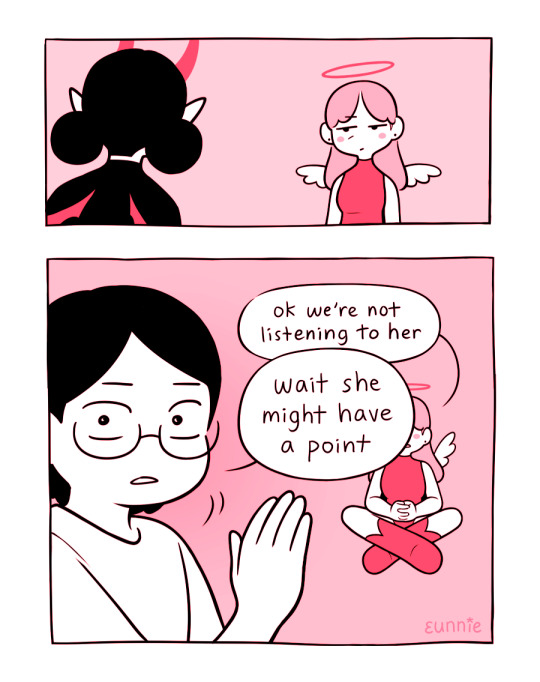
Text

Dark Science #146 - Nothing to See Here
What? WHAT.
Patreon | Gumroad | Store | Ko-Fi | Paypal
198 notes
·
View notes
Text

Dark Science #146 - Nothing to See Here
What? WHAT.
Patreon | Gumroad | Store | Ko-Fi | Paypal
#dresden codak#dark science#comics#illustration#kimiko ross#cyberpunk#art deco#my art#sen#xiaoling chavez#elith heksen#vela#matthias melchior#lgbtq comics#gayyyy#sapphic#queer comics
198 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Century of Glamour Ghouls: 1990s
Nancy Downs in The Craft (1996)

The Movie
The Craft (1996) is widely thought of as a guilty pleasure for women who came of age in the 90s but in recent years its cult following has grown considerably and its reputation is being reconsidered. It’s a more complicated movie than most give it credit for despite its faults.

Sarah (Robin Tunney) moves to LA from San Francisco with her father and stepmother following a suicide attempt. As she gets the lay of the land at her new Catholic high school, a fledgling coven of witches at the school recognize her natural talent for witchcraft and set their sights on her. Sarah’s new sisters all have struggles of their own and use witchcraft as a coping mechanism and as a means of empowerment. Nancy (Fairuza Balk), the de-facto leader, is deeply depressed and poor. Rochelle (Rachel True) is the only black girl in school and her teammates’ overt racism is holding her back from pursuing her passion for diving. Bonnie (Neve Campbell) is disfigured with burn scars covering much of her body. With the addition of Sarah to their coven, their witchcraft begins to produce real results. At first, their problems seems to be solved. The boy who spread rumours about Sarah after she turned him down for sex is now hopelessly obsessed with her. Nancy’s abusive father is dead and she and her mother now have a better lifestyle living on insurance money. Rochelle’s most violent tormentor starts to go bald. The painful treatment for Bonnie’s scars is suddenly successful. It doesn’t take long for things to spiral out of control though. Intra-coven conflict and a misunderstanding of the nature of magic(k) have dangerous consequences for all four of them.

The Craft is one of the more interesting pieces of fiction to emerge from the ashes of the satanic panic of the 1980s. In the 1980s a moral panic was created around a number of later discredited stories about satan worship. While the initial panic focused mainly on child abuse and day care centers, once it settled into the cultural zeitgeist, satanism (and by extension witchcraft) became the scapegoat for all sorts of social issues. It’s a bit difficult to convey to anyone who didn’t live through it how pervasive this fear was in certain communities in the US. But honestly, if you go back and watch some episodes of the first seasons of Unsolved Mysteries, you’ll be a bit flabbergasted at how often parents and husbands tack satanism and witchcraft onto straight-forward crimes & missing-persons stories. The Craft was released in the aftermath of the panic just as it was receding. (As someone who was way into Marilyn Manson in the late 1990s, I can tell you for a fact that it didn’t die.) Quite cleverly, the film took the worst fears of gullible parents and realized them while simultaneously presenting a realistic depiction of the practice of witchcraft and Wiccan beliefs. Funnily enough, The Craft definitely encouraged a whole generation of kids to try out spells or witchy games at slumber parties across the country.

The Look
Nancy Downs is a very mid-90s Southern Californian goth. She rocks a whole mess of styles throughout the film, some of which are very inappropriate for the weather (desert goth life), all of which are very inappropriate for Catholic school attendance. So, there are a lot of styling options for a Nancy cosplay.

The Clothes
The base for many of Nancy’s outfits is her school uniform; white button up shirt and blue-and-green kilt. At school, she’s usually bare-legged and mixes up the uniform pieces with black undershirts or black mesh and a black leather jacket. More often later in the film, she goes full 90s goth witch with a long black jacket with flared sleeves and big flowy black and dark red skirts. Nancy’s ever-present accessories are rosaries worn as jewelry, a dog-collar choker, upside down cross earrings, a nose ring, and pointy lace-up ankle boots.

I went the simple route: a play on the school uniform. I don’t own anything resembling a uniform kilt because I went to Catholic school myself for 16 years and will never own a skirt like that again. I also don’t own any black mesh, but I do have a pair of fishnets that I put on as sleeves. If you want to add color to a Nancy look, I’d recommend blood red in your accessories.

The Makeup

Nancy’s makeup is harsh though the face makeup is rarely very heavily applied. Nancy’s eyebrows are sharp and thin and her eyes are smoky and smudgy, later in the film her eye makeup gets deeper and less shimmery.

It seems that is every scene, even if it’s directly contiguous with the scene prior, Nancy has reapplied her lipstick in a different shade. I love this because it subtly reinforces the notion that she exhibits compulsive behaviors and also suggests that perhaps her “five-finger discount” attitude extends beyond the magic shop to makeup counters and drug stores.

Start with a neutral base and set it lightly with powder a shade lighter than your skin tone to get a California-goth pallor I concentrated some extra light powder under the hollows of my cheekbones to make my cheeks look fuller, more like Balk’s and more like a teenager’s.
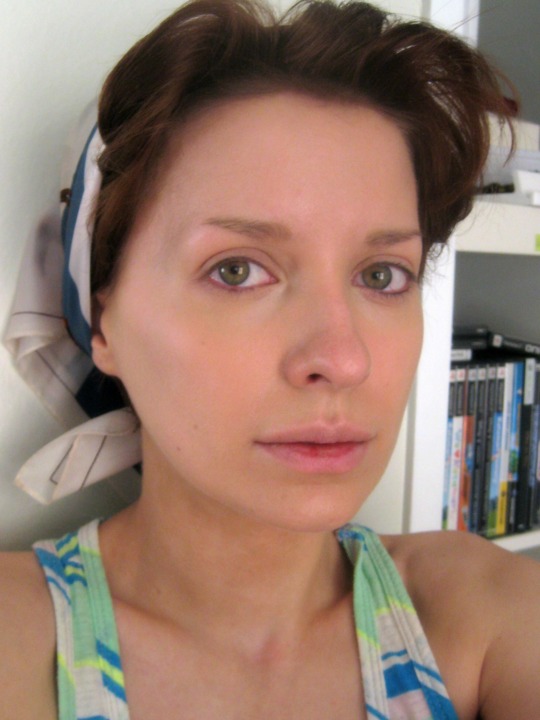

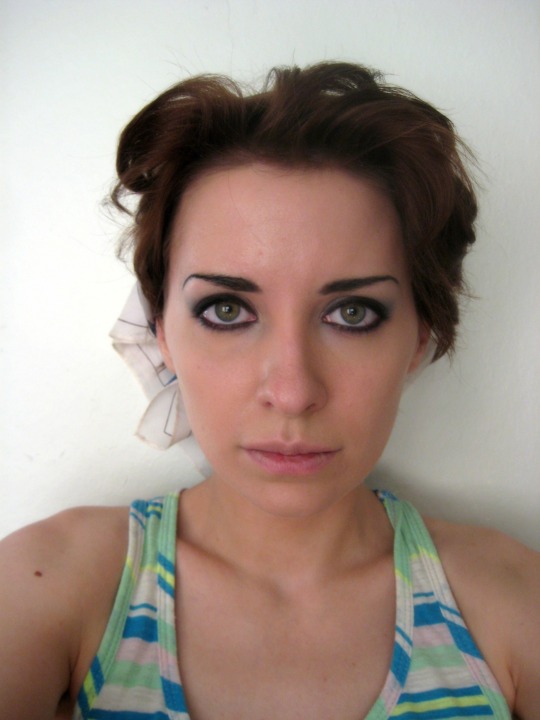
Deconstructing Nancy’s eye makeup was fun because I realized for the first time that it’s actually a pretty standard late-90s smoky eye with heavier liner. (1.) Start with a neutral gray shade as a blending base. (2.) Take a darker gray shade to build up the outer V of the eye concentrating the pigment at the crease and lashline. (3.) Take a black shadow (I went cool black with this, but you can go warm instead) and build up the deeper areas of shadow, take an angled brush and bring it along your lashline. Take what’s left on the brush and bring it under your eyes. (4.) Next take black liner and draw a thick line all around your eye with very little flaring at the outer edge. (5.) Go back in with your black shadow to set the liner and smudge the line a bit. Basically try to make it look like you didn’t wash off yesterday’s makeup and just reapplied more in the morning. (6.) For the highlighted parts of the eye, silver would be perfect. I don’t have any silver shadow, so I went in with white shadow and a pearl-colored highlighter to get the shimmer. Concentrate the silvery shade on the inner and middle part of the mobile lid and on the browbone. (7.) To finish off the eye, tightline your eyes with black liner and load up your eyelashes with black mascara.

For the brows, go in with black powder on a wet brush so it’ll be easier to correct mistakes. The head is a lot fuller than the tail, which tapers dramatically. It’s a more natural shape than the sperm brow that was starting to take over at the time.

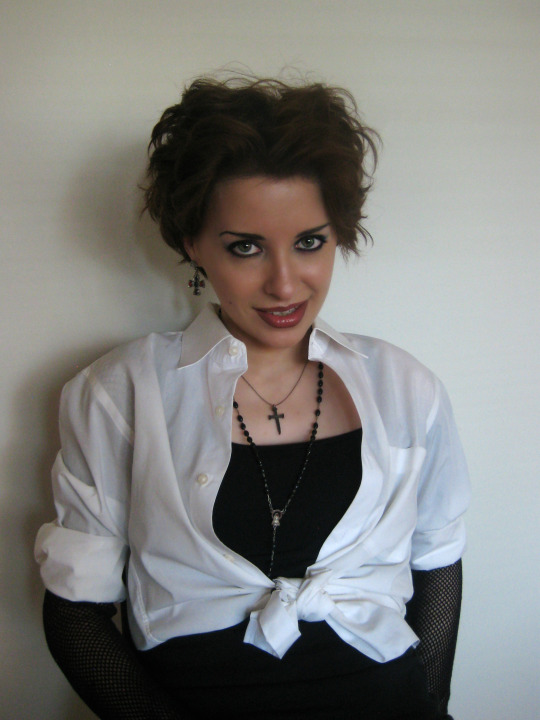
For my Nancy look, I chose to go with a brownish lip because most Nancy cosplayers gravitate toward the bright red and black combo. The same method applies, just choose the colors you like best. Take a brown, black, or burgundy liner and fill out your bottom lip and line your upper lip to be just a touch smaller than your lower lip. Fill in the center of your lips with a nude brown or red lipstick and blend it into the liner. Don’t blend too much though because you want to keep the liner distinct.
With your liner brush at the ready, draw a small beauty mark on your right cheek an inch or two from your mouth. I already have a beauty mark here, so I just filled it in.


The 1910s | The 1920s | The 1930s | The 1940s | The 1950s | The 1960s | The 1970s | The 1980s | The 2000s
513 notes
·
View notes
Text

The next Extremely Heterosexual Dark Science page will go up next week, but you can read it early right now over on my Patreon!
#dresden codak#dark science#kimiko ross#xiaoling#lgbtq comics#an extremely normal time#just gal#just gals being pals
141 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cosplay the Classics: Natacha Rambova
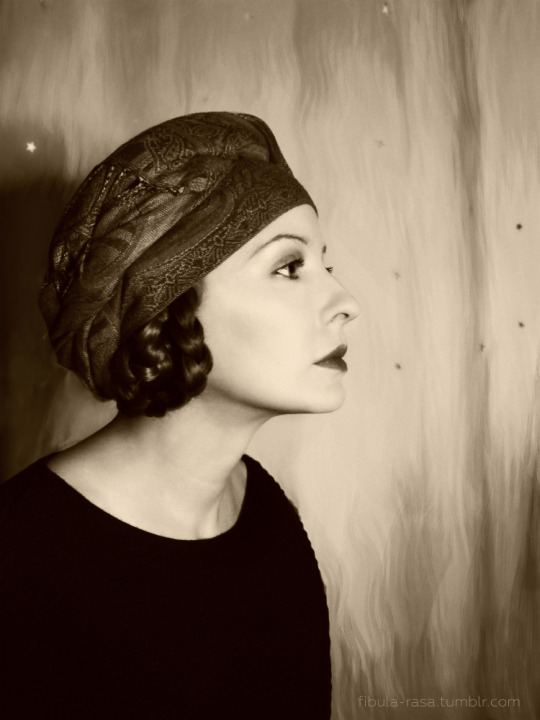

My closet cosplay of Natacha Rambova’s signature look from the 1920s
It’s unbearably common for people who have written about Natacha Rambova to emphasize that her “real” name was “Winifred Hudnut.” In reality, Rambova had about a half dozen names she went by (or could have gone by). Natacha Rambova was the name she took when she began her working life as a teenager with Theodore Kosloff’s ballet company—hence the Russophone name. And, as Rambova was a person who first and foremost lived to work, sticking with her professional name seems true to her character, Slav or not. You see, the primary reason Rambova was (and is) subjected to this passive-aggressiveness is part of a lingering effort to delegitimize her and her work. Sometimes that takes the form of calling her Winifred Hudnut and sometimes “Mrs. Valentino.” While there are valid reasons to criticize Rambova and her work, the aspersions typically lobbed at her fully miss their mark because they’re motivated by the desire to belittle a woman who knew the value of her work and her art and had the necessary privilege to fight for it.
"Natacha Rambova seems to belong most to me, the individual I think I am, but of course, I wasn’t born that way."
—“Wedded and Parted” by Ruth Waterbury, Photoplay, December 1922

Collage of portraits of Rambova from the 1920s
READ ON below the JUMP!
To begin at the beginning, Rambova was born as Winifred “Wink” Shaughnessy in Utah in 1897. Her father, who was significantly older than her mother, was found lacking as a parent and a spouse, and the Shaughnessy’s divorced when Rambova was young. Her youth was spent bouncing between her mother’s home in San Francisco, boarding school in England, and her aunt’s villa in France. Early on Rambova discovered two of the great passions of her life, ballet and mythology. The latter became an enduring fascination that guided Rambova’s varied pursuits throughout her life.
At first, her family encouraged Rambova’s interest in ballet. However, around 1914, when Rambova was 17, the shady nature of Rambova’s relationship with Kosloff was discovered by her mother, who tried to have Kosloff deported. At the time, Kosloff was supporting a wife and child back in England while keeping house with Rambova and another of his dancers, Vera Fredova (who was also legally named Winifred and also a teenager btw). Mom called off the lawsuit, and for years Kosloff, Rambova, and Fredova ran the ballet company together.
The company relocated to Los Angeles where Kosloff entered into a contract with Cecil B. DeMille. The company would provide art and costume designs for DeMille’s films and Kosloff himself would appear in the films. While Kosloff’s name is found in the credits for most of these films, it’s now widely accepted that Rambova was doing most, if not all, of the research and design work.

Theodore Kosloff in his costume from The Woman God Forgot (1917) on the left with Rambova (who does not appear in the film)
In this creatively productive period, Rambova shifted her focus away from dance toward historical research and costume and set design as her primary endeavor. For DeMille, Rambova contributed designs for The Woman God Forgot (1917), Why Change Your Wife? (1920), Something to Think About (1920), and also designed the Cinderella fantasy sequence of Forbidden Fruit (1921).

from the Cinderella sequence of Forbidden Fruit [more gifs here]
The work caught the eye of Nazimova, who was still working at Metro at the time. Once Nazimova realized that Rambova was the one doing the work, she engaged her directly to work on her now lost film Billions (1920). Rambova would receive on-screen credit for her art direction on Nazimova’s final film for Metro, the deco-bonanza Camille (1921).

from Camille [more gifs here]
Camille features designs verging on the bizarre, using circles and half-circles as a consistent symbolic motif throughout the film. One of my personal favorite touches however, is the sequence taking place at Armand’s country cottage. Where the Paris sets are oversized and characterized by rounded edges, the cottage is excessively square and feels almost claustrophobic. At this point in the story, Marguerite is conflicted, she feels happier and freer than ever before in her love with Armand, but is also haunted by the notion that she’s dooming him given her past and her illness. The interior of the cottage feels more artificial because of its realism, almost like a doll house, in comparison to the more heavily designed Paris settings. This highlights the feeling in Marguerite that she’s just playing pretend at a happy, heteronormative fantasy.

country house setting from Camille
Influenced by the highly stylized visuals of ballet but also preoccupied with historical research and symbology, Rambova’s designs stand out from anything else produced in this period, especially in the US. The more I study her designs and think about how young she was when she created them, the more impressed I am by them. Faced with challenging assignments, Rambova balanced accuracy and perceived authenticity with her penchant for larger-than-life symbolism. On top of all that, they photograph beautifully! Being able to create interesting and appropriate costume and set designs with a demonstrated understanding of how they would register on film is a sophisticated skill set which Rambova deserves significant credit for.
When Nazimova went independent following Camille, she brought Rambova with her. The first two projects Rambova would work on for Nazimova’s company were A Doll’s House (now a lost film, which I profiled on my Lost, but Not Forgotten series) and Salomé (1922). The latter has become regarded as Nazimova’s magnum opus on film and often referred to as America’s first art film. For Salomé, Rambova translated illustrations made by Aubrey Beardsley into three-dimensional sets and costumes and character designs for film. If you’ve seen Beardsley’s illustrations and you’ve seen the film, you know this was no simple task and that Rambova did a phenomenal job of re-working the illustrations into wearable costumes and weaving elements of Beardsley’s illustrations into the set design.

from Salomé [more gifs here]
Taking a second to emphasize Rambova’s range, her work on Why Change Your Wife?, Something to Think About, and A Doll’s House (which we can only judge by surviving stills) are contemporary settings with more realistic, grounded set and costume designs. Rambova executes the designs for these films with just as much skill, although as she admitted herself, with less gusto because they didn’t scratch the historical-research/symbology itch.

production still from A Doll’s House
It was in this same period of creative growth that Rambova split from Kosloff (and he shot her in the leg on the way out) and she started seeing her future husband, Rudolph Valentino. Valentino, however, was still legally married to another woman. This would lead to significant trouble for the couple in the first few years of their relationship.
Perhaps too much time has been spent picking apart the nature of the Valentino-Rambova pairing—most of it spent trying to characterize her as a Svengali type and Valentino as too immature or unintelligent to have any opinions of his own. Now, having read most of what Rambova has written about Valentino, both before and after their divorce, she often takes a paternalistic attitude toward Valentino, but one tempered by real affection. And, given how close Valentino became with her family (and remained close after the divorce, even leaving a significant part of his estate to her aunt), to doubt the legitimacy of their partnership feels willfully disingenuous. Valentino shared Rambova’s desires to elevate the artistic qualities of film, oftentimes beyond their means. Together they crafted the romantic idol of Valentino. Together they challenged the studios for underpaying him.
“Some producers find an unusual personality. They use up thousands of dollars to exploit it. They put that personality into a picture and the picture goes over and makes a million. Then, instead of letting the actor who does fine work go on doing it, they give him cheap material, cheap sets, cheap casts, cheap everything. The idea then is to make just as much money from that personality as possible with the least outlay.
“Isn’t it short-sighted? Isn’t it unwise? Yet they do it again and again. But they can’t keep it up forever. The fans are beginning to wake up. They refuse to take second rate products even when a big personality is exploited. They are doing the one thing that will affect the producer—when poor pictures are offered them, they are staying home.”
—from “Wedded and Parted” by Ruth Waterbury, Photoplay, December 1922
Something I mentioned in the last installment of “Lost, but Not Forgotten” was that in this period, a number of film artists in Hollywood were recognizing the true value of their work and going independent of the emergent studio system. Studio heads saw no problem in curtailing the creative freedom of their artists to further pad their overflowing wallets. For the founders of United Artists, the system was usually able to be bent in their favor, with their films getting wide releases with decent promotion budgets. For a number of other independent artists, the road was rockier as distributors and exhibitors were reluctant to offend the increasingly powerful studios. Nazimova was one of those who eventually ran out of funds to produce their own work. Valentino’s star rose precipitously after The Sheik (1921) and Blood and Sand (1922) was a massive box-office hit, but Valentino’s salary did not match that bankability. This financial dispute, complicated by negative press around his relationship with Rambova, left Valentino out of work in film for a year. In turn, Valentino and Rambova went on a dancing tour of the country, which raised her profile as a public figure while bolstering his star image despite not appearing in any new films.

Valentino and Rambova in a promotional photo for their dance tour
Unfortunately, crossing the studio system as they did resulted in a coordinated campaign to take them down a notch. Reading film magazines from the period will give you whiplash. Many of these magazines had established relationships with studios and ran news items in keeping with whatever narratives the studios wished to push. However, the stars and their managers (if they had them) had their own relationships with the magazines. So, occasionally, you’ll find items deriding Rambova as some kind of artsy-fartsy manipulative phony and then a profile piece of her or Valentino that’s sympathetic to their business woes. This is the period where the narrative emerges of Rambova as a calculating climber, using Valentino to build her own career. This talking point is often repeated today, despite the fact that Rambova had already been working on big productions for DeMille and Nazimova for years before meeting Valentino. While Rambova was certainly a key figure in developing Valentino’s star image, the plain facts make it apparent that they were working as a team—hardly abnormal. Unfortunately, neither member of said team had much in the way of business sense.
As I mentioned earlier, Rambova fashioned her life around her work. Something I didn’t mention earlier is that she was an heiress. At this point in her life, Rambova was determined to live off her own labour and not touch her inheritance. When they were battling the studios, the couple continued to not touch Rambova’s inheritance. And, both desperate to return to filmmaking, they were subject to the studio’s will. While their split is often framed as Rambova abandoning Valentino when she was denied the ability to control his career, a slightly different scenario emerges upon closer inspection. Both Valentino and Rambova were highly dedicated to their work and their work was intertwined with their relationship, a similar dynamic to Rambova’s relationship with Kosloff and later with her second husband Álvaro de Urzáiz, with whom she restored villas. With Urzáiz, their relationship degraded when they no longer had a shared project to work on. (In this case due to the Spanish Civil War.) It’s neither sensational nor romantic, but following Valentino’s reconciliation with Hollywood, after a few films, the pair was intentionally separated creatively. (This was at least partly due to the machinations of their new business manager, George Ullman, who we now know was manipulating Valentino’s finances after litigation regarding the disposition of Valentino’s estate.)
“What I desire personally is simply to be known for the work which I have always done, and that has brought me a reputation entirely independent of my marriage.”
—“Natacha Rambova Emerges” by Edwin Schallert, Picture Play Magazine, August 1925
Rambova worked on one film independently from Valentino before their divorce, What Price Beauty? (1925), starring mutual friend (for the moment) Nita Naldi. The film is now lost and its production and release seems awfully sus, so I hope to cover that for “Lost, but Not Forgotten” soon. Regardless of the film’s success or failure, the whole endeavor soured Rambova on Hollywood.
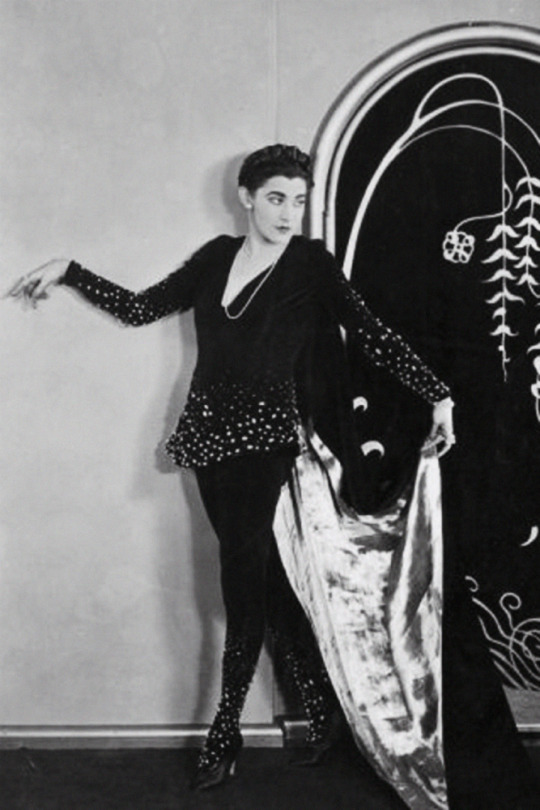

Nita Naldi in a promotional photo from What Price Beauty?
In her book about her life with Valentino, Rambova opined:
“Hollywood—all the joys of the petty community life of ‘Main Street’ with an additional coating of gold dust thrown in for good measure!… it is merely an imitation gilded hell of a make-believe realm. Nothing but sham—sham—and more sham.
“Hollywood—one continuous struggle of nobodies to become somebodies, all pretending to be what they are not.”
Through their divorce and Valentino’s untimely death the year following, Rambova never stopped working. Rambova operated boutiques selling her original designs in New York and then in France. Around this same time Rambova also got more deeply involved in spiritualism. In an odd move, she published Rudy with the final third of the book “dictated” by Valentino’s spirit. I won’t say that I don’t find that pretty distasteful, but having read the book, it reveals two key things: Rambova’s genuine affection for Valentino, patronizing as it may be, and a sincere belief in the spiritualism movement that she and her mother had been drawn into. There have been critics who have framed the book as some sort of cash-in or vengeful act against Valentino for excluding her from his will, but the facts do not support that. Rambova, to reiterate, was an heiress who did not need to work for a living. She also states directly that it is Rambova’s spiritual leader who encouraged her to publish the book as a way to promote spiritualism. That’s not necessarily any better than the false narrative, but the truth has value (and is more interesting in this case!)
In the 1930s, Rambova relocated to Spain where she finally began using that inheritance to develop rental properties on Mallorca with her aristocrat husband. If you know anything about 20th century European history, you may know what happened next. Urzáiz joined the fascists in the Spanish Civil War, and despite her abiding fear of Communists, Rambova stuck around in Spain for as long as she could before fleeing to France. Of course, it wasn’t long before the Nazi Germany invaded France, so Rambova relocated back to the United States.
During her time abroad, Rambova’s preoccupation with symbology was reignited by a trip to Egypt. This sparked the next big passion of her life, which she would pursue for over two decades: Egyptology.

Rambova in Egypt
Rambova became a writer, researcher, and lecturer on symbolism and cosmology in Ancient Egypt (as well as spiritualism). Much of Rambova’s work was done in collaboration with Alexandre Piankoff and the French Institute for Oriental Archaeology in Cairo (IFAO). With various grants, Rambova travelled to Egypt to document important sites, via photography and illustration. Rambova also used much of her inheritance to source objects from Egypt, which she donated to museums and universities in the US. (There’s a huge discussion about that to be had, which, as an archivist myself, I am drawn to explore. But, it falls outside the purview of this blog, so it’ll have to stay a discussion for another time and place.) These collections are still accessible to researchers and the public today. Rambova continued this work until her death in the 1960s.
Without doubt there are meaningful reasons to criticise Rambova and her work. Some of her design work is appropriative at best, overtly racist at worst. She had ignorant and arrogant attitudes toward class politics bred from her uber-privileged upbringing, which occasionally bled into her work and interfered with her ability to collaborate with other artists. She definitely lacked the social skills and business sense that were very necessary for artists working in a mass-media format like film. It’s typical, but disappointing still, that so much effort has been put into demonizing Rambova for reasons that were either completely fabricated, or rooted solely in the fact that she was a woman who knew her value, but by society’s standards, didn’t know her place. All that said, maybe we are due to spend a bit more time as film enthusiasts genuinely engaging with the art Rambova created and recognizing how much of a force she was in standing up for artistry in the American film industry.
☕Appreciate my work? Buy me a coffee! ☕
Postscript: This piece was a monster, so excuse me for not diving into rumours about Rambova’s potential queerness, as it eventually fell out of the scope of the essay. But, for those in the know: my personal take is that she likely was queer, though probably not romantically entwined with Nazimova, but maybe with Fredova. I also think her marriage with Valentino was not lavender. And, even if Rambova wasn’t queer, I appreciate what a keen collaborator she was with queer colleagues and what a good friend she apparently was to queer people in her social circles and her family, despite how often her detractors would try to use accusations of lesbianism as a weapon against her. IMO if someone were of weaker character, those types of aspersions would have driven a wedge between the object and their friends and colleagues.
Bibliography/Further Reading:
Madam Valentino: The Many Lives of Natacha Rambova by Michael Morris
Rudy: An Intimate Portrait of Rudolph Valentino by His Wife Natacha Rambova
Valentino As I Knew Him by George Ullman
Picture Play Magazine, August 1925
Photoplay Magazine, December 1922
Mythological Papyri – Texts by Alexandre Piankoff & Natacha Rambova
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
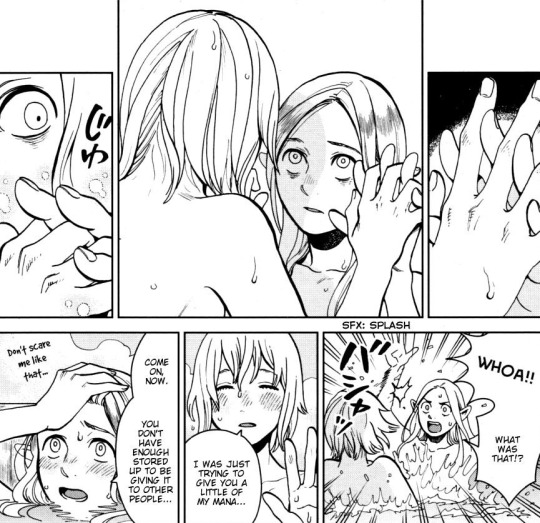





what if i risked my life and put up (affectionate) with your unhinged monsterfucker brother to save you. and then revealed i was an expert in illegal black magic just so i could resurrect you from a pile of bones. and what if i later explored your body in the bath. and you laced our fingers together and offered to share your energy with me. and what if after all that… there was only one bed. what then.
update: it's been ANIMATED. gifs here

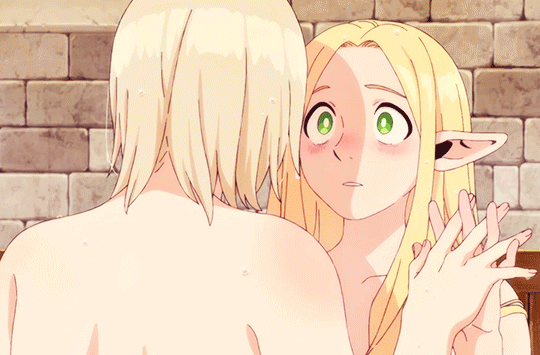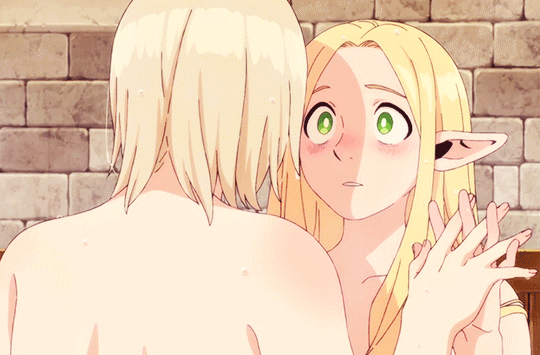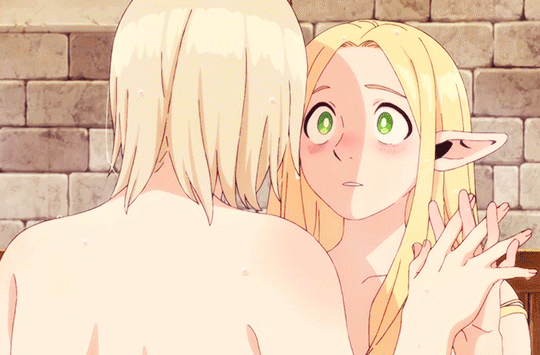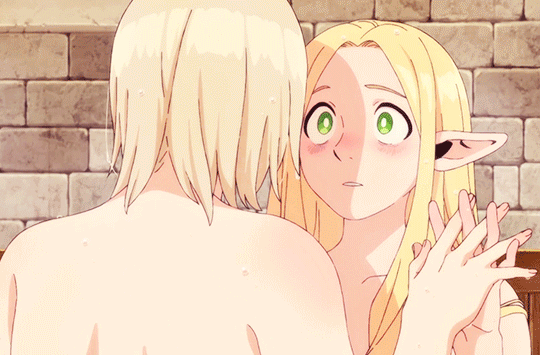
21K notes
·
View notes
Text








Twilight Q / トワイライトQ (1987)
segment: "Time Knot: Reflection / 時の結び目 Reflection"
[letterboxd | imdb]
Director: Tomomi Mochizuki
Animation Director: Masako Gotō
Art Director: Shichirō Kobayashi
Key Animators: Hiroki Takagi, Kazunari Kume, Kazuya Takeda, Michitaka Kikuchi, Takayuki Goto
Studio: Ajia-do Animation Works
25 notes
·
View notes
Text







Twilight Q / トワイライトQ (1987)
segment: "Time Knot: Reflection / 時の結び目 Reflection"
[letterboxd | imdb]
Director: Tomomi Mochizuki
Animation Director: Masako Gotō
Art Director: Shichirō Kobayashi
Key Animators: Hiroki Takagi, Kazunari Kume, Kazuya Takeda, Michitaka Kikuchi, Takayuki Goto
Studio: Ajia-do Animation Works
34 notes
·
View notes
Photo
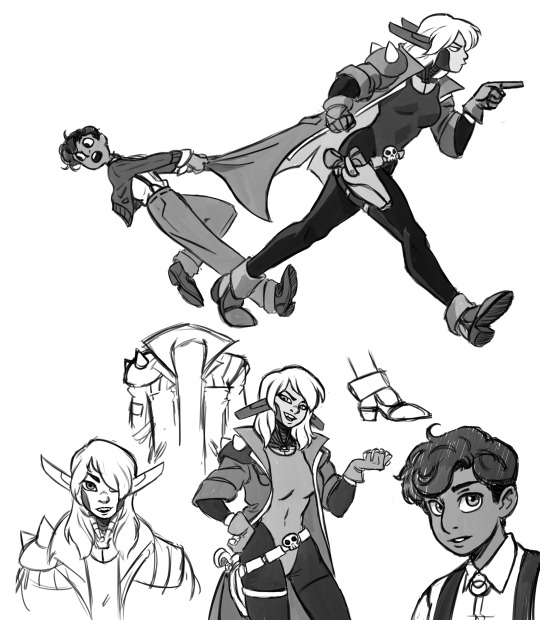

Concept sketches for Ling and Elith from this chapter! Did you know I have lots of behind-the-scenes art and other goodies like this on my Patreon?
http://patreon.com/dresdencodak
299 notes
·
View notes
Text
Panzer Dragoon Orta deserves more respect than it gets, that game was a masterpiece!

265 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dungeon Meshi has it all, except literally any straight people.

this specific shot is still rotating round and round in my head like a spinning top
18K notes
·
View notes
Text

Just FYI you can download super high resolution images of all my Dark Science pages over on my Patreon, if you ever wanted to get a true handle on how much obsessive detail I put into this comic.
54 notes
·
View notes
Text
(Mostly) Lost, but Not Forgotten: Omar Khayyam (1923) / A Lover’s Oath (1925)
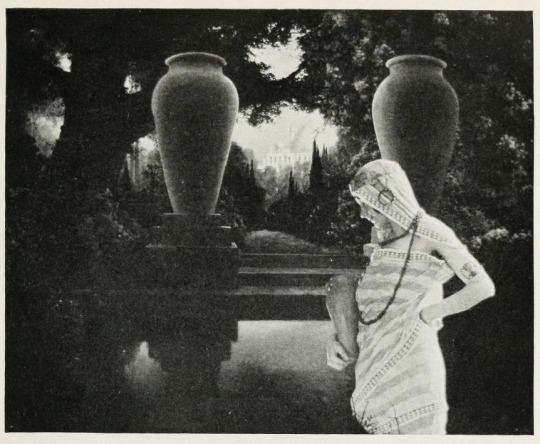
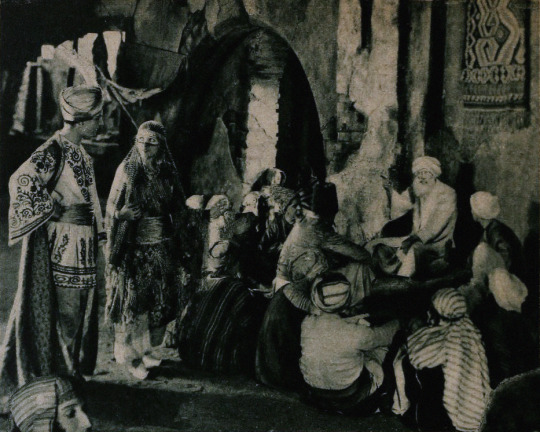
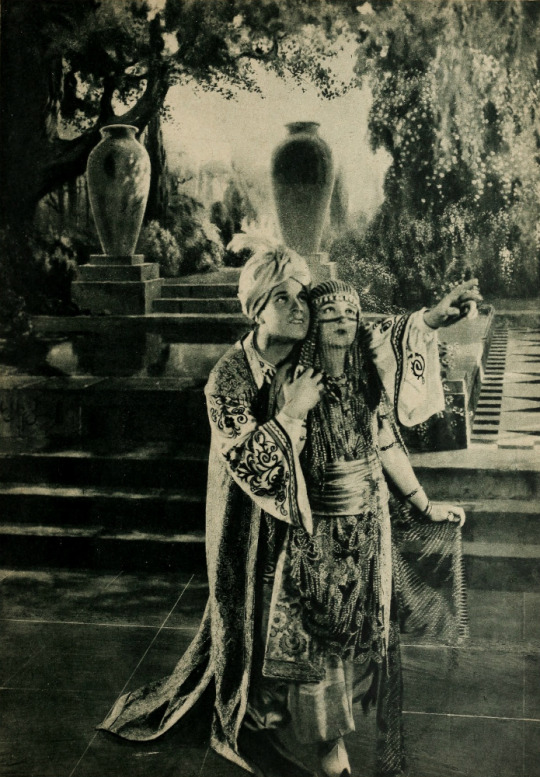
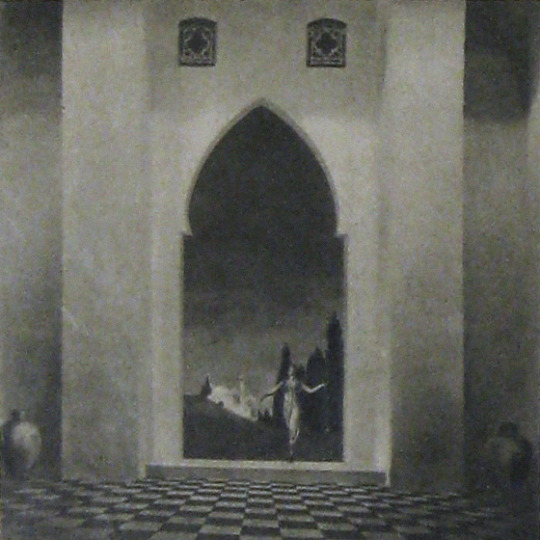
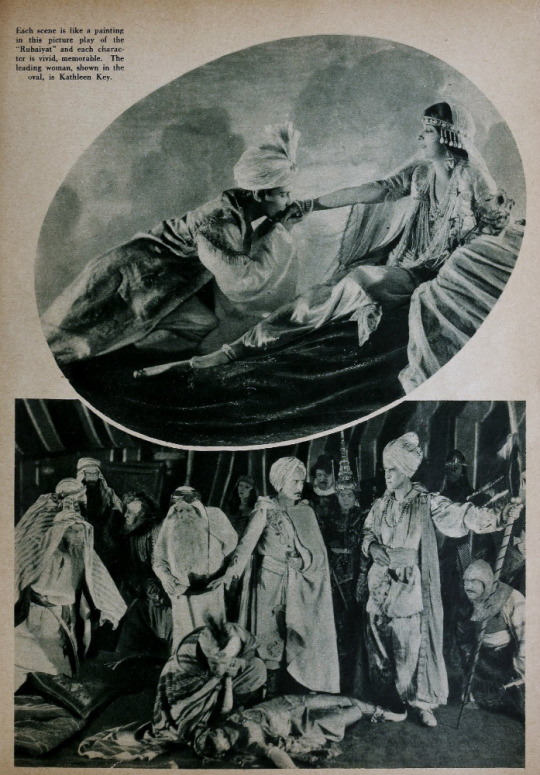
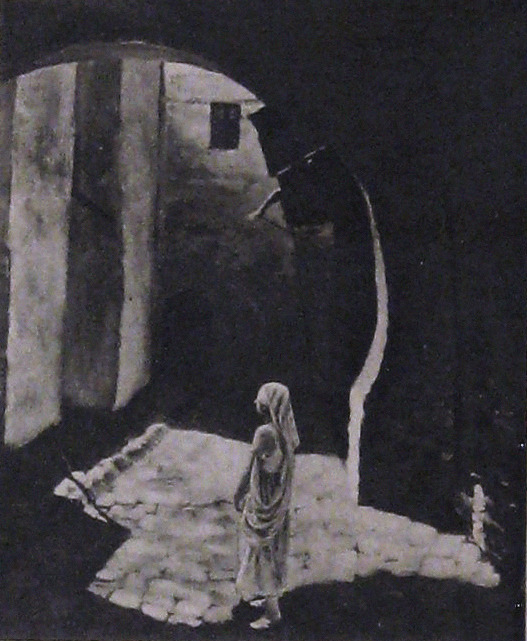
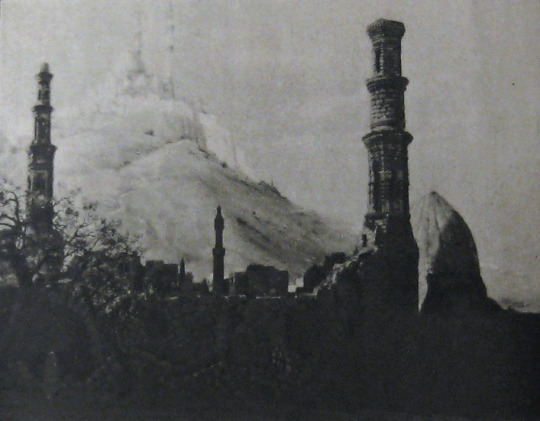







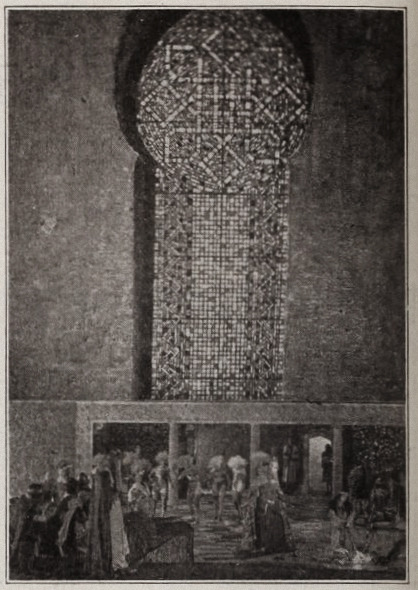





Alternate Titles: The Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam, The Rubaiyat, Omar Khayyam, Omar
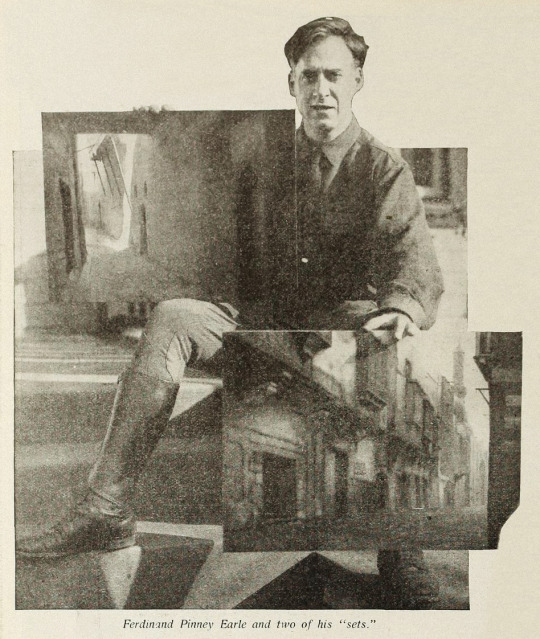
Direction: Ferdinand Pinney Earle; assisted by Walter Mayo
Scenario: Ferdinand P. Earle
Titles: Marion Ainslee, Ferdinand P. Earle (Omar), Louis Weadock (A Lover’s Oath)
Inspired by: The Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam, as edited & translated by Edward FitzGerald
Production Manager: Winthrop Kelly
Camera: Georges Benoit
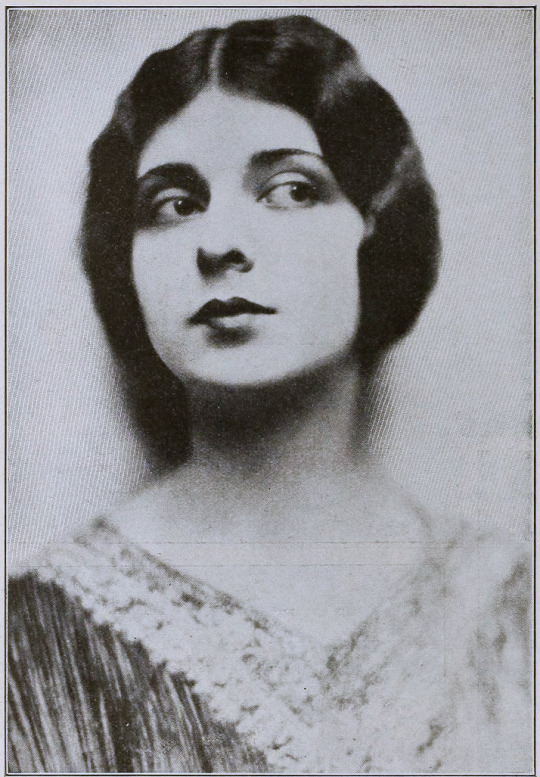
Still Photography: Edward S. Curtis
Special Photographic Effects: Ferdinand P. Earle, Gordon Bishop Pollock
Composer: Charles Wakefield Cadman
Editors: Arthur D. Ripley (The Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam version), Ethel Davey & Ferdinand P. Earle (Omar / Omar Khayyam, the Director’s cut of 1922), Milton Sills (A Lover’s Oath)
Scenic Artists: Frank E. Berier, Xavier Muchado, Anthony Vecchio, Paul Detlefsen, Flora Smith, Jean Little Cyr, Robert Sterner, Ralph Willis
Character Designer: Louis Hels
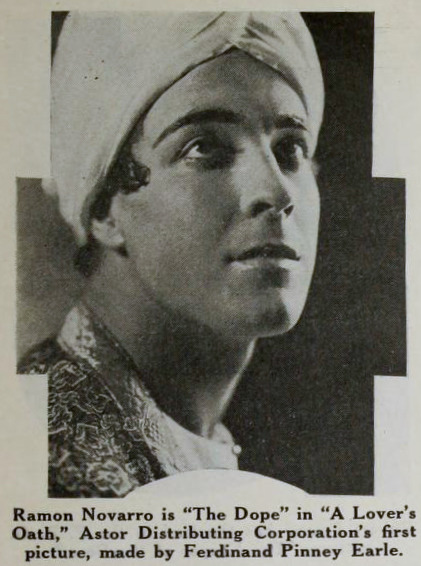
Choreography: Ramon Novarro (credited as Ramon Samaniegos)
Technical Advisors: Prince Raphael Emmanuel, Reverend Allan Moore, Captain Dudley S. Corlette, & Captain Montlock or Mortlock
Studio: Ferdinand P. Earle Productions / The Rubaiyat, Inc. (Production) & Eastern Film Corporation (Distribution, Omar), Astor Distribution Corporation [States Rights market] (Distribution, A Lover’s Oath)
Performers: Frederick Warde, Edwin Stevens, Hedwiga Reicher, Mariska Aldrich, Paul Weigel, Robert Anderson, Arthur Carewe, Jesse Weldon, Snitz Edwards, Warren Rogers, Ramon Novarro (originally credited as Ramon Samaniegos), Big Jim Marcus, Kathleen Key, Charles A. Post, Phillippe de Lacy, Ferdinand Pinney Earle
Premiere(s): Omar cut: April 1922 The Ambassador Theatre, New York, NY (Preview Screening), 12 October 1923, Loew’s New York, New York, NY (Preview Screening), 2 February 1923, Hoyt’s Theatre, Sydney, Australia (Initial Release)
Status: Presumed lost, save for one 30 second fragment preserved by the Academy Film Archive, and a 2.5 minute fragment preserved by a private collector (Old Films & Stuff)
Length: Omar Khayyam: 8 reels , 76 minutes; A Lover’s Oath: 6 reels, 5,845 feet (though once listed with a runtime of 76 minutes, which doesn’t line up with the stated length of this cut)
Synopsis (synthesized from magazine summaries of the plot):
Omar Khayyam:
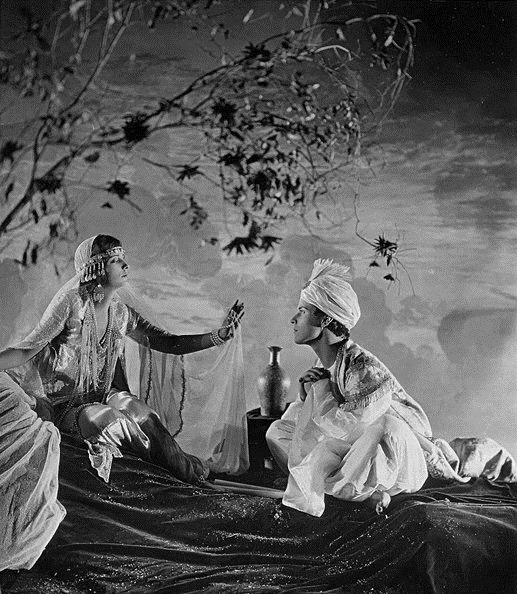
Set in 12th century Persia, the story begins with a preface in the youth of Omar Khayyam (Warde). Omar and his friends, Nizam (Weigel) and Hassan (Stevens), make a pact that whichever one of them becomes a success in life first will help out the others. In adulthood, Nizam has become a potentate and has given Omar a position so that he may continue his studies in mathematics and astronomy. Hassan, however, has grown into quite the villain. When he is expelled from the kingdom, he plots to kidnap Shireen (Key), the sheik’s daughter. Shireen is in love with Ali (Novarro). In the end it’s Hassan’s wife (Reicher) who slays the villain then kills herself.
A Lover’s Oath:
The daughter of a sheik, Shireen (Key), is in love with Ali (Novarro), the son of the ruler of a neighboring kingdom. Hassan covets Shireen and plots to kidnap her. Hassan is foiled by his wife. [The Sills’ edit places Ali and Shireen as protagonists, but there was little to no re-shooting done (absolutely none with Key or Novarro). So, most critics note how odd it is that all Ali does in the film is pitch woo, and does not save Shireen himself. This obviously wouldn’t have been an issue in the earlier cut, where Ali is a supporting character, often not even named in summaries and news items. Additional note: Post’s credit changes from “Vizier” to “Commander of the Faithful”]
Additional sequence(s) featured in the film (but I’m not sure where they fit in the continuity):
Celestial sequences featuring stars and planets moving through the cosmos
Angels spinning in a cyclone up to the heavens
A Potters’ shop sequence (relevant to a specific section of the poems)
Harem dance sequence choreographed by Novarro
Locations: palace gardens, street and marketplace scenes, ancient ruins
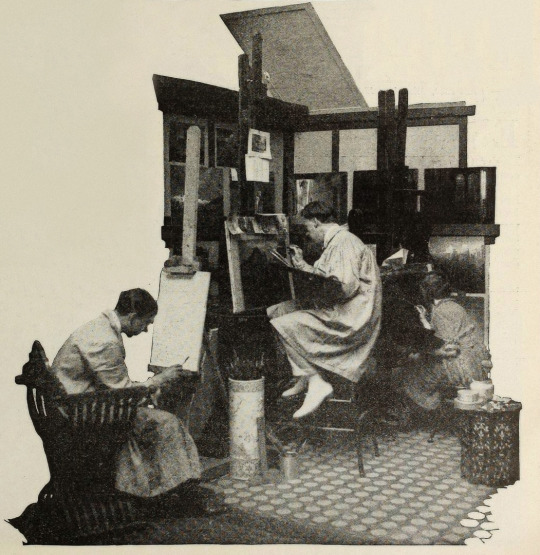
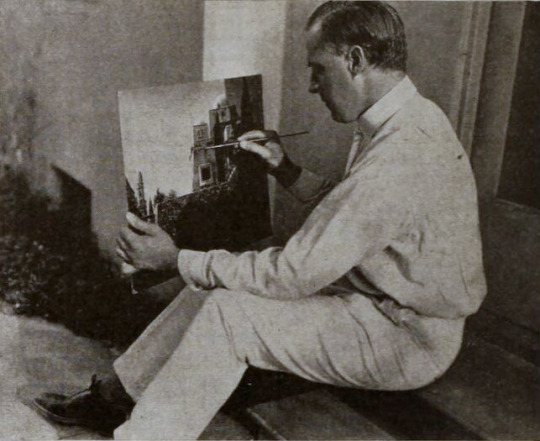





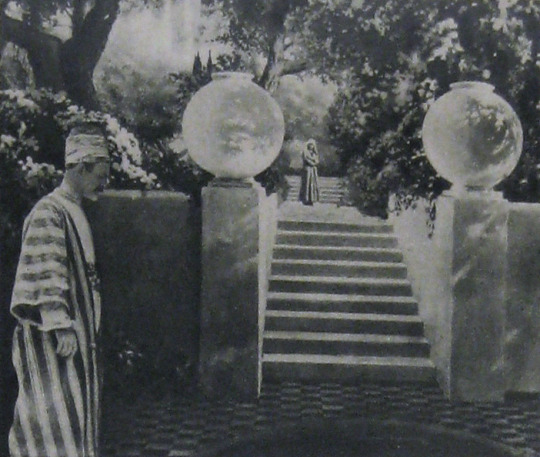
Points of Interest:
“The screen has been described as the last word in realism, but why confine it there? It can also be the last word in imaginative expression.”
Ferdinand P. Earle as quoted in Exhibitors Trade Review, 4 March 1922
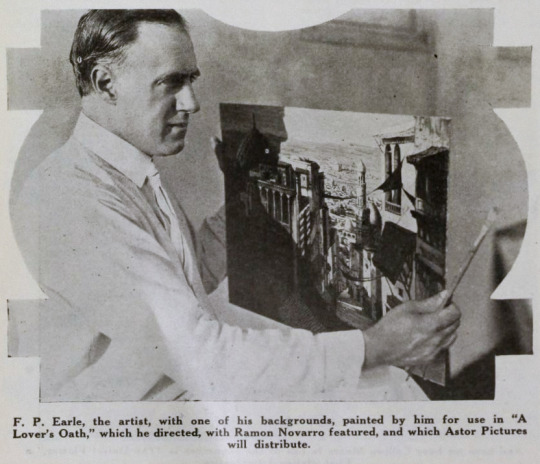
The Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam was a massive best seller. Ferdinand Pinney Earle was a classically trained artist who studied under William-Adolphe Bougueraeu and James McNeill Whistler in his youth. He also had years of experience creating art backgrounds, matte paintings, and art titles for films. Charles Wakefield Cadman was an accomplished composer of songs, operas, and operettas. Georges Benoit and Gordon Pollock were experienced photographic technicians. Edward S. Curtis was a widely renowned still photographer. Ramon Novarro was a name nobody knew yet—but they would soon enough.
When Earle chose The Rubaiyat as the source material for his directorial debut and collected such skilled collaborators, it seemed likely that the resulting film would be a landmark in the art of American cinema. Quite a few people who saw Earle’s Rubaiyat truly thought it would be:
William E. Wing writing for Camera, 9 September 1922, wrote:
“Mr. Earle…came from the world of brush and canvass, to spread his art upon the greater screen. He created a new Rubaiyat with such spiritual colors, that they swayed.”
…
“It has been my fortune to see some of the most wonderful sets that this Old Earth possesses, but I may truly say that none seized me more suddenly, or broke with greater, sudden inspiration upon the view and the brain, than some of Ferdinand Earle’s backgrounds, in his Rubaiyat.
“His vision and inspired art seem to promise something bigger and better for the future screen.”
As quoted in an ad in Film Year Book, 1923:
“Ferdinand Earle has set a new standard of production to live up to.”
Rex Ingram
“Fifty years ahead of the time.”
Marshall Neilan
The film was also listed among Fritz Lang’s Siegfried, Chaplin’s Gold Rush, Fairbanks’ Don Q, Lon Chaney’s Phantom of the Opera and The Unholy Three, and Erich Von Stroheim’s Merry Widow by the National Board of Review as an exceptional film of 1925.
So why don’t we all know about this film? (Spoiler: it’s not just because it’s lost!)
The short answer is that multiple dubious legal challenges arose that prevented Omar’s general release in the US. The long answer follows BELOW THE JUMP!
Earle began the project in earnest in 1919. Committing The Rubaiyat to film was an ambitious undertaking for a first-time director and Earle was striking out at a time when the American film industry was developing an inferiority complex about the level of artistry in their creative output. Earle was one of a number of artists in the film colony who were going independent of the emergent studio system for greater protections of their creative freedoms.
In their adaptation of The Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam, Earle and Co. hoped to develop new and perfect existing techniques for incorporating live-action performers with paintings and expand the idea of what could be accomplished with photographic effects in filmmaking. The Rubaiyat was an inspired choice. It’s not a narrative, but a collection of poetry. This gave Earle the opportunity to intersperse fantastical, poetic sequences throughout a story set in the lifetime of Omar Khayyam, the credited writer of the poems. In addition to the fantastic, Earle’s team would recreate 12th century Persia for the screen.
Earle was convinced that if his methods were perfected, it wouldn’t matter when or where a scene was set, it would not just be possible but practical to put on film. For The Rubaiyat, the majority of shooting was done against black velvet and various matte photography and multiple exposure techniques were employed to bring a setting 800+ years in the past and 1000s of miles removed to life before a camera in a cottage in Los Angeles.
Note: If you’d like to learn a bit more about how these effects were executed at the time, see the first installment of How’d They Do That.
Unfortunately, the few surviving minutes don’t feature much of this special photography, but what does survive looks exquisite:

see all gifs here
Earle, knowing that traditional stills could not be taken while filming, brought in Edward S. Curtis. Curtis developed techniques in still photography to replicate the look of the photographic effects used for the film. So, even though the film hasn’t survived, we have some pretty great looking representations of some of the 1000s of missing feet of the film.

Nearly a year before Curtis joined the crew, Earle began collaboration with composer Charles Wakefield Cadman. In another bold creative move, Cadman and Earle worked closely before principal photography began so that the score could inform the construction and rhythm of the film and vice versa.
By the end of 1921 the film was complete. After roughly 9 months and the creation of over 500 paintings, The Rubaiyat was almost ready to meet its public. However, the investors in The Rubaiyat, Inc., the corporation formed by Earle to produce the film, objected to the ample reference to wine drinking (a comical objection if you’ve read the poems) and wanted the roles of the young lovers (played by as yet unknown Ramon Novarro and Kathleen Key) to be expanded. The dispute with Earle became so heated that the financiers absconded with the bulk of the film to New York. Earle filed suit against them in December to prevent them from screening their butchered and incomplete cut. Cadman supported Earle by withholding the use of his score for the film.
Later, Eastern Film Corp. brokered a settlement between the two parties, where Earle would get final cut of the film and Eastern would handle its release. Earle and Eastern agreed to change the title from The Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam to simply Omar. Omar had its first official preview in New York City. It was tentatively announced that the film would have a wide release in the autumn.
However, before that autumn, director Norman Dawn launched a dubious patent-infringement suit against Earle and others. Dawn claimed that he owned the sole right to use multiple exposures, glass painting for single exposure, and other techniques that involved combining live action with paintings. All the cited techniques had been widespread in the film industry for a decade already and eventually and expectedly Dawn lost the suit. Despite Earle’s victory, the suit effectively put the kibosh on Omar’s release in the US.
Earle moved on to other projects that didn’t come to fruition, like a Theda Bara film and a frankly amazing sounding collaboration with Cadman to craft a silent-film opera of Faust. Omar did finally get a release, albeit only in Australia. Australian news outlets praised the film as highly as those few lucky attendees of the American preview screenings did. The narrative was described as not especially original, but that it was good enough in view of the film’s artistry and its imaginative “visual phenomena” and the precision of its technical achievement.
One reviewer for The Register, Adelaide, SA, wrote:
“It seems almost an impossibility to make a connected story out of the short verse of the Persian of old, yet the producer of this classic of the screen… has succeeded in providing an entertainment that would scarcely have been considered possible. From first to last the story grips with its very dramatic intensity.”
While Omar’s American release was still in limbo, “Ramon Samaniegos” made a huge impression in Rex Ingram’s Prisoner of Zenda (1922, extant) and Scaramouche (1923, extant) and took on a new name: Ramon Novarro. Excitement was mounting for Novarro’s next big role as the lead in the epic Ben-Hur (1925, extant) and the Omar project was re-vivified.

A new company, Astor Distribution Corp., was formed and purchased the distribution rights to Omar. Astor hired actor (note, not an editor) Milton Sills to re-cut the film to make Novarro and Key more prominent. The company also re-wrote the intertitles, reduced the films runtime by more than ten minutes, and renamed the film A Lover’s Oath. Earle had moved on by this point, vowing to never direct again. In fact, Earle was indirectly working with Novarro and Key again at the time, as an art director on Ben-Hur!
Despite Omar’s seemingly auspicious start in 1920, it was only released in the US on the states rights market as a cash-in on the success of one of its actors in a re-cut form five years later.
That said, A Lover’s Oath still received some good reviews from those who did manage to see it. Most of the negative criticism went to the story, intertitles, and Sills’ editing.
What kind of legacy could/should Omar have had? I’m obviously limited in my speculation by the fact that the film is lost, but there are a few key facts about the film’s production, release, and timing to consider.
The production budget was stated to be $174,735. That is equivalent to $3,246,994.83 in 2024 dollars. That is a lot of money, but since the production was years long and Omar was a period film set in a remote locale and features fantastical special effects sequences, it’s a modest budget. For contemporary perspective, Robin Hood (1922, extant) cost just under a million dollars to produce and Thief of Bagdad (1924, extant) cost over a million. For a film similarly steeped in spectacle to have nearly 1/10th of the budget is really very noteworthy. And, perhaps if the film had ever had a proper release in the US—in Earle’s intended form (that is to say, not the Sills cut)—Omar may have made as big of a splash as other epics.
It’s worth noting here however that there are a number of instances in contemporary trade and fan magazines where journalists off-handedly make this filmmaking experiment about undermining union workers. Essentially implying that that value of Earle’s method would be to continue production when unionized workers were striking. I’m sure that that would absolutely be a primary thought for studio heads, but it certainly wasn’t Earle’s motivation. Often when Earle talks about the method, he focuses on being able to film things that were previously impossible or impracticable to film. Driving down filming costs from Earle’s perspective was more about highlighting the artistry of his own specialty in lieu of other, more demanding and time-consuming approaches, like location shooting.
This divide between artists and studio decision makers is still at issue in the American film and television industry. Studio heads with billion dollar salaries constantly try to subvert unions of skilled professionals by pursuing (as yet) non-unionized labor. The technical developments of the past century have made Earle’s approach easier to implement. However, just because you don’t have to do quite as much math, or time an actor’s movements to a metronome, does not mean that filming a combination of painted/animated and live-action elements does not involve skilled labor.
VFX artists and animators are underappreciated and underpaid. In every new movie or TV show you watch there’s scads of VFX work done even in films/shows that have mundane, realistic settings. So, if you love a film or TV show, take the effort to appreciate the work of the humans who made it, even if their work was so good you didn’t notice it was done. And, if you’ve somehow read this far, and are so out of the loop about modern filmmaking, Disney’s “live-action” remakes are animated films, but they’ve just finagled ways to circumvent unions and low-key delegitimize the skilled labor of VFX artists and animators in the eyes of the viewing public. Don’t fall for it.
VFX workers in North America have a union under IATSE, but it’s still developing as a union and Marvel & Disney workers only voted to unionize in the autumn of 2023. The Animation Guild (TAG), also under the IATSE umbrella, has a longer history, but it’s been growing rapidly in the past year. A strike might be upcoming this year for TAG, so keep an eye out and remember to support striking workers and don’t cross picket lines, be they physical or digital!
Speaking of artistry over cost-cutting, I began this post with a mention that in the early 1920s, the American film industry was developing an inferiority complex in regard to its own artistry. This was in comparison to the European industries, Germany’s being the largest at the time. It’s frustrating to look back at this period and see acceptance of the opinion that American filmmakers weren’t bringing art to film. While yes, the emergent studio system was highly capitalistic and commercial, that does not mean the American industry was devoid of home-grown artists.
United Artists was formed in 1919 by Douglas Fairbanks, Charlie Chaplin, Mary Pickford, and D.W. Griffith precisely because studios were holding them back from investing in their art—within the same year that Earle began his Omar project. While salaries and unforgiving production schedules were also paramount concerns in the filmmakers going independent, a primary impetus was that production/distribution heads exhibited too much control over what the artists were trying to create.
Fairbanks was quickly expanding his repertoire in a more classical and fantastic direction. Cecil B. DeMille made his first in a long and very successful string of ancient epics. And the foreign-born children of the American film industry, Charlie Chaplin, Rex Ingram, and Nazimova, were poppin’ off! Chaplin was redefining comedic filmmaking. Ingram was redefining epics. Nazimova independently produced what is often regarded as America’s first art film, Salome (1923, extant), a film designed by Natacha Rambova, who was *gasp* American. Earle and his brother, William, had ambitious artistic visions of what could be done in the American industry and they also had to self-produce to get their work done.
Meanwhile, studio heads, instead of investing in the artists they already had contracts with, tried to poach talent from Europe with mixed success (in this period, see: Ernst Lubitsch, F.W. Murnau, Benjamin Christensen, Mauritz Stiller, Victor Sjöström, and so on). I’m in no way saying it was the wrong call to sign these artists, but all of these filmmakers, even if they found success in America, had stories of being hired to inject the style and artistry that they developed in Europe into American cinema, and then had their plans shot down or cut down to a shadow of their creative vision. Even Stiller, who tragically died before he had the opportunity to establish himself in the US, faced this on his first American film, The Temptress (1926, extant), on which he was replaced. Essentially, the studio heads’ actions were all hot air and spite for the filmmakers who’d gone independent.
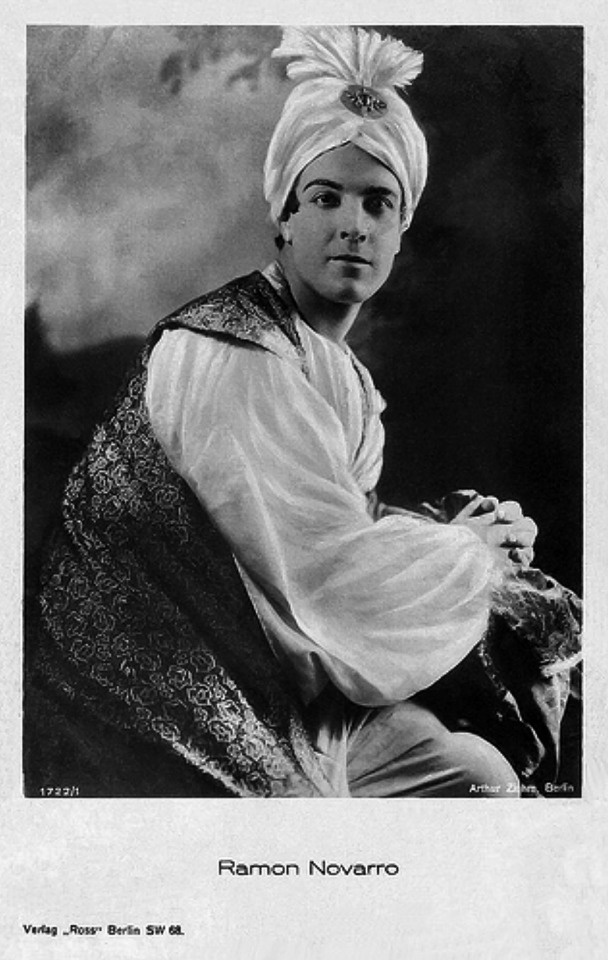





Finally I would like to highlight Ferdinand Earle’s statement to the industry, which he penned for from Camera in 14 January 1922, when his financial backers kidnapped his film to re-edit it on their terms:
MAGNA CHARTA
Until screen authors and producers obtain a charter specifying and guaranteeing their privileges and rights, the great slaughter of unprotected motion picture dramas will go merrily on.
Some of us who are half artists and half fighters and who are ready to expend ninety per cent of our energy in order to win the freedom to devote the remaining ten per cent to creative work on the screen, manage to bring to birth a piteous, half-starved art progeny.
The creative artist today labors without the stimulus of a public eager for his product, labors without the artistic momentum that fires the artist’s imagination and spurs his efforts as in any great art era.
Nowadays the taint of commercialism infects the seven arts, and the art pioneer meets with constant petty worries and handicaps.
Only once in a blue moon, in this matter-of-fact, dollar-wise age can the believer in better pictures hope to participate in a truely [sic] artistic treat.
In the seven years I have devoted to the screen, I have witnessed many splendid photodramas ruined by intruding upstarts and stubborn imbeciles. And I determined not to launch the production of my Opus No. 1 until I had adequately protected myself against all the usual evils of the way, especially as I was to make an entirely new type of picture.
In order that my film verison [sic] of the Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam might be produced under ideal conditions and safeguarded from intolerable interferences and outside worries, I entered into a contract with the Rubaiyat, Inc., that made me not only president of the corporation and on the board of directors, but which set forth that I was to be author, production manager, director, cutter and film editor as well as art director, and that no charge could be made against the production without my written consent, and that my word was to be final on all matters of production. The late George Loane Tucker helped my attorney word the contract, which read like a splendid document.
Alas, I am now told that only by keeping title to a production until it is declared by yourself to be completed is it safe for a scenario writer, an actor or a director, who is supposedly making his own productions, to contract with a corporation; otherwise he is merely the servant of that corporation, subject at any moment to discharge, with the dubious redress of a suit for damages that can with difficulty be estimated and proven.
Can there be any hope of better pictures as long as contracts and copyrights are no protection against financial brigands and bullies?
We have scarcely emerged from barbarism, for contracts, solemnly drawn up between human beings, in which the purposes are set forth in the King’s plainest English, serve only as hurdles over which justice-mocking financiers and their nimble attorneys travel with impunity, riding rough shod over the author or artist who cannot support a legal army to defend his rights. The phrase is passed about that no contract is invioliable [sic]—and yet we think we have reached a state of civilization!
The suit begun by my attorneys in the federal courts to prevent the present hashed and incomplete version of my story from being released and exhibited, may be of interest to screen writers. For the whole struggle revolves not in the slightest degree around the sanctity of the contract, but centers around the federal copyright of my story which I never transferred in writing otherwise, and which is being brazenly ignored.
Imagine my production without pictorial titles: and imagine “The Rubaiyat” with a spoken title as follows, “That bird is getting to talk too much!”—beside some of the immortal quatrains of Fitzgerald!
One weapon, fortunately, remains for the militant art creator, when all is gone save his dignity and his sense of humor; and that is the rapier blade of ridicule, that can send lumbering to his retreat the most brutal and elephant-hided lord of finance.
How edifying—the tableau of the man of millions playing legal pranks upon men such as Charles Wakefield Cadman, Edward S. Curtis and myself and others who were associated in the bloody venture of picturizing the Rubaiyat! It has been gratifying to find the press of the whole country ready to champion the artist’s cause.
When the artist forges his plowshare into a sword, so to speak, he does not always put up a mean fight.
What publisher would dare to rewrite a sonnet of John Keats or alter one chord of a Chopin ballade?
Creative art of a high order will become possible on the screen only when the rights of established, independent screen producers, such as Rex Ingram and Maurice Tourneur, are no longer interferred with and their work no longer mutilated or changed or added to by vandal hands. And art dramas, conceived and executed by masters of screen craft, cannot be turned out like sausages made by factory hands. A flavor of individuality and distinction of style cannot be preserved in machine-made melodramas—a drama that is passed from hand to hand and concocted by patchworkers and tinkerers.
A thousand times no! For it will always be cousin to the sausage, and be like all other—sausages.
The scenes of a master’s drama may have a subtle pictorial continuity and a power of suggestion quite like a melody that is lost when just one note is changed. And the public is the only test of what is eternally true or false. What right have two or three people to deprive millions of art lovers of enjoying an artist’s creation as it emerged from his workshop?
“The Rubaiyat” was my first picture and produced in spite of continual and infernal interferences. It has taught me several sad lessons, which I have endeavored in the above paragraphs to pass on to some of my fellow sufferers. It is the hope that I am fighting, to a certain extent, their battle that has given me the courage to continue, and that has prompted me to write this article. May such hubbubs eventually teach or inforce a decent regard for the rights of authors and directors and tend to make the existence of screen artisans more secure and soothing to the nerves.
FERDINAND EARLE.
---
☕Appreciate my work? Buy me a coffee! ☕
Transcribed Sources & Annotations over on the WMM Blog!
See the Timeline for Ferdinand P. Earle's Rubaiyat Adaptation
41 notes
·
View notes
Photo

How to start reading Dresden Codak
I know a lot of people who follow me here don’t know how or where to start my comic series, so here’s a quick guide for newbies! I have two types of comics on my site, one-shots and storylines, the latter just being multipage stories. If you start at my earliest comic and go forward, you’ll actually read through all of my comics in order. That’s probably the easiest way to start reading, as that way you don’t miss anything.
However, you can also start at two of the big storylines and then go back and read the others.
Hob - This is the first storyline in Dresden Codak. It fleshes out Kim, the series protagonist, pretty well and is a fairly good jumping-off point for new readers.
Dark Science - The current story that’s been running for a couple years now. It features established characters, but the story is 100% self-contained, and can be read without any issues.
I hope that helps!
758 notes
·
View notes
Photo


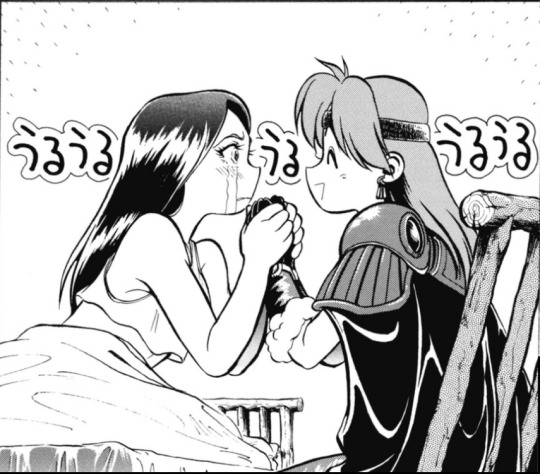

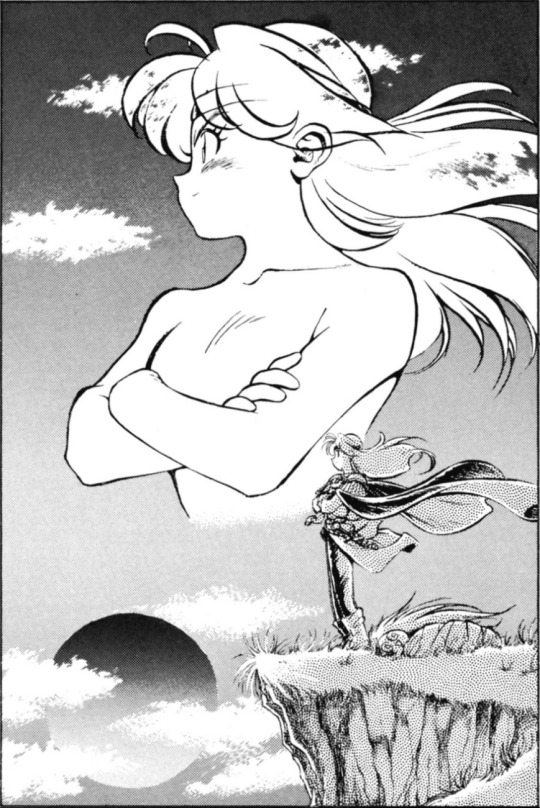







Slayers Special #1 Part 3- Black & White Art by Rui Araizumi
590 notes
·
View notes
Text
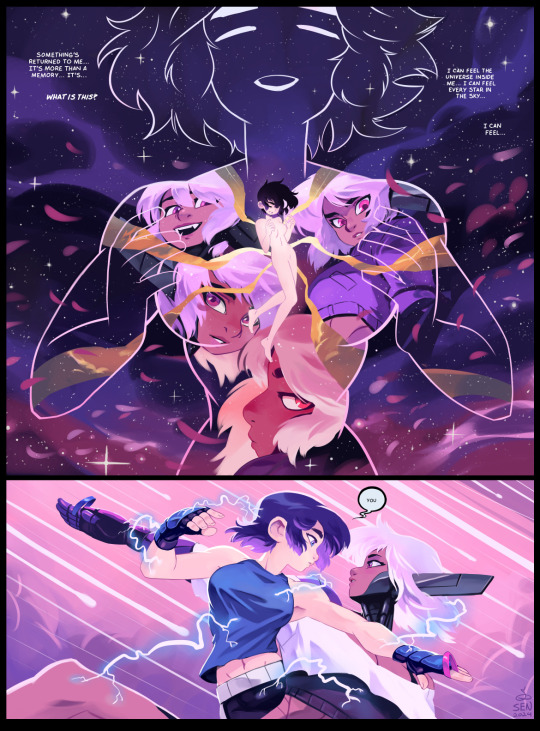

Dark Science #145 - Starlight
Something's certainly returned to Kim… but what could it be?
Patreon | Gumroad | Store | Ko-Fi | Payp
#dresden codak#dark science#comics#illustration#kimiko ross#art deco#my art#sen#xiaoling chavez#gayyyy#lgbtq comics#cyberpunk#queer comics
251 notes
·
View notes



