#years active 1917-26 & 1936
Photo

Sylvia Breamer (ca.1917-19)
Pic Source: classicactress (Instagram)
#sylvia breamer#ca.1917-19#beautiful australian actress#silent screen beauty#48 acting credits#years active 1917-26 & 1936#in american plays in australia and on broadway#1910's#cropped photo#b/w photography#pic source: classicactress (instagram)
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
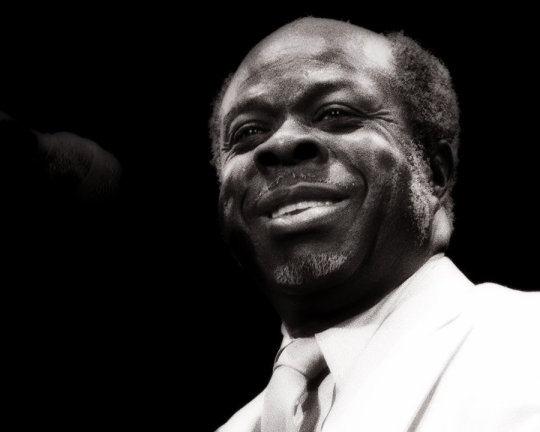
Rufus Thomas

Rufus C. Thomas, Jr. (March 26, 1917 – December 15, 2001) was an American rhythm-and-blues, funk, soul and blues singer, songwriter, dancer, DJ and comic entertainer from Memphis, Tennessee. He recorded for several labels, including Chess Records and Sun Records in the 1950s, before becoming established in the 1960s and 1970s at Stax Records. He is best known for his novelty dance records, including "Walking the Dog" (1963), "Do the Funky Chicken" (1969) and "(Do the) Push and Pull" (1970). According to the Mississippi Blues Commission, "Rufus Thomas embodied the spirit of Memphis music perhaps more than any other artist, and from the early 1940s until his death . . . occupied many important roles in the local scene."
He began his career as a tap dancer, vaudeville performer, and master of ceremonies in the 1930s. He later worked as a disc jockey on radio station WDIA in Memphis, both before and after his recordings became successful. He remained active into the 1990s and as a performer and recording artist was often billed as "The World's Oldest Teenager". He was the father of the singers Carla Thomas (with whom he recorded duets) and Vaneese Thomas and the keyboard player Marvell Thomas.
Early life
Thomas was born in the rural community of Cayce, Mississippi, the son of a sharecropper. He moved with his family to Memphis, Tennessee, around 1920. His mother was a "church woman". Thomas made his debut as a performer at the age of six, playing a frog in a school theatrical production. By the age of 10, he was a tap dancer, performing on the streets and in amateur productions at Booker T. Washington High School, in Memphis. From the age of 13, he worked with Nat D. Williams, his high-school history teacher, who was also a pioneer black DJ at radio station WDIA and columnist for black newspapers, as a master of ceremonies at talent shows in the Palace Theater on Beale Street. After graduating from high school, Thomas attended Tennessee A&I University for one semester, but economic constraints led him to leave to pursue a career as a full-time entertainer.
Early career as a performer
Thomas began performing in traveling tent shows. In 1936 he joined the Rabbit Foot Minstrels, an all-black revue that toured the South, as a tap dancer and comedian, sometimes part of a duo, Rufus and Johnny. He married Cornelia Lorene Wilson in 1940, at a service officiated by Rev. C. L. Franklin, the father of Aretha Franklin, and the couple settled in Memphis. Thomas worked a day job in the American Finishing Company textile bleaching plant, which he continued to do for over 20 years. He also formed a comedy and dancing duo, Rufus and Bones, with Robert "Bones" Couch, and they took over as MCs at the Palace Theater, often presenting amateur hour shows. One early winner was B.B. King, and others discovered by Thomas later in the 1940s included Bobby Bland and Johnny Ace.
In the early 1940s, Thomas began writing and performing his own songs. He regarded Louis Armstrong, Fats Waller and Gatemouth Moore as musical influences. He made his professional singing debut at the Elks Club on Beale Street, filling in for another singer at the last minute, and during the 1940s became a regular performer in Memphis nightclubs, such as Currie's Club Tropicana. As an established performer in Memphis, aged 33 in 1950, Thomas recorded his first 78 rpm single, for Jesse Erickson's small Star Talent label in Dallas, Texas. Thomas said, "I just wanted to make a record. I never thought of getting rich. I just wanted to be known, be a recording artist. . . . [But] the record sold five copies and I bought four of them." The record, "I'll Be a Good Boy" backed with "I'm So Worried", gained a Billboard review, which stated that "Thomas shows first class style on a slow blues". He also recorded for the Bullet label in Nashville, Tennessee, when he recorded with Bobby Plater's Orchestra and was credited as "Mr. Swing"; the recordings were not recognised by researchers as being by Thomas until 1996. In 1951 he made his first recordings at Sam Phillips's Sun Studio, for the Chess label, but they were not commercially successful.
He began working as a DJ at radio station WDIA in 1951, and hosted an afternoon R&B show called Hoot and Holler. WDIA, featuring an African-American format, was known as "the mother station of the Negroes" and became an important source of blues and R&B music for a generation, its audience consisting of white as well as black listeners. Thomas used to introduce his shows saying, "I'm young, I'm loose, I'm full of juice, I got the goose so what's the use. We're feeling gay though we ain't got a dollar, Rufus is here, so hoot and holler." He also used to lead tours of white teenagers on "midnight rambles" around Beale Street.
His celebrity in the South was such that in 1953, at Sam Phillips's suggestion, he recorded "Bear Cat" for Sun Records, an "answer record" to Big Mama Thornton's R&B hit "Hound Dog". The record became the label's first national chart hit, reaching number 3 on the Billboard R&B chart. However, a copyright-infringement suit brought by Don Robey, the original publisher of "Hound Dog", nearly bankrupted the record label. After only one recording there, Thomas was one of the African-American artists released by Phillips, as he oriented his label more toward white audiences and signed Elvis Presley, who later recorded Thomas's song "Tiger Man". Thomas did not record again until 1956, when he made a single, "I'm Steady Holdin' On", for the Bihari brothers' Meteor label; musicians on the record included Lewie Steinberg, later a founding member of Booker T and the MGs.
Stax Records
In 1960 he made his first recordings with his 17-year-old daughter Carla, for the Satellite label in Memphis, which changed its name to Stax the following year. The song, "Cause I Love You", featuring a rhythm borrowed from Jesse Hill's "Ooh Poo Pa Doo", was a regional hit; the musicians included Thomas' son Marvell on keyboards, Steinberg, and the 16-year-old Booker T. Jones. The record's success led to Stax gaining production and distribution deal with the much larger Atlantic Records.
Rufus Thomas continued to record for the label after Carla's record "Gee Whiz (Look at His Eyes)" reached the national R&B chart in 1961. He had his own hit with "The Dog", a song he had originally improvised in performance based on a Willie Mitchell bass line, complete with imitations of a barking dog. The 1963 follow-up, "Walking the Dog", engineered by Tom Dowd of Atlantic, became one of his most successful records, reaching #10 on the Billboard pop chart. He became the first, and still the only, father to debut in the Top 10 after his daughter had first appeared there. The song was recorded in early 1964 by the Rolling Stones on their debut album, and was a minor UK chart hit for Merseybeat group the Dennisons later that year.
As well as recording and appearing on radio and in clubs, Thomas continued to work as a boiler operator in the textile plant, where he claimed the noises sometimes suggested musical rhythms and lyrics to him, before he finally gave up the job in 1963, to focus on his role as a singer and entertainer. He recorded a series of novelty dance tracks, including "Can Your Monkey Do the Dog'" and '"Somebody Stole My Dog" for Stax, where he was often backed by Booker T. & the MGs or the Bar-Kays. He also became a mentor to younger Stax stars, giving advice on stage moves to performers like Otis Redding, who partnered daughter Carla on record.
After "Jump Back" in 1964, the hits dried up for several years, as Stax gave more attention to younger artists and musicians. However, in 1970 he had another big hit with "Do the Funky Chicken", which reached #5 on the R&B chart, #28 on the pop chart, and #18 in Britain where it was his only chart hit. Thomas improvised the song while performing with Willie Mitchell's band at a club in Covington, Tennessee, including a spoken word section that he regularly used as a shtick as a radio DJ: "Oh I feel so unnecessary - this is the kind of stuff that makes you feel like you wanna do something nasty, like waste some chicken gravy on your white shirt right down front." The recording was produced by Al Bell and Tom Nixon, and used the Bar-Kays, featuring guitarist Michael Toles. Thomas continued to work with Bell and Nixon as producers, and later in 1970 had his only number 1 R&B hit [and his second-highest pop charting record] with another dance song, "Do the Push and Pull". A further dance-oriented release in 1971, "The Breakdown", climbed to number 2 R&B and number 31 Pop. In 1972, he featured in the Wattstax concert, and he had several further, less successful, hits before Stax collapsed in 1976.
Later career
Thomas continued to record and toured internationally, billing himself as "The World's Oldest Teenager" and describing himself as "the funkiest man alive". He "drew upon his vaudeville background to put [his songs] over on stage with fancy footwork that displayed remarkable agility for a man well into his fifties", and usually performed "while clothed in a wardrobe of hot pants, boots and capes, all in wild colors."
He continued as a DJ at WDIA until 1974, and worked for a period at WLOK before returning to WDIA in the mid 1980s to co-host a blues show. He appeared regularly on television and recorded albums for various labels. Thomas performed regularly at the Porretta Soul Festival in Italy; the outdoor amphitheater in which he performed was later renamed Rufus Thomas Park.
He played an important part in the Stax reunion of 1988, and appeared in Jim Jarmusch's 1989 film Mystery Train, Robert Altman's 1999 film Cookie's Fortune, and D. A. Pennebaker’s documentary Only the Strong Survive. Thomas released an album of straight-ahead blues, That Woman is Poison!, with Alligator Records in 1990, featuring saxophonist Noble "Thin Man" Watts. In 1996, he and William Bell headlined at the Olympics in Atlanta, Georgia. In 1997, he released an album, Rufus Live!, on Ecko Records. In 1998, he hosted two New Year's Eve shows on Beale Street.
In 1997, to commemorate his 80th birthday, the City of Memphis renamed a road off Beale Street, close to the old Palace Theater, as Rufus Thomas Boulevard. He received a Pioneer Award from the Rhythm and Blues Foundation in 1992, and a lifetime achievement award from ASCAP in 1997. He was inducted into the Blues Hall of Fame in 2001.
Death and legacy
He died of heart failure in 2001, at the age of 84, at St. Francis Hospital in Memphis. He is buried next to his wife Lorene, who pre-deceased him in 2000, at the New Park Cemetery in Memphis.
Writer Peter Guralnick said of him:
His music... brought a great deal of joy to the world, but his personality brought even more, conveying a message of grit, determination, indomitability, above all a bottomless appreciation for the human comedy that left little room for the drab or the dreary in his presence.
Thomas was honored with a marker on the Mississippi Blues Trail in Byhalia.
On June 25, 2019, The New York Times Magazine listed Rufus Thomas among hundreds of artists whose material was reportedly destroyed in the 2008 Universal fire.
In popular culture
Bobby Brown portrays Thomas in the BET television series American Soul.
10 notes
·
View notes
Photo
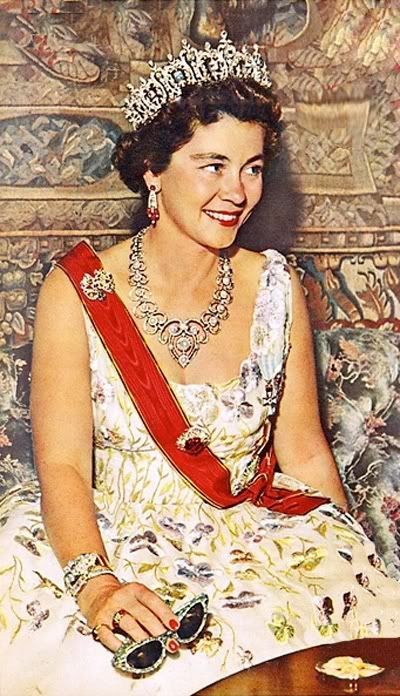

People that have married in to Royal Families since 1800
Greece
Frederica of Hanover born 18 April 1917 and died 6 February 1981
Born Her Royal Highness Princess Frederica of Hanover, of Great Britain and Ireland, and of Brunswick-Lüneburg on 18 April 1917 in Blankenburg am Harz, in the German Duchy of Brunswick, she was the only daughter of Ernest Augustus, then reigning Duke of Brunswick, and his wife Princess Viktoria Luise of Prussia, herself the only daughter of the German Emperor Wilhelm II. Both her father and maternal grandfather would abdicate their crowns in November 1918 following Germany's defeat in World War I, and her paternal grandfather would be stripped of his British royal dukedom the following year.
As a descendant of Queen Victoria, she was, at birth, 34th in the line of succession to the British throne. In 1934, Adolf Hitler, in his ambition to link the British and German royal houses, asked for Frederica's parents to arrange for the marriage of their seventeen-year-old daughter to the Prince of Wales. In her memoirs, Frederica's mother described that she and her husband were "shattered" and such a possibility "had never entered our minds". Victoria Louise herself had once been considered as a potential bride for the very same person prior to her marriage. Moreover, the age difference was too great (the Prince of Wales was twenty-two years Frederica's senior), and her parents were unwilling to "put any such pressure" on their daughter.
Prince Paul of Greece, her mother's paternal first cousin, proposed to her during the summer of 1936, while he was in Berlin attending the 1936 Summer Olympics. Paul was a son of King Constantine I and Frederica's grand-aunt Sophia. Their engagement was announced officially on 28 September 1937, and Britain's King George VI gave his consent pursuant to the Royal Marriages Act 1772 on 26 December 1937. They married in Athens on 9 January 1938. Frederica became Hereditary Princess of Greece, her husband being heir presumptive to his childless elder brother, King George II. During the early part of their marriage, they resided at a Villa in Psychiko in the suburbs of Athens. Ten months after their marriage, their first child, the future Queen Sofia of Spain, was born on 2 November 1938. On 2 June 1940, Frederica gave birth to the future King Constantine II.
At the peak of World War II, in April 1941, the Greek Royal Family was evacuated to Crete in a Sunderland flying boat. Shortly afterwards, the German forces attacked Crete. Frederica and her family were evacuated again, setting up a government-in-exile office in London. In exile, King George II and the rest of the Greek Royal Family settled in South Africa. Here Frederica's last child, Princess Irene, was born on 11 May 1942. The South African leader, General Jan Smuts, served as her godfather. The family eventually settled in Egypt in February 1944. On 1 September 1946, after the war, the Greek people decided by referendum to restore King George to the throne. The Hereditary Prince and Princess returned to their villa in Psychiko.
On 1 April 1947, George II died and Frederica's husband ascended the throne as Paul I, with Frederica as queen consort. Communist political instability in Northern Greece led to the Greek Civil War. The King and Queen toured Northern Greece under severe security to try to appeal for loyalty in the summer of 1947. Queen Frederica was constantly attacked for her German ancestry. Left-wing politicians in Greece repeatedly used the fact that the Kaiser was her grandfather, and that she had brothers who were members of the SS, as propaganda against her. She was also criticized variously as "very Prussian" and "was a Nazi". When she was in London representing her sick husband at the wedding of his first cousin Prince Philip to King George VI's elder daughter Princess Elizabeth in November 1947, Winston Churchill remarked on the Kaiser being her grandfather. Queen Frederica had replied acknowledging the fact, but reminding him that she was also descended from Queen Victoria, and that her father would be the British king if the country had operated under Salic Law (allowing only males to inherit the crown).
During the civil war, Queen Frederica set the Queen's Camps or Child Cities (translation of: Παιδο(υ)πόλεις / Paidopoleis or Paidupoleis) a network of 53 camps around Greece where she would gather mostly orphans and children of poor families. These camps provided much needed shelter, food, and education to these children who were aged 3 years old to adolescence.[The role of these Queen's Camps is disputed as a means of propaganda by the monarchy through the educational program. The Queen's Camps were a way to care for the children who were victims of the civil war. There were allegations, generally by opposition or communist sources, which held that children were illegally adopted by American families while they were in the Queen's Camps.
The Greek Civil War ended in August 1949. The Sovereigns took this opportunity to strengthen the monarchy, they paid official visits to Marshal Josip Broz Tito in Belgrade, Presidents Luigi Einaudi of Italy in Rome, Theodor Heuss of West Germany, and Bechara El Khoury of Lebanon, Emperor Haile Selassie I of Ethiopia, Chakravarthi Rajagopalachari of India, King George VI of the United Kingdom, and the United States as guest of President Dwight D. Eisenhower.
However, at home in Greece and abroad in the United Kingdom, Queen Frederica was targeted by the opposition, because as a girl she had belonged to the Bund Deutscher Mädel (League of German Girls), a branch of the Hitler Youth group for young women; her supporters argued that evading membership in the group would be difficult under the existing political climate in Nazi Germany at the time. Her 16 November 1953 appearance in Life as America's guest was taken on one of the many state visits she paid around the world. Also that year she appeared on the cover of Time.
On 14 May 1962 her eldest daughter Sofia married Prince Juan Carlos of Spain, (later King Juan Carlos I of Spain) in Athens.
Frederika has been described as "inherently undemocratic" She was notorious for her numerous arbitrary and unconstitutional interventions in Greek politics and clashes with democratically elected governments. She actively politicked against the election of Alexander Papagos.At home in Greece and abroad in the United Kingdom, she was targeted by the opposition. In 1963 while visiting London, rioting by Greek leftists demonstrating against the situation with the political prisoners of the Greek civil war, forced her to temporarily seek refuge in a stranger's house. Her interference in politics was harshly criticized and possibly was a significant factor in the strengthening of republican sentiments
On 6 March 1964, King Paul died of cancer. When her son, the new King, married Princess Anne-Marie of Denmark later that year on 18 September, Queen Frederica stepped back from the majority of her public duties in favor of her daughter-in-law. She remained a figure of controversy and was accused in the press of being the éminence grise behind the throne. She retired to the countryside where she lived an almost reclusive life. However, she continued to attend Royal events that were family-oriented, such as the baptisms of her grandchildren in both Spain and Greece.
King Constantine II's clashes with the democratically elected Prime Minister George Papandreou Sr. were blamed by critics for causing the destabilisation that led to a military coup on 21 April 1967 and the rise of the regime of the colonels. Faced with a difficult situation, King Constantine initially collaborated with the military dictatorship, swearing in their government under a royalist prime minister. Later that year he attempted a counter-coup in an attempt to restore democracy, whose failure forced him into exile. Following this, the junta appointed a Regent to carry out the tasks of the exiled Monarch. In 1971, she published an autobiography, A Measure of Understanding. On 1 June 1973 the junta abolished the Greek Monarchy without the consent of the Greek people and then attempted to legitimize its actions through a 1973 plebiscite that was widely suspected of being rigged. The new head-of-state became President of Greece George Papadopoulos. The dictatorship ended on 24 July 1974 and the pre-junta constitutional monarchy was never restored. A plebiscite was held on 8 December 1974 in which Constantine (who was able to campaign only from outside the country) freely admitted his past errors, promised to support democracy, and in particular, promised to keep his mother Frederica away from Greece and out of Greek politics. However, 69% of Greeks voted to make Greece a democratic republic.
Frederica died on 6 February 1981 in exile in Madrid during ophthalmic surgery. In its obituary of the former Queen, The New York Times reported that she died during "eyelid surgery," which led to frequent but unsubstantiated rumours that she died while undergoing cosmetic surgery Other sources state that her cause of death was a heart attack while undergoing the removal of cataracts. She was interred at Tatoi (the Royal family's palace and burial ground in Greece). Her son and his family were allowed to attend the service but had to leave immediately afterwards.
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Walt Disney Story

Rising - The Walt Disney Story
The Walt Disney Story is very inspirational. Walter Elias Disney was born on December 5th, 1901, in Chicago, Illinois. Walt is the fourth of 5 children. Elias and Flora Disney were their parents. His childhood set apart by economic hardship; his dad was always changing from one job to another. He spent his childhood on a farm, in a village of Missouri. There, he lived surrounded by nature and animals. His mom would read classic tales to him, and that's when his interest in drawing started to grow inside him.
In 1909, his dad got sick, and the whole family had to move to Kansas City. During that time, Walt was selling newspapers and occasionally making some money with his caricatures. He enrolled in the Kansas City Art Institute, where he learned his first notions about drawing techniques. It was then, during those teenage years when he discovered the cinema - an invention, he was passionate about since the very beginning.
In 1917, he went back to Chicago with his family, and in 1918, he faked his birth certificate and enlisted at the age of 17 in the Red Cross to fight in WWI". He made it to Europe when there was peace already, but he was based on France and Germany until September 1919.
When he got back, he found a job at an advertising agency, where he met Ubbe Iwerks (UB Iwerks) a talented cartoonist, who would become his partner in all their adventures throughout years. They together decided to create their own company of animated films. However, they had to close it down soon after because of the financial failure of one of their most important clients.

Disney Brothers Studio - The Walt Disney Story
In 1923, Disney decided to move to Hollywood. However, the film industry didn't welcome Disney as nicely as he had expected. So he decided to create his own animation business with his brother Roy. In October 1923, Disney Brothers Studio was created. A year later, Ubbe Iwerks joined the company, and Walt could stop working as an animator to dedicate his time to the task he had always been more qualified for: the creation of characters, plots and directing.
In 1925, Walt married Lillian Bounds, a young worker of the studio, with whom he had two daughters: Diane Marie, born in 1935, when the couple already thought they could never have children, and Sharon Mae (mei), adopted in 1936.
In 1926, they moved to bigger studios, and they changed the name to Walt Disney Studios. Everything seemed to be going full steam ahead. However, the company suffered a severe misfortune when its most crucial client took over the rights of Oswald the Lucky Rabbit. This character, created by Disney, had been the protagonist of the most famous short films of the studio.
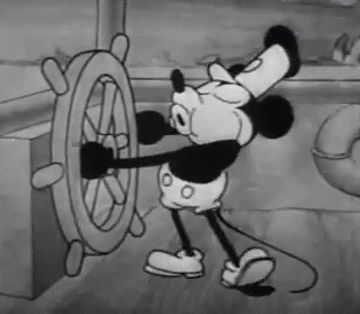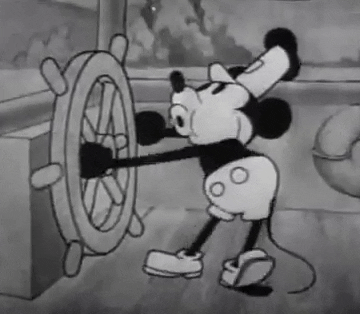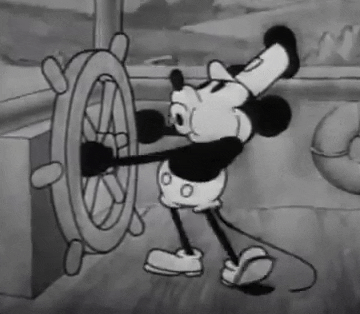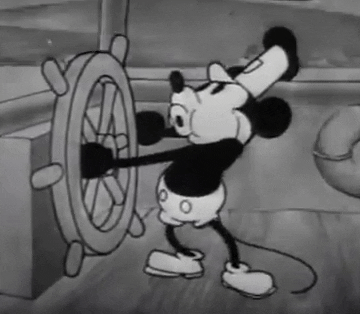
In 1928, convinced not to fall into a similar trap, they looked for a new character. Designed by Iwerks and using Walt's voice, Mortimer Mouse came to the world, who would soon be renamed as Micky Mouse.
A star had been born. Mickey Mouse turned into a success in no time. Walt, always on the lookout for innovation, hurried to incorporate sound in the Mickymovies, and in November 28th Steamboat Willy was released - a total success for both the public and the critics.
A workaholic himself, Disney had a series of health crises that led him at the end of 1931, to go on a long vacation to Europe with his wife. There, they were influenced by European arts. Back to Hollywood, he joined a sports club where he practised boxing, wrestling and golf. Soon after, he discovered horse riding, and finally polo. He was a big fan of polo for the rest of his life - a hobby as essential for him to as his passion for trains and miniatures.
First full-length cartoon film
Always supported by a team of excellent cartoonists and illustrators, Disney let all his creative spirit do its work in his first series of silly Symphonies (1932), created in technicolour. They were the reason why he got the beginning of the 26 Oscars he would receive throughout his whole career.
In 1934, Micky was already surrounded by Minnie, Pluto, Goofy and the short-tempered and wicked Donald Duck. When he had already built a name in the Hollywood industry, Walt Disney decided to produce the first full-length cartoon film in the history of movies - SnowWhite and the seven dwarfs(1937).
This movie was a total success, but if left Disney in debt for almost the rest of his life. The film was inspired by the Grimms brothers tale, the first of many adaptations of these classic tales that fascinated Walt so much. After Snowwhite came to Pinocchio, it was a triumph with critics, but a failure with the public. The company recovered thanks Dumbo the elephant and the touching Bambi, during the times marked by WWII.
It was then that Walt Disney, a convinced anti-communist, filmed pro-capitalism Propaganda Movies and started collaborating actively with the FBI in witch hunts, promoted by the senator Joseph McCarthy.
In the 50s, with the help of an investment from the Texan Howard Hughes (jiús), Disney released some of the most acclaimed classics in the history of animation: Cinderella (1950), Alicein Wonderland (1951) and Peter Pan (1953).
In December 15th 1966, after making a dream come true by constructing Disneyland, a vast amusement park based on his characters, The Burbank magician died due to lung cancer, this was only a few months before The JungleBook was released. Same as his movies, Walt Disney himself is surrounded by legends, since the minute he was born, till his death.
There's a rumour that says Disney was born in Spain, specifically in Mojácar, and emigrated when he was a kid with his single mom to the US.
Is Walt Disney's body frozen? - The Walt Disney Story
We can't forget about one of the most spread urban legends in the world: Is Walt Disney's body frozen? Hmmm nope. Disney died at the St. Joseph's Hospital and his family had a close funeral for him so that only a few people could see his body, hence the legend. Two days after his death, he was cremated and moved to their family cemetery.
You may also like to read: Walt Disney’s Multiplane Camera: Illusion King
Walt Disney was a complete pioneer, and his movies meant a turning point in the history of cinema. His legacy is still growing, and his more than 100 full-length movies are always enjoyed all around the world!. this is all for Walt Disney Story, Please do comment and let us know what you think.
Read the full article
0 notes
Text
1:72 IAI “Kfir” C.10P, “308”, BuNo (20)14-(0)015”, of the Hukbong Himpapawid ng Pilipinas (Philippine Air Force/PAF) 6th Tactical Fighter Squadron “Cobras”, 5th Fighter Wing; Basa Air Base, 2017 (Whif/modified Italeri kit)
+++ DISCLAIMER +++
Nothing you see here is real, even though the conversion or the presented background story might be based on authentic facts. BEWARE!
Some background:
The forerunners of the Philippine Air Force was the Philippine Militia, otherwise known as Philippine National Guard (PNG). On March 17, 1917 Senate President Manuel L. Quezon enacted a bill (Militia Act 2715) for the creation of the Philippine Militia, in anticipation that there would be an outbreak of hostilities between United States and Germany.
The early aviation unit was lacking enough knowledge and equipment to be considered as an air force and was then limited only to air transport duties. In 1935, Philippine Military Aviation was activated when the 10th Congress passed Commonwealth Act 1494 that provided for the organization of the Philippine Constabulary Air Corps (PCAC). PCAC was renamed as the Philippine Army Air Corps (PAAC) in 1936 and started with only three planes on its inventory. In 1941, PAAC had a total of 54 aircraft including fighters and light bombers, reconnaissance aircraft, light transport and trainers. They later engaged the Japanese when they invaded the Philippines in 1941–42, and were reformed in 1945 after the country’s liberation.
The PAF became a separate military service on July 1, 1947, and the main aircraft type became the P-51 Mustang, flown from 1947 to 1959. Ground attack missions were flown against various insurgent groups, with aircraft hit by ground fire but none shot down. The Mustangs would be replaced by the jet-powered North American F-86 Sabres in the late 1950s, assisted by Lockheed T-33 Shooting Star and Beechcraft T-34 Mentor trainers.
During the 70s, the PAF was actively providing air support for the AFP campaign against the MNLF forces in Central Mindanao, aside from doing the airlifting duties for troop movements from Manila and Cebu to the warzone. In late 1977, the Philippine government purchased 35 secondhand U.S. Navy F-8Hs that had been stored at Davis-Monthan AFB in Arizona. Twenty-five of them were refurbished by Vought and the remaining 10 were used for spare parts. As part of the deal, the U.S. would train Philippine pilots in using the (only) TF-8A, and they were mostly used for intercepting Soviet bombers. The F-8s were grounded in 1988 and were finally withdrawn from service in 1991 after they were badly damaged by the Mount Pinatubo eruption, and have since been offered for sale as scrap.
This left the PAF with the F-5 Freedom Fighter as the only jet-powered combat aircraft. The Philippine Air Force acquired 37 F-5A and F-5B from 1965 to 1998 (from Taiwan and South Korea). The F-5A/Bs were used by the 6th Tactical Fighter Squadron (Cobras) of the 5th Fighter Wing and the Blue Diamonds aerobatic team. The F-5s also underwent an upgrade which equipped it with surplus AN/APQ-153 radars with significant overhaul at the end of the 1970s to stretch their service lives another 15 years.
Since the retirement of the Northrop F-5s in September 2005, the Philippine Air Force was left without any fighter jets and thus also without any serious air cover, considerably weakening the countries position in the region. Financial constraints prevented the procurement of refurbished F-16A/Bs from US surplus stocks, so that the PAF initially resorted to Aermacchi S-211 trainer jets to fill the void left by the F-5’s. These S-211’s were later upgraded to light attack capability and used for air and sea patrol and also performed counter-insurgency operations from time to time. Apart from these trainers, the only active fixed wing aircraft to fill the roles were SF-260 trainers with light attack capability, and a handful of obsolete OV-10 Bronco light attack and reconnaissance aircraft.
With rising tensions and frequent incidents with Chinese forces, however, the PAF settled upon the “Flight Plan 2028”, a long-term modernization and procurement plan. One of the first investments in order to re-build the PAF’s jet fighter force was eventually settled in 2010, when the Philippines started negotiations with Israel to purchase refurbished IAI Kfir fighter-bombers. In August 2012 Israel Aerospace Industries officially announced that it would deliver twenty-one pre-owned Kfir fighter jets to the Philippines, with a 40-year guarantee and a supply of Python 4 IR-homing AAMs, at a rumored unit price of USD $20 million – a price that represents 1/3 the cost of a brand new fighter with similar capability, but without the weaponry.
These machines were Kfir C.10s, a variant developed especially for export, basically an updated C.7. The aircraft for the Philippines received the designation C.10P in order to reflect the new operator’s specifications. The most important changes of the C.10 update were the adaptation of an Elta EL/M-2032 multi-role radar and the integration of two 127×177mm MFDs in the cockpit.
The EL/M-2032 is an advanced Multimode Airborne Fire Control Radar designed for multi-mission fighters, oriented for both air-to-air and strike missions. Modular hardware design, software control and flexible avionic interfaces ensure that the radar can be installed in a wide range of existing fighter aircraft (such as F-16, F-5, Mirage, Harrier variants, F-4, MiG-21, etc.), and it can be customized to meet specific user requirements.
The EL/M-2032 greatly enhances the Air-to-Air, Air-to-Ground and Air-to-Sea capabilities of the aircraft, even though the PAF’s machines did not feature the optional Helmet Mounted Display System (as installed on board of the upgraded Ecuadorean Kfir C.10s). In the Air-to-Air modes, the radar enables long-range target detection and tracking for weapon delivery or automatic target acquisition in close combat engagements. The EL/M-2032 has a maximum range of 150 km and can detect and track an aerial target with a 1m² radar reflection surface equivalent at 100 km. Up to 64 aerial targets can be tracked at the same time, and this information can be shared with other aircraft, including the status which aircraft actually tracks which target.
In Air-to-Ground missions, the radar provided very high-resolution mapping (SAR), surface target detection and tracking over RBM, DBS and SAR maps in addition to A/G ranging. In Air-to-Sea missions, the radar provided long-range target detection and tracking, including target classification capabilities (RS, ISAR).
The first Kfir C.10Ps were quickly delivered, and in September 2014 the PAF’s 6th Tactical Fighter Squadron “Cobras” at Basa AB was reformed, the unit which had formerly operated the country’s last F-5s until 2005. Despite the type’s multirole capability, the Filipino Kfirs primarily fulfill interceptor and air patrol tasks against intrusions into Philippine airspace. Their prime task is to act as a general repellant against Chinese aggressions in the South China Sea, esp. in defense of the Scarborough Shoal fishing ground that Manila claims as part of its territorial waters.
Since 2015, the PAF’s jet fighter force has also been augmented by supersonic FA-50 trainers, procured from South Korea, and the PAF’s updated “Flight Plan 2028” lists another 16 Kfirs C.10Ps (including four TC.10P two-seaters), as well as more FA-50s, planned for the future.
Since their introduction the FAP’s Kfirs frequently intercepted Chinese and Russian reconnaissance aircraft (typically Y-8 maritime patrol aircraft, but also H-6 missile strike bombers and reconnaissance aircraft) over the Spratly Islands in the South China Sea, even though with no serious confrontations so far.
Beyond these standard duties, the PAF’s new type also took part in several other deployments: On 26 January 2017, two Philippine Air Force Kfir C.10s demonstrated their strike capabilities for the first time and conducted a nighttime attack on terrorist hideouts in Butig, Lanao del Sur province in Mindanao, the first “hot” combat sortie flown by these aircraft. In June 2017, Kfirs and FA-50s were sent out to conduct airstrikes against Maute terrorists entrenched in the city of Marawi, starting in May 2017.
General characteristics:
Crew: One
Length: 15.65 m (51 ft 4¼ in)
Wingspan: 8.22 m (26 ft 11½ in)
Height: 4.55 m (14 ft 11¼ in)
Wing area: 34.8 m² (374.6 sq ft)
Empty weight: 7,285 kg (16,060 lb)
Loaded weight: 11,603 kg (25,580 lb) two 500 L drop tanks, two AAMs
Max. takeoff weight: 16,200 kg (35,715 lb)
Powerplant:
1× IAl Bedek-built General Electric J-79-J1E turbojet with a dry thrust of 52.9 kN (11,890 lb st)
and 79.62 kN (17,900 lb st) thrust with afterburner
Performance:
Maximum speed: 2,440 km/h (2 Mach, 1,317 knots, 1,516 mph) above 11,000 m (36,000 ft)
Combat radius: 768 km (415 nmi, 477 mi) in ground attack role, with, hi-lo-hi profile, seven 500 lb
bombs, two AAMs, two 1,300 L drop tanks
Maximum range: 3,232 km (2,008 miles, 1744 nm), high profile, with two 1,300 L drop tank
Service ceiling: 22,860 m (75,000 ft)
Rate of climb: 233 m/s (45,950 ft/min)
Armament:
2× Rafael-built 30 mm (1.18 in) DEFA 553 cannons, 140 RPG
9× hardpoints for a total payload of 5,775 kg (12,730 lb), including an assortment of unguided
air-to-ground rockets, guided missiles (AIM-9 Sidewinders, Shafrir or Python-series AAMs; Shrike
ARMs and AGM-65 Maverick ASMs) or bombs such as the Mark 80 series, Paveway and Griffin
LGBs, SMKBs,TAL-1 OR TAL-2 CBUs, BLU-107 Matra Durandal, reconnaissance pods or Drop tanks
The kit and its assembly:
Like many of my what-if models, this one is rooted in real life. AFAIK, the PAF actually considered the procurement of refurbished, ex-Israeli Kfirs after the purchase of 2nd hand F-16s had turned out to be too costly – but even the Kfir deal did not materialize due to budgetary restrictions. However, whifworld can change this… And eventually, the PAF procured the South Korean FA-50 Golden Eagle multi-role advanced trainer.
The kit is the Italeri Kfir C.2/7, a sound and priceworthy offering, but it comes with some inherent flaws – the alternative Hasegawa kit is IMHO much easier to build, even though it is not much more detailed. Problem zones of the Italeri kit include the complex intersection between the air intakes, wings and the fuselage (nothing fits well, gaps galore!), ejector pin markings on the landing gear and on the wheels, sinkholes on the wings’ upper side towards the leading edges and the cockpit tub as a whole, which seems to stem from a different kit – including the dashboard, which is too wide, too.
In order to keep things simple and plausible, the kit was mostly built OOB, which is in itself enough work, with only a few cosmetic changes:
– a new nose section with a bigger radome from the scrap box and transplanted chines and pitot
– replacement of the early OOB Shafrir AAMs with Python AAMs, left over from a Trumpeter J-8
– additional/modified antennae and air sensors, including a RHAWS sensor at the top of the fin
– a refueling probe above the right air intake, from a Harrier GR.3, modified
– a Martin Baker ejection seat and some cockpit interior details
Painting and markings:
Since the fictional PAF Kfirs were to be primarily operated in the interceptor role, I gave the aircraft an air superiority scheme. Inspiration was taken from the type’s predecessor, the PAF’s F-8 Crusaders and their late Eighties livery, a wraparound scheme in two grey tones, coupled with low-viz (black) markings.
I actually used the F-8 camouflage pattern as benchmark and tried to adapt it to the delta-wing Kfir, but this eventually ended in almost complete improvisation. The colors are – based on visual impressions of some PAF Crusaders rather than on hard facts (since these turned out to be quite contradictive and/or implausible) – FS 36440 and 36270, Humbrol 129 and 126, respectively. The result appears a bit pale and reminds a lot of the French air superiority scheme (which is more bluish, though), but it does not look bad at all.
The radome and other dielectric fairings were slightly set apart from the camouflage tones (with Revell 47). The landing gear as well as the air intake interior were painted in gloss white (Humbrol 22), while the cockpit was painted in Sea Grey (Humbrol 27).
The model only received a light weathering treatment through a black ink washing and some post-shading with slightly lighter tones, since the aircraft would be relatively new in service – even though I have the impression that any PAF aircraft’s exterior quickly suffered under the local climate?
The national markings belong to a Philippine F-5 (a late camouflaged aircraft, hence the insignias’ small size), taken from an Aztec Decal sheet. The modex was created from code markings for a Bréguet Alizé and the cobra emblems on the fin belong to a Malaysian MiG-29 (Begemot sheet). The contemporary USAF-style BuNo for PAF aircraft was created with single decal letters – a fiddly affair.
Only a few stencils were actually taken from the OOB sheet and many of the original red markings were replaced. Most stencils became black and the walkway markings on the wings were replaced by segmented lines from a Mirage 2000.
After some final, very light weathering with graphite the kit was finally sealed with a coat of matt acrylic varnish (Italeri) and completed.
Nothing spectacular, but rather an exotic and still plausible what-if build, rooted in real life. While the paint scheme as such is not outstanding, I must say that the two-tone grey scheme suits the Kfir well, esp. together with the subdued markings.
Posted by dizzyfugu on 2018-10-27 14:26:09
Tagged: , 1:72 , IAI , Israel , aircraft , industries , Kfir , c10 , f-21 , lion , PAF , Philippine , air , force , Hukbong , Himpapawid , ng , Pilipinas , 6 , TFS , baza , cobras , f-5 , f-8 , china , sea , interceptor , fictional , aviation , whif , what-if , dizzyfugu , modellbau , italeri , model , kit , conversion , grey , low-viz , superiority , python , aam
The post 1:72 IAI “Kfir” C.10P, “308”, BuNo (20)14-(0)015”, of the Hukbong Himpapawid ng Pilipinas (Philippine Air Force/PAF) 6th Tactical Fighter Squadron “Cobras”, 5th Fighter Wing; Basa Air Base, 2017 (Whif/modified Italeri kit) appeared first on Good Info.
0 notes
Text
List Of Governors-General of India & Viceroys During British Period
List Of Governors-General of India & Viceroys During British Period
General Awareness is considered an integral part of the competitive exams. From history to polity, facts regarding General Science, Physics, Biology, our constitution, economy, banks and almost everything. Questions from these spheres can be found in SSC Exam and Railways Exam Question Papers.
Being an SSC exam or Railway exam appearing aspirant, this list will help you to know the complete details of the Governor General and Viceroy of India from the year 1772 to 1947. It also covers the important achievements and events that took place during their time.
First governor general of British India was LORD WILLIAM BENTICK.
Chartet act of 1833 made the Governor General of Bengal as the Governor General of India. And first such one was LORD WILLIAM BENTICK.
LORD WARREN HASTINGS was the first Governor general of bengal. Many confuse Warren hastings as first governor general of India.
And in 1858 after the Revolt of 1857, British government enacted an act called Act for the Good Government of India.
By this act, the designation of the Governor General of India was changed to the VICEROY OF INDIA.
And the first such VICEROY OF INDIA was LORD CANNING.
Following is the Gk Notes On Governor Generals Of India
Name
Took office
Left office
Happenings
Warren Hastings
20 October 1773
1 February 1785
» Regulating Act of 1773
(1732–1818)
» Supreme Court at Calcutta
» Asiatic Society of Bengal
» English Translation of Bhagwat Gita
Sir John Macpherson
1 February 1785
12 September 1786
(acting)
(1745–1821)
The Earl Cornwallis
12 September 1786
28 October 1793
»Established lower courts and appellate courts
(1738–1805)
»Sanskrit College established by Jonathan Duncan
»Permanent Settlement in Bihar and Bengal in 1793
» Introduction of Cornwallis Code
» Introduction of Civil Services in India
Sir John Shore
28 October 1793
18 March 1798
» Policy of Non-intervention
(1751–1834)
» Charter Act of 1793
Sir Alured Clarke
18 March 1798
18 May 1798
(acting)
(1744–1832)
The Marquess Wellesley
18 May 1798
30 July 1805
»Introduction of Subsidiary Alliance
(1760–1842)
» Fourth Anglo-Mysore War 1799
» Fort William College at Calcutta
» Formation of Madras Presidency in 1801
The Marquess Cornwallis
30 July 1805
5 October 1805
(1738–1805)
Sir George Barlow, Bt
10 October 1805
31 July 1807
(acting)
(1762–1847)
The Lord Minto
31 July 1807
4 October 1813
» Charter Act of 1813
(1751–1814)
The Marquess of Hastings
4 October 1813
9 January 1823
»Ended the policy of Non-intervention
(1754–1826)
» Third Anglo-Maratha War (1816-1818)
»Creation of Bombay Presidency in 1818
»Establishment of Ryotwari System in Madras
John Adam
9 January 1823
1 August 1823
(acting)
(1779–1825)
The Lord Amherst
1 August 1823
13 March 1828
(1773–1857)
William Butterworth Bayley
13 March 1828
4 July 1828
(acting)
(1782–1860)
Lord William Bentinck
4 July 1828
1833
» Charter Act 1833
(1774–1839)
Lord William Bentinck
1833
20 March 1835
(1774–1839)
Sir Charles Metcalfe, Bt
20 March 1835
4 March 1836
(acting)
(1785–1846)
The Lord Auckland
4 March 1836
28 February 1842
(1784–1849)
The Lord Ellenborough
28 February 1842
June 1844
(1790–1871)
William Wilberforce Bird
June 1844
23 July 1844
(acting)
(1784–1857)
Sir Henry Hardinge
23 July 1844
12 January 1848
(1785–1856)
The Marquess of Dalhousie
12 January 1848
28 February 1856
» Doctrine of Lapse
(1812–1860)
» Charles Wood Dispatch
»1st Railway line connecting Bombay and Thane
» Post Office Act, 1854
»Established Public Works Department
»Engineering College was established at Roorkee
The Viscount Canning
28 February 1856
1 November 1858
»University of Bombay, Calcutta and Madras were set up in 1857
(1812–1862)
» The revolt of 1857
»The Government of India Act, 1858
»Withdrew Doctrine of Lapse.
The Earl Canning
1 November 1858
21 March 1862
(1812–1862)
The Earl of Elgin
21 March 1862
20 November 1863
(1811–1863)
Sir Robert Napier
21 November 1863
2 December 1863
(acting)
(1810–1890)
Sir William Denison
2 December 1863
12 January 1864
(acting)
(1804–1871)
Sir John Lawrence, Bt
12 January 1864
12 January 1869
»Telegraphic communication was opened with Europe.
(1811–1879)
»High Courts were established at Calcutta, Bombay and Madras in 1865.
»Created the Indian Forest department.
The Earl of Mayo
12 January 1869
8 February 1872
»Started the process of financial decentralization in India.
(1822–1872)
»For the first time in Indian history, a census was held in 1871.
»Organised the Statistical Survey of India.
»Was the only Viceroy to be murdered in office by a Pathan convict in the Andamans in 1872.
Sir John Strachey
9 February 1872
23 February 1872
(acting)
(1823–1907)
The Lord Napier
24 February 1872
3 May 1872
(acting)
(1819���1898)
The Lord Northbrook
3 May 1872
12 April 1876
(1826–1904)
The Lord Lytton
12 April 1876
8 June 1880
»Known as the Viceroy to reverse characters.
(1831–1891)
»Organised the Grand ‘Delhi Durbar’ in 1877 to decorate Queen Victoria with the title of ‘Kaiser I Hind’.
»Arms act (1878) made it mandatory for Indians to acquire license for arms.
»Passed the infamous Vernacular Press act (1878).
The Marquess of Ripon
8 June 1880
13 December 1884
»Liberal person, who sympathized with Indians.
(1827–1909)
»Repeated the Vernacular Press act (1882)
»Passed the local self government act (1882)
»Took steps to improve primary & secondary education (on William Hunter Commission’s recommendations).
»The I Factory act, 1881, aimed at prohibiting child labour.
»Passed the libert Bill (1883) which enabled Indian district magistrates to try European criminals. But this was withdrawn later.
The Earl of Dufferin
13 December 1884
10 December 1888
»Indian National Congress was formed during his tenure.
(1826–1902)
The Marquess of Lansdowne
10 December 1888
11 October 1894
»II Factory act (1891) granted a weekly holiday and stipulated working hours for women and children, although it failed to address concerns such as work hours for men.
(1845–1927)
»Categorization of Civil Services into Imperial, Provincial and Subordinate.
»Indian Council act of 1892 was passed.
»Appointment of Durand Commission to define the line between British India and Afghanistan.
The Earl of Elgin
11 October 1894
6 January 1899
»Great famine of (1896 – 1897)
(1849–1917)
»Lyall Commission was appointed.
The Lord Curzon of Kedleston
6 January 1899
18-Nov-05
»Passed the Indian Universities act (1904) in which official control over the Universities was increased.
(1859–1925)
»Partitioned Bengal (October 16, 1905) into two provinces Bengal (proper) & East Bengal & Assam.
»Appointed a Police Commission under Sir Andrew Frazer to enquire into the police administration of every province.
»The risings of the frontier tribes in 1897 – 98 led him to create the North Western Frontier Province (NWFP).
»Passed the Ancient Monuments Protection act (1904), to restore India’s cultural heritage. Thus the Archaeological Survey of India was established.
»Passed the Indian Coinage and Paper Currency act (1899) and put India on a gold standard.
»Extended railways to a great extent.
The Earl of Minto
18-Nov-05
23-Nov-10
»There was great political unrest in India. Various acts were passed to curb the revolutionary activities. Extremists like Lala Laipat Rai and Ajit Singh (in May, 1907) and Bal Gangadhar Tilak (in July, 1908) were sent to Mandalay jail in Burma.
(1845–1914)
»The Indian Council act of 1909 or the Morley Minto Reforms was passed.
The Lord Hardinge of Penshurst
23-Nov-10
4 April 1916
»Held a durbar in December, 1911 to celebrate the coronation of King George V.
(1858–1944)
»Partition of Bengal was cancelled (1911), capital shifted from Calcutta to Delhi (1911).
»A bomb was thrown at him; but he escaped unhurt (December 23, 1912).
»Gandhi ji came back to India from South Africa (1915).
»Annie Besant announced the Home Rule Movement.
The Lord Chelmsford
04-Apr-16
2 April 1921
»August Declaration of 1917, whereby control over the Indian government would be gradually transferred to the Indian people.
(1868–1933)
»The government of India act in 1919 (Montague Chelmsford reforms) was passed.
»Rowlatt act of 1919; Jallianwala Bagh Massacre (April 13, 1919).
»Non Cooperation Movement.
»An Indian Sir S.P.Sinha was appointed the Governor of Bengal.
»A Women’s university was founded at Poona in 1916.
»Saddler Commission was appointed in 1917 to envisage new educational policy.
The Earl of Reading
02-Apr-21
3 April 1926
»Rowlatt act was repeated along with the Press act of 1910.
(1860–1935)
»Suppressed non – cooperation movement.
»Prince of Wales visited India in November, 1921.
»Moplah rebellion (1921) took place in Kerala.
»Ahmedabad session of 1921.
»Formation of Swaraj Party.
»Vishwabharati University started functioning in 1922.
»Communist part was founded in 1921 by M.N. Roy.
»Kakory Train Robbery on August 9, 1925.
»Communal riots of 1923 – 25 in Multan, Amritsar, Delhi, etc.
»Swami Shraddhanand, a great nationalist and a leader of the Arya Samajists, was murdered in communal orgy.
The Lord Irwin
03-Apr-26
18-Apr-31
»Simon Commission visited India in 1928.
(1881–1959)
»Congress passed the Indian Resolution in 1929.
»Dandi March (March 12, 1930).
»Civil Disobedience Movement (1930).
»First Round Table Conference held in England in 1930.
»Gandhi Irwin Pact (March 5, 1931) was signed and Civil Disobediance Movement was withdrawn.
»Martydorm of Jatin Das after 64 days hunger strike (1929).
The Earl of Willingdon
18-Apr-31
18 pril 1936
»Second Round Table conference in London in 1931.
(1866–1941)
»On his return Gandhi ji was again arrested and Civil Disobedience Movement was resumed in January, 1932.
»Communal Awards (August 16, 1932) assigned seats to different religious communities. Gandhi ji went on a epic fast in protest against this division.
»Third Round Table conference in 1932.
»Poona Pact was signed.
»Government of India act (1935) was passed
The Marquess of Linlithgow
18-Apr-36
1 October 1943
»Government of India act enforced in the provinces. Congress ministries formed in 8 out of 11 provinces. They remained in power for about 2 years till October 1939, when they gave up offices on the issue of India having been dragged into the II World War. The Muslim League observed the days as ‘Deliverance Say’ (22 December)
(1887–1952)
»Churchill became the British PM in May, 1940. He declared that the Atlantic Charter (issued jointly by the UK and US, stating to give sovereign rights to those who have been forcibly deprived of them) does not apply to India.
»Outbreak of World War II in 1939.
»Cripps Mission in 1942.
»Quit India Movement (August 8, 1942).
The Viscount Wavell
01-Oct-43
21 February 1947
»Arranged the Shimla Conference on June 25, 1945 with Indian National Congress and Muslim League; failed.
(1883–1950)
»Cabinet Mission Plan (May 16, 1946).
»Elections to the constituent assembly were held and an Interim Government was appointed under Nehru.
»First meeting of the constituent assembly was held on December 9, 1946.
The Viscount Mountbatten of Burma
21-Feb-47
15 August 1947
»Last Viceroy of British India and the first Governor General of free India.
(1900–1979)
»Partition of India decided by the June 3 Plan.
»Indian Independence Act passed by the British parliament on July 4, 1947, by which India became independent on August 15, 1947.
»Retried in June 1948 and was succeeded by C. Rajagopalachari (the first and the last Indian Governor General of free India).
Read the full article
#BritishGovernorGeneralsAndViceroys#BritishGovernors#FirstGovernorGeneralOfBengal#FirstGovernorGeneralOfIndependentIndia#FirstGovernorGeneralOfPakistan#FirstViceroyOfIndiaUnderBritishRule#GeneralKnowledgeForIasExams#GkNotesOnGovernorGeneralsOfIndia#GovernorGeneralOfBritishIndia#GovernorGeneralOfIndia2016#Governors-GeneralOfIndia(1772-1857)#LastViceroyOfIndia#ListofBritishGovernorsGeneralsduringBritishPeriodinIndia#ListofGovernors-GeneralofIndia&ViceroysDuringBritishPeriod#PresentGovernorGeneralOfIndia
0 notes
Video
youtube
In this Video Infotainment Will Explain Zsa Zsa Gabor Net Worth, Cars, House, Income and Luxurious Lifestyle. Subscribe Our Channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCCDb... Zsa Zsa Gabor Net Worth, Cars, House, Private Jets and Luxurious Lifestyle are here for you. If you are looking for Zsa Zsa Gabor Net Worth, Cars, House, Private Jets and Luxurious Lifestyle , you have just clicked at the right page. This Video has all the right information for you regarding Zsa Zsa Gabor Net Worth, Cars, House, Private Jets and Luxurious Lifestyle.Check out Zsa Zsa Gabor Net Worth, Cars, House, Private Jets and Luxurious Lifestyle and you will be amazed to see these new things.We will let you know about the earning income salary biography and how rich is Zsa Zsa Gabor. Zsa Zsa Gabor Net Worth, Cars, House, Private Jets and Luxurious Lifestyle is super fun, take a look at it. Zsa Zsa Gabor Net Worth, Cars, House, Private Jets and Luxurious Lifestyle is given here for you.We will let you know about the earning income salary biography and how rich is Zsa Zsa Gabor. She was not just renowned for being well known: she was the model, the first model. Zsa Gabor had excellence, surely, and enough Hungarian-complemented mind to gain innumerable television show bookings.Zsa Zsa was conceived Sári Gábor in Budapest, Austria-Hungary, to resigned fighter Vilmos Gábor and his better half Jolie, a gem specialist of Jewish plunge. There was, broadly, a more seasoned sister Magda and a more youthful sister Eva. Zsa's introduction to the world date was most presumably February 6, 1917, however she was known to quick forward the year to as late as 1931. That would have made her a phenomenally energetic Miss Hungary in 1936, and a greatly intelligent first-time lady of the hour in 1937. We will let you know about the earning income salary biography and how rich is Zsa Zsa Gabor. Kate Hudson Net Worth, Cars, House, Income and Luxurious Lifestyle https://youtu.be/IWfa1P2CQE0 Milla Jovovich Net Worth, Cars, House, Income and Luxurious Lifestyle https://youtu.be/-E9jyjmE7h0 Patricia Heaton Net Worth, Cars, House, Income and Luxurious Lifestyle https://youtu.be/iI9juZJK-KU Zsa Zsa Gabor Net Worth, Cars, House, Income and Luxurious Lifestyle https://youtu.be/s8ioOiMZsFU Amy Adams Net Worth, Cars, House, Income and Luxurious Lifestyle https://youtu.be/gvmDnNEk4ng Zsa Gabor, has an expected total assets of $40 million. She is the first and most likely the greatest Hollywood celeb to end up distinctly the prototypical "expert superstar": acclaimed for being well known. She began her stage vocation in 1933 and after three years, she won the Miss Hungary title. She took after her sister Eva to America in 1941, however dissimilar to Eva, did not give herself to acting. Zsa Gabor has a 60-year vocation. She is frequently associated with her witty remarks, abundant way of life, and nine relational unions We will let you know about the earning income salary biography and how rich is Zsa Zsa Gabor. From Bentleys to the finest of offerings from Mercedes-Benz, Zsa Gabor has been gotten in the driver's seat of different flawless autos. Having possessed a bigger number of autos than she has spouses, the autos in her life seem to have gotten away from the pointed remarks saved for men. Gabor's white $215,000 Rolls-Royce Corniche made front-page news in September 1989 when she slapped a cop in the wake of being pulled over amid a standard activity stop As an indication of appreciation for demonstrating his nephew around Hollywood, Dominican representative, dashing auto driver and polo player Porfirio Rubirosa sent Zsa a Mercedes-Benz 300SL Gullwing. Zsa's Silver Cloud II is a unique case. Just 299 cases of the 2716 Cloud IIs constructed were long wheelbase vehicles - and Gabor's gotten lashings of personalisation. The Hollywood star lived with spouse Prince Frederic von Anhalt in the upmarket LA suburb of Bel Air in a $28million property, finish with its own pool, clearing carport and 26 rooms loaded down with pricy collectibles and furnishings. The couple were compelled to put the manor available in 2011 after medical issues implied they could just utilize two rooms – also that upkeep of the entire property and grounds cost them $30,000 a month. With around 8,000 square feet of space, Zsa and the Prince had a lot of space to store their excellent furniture and belonging – including various steed head adornments.
0 notes
Text
Israel – Palestine For Critical Thinkers
This post describes the ways in which the Allied Powers remapped the Middle East creating the British Mandate and French Mandate. The British designated Palestine as the Jewish national home.
Dividing up the Ottoman Empire after WWI
The Mandate system was instituted by the League of Nations in the early 20th century to temporarily administer non-self-governing territories. Great Britain, France and Czarist Russia planned to divide the plunder among themselves before the end of the war (Sykes–Picot Agreement, 1916). Czarist Russia dropped out when they made a separate peace with the Central Powers (Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Turkey).
The Balfour Declaration
In November 1917 the British government made a pledge with the Jewish people through the Balfour Declaration to help establish a Jewish National Home in the territory known as Palestine. Note that this does not mention a “Jewish State”.
Balfour_Portrait_and_Declaration
The British Mandate
At the Paris Peace Conference in 1919, Emir Faisal asked for Arab independence, or at minimum the right to choose the United Kingdom as the mandatory. The World Zionist Organization also asked for a British mandate because of the Balfour declaration. The WZO submitted a map of the areas they asked to be included in the British Mandate of Palestine. Unfortunately, this map was not accepted. Lord Curzon replaced Arthur Balfour as British Foreign Secretary and tried unsuccessfully to omit any recognition of the historical connection of the Jewish people with Palestine.
Map showing boundaries (in red) of the proposed protectorate of Palestine, as suggested by the Zionist representatives at the 1919 Paris Peace Conference, superimposed on modern boundaries.
Photo: Briangotts
San Remo Conference
On April 25, 1920 the San Remo Conference assigned the Palestine Mandate to Britain. The League of Nations entrusted Great Britain with the Mandate for Palestine (فلسطين – א״י) and Mesopotamia on July 24, 1922. Syria and Lebanon likewise became French mandates. France demanded the continuation of its religious protectorate in Palestine but Italy and Great Britain opposed it. The British Mandate came into effect on September 29, 1923 after the Conference of Lausanne finalized the Peace Treaty with the new Ataturk Turkish regime. The British territory included the Ottoman Empire sanjaks of Nablus, Acre, the Southern part of the Vilayet of Syria, the Southern portion of the Beirut Vilayet, and the Mutasarrifate of Jerusalem.
Occupied Enemy Territory Administrations, 1918 Syria
Photo: Busterof666
The British Mandate in Palestine had no end date and merely stated as “until such time as they are able to stand alone.”
The League of Nations and Great Britain decided In September 1922 that the area east of the Jordan River. This constituted 3/4th of the territory included in the Palestine Mandate which would become the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan. The United Kingdom had made conflicting and shifting commitments regarding Trans-Jordan. They had previously promised in the McMahon–Hussein Correspondence that it would honour Arab independence if they revolted against the Ottomans. Unfortunately both sides had different interpretations.
British civilian administration operated in Palestine from 1920 until 1948.
Great Britain’s Betrayal of the Jews
During the period of the British Mandate the Palestine experienced the ascent of two major nationalist movements. One was among the Jews and the other among the Arabs. Arab pressure forced the British to withdraw from its original commitment to the Jewish people with respect to immigration and land acquisition. The White Papers of 1930 and 1939 restricted immigration and acquisition of land by Jews. Jewish land acquisition was severely restricted by the 1940 Land Transfer Regulations.
Jerusalem 1918
British Mandate 1920-1939: The Arab Side
British High Commissioner Herbert Samuel granted the most important posts to two competing Arab families, the Husseinis and the Nashashibis. The Husseinis were given the most powerful posts. In 1921 Samuel appointed Hajj Amin al Husayni, an ardent anti-Zionist and a major figure behind the April 1920 riots, as mufti (chief Muslim religious jurist) of Jerusalem. Increased Jewish land purchases caused property prices to spiral. Both the Arab landowning class and absentee landlords, many of whom resided outside Palestine, were quick to sell for unprecedented profits. During this period the British authorities had to deal with riots of 1920, 1929 riots, the Arab Revolt of 1936–1939.
British Mandate 1920-1939: The Zionist Side
Zionists settlers in Palestine brought unique organizational shrewdness. The World Zionist Organization (WZO) immediately founded the formalized Jewish Agency in August 1929. The two organizations became a quasi-governmental leadership. Next came an elected Vaad Leumi (National Council), Chief Rabbinate, Hebrew school system, Technion, Hebrew University, Histadrut and political parties.
Early Jewish Defense – Jewish insurgency in Palestine
The earliest Jewish involvement was an intelligence service, Nili, operating behind Turkish lines for the British. The Zion Mule Corps was established in 1915 but disbanded just a year later. In 1918 the Jewish Legion was formed and fought for Palestine. In 1907, the first self-defense organization, Bar-Giora, was established by Yitzhak Ben Zvi. The Haganah was founded on June 12, 1920 to protect Jewish settlers. The Irgun Zvai Leumi was activated in 1931.
Hostile attacks by Arabs began during the 1936-39 riots. The Arab violence in Palestine in 1938 took a heavy toll. The Jewish Agency, tried to obtain a political settlement, while the Irgun retaliated.
Commissions & Reports
British beaurocracy produced many good-intentioned conferences and reports dealing with Palestine.
San Remo Conference (1920): Post-World War I Allied Supreme Council following the Paris Peace Conference. The conference was held in Sanremo, Italy, from 19 to 26 April 1920.
Shaw Commission (1930): An investigation of the violent Arab rioting in Palestine in late August 1929. It’s conclution was that the cause of the rioting was Arab fear of continual Jewish immigration and land purchases.
Hope-Simpson Report (October 1, 1930): The report recommended limiting Jewish immigration. The Passfield White Paper was also dated October 1, 1930, recommended similar limitation of Jewish immigration.
Peel Commission (1937): Investigation of the causes of the Arab unrest in Mandatory Palestine following the six-month-long Arab general strike.
Peel Commission Report (July 7, 1937): The report stated that the League of Nations Mandate had become unworkable and recommended partition. All the Arab representatives rejected the partition plan. Chaim Weizmann and Ben-Gurion and the Zionist Congress approve the Peel recommendations ambiguously as a basis for more negotiation.
St. James Conference (1939): A conference on the Partition for Palestine (February 7, 1939 – March 17, 1939). The Arab delegates refused to sit at the same table with the Jewish representatives. The meeting adjourned without result.
Jerusalem (1920-1939)
The British Mandate in Palestine 1939-1948
In 1940, the Irgun split up. More militant members of the organization, led by Avraham Stern, decided to form a new group, Lohamey Heruth Israel – Lehi – the Stern Gang.
In 1941, the Haganah created the Palmach to defend the Yishuv in the event of an emergency. The Palestine administration devoted a large part of its energy and ability to preventing Palestinian Jews from fighting Hitler. The British finally did allow the Jews to form a fighting unit to participate in the War effort. On September 20, 1944, a Jewish brigade was created.
Between November 29, 1947 and May 14, 1948 there was a Civil War between Arab and Jews in Palestine. This was actually the first half of the Israeli War of Independence (May 15, 1948 –March 10, 1949).
.
Jewish_immigration_to_Mandatory_Palestine_(1920-1945)
Photo: Paasikivi
An interview with Gerald Green who served in the Palestine Police from 1946 till 1948. Filmed in September 2009.
The Flag of Palestine and the Anthem of Palestine
United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine
The Arab revolt that ensued made life impossible for the British sovereign. The British government proposed proposed to resolve the situation by “partition” of Palestine. But with growing Nazi power, and the war afoot, circumstances only intensified in the region.
The Resolution 181 to partition Palestine was adopted on November 29, 1947 by the UN General Assembly. This resolution envisaged the creation of separate Jewish and Arab states. Each state would operate under economic union with Jerusalem being transferred to UN trusteeship. The Mandate terminated on 14 May 1948. On the last day of the Mandate, the creation of the State of Israel was proclaimed.
UN_Palestine_Partition_Versions_1947
British Mandate in Palestine * Israel - Palestine For Critical Thinkers This post describes the ways in which the Allied Powers remapped the Middle East creating the British Mandate and French Mandate.
0 notes
Text
Myron Herbert Burgess
Synopsis of My Life History: Written earlier by Myron H. Burgess Retyped by Sandra Burgess 24 Jul 2005, Words in Parentheses added by Sandra Burgess)
I was born in Knightsville, Juab Co., Utah on 31 Dec, 1917 to Herbert Alfred and Della Whitby Burgess. I was a 2nd child. My sister Laura, who was born premature passed away some three months before my birth. Shortly after my birth, my parents moved to Toole where my father obtained employment as an Iceman in the summer and he worked on the Power and Light crew in the winter.
Childhood: As a result of the flue epidemic of 1918, my parents passed away on 28 and 29 Nov, 1918 (respectively), leaving me for my grandparents (of Alpine, UT) to raise. My grandmother died of cancer when I was six years old. One of my earlier recollections was that of visiting her in the American Fork Hospital.
My schooling: My first 8 grades were at Alpine (except for the third grade where I attended school in Levan.) The next 4 years were at American Fork High School, where I graduated in 1936. I then spent the next year at USAC (known now as Utah State University). I then decided it was time to seek my fortune.
Margaret: In the Spring of 1938 I met Margaret Banks and we were marriedSeptember 20, 1939. About three weeks later we moved into a basement home that we were building. At the time all you could say for it was that it was enclosed. (Finally, Myron felt he had a family of his very own to love.) Since that time we lived in Alpine, Salt Lake, Alpine, Lehi, UT; Tacoma, WA, Richland Washington; Lehi UT;. and finally in SLC. UT, since 1946 (until death on 16 Feb, 1995). I owned and ran Burgess Plumbing and Heating Company in SLC for many, many years.
Children: We have five children: Allan Karl (1940), Merril Myron (1942) , Yvonne (1946), Laura Jo (1949), and Paul Leon (1951), whom, along with their spouses and children, we love dearly. This was a good marriage and we were kept very busy in many callings in the church. However, Margaret’s health began to give her problems and for the last 30 years of her life it got gradually worse. She passed away 1 Mar 1981 of pneumonia, but the contributing causes were Rheumatic Fever, which she had 7 times, plus Rheumatoid Arthritis…which plagued her for 30 years and the side effects from the medications used to control them. Her body is resting at the Elysian Gardens Cemetery. (Married 42½ Yrs.)
Second Marriage: It had been my habit to spend some time at the Ogden Temple each month . In May of 1981, I had been taking my loneliness to our Heavenly Father. I had the feeling that day that I should go to the temple. I obeyed! During the 4th session I attended that day (I usually always attended only once), it was made know to me that the next Sister Burgess was to be in the such, and I should not doubt. We were married and sealed on 7 Aug 1981 in the Ogden Temple. Two of her three sons were sealed to us that day. She has three sons and their lovely families and I love them as my own. This means that now I have 8 children and 38 grandchildren. Thelma and I got along well together. We served a Family History Church Service Mission in the Processing Division of the Church. (Married 14 yrs.)
Testimony: Before closing, I want to leave my testimony that Jesus is the Christ and that Joseph Smith is a Prophet of the Lord and that the Church of Jesus Christ is the only true church upon the earth. Myron is resting beside his beloved Margaret at the Elysian Gardens Burial (Cemetery) at 1075 E 4580 S, Murray, UT. He died 16 Feb 1995. (Thelma is still alive and living in California at this entry.)
Margaret Banks
Margaret Banks was born 26 Mar 1921 to Junius Crossland Banks and Edna Myrtle Hackett. She was the youngest child having 3 Brothers and 1 sister. She never knew her sister, as she passed away before Margaret was born. Her brother Merril passed away following his mission of cancer. Margaret was very bright and excelled in School. She was a dedicated woman. Her parents were both teachers and her mother was a principal. She had a wonderful heritage. She held many responsible callings in the ward. She was well admired by many for her endurance of pain and suffering, but more importantly her character and integrity. Most looked at her as a saint. She did her very best in the circumstances she was given. She loved her family and her husband.
Thelma Ellen Ross (Taken from her writings of her life history)
Born to Ferrie James and Carrie Ellen Prows in Ogden, UT 8 Jul 1916. She was the eldest of five girls and one boy. Schooled in Ogden, UT, graduated in 1935. Married Harry E. Chappel about 2 years later. They had 3 sons: Ben (1938), LeRoy (1939), Lenard (1944). After 11 years of marriage, they left their husband and father because he was an alcoholic and was unsafe to live with. They lived in California in various places until all of the boys were adults and on their own. (She did an excellent job raising her sons. All three served missions and remain active. Ben eventually was sealed to Myron in the temple as well.) Thelma decided to move back home to Ogden, UT to take care of her father. She had been working at the Ogden Temple in the Laundry Dept. for about 6 years when she met Myron. She too had been praying for acompanion and made it a habit to go on a session at least once a week. She met Myron there, he sent her a letter addressed to the temple, she answered it, and that was it. They were married August 7, 1981 The Lord answered their prayers.
#Myron Herbert Burgess#Margaret Banks#Thelma Ellen Ross#Herbert Alfred Burgess#Della Whitby#History#Autobiography
0 notes
Text
Rufus Thomas






Rufus C. Thomas, Jr. (March 26, 1917 – December 15, 2001) was an American rhythm and blues, funk, soul and blues singer, songwriter, dancer, DJ and comic entertainer from Memphis, Tennessee. He recorded for several labels including Chess and Sun in the 1950s, before becoming established in the 1960s and 1970s at Stax Records. He is best known for his novelty dance records including "Walking the Dog" (1963), "Do the Funky Chicken" (1969) and "(Do the) Push and Pull" (1970). According to the Mississippi Blues Commission, "Rufus Thomas embodied the spirit of Memphis music perhaps more than any other artist, and from the early 1940s until his death... occupied many important roles in the local scene."
His career began as a tap dancer, vaudeville performer, and master of ceremonies in the 1930s, and he later also worked as a disc jockey on radio station WDIA in Memphis, both before and after his recordings became successful. He remained active into the 1990s, and as a performer and recording artist was often billed as "The World's Oldest Teenager". He was the father of singers Carla Thomas (with whom he recorded duets) and Vaneese Thomas, and keyboard player Marvell Thomas.
Early life
Born a sharecropper's son in the rural community of Cayce, Mississippi, Thomas moved to Memphis, Tennessee, with his family around 1920. His mother was "a church woman". Thomas made his debut as a performer at the age of six, playing a frog in a school theatrical production. By the age of 10, he was a tap dancer, performing on the streets as well as in amateur productions at Memphis' Booker T. Washington High School. From the age of 13, he worked with Nat D. Williams, his high school history teacher who was also a pioneer black DJ at WDIA and columnist for black newspapers, as a master of ceremonies at talent shows in the Palace Theater on Beale Street.
Early career as a performer
Thomas also began performing in traveling tent shows. After graduating from high school, he attended one semester at Tennessee A&I University, but due to economic constraints left to pursue a career as a full-time entertainer. In 1936 he joined the Rabbit Foot Minstrels, an all-black revue that toured the South, as a tap dancer and comedian, sometimes part of a duo, Rufus and Johnny. He married Cornelia Lorene Wilson in 1940, at a service officiated by Aretha Franklin's father, Rev. C. L. Franklin, and the couple settled in Memphis. Thomas worked a day job in the American Finishing Company textile bleaching plant, which he continued to do for over 20 years. He also formed a comedy and dancing duo, Rufus and Bones, with Robert "Bones" Couch, and they took over as MCs at the Palace Theater, often presenting amateur hour shows. One early winner was B. B. King, and others first discovered by Thomas later in the 1940s included Bobby Bland and Johnny Ace.
In the early 1940s, Thomas began writing and performing his own songs. He regarded Louis Armstrong, Fats Waller and Gatemouth Moore as his musical influences. He made his professional singing debut at the Elks Club on Beale Street, filling in for another singer at the last minute, and during the 1940s became a regular performer in Memphis nightclubs such as Currie`s Club Tropicana. As an established performer in Memphis, aged 33 in 1950, Thomas recorded his first 78 rpm single, for Jesse Erickson's small Star Talent label in Dallas, Texas. Thomas said: "I just wanted to make a record. I never thought of getting rich. I just wanted to be known, be a recording artist..... [But] the record sold five copies and I bought four of them." The record, "I'll Be a Good Boy"/"I'm So Worried", gained a Billboard review stating: "Thomas shows first class style on a slow blues". He also recorded for the Bullet label in Nashville, Tennessee, when he recorded with Bobby Plater's Orchestra and was credited as "Mr. Swing"; the recordings were not recognised by researchers as being by Thomas until 1996. In 1951 he made his first recordings at Sam Phillips' Sun Studio, for the Chess label, but they were not commercially successful.
He began working as a DJ at radio station WDIA in 1951, and hosted an afternoon R&B show called Hoot and Holler. WDIA, featuring an African-American format, was known as "the mother station of the Negroes" and became an important source of blues and R&B music for a generation, its audience consisting of white as well as black listeners. Thomas used to introduce his shows saying: "I'm young, I'm loose, I'm full of juice, I got the goose so what's the use. We're feeling gay though we ain't got a dollar, Rufus is here, so hoot and holler." He also used to lead tours of white teenagers on "midnight rambles" around Beale Street.
His celebrity in the South was such that in 1953, at Sam Phillips' suggestion, he recorded an "answer record" to Big Mama Thornton's R&B hit, "Hound Dog", called "Bear Cat" released on Sun Records. The record became the label's first national chart hit, reaching #3 on the Billboard R&B chart. However, a copyright-infringement suit placed by Don Robey, the original publisher of "Hound Dog", nearly bankrupted the record label. After only one recording there, Thomas was one of the African-American artists released by Phillips, as he oriented his label more toward white audiences and signed Elvis Presley, who later recorded Thomas' song "Tiger Man". Thomas did not record again until 1956, when he made a single, "I'm Steady Holdin' On", for the Bihari brothers' Meteor label; musicians on the record included Lewie Steinberg, later a founding member of Booker T and the MGs.
Stax Records
In 1960 he made his first recordings with his 17-year-old daughter Carla, for the Satellite label in Memphis, which changed its name to Stax the following year. The song, "Cause I Love You", featuring a rhythm borrowed from Jesse Hill's "Ooh Poo Pa Doo", was a regional hit; the musicians included Thomas' son Marvell on keyboards, Steinberg, and the 16-year-old Booker T. Jones. The record's success led to Stax gaining production and distribution deal with the much larger Atlantic Records.
Rufus Thomas continued to record for the label after Carla's record "Gee Whiz" reached the national R&B chart in 1961. He had his own hit with "The Dog", a song he had originally improvised in performance based on a Willie Mitchell bass line, complete with imitations of a barking dog. The 1963 follow-up, "Walking the Dog", engineered by Tom Dowd of Atlantic, became one of his most successful records, reaching #10 on the Billboard pop chart. He became the first, and still the only, father to debut in the Top 10 after his daughter had first appeared there. The song was recorded in early 1964 by the Rolling Stones on their debut album, and was a minor UK chart hit for Merseybeat group the Dennisons later that year.
As well as recording and appearing on radio and in clubs, Thomas continued to work as a boiler operator in the textile plant, where he claimed the noises sometimes suggested musical rhythms and lyrics to him, before he finally gave up the job in 1963, to focus on his role as a singer and entertainer. He recorded a series of novelty dance tracks, including "Can Your Monkey Do the Dog'" and '"Somebody Stole My Dog" for Stax, where he was often backed by Booker T. & the MGs or the Bar-Kays. He also became a mentor to younger Stax stars, giving advice on stage moves to performers like Otis Redding, who partnered daughter Carla on record.
After "Jump Back" in 1964, the hits dried up for several years, as Stax gave more attention to younger artists and musicians. However, in 1970 he had another big hit with "Do the Funky Chicken", which reached #5 on the R&B chart, #28 on the pop chart, and #18 in Britain where it was his only chart hit. Thomas improvised the song while performing with Willie Mitchell's band at a club in Covington, Tennessee, including a spoken word section that he regularly used as a shtick as a radio DJ: "Oh I feel so unnecessary - this is the kind of stuff that makes you feel like you wanna do something nasty, like waste some chicken gravy on your white shirt right down front." The recording was produced by Al Bell and Tom Nixon, and used the Bar-Kays, featuring guitarist Michael Toles. Thomas continued to work with Bell and Nixon as producers, and later in 1970 had his only number 1 R&B hit, and his highest pop charting record, with another dance song, "Do the Push and Pull". A further dance-oriented release in 1971, "The Breakdown", climbed to number 2 R&B and number 31 Pop. In 1972, he featured in the Wattstax concert, and he had several further, less successful, hits before Stax collapsed in 1976.
Later career
Thomas continued to record and toured internationally, billing himself as "The World's Oldest Teenager" and describing himself as "the funkiest man alive". He "drew upon his vaudeville background to put [his songs] over on stage with fancy footwork that displayed remarkable agility for a man well into his fifties", and usually performed "while clothed in a wardrobe of hot pants, boots and capes, all in wild colors."
He continued as a DJ at WDIA until 1974, and worked for a period at WLOK before returning to WDIA in the mid 1980s to co-host a blues show. He appeared regularly on television and recorded albums for various labels. Thomas performed regularly at the Porretta Soul Festival in Italy; the outdoor amphitheater in which he performed was later renamed Rufus Thomas Park.
He played an important part in the Stax reunion of 1988, and appeared in Jim Jarmusch's 1989 film Mystery Train, Robert Altman's 1999 film Cookie's Fortune, and D. A. Pennebaker’s documentary Only the Strong Survive. Thomas released an album of straight-ahead blues, That Woman is Poison!, with Alligator Records in 1990, featuring saxophonist Noble "Thin Man" Watts. In 1996, he and William Bell headlined at the Olympics in Atlanta, Georgia. In 1997, he released an album, Rufus Live!, on Ecko Records. In 1998, he hosted two New Year's Eve shows on Beale Street.
In 1997, to commemorate his 80th birthday, the City of Memphis renamed a road off Beale Street, close to the old Palace Theater, as Rufus Thomas Boulevard. He received a Pioneer Award from the Rhythm and Blues Foundation in 1992, and a lifetime achievement award from ASCAP in 1997. He was inducted into the Blues Hall of Fame in 2001.
Death and legacy
He died of heart failure in 2001, at the age of 84, at St. Francis Hospital in Memphis. He is buried next to his wife Lorene, who pre-deceased him in 2000, at the New Park Cemetery in Memphis.
Writer Peter Guralnick said of him:
His music... brought a great deal of joy to the world, but his personality brought even more, conveying a message of grit, determination, indomitability, above all a bottomless appreciation for the human comedy that left little room for the drab or the dreary in his presence.
Wikipedia
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Walt Disney Story

Rising - The Walt Disney Story
The Walt Disney Story is very inspirational. Walter Elias Disney was born on December 5th, 1901, in Chicago, Illinois. Walt is the fourth of 5 children. Elias and Flora Disney were their parents. His childhood set apart by economic hardship; his dad was always changing from one job to another. He spent his childhood on a farm, in a village of Missouri. There, he lived surrounded by nature and animals. His mom would read classic tales to him, and that's when his interest in drawing started to grow inside him.
In 1909, his dad got sick, and the whole family had to move to Kansas City. During that time, Walt was selling newspapers and occasionally making some money with his caricatures. He enrolled in the Kansas City Art Institute, where he learned his first notions about drawing techniques. It was then, during those teenage years when he discovered the cinema - an invention, he was passionate about since the very beginning.
In 1917, he went back to Chicago with his family, and in 1918, he faked his birth certificate and enlisted at the age of 17 in the Red Cross to fight in WWI". He made it to Europe when there was peace already, but he was based on France and Germany until September 1919.
When he got back, he found a job at an advertising agency, where he met Ubbe Iwerks (UB Iwerks) a talented cartoonist, who would become his partner in all their adventures throughout years. They together decided to create their own company of animated films. However, they had to close it down soon after because of the financial failure of one of their most important clients.
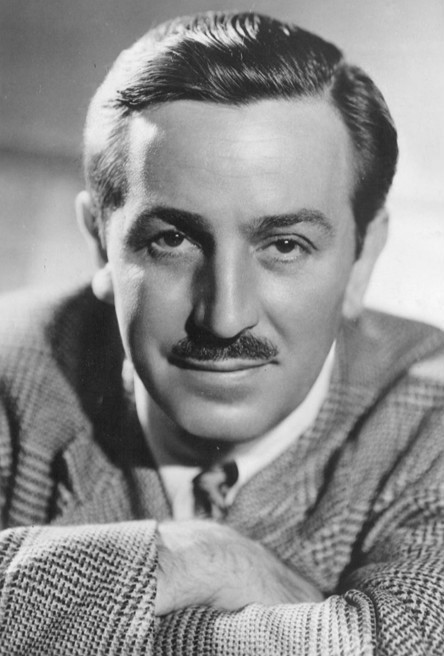

Disney Brothers Studio - The Walt Disney Story
In 1923, Disney decided to move to Hollywood. However, the film industry didn't welcome Disney as nicely as he had expected. So he decided to create his own animation business with his brother Roy. In October 1923, Disney Brothers Studio was created. A year later, Ubbe Iwerks joined the company, and Walt could stop working as an animator to dedicate his time to the task he had always been more qualified for: the creation of characters, plots and directing.
In 1925, Walt married Lillian Bounds, a young worker of the studio, with whom he had two daughters: Diane Marie, born in 1935, when the couple already thought they could never have children, and Sharon Mae (mei), adopted in 1936.
In 1926, they moved to bigger studios, and they changed the name to Walt Disney Studios. Everything seemed to be going full steam ahead. However, the company suffered a severe misfortune when its most crucial client took over the rights of Oswald the Lucky Rabbit. This character, created by Disney, had been the protagonist of the most famous short films of the studio.
In 1928, convinced not to fall into a similar trap, they looked for a new character. Designed by Iwerks and using Walt's voice, Mortimer Mouse came to the world, who would soon be renamed as Micky Mouse.
A star had been born. Mickey Mouse turned into a success in no time. Walt, always on the lookout for innovation, hurried to incorporate sound in the Mickymovies, and in November 28th Steamboat Willy was released - a total success for both the public and the critics.
A workaholic himself, Disney had a series of health crises that led him at the end of 1931, to go on a long vacation to Europe with his wife. There, they were influenced by European arts. Back to Hollywood, he joined a sports club where he practised boxing, wrestling and golf. Soon after, he discovered horse riding, and finally polo. He was a big fan of polo for the rest of his life - a hobby as essential for him to as his passion for trains and miniatures.
First full-length cartoon film
Always supported by a team of excellent cartoonists and illustrators, Disney let all his creative spirit do its work in his first series of silly Symphonies (1932), created in technicolour. They were the reason why he got the beginning of the 26 Oscars he would receive throughout his whole career.
In 1934, Micky was already surrounded by Minnie, Pluto, Goofy and the short-tempered and wicked Donald Duck. When he had already built a name in the Hollywood industry, Walt Disney decided to produce the first full-length cartoon film in the history of movies - SnowWhite and the seven dwarfs(1937).
This movie was a total success, but if left Disney in debt for almost the rest of his life. The film was inspired by the Grimms brothers tale, the first of many adaptations of these classic tales that fascinated Walt so much. After Snowwhite came to Pinocchio, it was a triumph with critics, but a failure with the public. The company recovered thanks Dumbo the elephant and the touching Bambi, during the times marked by WWII.
It was then that Walt Disney, a convinced anti-communist, filmed pro-capitalism Propaganda Movies and started collaborating actively with the FBI in witch hunts, promoted by the senator Joseph McCarthy.
In the 50s, with the help of an investment from the Texan Howard Hughes (jiús), Disney released some of the most acclaimed classics in the history of animation: Cinderella (1950), Alicein Wonderland (1951) and Peter Pan (1953).
In December 15th 1966, after making a dream come true by constructing Disneyland, a vast amusement park based on his characters, The Burbank magician died due to lung cancer, this was only a few months before The JungleBook was released. Same as his movies, Walt Disney himself is surrounded by legends, since the minute he was born, till his death.
There's a rumour that says Disney was born in Spain, specifically in Mojácar, and emigrated when he was a kid with his single mom to the US.
Is Walt Disney's body frozen? - The Walt Disney Story
We can't forget about one of the most spread urban legends in the world: Is Walt Disney's body frozen? Hmmm nope. Disney died at the St. Joseph's Hospital and his family had a close funeral for him so that only a few people could see his body, hence the legend. Two days after his death, he was cremated and moved to their family cemetery.
You may also like to read: Walt Disney’s Multiplane Camera: Illusion King
Walt Disney was a complete pioneer, and his movies meant a turning point in the history of cinema. His legacy is still growing, and his more than 100 full-length movies are always enjoyed all around the world!. this is all for Walt Disney Story, Please do comment and let us know what you think.
Read the full article
0 notes
Text
The Walt Disney Story

Rising - The Walt Disney Story
The Walt Disney Story is very inspirational. Walter Elias Disney was born on December 5th, 1901, in Chicago, Illinois. Walt is the fourth of 5 children. Elias and Flora Disney were their parents. His childhood set apart by economic hardship; his dad was always changing from one job to another. He spent his childhood on a farm, in a village of Missouri. There, he lived surrounded by nature and animals. His mom would read classic tales to him, and that's when his interest in drawing started to grow inside him.
In 1909, his dad got sick, and the whole family had to move to Kansas City. During that time, Walt was selling newspapers and occasionally making some money with his caricatures. He enrolled in the Kansas City Art Institute, where he learned his first notions about drawing techniques. It was then, during those teenage years when he discovered the cinema - an invention, he was passionate about since the very beginning.
In 1917, he went back to Chicago with his family, and in 1918, he faked his birth certificate and enlisted at the age of 17 in the Red Cross to fight in WWI". He made it to Europe when there was peace already, but he was based on France and Germany until September 1919.
When he got back, he found a job at an advertising agency, where he met Ubbe Iwerks (UB Iwerks) a talented cartoonist, who would become his partner in all their adventures throughout years. They together decided to create their own company of animated films. However, they had to close it down soon after because of the financial failure of one of their most important clients.
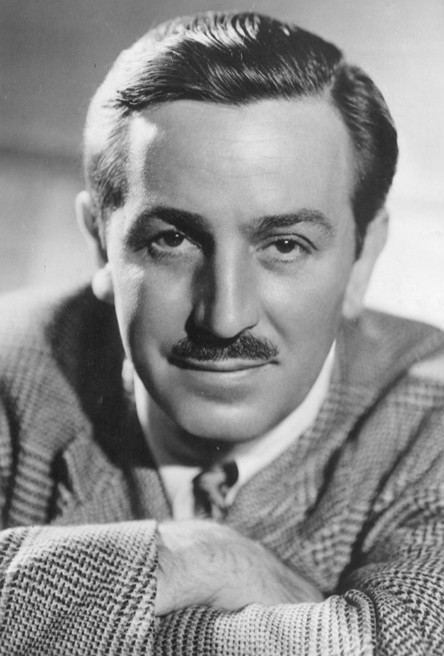

Disney Brothers Studio - The Walt Disney Story
In 1923, Disney decided to move to Hollywood. However, the film industry didn't welcome Disney as nicely as he had expected. So he decided to create his own animation business with his brother Roy. In October 1923, Disney Brothers Studio was created. A year later, Ubbe Iwerks joined the company, and Walt could stop working as an animator to dedicate his time to the task he had always been more qualified for: the creation of characters, plots and directing.
In 1925, Walt married Lillian Bounds, a young worker of the studio, with whom he had two daughters: Diane Marie, born in 1935, when the couple already thought they could never have children, and Sharon Mae (mei), adopted in 1936.
In 1926, they moved to bigger studios, and they changed the name to Walt Disney Studios. Everything seemed to be going full steam ahead. However, the company suffered a severe misfortune when its most crucial client took over the rights of Oswald the Lucky Rabbit. This character, created by Disney, had been the protagonist of the most famous short films of the studio.
In 1928, convinced not to fall into a similar trap, they looked for a new character. Designed by Iwerks and using Walt's voice, Mortimer Mouse came to the world, who would soon be renamed as Micky Mouse.
A star had been born. Mickey Mouse turned into a success in no time. Walt, always on the lookout for innovation, hurried to incorporate sound in the Mickymovies, and in November 28th Steamboat Willy was released - a total success for both the public and the critics.
A workaholic himself, Disney had a series of health crises that led him at the end of 1931, to go on a long vacation to Europe with his wife. There, they were influenced by European arts. Back to Hollywood, he joined a sports club where he practised boxing, wrestling and golf. Soon after, he discovered horse riding, and finally polo. He was a big fan of polo for the rest of his life - a hobby as essential for him to as his passion for trains and miniatures.
First full-length cartoon film
Always supported by a team of excellent cartoonists and illustrators, Disney let all his creative spirit do its work in his first series of silly Symphonies (1932), created in technicolour. They were the reason why he got the beginning of the 26 Oscars he would receive throughout his whole career.
In 1934, Micky was already surrounded by Minnie, Pluto, Goofy and the short-tempered and wicked Donald Duck. When he had already built a name in the Hollywood industry, Walt Disney decided to produce the first full-length cartoon film in the history of movies - SnowWhite and the seven dwarfs(1937).
This movie was a total success, but if left Disney in debt for almost the rest of his life. The film was inspired by the Grimms brothers tale, the first of many adaptations of these classic tales that fascinated Walt so much. After Snowwhite came to Pinocchio, it was a triumph with critics, but a failure with the public. The company recovered thanks Dumbo the elephant and the touching Bambi, during the times marked by WWII.
It was then that Walt Disney, a convinced anti-communist, filmed pro-capitalism Propaganda Movies and started collaborating actively with the FBI in witch hunts, promoted by the senator Joseph McCarthy.
In the 50s, with the help of an investment from the Texan Howard Hughes (jiús), Disney released some of the most acclaimed classics in the history of animation: Cinderella (1950), Alicein Wonderland (1951) and Peter Pan (1953).
In December 15th 1966, after making a dream come true by constructing Disneyland, a vast amusement park based on his characters, The Burbank magician died due to lung cancer, this was only a few months before The JungleBook was released. Same as his movies, Walt Disney himself is surrounded by legends, since the minute he was born, till his death.
There's a rumour that says Disney was born in Spain, specifically in Mojácar, and emigrated when he was a kid with his single mom to the US.
Is Walt Disney's body frozen? - The Walt Disney Story
We can't forget about one of the most spread urban legends in the world: Is Walt Disney's body frozen? Hmmm nope. Disney died at the St. Joseph's Hospital and his family had a close funeral for him so that only a few people could see his body, hence the legend. Two days after his death, he was cremated and moved to their family cemetery.
You may also like to read: Walt Disney’s Multiplane Camera: Illusion King
Walt Disney was a complete pioneer, and his movies meant a turning point in the history of cinema. His legacy is still growing, and his more than 100 full-length movies are always enjoyed all around the world!. this is all for Walt Disney Story, Please do comment and let us know what you think.
Read the full article
0 notes