modern retail outlets or ensuring seamless online deliveries.
Awareness and Education: Educating consumers about product offerings, quality, and benefits may be required, especially in markets where modern retail is still evolving.
Cost Structure: Operating costs, including real estate, may be lower in tier cities, but retailers need to strike a balance between affordability and maintaining quality services.
Future Outlook:
The growth of tier cities in terms of population, economic activity, and consumer aspirations presents a significant opportunity for the retail industry. Retailers that adapt to the unique characteristics of tier cities, adopt localized strategies, and offer a mix of offline and online options stand to tap into this vast and evolving consumer market.
Regulatory Changes and Challenges
The Indian retail sector witnessed regulatory changes such as the introduction of Goods and Services Tax (GST) and discussions around FDI regulations in multi-brand retail. These changes, while aimed at simplifying taxation and encouraging investment, also brought about challenges and debates.
Post-Pandemic and Future Trends
Figure 11: Retail Market Size (Image Source: IBEF)
According to Kearney Research, India's retail industry is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9% from 2019 to 2030. The market size is expected to reach $1.407 trillion by 2026 and $1.8 trillion by 2030.
The revenue of India's offline retailers, also known as brick-and-mortar (B&M) retailers, is expected to increase by $1.39-2.77 billion in fiscal year (FY) 2020.
India's direct selling industry is expected to be valued at $2.14 billion by the end of 2021. E-retail has been a boon during the pandemic. According to a report by Bain & Company in association with Flipkart, the e-retail market is expected to grow to $120-140 billion by FY26, increasing at a CAGR of approximately 25-30% over the next 5 years.
Despite unprecedented challenges, the Indian consumption story is still robust. Driven by affluence, accessibility, awareness, and attitude, household consumption stood at $1.63-1.75 trillion in 2021.
The COVID-19 pandemic further accelerated e-commerce adoption as consumers turned to online shopping for safety reasons. Retailers had to adopt contactless delivery methods and enhance their online presence to stay competitive.
Conclusion
The evolution of retail in India reflects a dynamic interplay of consumer preferences, technological advancements, policy changes, and economic growth. The future of retail in India is likely to continue embracing digital innovations, convenience-focused models, and strategies that cater to diverse consumer segments across both urban and rural areas.
Global Launch Base helps international startups expand in India. Our services include market research, validation through surveys, developing a network, building partnerships, fundraising, and strategy revenue growth. Get in touch to learn more about us.
Contact Info:
Website: www.globallaunchbase.com
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/globallaunchbase/
Email: [email protected]
#retailindustry#india#evolution#ecommerce#brickandmortar#onlineshopping#consumerbehavior#digitalization#technology#omnichannelretailing#mobileshopping#urbanization#supplychain#modernretail#traditionalmarkets#shoppingtrends#paymentsystems#customerexperience#marketplaces#fdiinretail#sustainability#ruralretail#hypermarkets#malls#shoppingapps#personalization#cashlesstransactions#retailstrategies#growthopportunities#competition
0 notes
Text
Which Model Will Make India Prosper? The Dravidian Model vs. the Gujarat Model
India’s political landscape is a complex one, with a wide range of ideologies and approaches to governance. In recent years, two models have emerged as the most prominent: the Dravidian model and the Gujarat model.
The Dravidian model is based on the principles of social justice, education, healthcare, and a universal public distribution system (PDS). This model is often associated with states…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
FCS UP
FCS UP refers to the Food and Civil Supplies Department (FCS) of the Uttar Pradesh (UP) state government in India. The department is responsible for managing the distribution of essential commodities like ration and food supplies to the poor and needy sections of society. One of the key initiatives undertaken by the FCS UP is the issuance and maintenance of the UP Ration Card List.
The UP Ration Card List 2023 has been introduced to ensure that only eligible individuals and families receive the benefits of subsidized ration. Ration cards are an important identification document that allows eligible beneficiaries to purchase essential food items at subsidized rates from fair price shops (FPS) under the Public Distribution System (PDS).
0 notes
Text
TDP's Role In Ensuring Food Security Through Civil Supplies
The Telugu Desam Party (TDP) has been instrumental in ensuring food security for the people of Andhra Pradesh. The party's commitment to providing basic necessities such as food, water, and shelter has been reflected in its policies and programs. One of the key initiatives of the TDP in this regard has been the Civil Supplies Department, which is responsible for the implementation of the Public Distribution System (PDS) under the leadership of N Chandrababu Naidu. Under the PDS, essential commodities such as rice, wheat, sugar, and kerosene are distributed to the poor and needy at subsidized rates.
The TDP has been successful in implementing this program effectively and efficiently, ensuring that the benefits reach the targeted beneficiaries. The TDP MLAs have been actively involved in monitoring the distribution of essential commodities in their respective constituencies, ensuring that there is no pilferage or diversion of supplies. In addition to the PDS, the TDP has also implemented other programs aimed at ensuring food security. One such initiative is the Anna Canteen Scheme, which provides affordable meals to the urban poor. The scheme has been widely appreciated by the people of Andhra Pradesh, and has been replicated in other states as well.

The TDP has also been at the forefront of efforts to increase agricultural productivity and ensure the welfare of farmers. The party's government, under the leadership of N Chandrababu Naidu, has implemented several measures to support farmers, such as the Rythu Bandhu Scheme, which provides financial assistance to farmers in purchasing the other inputs and some of the seeds and fertilizers. Apart from these initiatives, The government has also made significant TDP Contributions to the development of the state. The party's Top TDP Achievements include the construction of world-class infrastructure, such as the new capital city of Amaravati, the completion of the Polavaram project, and the development of the state's road network. The TDP's focus on development has earned it widespread support from the people of Andhra Pradesh. The party's commitment to ensuring the welfare of the people has been reflected in its policies and programs, which have had a tangible impact on the lives of the people. To keep the people of Andhra Pradesh updated on the party's activities, the TDP regularly provides TDP Live Updates on its website and social media handles. These updates cover a range of topics, including the party's events, meetings, and other activities.
In conclusion, the TDP has been at the forefront of efforts to ensure food security and welfare of the people of Andhra Pradesh. The party's initiatives, such as the PDS and the Rythu Bandhu Scheme, have had a significant impact on the lives of the people. With the party's focus on development and its commitment to the welfare of the people, it is no surprise that it has gained widespread support in the state.
0 notes
Text
AMS’s second new life
AMS’s second new life
In 2011, the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS) was installed on the International Space Station (ISS). Since then, it has recorded more than 200 billion cosmic ray events and, while most of their sources are known, a few signatures in the data could point to dark matter. The detector’s latest upgrade will enable scientists to investigate this further.
AMS collects cosmic ray particles that reach Earth coming either directly from the Sun or from far-away sources such as stars ending in supernovae or black holes. Most of the cosmic rays that AMS detects are protons, but heavy nuclei like iron or silicon also reach the detector. However, one signature is particularly intriguing. AMS has detected an unusually high flux of positrons – the antimatter partners of electrons. Positrons and other antimatter particles are rare in the Universe and hence not expected to be seen in the observed data at the strength found by AMS. Their origin is not yet confirmed; they could come from pulsars (fast rotating remnants of stars that emit regular signals), a yet-unknown astrophysical source or dark matter. The observed positron flux fits very well with dark matter models. But in order to investigate this more accurately, the AMS collaboration is now working on refurbishing the detector.
The main upgrade will be a new detector layer with a higher number of silicon strips that will increase the acceptance of recording infalling particles by 300%. “By 2030, AMS will extend the energy range of the positron flux and reduce the error by a factor of two compared with current data,” says AMS spokesperson Sam Ting (MIT). This will allow the detector to investigate the positron signature even further.
A second important addition will be three new radiative surfaces. Because AMS is exposed to direct sunlight, it was painted white to reflect excess heat and remain at operational temperatures. After 13 years in the demanding conditions of space, the paint has degraded and, to compensate for this, the new radiators will keep AMS cool again.
Astronauts training at NASA’s “Neutral Buoyancy Lab” on a full-scale ISS model submerged under water where they learn to mount the new AMS upgrade parts (Image: Corrado Gargiulo/NASA)
Currently, all the parts of the new upgrade, including electronics and hardware, are being built as “validation” and “qualification” models. If they pass all the tests happening at CERN, INFN Perugia and IABG in Germany, the final flight model will go into production. Astronauts are already training with the prototypes in space-like environments on Earth. In 2026, when the upgrade is launched, the astronauts will mount the new detector parts onto AMS during spacewalks. “Everything is going very, very fast,” says chief engineer Corrado Gargiulo (CERN). “This is a requirement, otherwise we arrive too late at the ISS for the upgrade to make sense.” Indeed, the mission now has an end date. NASA has scheduled the deorbiting of the ISS for 2030 and, until then, AMS will have plenty of cosmic ray events to record to explore the positron signature.
A mock-up detector for the next AMS upgrade, which will be installed during the next anticipated spacewalk for AMS. Another part of the upgrade includes a large power distribution system (PDS) radiator to restore AMS’s optimal thermal performance. (Image: Chetna Krishna/CERN)
ckrishna
Tue, 03/26/2024 - 13:40
Byline
Sanje Fenkart
Publication Date
Tue, 04/02/2024 - 10:00 https://home.cern/news/news/experiments/amss-second-new-life (Source of the original content)
0 notes
Text
The Crucial Link Between Ration Card and Aadhaar
This article delves into the importance, benefits, challenges, and the overall impact of the ration card Aadhaar link.
I. The Need for Integration:
Background of the Public Distribution System (PDS): The PDS is a cornerstone of India's social welfare system, providing subsidized food grains to millions of households. However, over the years, the system faced challenges such as leakages, inefficiencies, and corruption, leading to food grains not reaching the intended beneficiaries.
Role of Aadhaar in Governance: Aadhaar, India's unique identification system, was introduced to address identity-related issues and ensure targeted service delivery. Linking Aadhaar to various services, including the PDS, became a crucial step towards eliminating duplications, ghost beneficiaries, and enhancing the efficiency of welfare programs.
II. The Benefits of Ration Card Aadhaar Link:
Elimination of Duplications: By linking Aadhaar to ration cards, the government aims to weed out duplicate and fake cards, ensuring that subsidies reach genuine beneficiaries. This has led to a more accurate identification of eligible households, reducing the chances of fraud and corruption.
Targeted Delivery and Inclusivity: Aadhaar-linked ration cards enable a more targeted approach in welfare distribution. This ensures that the benefits of the PDS reach those who genuinely require assistance, fostering inclusivity and reducing the possibility of well-off individuals availing themselves of subsidized food grains.
Reduction in Leakages and Corruption: The integration of Aadhaar with the PDS minimizes leakages and corruption by creating a digital trail of transactions. This transparency not only helps in holding accountable those involved in malpractices but also builds trust in the welfare delivery system.
Efficiency in Service Delivery: The Aadhaar link enhances the efficiency of the PDS by eliminating bureaucratic hurdles and reducing the time and resources required for manual verification. This streamlined process ensures a quicker and more reliable distribution of food subsidies.
III. Challenges and Concerns:
Privacy and Data Security: The Aadhaar linkage has raised concerns about privacy and data security. Safeguarding personal information is paramount, and the government needs to ensure robust mechanisms to protect citizens' data from unauthorized access or misuse.
Technological Challenges: The success of the ration card Aadhaar link relies heavily on the technological infrastructure in place. Challenges such as connectivity issues, power outages, and the digital literacy of the population may hinder the seamless implementation of the system, especially in remote areas.
Exclusion Errors: There have been instances of exclusion errors, where eligible beneficiaries are wrongly denied their entitlements due to issues like biometric authentication failures or data discrepancies. It is imperative to address these issues promptly to maintain the credibility of the system.
IV. Future Implications and Recommendations:
Expansion of Aadhaar-Linked Services: The success of the ration card Aadhaar link serves as a blueprint for expanding the linkage to other welfare programs. This could include healthcare, education, and financial services, creating a comprehensive ecosystem that ensures targeted and efficient service delivery.
Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation: Regular monitoring and evaluation mechanisms should be established to identify and rectify any shortcomings in the system promptly. This involves addressing technical glitches, resolving exclusion errors, and continually refining the process to enhance its effectiveness.
Enhanced Data Security Measures: Strengthening data security measures is crucial to address privacy concerns. The government must invest in robust encryption technologies, implement stringent access controls, and educate the public about the steps taken to safeguard their personal information.
Public Awareness and Education: To overcome resistance and skepticism, a comprehensive public awareness campaign is essential. Educating citizens about the benefits of Aadhaar linkage, addressing concerns, and providing assistance in the enrollment process can contribute to the successful implementation of the initiative.
Conclusion:
The ration card Aadhaar link represents a significant stride towards achieving a more efficient, transparent, and accountable governance system. While challenges exist, the potential benefits in terms of targeted welfare delivery, reduced leakages, and enhanced inclusivity make the integration a crucial component of India's socio-economic development. Through continuous innovation, robust security measures, and public awareness campaigns, the nation can harness the full potential of this transformative initiative, setting the stage for a more equitable and digitally empowered future.
0 notes
Text
Govt Extends Deadline To Link Aadhaar With Ration Card Till June 30; Check How To Do Both Online & Offline
Linking Ration Card with Aadhaar will help to weed out duplicate and bogus ones and ensure transparency in the Public distribution system (PDS) centres.
source https://zeenews.india.com/personal-finance/govt-extends-deadline-to-link-aadhaar-with-ration-card-till-june-30-check-how-to-do-both-online-offline-2587396.html
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
White Oak Industrial Finance Delivers $3 Million Non-recourse Factoring Facility To Womens Apparel Producer Trend Mannuscript
The guarantee should be evidenced in writing, non-cancellable on the part of the guarantor, in force until the debt is satisfied in full and legally enforceable in opposition to the guarantor in a jurisdiction where the guarantor has property to connect and implement a judgement. However, in distinction to the inspiration strategy to company, bank, and sovereign exposures, guarantees prescribing situations underneath which the guarantor may not be obliged to carry out may be recognised under certain situations. Specifically, the onus is on the bank to reveal that the task criteria adequately tackle any potential discount within the threat mitigation impact. In no case can the bank assign the guaranteed exposure an adjusted PD or LGD such that the adjusted risk weight would be decrease than that of a comparable, direct exposure to the guarantor. Neither standards nor rating processes are permitted to consider possible beneficial effects of imperfect anticipated correlation between default events for the borrower and guarantor for purposes of regulatory minimum capital requirements.
The DUCA Impact Lab brings collectively a neighborhood of specialists to dynamically test new concepts, products and services, appearing as an ongoing car to discover and deal with challenges presently faced by all participants in the financial system and the underbanked. The DUCA Impact Lab has been purposefully designed to check and prove new fashions of banking and finance to unlock the positive impression and social value banking can have for people Invoice Factoring for Government Contractors, companies, and communities. A major distinction between debt and fairness financing is that promoting shares is everlasting, while debt is momentary. For different corporations, similar to publicly listed firms, the ITC is 20%. This can be utilized in opposition to different taxes payable and is non-refundable. SR&ED Financing or SR&ED Advance Funding as it's sometimes referred to as, is still a largely unknown form of financing in Canada.
To speak to a GreenFlow skilled about how you can enhance your cash move, click here. The proposed amendments are not anticipated to change the demographics of CSBFP debtors. Regional impacts as a end result of direct GDP impact are estimated using the distribution of CSBFP loan value by province in 2020–21. The direct GDP impacts are largest in Ontario and Western Canada, adopted by Quebec and Atlantic Canada. Specifically, Ontario contributed to 45% of the entire direct GDP impacts for a total of $220 million. Western Canada contributed to 29% of the total direct GDP impacts for a total of $141 million.
While factoring firms are comparatively lenient about who they’ll tackle, you typically should fulfill at least a number of requirements necessities. Don’t waste your time with an organization that in the end won’t work with you. “Costs are primarily based on the amount of financing you want and the creditworthiness of your purchasers. Invoice factoring rates range from 1.5% to 4% per 30 days depending on these standards,” according government contractor financing to the net site of Commercial Capital LLC Canada. Whether you employ a cash circulate forecasting app like Float or use Excel spreadsheets to do it manually, money move forecasting ought to be a weekly business activity carried out as rigorously as depositing cheques at the financial institution. When potential gaps in money flow are recognized, you probably can kick your administration strategies into gear to stop them.
The bank's standards should also think about the extent to which residual danger to the borrower remains, for instance a foreign money mismatch between the assure and the underlying publicity. Irrespective of whether or not banks are using exterior, inside, pooled information sources, or a mix of the three, for their estimation of loss characteristics, the length of the underlying historical observation interval Government contractor factoring used must be no much less than 5 years. If the available observation spans an extended interval for any supply, and these information are relevant, this longer period must be used. A financial institution need not give equal significance to historic information if it could persuade its supervisor that more recent information are a better predictor of loss rates.
You could additionally be anticipated to fulfill more strict eligibility criteria than other small businesses, especially in case your work is seasonal. You can use a microloan for smaller bills corresponding to topping up your building provides or buying a brand new piece of apparatus financing for government contractors. To be eligible, you should have been in enterprise for no much less than 6 months with a minimum annual gross revenue of $100,000. This is a straightforward savings account with no minimum balance requirement and no mounted month-to-month charges.
One of essentially the most important advantages is that the business receives quick cost on its invoices, as a substitute of getting to wait up to several months for its customers to pay their outstanding invoices. The factoring company benefits as nicely, as a end result of it collects a payment for every invoice it purchases. Vendors and suppliers normally require payments through the life of the contract. On contracts that final a number of months, the contractor will incur important value and can want the project to pay for these prices as early as possible. Rather than wait until the end of the contract, a schedule of funds is typically developed as a half of the contract and is related to the completion of a defined amount of labor or project milestones. These funds made before the top of the project and based on the progress of the work are known as progress funds.
government contractor financing
0 notes