#HDSuperAMOLED
Text
AMOLED display phones Review

Of course, a modern smartphone is one of the most complex electronic devices that uses a large number of complex components. Their technical characteristics directly affect the functionality and, as a result, the choice of the optimal model. This list includes the number and set of cameras in multi-camera smartphones and specs on main camera, smartphone performance and smartphone storage, operation system, etc.
Of course, the display is one of the main components. But its specs, service life and safety for vision depend on the matrix type. All modern TVs and smartphones use AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) or LCD screens.
As known, the first light-emitting p-phenylene vinylene (or PPV, or polyphenylene vinylene) polymer was synthesized in the Cavendish Laboratory of the University of Cambridge in 1989. Already in 1992, Cambridge Display Technolodgy (CDT) was established to produce polymer light-emitting materials.
In 2004, Samsung introduced the first X120 phone with an OLED screen.

In August 2008, Nokia introduced the N85 with an AMOLED display.

As known, OLED matrices (Organic light-emitting diode) use multilayer organic polymers that emit light under the influence of an electric current. Accordingly, they do not require backlighting. This factor is their main difference from traditional LCD technology. Today, all companies use OLED matrices with Active Matrix only and are called AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic light-emitting diode). In the TVs segment, companies continue to use OLED abbreviation without adding AM.
Pros & Cons
Pros
- perfect black due to lack of backlight provides almost endless contrast (2,000,000: 1 and above);
- large viewing angles eliminate color distortion even when viewing at an angle;
- PWM (pulse-width modulation) provides a wide range of brightness and very accurate color reproduction;
- smaller dimensions and weight;
- instant response due to lack of inertia;
- the ability to create flexible screens;
- wide range of operating temperatures from −40 to +70°C.
Cons
- high price;
- screen flicker due to PWM increases eye strain;
- low maximum brightness;
- high sensitivity to moisture;
- slight purple hue due to the eye’s reaction to the blue subpixels.
- the limited service life of the blue phosphor due to its chemical characteristics violates the color balance after several years.
The service life of green diodes reaches 130,000 hours, red - 50,000 hours, blue - only 15,000 hours. Of course, this problem significantly reduces the competitiveness of AMOLED vs LCD.
PenTile, Pixel Shifting and parallax backgrounds
Today, companies use several basic ways to solve this problem.
PenTile (penta + tile) technology integrates a family of proprietary sub-pixel configurations in electronic displays. It was developed in the early 1990s. This method uses the placement in a staggered manner of the five subpixels in each pixel, including two red, two green, and one central blue.
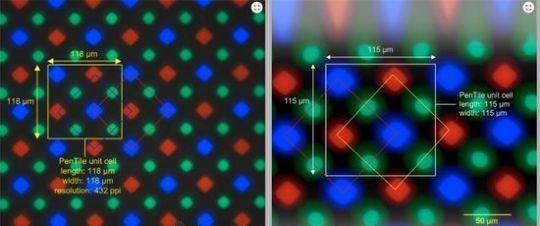
It is based on the characteristics of the retina of the human eye, which contains S (short)-cones, M (medium)-cones and L (long)-cones. Wherein, the number of S-cones significantly exceeds the number of M and L-cones. As known, S-cones provide recognition of blue color. Moreover, blue color almost does not affect the perception of brightness.
In March 2008, Samsung Electronics acquired PenTile from Clairvoyante and funded Nouvoyance, Inc. to continue developing this technology.
Technologically, PenTile adds subpixels to the device matrix. Modern smartphones use RGBG (additional green sub-pixel) or RGBW (additional white sub-pixel).

RGBG provides provides constant brightness while reducing the number of subpixels by 1/3 due to the high perception of green by the human eye. Today AMOLED, Super AMOLED and Super AMOLED HD often use this configuration.
RGBW increases brightness without increasing power consumption and is commonly used in LTPS matrices.
PenTile technology allowed Samsung to use half as many blue and red subpixels compared to green. Moreover, the most powerful blue diodes operate at half power, saving a resource. It increases their service life, and all subpixels burn out evenly.
Pixel Shifting software algorithm shifts the image by 1 pixel for a prolonged static image.
Recently, Google and Apple often use parallax backgrounds, preventing a static image on the screen.

AMOLED technology
Like LCD, AMOLED matrices use TFT technology. Each pixel uses its own transistor and capacitor for control. AMOLED technology has no size restrictions and is used for 10-inch screens and more.
Super AMOLED is an improved version of AMOLED. They do not have an air gap between the touch layer of the screen and the matrix. In this case, the engineers integrated the sensor layer directly into the screen instead of its surface.
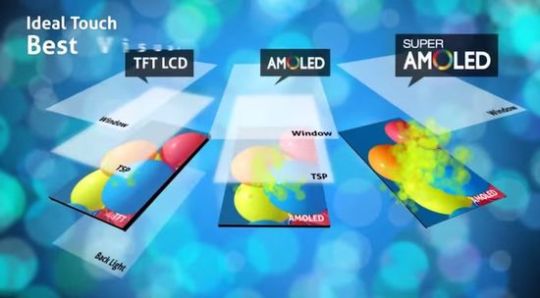
As a result, these screens are thinner, have less power consumption, provide absolute dust protection, a wider saturation of colors and a better image in direct sunlight. Unfortunately, they are more expensive compared to traditional AMOLED screens, and have high image grain due to the use of PenTile RGBG.
A similar technology in IPS matrices is called OGS (One Glass Solution).
Super AMOLED Plus and HD Super AMOLED differ only in the number of sub-pixels and, accordingly, size.

P-OLED matrices use a plastic screen backing instead of a glass. In addition to the traditional pros of OLED technology, this solution provides several additional advantages, including the ability to change the form factor of screens (flexible displays).

Samsung's latest Dynamic AMOLED version in Galaxy S10 5G is Super AMOLED with HDR10 support.

In addition, they form a less intense blue, which reduces eye strain and increases screen life.
Conclusion
In general, we can state the rapid development of AMOLED technology. Despite the higher price, AMOLED successfully competes with LCD displays, including Retina. Apparently, Samsung will continue to lead in this segment. But its success will significantly depend on the pricing strategy. In comparison, LG, the leader in the OLED TVs segment, has already offered the gorgeous 65-inch LG OLED C9 PUA for less than $ 2,500, which seemed unrealistic just a couple of years ago. It can be assumed that Samsung will also make efforts to lower the price of AMOLED screens.
This video shows a comparison of the iPhone 7+ with Retina LCD Display vs Samsung Galaxy S7 with Super Amoled.
Read the full article
#ActiveMatrixOrganiclight-emittingdiode#AMOLED#AMOLEDdisplayphones#dynamicAMOLED#GalaxyS105G#HDSuperAMOLED#OGS#OneGlassSolution#P-OLED#parallaxbackgrounds#PenTile#pixelshifting#RGBG#RGBW#superAMOLED
0 notes
Photo
Another extra #SamsungGalaxyS4 #globegalaxys4 #textclarity #441ppi #highdefinition #HDsuperamoled (at At Home)
0 notes
Text
Main factors to consider when buying a smartphone
The huge popularity of smartphones in the consumer electronics segment is beyond doubt. But first, the idea of combining the functionality of a cell phone and a personal digital assistant (PC) appeared in the early 1990s. Already in 1992, IBM introduced the first IBM Simon model.
In 1994, the US mobile operator BellSouth launched it for sale. Its price reached $ 900 with a contract and more than $ 1,000 without a contract. But the high price, weight of more than 2 pounds and large sizes became the main reasons for its low popularity.
In early 1996, Hewlett-Packard and Nokia launched the OmniGo HP 700LX.
In fact, it has combined the HP 200LX with the Nokia 2110. Of course, the software has also been refined for effective interaction with a mobile phone. The HP OmniGo 700LX had a four-color gray LCD screen with 640 × 200 resolution.
Introduction
Of course, modern models are radically different from their prototypes. In the conditions of fierce competition, companies are constantly expanding the functionality of their models. Very popular Blackview MAX 1 Projector Mobile Phone with a projector function perfectly illustrates this trend.
Of course, companies adequately respond to huge demand by offering a wide range of different models. On the one hand, such a variety pleases consumers. But sometimes this factor significantly complicates the choice of the optimal model. Analysis of basic specs will help to solve this problem.
This list includes:
- OS;
- phone performance;
- smartphone storage;
- battery capacity;
- camera set in multi-camera smartphones and main camera spec;
- size, type, and specs of the screen;
- protection level.
OS
Just 5 years ago, smartphones used up to ten different popular OSs. As a result, the operating system was one of the main criteria when choosing the optimal model. But fierce competition mercilessly eliminated most of them, leaving only a few of the most successful platforms. Of course, many smartphones still use OS with discontinued developer support. But it is unlikely that the efforts of enthusiasts will be able to extend their work for a long time.
Basically, modern models use:
- Android;
- Apple iOS;
- Windows Phone;
- Symbian.
But Microsoft in December 2019 stops supporting the latest Windows 10 Mobile. Additionally, the Finnish HMD Global also abandoned the Symbian platform, releasing the latest Delight 1.7 firmware for the Nokia E7, N8 and 808 PureView.
The share of other operating systems, including Bada, Palm OS, Open WebOS, Maemo, etc. is insignificant. Therefore, according to many experts, in the coming years, the main competition will continue between Android and Apple iOS. But today, a wider range of apps and a lower price with the same functionality provide an advantage for Android devices.
Most modern models from Samsung, HTC, Motorola and almost all Chinese companies use Android. Of course, huge versatility is one of the main reasons for its popularity. Today, most of smart gadgets, including TVs, projectors, music bars, kitchen appliances, watches, bicycles and even cars use the Android OS.
Today, some smartphones already have latest Android 10:
- Google Pixel 3 / Pixel 3 XL;
- Google Pixel 3a / Pixel 3a XL;
- Essential Phone;
- Google Pixel 2 / Pixel 2 XL;
- Google Pixel / Pixel XL;
- OnePlus 7T and OnePlus 7T Pro.
Phone performance
Of course, phone performance depends on the processor (or chipset, or SoC ) performance and RAM of the phone. In turn, CPU performance directly depends on its frequency, which varies in the range of 1-3 GHz.
But the computing system distributes different types of tasks between several specialized processor subsystems (CPU, GPU, ISP, DSP, DPU, VPU, NPU), a cellular modem, and memory integrated into the chipset.
Chipset performance also depends on the number of cores, the frequencies of which may vary. The combination of their specs directly affects the overall chipset performance. Therefore, companies are actively experimenting with the chipset configuration, trying to provide the optimal configuration with maximum performance. For example, one of the best Snapdragon 855 uses the traditional 4 + 4 layout (high-performance and energy-efficient clusters), including 4 cores with a modified Cortex A76 architecture, and 4 cores with Cortex A55. But one of the 4 cores of the A76 runs at an increased frequency (up to 2.84 GHz) and has 512 KB of cache. The remaining three use 256 KB of cache and overclock to 2.42 GHz. Economical A55 cores can reach frequencies up to 1.8 GHz.
Today, some companies already use eight-core octacores. But in the future, a simple increase in the number of cores is unlikely to be effective without taking into account the balance of the distribution of specialized tasks between subsystems due to Amdahl's law and some other factors.
The amount of RAM also significantly affects phone performance. Of course, the amount of RAM should correspond to the processor frequency for the correct operation of apps.
Today, the AnTuTu Benchmark app provides the most objective assessment of real performance, which ranges from 300,000 to 370,000 benchmarking score for top models.
Battery capacity
Of course, battery life is one of the main specs of a smartphone. In turn, it depends on the battery capacity and operation mode.
Typically, models with 2 GB RAM and a processor frequency of 2 GHz use a battery with a capacity of at least 3000 mAh. It provides about two days of work in the browser with moderate use of the game mode. Of course, “heavy” games, for example, GTA or Nova 3, drastically reduce operating time, draining the battery in about 6 hours. But even the top-end modern models rarely use batteries with a capacity of more than 4000 mAh. Some little-known companies for marketing purposes sometimes indicate a capacity of 5000 mAh or more. But more often, this information is not true.
Budget models with a less powerful processor and relatively small memory often use batteries with a capacity of about 2000 mAh. Thus, modern models usually use batteries with capacities ranging from 2000 mAh to 4000 mAh.
Today, the Internet abounds with comparative TOPs of various batteries.
Innovative Battery Charging Methods
The list of innovations in recharging batteries includes fast, wireless and wireless reverse charging.
Today, Chinese Huawei and Oppo are leading the fast recharging segment. For example, the Huawei Mate 20 Pro with a power of 40 W charges 70% of the battery in just 30 minutes. Oppo RX17 Pro shows even more impressive results. Their 50-W SuperVOOC Flash Charge charges 40% of the battery in just 10 minutes. But after a while, the charging speed, of course, decreases.
As known, most methods of fast charging usually use a two-way USB-C.
Companies are also actively improving wireless charging. For example, some Android smartphones have been using it for a long time. Recently, Apple has also increased its efforts in this direction.
But today Chinese Huawei is leading the way with the Wireless15-W Qi Charging for the Mate 20 Pro.
Reverse wireless charging was first introduced by Huawei in the same Mate 20 Pro. It uses a mechanical touch between two smartphones, one of which supports wireless charging. Unfortunately, today this promising technology is too slow. But in 2019, several leading manufacturers presented their flagships with this innovative option.
Smartphone Storage
Functionally, Smartphone memory includes ROM (Read Only Memory), RAM (Random Access Memory), internal memory, and external memory cards. By analogy with a PC, ROM corresponds to the C drive with OS on the HDD or SSD, and internal memory corresponds to the user partitions.
ROM of modern smartphones have eMMC or UFS storage. Innovative UFS (Universal Flash Storage) standatd uses new operation principle that provides significantly faster read / write speeds. In particular, eMMC uses sequential organization of read / write processes (Half Duplex), while UFS implements them simultaneously (Full Duplex).
The volatile RAM (Random Access Memory) does not save information after shutdown. Typically, RAM stores only temporary information, for example, operating system or open apps, that are loaded into memory at startup. Its volume directly affects multitasking and device performance. Today companies use LPDDR (mDDR or Low Power DDR) standard, including LPDDR3, 4, and 4X with maximum frequencies of 2133 MHz. But Samsung promises to introduce a faster LPDDR5 in 2020.
The internal flesh memory of the phones is slower compared to RAM and ROM, but much faster than the external memory on the SD card. Therefore, many companies, including the iPhone, install a fairly capacious internal memory from 16 to 128 GB.
Using a memory card has some nuances. For example, companies often offer models with support for SD cards up to 1 TB. Unfortunately, a smartphone with such an SD card is unlikely to work correctly. Too many files, for example, 100 GB or more, will slow down the OS due to the high processor load. Therefore, SD cards up to 100 GB are more optimal.
Camera
Today, the company improve the shooting quality of in two directions.
First, they increase the number of different cameras, expanding shooting modes. As a result, modern multi-camera smartphones provide high image quality when shooting in almost any conditions. A list of the most popular add-on modules includes Ultra-Wide, Telefoto, Depth and ToF cameras.
Today even budget models often use two cameras. Modern flagships usually have three or more modules. Moreover, Sony announced a smartphone with an unprecedented 8 cameras.
Secondly, companies continue to traditionally improve the main specs of image sensors. In principle, checking the quality of any camera is quite simple. The maximum zooming of any frame fragment perfectly illustrates the real quality of the camera. High-quality cameras provide high definition even at maximum zoom. Unfortunately, such a check is not always available. In this case, specs will be helpful. In particular, pixel and matrix size, its resolution and aperture directly affect the picture quality.
Camera specs
Pixel size directly affects the amount of light captured, which is very important when shooting in low light conditions. Its gradations are:
- 1.55 μm-1.40 μm - high quality even in low light;
- 1.40 μm-1.22 μm - high quality in normal lighting, image noise in low light;
- 1.12 μm or less - high quality only in bright conditions.
But increasing the pixel size with the same resolution requires an increase in the matrix size and optics, which increases the thickness and width of the smartphone. Therefore, companies are forced to constantly seek compromise solutions.
The effect of aperture on quality:
- low quality - f/2.6, f/2.4;
- usually used in budget models - f/2.2, f/2.0;
- the optimal aperture - f/1.8, f/1.7, f/1.6.
Image sensor size:
- budget smartphones - 1/3";
- mid-level models - 1/2.9", 1/2.8";
- flagship smartphones - 1/2.6", 1/2.3".
At a constant matrix size, increasing resolution requires a reduction in pixels size with a decrease in absorption of light by each of them. Therefore, companies are forced to choose the optimal resolution ratio and pixel size for maximum image quality.
Having reached a huge resolution (64 MP in latest Sony IMX686), companies began to look for other ways to further improve the camera. As a result, Super Pixel technology using Pixel Binning was developed. In fact, this algorithm combines four small pixels into one large pixel using filters.
Sony calls it Quad Bayer, Samsung uses the TetraCell term.
Screen
Of course, the model screen also belongs to the main selection criteria. As known, image quality depends on its specs, including contrast, resolution, color space coverage and color accuracy. But, of course, the screen diagonal also directly affects the image perception. Today, companies offer models with screen sizes ranging from 3.5 to 7 inches.
For example, Huawei Mate 20X has the largest frameless 7.2-inch IPS screen with 2244 x 1080 resolution.
Of course, the screen resolution depends on the diagonal. Modern models provide the following resolution:
- up to 4 inches - 480 x 800;
- 4-5 inches - 960 x 540;
- 5 inches and above - 1280 x 720 (HD), 1920 x 1080 (FullHD), 2560 x 1440 (QuadHD), or 3840 x 2160 (4K Ultra HD).
PPI (pixels per inch) characterizes the number of pixels in one inch of the screen and directly affects the image clarity.
In fact, it mathematically relates the screen resolution to its size, providing the most complete information about the real image quality. For example, two screens may have the same number of pixeles, but different diagonal sizes. In this case, a screen with a smaller diagonal will provide a clearer image and will have a higher PPI. Typically, screens with a resolution of 1280 x 720 provide up to 300 PPI.
AMOLED vs LCD displays in phones
All modern smartphones use AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) or LCD screens. Of course, each of them includes its own set of matrix types manufactured using a specific technology. In particular, companies today use IPS, DSTN, PLS, IGZO, LTPS LCD matrices, each of which has pros and cons. Samsung leads in the development and production of AMOLED matrices. The list of its modifications includes AMOLED, Super AMOLED, HD Super AMOLED and Dynamic AMOLED. However, Apple also produces OLED Retina screens. Today AMOLED retains a slight advantage in image quality, but LCD successfully compensates for it due to price.
Experts sometimes compare them in terms of eye strain. On the one hand, OLED models with higher PPI minimize eye strain. But, the relatively low brightness of OLED screens reduces the saturation of colors. Despite the reduction in eye strain, some users consider this a drawback. Unfortunately, screen flicker due to PWM in OLED screen increases eye strain. Thus, the final answer is ambiguous.
The brand
Almost every brand has some features. For example, Samsung, Lenovo, Fly, Prestigio, Asus, Philips, Sony, Lg provide excellent technical service. Sony, Xiaomi, Meizu, ZTE, and most other Chinese brands have high performance. Samsung, Sony, Apple, Lg, HTC, Lumia and some Lenovo models use high-quality cameras. Google Pixel phones have better access to Android updates. Android OS are leading in terms of usability. DEXP, Fly, Philips, Highscreen, Lenovo and Samsung have capacious batteries, providing high battery life. Sony, Samsung and Lg are leading in terms of reliability. For example, many models of other brands often fail during the first year. Models of these companies usually work 5 years or more. Typically, Xiaomi, Meizu and other Chinese brands specialize in the budget and mid-price segment. iPhone traditionally leads in the top segment. Unfortunately, the high price is sometimes due to aggressive advertising.
Of course, these factors are rather arbitrary, but they can help to orient oneself when choosing a model.
Protection
Of course, this factor is quite important for any expensive device, especially considering its use outside the home in various conditions. Of course, the metal case is more reliable than plastic. In addition, the modern market offers a wide selection of different covers, but they, as a rule, reduce usability.
Typically, specs contain information about the protection level in the form of "IP ...". Today “IP67” corresponds to the maximum level of protection. For example, Samsung Galaxy xCover S5690 with IP67 has high moisture resistance and dust protection, and can even withstand a car weight in certain circumstances. Some models have a special protective Gorilla Glass.
It has a high degree of resistance to scratches and impacts and can easily withstand falling onto an asphalt road.
Conclusion
Of course, the price significantly affects the choice. But the choice of the optimal model also significantly depends on the features of its use. For example, games require high phone performance and a large enough screen with high PPI. Cameras in multi-camera smartphones and main camera specs are essential for high-quality shooting in any environment. A good screen is important for multimedia apps. OS, battery capacity, smartphone storage and protection level directly affect usability.
This video demonstrates the Google Pixel 4 XL vs Samsung Galaxy S10 Plus.
Read the full article
#AMOLED#Android10#Double-layerSuperTwistedNematic#DSTNscreen#dynamicAMOLED#eMMCstorage#HDSuperAMOLED#IGZOscreen#LowPowerDDR#LPDDR#LTPSscreen#multi-camerasmartphones#PixelBinning#PLSscreen#ppi#QuadBayer#Reversewirelesscharging#smartphonebuying#smartphonechoice#Snapdragon855#SonyIMX686#superAMOLED#SuperPixeltechnology#SuperVOOCFlashCharge#TetraCell#UFSstorage
0 notes
Text
AMOLED vs LCD displays in phones
A modern smartphone uses a large number of complex components, including main camera and several additional cameras in multi-camera smartphones, chipset, RAM and ROM, operation system, etc. Their specs directly affect the functionality and, as a result, the choice of the optimal model.
But of course, the display is one of the main components. Its specs, service life and safety for vision depend on the matrix type. All modern TVs and smartphones use AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) or LCD screens.
As known, before the invention of OLED technology, LED LCD displays dominated the market. The first light-emitting p-phenylene vinylene (or PPV, or polyphenylene vinylene) polymer was synthesized in the Cavendish Laboratory of the University of Cambridge in 1989. Already in 1992, Cambridge Display Technolodgy (CDT) was established to produce polymer light-emitting materials.
But the fierce competition between them began only in the 21st century, provoking their rapid development.
LCD
As known, LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) technology uses fluidity and anisotropy of crystals. In fact, they perform the function of a light filter, forming a pixel of the desired color on the screen surface. Of course, this technology requires a backlight that uses LEDs.
In February 2011, Samsung introduced the first QLED display with improved LED backlighting on quantum dots. In fact, engineers added an LED panel instead of traditional cold cathode fluorescent tubes.
This technology has significantly expanded the color gamut of the matrix. Further, other companies developed their own technologies based on this idea. Today they use their own marketing names, including NanoCell from LG, Triluminos from Sony and ULED from Hisense.
In parallel, companies developed backlight technology. As a result, FALD (full-array local dimming) backlighting was developed.
Today, experts expect LCD with innovative miniLED-based backlighting. Unlike traditional backlighting, the size of its diode modules does not exceed 100 microns.
The reduction in size promises to drastically reduce energy consumption, increase contrast and color accuracy by increasing the number of local dimming zones. TVs already use this technology.
For example, TCL announced 8-series MiniLED Roku TV with 1,000 local dimming zones. In comparison, today the best expensive LCD TVs use no more than a few hundred. This technology promises to bring the quality of LCD screens closer to AMOLED. Some experts were expecting these smartphones in 2019. Unfortunately, their hopes did not materialize.
OLED
OLED matrices (Organic light-emitting diode) use multilayer organic polymers that emit light under the influence of electricity and do not require backlighting. In fact, it's the main difference between these technologies. All modern phones use only AMOLED (Active Matrix OLED) matrices with Active Matrix. But in the TV segment, companies continue to use the acronym OLED without adding AM.
In the summer of 2009, LG announced the first 15-inch OLED TV. A few years later, at CES 2012, Samsung and LG introduced 55-inch OLED TVs. At IFA 2013, LG has already announced the world's first 77-inch 4K OLED TV.
At CES 2013, Samsung announced the Galaxy S4 with 5 "Super AMOLED Full HD panel. In the second half of 2014, Samsung Display began production of AMOLED flexible panels.
Modern models already use AMOLED, Super AMOLED, HD Super AMOLED, Dynamic AMOLED and P-OLED matrices.
MicroLED (mLED or μLED or ILED)
MicroLED is the next step in the development of OLED technology. Like OLED, MicroLED uses subpixel LEDs with its own radiation and does not require backlighting. But as a light-emitting material, OLED uses sm-OLED (Small Molecule-Organic LED), POLED, or PHOLED (phosphorescent OLED). MicroLED uses inorganic GaN (gallium nitride) with a size of only 5-10 microns, which is its main advantage.
The new technology has great prospects. In particular, high light output can drastically reduce energy consumption to about 10% LCD and 50% OLED displays, and the miniature size will allow companies to achieve pixel densities of up to 1,500 PPI, providing huge resolution even for large matrices.
In 2018, Apple announced plans to produce MicroLED panels. But in 2019, serial microLED displays did not appear on the market. However, Sony and Samsung are already selling microLED The Wall.
OLED advantages
1. As known, contrast characterizes the ratio brightest white to the darkest black pixels on the screen and is measured in the ratio of "maximum brightness" / 1. Thus, a screen with a contrast ratio of 1000: 1 displays white 1000 times brighter than black.
But in the OLED display, black color corresponds to a completely off diode with a brightness of "0". Therefore, companies often use the term "Infinite contrast", although, as you know, mathematics prohibits the division by "0". Sometimes companies indicate 2,000,000: 1 and above, which is probably more correct.
Unfortunately, LED backlight in the LCD screen fundamentally eliminates the perfect black.
2. Smartphones with OLED screens support Always On-Display mode. In this case, the smartphone’s display can display information by controlling individual pixels. This mode provides a significant reduction in energy consumption when choosing interface in dark colors.
But black color of the IPS matrix corresponds to the on backlight, which we do not see due to the light wave damping by the second polarizer. Thus, the IPS matrix cannot provide this useful option because its backlight constantly illuminates the matrix.
3. As known, the image brightness decreases when viewed at an angle. For example, the brightness drop in smartphones with IPS-screen reaches 55% for an angle of 30 degrees. For comparison, brightness reduction of the OLED screen at the same angle does not exceed 25%.
4. The absence of a backlight in OLED screen eliminates problems with its uniformity. Unfortunately, it's relevant for the IPS screen. Typically, companies place backlight diodes along the bottom edge of the IPS screen. During operation, their light passes through a special flexible diffuser made of a thin film. Unfortunately, many LCD screens display a brighter bar at the bottom of the screen near the diodes.
LCD advantages
1. IPS-screen is much cheaper than OLED-analogue, including repair.
2. Almost all OLED screens have problems with Screen burn-in.
The service life of green diodes reaches 130,000 hours, red - 50,000 hours, blue - only 15,000 hours.
However, today companies successfully solve this problem using PenTile. For example, PenTile technology allowed Samsung to use half as many blue and red subpixels compared to green. Moreover, the most powerful blue diodes operate at half power, saving a resource. It increases their service life, and all subpixels burn out evenly. Typically, companies use RGBG (additional green sub-pixel) or RGBW (additional white sub-pixel).
Today AMOLED, Super AMOLED and HD Super AMOLED often use this configuration.
On the other hand, 15,000 hours of service life for blue diodes corresponds to more than 5 years of operation, even with heavy use. Most people change models more often.
In addition, static displaying for a long time at maximum brightness may form a residual image on the screen. But Pixel Shifting and Parallax Backgrounds successfully solve this problem.
Pixel Shifting software algorithm shifts the image by 1 pixel for a prolonged static image. Recently, Google and Apple often use parallax backgrounds, preventing a static image on the screen.
3. Screen flicker due to PWM in OLED screen increases eye strain. As known, the diode brightness depends on the current strength. With its increase, it gradually rises. Unfortunately, the decrease in brightness does not occur smoothly. Instead of smooth dimming, the diodes begin to work with small pauses. For example, diodes burn 0.9 ms for 1 second at 100% brightness. But at 50% brightness, these LEDs only work for 0.45 ms for 1 second. Of course, this flicker significantly increases the load on the eyesight, causing discomfort in the eyes.
Brands
Today, budget and mid-budget Android, and Apple, mainly use LCD displays. This list includes:
- iPhone 11;
- iPhone XR;
- Honor 20/20 Pro;
- iPhone 8/8 Plus, iPhone 7/7 Plus;
- Xiaomi Redmi Note 7;
- Huawei P30 Lite.
AMOLED screens are used on almost all flagships and even on mid-range smartphones. This list includes:
- the entire line of Samsung Galaxy S-series, Note-series, etc;
- iPhone 11 Pro / 11 Pro Max, iPhone XS / XS Max and iPhone X;
- Huawei flagships (P30, Mate 30);
- Xiaomi flagships (the entire line of Mi 9, etc.);
- Sony Xperia XZ3 and Xperia 1.
Conclusion
In general, the trend clearly demonstrates the rapid convergence of technology. The active use of effective innovative technologies has ensured the convergence of consumer qualities of models with AMOLED and LCD matrices. Of course, AMOLED retains a slight advantage in image quality, but LCD successfully compensates for it due to price.
Today we can assume the direction of their further improvement. Apparently, the market will soon offer LCD screens with miniLED-based backlighting. In the segment of OLED technology, MicroLED displays have good prospects over time to replace modern AMOLED screens. In this case, LCD with miniLED will compete with MicroLED in the next step.
This video shows the 75-inch and 219-inch Samsung Micro LED Modular TVs at CES 2019.
Read the full article
#ActiveMatrixOrganiclight-emittingdiode#AlwaysOn-Displaymode#AMOLEDvsLCDdisplays#dynamicAMOLED#FALD#HDSuperAMOLED#MicroLED#miniLEDbacklight#NanoCell#P-OLED#parallaxbackground#PenTile#pixelshifting#QLED#superAMOLED#Triluminos#ULED
0 notes