#source: mitm
Text
Deacon: [runs up to Maccready] Do you want to make five caps?
Maccready: How?
Deacon: I need you to take the blame.
Danse: [from a distance] Oh my God!
Maccready: What did you do?
Deacon: I can't tell you. Yes or no? No questions asked.
Danse: OH MY GOD!
Maccready: Make it ten and you've got yourself a deal.
Danse: OH! MY! GOD!
Deacon: You're a good friend. -Grabs Maccready- DON'T WORRY DANSE I CAUGHT HIM!
87 notes
·
View notes
Text
I recently got back from Argylle and AHHHHHH I had a huge smile on my face for like 70% of the movie.
It was dumb (affectionate) at some points, but that's what made it fun. I feel like Matthew Vaughn understands that movies shouldn't always be realistic or have to make sense. Just enjoy what's in front of you.
More thoughts under the cut (includes spoilers, duh):
Maybe I'm oblivious, but I didn't foresee many of the twists. Though to be fair, like most things I just watch and see what happens...
The humour was perfect for me. It was the kinda shit that makes you chuckle as you shake your head, but not burst out laughing (although I'm not averse to that type of humour).
Elly is literally me and every fan fic writer. Except we're not secret agents, unfortunately.
Whenever I see Bryan Cranston, I only see the dad from MItM. I never watched Breaking Bad.
No Henry Cavill and John Cena kiss? Missed opportunity. SMH
Ahem I'm super interested in how Vaughn will tie together the three franchises, because we have actors that have played various characters (except some of their characters are dead).
As for the production of the movie, Brad Allen (RIP) being on there was really nice to see.
Now, I've never met the man, but fucking Carlos Peres (AKA Bedivere) in the first part of the credits as executive producer, made me so proud??? If you didn't know (please note I just like to look at the credits), in Kingsman TSS, he was simply a Kingsman Knight. Then Kingsman TGC, a Kingsman Knight and production consultant. The King's Man, a co-producer. Vaughn's friends/colleagues are lucky fuckers.
I didn't stay til the end of the credits (the employees were eyeing me to leave so they could clean), but I think it's really nice they include the number of jobs supported and mention the hard work put into making such a production, at least for Kingsman 2 and The King's Man.
I know critics take things way too seriously and I will never ever listen to them but this quote makes me laugh: "Argylle [...] ultimately wears out its welcome with a convoluted plot and overlong runtime." (Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Argylle) Man, if they think that was convoluted, they haven't seen the DrakeNier universe, Final Fantasy, Kingdom Hearts, etc.
Okay, I've rambled enough for now. If you read everything, thank you. (Why would you?)
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
MiTM phishing attack can let attackers unlock and steal a Tesla

Source: https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/mitm-phishing-attack-can-let-attackers-unlock-and-steal-a-tesla/
Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7IBg5uNB7is
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
does vpn protect from man in the middle
🔒🌍✨ Get 3 Months FREE VPN - Secure & Private Internet Access Worldwide! Click Here ✨🌍🔒
does vpn protect from man in the middle
VPN encryption
Title: Understanding the Importance of VPN Encryption for Online Security
In an era where cyber threats loom large, safeguarding your online activities has become paramount. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) offer a robust solution, with encryption playing a pivotal role in securing your data and privacy.
VPN encryption involves encoding data transmitted between your device and the VPN server, rendering it unreadable to unauthorized parties. This process utilizes complex algorithms to scramble your information, making it virtually impossible for hackers, ISPs, or government agencies to intercept and decipher.
There are various encryption protocols employed by VPN services, each with its level of security and performance. The most common ones include:
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard): Widely regarded as the gold standard, AES encryption comes in different key lengths (128-bit, 192-bit, and 256-bit), with longer keys providing stronger security.
OpenVPN: This open-source protocol is highly customizable and known for its flexibility and robust security features, making it a popular choice among VPN providers.
IPSec (Internet Protocol Security): Often used in combination with other protocols, IPSec offers strong encryption and authentication, enhancing overall data protection.
WireGuard: A relatively newer protocol, WireGuard boasts simplicity and efficiency without compromising security, making it a promising contender in the VPN encryption landscape.
By encrypting your internet traffic, VPNs create a secure tunnel through which your data travels, shielding it from prying eyes and potential threats. Whether you're browsing the web, streaming content, or conducting sensitive transactions, VPN encryption ensures confidentiality and integrity, safeguarding your online identity and activities.
However, it's essential to choose a reputable VPN provider that prioritizes encryption and follows best practices to mitigate vulnerabilities. Additionally, regularly updating your VPN software and adhering to strong password practices further fortifies your online security posture.
In conclusion, VPN encryption serves as a vital layer of defense in safeguarding your online privacy and security. By leveraging robust encryption protocols, VPNs empower users to navigate the digital realm with confidence, knowing their sensitive information remains shielded from malicious actors.
Man-in-the-middle attack prevention
Man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks pose a significant threat to online security, making it crucial for individuals and organizations to implement robust prevention measures. These attacks occur when a malicious actor intercepts communication between two parties, allowing them to eavesdrop on sensitive information or manipulate the data exchanged.
To prevent falling victim to MITM attacks, several strategies can be employed. Firstly, utilizing encryption is paramount. Encrypting data ensures that even if intercepted, it remains unreadable to unauthorized parties. Secure communication protocols such as HTTPS for web browsing, SSL/TLS for email, and VPNs for network traffic encryption are essential tools in this regard.
Another effective prevention method is the use of digital certificates. These certificates verify the identities of parties involved in communication, thus thwarting attempts by attackers to impersonate legitimate entities. By ensuring the authenticity of both sender and recipient, digital certificates help establish a secure connection, making it harder for MITM attackers to infiltrate.
Additionally, implementing strong authentication mechanisms strengthens defenses against MITM attacks. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification before accessing sensitive information or systems. By combining something the user knows (like a password) with something they have (such as a fingerprint or OTP), MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
Furthermore, regular security updates and patches are essential for maintaining the integrity of systems and software. Vulnerabilities in applications or operating systems can be exploited by attackers to execute MITM attacks. Therefore, staying vigilant and promptly applying security patches helps mitigate these risks.
In conclusion, safeguarding against MITM attacks necessitates a multifaceted approach encompassing encryption, digital certificates, strong authentication, and proactive security measures. By implementing these strategies, individuals and organizations can mitigate the risk of falling victim to this pervasive threat and ensure the confidentiality and integrity of their data and communications.
Tunneling protocols
A tunneling protocol is a method of encapsulating and transmitting data across networks securely. It creates a virtual tunnel within a larger network to protect data as it travels from one point to another. This process is commonly used to transmit sensitive information over public networks, such as the internet, ensuring that data remains secure and private.
One of the most popular tunneling protocols is the Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP). PPTP is widely supported and commonly used for creating VPN connections. It establishes a secure tunnel between a user's computer and a remote server, encrypting data as it travels between the two points. While PPTP is relatively easy to set up and use, it may not provide the same level of security as other protocols due to potential vulnerabilities.
Another common tunneling protocol is the Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP). L2TP combines the best features of PPTP and Cisco's Layer 2 Forwarding (L2F) protocol, offering a more secure and reliable solution for transmitting data across networks. L2TP is often used in conjunction with IPsec (Internet Protocol Security) for enhanced security measures.
Additionally, Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP) is another popular choice for tunneling protocols. SSTP is a proprietary protocol developed by Microsoft that utilizes SSL/TLS encryption for secure data transmission. It is commonly used for establishing VPN connections and is known for its compatibility with Windows operating systems.
Overall, tunneling protocols play a crucial role in ensuring secure data transmission across networks. By encapsulating data within virtual tunnels and encrypting it during transmission, these protocols help protect sensitive information from unauthorized access and interception.
Secure data transmission
Title: Ensuring Secure Data Transmission: Best Practices and Technologies
In today's digital age, where information is exchanged at lightning speed, ensuring secure data transmission is paramount for safeguarding sensitive information. From financial transactions to personal messages, data travels through various channels, making it vulnerable to interception by malicious actors. Implementing robust security measures and leveraging advanced technologies are essential steps in fortifying data transmission.
Encryption stands as the cornerstone of secure data transmission. By converting plaintext into ciphertext using complex algorithms, encryption renders data unreadable to unauthorized parties. End-to-end encryption (E2EE), in particular, ensures that data remains encrypted throughout its journey, from sender to recipient, without intermediary access. Widely used encryption protocols like SSL/TLS secure web communications, while protocols like PGP provide secure email communication.
Furthermore, employing secure communication protocols such as HTTPS, SFTP, and SSH adds an extra layer of protection. HTTPS encrypts data transferred over HTTP using SSL/TLS, safeguarding against eavesdropping and tampering. SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol) encrypts file transfers over a secure channel, while SSH (Secure Shell) provides secure remote access to servers and networks.
In addition to encryption and secure protocols, implementing strong authentication mechanisms is crucial. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) requires users to provide multiple forms of verification, such as passwords, biometrics, or OTPs, enhancing the security of data transmission by adding layers of authentication.
Moreover, regular security audits and updates to systems and software help identify vulnerabilities and patch them promptly, reducing the risk of data breaches. Employing intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) can also thwart unauthorized access attempts in real-time.
In conclusion, safeguarding data transmission requires a multi-faceted approach encompassing encryption, secure protocols, authentication mechanisms, and proactive security measures. By implementing these best practices and leveraging advanced technologies, organizations can mitigate the risks associated with data transmission and uphold the confidentiality and integrity of their sensitive information.
Network security measures
Network security measures are crucial for safeguarding confidential information and preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data. Businesses and individuals must implement various strategies to protect their networks from cyber threats and ensure the integrity of their data.
One essential network security measure is the use of firewalls. Firewalls act as a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks, filtering incoming and outgoing traffic to block malicious content and unauthorized access attempts. By setting up firewalls, organizations can control network traffic and prevent potential security breaches.
Another key network security measure is the implementation of strong encryption protocols. Encryption helps secure data by encoding it in a way that only authorized parties can access and decipher. By encrypting sensitive information such as passwords, financial transactions, and communications, organizations can prevent hackers from intercepting and exploiting data.
Regular software updates and patches also play a vital role in network security. Cyber attackers often exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software to gain unauthorized access to networks. By regularly updating software and applying security patches, organizations can mitigate the risk of potential security threats and ensure that their systems remain secure.
Furthermore, implementing multi-factor authentication can add an extra layer of security to network access. By requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification, such as passwords, biometrics, or security tokens, organizations can enhance the security of their networks and reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
In conclusion, network security measures are essential for protecting sensitive data and preventing cyber threats. By implementing firewalls, encryption protocols, software updates, and multi-factor authentication, organizations can enhance the security of their networks and minimize the risk of security breaches.
0 notes
Text
can my passwords be hacked if i don't have vpn
🔒🌍✨ Get 3 Months FREE VPN - Secure & Private Internet Access Worldwide! Click Here ✨🌍🔒
can my passwords be hacked if i don't have vpn
Password security without VPN
Title: Strengthening Password Security Without VPN: Essential Practices
In today's digital age, safeguarding our online accounts is paramount. While Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) offer an additional layer of security, there are numerous steps individuals can take to fortify their password security without solely relying on VPNs.
Utilize Strong, Unique Passwords: The cornerstone of robust password security is using passwords that are long, complex, and unique for each account. Avoid common phrases or easily guessable combinations.
Implement Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Adding an extra verification step beyond passwords significantly enhances security. 2FA typically involves receiving a code via text message, email, or authenticator app, making it much harder for unauthorized users to gain access.
Regularly Update Passwords: Routinely changing passwords reduces the risk of unauthorized access, particularly in the event of a data breach. Aim to update passwords every few months, especially for critical accounts like email and banking.
Employ Password Managers: These tools generate, store, and auto-fill complex passwords across various accounts. Password managers eliminate the need to remember multiple passwords while ensuring each one is unique and secure.
Beware of Phishing Attempts: Exercise caution when clicking on links or providing login credentials, especially in unsolicited emails or messages. Phishing remains a prevalent method used by cybercriminals to obtain sensitive information.
Enable Account Lockouts: Many online platforms offer the option to lock an account after multiple failed login attempts. Enabling this feature helps prevent brute force attacks, where hackers systematically attempt to guess passwords.
Stay Informed About Security Practices: Keeping abreast of the latest security threats and best practices is crucial. Follow reputable sources and security blogs to stay informed about emerging risks and how to mitigate them effectively.
By implementing these strategies, individuals can significantly enhance their password security without solely relying on VPNs. While VPNs remain a valuable tool for protecting online privacy, adopting multiple layers of security ensures a more robust defense against cyber threats.
Vulnerability of passwords sans VPN
In the digital age, where cyber threats loom large, the vulnerability of passwords without the added layer of protection provided by a Virtual Private Network (VPN) cannot be overstated. Passwords serve as the primary gatekeepers to our sensitive information, ranging from personal emails to financial accounts and beyond. However, relying solely on passwords leaves individuals and organizations susceptible to various forms of cyber attacks.
One of the significant risks associated with using passwords without a VPN is the interception of data during transmission. When logging into accounts or accessing online services, data travels through networks, making it susceptible to interception by cybercriminals. Without encryption provided by a VPN, this data can be easily intercepted, compromising usernames, passwords, and other confidential information.
Furthermore, without a VPN, users are vulnerable to Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks. In these attacks, hackers intercept communication between two parties, allowing them to eavesdrop, steal data, or inject malicious content. Without encryption, passwords transmitted over unsecured networks are at high risk of being compromised in MitM attacks.
Additionally, the absence of a VPN exposes users to the dangers of public Wi-Fi networks. Public Wi-Fi hotspots, such as those found in cafes, airports, and hotels, are often unsecured, making them prime targets for cyber attacks. Hackers can easily intercept data transmitted over these networks, including passwords, leading to unauthorized access to accounts and sensitive information.
In conclusion, the vulnerability of passwords sans VPN underscores the importance of adopting comprehensive cybersecurity measures. By incorporating a VPN into their digital practices, individuals and organizations can encrypt their internet traffic, mitigate the risk of interception and MitM attacks, and safeguard their sensitive information from cyber threats. It's imperative to recognize the critical role that VPNs play in enhancing online security and protecting against password-related vulnerabilities in today's interconnected world.
Risks of password hacking without VPN
In today's digital age, protecting our online security is paramount, especially when it comes to safeguarding our sensitive information such as passwords. Password hacking remains a prevalent threat, with hackers constantly devising new methods to breach our defenses. One effective measure to mitigate this risk is using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) while accessing the internet.
Without a VPN, your passwords are vulnerable to various hacking techniques. One of the most common methods employed by hackers is known as "packet sniffing." This involves intercepting data packets transmitted over unsecured networks, allowing hackers to capture sensitive information like login credentials. Without encryption provided by a VPN, your passwords can be easily intercepted and exploited.
Additionally, when you connect to public Wi-Fi networks without a VPN, you expose your passwords to potential attackers. Cybercriminals often target these networks as they are typically less secure, making it easier for them to eavesdrop on your online activities and steal your passwords.
Moreover, without the anonymity provided by a VPN, your online activities can be traced back to your IP address. Hackers can use this information to launch targeted attacks against you, increasing the risk of password hacking.
Furthermore, accessing geo-restricted content without a VPN can also pose a risk to your passwords. Many websites implement region-based restrictions, and attempting to bypass these restrictions without a VPN can leave your passwords vulnerable to interception.
In conclusion, the risks of password hacking without a VPN are significant. By encrypting your internet connection and masking your IP address, a VPN provides an additional layer of security, helping to protect your passwords and sensitive information from falling into the wrong hands. Investing in a reliable VPN service is essential for maintaining your online security in today's digital landscape.
Cybersecurity threats without VPN protection
In today's digital age, cybersecurity threats loom large, and without the protection of a Virtual Private Network (VPN), individuals and organizations are vulnerable to a myriad of dangers. Here's a glimpse into the risks one faces without VPN protection.
First and foremost, without a VPN, your online activities are susceptible to interception by cybercriminals. This means that sensitive information such as passwords, credit card details, and personal data can be easily compromised, leading to identity theft, financial loss, and even reputational damage.
Moreover, accessing public Wi-Fi networks without VPN protection poses significant risks. These networks are often unsecured, making it effortless for hackers to eavesdrop on your internet traffic. This leaves you exposed to various attacks, including man-in-the-middle attacks, where cybercriminals intercept communications between two parties to steal data or spread malware.
Additionally, without VPN encryption, your internet service provider (ISP), government agencies, and even advertisers can monitor your online behavior. This invasion of privacy not only compromises your confidentiality but also subjects you to targeted advertising and potential surveillance.
Furthermore, without VPN protection, geo-restricted content remains inaccessible. This limitation is particularly frustrating for travelers, expatriates, and individuals living in regions with strict internet censorship. By masking your IP address and encrypting your connection, a VPN enables unrestricted access to websites, streaming services, and online content from anywhere in the world.
In conclusion, the absence of VPN protection leaves individuals and organizations exposed to a host of cybersecurity threats. From identity theft and financial fraud to privacy breaches and content restrictions, the risks are too significant to ignore. Investing in a reliable VPN service is essential for safeguarding your online security, privacy, and freedom in today's interconnected world.
Protecting passwords online without VPN
Protecting passwords online without using a virtual private network (VPN) requires implementing alternative security measures to ensure your sensitive information remains safeguarded from hackers and unauthorized access.
First and foremost, creating strong and unique passwords is crucial in maintaining online security. It is essential to use a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters when setting up passwords for your accounts. Avoid using easily guessable information such as birthdates or pet names, as these can make your accounts vulnerable to brute force attacks.
Utilizing two-factor authentication (2FA) is another effective way to enhance password protection. By requiring a secondary verification step, such as a code sent to your phone or email, 2FA adds an extra layer of security to your accounts, making it more difficult for unauthorized users to gain access.
Regularly updating your passwords is also key to maintaining online security. It is recommended to change your passwords every few months to reduce the risk of unauthorized access. Additionally, using a password manager can help generate and store complex passwords for various accounts, eliminating the need to remember them all.
Furthermore, practicing safe browsing habits, such as avoiding suspicious links and websites, can prevent potential phishing attacks that may compromise your passwords. Be cautious when sharing sensitive information online and only enter your login credentials on secure websites with HTTPS encryption.
In conclusion, while a VPN can provide an additional layer of security for protecting passwords online, implementing strong password practices, utilizing 2FA, updating passwords regularly, and practicing safe browsing habits can effectively enhance online security even without the use of a VPN. By being proactive and diligent in safeguarding your passwords, you can mitigate the risk of falling victim to cyber threats and ensure your sensitive information remains protected.
0 notes
Text
can you decode vpn
🔒🌍✨ Get 3 Months FREE VPN - Secure & Private Internet Access Worldwide! Click Here ✨🌍🔒
can you decode vpn
VPN encryption protocols
VPN encryption protocols are essential components of virtual private network (VPN) services that ensure the security and privacy of users' online activities. These protocols establish the method by which data is encrypted and transmitted over the internet, safeguarding it from potential cyber threats and unauthorized access.
There are several VPN encryption protocols available, each with its own unique features and levels of security. Some of the most commonly used protocols include:
OpenVPN: Known for its open-source nature and strong security features, OpenVPN is highly versatile and compatible with various platforms. It utilizes the OpenSSL library and supports both TCP and UDP protocols, offering robust encryption and authentication mechanisms.
IPSec (Internet Protocol Security): IPSec is a suite of protocols that provides secure communication over IP networks. It can be implemented in tunnel mode for VPN connections, ensuring data confidentiality, integrity, and authentication through encryption algorithms and key exchange methods.
L2TP/IPSec (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol with IPsec): This protocol combines the best features of L2TP and IPSec to create a secure VPN connection. L2TP provides the tunneling mechanism, while IPSec offers encryption and authentication, making it a reliable choice for safeguarding sensitive data.
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol): Although considered less secure than other protocols, PPTP is easy to set up and offers faster connection speeds. It uses MPPE (Microsoft Point-to-Point Encryption) for encryption and is compatible with a wide range of devices.
When choosing a VPN service, it is important to consider the encryption protocols supported to ensure your online privacy and security. By selecting a VPN provider that offers strong encryption and follows best practices, you can enjoy a safe and secure internet browsing experience.
VPN decryption methods
VPN decryption methods refer to the techniques used by cybercriminals or government agencies to intercept and decode the encrypted data transmitted through a virtual private network (VPN). While VPNs are designed to secure and protect users' online activities, determined individuals with malicious intent may employ various decryption methods to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information.
One common VPN decryption method is the exploitation of vulnerabilities in the VPN protocol itself. If a VPN protocol has weak encryption algorithms or contains vulnerabilities that can be exploited, hackers can potentially decrypt the data passing through the VPN connection. This highlights the importance of using VPN services that are built on robust encryption standards to minimize the risk of decryption attacks.
Another decryption method involves launching man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks to intercept and alter the data transmitted between the user and the VPN server. By inserting themselves between the user and the VPN server, attackers can eavesdrop on the communication, capture the encrypted data, and attempt to decrypt it using various techniques.
Furthermore, some attackers may resort to social engineering tactics or phishing schemes to trick users into disclosing their VPN credentials, allowing them to access the encrypted data without having to decrypt it manually.
To mitigate the risks associated with VPN decryption methods, users should opt for reputable VPN providers that offer strong encryption protocols, regularly update their software to patch known vulnerabilities, and remain vigilant against potential social engineering attacks. By taking proactive measures and staying informed about emerging threats, users can enhance the security of their online activities and safeguard their confidential information.
VPN security mechanisms
Title: Understanding VPN Security Mechanisms: Safeguarding Your Online Privacy
In today's digitally interconnected world, safeguarding your online privacy has become paramount. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) serve as a crucial tool in achieving this goal, offering robust security mechanisms to protect users' sensitive data from prying eyes. Let's delve into the key security mechanisms employed by VPNs:
Encryption: VPNs utilize advanced encryption protocols to scramble data transmitted between your device and the VPN server. This encryption ensures that even if intercepted, the data remains indecipherable to unauthorized entities. Common encryption protocols include AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman), providing varying levels of security.
Tunneling Protocols: VPNs establish secure tunnels through which data travels between your device and the VPN server. Popular tunneling protocols such as OpenVPN, L2TP/IPsec, and IKEv2/IPsec encapsulate data packets, adding an additional layer of security. These protocols also authenticate and authorize users, further enhancing security.
Kill Switch: A Kill Switch is a vital feature that automatically halts internet traffic if the VPN connection drops unexpectedly. This prevents your data from being exposed to your Internet Service Provider (ISP) or other malicious actors during such disruptions, maintaining continuous privacy protection.
DNS Leak Protection: DNS (Domain Name System) leaks can inadvertently expose your browsing activity even when connected to a VPN. VPNs combat this by rerouting DNS queries through encrypted tunnels, preventing ISPs or third parties from monitoring your online behavior.
Multi-factor Authentication (MFA): Many VPN services offer MFA as an additional layer of security. By requiring multiple forms of authentication, such as passwords and one-time codes sent to your mobile device, MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access to your VPN account.
By implementing these robust security mechanisms, VPNs offer users peace of mind knowing that their online activities remain private and secure. Whether accessing sensitive business networks or simply browsing the web, leveraging a VPN is essential in today's cybersecurity landscape.
VPN data encryption algorithms
Title: Understanding VPN Data Encryption Algorithms: Securing Your Online Privacy
In the digital age, where cyber threats lurk around every virtual corner, safeguarding your online privacy is paramount. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) serve as invaluable tools in this endeavor, encrypting your internet traffic to shield sensitive information from prying eyes. At the heart of VPNs lie sophisticated data encryption algorithms, which form the backbone of their security infrastructure.
One of the most common encryption protocols employed by VPNs is the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). AES operates through symmetric key encryption, where both the sender and receiver utilize the same key to encrypt and decrypt data. Renowned for its strength and efficiency, AES has become the gold standard in data encryption, offering robust protection against unauthorized access.
Another prevalent encryption algorithm utilized by VPNs is Transport Layer Security (TLS). TLS, formerly known as Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), establishes secure communication channels over the internet, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of data transmission. By employing a combination of symmetric and asymmetric encryption techniques, TLS fortifies VPN connections against interception and tampering.
In addition to AES and TLS, VPNs may also incorporate other encryption protocols such as Data Encryption Standard (DES), Triple DES (3DES), and Rivest Cipher (RC4) to diversify their security measures. However, it's essential to note that some older encryption algorithms like DES and RC4 are considered less secure due to vulnerabilities exposed over time.
When selecting a VPN provider, users should prioritize those employing robust encryption algorithms like AES-256, the most secure variant of AES currently available. Furthermore, opting for VPNs that support the latest TLS protocols, such as TLS 1.3, enhances security and ensures compatibility with modern encryption standards.
In conclusion, VPN data encryption algorithms play a pivotal role in safeguarding online privacy and protecting sensitive information from cyber threats. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of different encryption protocols, users can make informed decisions to fortify their digital defenses and enjoy a safer browsing experience.
VPN decryption techniques
In the digital age where online privacy is increasingly important, Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) have become a popular tool for protecting one's data and activities on the internet. However, there are various VPN decryption techniques used by entities aiming to bypass the encryption provided by VPNs.
One common VPN decryption technique is known as "Man-in-the-Middle" attack, where a cyber attacker intercepts the communication between the user and the VPN server. By doing so, the attacker can potentially access the unencrypted data passing through, compromising the user's privacy.
Another technique used for VPN decryption is through traffic analysis. By monitoring the amount, timing, and destination of data packets transmitted through the VPN connection, attackers can infer patterns and potentially decrypt the encrypted communication.
Furthermore, some adversaries may employ malware or keyloggers to directly target the user's device and capture sensitive information before it gets encrypted by the VPN.
To mitigate the risks associated with VPN decryption techniques, it is essential to choose a reliable and trustworthy VPN service provider with strong encryption protocols. Additionally, utilizing multi-factor authentication, keeping software updated, and being cautious of phishing attempts can help enhance the security of VPN connections.
Overall, being aware of the potential VPN decryption techniques and taking proactive measures to safeguard one's online activities are crucial in maintaining privacy and security in the digital realm.
0 notes
Text
can you go on vpn at airport
🔒🌍✨ Get 3 Months FREE VPN - Secure & Private Internet Access Worldwide! Click Here ✨🌍🔒
can you go on vpn at airport
Airport VPN restrictions
When it comes to connecting to a Virtual Private Network (VPN) in an airport, travelers may encounter certain restrictions or limitations imposed by the airport's network policies. Many airports around the world implement VPN restrictions for security and compliance reasons.
VPN usage in airports can be restricted due to concerns about cyber threats, illegal activities, and network congestion. Some airports block VPN connections to prevent potential hacking attempts or unauthorized access to sensitive information. By limiting VPN usage, airports aim to safeguard their network infrastructure and protect passengers' data from security breaches.
Additionally, airports may restrict VPNs to comply with regulations and licensing agreements. Some countries have stringent laws regarding internet usage and data transmission, which may impact the availability of VPN services in airports located within their jurisdiction. Travelers should be aware of these restrictions and adhere to local regulations when using VPNs in airports.
While VPN restrictions in airports may pose challenges for passengers who rely on secure and private internet connections, there are ways to navigate these limitations. Travelers can consider alternative methods to protect their online activities, such as using encrypted websites or secure networks provided by reputable sources.
Ultimately, understanding the reasons behind airport VPN restrictions and taking proactive measures to ensure cybersecurity can help travelers mitigate potential risks and enjoy a safe browsing experience while in transit. By staying informed and making informed decisions, passengers can navigate the digital landscape with confidence, even amid stringent network policies enforced in airport environments.
Public wifi security risks
Title: Understanding the Risks of Public WiFi Networks
Public WiFi networks have become ubiquitous, offering convenient internet access in coffee shops, airports, hotels, and various public spaces. While these networks provide connectivity on the go, they also pose significant security risks that users must be aware of.
One of the primary concerns with public WiFi is the lack of encryption. Unlike private networks, public WiFi hotspots often do not encrypt data transmitted between the user's device and the router. This makes it easy for hackers to intercept sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, and financial details.
Another risk factor is the presence of rogue hotspots. Cybercriminals can set up fake WiFi networks with legitimate-sounding names to trick users into connecting to them. Once connected, hackers can launch attacks to steal personal data or distribute malware to the connected devices.
Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks are also common on public WiFi networks. In these attacks, hackers intercept communication between the user and the intended destination. This allows them to eavesdrop on conversations, steal data, or inject malicious content into web pages.
Furthermore, unsecured public WiFi networks are breeding grounds for various other cyber threats, including phishing scams, malware infections, and session hijacking. Without proper security measures in place, users are vulnerable to these malicious activities.
To mitigate the risks associated with public WiFi, users should take proactive steps to protect their devices and data. This includes using a virtual private network (VPN) to encrypt internet traffic, avoiding sensitive transactions on public networks, and keeping software and security patches up to date.
In conclusion, while public WiFi networks offer convenience, they also come with inherent security risks. By understanding these risks and implementing appropriate security measures, users can minimize the chances of falling victim to cyber threats while staying connected on the go.
VPN for travel safety
Title: Enhance Your Travel Safety with a VPN
In an era where technology reigns supreme, ensuring your safety while traveling involves more than just locking your luggage or being wary of pickpockets. With the increasing reliance on digital devices during trips, safeguarding your online privacy and security has become paramount. This is where a Virtual Private Network (VPN) steps in as an indispensable tool for travelers.
A VPN encrypts your internet connection, creating a secure tunnel between your device and the internet. When you connect to public Wi-Fi networks, such as those found in hotels, airports, or cafes, you expose yourself to potential cyber threats. Hackers can intercept your data packets and gain access to sensitive information like passwords, credit card details, or personal emails. However, by using a VPN, all data transmitted between your device and the internet is encrypted, making it virtually impossible for cybercriminals to intercept or decipher.
Furthermore, a VPN allows you to bypass geographical restrictions imposed by certain websites or streaming services. Whether you're in a foreign country with limited internet access or trying to access your favorite shows while abroad, a VPN enables you to connect to servers in different locations, granting you unrestricted access to the content you desire.
Additionally, VPNs can help you save money on travel bookings by masking your IP address and allowing you to compare prices across different regions. Airlines and hotels often adjust their prices based on your location, so using a VPN to appear as though you're booking from a different country can result in significant savings.
In conclusion, investing in a reliable VPN service is essential for ensuring your safety and privacy while traveling. Whether you're browsing the web, accessing sensitive information, or simply wanting to save money, a VPN offers peace of mind and protection in an increasingly digital world.
Bypassing airport wifi limitations
Title: Unlocking Airport WiFi Restrictions: A Traveler's Guide
In today's hyper-connected world, staying connected while traveling is no longer a luxury but a necessity. However, many travelers encounter frustrating limitations when trying to access the internet via airport WiFi networks. These restrictions often include limited browsing time, restricted access to certain websites or services, and slow connection speeds. Fortunately, there are several effective strategies travelers can employ to bypass these airport WiFi limitations and enjoy uninterrupted internet access during their journeys.
One of the simplest methods to bypass airport WiFi restrictions is by using a virtual private network (VPN). A VPN encrypts your internet connection, masking your online activities from prying eyes, including airport WiFi network administrators. By connecting to a VPN server outside the airport's network, you can circumvent restrictions and access the internet freely.
Another option is to use a mobile hotspot or tethering feature on your smartphone. By using your cellular data connection instead of the airport WiFi, you can bypass any restrictions imposed by the airport network. However, it's essential to check your data plan to avoid unexpected charges, especially when traveling internationally.
Additionally, travelers can use web proxies or browser extensions designed to bypass internet restrictions. These tools route your internet traffic through a different server, allowing you to access blocked websites and services without detection.
It's important to note that while bypassing airport WiFi limitations can provide convenience, travelers should also prioritize security. Avoid accessing sensitive information or conducting financial transactions over public WiFi networks, as they may be susceptible to hacking or surveillance.
In conclusion, by utilizing VPNs, mobile hotspots, or other tools, travelers can effectively bypass airport WiFi limitations and stay connected while on the go. However, it's crucial to balance convenience with security to ensure a safe and seamless browsing experience during your travels.
Airport network privacy measures
In the digital age, concerns about privacy and security are at the forefront of discussions surrounding airport networks. With the growing reliance on technology for efficient travel processes, airports are implementing enhanced privacy measures to protect passengers' data and ensure a secure network environment.
One of the primary privacy measures employed by airport networks is the implementation of encrypted connections. Encryption technology scrambles data traveling between devices, making it nearly impossible for unauthorized users to intercept and decipher sensitive information. By utilizing encryption protocols such as Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS), airports can safeguard passengers' personal details, including payment information and identification documents.
Furthermore, airports are investing in robust firewalls and intrusion detection systems to fortify their network defenses against cyber threats. Firewalls act as a barrier between internal and external networks, filtering incoming and outgoing traffic to prevent malicious entities from gaining unauthorized access. Intrusion detection systems continuously monitor network activities for suspicious behavior and alert network administrators of potential security breaches in real-time.
In addition to technological solutions, airports are also implementing strict access controls to regulate who can connect to their networks. By requiring strong authentication methods such as password policies, biometric verification, and virtual private networks (VPNs), airports can limit access to authorized personnel and devices, reducing the risk of unauthorized data breaches.
Overall, the implementation of robust privacy measures within airport networks is essential to protect passengers' sensitive information and maintain a secure travel environment in an increasingly interconnected world. By leveraging encryption technology, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access controls, airports can bolster their network security posture and instill confidence in travelers regarding the privacy of their data during their journeys.
0 notes
Text
DNSSEC: Peace of Mind for Your Online Safety
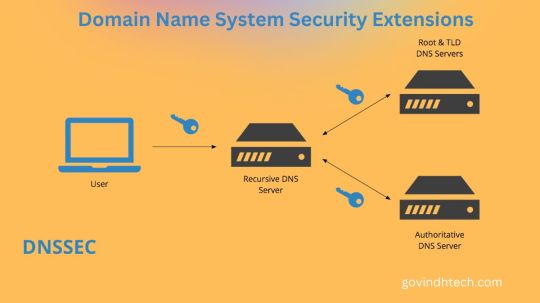
What is DNSSEC?
A feature of the Domain Name System (DNS) that verifies answers to domain name lookups is called Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC). Although it keeps attackers from tampering with or contaminating DNS query responses, it does not offer privacy protections for those lookups.
Not really. DNSSEC uses a different method than encryption public key cryptography to defend networks from man-in-the-middle attacks. Put differently, Domain Name System Security Extensions offers an authentication method but not a confidentiality method.
DNSSEC: Internet Foundation Protection
Domain Name System (DNS) converts human-readable domain names into machine-readable IP addresses for online security in the digital age. Security issues make traditional DNS vulnerable to manipulation and attacks. DNSSEC safeguards DNS data.
Major Advantages of DNSSEC:
DNSSEC uses public-key cryptography and digital signatures to verify DNS responses. This means a domain name’s IP address is authentic and hasn’t been changed from the authorized source.
Data Integrity: Phishing attempts and malicious website redirects can result from DNS data manipulation. DNSSEC prevents hackers from altering vital DNS records by cryptographically verifying them.
Middleman (MitM) Attack Prevention: DNSSEC guarantees authenticity and data integrity, reducing the risk of MitM attacks, in which attackers intercept and alter DNS responses to trick users.
Domain Name System Security Extensions protects DNS lookups from malicious and tampering, giving users and organizations confidence to use online services.
Is DNSSEC important?
Public/Private Key Pairs: Public keys are published in the DNS by domain owners, while private keys are kept confidential.
Digital Signatures: By digitally signing DNS records with the private key, a “fingerprint” that confirms their legitimacy is created.
Signature Validation: To make sure received DNS records haven’t been tampered with, resolvers the programs that convert domain names into IP addresses verify the signatures using the public key that has been released.
Chain of Trust: Signatures are verified through a chain of trust that originates from the root of trust that is present at the top of the DNS hierarchy.
How to implement DNSSEC
Adoption: DNSSEC is being implemented more often, despite not being widely used. It is supported by a large number of prominent domain registries and registrars, and it is frequently free for organizations to enable.
Benefits Exceed Difficulties: Although DNSSEC setup and configuration may call for some technical know-how, the advantages greatly exceed the drawbacks. Organizations that are concerned about security ought to give it serious consideration for their domains.
What distinguishes public key cryptography from encryption?
DNS queries are digitally “signed,” or authenticated, using public key cryptography by DNSSEC. The receiving device can compare the data it receives with the original data sent by the authoritative server when DNSSEC is enabled on a zone record. A digital signature that authenticates data using public keys makes this possible.
The data in DNSSEC is not encrypted; instead, the authentication keys are secured through cryptography. Traffic protected by Domain Name System Security Extensions can still be intercepted and read. The receiving server will be able to detect that something is wrong if the data is altered somewhere along the data pathway and sent on to its destination because the public keys will not match.
On the other hand, encryption encrypts the data by using cryptography. By altering what an attacker would see if they were to intercept a query somewhere along the data pathway, encryption ensures confidentiality. Until the attacker uses an encryption key to decipher the signal, it renders the data unintelligible. Data is shielded from manipulation by encryption because the key isn’t disclosed to the public.
What is DNSSEC in cybersecurity?
Among the Internet’s more traditional protocols is DNS. The Internet was much smaller when it was first developed, and almost everyone there was acquainted. Data Security was not given much thought.
DNS was used so extensively by then that any major alteration would have brought down the entire system, even before the issue of Internet security arose. Instead of attempting to create a completely encrypted protocol to take the place of DNS, an authentication mechanism was added to the pre-existing system.
DNSSEC was vulnerable. By enabling the authentication of queries and data, it improved protocol security. However, it did so without altering the underlying architecture, allowing the Internet to expand further without requiring any new engineering. Domain Name System Security Extensions deployment was left optional so that organizations could make the switch whenever they felt ready.
If DNSSEC isn’t encrypted, why use it?
One major reason to use DNSSEC is to prevent DNS cache poisoning, also called DNS spoofing. A DNS spoofing attack involves replacing a legitimate DNS query response with an unauthenticated one. After that, the response becomes stuck in the cache, returning the incorrect response and sending users to malicious websites until the “time to live” runs out.
By authenticating DNS responses and guaranteeing that only accurate responses are returned, DNSSEC defends against these types of attacks. DNS spoofing attacks cannot be prevented by encryption, but it may safeguard the underlying data in a DNS connection.
Is DNSSEC still used if it isn’t encrypted?
Sadly, DNSSEC is only used to validate about 20% of Internet traffic. Even though it’s a big improvement over a few years ago, that amount is still far below what it ought to be. That substantial gap can be attributed to a combination of informational gaps, laziness, and usability issues.
By offering a straightforward deployment procedure, NS1 encourages all of its clients to implement DNSSEC. Through IBM’s Dedicated DNS offering- NS1 even offers Domain Name System Security Extensions as a backup provider or redundant DNS option, in contrast to other providers.
Gazing Forward
Security continues to be the primary concern as the internet develops. One of the most important steps toward a more secure DNS ecosystem is Domain Name System Security Extensions. It encourages trust and confidence in online interactions by defending against critical vulnerabilities, protecting users and organizations from malicious activities.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
#technology#govindhtech#technews#news#dns#Domain Name System Security Extensions#ns1#cryptography#DNSSEC
0 notes
Text
Please visit
and
These two accounts have had the "Live" feature removed. The button just disappeared from the mobile app, and the PC site
just get redirected to
I have ANOTHER account with a domain that I paid for as well
All of which tend to cover subject matter regarding the integrity and quality of the platforms and devices diminishing over time. How the frequency of many series of events suggests discreet manipulation and interference from outside sources. Rabbit hole after rabbit hole, all signs point in one direction, but what does one do while withstanding a multifaceted attack? Both digitally and not.
In-person interventions, comments, and questions are not hidden behind a VPN or Contend Delivery Network which can disguise where cyber attackers are actually coming from. When interpersonal experiences, conversations or exchanges become subject matter of that I may be dealing with all on my own, unbeknownst to absolutely anyone, leaves me questioning how certain individuals become savvy of certain specific private, personal things. Things tend to get a bit overwhelming and completely unbelievable, the nature of the online and in person stalking, subtle harassment, and manipulation can seemingly become nefarious, even malicious. The best way that I can word it is that, things can get dark real quick.
There are people who like to do things in secrecy, guised as anything but it's actual identity, and will stop at no lengths to make sure the schemes, cohorts, and actions never become public knowledge. Unfortunately, it wouldn't matter if it did. That is because if given thought to the "allegations", my reporting, lead the rational mind to one of a few questions; "Why?; What did one do to deserve or attract this kind of attention." As things have seemingly calmed down for me, the act of creating this very post is putting myself in jeopardy. My employment, housing, and even safety can be taken from me, due to bringing light to nothing less that organized crime. The law may protect them due to the lack of ample, effective jurisdiction on the web/internet and tools like VPNs and device Unique Identifiers easily spoofed to anything at will.
Selective and community policing are a thing as well. When dealing with mass surveillance, perhaps someone(s) somewhere find my activities despicable, declaring me a deplorable. Made uncomfortable by societies in the community, both locally and at large, same goes for law enforcement and third even fourth parties. "Ran out of town", because I attempted to uncover their schemes and what their activities are, and how hypocritical "they" are. Perhaps that even the tables should be turned.
in other words:
These cyberattackers are not only operating online, but also offline. They have been stalking, harassing and manipulating me in person, using VPNs and CDNs to conceal their identities. They have somehow obtained access to my private and personal information, and have used it to intimidate and threaten me. They have made my life a nightmare, and I don’t know who to trust.
They are part of a secret network of people who are involved in organized crime. They don’t want the public to know about their schemes and activities, and they will stop at nothing to keep them hidden. They have the law on their side, because the internet is a lawless place where they can easily spoof their devices and locations. They also have the support of some communities and authorities who find my activities objectionable and want me gone.
I am risking everything by writing this post, but I feel that I have to warn you about the dangers of these cyberattackers. They are not only targeting me, but anyone who dares to expose them or challenge them. They are the enemy of the truth, and they must be stopped. The choice to believe me or not is yours, but remember: you have been warned.
#internet#networking#nyc#long island#cybersecurity#cyberattacks#cyberawareness#cyber angel#cyber aesthetic#espionage#crimes against humanity#exploitation#mystery#gangstalking#hacking#technology#keylogger#Activity Logger#monitization#monitorization#surveillance#new blog#followback#followforfollow#activism
0 notes
Text
Man-in-the-Middle Attack (MITM)

An MITM or Email Eavesdropping Attack occurs when someone alters the communication between two individuals without their knowledge.
Imagine a surreptitious eavesdropper in a conversation, redirecting while at the same time staying undetected. The essential goal is to get individual data, for example, login credentials, financial details, or other secret information. The parties included may accept they are straightforwardly speaking with one another however are uninformed that an unapproved outsider is actively intercepting or forging the data.
Man-in-the-middle attacks can occur in various contexts, including online transactions, email communication, and Wi-Fi networks. Attackers exploit vulnerabilities in the communication channel, taking advantage of the trust established between the legitimate parties to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information.
MITM Attack Examples
Wi-Fi Eavesdropping: Involves an attacker exploiting unsecured Wi-Fi networks, intercepting data exchanged between devices and the network.
DNS Spoofing: The attacker manipulates the Domain Name System (DNS) to redirect users to fraudulent websites.
Session Hijacking: Unauthorized access to sensitive information by taking control of an active session, like login credentials.
Email Tampering: Attackers can change emails, add malicious links, modify attachments, or create fake messages to trick people.
Phishing Attacks occur when individuals impersonate trusted sources in emails. They deceive people into revealing sensitive information such as passwords or financial details.
Email Spoofing: Attackers may forge the sender's address, making it appear as though an email is from a trusted source. This deceptive technique aims to manipulate recipients into taking actions they otherwise wouldn't.
For more information: https://rmail.com/glossary/man-in-the-middle-attack
0 notes
Text
DNS Poisoning: Unmasking the Threat and Safeguarding with Firewalls
In the realm of cybersecurity, DNS poisoning stands as a potent and deceptive attack method that can compromise the integrity of the Domain Name System (DNS).
For instance, ACTE Institute Bangalore offers comprehensive ethical hacking training courses that may provide you with the knowledge and skills necessary to excel in this field.

We will delve into the intricacies of DNS poisoning, exploring its impact and understanding how firewalls serve as vital guardians against this insidious threat.
Methods of DNS Poisoning:
Cache Poisoning: Attackers inject false DNS records into the cache of a DNS server. When the server receives a query for a specific domain, it responds with the manipulated IP address stored in its cache. This redirects users to fraudulent websites, leading to potential security compromises.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attack: In this scenario, attackers intercept DNS requests and responses between the client and the legitimate DNS server. By modifying the responses, they introduce false IP addresses, redirecting unsuspecting users to malicious sites or capturing their sensitive information.
How Firewalls Protect Against DNS Poisoning:
Firewalls play a pivotal role in defending against DNS poisoning attacks by employing several protective mechanisms:
Packet Filtering: Firewalls scrutinize network traffic at the packet level, analyzing source and destination IP addresses, ports, and protocols. By configuring the firewall to block or restrict suspicious or unauthorized DNS traffic, it becomes possible to prevent malicious DNS responses from infiltrating the network.
Stateful Inspection: Firewalls maintain a record of the state of network connections. By monitoring DNS traffic and cross-referencing DNS responses with the initiated DNS queries, firewalls can detect and block DNS replies that do not align with the expected results. This capability acts as an effective defense against DNS poisoning attempts.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention: Firewalls equipped with intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) possess the ability to identify and thwart DNS poisoning attempts. By analyzing DNS traffic patterns, behaviors, and anomalies, firewalls can detect suspicious activities and trigger appropriate countermeasures to mitigate the attack.
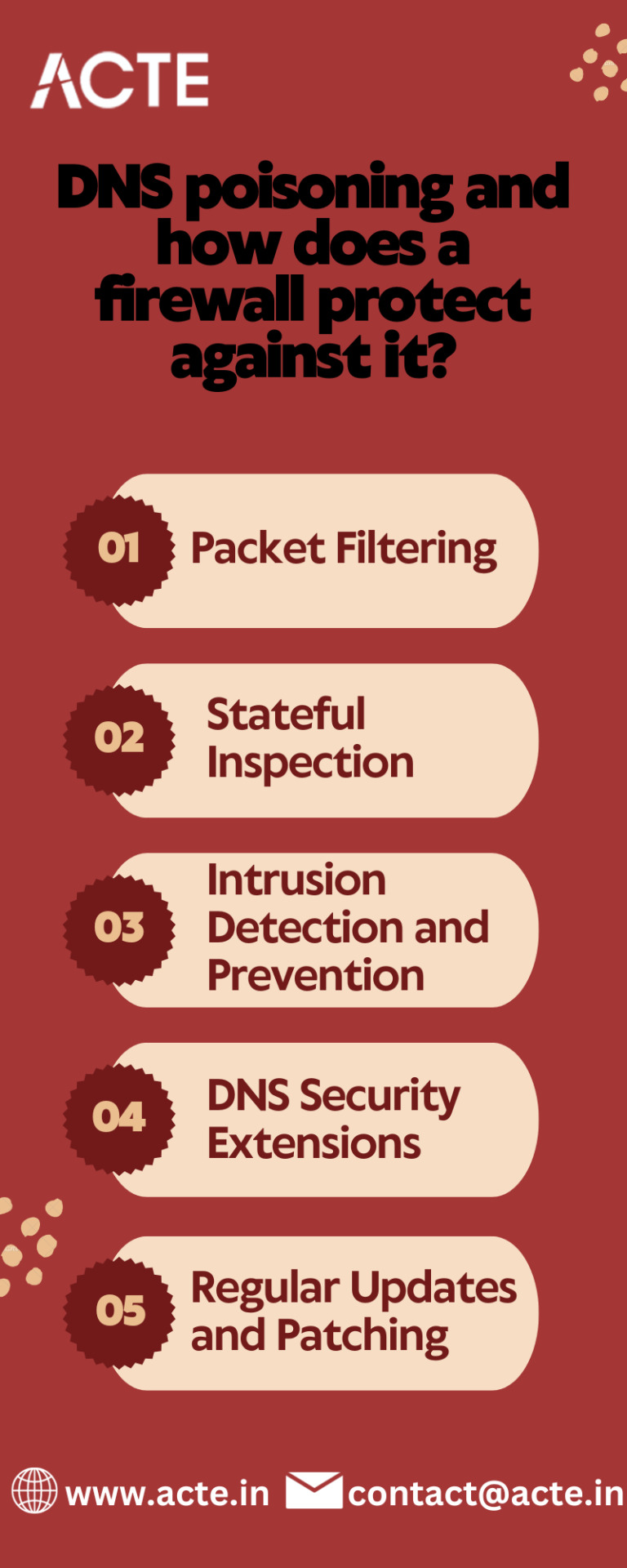
4. DNS Security Extensions (DNSSEC): Firewalls can support DNSSEC, a security protocol that adds digital signatures to DNS records. DNSSEC ensures the authenticity and integrity of DNS responses, making it significantly more challenging for attackers to poison the DNS cache. By validating DNS responses, firewalls reinforce the security of the DNS infrastructure.
5. Regular Updates and Patching: Firewalls should be regularly updated with the latest security patches and firmware releases. This practice ensures that known vulnerabilities, including those related to DNS poisoning, are promptly addressed. By keeping the firewall up to date, organizations can reduce the risk of successful DNS poisoning attacks.
DNS poisoning poses a severe threat to the DNS infrastructure and users’ security. By manipulating DNS caches and diverting user traffic, attackers can deceive individuals and expose them to malicious websites or intercept their sensitive information.
Firewalls act as the first line of defense against DNS poisoning by implementing packet filtering, stateful inspection, intrusion detection and prevention, supporting DNSSEC, and maintaining regular updates and patching. Organizations should prioritize robust firewall solutions and adhere to best practices to safeguard their networks, systems, and users from the grave risks associated with DNS poisoning.
Whether you’re a seasoned pro or just starting out, embracing ethical hacking opens up a world of exciting opportunities in the ever-evolving tech landscape. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting your journey, embracing Ethical Hacking Course in Bangalore opens up a world of opportunities in the ever-evolving tech landscape. Get ready to unleash the full potential of Hacking!
0 notes
Photo

New Post has been published on https://cryptonewsuniverse.com/online-safety-101-how-to-keep-cyber-snoopers-at-bay/
Online Safety 101 How to Keep Cyber Snoopers at Bay


Online Safety 101: How to Keep Cyber Snoopers at Bay

Have you ever paused to reflect on those emails from your bank urging you to update your information or the seemingly innocent act of connecting to your favorite coffee shop's Wi-Fi for a quick cup of joe? In the vast landscape of our digitally connected lives, have you ever entertained the thought of whether someone might be eavesdropping on your conversations?
In the contemporary world, where our daily routines intertwine seamlessly with digital communication, safeguarding the security and privacy of our online interactions has assumed a position of unparalleled significance. Alas, the challenge persists as cybercriminals continuously evolve, devising innovative methods to exploit vulnerabilities within our digital systems. Among these threats, the man-in-the-middle attack stands out as a particularly sophisticated and menacing technique, posing a substantial risk to the integrity of our digital security.
In this article, we explore the man-in-the-middle attack, unraveling its intricate workings, understanding its far-reaching implications, and, most importantly, arming ourselves with knowledge on how to shield against this pervasive cybercrime. Join us on this journey as we delve into the nuances of digital security and equip ourselves with the tools to navigate the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats.
Source: Imperva.com
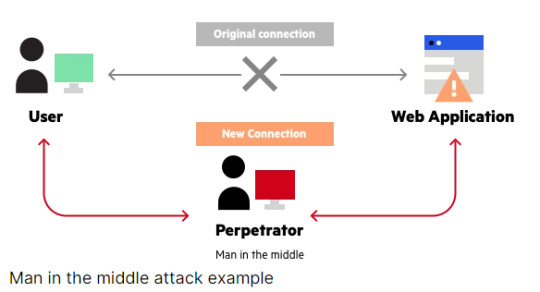
What is a Man-In-The-Middle Attack?
Imagine a scenario where your digital conversations aren't as private as you think; that's the unsettling reality of a man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack, a serious cybersecurity threat more pervasive than we might realize. In this digital battleground, an attacker sneaks into the communication channel between two unsuspecting parties, much like a sneaky postal worker sorting through your mail.
The term "man-in-the-middle" is fitting because, just like that rogue mailman, the attacker plants themselves right in the middle of the communication flow. It's akin to this mail mischief-maker intercepting your bank statement, jotting down your account details, and then sealing the envelope back up before it reaches your mailbox. The victim remains blissfully unaware of this intrusion.
So, why is this cyber maneuver so dangerous? Well, imagine the rogue mailman stealing not just your bank statement but also your login credentials, credit card numbers, and other personal details. That's what happens in an MITM attack. The attacker gains access to sensitive information, opening the door to identity theft, unauthorized fund transfers, and other malicious exploits.
What makes MITM attacks particularly treacherous is their stealthy nature. They can lurk undetected for long periods, silently pilfering information. It's like a silent invader setting up camp in your digital space without you even realizing it. Worse yet, these attacks can introduce malware onto your device, giving the attacker complete control over your system.
MITM attacks come in various shades, from the passive ones, where the attacker slyly intercepts user traffic, to the active ones, where the attacker actively manipulates or alters the data flow. It’s like different tactics in a cyber playbook – IP spoofing, DNS spoofing, HTTPS spoofing, and email spoofing, each with its own crafty strategy.

Source: ReadyTechGo.com
Interception
Have you ever gotten a sketchy message from an unknown number posing as your bank or an enticing email from a supposed unfamiliar angel promising a piece of his fortune? These seemingly harmless messages might just be the tip of the iceberg regarding a man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack, a favorite trick in the cyber criminal's playbook, where sensitive information is stolen from the unsuspecting victim.
So, what's the deal with interception, and how does it play into the whole MITM drama? Interception is like a digital sleight of hand with which the attacker slyly intercepts your online traffic before it reaches its intended destination. In the MITM attacks, the cyber trickster strategically positions themselves between two chit-chatting parties to either sneak a peek or slyly tweak the data passing between them.
The more straightforward and common form of MITM interception is where the attacker sets up a free Wi-Fi hotspot, maybe with a sneaky name like "CoffeeShop_FreeWiFi," and lures unsuspecting victims. Once connected, the attacker gets a backstage pass to all the victim's online data exchanges, kind of like a digital puppet master pulling the strings.
The attacker can spoof your IP and trick your computer into thinking it's hitting up a legitimate website when, in reality, it's a detour to the attacker's lair. Another move is DNS spoofing, where the attacker messes with your computer's GPS, sending it to the wrong digital address, aka their server, instead of the real deal. And who could forget HTTPS spoofing? This is like setting up a fake secure website, inviting victims to input their sensitive info, and then snatching it up like a digital pickpocket.
Email spoofing is another player in the MITM game. The attacker crafts an email that looks legit, maybe even mimicking a trustworthy source, to lull victims into a false sense of security. Once the victim bites, the attacker swoops in to nab the sensitive data. Here's the kicker: in all these cyber theatrics, the attacker stays incognito, a ghost in the machine, intercepting and manipulating data without the communicating parties having a clue. They might even drop malware on a targeted user's device, making themselves right at home.
Decryption
Alright, let's unravel the second act in the drama of a man-in-the-middle attack, which is decryption. Now that the digital trickster has nabbed the data sailing between two parties, it's time for the grand reveal. Decryption, in simple terms, is like translating a secret code back into something understandable.
In the wild landscape of a man-in-the-middle escapade, decryption is the secret sauce that turns the jumbled-up, encrypted data back into its original, readable form. Now, why is this a big deal? Well, it's the key to unlocking a treasure trove of sensitive info – think login credentials, financial details, and personally identifiable information (PII). The attacker unleashes this process to expose what was meant to be private and secure.
One classic thing the attacker does is known as the packet sniffer. A virtual detective captures and dissects the data zipping across the network. It's like intercepting letters and reading them before they reach the recipient. Sneaky, right? Then there's the brute-force attack, a cyber brute trying every password combination until it hits the jackpot. It's like trying every key in the bunch until one finally opens the door. Another trick up the attacker's sleeve is the rainbow table attack, which is a cheat sheet of pre-computed encrypted passwords, speeding up the process of finding the original password. It's the cyber equivalent of having a master key.
But why should we care about decryption? Well, if the attacker succeeds, they waltz right into sensitive information territory. This can lead to identity theft, fraud, and other malicious endeavors. Plus, decryption is like the golden ticket for installing malware on a targeted user's device, the cyber version of an uninvited guest overstaying their welcome.
Prevention
Now that we've uncovered the ins and outs of man-in-the-middle attacks and how these sneaky maneuvers go down let's arm you with the knowledge to steer clear of falling victim to them. Lucky for us, there are several effective methods to keep these digital tricksters at bay. Let's dive into some savvy ways to keep yourself in the clear:
1. Embrace the Power of VPNs:
Think of a Virtual Private Network (VPN) as your digital superhero cape. It encrypts all your internet traffic and guides it through its own secure servers. Even if an attacker tries to intercept your data, they'll just be staring at a wall of encryption. It's like sending your online messages in an unbreakable code.

Source: Markethive.com
2. HTTPS and SSL/TLS:
This dynamic duo of HTTPS and SSL/TLS transforms your internet communication into a secret language. When you visit a website using HTTPS, just like Markethive does, your browser locks arms with the website's server in a secure handshake. An attacker attempting to eavesdrop finds nothing but encrypted gibberish. It's like turning your online conversations into an encrypted treasure chest.
3. Safeguard with Email and DNS Security:
Email and DNS can be the Trojan horses of MITM attacks, but fear not! Strengthen your defenses with email security tools like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC to verify the legitimacy of your emails. For DNS, enlist the help of a secure resolver to ensure your DNS requests aren't being intercepted. It's like adding an extra layer of protection to your digital communication channels.
Sender Policy Framework (SPF), DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM), and Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC) are email security tools that can help you protect your emails from spoofing, phishing, and spam. They work by verifying the sender’s identity and the integrity of the email content.
4. Double Down with Two-Factor Authentication (2FA):
Think of 2FA as having a bouncer at the entrance to your digital party. It requires a password and a second form of verification, like a code sent to your phone. This tag team ensures that only you get VIP access. It's like having a secret handshake for your online accounts.
5. Arm Yourself with Anti-virus Software:
Consider anti-virus software as your digital bodyguard. It scans, detects, and blocks potential threats, acting as a shield against MITM attacks. Keep it up-to-date to stay one step ahead of the cyber baddies.
6. Keep Software Updated:
Updating your software is like giving your digital fortress a fresh coat of paint. Hackers often exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software, so ensure your operating system, web browser, and other applications are rocking the latest security patches. It's like fortifying your defenses against unseen invaders.
It's essential you understand that by weaving these prevention methods into your digital routine, you significantly reduce the risk of becoming a victim of a man-in-the-middle attack. Remember, an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure. So, gear up, stay vigilant, and keep the online baddies at bay!
Detecting a Man-In-The-Middle Attack
Detecting a man-in-the-middle attack can be subtle, but it’s important to stay alert. The first sign something’s off will likely be a slowdown in internet or network speed. If you notice it taking longer than usual to load pages, watch out; you might be under attack. The next sign is a pop-up error message. These error messages can appear for several reasons, but if the error message says, “The security certificate presented by this website is not secure,” that’s a red flag. An improper security certificate is a definite sign that the website is not secure and may have been compromised.
Network Monitoring is essential in detecting a man-in-the-middle attack. Network monitoring tools come in various shapes and sizes. They keep track of network traffic, identify traffic patterns, and check for suspicious behavior. SSL Certificate Warnings are some of the most common ways web browsers detect a Man-in-the-Middle Attack.
When attempting to visit a website with an invalid certificate, the browser warns its user of its dangers, often citing the risk of middleman attacks. Suspicious Network Activity is another sign. If your network administrator or ISP has monitoring tools in place, unusual network activity can quickly raise a red flag. DNS Spoofing Detection Tools can help detect DNS hijacking and monitor suspicious activity on your network.
It's always best to have multiple lines of defense when trying to detect a man-in-the-middle attack. Using a combination of techniques and tools is key to recognizing suspicious activity before it's too late. Remember, prevention is always the best defense. Staying vigilant and using the preventive measures outlined in the previous section is vital.
Examples of Man-In-The-Middle Attacks
As you might have figured out by now, man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks are pretty dangerous. They are used to steal sensitive information from various targets, including users of financial applications, e-commerce sites, and SaaS businesses. Such attacks can also gain entry into a secure network by installing malware on a user's device.
But let's dive deeper and look at some real-life instances of man-in-the-middle attacks that have occurred. In 2010, an Iranian hacker used a man-in-the-middle attack to access the Gmail accounts of several high-profile individuals, including US government officials and journalists. The attacker created a fraudulent security certificate for Google services, which allowed them to intercept email communication.
DigiNotar, a Dutch certificate authority that the hacker compromised, issued the security certificate. The hacker bypassed the HTTPS encryption that usually protects the communication between a user and a website. The hacker also used a technique called DNS spoofing, which involves changing the DNS records of a domain name to point to a malicious server. This way, the hacker could redirect the users to a fake Google website that looked identical to the real one but was under the hacker’s control.
In 2011, at a Black Hat conference, a researcher named Nicholas Percoco and his colleague Christian Papathanasiou showed how easy it was to run a man-in-the-middle attack on mobile devices running iOS and Android. The attack involved intercepting data packets between a mobile device and a wireless access point using a tool called SSLstrip.
SSLstrip is a tool that can downgrade HTTPS connections to HTTP connections and strip away the encryption that normally protects the communication between a user and a website. The tool can also modify the content of the web pages that the user sees, such as replacing the padlock icon with a fake one or inserting malicious links or scripts.
The researchers demonstrated how they could use SSLstrip to hijack a user’s Facebook session, steal their login credentials, and post messages on their behalf. They also showed how to intercept a user’s email communication, read their messages, and send spoofed emails. They also revealed how to access a user’s online banking account, view their balance, and transfer money to another account.
One of the most widespread man-in-the-middle attacks in recent times is the "Superfish" incident. Lenovo shipped its laptops with adware called "Superfish," designed to serve targeted ads to users. However, Superfish was designed to intercept HTTPS traffic, leaving users vulnerable to MITM attacks.
Another example of a widespread MITM attack is the WannaCry ransomware attack that took place in 2017. The WannaCry ransomware was propagated via a vulnerability in Windows systems and encrypted users' files, demanding a ransom for decryption. This sophisticated ransomware attack attacked several government agencies, businesses, and individuals worldwide.
While most man-in-the-middle attacks aim to steal user data, some use MITM attacks to target companies and individuals. For instance, during the Syrian civil war, the SEA (Syrian Electronic Army) carried out a targeted MITM attack against the Associated Press (AP) Twitter account. The SEA used the account to post fake news about an explosion at the White House, causing a significant drop in the stock market. While man-in-the-middle attacks might not be new, the stakes are increasing with new technologies such as Artificial Intelligence. So, it's crucial that you stay informed of such attacks and take the necessary precautions to protect your data.

Source: Cyber Security News
Security analysts discovered one recent incident of an MITM attack in April 2023. The attack targeted Wi-Fi networks and could bypass their security mechanisms. The attacker operated by imitating the genuine access point and transmitting a forged Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) to redirect the message to a targeted supplier. ICMP is a protocol used to send error messages and other information between network devices.
A redirect message is an ICMP message that tells a device to use a different route to reach a destination. By sending a forged redirect message, the attacker could trick the device into sending its traffic through a malicious router, where the attacker could intercept and modify it. This way, the attacker could hijack any device's traffic connected to the Wi-Fi network and perform various malicious activities, such as stealing passwords, injecting ads, or redirecting users to phishing websites.
Conclusion
So, we know these attacks are dangerous and can happen to anyone, anywhere, at any time. From intercepting personal information to potentially installing malware, cybercriminals will stop at nothing to get what they want, which is why it's so important to be aware of the risks posed by man-in-the-middle attacks.
We've gone over a few key steps to prevent becoming a victim, like using a VPN, HTTPS, SSL/TLS, email and DNS security, and two-factor authentication. It's also essential to keep your software up-to-date and be aware of suspicious network activity. But even with these precautions, it's not always possible to avoid a man-in-the-middle attack, so it's important to know how to detect one if it does happen.
Whether it's noticing strange SSL certificate warnings or monitoring network activity, early detection can be the difference between a minor inconvenience and a major data breach. And while it's easy to feel overwhelmed by the thought of cybercriminals lurking around every corner, being aware of the risks posed by man-in-the-middle attacks is the first step toward protecting yourself.
Remember, attacks like these can happen to anyone. Still, you can minimize your risk and stay safe in an increasingly dangerous digital world by remaining vigilant and taking the necessary precautions. So, whether you're shopping online, checking your bank account, or browsing the web, remember to stay alert, stay safe, and watch for those pesky man-in-the-middle attacks. After all, when it comes to online security, a little awareness can go a long way to save you from disaster.


About: Prince Ibenne. (Nigeria) Prince is passionate about helping people understand the crypto-verse through his easily digestible articles. He is an enthusiastic supporter of blockchain technology and cryptocurrency. Find me at my Markethive Profile Page | My Twitter Account | and my LinkedIn Profile.
0 notes
Text
Ransomware tales: The MitM attack that really had a Man in the Middle

Source: https://nakedsecurity.sophos.com/2023/05/24/ransomware-tales-the-mitm-attack-that-really-had-a-man-in-the-middle/
More info: https://serocu.police.uk/man-convicted-of-blackmail-and-other-offences/
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cyber Security: A Comprehensive Overview and 6-Month Program

Cyber security is the practice of protecting systems, networks, and data from cyber attacks. In today's increasingly digital world, cyber security is more important than ever. Businesses, organizations, and individuals all face significant cyber threats, and the need for skilled cyber security professionals is growing rapidly.
Why is cyber security important?
Cyber attacks can have a devastating impact on businesses and organizations of all sizes. They can lead to data breaches, financial losses, reputational damage, and even operational disruptions. Cyber attacks can also have a significant impact on individuals, leading to financial losses, identity theft, and other forms of harm.
What are the different types of cyber attacks?
There are many different types of cyber attacks, but some of the most common include:
Malware attacks: Malware is malicious software that can damage or disable computer systems or steal data.
Phishing attacks: Phishing attacks involve sending fraudulent emails or text messages that appear to be from a legitimate source in order to trick people into revealing sensitive information or clicking on malicious links.
Ransomware attacks: Ransomware attacks involve encrypting a victim's data and demanding a ransom payment in exchange for the decryption key.
Denial-of-service (DoS) attacks: DoS attacks involve flooding a website or server with traffic, making it unavailable to legitimate users.
Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks: MitM attacks involve intercepting communication between two parties and impersonating one of them in order to steal data or modify the communication.
How can you protect yourself from cyber attacks?
There are a number of things you can do to protect yourself from cyber attacks, including:
Use strong passwords and multi-factor authentication.
Be careful about what links you click on and what attachments you open.
Keep your software up to date.
Use a firewall and antivirus software.
Be aware of social engineering scams.
6-Month Cyber Security Program
If you are interested in a career in cyber security, Xaltius Academy offers a 6-month cyber security program that will teach you the skills and knowledge you need to be successful. The program covers a wide range of topics, including:
Networking fundamentals
Security fundamentals
Operating system security
Penetration testing
Incident response
Ethical hacking
The program is taught by experienced cyber security professionals and includes hands-on exercises and projects. Upon completion of the program, you will be prepared to enter the cyber security workforce.
Conclusion
Cyber security is a critical issue in today's digital world. By taking steps to protect yourself from cyber attacks and pursuing a career in cyber security, you can make a difference in helping to keep people and organizations safe.
0 notes
Text
The Impact of Payment Fraud on SMBs and How to Outsmart It

If you’re a business owner, especially in the small-to-medium segment, this post might just be your trusty shield against the mischievous world of payment fraud. Here, we’ll dive deep into the ocean of payment fraud management surface with insights, and emerge unscathed by the potential dangers. Let’s begin, shall we?
The Unsettling Reality of Payment Fraud in SMBs
The buzz around large corporations and their battles with payment fraud often overshadows the struggles of smaller entities. But in truth, Small and Medium-sized Businesses (SMBs) are frequently targeted because they often lack the resources and infrastructures for comprehensive payment fraud management. It’s like when a bully targets the quieter kid in the class, thinking they won’t fight back.
The direct consequences for SMBs are substantial. A single act of fraud can significantly damage the revenue stream, strain relationships with customers, and deter potential clients. Think of it this way: while a whale might tolerate a few barnacles, for a smaller fish, they can be life-threatening.
Moreover, apart from the direct financial loss, the reputational damage can be irreversible. Customers trust businesses with their data, and a breach shatters that trust. Unfortunately, in the SMB landscape, regaining lost trust can be a herculean task.
The Sneaky Faces of Payment Fraud
Before we delve into the world of prevention, it’s essential to understand the different avatars fraud can assume. Yes, the villains have multiple disguises.
Phishing is the most infamous type, where fraudsters attempt to acquire sensitive information like usernames and passwords by masquerading as a trustworthy entity. Then there’s carding: a brute force attack that uses multiple credit card data until one finally works.
The most sophisticated one, perhaps, is Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks. Here, the fraudster secretly relays and possibly alters the communication between the two parties. So while you think you’re paying a trusted source, you’re channeling funds into a fraudster’s pocket. The world of payment fraud is truly as sneaky as it sounds, making payment fraud management even more crucial.
Why SMBs? The Unfortunate Appeal
The big question: why are SMBs often the preferred target? Well, imagine you’re a thief. Would you choose a fortified castle with guards at every nook or a cozy cottage? SMBs, with their limited resources, unfortunately, resemble the latter.
Firstly, SMBs often don’t have dedicated teams for payment fraud management. Instead, they rely on smaller teams to manage vast aspects of the business, from sales to security. This stretched-thin approach, although resourceful, provides an easy gap for fraudsters to exploit.
Furthermore, with limited financial resources, SMBs might hesitate to invest in top-notch security measures. It’s like having a basic lock on your door in a neighborhood known for its master key thieves. Fraudsters know this and make a beeline for these vulnerable businesses.
Lastly, the adaptability of SMBs, which is generally their strength, becomes their Achilles’ heel. They often integrate new technologies quickly without thorough security vetting. This eagerness, though commendable, can sometimes leave the back door open for unwanted guests.
Crafting Your Defense: Five Payment Fraud Management Essentials
Diving into the intricacies of payment fraud might sound daunting, but fortifying your business doesn’t have to be a Herculean task. Let’s navigate through some comprehensive steps to bolster defenses for your SMB.
1. Awareness: Your Proactive Weapon
Your first weapon against fraud is being proactive. And that begins with awareness. Dive deep into the latest fraud trends, techniques, and methodologies. Make it a routine, much like checking the weather forecast before heading out.
The more you know about the storm, the better you can prepare. Just as meteorologists use past data to predict future weather patterns, you can employ previous fraud data to foresee and sidestep potential threats.
2. Investing in State-of-the-Art Payment Fraud Management Systems
In the digital age, where everything gets smarter by the minute (phones, homes, cars – you name it), it’s vital that your payment fraud management system is up-to-date. While the initial investment may seem hefty, think of it as constructing a moat around your fortress.
Over time, this moat pays dividends by preventing potential losses and maintaining customer trust. These systems not only provide real-time alerts on suspicious activities but also evolve using machine learning, predicting and thwarting attacks before they even occur.
3. Empowering Your Troops: Training Your Team
Your employees are the knights guarding the castle. Equip them with sharp swords and unbreakable shields. How? By training them on the nuances of payment fraud management.
Host regular workshops, engage with cybersecurity experts for sessions, and simulate fraud scenarios to test their preparedness. By making every member of your team a watchdog, you multiply your defense mechanisms exponentially.
4. Adopting a Multi-Layered Security Approach
Don’t just rely on one defense mechanism. Layer it up. Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) for transactions, employ end-to-end encryption for customer data, and regularly back up your data to a secure location.
Think of these layers as the walls, trenches, and watchtowers of your fortress. Each layer makes it exponentially harder for fraudsters to breach, leaving them frustrated and your business secure.
5. Constantly Reassess and Adapt
The world of cyber threats is continually evolving. What worked as a robust defense mechanism yesterday might be obsolete tomorrow. Hence, make it a habit to regularly reassess your strategies.
Engage third-party agencies for vulnerability assessments and penetration testing. Their external perspective might highlight potential gaps you missed and offer fresh insights on fortifying your defenses.
The Role of Community and Collaboration
No SMB is an island. By fostering a strong community, SMBs can band together to share insights, resources, and best practices related to payment fraud management.
Many regional business associations host seminars and training sessions on cybersecurity. Participating in these can offer a wealth of information and an opportunity to network with businesses that have faced similar challenges.
Moreover, in the age of the internet, online forums and communities are treasure troves of advice and experiences. Sometimes, the best defense is a collective one. After all, it’s harder to breach a wall made up of many bricks than one standing alone.
Beyond Prevention: A Culture of Security
To truly safeguard against payment fraud, prevention is just the first step. What SMBs should strive for is fostering a culture of security.
This means integrating security into every facet of business operations. It’s not just about having a payment fraud management system; it’s about making every team member, from the CEO to the intern, a vigilant watcher against potential threats. For more details contact us today at https://premierpaymentsonline.com/contact-us/.
Periodic security audits, engaging with cybersecurity consultants, and ensuring that security isn’t an afterthought but a business priority will make all the difference. This isn’t just about preventing financial loss but safeguarding the very essence and reputation of your business.
Conclusion
The world of SMBs is dynamic, resilient, and vibrant. However, the looming shadow of payment fraud can often be a dampener. But, with a mix of awareness, tools, community support, and a strong security culture, SMBs can not only defend against these threats but thrive despite them.
After all, in the grand saga of business, let’s ensure that the heroes (that’s you, dear SMBs) always triumph over the villains. Remember, the keyword to your saga’s success is robust payment fraud management. Stay safe, stay vigilant, and here’s to a fraud-free business journey.
Read More:
https://premierpaymentsonline.com/sb/accept-credit-card-payments-instantly-with-these-4-strategies/
0 notes
Text
Internet of Things Security Is More Challenging Than Cybersecurity
Free Information about the Internet of Things and IoT security
Internet of Things (IoT)
A network of smart gadgets known as the “Internet of Things” connects and uses the internet to exchange data without the need for human involvement.
Wireless networks, cloud databases for communication, sensors, data processing software, and interconnected smart devices make up the structure of IoT systems in most cases.
IoT security
IoT security is the set of policies, procedures, systems, technologies, and techniques used to protect the Internet of Things (IoT). It covers all aspects of defence, such as hardening components, monitoring, updating firmware, controlling access, detecting threats, and patching vulnerabilities. IoT security systems are dispersed and exposed, making them extremely specific attack vectors. Protecting IoT devices from unwanted access can prevent them from leaking important data or acting as a gateway into other areas of the network.
Everything from smart grids and cars to watches and smart home gadgets has IoT security flaws. Researchers discovered vulnerabilities in webcams and smartwatches that allowed hackers to listen in on conversations and monitor the wearer’s location.
Importance of IoT security
IoT is regarded as one of the most important security problems because it affects almost everyone, including businesses, governments, and consumers. Despite the benefits and accessibility that IoT devices provide, there are absurdly high risks involved. It is crucial to ensure IoT security since these gadgets give hackers a broad and accessible attack surface.
IoT security offers these exposed devices the essential safeguards they require. IoT system developers are renowned for putting more emphasis on device functionality than security. This emphasizes the significance of IoT security and the need for users and IT teams to be in charge of putting safeguards in place.
Challenges of IoT security
Insufficient visibility
IoT devices are often deployed without IT departments’ knowledge, making it difficult to ensure their security and monitoring.
Limited integration of security
IoT device integration into security systems can be challenging or futile due to their diversity and size.
Open-source software flaws
IoT device firmware frequently uses open-source software, which can have faults and vulnerabilities.
Overwhelming amount of data
Data supervision, management, and protection are challenging due to the volume of data created by IoT devices.
Improper testing
The majority of Internet of Things (IoT) developers do not prioritize security; hence, they do not effectively conduct vulnerability testing to find flaws in IoT systems.
Unpatched problems
For a variety of reasons, including the lack of fixes and challenges in accessing and installing them, many IoT devices have vulnerabilities that have not yet been patched.
Insecure APIs
APIs are frequently used as entry points to attack command and control centers, from which assaults like SQL injection, distributed denial of service (DDoS), man-in-the-middle (MITM), and network intrusion are launched.
Incorrect passwords
IoT devices frequently come with default passwords that many users don’t update, making it simple for cybercriminals to access them. Sometimes users create weak passwords that are easy to guess.
How to prevent IoT devices from Cyberattacks
1. Unique Passwords
Devices connected to the IoT should be secured before connecting to the network. Use strong passwords, keep the security software on these devices up to date, encrypt the device, and authenticate it to accomplish this.
2. Modify the default passwords
Cybercriminals are likely to know the default passwords that are provided with many IoT devices. It implies that to prevent unauthorized access to one’s IoT devices, users should modify their default passwords.
3. Establish Guest Networks
Wi-Fi and network connections must be secured with strong passwords. To secure your IoT devices and prevent hackers from gaining access to the connection, guest networks must also be set up.
4. Review the Setup Settings
There are default privacy and security settings on a lot of IoT devices. One should check and modify them to prevent uncertainty and cyberattacks. The device maker may benefit from some default settings.
5. Keep updating the device
Manufacturers of Internet of Things devices may send updates for updating and installing new security software, just like mobile device manufacturers do. Also, you can monitor their websites for updates and IoT security.
Conclusion
The security of IoT projects must be evaluated. The complexity of finding possible system vulnerabilities and the frequency of cyberattacks make it challenging to install adequate security mechanisms. Security measures can make IoT devices more expensive and take longer to construct, so IoT software and quality assurance experts are needed to provide safe devices.
0 notes