Text
Fans' attitudes toward AI-generated works
Irina Cisternino, a PhD candidate of Stony Brooke University, is writing their research on topics related to technology, art and fandom. You can participate by filling out a survey and additionally, signing up for an interview. The survey is expected to last until at least the end of April, those, who signed up for the interview, will be contacted later. You need to be at least 18 years old to participate in either, be able to understand and speak English and identify as a fan.
After the completion of the research, it will be accessible as the dissertation of the researcher. If you have further questions, you can contact Irina Cisternino at [email protected] or Lu-Ann Kozlowsky at [email protected].
13K notes
·
View notes
Photo
The corollary is: yeah, that means you need to know context and accept that the decision of where the line of action/inaction should be, where your interaction vs. isolation should be, is complex. Life is nuanced.
That's a good thing, though. That's important. Knowing that you have agency, should use it, and get to decide for yourself where there is harm or nonharm or good or, at least, the least harm? That's much more important than "there is no moral way to continue your life in society". Because a lot of 'protest'/never-okay drawback (nonvoting, non-acceptability of purchases, or quality of life actions like the above) ultimately deny you the agency to exist in your society, and the point should be that we can.


119K notes
·
View notes
Text

the absolute most melted-brain take from anti-boycott goofs is the inevitable 'oh you dont like THIS where were you for THAT?' i dont know maybe because THEY ARE TWO DIFFERENT THINGS FROM DIFFERENT PLACES IN DIFFERENT AMOUNTS AT DIFFERENT TIMES
i know this is usually bad faith argument from conservative scoundrels but i see others trot it out sometimes and it is biggest eyeroll. the ‘all things need to mean the same amount to you at all times or you are WRONG AND ILLOGICAL about your convictions’ crowd is such a mess
‘youre vegetarian now? where were you in 4th grade when you had cheeseburger?’ ‘oh you boycott this ai thing? where were you when other thing youve never even heard of happened?’ absolutely braindead trot. sorry devil its ok for buds to start taking action they didnt take before
goofballs: 'HOW DARE YOU START CARING ABOUT THIS THING? THE ONLY LEGITIMATE BOYCOTTS DEFY SPACE AND TIME EXISTING IN A PERPETUAL STATE OF UNDERSTANDING EVENLY DISTRIBUTED ACROSS ALL TIMELINES ENDLESSLY INTO BOTH FUTURE AND PAST'
3K notes
·
View notes
Text

#this is a vibe I should have tried more to capture and never did in the Cypher#it's personally not one I could do very well but it's such a good vibe!#you go little ad!
132 notes
·
View notes
Text

This is.....niche. Do period-appropriate chickens even still exist? Idk anything about chickens. I like the fancy ones.
70K notes
·
View notes
Text


thousands of years apart, ships are burning
find me on instagram!
17K notes
·
View notes
Text
One of the rare benefits of the algorithm is that Youtube's throwing users' filk tapes at me more often now. I'll stumble on the most heartfelt, beautiful, deep song about life, right next to fan fic-bits, or someone's raunchy ode to a fandom and ... you know what? fandom's as deep and broad as I always suspected it had to be. Even when I was a kid who though, hey, no one will ever consider these ideas I have valid, I suspected that it had to be. And that's exactly how it turns out.
Fandom isn't an act of purchase and consumption, and it's never puerile (even when it's unhinged and fun). It's finding meaning, it's social interaction, it's what we build, it's the stories we create and share, it's the music people write, and it's social commentary and rebellion right alongside the goofiest (or porniest) shenanigans you'll ever see. It's a thousand different spaces that people have eked out for themselves in society, where those people can exist. Drama can drama all it wants, things can go wrong, but still: fandom will be these amazing things, given that people can have spaces at all.
And the fact that I live in a time when I can see some of that breadth, even from times that I wasn't or couldn't have been there... that's nice.
0 notes
Text

This is a tribute to Peter Benchley, not the movie Jaws (1975)
The author of 'Jaws' dedicated the rest of his life to reversing the unexpected negative impact his book had on the image of sharks.
Not only were sharks supposedly killed to create props for the movie, but 'Jaws' ended up awakening a bloody sea of ignorance in people at the time, who, haunted by an irrational fear and lack of understanding about marine predators, felt motivated to take to their boats and kill thousands of great white sharks in the most feared ways.
Such as the promotion of great white shark hunting championships that targeted the biggest ones, which were mostly pregnant females who, after being displayed as a trophy, had their jaws ripped off and their bodies discarded in the garbage.
Fear spread widely to all shark species, creating a lack of sensitivity that made it convenient to exterminate entire shark populations around the world that for a long time remained invisible to people's perception.
And this has continued to resonate for a long time with the entertainment media perpetuating the portrayal of sharks as monsters, newspapers favoring sensationalism about shark incidents, governments promoting shark culls, the advance of the unregulated predatory fishing industry, scientists not being supported in their studies of marine predators, the destruction of their natural habitats and the pollution of the oceans.
For thousands of years, sharks have taken care of the health of our oceans, older than the dinosaurs or the first trees, they have gone through great mass extinctions, they have been worshipped and respected as gods and guardians by oceanic peoples and now we demonize them in our media and exterminate them by the millions every year, who is the real monster?
We are shark-eaters.
I hope you can also hear what Peter Benchley himself had to say about all this:
I finally finished this artwork! Hope you like it. At some point I will adapt it for my little Redbubble store.🛍️
I reduced the quality to try to prevent them from stealing. I hope it's enough! 🙁
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
Amazon’s financial shell game let it create an “impossible” monopoly

I'm on tour with my new, nationally bestselling novel The Bezzle! Catch me in TUCSON (Mar 9-10), then San Francisco (Mar 13), Anaheim, and more!

For the pro-monopoly crowd that absolutely dominated antitrust law from the Carter administration until 2020, Amazon presents a genuinely puzzling paradox: the company's monopoly power was never supposed to emerge, and if it did, it should have crumbled immediately.
Pro-monopoly economists embody Ely Devons's famous aphorism that "If economists wished to study the horse, they wouldn’t go and look at horses. They’d sit in their studies and say to themselves, ‘What would I do if I were a horse?’":
https://pluralistic.net/2022/10/27/economism/#what-would-i-do-if-i-were-a-horse
Rather than using the way the world actually works as their starting point for how to think about it, they build elaborate models out of abstract principles like "rational actors." The resulting mathematical models are so abstractly elegant that it's easy to forget that they're just imaginative exercises, disconnected from reality:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/03/all-models-are-wrong/#some-are-useful
These models predicted that it would be impossible for Amazon to attain monopoly power. Even if they became a monopoly – in the sense of dominating sales of various kinds of goods – the company still wouldn't get monopoly power.
For example, if Amazon tried to take over a category by selling goods below cost ("predatory pricing"), then rivals could just wait until the company got tired of losing money and put prices back up, and then those rivals could go back to competing. And if Amazon tried to keep the loss-leader going indefinitely by "cross-subsidizing" the losses with high-margin profits from some other part of its business, rivals could sell those high margin goods at a lower margin, which would lure away Amazon customers and cut the supply lines for the price war it was fighting with its discounted products.
That's what the model predicted, but it's not what happened in the real world. In the real world, Amazon was able use its access to the capital markets to embark on scorched-earth predatory pricing campaigns. When diapers.com refused to sell out to Amazon, the company casually committed $100m to selling diapers below cost. Diapers.com went bust, Amazon bought it for pennies on the dollar and shut it down:
https://www.theverge.com/2019/5/13/18563379/amazon-predatory-pricing-antitrust-law
Investors got the message: don't compete with Amazon. They can remain predatory longer than you can remain solvent.
Now, not everyone shared the antitrust establishment's confidence that Amazon couldn't create a durable monopoly with market power. In 2017, Lina Khan – then a third year law student – published "Amazon's Antitrust Paradox," a landmark paper arguing that Amazon had all the tools it needed to amass monopoly power:
https://www.yalelawjournal.org/note/amazons-antitrust-paradox
Today, Khan is chair of the FTC, and has brought a case against Amazon that builds on some of the theories from that paper. One outcome of that suit is an unprecedented look at Amazon's internal operations. But, as the Institute for Local Self-Reliance's Stacy Mitchell describes in a piece for The Atlantic, key pieces of information have been totally redacted in the court exhibits:
https://www.theatlantic.com/ideas/archive/2024/02/amazon-profits-antitrust-ftc/677580/
The most important missing datum: how much money Amazon makes from each of its lines of business. Amazon's own story is that it basically breaks even on its retail operation, and keeps the whole business afloat with profits from its AWS cloud computing division. This is an important narrative, because if it's true, then Amazon can't be forcing up retail prices, which is the crux of the FTC's case against the company.
Here's what we know for sure about Amazon's retail business. First: merchants can't live without Amazon. The majority of US households have Prime, and 90% of Prime households start their ecommerce searches on Amazon; if they find what they're looking for, they buy it and stop. Thus, merchants who don't sell on Amazon just don't sell. This is called "monopsony power" and it's a lot easier to maintain than monopoly power. For most manufacturers, a 10% overnight drop in sales is a catastrophe, so a retailer that commands even a 10% market-share can extract huge concessions from its suppliers. Amazon's share of most categories of goods is a lot higher than 10%!
What kind of monopsony power does Amazon wield? Well, for one thing, it is able to levy a huge tax on its sellers. Add up all the junk-fees Amazon charges its platform sellers and it comes out to 45-51%:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/25/greedflation/#commissar-bezos
Competitive businesses just don't have 45% margins! No one can afford to kick that much back to Amazon. What is a merchant to do? Sell on Amazon and you lose money on every sale. Don't sell on Amazon and you don't get any business.
The only answer: raise prices on Amazon. After all, Prime customers – the majority of Amazon's retail business – don't shop for competitive prices. If Amazon wants a 45% vig, you can raise your Amazon prices by a third and just about break even.
But Amazon is wise to that: they have a "most favored nation" rule that punishes suppliers who sell goods more cheaply in rival stores, or even on their own site. The punishments vary, from banishing your products to page ten million of search-results to simply kicking you off the platform. With publishers, Amazon reserves the right to lower the prices they set when listing their books, to match the lowest price on the web, and paying publishers less for each sale.
That means that suppliers who sell on Amazon (which is anyone who wants to stay in business) have to dramatically hike their prices on Amazon, and when they do, they also have to hike their prices everywhere else (no wonder Prime customers don't bother to search elsewhere for a better deal!).
Now, Amazon says this is all wrong. That 45-51% vig they claim from business customers is barely enough to break even. The company's profits – they insist – come from selling AWS cloud service. The retail operation is just a public service they provide to us with cross-subsidy from those fat AWS margins.
This is a hell of a claim. Last year, Amazon raked in $130 billion in seller fees. In other words: they booked more revenue from junk fees than Bank of America made through its whole operation. Amazon's junk fees add up to more than all of Meta's revenues:
https://s2.q4cdn.com/299287126/files/doc_financials/2023/q4/AMZN-Q4-2023-Earnings-Release.pdf
Amazon claims that none of this is profit – it's just covering their operating expenses. According to Amazon, its non-AWS units combined have a one percent profit margin.
Now, this is an eye-popping claim indeed. Amazon is a public company, which means that it has to make thorough quarterly and annual financial disclosures breaking down its profit and loss. You'd think that somewhere in those disclosures, we'd find some details.
You'd think so, but you'd be wrong. Amazon's disclosures do not break out profits and losses by segment. SEC rules actually require the company to make these per-segment disclosures:
https://scholarship.law.stjohns.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=3524&context=lawreview#:~:text=If%20a%20company%20has%20more,income%20taxes%20and%20extraordinary%20items.
That rule was enacted in 1966, out of concern that companies could use cross-subsidies to fund predatory pricing and other anticompetitive practices. But over the years, the SEC just…stopped enforcing the rule. Companies have "near total managerial discretion" to lump business units together and group their profits and losses in bloated, undifferentiated balance-sheet items:
https://www.ucl.ac.uk/bartlett/public-purpose/publications/2021/dec/crouching-tiger-hidden-dragons
As Mitchell points you, it's not just Amazon that flouts this rule. We don't know how much money Google makes on Youtube, or how much Apple makes from the App Store (Apple told a federal judge that this number doesn't exist). Warren Buffett – with significant interest in hundreds of companies across dozens of markets – only breaks out seven segments of profit-and-loss for Berkshire Hathaway.
Recall that there is one category of data from the FTC's antitrust case against Amazon that has been completely redacted. One guess which category that is! Yup, the profit-and-loss for its retail operation and other lines of business.
These redactions are the judge's fault, but the real fault lies with the SEC. Amazon is a public company. In exchange for access to the capital markets, it owes the public certain disclosures, which are set out in the SEC's rulebook. The SEC lets Amazon – and other gigantic companies – get away with a degree of secrecy that should disqualify it from offering stock to the public. As Mitchell says, SEC chairman Gary Gensler should adopt "new rules that more concretely define what qualifies as a segment and remove the discretion given to executives."
Amazon is the poster-child for monopoly run amok. As Yanis Varoufakis writes in Technofeudalism, Amazon has actually become a post-capitalist enterprise. Amazon doesn't make profits (money derived from selling goods); it makes rents (money charged to people who are seeking to make a profit):
https://pluralistic.net/2023/09/28/cloudalists/#cloud-capital
Profits are the defining characteristic of a capitalist economy; rents are the defining characteristic of feudalism. Amazon looks like a bazaar where thousands of merchants offer goods for sale to the public, but look harder and you discover that all those stallholders are totally controlled by Amazon. Amazon decides what goods they can sell, how much they cost, and whether a customer ever sees them. And then Amazon takes $0.45-51 out of every dollar. Amazon's "marketplace" isn't like a flea market, it's more like the interconnected shops on Disneyland's Main Street, USA: the sign over the door might say "20th Century Music Company" or "Emporium," but they're all just one store, run by one company.
And because Amazon has so much control over its sellers, it is able to exercise power over its buyers. Amazon's search results push down the best deals on the platform and promote results from more expensive, lower-quality items whose sellers have paid a fortune for an "ad" (not really an ad, but rather the top spot in search listings):
https://pluralistic.net/2023/11/29/aethelred-the-unready/#not-one-penny-for-tribute
This is "Amazon's pricing paradox." Amazon can claim that it offers low-priced, high-quality goods on the platform, but it makes $38b/year pushing those good deals way, way down in its search results. The top result for your Amazon search averages 29% more expensive than the best deal Amazon offers. Buy something from those first four spots and you'll pay a 25% premium. On average, you need to pick the seventeenth item on the search results page to get the best deal:
https://scholarship.law.bu.edu/faculty_scholarship/3645/
For 40 years, pro-monopoly economists claimed that it would be impossible for Amazon to attain monopoly power over buyers and sellers. Today, Amazon exercises that power so thoroughly that its junk-fee revenues alone exceed the total revenues of Bank of America. Amazon's story – that these fees barely stretch to covering its costs – assumes a nearly inconceivable level of credulity in its audience. Regrettably – for the human race – there is a cohort of senior, highly respected economists who possess this degree of credulity and more.
Of course, there's an easy way to settle the argument: Amazon could just comply with SEC regs and break out its P&L for its e-commerce operation. I assure you, they're not hiding this data because they think you'll be pleasantly surprised when they do and they don't want to spoil the moment.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/03/01/managerial-discretion/#junk-fees

Image:
Doc Searls (modified)
https://www.flickr.com/photos/docsearls/4863121221/
CC BY 2.0
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/
590 notes
·
View notes
Text
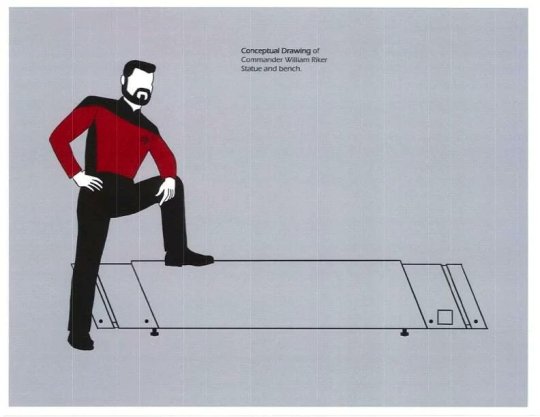

RIKER STATUE
RIKER STATUE
RIKER STATUE
(Maybe)
link
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Sokath, his eyes uncovered!
Me: So yeah, casual english has completely changed since then. Nowadays instead of 'There was a crying baby on the bus today' you would say 'Me when I'm in a being loud and annoying competition and my opponent is crying baby on bus.' And then you'd post this picture of Squidward. Oh, uh, Squidward is a guy from a cartoon-"
Reanimated Corpse of John Wilkes Booth: *Has been staring angrily at a penny for the last 15 minutes and not listened to a word I've said*
96K notes
·
View notes
Text
RB if you think CD drives in computers are not obsolete, but in fact still necessary, despite being artificially phased out
98K notes
·
View notes
Text
For the IDIC's still the way to god, Spock's still logical of course
We've still got full main phasers, so tell me, who needs the Force?
I'm not saying I'm a geek but I momentarily forgot that "infinite diversity in infinite combinations" isn't from the Bible
200 notes
·
View notes