#drv clinic
Text
Double Chin Treatment London | DRV Clinic
Say goodbye to your double chin with our non-surgical treatment in London. Experience effective chin fat dissolving injections for a sculpted jawline. Trust DRV Clinic to deliver personalized treatments tailored to your needs, bringing out the best version of you.
0 notes
Text
Structural Adaptation of Darunavir Analogs Against Primary Resistance Mutations in HIV-1 Protease
HIV-1 protease is one of the prime targets of agents used in antiretroviral therapy against HIV. However, under selective pressure of protease inhibitors, primary mutations at the active site weaken inhibitor binding to confer resistance. Darunavir (DRV) is the most potent HIV-1 protease inhibitor in clinic; resistance is limited, as DRV fits well within the substrate envelope. Nevertheless, resistance is observed due to hydrophobic changes at residues including I50, V82 and I84 that line the S1/S1’ pocket within the active site. Through enzyme inhibition assays and a series of 12 crystal structures, we interrogated susceptibility of DRV and two potent analogs to primary S1’ mutations. The analogs had modifications at the hydrophobic P1’ moiety to better occupy the unexploited space in the S1’ pocket where the primary mutations were located. Considerable losses of potency were observed against protease variants with I84V and I50V mutations for all three inhibitors.
The crystal structures revealed an unexpected conformational change in the flap region of I50V protease bound to the analog with the largest P1’ moiety, indicating interdependency between the S1’ subsite and the flap region. Collective analysis of protease-inhibitor van der Waals (vdW) interactions in the crystal structures using principle component analysis indicated I84V mutation underlying the largest variation in the vdW contacts. Interestingly, the principle components were able to distinguish inhibitor identity and relative potency solely based on vdW interactions of active site residues in the crystal structures. Our results reveal the interplay between inhibitor P1’ moiety and primary S1’ mutations, as well as suggesting a novel method for distinguishing the interdependence of resistance through principle component analyses.
0 notes
Photo

One of my favorite #Seuss #quotes4soaring . . . . . #quotestagram #readacrossamerica #readacrossamericaweek #drseussweek #thecatinthehat #instaquote #medico #doctor #nurse #drv #seuss #clinical #quotestoliveby #drseussday #qotd #happybirthdaydrseuss #drseuss #dailyquote #quote #doctor #lifequotes #inspirationalquotes #catinthehat #quotes #quoteoftheday #quotesoftheday #dr via @hashtagexpert (at Summerville, South Carolina) https://www.instagram.com/p/B91FQ8Mljfs/?igshid=t05cddairrt5
#seuss#quotes4soaring#quotestagram#readacrossamerica#readacrossamericaweek#drseussweek#thecatinthehat#instaquote#medico#doctor#nurse#drv#clinical#quotestoliveby#drseussday#qotd#happybirthdaydrseuss#drseuss#dailyquote#quote#lifequotes#inspirationalquotes#catinthehat#quotes#quoteoftheday#quotesoftheday#dr
1 note
·
View note
Text
Exploring Potential Synergism Between Darunavir/Cobicistat and Ribavirin for the Treatment of Covid-19 Patients: A Retrospective Comparison Study: OAJBS Publishers
Exploring Potential Synergism Between Darunavir/Cobicistat and Ribavirin for the Treatment of Covid-19 Patients: A Retrospective Comparison Study by Reem Elajez* in Open Access Journal of Biomedical Science (OAJBS)
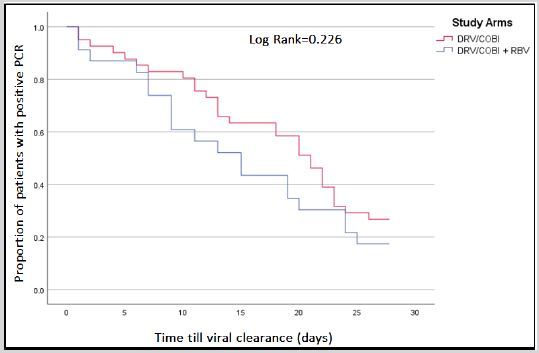
Objective: Exploring potential synergistic effect of darunavir/cobicistat (DRV/COBI) plus ribavirin (RBV) in COVID-19 treatment.
Methods: Retrospective, observational comparison study conducted in Qatar. Adult patients with confirmed positive SARSCoV-2 who received either DRV/COBI or DRV/COBI+RBV were included. Primary outcome was time to viral clearance, while secondary outcomes. include clinical improvement (resolution of fever/tachypnea), development of acute respiratory distress syndromes (ARDS) and 28-days all-cause mortality, and incidence of adverse reactions.
Results: Sixty-four patients were included (41 received DRV/COBI and 23 received DRV/COBI+ RBV). Mean age of patients was 48.4±14.6 years with predominant male gender (58/64; 90.6%). Median time from starting therapy till viral clearance was 11 days in DRV/COBI+RBV vs. 16 days in DRV/COBI groups (P=0.295). At day-28, viral clearance was observed in 82.6% (19/23) and 73.2% (30/41) in DRV/COBI+RBV and DRV/COBI groups, respectively (P=0.392). Patients receiving DRV/COBI+RBV did not achieve faster resolution of fever or tachypnea compared to those receiving DRV/COBI. Three patients in DRV/COBI+RBV group developed ARDS, while none in DRV/COBI group. Frequency of hemoglobin drop of ≥2g/dl was significantly higher in DRV/COBI+RBV group than in DRV/COBI group (34.8% vs. 7.9%, P=0.008, respectively).
Conclusion: Use of darunavir/cobicistat plus ribavirin was not associated with faster viral clearance or better clinical outcomes.
https://biomedscis.com/fulltext/exploring-potential-synergism-between-darunavir-cobicistat-and-ribavirin-for-the-treatment-of-covid-19-patients-a-retrospective-comparison-study.ID.000262.php
To Know More About Open Access Journal of Biomedical Science Please Visit: Biomedscis
Are Click on: https://Biomedscis.Com/
#OAJBS#Biomedscis#Open Access Journal of Biomedical Science#Open Access Journal of Biomedical Science and Research
0 notes
Text
Liposome Drug Delivery Market to Witness Comprehensive Growth by 2025
Liposomes are small spherical-shaped artificial vesicles synthesized from phospholipids and cholesterol. They are colloidal carriers and range from 0.01 to 5.0 μm in diameter. These are lipid bilayer vesicles having hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties. Due to these properties liposomes have an advantage of encapsulating hydrophobic as well as hydrophilic drugs and delivering them to the targeted site in the body. Thus, liposomes are promising systems for targeted drug delivery. Liposomes are successfully used for encapsulating various drug molecules such as acyclovir, tropicamaide, chloroquine diphosphate, paclitaxel, and cyclosporine. Many therapeutic agents such as antimicrobials, anticancer drugs, genetic materials, vaccines, macromolecules, and proteins can be encapsulated in liposomes. Liposomes are employed as drug carriers for targeted drug therapy for various diseases, as they are biocompatible and biodegradable.
The classification of liposomes is based on its structural properties or on the method of preparation used. Structurally, liposomes are classified into the following groups: multilamellar large vesicles (MLV), oligolamellar vesicles (OLV), unilamellar vesicles (UV), small unilamellar vesicles (SUV), medium-sized unilamellar vesicles (MUV), large unilamellar vesicles (LUV), giant unilamellar vesicles (GUV), and multivesicular vesicles (MVV). In terms of preparation method used, liposomes can be classified into the following types: reverse phase evaporation method for single or oligolamellar vescile (REV), multilamellar vesicles (MLV) made by reverse phase evaporation method, stable plurilamellar vesicles, (FATMLV) frozen and thawed, vesicles prepared by extrusion method (VET), vesicles prepared by fusion (FUV), vesicles prepared by french press (FPV), dehydration?rehydration vesicles (DRV), and bubblesomes (BSV).
Development in scientific research in recent years has led to the rapid expansion of the global Liposome Drug Delivery Market. Increased understanding of targeted drug delivery system has fuelled the liposome drug delivery system market. Advantages such as improvement and control over pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, decreased toxicity, and enhanced activity of drugs against intracellular pathogens are key divers for pharmaceutical companies to invest in the global liposomes drug delivery market. Currently, there are a number of liposomal products such as ambisome, myocet, doxil, depoCyt, etc., approved by the FDA for commercial usage. However, low solubility, short half-life and high production cost are key restraints of the global liposome drug delivery market.
Request to View Brochure of Report -
https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/sample/sample.php?flag=B&rep_id=28571
In terms of type of industry, the liposome drug delivery market can be segmented into pharmaceutical, cosmetic, food, and farming. The pharmaceutical industry segment led the global liposomes market due to rapid advancements in targeted drug delivery systems. In terms of product, the market can be segmented into liposomal doxorubicin, liposomal amphoteracin B, and liposomal paclitaxel. Liposomal amphoteracin B is used in the treatment of various fungal and parasitic infections. In terms of application, the global liposomes drug delivery market can be segmented into therapeutic and clinical. Therapeutic applications include occular and pulmonary applications, whereas clinical applications consists of cancer (antitumor) therapy and fungal and microbial infection therapy. Ongoing research and advancement in liposome design are leading to new applications for the delivery of new biotechnology products such as recombinant proteins antisense oligonucleotides and cloned genes.
In terms of geography, the global liposomes drug delivery market can be segmented into North America (Canada, the U.S., and Mexico), Europe (Germany, France, the U.K., Russia, and Italy), Asia Pacific (Japan, China, Korea, India, and Southeast Asia), Latin America, and Middle East & Africa. North America is a leading market for liposomes drug delivery systems due to increase in novel technologies in targeted drug delivery systems. The market is anticipated to expand during the forecast period in other parts of the globe as well.
Request to View ToC of the report -
https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/sample/sample.php?flag=T&rep_id=28571
Prominent manufacturers operating in the global liposome drug delivery market include Johnson & Johnson, Sun Pharmaceutical, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Novartis AG, Gilead Sciences, Inc., Kingond Pharm, and Celsion Corporation.
0 notes
Text
Liposome Drug Delivery Market Size, Application Analysis, Regional Outlook, 2017 - 2025
Liposomes are small spherical-shaped artificial vesicles synthesized from phospholipids and cholesterol. They are colloidal carriers and range from 0.01 to 5.0 μm in diameter. These are lipid bilayer vesicles having hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties. Due to these properties liposomes have an advantage of encapsulating hydrophobic as well as hydrophilic drugs and delivering them to the targeted site in the body. Thus, liposomes are promising systems for targeted drug delivery. Liposomes are successfully used for encapsulating various drug molecules such as acyclovir, tropicamaide, chloroquine diphosphate, paclitaxel, and cyclosporine. Many therapeutic agents such as antimicrobials, anticancer drugs, genetic materials, vaccines, macromolecules, and proteins can be encapsulated in liposomes. Liposomes are employed as drug carriers for targeted drug therapy for various diseases, as they are biocompatible and biodegradable.
Read Report Overview:
https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/liposome-drug-delivery-market.html
The classification of liposomes is based on its structural properties or on the method of preparation used. Structurally, liposomes are classified into the following groups: multilamellar large vesicles (MLV), oligolamellar vesicles (OLV), unilamellar vesicles (UV), small unilamellar vesicles (SUV), medium-sized unilamellar vesicles (MUV), large unilamellar vesicles (LUV), giant unilamellar vesicles (GUV), and multivesicular vesicles (MVV). In terms of preparation method used, liposomes can be classified into the following types: reverse phase evaporation method for single or oligolamellar vescile (REV), multilamellar vesicles (MLV) made by reverse phase evaporation method, stable plurilamellar vesicles, (FATMLV) frozen and thawed, vesicles prepared by extrusion method (VET), vesicles prepared by fusion (FUV), vesicles prepared by french press (FPV), dehydration?rehydration vesicles (DRV), and bubblesomes (BSV).
Development in scientific research in recent years has led to the rapid expansion of the global liposome drug delivery market. Increased understanding of targeted drug delivery system has fuelled the liposome drug delivery system market. Advantages such as improvement and control over pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, decreased toxicity, and enhanced activity of drugs against intracellular pathogens are key divers for pharmaceutical companies to invest in the global liposomes drug delivery market. Currently, there are a number of liposomal products such as ambisome, myocet, doxil, depoCyt, etc., approved by the FDA for commercial usage. However, low solubility, short half-life and high production cost are key restraints of the global liposome drug delivery market.
In terms of type of industry, the liposome drug delivery market can be segmented into pharmaceutical, cosmetic, food, and farming. The pharmaceutical industry segment led the global liposomes market due to rapid advancements in targeted drug delivery systems. In terms of product, the market can be segmented into liposomal doxorubicin, liposomal amphoteracin B, and liposomal paclitaxel. Liposomal amphoteracin B is used in the treatment of various fungal and parasitic infections. In terms of application, the global liposomes drug delivery market can be segmented into therapeutic and clinical. Therapeutic applications include occular and pulmonary applications, whereas clinical applications consists of cancer (antitumor) therapy and fungal and microbial infection therapy. Ongoing research and advancement in liposome design are leading to new applications for the delivery of new biotechnology products such as recombinant proteins antisense oligonucleotides and cloned genes.
In terms of geography, the global liposomes drug delivery market can be segmented into North America (Canada, the U.S., and Mexico), Europe (Germany, France, the U.K., Russia, and Italy), Asia Pacific (Japan, China, Korea, India, and Southeast Asia), Latin America, and Middle East & Africa. North America is a leading market for liposomes drug delivery systems due to increase in novel technologies in targeted drug delivery systems. The market is anticipated to expand during the forecast period in other parts of the globe as well.
Request Brochure of the Report:
https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/sample/sample.php?flag=B&rep_id=28571
Prominent manufacturers operating in the global liposome drug delivery market include Johnson & Johnson, Sun Pharmaceutical, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Novartis AG, Gilead Sciences, Inc., Kingond Pharm, and Celsion Corporation.
About us
Transparency Market Research is a global market intelligence company, providing global business information reports and services. Our exclusive blend of quantitative forecasting and trends analysis provides forward-looking insight for thousands of decision makers. Our experienced team of Analysts, Researchers, and Consultants, use proprietary data sources and various tools and techniques to gather, and analyze information.
Our data repository is continuously updated and revised by a team of research experts, so that it always reflects the latest trends and information. With a broad research and analysis capability, Transparency Market Research employs rigorous primary and secondary research techniques in developing distinctive data sets and research material for business reports.
Contact
Transparency Market Research
90 Sate Street, Suite 700
Albany, NY 12207
Tel: +1-518-618-1030
USA - Canada Toll Free: 866-552-3453
Email: [email protected]
Website: https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/
0 notes
Text
Ready! Set! Go!
New Post has been published on https://brownfamily-dc.com/product/ready-set-go/
Ready! Set! Go!
OVERVIEW
While there is no daily recommended value (DRV) for dietary fiber, the American Heart Association recommends children consume between 19 g and 31 g per day depending on age. The lack of adequate dietary fiber intake can lead to many digestive problems, such as occasional constipation, gas and bloating. Occasional constipation is a common condition, caused in part by poor diet and lifestyle. The prevalence of refined sugars and carbohydrates and the low presence of fiber in the Western diet has been linked to the slowing of bowel transit time and the alteration of the colon environment. Dietary fiber, which is mostly obtained from plant foods, consists of the indigestible portion of the plant while the sugars, starches and vitamins are broken down into nutrients and absorbed by the intestines. These cell walls of plants are not digested and become the bulk or roughage component of the stool, which help maintain bowel health and regularity.
Ready! Set! Go! is a blend of all-natural fruits and plant extracts for children with occasional constipation. The ingredients in this blend, which include prunes, psyllium husks, and ginger, have been used historically for the relief of occasional constipation and to soothe an achy stomach. Ready! Set! Go! has a pleasant flavor for easy compliance.
Suggested Use:
Children up to 6: 1-3 teaspoons daily as needed or as recommended by your health care professional
Children 6-12: 1-2 tablespoons daily as needed or as recommended by your health care professional
Adults: 2-3 tablespoons daily as needed or as recommended by your health care professional
INGREDIENT BENEFITS
Psyllium Seeds
Several clinical trials have shown psyllium to be superior to other laxatives. A systematic review found psyllium husk to improve overall bowel regularity more effectively than lactulose. Psyllium has been found to be more effective than placebo at increasing stool output and was found to improve symptoms of occasional constipation.
Fig (Ficus carica)
The phytochemical properties of fig’s laxative effect are due to the bulk of seeds and fibers. Fig supplementation also improved most of the symptoms in the patients suffering with functional bowel irregularity, and the fruit has also been shown to support regulation of loose bowels.
Prune (Prunus domestica)
Prunes have 6.1 g of dietary fiber per 100 g, as well as large amounts of phenolic compounds, which may aid in their efficacy for occasional constipation.
#Childrens, #ChildrensConstipation, #Constipation, #Gastrointestinal, #GI, #Gut, #Regularity
0 notes
Text
HIV: Hopeful Results of Doravirine vs Ritonavir-Boosted Darunavir at 96 Weeks
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:

Kathleen Squires MD
Director, Division of Infectious Diseases
Jefferson University Hospitals and
Ming-Tai Lai, PhD
Senior Principal Scientist, Biology Discover
Merck
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Dr. Squires: The DRIVE-FORWARD study is a pivotal, randomized, double-blind, Phase 3 study that evaluated the safety and efficacy of doravirine (DOR), a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) in treatment-naïve adults with HIV-1 infection. Data from week 48 of this trial have previously been presented demonstrating that doravirine met its primary endpoint of non-inferior efficacy compared to ritonavir-boosted darunavir (DRV+r). In addition, at 48 weeks, a secondary endpoint showed that the doravirine-treated group had statistically significant lower levels of fasting LDL-C and non-HDL-C versus the DRV+r group.
The data presented at AIDS 2018 are week 96 data from the DRIVE-FORWARD trial.
At week 96, the doravirine group demonstrated efficacy of 73.1% compared with 66.0% in the DRV+r group, a treatment difference of 7.1% (95% CI: 0.5, 13.7) Two participants in the DOR treatment group developed genotypic and phenotypic resistance to DOR through 96 weeks of treatment. The rate of discontinuation of therapy due to adverse events was 1.6 percent in the DOR group and 3.4 percent in the DRV+r group.
Doravirine is a late-stage investigational NNRTI for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in treatment-naïve adults and is being evaluated both as a once-daily single-entity tablet in combination with other antiretroviral agents, and as a once-daily fixed-dose combination regimen with lamivudine (3TC) and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF). Earlier this year, Merck announced that the FDA accepted for review two New Drug Applications (NDAs) for doravirine for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in treatment-naïve adults. The NDAs are based upon the findings at week 48 of two ongoing Phase 3 trials, DRIVE-FORWARD and DRIVE-AHEAD, evaluating the efficacy and safety of doravirine and the fixed-dose combination regimen of DOR/3TC/TDF, respectively. The FDA has set a target action date of October 23, 2018 for both applications.
Dr. Lai: This study aimed to characterize the mutant viruses selected in treatment-naïve participants through week 48 from DRIVE-FORWARD and DRIVE-AHEAD, and to assess the impact of selected mutations on non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) susceptibility and viral fitness. All of the seven doravirine (DOR)-resistant mutants are either partially susceptible or susceptible to etravirine. Mutants containing the F227C substitution were shown to be hypersusceptible to some nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) such as azidothymidine (AZT), tenofovir (TFV), lamivudine (3TC), and MK-8591. Among the 12 participants who developed efavirenz (EFV) resistance, 9 of the EFV-resistant clinical mutants were susceptible to DOR with fold-change
Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Get the Best Hair Loss Treatment in London | DRV Clinic
Struggling with hair loss? No worries! The DRV Clinic is here for your Hair Loss Treatment in London. Our dedicated team offers compassionate care and advanced treatments to combat hair loss. With our expertise and personalized approach, regain your confidence and youthful appearance. Say goodbye to thinning hair and hello to confidence. Schedule your consultation today and take the first step towards reclaiming your hair and confidence!
0 notes
Text
Get Your Dark Circles Treatment Done with DRV Clinic
Get rid of those pesky dark circles under your eyes with top-notch Dark Circles treatment at DRV Clinic in London. Our experts offer personalized solutions to tackle discoloration and puffiness, leaving your under-eye skin looking refreshed and radiant. Using the latest techniques and high-quality products, we ensure effective results and expert care. Trust DRV Clinic for all your dark circles treatment needs in London.
1 note
·
View note