Photo

(via After Months of Gibberish, Voyager 1 Is Communicating Well Again | Scientific American)
NASA scientists spent months coaxing the 46-year-old Voyager 1 spacecraft back into healthy communication
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
Our Star
So hot yet so cool.
Solar activity April 7-April 9. Eclipse day included.
Credit: NASA/SDO/Helioviewer.org
7 notes
·
View notes
Photo


(via An Event Even Rarer Than The Eclipse Is Happening Soon - Videos from The Weather Channel)
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Messier 16 - The Eagle Nebula
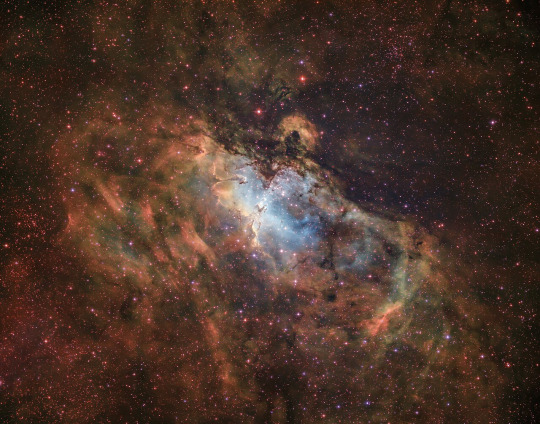

5,700 light years away in the constellation of Serpens lies this iconic area of star formation, an open cluster, but also an emissions nebula with a web of dark dust strands and columns.
Made famous by Hubble in the "Pillars of Creation" image.
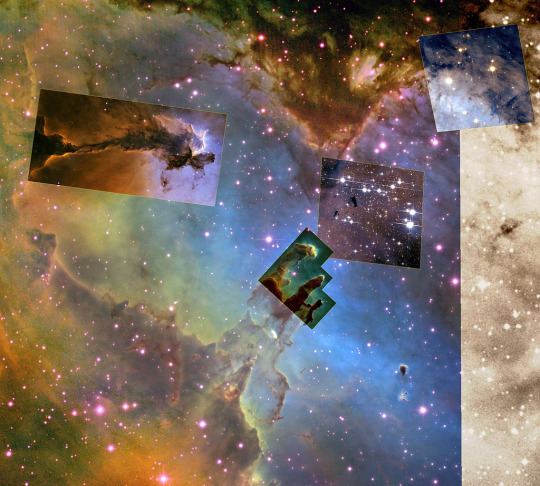
The cluster itself has an estimated 8,100 stars and is thought to be between 1 and 2 million years old. The brightest star HD168076 is two O type stars in binary partnership, some 80 times the mass of our star, and 1 million times brighter.
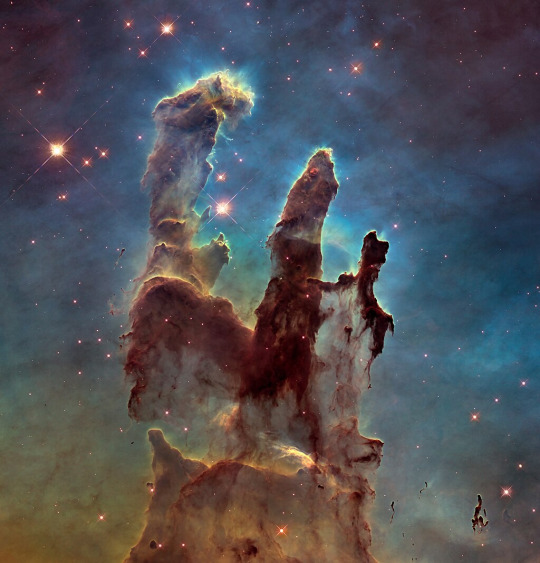

The classic columns with their bright tips is seen in many nebulous regions, and is thought to contain proto stars developing inside.

And another larger example, thought to extend over 9.5 light years.
The structure is just out of reach of naked eyes, but visible in binoculars or small telescopes, but don't expect to see this kind of detail, a smudge may be the best you'll see.
45 notes
·
View notes
Photo
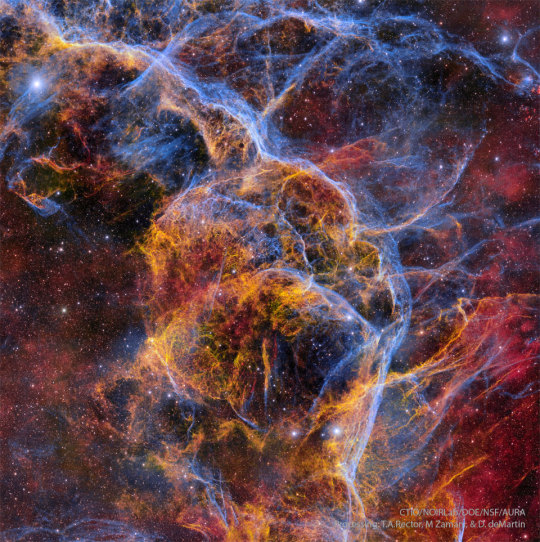

2024 April 16
Filaments of the Vela Supernova Remnant
Image Credit: CTIO, NOIRLab, DOE, NSF, AURA; Processing: T. A. Rector (U. Alaska Anchorage), M. Zamani & D. de Martin (’s NOIRLab)
Explanation: The explosion is over, but the consequences continue. About eleven thousand years ago, a star in the constellation of Vela could be seen to explode, creating a strange point of light briefly visible to humans living near the beginning of recorded history. The outer layers of the star crashed into the interstellar medium, driving a shock wave that is still visible today. The featured image captures some of that filamentary and gigantic shock in visible light. As gas flies away from the detonated star, it decays and reacts with the interstellar medium, producing light in many different colors and energy bands. Remaining at the center of the Vela Supernova Remnant is a pulsar, a star as dense as nuclear matter that spins around more than ten times in a single second.
∞ Source: apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap240416.html
109 notes
·
View notes
Text
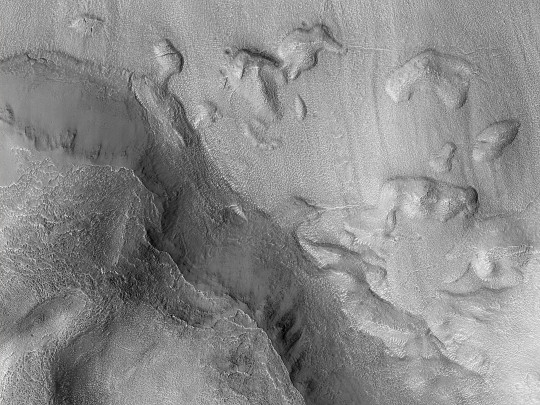
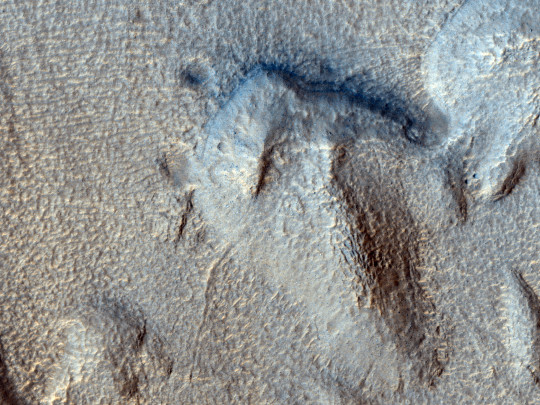


HiPOD: Fluvial Erosion in Harmakhis Vallis
This observation was requested by a Mars class to examine fluvial processes in one of the large channels leading into Harmakhis Vallis. The requested image is in a corner pointing opposite of the flow, possibly creating an eddy/turbulent area. The goal is to get a high resolution look for shoreline markings and erosion effects. Harmakhis Vallis probably formed by a combination of surface collapse and flowing water. (Grayscale cutout is less than 5 km across; enhanced color is less than 1 km.)
ID: ESP_075006_1410
date: 27 July 2022
altitude: 257 km
NASA/JPL-Caltech/UArizona
35 notes
·
View notes
Photo

2024 April 11
Eclipse in Seven
Image Credit & Copyright: Xiaofeng Tan
Explanation: Start at the upper left above and you can follow the progress of April 8’s total eclipse of the Sun in seven sharp, separate exposures. The image sequence was recorded with a telescope and camera located within the narrow path of totality as the Moon’s shadow swept across Newport, Vermont, USA. At center is a spectacular view of the solar corona. The tenuous outer atmosphere of the Sun is only easily visible to the eye in clear dark skies during the total eclipse phase. Seen from Newport, the total phase for this solar eclipse lasted about 3 minutes and 26 seconds.
∞ Source: apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap240411.html
122 notes
·
View notes
Link
6 notes
·
View notes
Link
8 notes
·
View notes
Text


HiPOD: Dune Monitoring in Renaudot Crater
This observation was requested as part of an imaging campaign to monitor frost deposition, evolution, and sublimation. The campaign is designed to capture the onset of seasonal frost, which means images taken near the polar hood have very high incidence angles that are important. The image can also be used for detailed surface measurements. (Grayscale cutout is less than 5 km across; enhanced color is less than 1 km.)
ID: ESP_074809_2225
date: 12 July 2022
altitude: 300 km
NASA/JPL-Caltech/UArizona
70 notes
·
View notes
Text

More Evidence of Neutron Star in 1987a Supernova
It's taken 37 years, but finally a combination of images from Hubble and JWST has finally found the most compelling evidence yet of the stellar remnants left behind by the supernova.

While it was predicted that a neutron star would be left behind, it's not as yet been directly spotted but this evidence shows the area just around it, the wind from the neutron star.

JWST was able to resolve the neutron star wind by looking for argon, it's not yet directly visible due to the amount of dust and gas in and around it, but it's the closest we've come to actually detecting it directly.
90 notes
·
View notes
Text
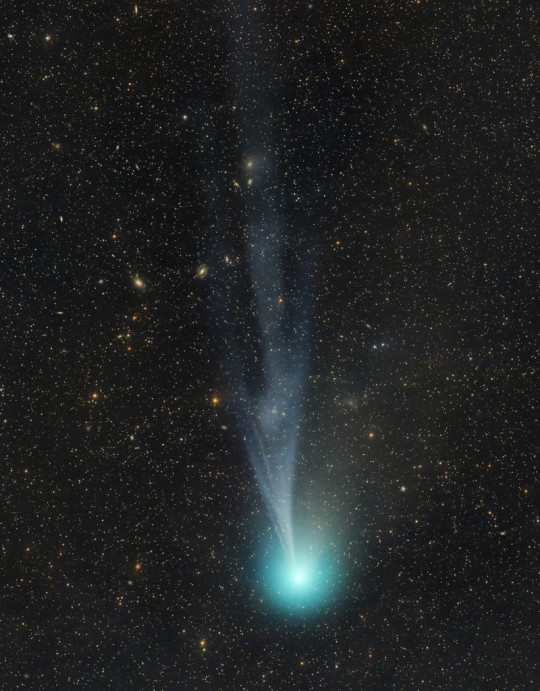

Structure in the Tail of Comet 12P/Pons-Brooks
Image Credit: Dan Bartlett
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

NGC 6752 - Globular Cluster
The third brightest globular cluster in our skies, and orbiting in the Milky Way's halo, this group of stars are over 10 billion years old (if not more), and yet, look closely and you'll spot a number of bright blue stars, how is this possible for a cluster of such age ? Most blue stars only last a few million years, so what is happening ?

Setting aside the one bright blue star in the image at 11o'clock which is a foreground star, you'll see countless red and blue stars in the cluster, yet there is no star formation going on here.
The vast majority of stars in the cluster are F,G,K,M type stars, stars a little larger than our sun down to red giants, as all the others have long since ended their stellar lives.
However, the blue stars are not new born stars as we often see in nebula, they are what is known as "blue stragglers".


The best theory for what is going on is that the dense cluster has meant some stars have actually merged, and the increase in mass has created a blue giant star, they won't last too long, but as globular clusters are some of the most dense areas of stars, there's a steady supply of mergers and blue stragglers.
60 notes
·
View notes
Photo

2024 February 18
Hoag’s Object: A Nearly Perfect Ring Galaxy
Image Credit: NASA, ESA, Hubble; Processing: Benoit Blanco
Explanation: Is this one galaxy or two? This question came to light in 1950 when astronomer Arthur Hoag chanced upon this unusual extragalactic object. On the outside is a ring dominated by bright blue stars, while near the center lies a ball of much redder stars that are likely much older. Between the two is a gap that appears almost completely dark. How Hoag’s Object formed, including its nearly perfectly round ring of stars and gas, remains unknown. Genesis hypotheses include a galaxy collision billions of years ago and the gravitational effect of a central bar that has since vanished. The featured photo was taken by the Hubble Space Telescope and reprocessed using an artificially intelligent de-noising algorithm. Observations in radio waves indicate that Hoag’s Object has not accreted a smaller galaxy in the past billion years. Hoag’s Object spans about 100,000 light years and lies about 600 million light years away toward the constellation of the Snake (Serpens). Many galaxies far in the distance are visible toward the right, while coincidentally, visible in the gap at about seven o'clock, is another but more distant ring galaxy.
∞ Source: apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap240218.html
132 notes
·
View notes
Text

NGC 7331 Acquired with the Schulman Telescope at the Mount Lemmon
Credit: Adam Block/Mount Lemmon SkyCenter/University of Arizona
887 notes
·
View notes
Photo
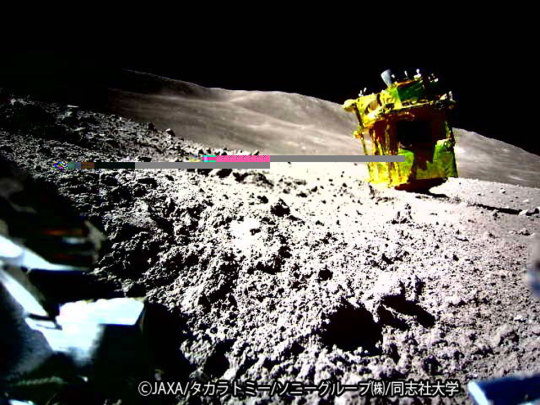

2024 January 30
SLIM Lands on the Moon
Image Credit & Copyright: JAXA, Takara Tomy, Sony Co., Doshisha U.
Explanation: New landers are on the Moon. Nearly two weeks ago, Japan’s Smart Lander for Investigating Moon (SLIM) released two rovers as it descended, before its main lander touched down itself. The larger of the two rovers can hop like a frog, while the smaller rover is about the size of a baseball and can move after pulling itself apart like a transformer. The main lander, nicknamed Moon Sniper, is seen in the featured image taken by the smaller rover. Inspection of the image shows that Moon Sniper’s thrusters are facing up, meaning that the lander is upside down from its descent configuration and on its side from its intended landing configuration. One result is that Moon Sniper’s solar panels are not in the expected orientation, so that powering the lander had to be curtailed and adapted. SLIM’s lander has already succeeded as a technology demonstration, its main mission, but was not designed to withstand the lunar night – which starts tomorrow.
∞ Source: apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap240130.html
62 notes
·
View notes
Text

A view of Mars made from pictures captured with the EXI camera aboard UAE's Hope Mars Mission spacecraft on August 21, 2023 from an orbital distance of 20,132 kilometers.
Credit: Jason Major
1K notes
·
View notes