#Europe Missile Tracking Systems Report
Text
The Europe missile tracking systems market is projected to reach $35.26 billion by 2033 from $21.34 billion in 2023, growing at a CAGR of 5.15% during the forecast period 2023-2033. Missile tracking systems typically use radar, infrared sensors, and satellite technology to detect, track, and intercept missiles. Radars identify the missile's location, while infrared sensors detect its heat signature. Satellite data enhances tracking accuracy. This information is processed to provide real-time data for effective defense measures against incoming missiles.
#Europe Missile Tracking Systems Market#Europe Missile Tracking Systems Report#Europe Missile Tracking Systems Industry#Defence and Security#BISResearch
0 notes
Text
Shortly before noon on Aug. 19, 2023, a Russian cruise missile sliced past the golden onion domes and squat apartment blocks of the Chernihiv skyline in northern Ukraine. The Iskander-K missile slammed into its target: the city’s drama theater, which was hosting a meeting of drone manufacturers at the time of the attack. More than 140 people were injured and seven killed. The youngest, 6-year-old Sofia Golynska, had been playing in a nearby park.
Fragments of the missile recovered by the Ukrainian armed forces and analyzed by Ukrainian researchers found numerous components made by U.S. manufacturers in the missile’s onboard navigation system, which enabled it to reach its target with devastating precision. In December, Ukraine’s state anti-corruption agency released an online database of the thousands of foreign-made components recovered from Russian weapons so far.
Russia’s struggle to produce the advanced semiconductors, electrical components, and machine tools needed to fuel its defense industrial base predates the current war and has left it reliant on imports even amid its estrangement from the West. So when Moscow launched its full-scale invasion of Ukraine in February 2022, major manufacturing countries from North America, Europe, and East Asia swiftly imposed export controls on a broad swath of items deemed critical for the Russian arms industry.
Russia quickly became the world’s most sanctioned country: Some 16,000 people and companies were subject to a patchwork of international sanctions and export control orders imposed by a coalition of 39 countries. Export restrictions were painted with such a broad brush that sunglasses, contact lenses, and false teeth were also swept up in the prohibitions. Even items manufactured overseas by foreign companies are prohibited from being sold to Russia if they are made with U.S. tools or software, under a regulation known as the foreign direct product rule.
But as the war reaches its two-year anniversary, export controls have failed to stem the flow of advanced electronics and machinery making their way into Russia as new and convoluted supply chains have been forged through third countries such as Kazakhstan, Turkey, and the United Arab Emirates, which are not party to the export control efforts. An investigation by Nikkei Asia found a tenfold increase in the export of semiconductors from China and Hong Kong to Russia in the immediate aftermath of the war—the majority of them from U.S. manufacturers.
“Life finds a way,” said a senior U.S. intelligence official, quoting the movie Jurassic Park. The official spoke on background to discuss Russia’s evasion of export controls.
Some of the weapons and components analyzed by investigators were likely stockpiled before the war. But widely available Russian trade data reveals a brisk business in imports. More than $1 billion worth of advanced semiconductors from U.S. and European manufacturers made their way into the country last year, according to classified Russian customs service data obtained by Bloomberg. A recent report by the Kyiv School of Economics found that imports of components considered critical for the battlefield had dipped by just 10 percent during the first 10 months of 2023, compared with prewar levels.
This has created a Kafkaesque scenario, the report notes, in which the Ukrainian army is doing battle with Western weapons against a Russian arsenal that also runs on Western components.
It is an obvious problem, well documented by numerous think tank and media reports, but one without an easy solution. Tracking illicit trade in items such as semiconductors is an exponentially greater challenge than monitoring shipments of conventional weapons. Around 1 trillion chips are produced every year. Found in credit cards, toasters, tanks, missile systems, and much, much more, they power the global economy as well as the Russian military. Cutting Russia out of the global supply chain for semiconductors is easier said than done.
“Both Russia and China, and basically all militaries, are using a large number of consumer electronic components in their systems,” said Chris Miller, the author of Chip War: The Fight for the World’s Most Critical Technology. “All of the world’s militaries rely on the same supply chain, which is the supply chain that primarily services consumer electronics.”
Export controls were once neatly tailored to keep specific items, such as nuclear technology, out of the hands of rogue states and terrorist groups. But as Washington vies for technological supremacy with Beijing while also seeking to contain Russia and Iran, it has increasingly used these trade restrictions to advance broader U.S. strategic objectives. For instance, the Biden administration has placed wide-ranging prohibitions on the export of advanced chips to China.
“At no point in history have export controls been more central to our collective security than right now,” Matthew Axelrod, the assistant secretary for export enforcement at the U.S. Commerce Department, said in a speech last September. U.S. National Security Advisor Jake Sullivan has described export controls as “a new strategic asset in the U.S. and allied toolkit.”
Russia’s ability to defy these restrictions doesn’t just have implications for the war in Ukraine. It also raises significant questions about the challenge ahead vis-à-vis China.
“The technological question becomes a key part of this story and whether or not we can restrict it from our adversaries,” said James Byrne, the director of open-source intelligence and analysis at the Royal United Services Institute, a British think tank.
In the Russian city of Izhevsk, home to the factory that manufactures Kalashnikov rifles, shopping malls are being converted into drone factories amid a surge in defense spending that has helped the country’s economy weather its Western estrangement. Arms manufacturers have been urged to work around the clock to feed the Russian war machine, while defense is set to account for one-third of the state budget this year.
“We have developed a concept to convert shopping centers—which, before the start of the SMO [special military operation], sold mainly the products of Western brands—to factories for assembly lines of types of domestic drones,” Alexander Zakharov, the chief designer of the Zala Aero drone company, said at a closed event in August 2022, according to the Russian business newspaper Vedomosti. “Special military operation” is what the Russian government calls its war on Ukraine. Zala Aero is a subsidiary of the Kalashnikov Concern that, along with Zakharov, was sanctioned by the United States last November.
Defense companies have bought at least three shopping malls in Izhevsk to be repurposed for the manufacture of drones, according to local media, including Lancet attack drones, which the British defense ministry described as one of the most effective new weapons that Russia introduced to the battlefield last year. Lancets, which cost about $35,000 to produce, wreaked havoc during Ukraine’s offensive last year and have been captured on video striking valuable Ukrainian tanks and parked MiG fighter jets.
Like a lot of Russia’s weapons systems, Lancets are filled with Western components. An analysis of images of the drones published in December by the Washington-based Institute for Science and International Security found that they contained several parts from U.S., Swiss, and Czech manufacturers, including image processing and analytical components that play a pivotal role in enabling the drones to reach their targets on the battlefield.
“The recurring appearance of these Western products in Russian drone systems shows a keen dependence on them for key capabilities in the drone systems,” the report notes. Lancets are not the only drones found to contain Western components. Almost all of the electronic components in the Iranian Shahed-136 drones, which Russia is now manufacturing with Iranian help to use in Ukraine, are of Western origin, a separate analysis published in November concluded.
Early in the war, the Royal United Services Institute analyzed 27 Russian military systems, including cruise missiles, electronic warfare complexes, and communications systems, and found that they contained at least 450 foreign-made components, revealing Russia’s dependence on imports.
One of the principal ways that Russia has evaded Western export controls has been through transshipment via third countries such as Turkey, the UAE, and neighboring states once part of the Soviet Union. Bloomberg reported last November that amid mounting Western pressure, the UAE had agreed to restrict the export of sensitive goods to Russia and that Turkey was considering a similar move. Kazakh officials announced a ban on the export of certain battlefield goods to Russia in October.
Suspected transshipment is often revealed by striking changes in trade patterns before and after the invasion. The Maldives, an island chain in the Indian Ocean that has no domestic semiconductor industry, shipped almost $54 million worth of U.S.-made semiconductors to Russia in the year after the invasion of Ukraine, Nikkei Asia reported last July.
Semiconductor supply chains often span several countries, with chips designed in one country and manufactured in another before being sold to a series of downstream distributors around the world. That makes it difficult for companies to know the ultimate end user of their products. This may seem odd—until you realize that this is the case for many everyday products that are sold around the world. “When Coca-Cola sells Coca-Cola, it doesn’t know where every bottle goes, and they don’t have systems to track where every bottle goes,” said Kevin Wolf, a former assistant secretary for export administration at the U.S. Commerce Department.
While a coalition of 39 countries, including the world’s major manufacturers of advanced electronics, imposed export restrictions on Russia, much of the rest of the world continues to trade freely with Moscow. Components manufactured in coalition countries will often begin their journey to Moscow’s weapons factories through a series of entirely legal transactions before ending up with a final distributor that takes them across the border into Russia. “It starts off as licit trade and ends up as illicit trade,” said a second senior U.S. intelligence official, who spoke on condition of anonymity.
The further items move down the supply chain, the less insight governments and companies have into their ultimate destination, although sudden changes in behavior of importers can offer a red flag. In his speech last September, Axelrod, the assistant secretary, used the example of a beauty salon that suddenly starts to import electronic components.
But the Grand Canyon of loopholes is China, which has stood by Moscow since the invasion. In the first days of the war, U.S. Commerce Secretary Gina Raimondo warned that Washington could shut down Chinese companies that ignored semiconductor export controls placed on Russia. Last October, 42 Chinese companies were added to export control lists—severely undercutting their ability to do business with U.S. companies—for supplying Russian defense manufacturers with U.S. chips.
But as the Biden administration carefully calibrates its China policy in a bid to keep a lid on escalating tensions, it has held off from taking Beijing to task. “I think the biggest issue is that we—the West—have been unwilling to put pressure on China that would get China to start enforcing some of these rules itself,” said Miller, the author of Chip Wars.
A spokesperson for the U.S. Commerce Department’s Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) said: “Due to the restrictions imposed by the United States and key allies and partners, Russia has been left with no choice but to spend more, lower its ambitions for high-tech weaponry, build alliances with other international pariah states, and develop nefarious trade networks to covertly obtain the technologies it needs.
“We are deeply concerned regarding [Chinese] support for Russia’s defense industrial base. BIS has acted to add over 100 [China]-based entities to the Entity List for supporting Russia’s military industrial base and related activities.”
Export controls have typically focused on keeping specific U.S.-made goods out of the hands of adversaries, while economic and financial sanctions have served broader foreign-policy objectives of isolating rogue states and cauterizing the financing of terrorist groups and drug cartels. The use of sanctions as a national security tool grew in wake of the 9/11 attacks; in the intervening decades, companies, government agencies, and financial institutions have built up a wealth of experience in sanctions compliance. By contrast, the use of export controls for strategic ends is relatively novel, and compliance expertise is still in its infancy.
“It used to be that people like me could keep export controls and sanctions in one person’s head. The level of complexity for each area of law is so intense. I don’t know anyone who is truly an export control and sanctions expert,” Wolf said.
Export controls, experts say, are at best speed bumps designed to make it harder for Russia’s defense industrial base to procure Western components. They create “extra friction and pressure on the Russian economy,” said Daniel Fried, who as the State Department coordinator for sanctions policy helped craft U.S. sanctions on Russia after its annexation of Crimea in 2014. Russia is now paying 80 percent more to import semiconductors than it did before the war, according to forthcoming research by Miller, and the components it is able to acquire are often of dubious quality.
But although it may be more cumbersome and expensive, it’s a cost that Moscow has been willing to bear in its war on Ukraine.
Western components—and lots of them—will continue to be found in the weapons Russia uses on Ukraine’s battlefields for the duration of the war. “This problem is as old as export controls are,” said Jasper Helder, an expert on export controls and sanctions with the law firm Akin Gump. But there are ways to further plug the gaps.
Steeper penalties could incentivize U.S. companies to take a more proactive role in ensuring their products don’t wind up in the hands of the Russian military, said Elina Ribakova, a nonresident senior fellow at the Peterson Institute for International Economics. “At the moment, they’re not truly motivated,” she said.
Companies that run afoul of sanctions and the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, a U.S. federal law that prohibits the payment of bribes, have been fined billions of dollars. Settlements of export control violations are often an order of magnitude smaller, according to recently published research.
In a speech last month, Axelrod said the United States would begin issuing steeper penalties for export control violations. “Build one case against one of the companies extremely well, put out a multibillion-dollar fine negotiation, and watch everybody else fall in line,” Ribakova said.
And then there’s the question of resources. BIS has an annual budget of just $200 million. “That’s like the cost of a few fighter jets. Come on,” said Raimondo, speaking at the Reagan National Defense Forum last December.
The agency’s core budget for export control has, adjusted for inflation, remained flat since 2010, while its workload has surged. Between 2014 and 2022, the volume of U.S. exports subject to licensing scrutiny increased by 126 percent, according to an agency spokesperson. A 2022 study of export control enforcement by the Center for Strategic and International Studies recommended a budget increase of $45 million annually, describing it as “one of the best opportunities available anywhere in U.S. national security.”
When it comes to enforcement, the bureau has about 150 officers across the country who work with law enforcement and conduct outreach to companies. The Commerce Department has also established a task force with the Justice Department to keep advanced technologies out of the hands of Russia, China, and Iran. “The U.S. has the most robust export enforcement on the planet,” Wolf said.
But compared with other law enforcement and national security agencies, the bureau’s budgets have not kept pace with its expanding mission. The Department of Homeland Security has more investigators in the city of Tampa, Florida, than BIS does across the entire country, Axelrod noted in his January speech.
On the other side, you have Russia, which is extremely motivated to acquire the critical technologies it needs to continue to prosecute its war. The Kremlin has tasked its intelligence agencies with finding ways around sanctions and export controls, U.S. Treasury Undersecretary Brian Nelson said in a speech last year. “We are not talking about a profit-seeking firm looking for efficiencies,” the second senior U.S. intelligence official said. “There will be supply if there is sufficient demand.”
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
Daily Wrap Up July 12, 2022
Under the cut:
The death toll from a weekend Russian missile attack on a residential apartment block in Chasiv Yar, eastern Ukraine, rose to at least 45
At least seven people were reportedly killed by a Ukrainian missile strike on a large ammunition store in the town of Nova Kakhovka, in Russia-occupied Kherson, in a strike attributed to recently acquired US weapons
The United States treasury announced is sending $1.7bn (£1.4bn) in economic aid to Ukraine to help continue funding the country’s “essential services” following an announcement by European foreign ministers approving €1bn
European Space Agency terminated cooperation with Russia on Mars mission
“According to the Infrastructure Ministry, 16 vessels have entered through the Danube-Black Sea Canal to load Ukrainian grain as of July 12. Other more than 90 ships are currently waiting for their turn. The ministry expects that it will be able to increase the monthly export of grain by 500,000 tons. The use of the canal opened up after Ukraine liberated Snake Island from Russian forces on June 30.”-via Ukraine Ministry of Infrastructure Facebook (Ukrainian source)
~
“The death toll from a weekend Russian missile attack on a residential apartment block in Chasiv Yar, eastern Ukraine, rose to at least 45 on Tuesday, according to the Kyiv Independent.
The newspaper reported that the state emergency service said it had now pulled 45 bodies out of the rubble, including a child.
Saturday’s missile attack destroyed the five-storey building and damaged several others in the Donetsk region city.
Nine people have been rescued, the newspaper says, and the rescue operation is ongoing.”-via The Guardian
~
“At least seven people were reportedly killed by a Ukrainian missile strike on a large ammunition store in the town of Nova Kakhovka, in Russia-occupied Kherson, in a strike attributed to recently acquired US weapons.
The claims of fatalities were made by the Russian-installed administration in the town and could not be immediately verified, though footage on social media showed a large explosion lighting up the night, burning ammunition and towering smoke.
The explosion hit a warehouse close to a key railway line and a dam on the Dnipro River. Imaging from Nasa’s Firms global fire tracking system showed a number of secondary blazes in buildings around the initial blast site.
Kyiv said it had launched artillery barrages that a destroyed a Russian arms depot, hitting artillery, armoured vehicles “and a warehouse with ammunition”, and in addition carried out a “special operation” to free military captives in the Moscow-controlled region. Russian-backed authorities accused Ukraine of damaging civilian infrastructure.
Pro-Russia officials and some Ukrainian commentators were quick to suggest that the explosion was the result of a strike by Ukraine’s newly supplied US Himars missile system. A number of recent strikes on ammunition warehouses and Russian command centres have been attributed to Himars.”
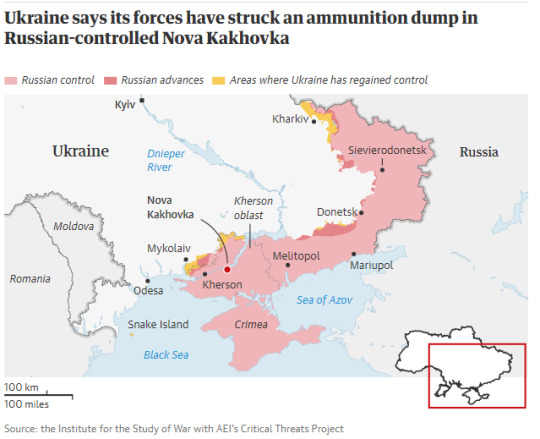
-via The Guardian
~
“The United States treasury announced on Tuesday it was sending an additional $1.7bn (£1.4bn) in economic aid to Ukraine to help continue funding the country’s “essential services”.
The move follows an announcement by European foreign ministers late on Monday approving €1bn (£850m), the first instalment of a €9bn rescue package agreed in May.
Like the European money, the US payment is also part of a wider package, $7.5bn (£6.3bn) in aid signed off by Joe Biden in May, and brings to almost £2.5bn the amount approved in aid for Ukraine from both sides of the Atlantic in just the last 24 hours.”-via The Guardian
~
“European Space Agency is terminating cooperation with Russia on the mission to launch Europe's first planetary rover, designed to search for signs of life on Mars, the agency’s chief said on Tuesday.
The ExoMars Rover, a collaboration between the ESA and the Russian space agency Roscosmos, had been on track to leave for Mars in September this year. But the ESA said in February that Russia's invasion of Ukraine had made that "very unlikely."
Then in March, the agency suspended cooperation with Roscosmos over their joint mission on Mars in the wake of the Ukraine invasion and sanctions imposed on Russia.
“Today @ESA Council addressed the ExoMars Rover and Surface Platform mission, acknowledging that the circumstances which led to the suspension of the cooperation with Roscosmos – the war in Ukraine and the resulting sanctions – continue to prevail,” ESA’s Director General Josef Aschbacher wrote on Twitter on Tuesday.
As a consequence, the agency’s board instructed him to officially terminate cooperation with Russia on the program, Aschbacher said.“-via CNN
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Digital Battlefield Market Soars: A Comprehensive Analysis of the $61.7 Billion Industry in 2024
The digital battlefield market is expected to be valued at US$ 61.7 billion in 2024. The demand is expected to progress at an exemplary rate over the forecast period, with a CAGR of 17.8%. By 2034, the value of the market is forecast to record a valuation of US$ 319.0 billion.
With army training becoming more extensive and military planning assuming an even more elevated stature, the digital battlefield space is becoming a prime concern for militaries. With geopolitical conflicts rising, militaries are becoming even more alert and spending on technology, thus laying out the groundwork for the digital battlefield. Governments, too, are encouraging the use of digital battlefields by granting more budget to technology adaption in militaries.
Technologies like AI, robotics, and drones are accelerating the use of digital battlefields. Software like AR/VR is aiding in the training of soldiers by replicating real-life battle situations with increasing accuracy. 5G technology is being used to improve the communication between various army elements.
Request for a Sample of this Research Report:
https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/sample/rep-gb-18824
Digital battlefield solutions allow military personnel to take on-the-fly decisions and better execute strategies. The tracking of own and enemy soldiers with the help of GIS and GPS technologies is also seeing the digital battlefield gain more prominence.
“The avenues for the digital battlefield are rapidly expanding. In addition to traditional land strategies, digital planning is also helping armies in naval, air, and even space platforms. Thus, the scope of investment in the market remains wide,” says an analyst at FMI.
Key Takeaways from the Digital Battlefield Market
The digital battlefield market is anticipated to be valued at US$ 61.7 billion in 2024.
Land remains a prominent platform in the digital battlefield market. From 2024 to 2034, the segment is forecast to progress at 17.6%.
Hardware is the leader in the solution segment. Hardware is predicted to progress at a CAGR of 17.4% for the forecast period.
South Korea is one of the promising countries in the market. The CAGR for South Korea over the forecast period is anticipated to be 20.1%.
Japan and China are other Asian countries poised to be lucrative for the market. For the 2024 to 2034 period, the CAGR for Japan and China is pegged at 19.6% and 18.7% respectively.
The market is expected to register a CAGR of 18.2% in the United States over the forecast period.
Competition Analysis
Market players focus on securing lucrative contracts from governments, with relationship building also an area of focus. Partnerships among players are also often seen for critical infrastructure, cyber threats, and technology. Some prominent companies in the market include Raytheon Technologies Corporation, BAE Systems, Elbit Systems Ltd., and General Dynamics Corporation.
Recent Developments
In June 2022, BAE Systems developed the Mobility Air Forces Automated Flight Planning Service, or MAFPS, for the United States Airforce.
In April 2021, Raytheon Technologies launched the Stinger Virtual Trainer System to equip soldiers with training for the Stinger Missile Launcher.
Elevate Your Business Strategy! Purchase the Report for Market-Driven Insights:
https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/checkout/18824
Key Segments
By Platform:
Land
Naval
Aircraft
Space
By Solution:
Hardware
Software
Solutions
By Technology:
Artificial Intelligence
Internet of Things (IoT)
Robotic Process Automation
Cloud Computing and Master Data Management
5G
Others
By Application:
Warfare Platform
Cyber Security
Surveillance and Situational Awareness
Command and Control
Mobile Communication
Simulation and Training
Design and Manufacturing
Electronic Warfare
Others
By Region:
North America
Latin America
Europe
South Asia
East Asia
Oceania
The Middle East and Africa (MEA)
0 notes
Text
Military Optronics Surveillance and Sighting Systems Market: Growth Overview

Sub-national conflicts involving strong cross-border dynamics are commonly witnessed across the globe, making it critical for nations to ensure military strength and advance their defense systems. In view of this, several countries have increased their defense budgets, especially for border security. This has increased the deployment of integrated observation equipment, fire control systems, mobile vehicle surveillance systems, and other such equipment, which is expected to bolster the global military optronics surveillance and sighting systems market.
Triton Market Research’s report estimates that the market will display a CAGR of 5.70% in the forecast years from 2023 to 2030. Military optronics surveillance and sighting systems enable rapid & early detection of illegal border activities and offer strong situational awareness by tracking movement across rough terrains, thus preparing armies for combat. Also, along with traditional warfare equipment, many countries are focusing on the R&D of modern warfare equipped with AI and other technologies, thus advancing market prospects.
Beyond Borders – Evaluating Regional Markets’ Performance
North America and Europe occupy key positions in the global market, which can be accredited to the presence of large-scale arms manufacturers and other key market players in these regions. Whereas, the Asia-Pacific military optronics surveillance and sighting systems market is also expected to flourish due to an increased focus on domestic manufacturing and extensive investments in R&D.
Israel, an important market in the Middle East and Africa, is a major supplier of advanced military systems, such as missiles, drones, radar systems, and others, and exported weapons worth over $345 million to 16 countries in 2020. On the other hand, in most Latin American countries, specific drug control units have been highly militarized to tackle the growing threat from transnational crime & drug trafficking organizations. This has necessitated the demand for guns, armored vehicles, clothing, and tactile equipment, to facilitate logistical support.
Military Optronics Surveillance and Sighting Systems Market Segmentation
Military Laser Systems is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.99% in the Machinery segment during 2023-2030
Fiber lasers, semiconductor diode lasers, solid-state lasers, and CO2 & other gas lasers are some of the laser systems used in the military. They are used for target designation & tracking, guidance, and range finding, and are also used in conjunction with squad weapons. Vectronix by Safran Group is a widely used military laser system; the high-performance handheld equipment is embedded with high resolution & superior quality optics.
Aerial is estimated to grow at a 6.03% CAGR in the Medium segment during the forecast period
Modernization of aerial warfare is being witnessed with the addition of combat aircraft and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). They are generally used for surveillance, target acquisition, intelligence gathering, and also for transporting aircraft ammunition. Advanced technologies like multispectral imaging are being increasingly used in UAVs. Besides, the use of some emerging technologies, such as hyperspectral imaging and infrared thermography, will offer lucrative opportunities for the growth of this segment.
Seismic and Acoustic Sensors held a revenue share of $4217.22 million in the Product Type segment in 2022
Seismic and acoustic sensors are used in the military because of their ability of identifying & tracking targets in non-LoS conditions and carrying out missions in a docile manner. These sensors are used in numerous applications, such as defense security, monitoring, and surveillance. They are also being used in several modern surveillance sensor systems called unattended ground sensors (UGS). A UGS has inbuilt sensors with magnetic, acoustic, seismic, and infrared capabilities. The combination of features from various sensor technologies largely optimizes their target recognition ability.
What Our Experts Say
Stealth technology presents growth scope due to growing investments by countries to gain a tactical advantage over enemy forces. Also called low observable technology, it is a core element of modern military warfare to make one’s own forces discreet and ideally invisible to the enemy. Some well-known stealth aircraft include the F-22 Raptor by Lockheed Martin Corporation and Chengdu J-20 by Chengdu Aerospace Corporation.
Also, there is an enhanced focus on developing defense systems with hypersonic technology. There are two main types of hypersonic weapons, which include hypersonic glide vehicles and hypersonic cruise missiles. The latter travel 5 times faster than the speed of sound, and on a lower trajectory in the atmosphere, potentially reaching a target more quickly. Moreover, these missiles can tackle the opponents by further compressing their counter-responses. As a result, major world powers are in a race to develop hypersonic military warfare. Further advancement of such technologies presents growth opportunities for the military optronics surveillance and sighting systems market.
FAQs:
Q 1) Which are the leading and fastest-growing regions in the global market?
North America (leading) and the Asia-Pacific (fastest-growing).
Q 2) Which industry components are covered in the market report?
Raw Material Suppliers, Manufacturers, Defense OEM/Prime Contractors, and End-users.
0 notes
Text
What Would Happen If World War 3 Started
Satellites, airpower, cyber combat, drones, and a coterie of different technical property have allowed for the comparatively small U.S. army to punch above its weight. Yet, the united states military and its leaders have come to fetishize high-technology and rely far an extreme quantity of on it to make up for real weaknesses in its total force construction. Policymakers right now are probably to overlook that wars are still fought and won by males, not machines. In this context, the double lesson of the world wars — calling America to guide the world but cautioning it not to overreach — narrowed to a single-minded exhortation to maintain and even increase American power discover more information here.

“Today the issue just isn't solely Donbas, the issue is not only Ukraine — what is at stake is the stability in Europe and the whole worldwide order,” he mentioned. “Or the outcry in opposition to the crimes towards humanity is so robust that we really feel compelled to take what we predict is a restricted and even handed action,” the analyst said, speaking on condition of anonymity because of the sensitivity of the scenario. Conflict may easily escalate right into a direct confrontation between Russia and the West, officers and analysts warn. There are channels of communication between the 2 sides to deconflict navy actions and to defuse the crisis should something unintentional happen. But the choice for Western allies of doing nothing to help Ukraine militarily would simply make Ukraine's defeat inevitable, enabling Russia to score the prize of locking its neighbour into facing east, rather than west. Instead, particular person allies, including the UK, the US and even - since Russia's invasion started - beforehand extra pacifist Germany, are attempting to track a center line between direct intervention and doing nothing when is WW3 going to start.
In particular, Zelensky discussed “finding efficient solutions within the field of logistics, growing the capability of ports, including the Black Sea port of Constanța, and river transport on the Danube River” with Romanian and Bulgarian officials. Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky mentioned the potential of offering free entry for Ukrainian agricultural merchandise to European Union countries throughout a meeting with several EU leaders on Wednesday. No casualties or injury have been reported so far by the Russian defense ministry or Russian regional officers. Russia intercepted 22 Ukrainian drone assaults early Thursday, Russia's Ministry of Defense said on Telegram. In February, JPMorgan despatched a delegation to Kyiv to brief Zelensky on choices to stabilize Ukraine’s beleaguered financial system and assist the country entry the capital required to rebuild it. Ukrainian officers signed a memorandum of understanding with JPMorgan to help create a roadmap for reconstruction.
It has additionally vaulted a Chinese invasion of Taiwan to the forefront of American fears and increased Washington’s willingness to reply with army pressure. As Russian forces pummel Kyiv and other cities, Western powers have maneuvered extraordinarily rigorously to keep away from direct battle with President Vladimir Putin, the man who controls the world’s largest nuclear arsenal and has shown no qualms in boasting about it. Reuters, the information and media division of Thomson Reuters, is the world’s largest multimedia news provider, reaching billions of people worldwide every day. Reuters offers enterprise, financial, national and worldwide news to professionals by way of desktop terminals, the world's media organizations, trade occasions and on to consumers. The longer the conflict goes on, the larger the chance of a stray Russian missile or rocket hitting one of the NATO countries that border Ukraine, or taking out an allied warship or jet working close by. For example, NATO allies have made it very clear that they gained't send troops into Ukraine to help the Ukrainian armed forces defend themselves.
If you’re making jokes about world war 3 whereas living in a safe nation nowhere near ukraine, you’re being incredibly insensitive. While he has claimed that it is a army action in Ukraine, explosions might be heard quickly after in the capital Kyiv and other elements of the country. Putin also referred to as on Ukrainian service members to "lay down their arms and go residence", including that the particular navy motion was meant for "demilitarisation and denazification" of Ukraine.
“But what we’ve seen, especially for the explanation that invasion, is China attempting to distance itself from Russia, providing itself up as a moderator and looking for a peaceable answer,” Cross says. Often described as coldly calculating, just like the chess participant and judo fighter that he is, his speech on Monday resembled more that of an indignant dictator than a shrewd strategist. They are feeling distinctly nervous that Russian forces may not cease at Ukraine and instead use some pretext to "come to the help" of the ethnic Russian minorities in the Baltics and invade. Only President Putin and his trusted inner circle know how deep into Ukraine he intends to send his troops.
This would especially be the case after early-warning missile satellites had been knocked out in the opening phases of a space war. Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky met Wednesday night with Wall Street CEOs and business power players to discuss efforts to rebuild his war-torn country and its financial system, an individual acquainted with the matter informed CNN. In the spring, Poland turned the first NATO country to send fighter jets to Ukraine – months ahead of the US, which solely agreed last month to approve the switch of F-16 fighter jets, pending the completion of training by Ukrainian forces. Poland and Ukraine share a lengthy border, an area where the war resonated fiercely on Tuesday after Russian drones struck warehouses within the western Ukrainian city of Lviv. President Joe Biden thanked fellow leaders for their work in addressing international challenges, together with Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, in remarks to the United Nations Leader’s Reception on the New York’s Metropolitan Museum of Art. While Biden called international institutions created at the end of World War II – the UN, the World Bank, the World Trade Organization and others – “an enduring bedrock of our progress,” he additionally acknowledged the necessity to reorient them toward a altering world.
But President Joe Biden and different allied officials have rejected the idea, citing the dangers of a navy confrontation between the West and Russia that might rapidly escalate into something worse. The SDI concept was to use ground-based and space-based systems to guard the United States from assault by strategic nuclear ballistic missiles. The initiative centered on strategic defense somewhat than the prior strategic offense doctrine of mutually assured destruction (MAD).
Ukraine's acknowledged desire to hitch the alliance was one reason Putin used to justify his invasion. A promise to stop pursuing NATO membership can additionally be one of his circumstances to end the war. "Nobody knows whether or not it could have already started. And what is the potential for this struggle if Ukraine will fall, in case Ukraine will? It's very onerous to say," Zelenskyy mentioned. "And we've seen this 80 years ago, when the Second World War had began ... nobody would be capable of predict when the full-scale struggle would begin." “I don’t assume either of them actually wants to alienate Russia, but nor does both nation have any reason to assist what Russia is doing,” D’Anieri continued. Some longtime Russia observers have been surprised by Putin’s decided stance on Ukraine.
Poland has been an ally of Ukraine for the explanation that Russian invasion, taking in additional than one million Ukrainian refugees and main the method in which in urging NATO companions to send extra military supplies to Kyiv. Western assist for Ukraine because it defends against Russia has globally vital consequences, Polish President Andrzej Duda mentioned Tuesday, urging Kyiv’s backers to remain steadfast. Instead, he talked about how climate change, inequality and different cross-border issues require the structure of an inclusive worldwide order. Speaking before Biden, Brazilian President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva, who needs to turn his nation into a frontrunner of the southern hemisphere, stated the Security Council “has been progressively losing its credibility” precisely because a few nations wield so much power.
The hesitance to impose the no-fly zone led Zelenskyy to say Tuesday that he sees no "open door" for Ukraine to affix NATO, according to a video of him talking with army officers posted to Telegram. As for Sarotte, she mentioned the scenario is among the most harmful in latest memory, and continues to be rapidly evolving. “If you had requested me two weeks ago what the chance of main nuclear conflict was, I would have mentioned pretty low, but now I would say I don’t know, and that’s not good,” she said.
A new generation, personally untouched by great energy struggle, reshaped the past, revering their elders however simplifying the often varied and painful experiences of veterans. Zelenskyy is scheduled to travel to the us this week to deal with the United Nations General Assembly and go to the White House and Congress. With reference to the numerous non-military targets Russia news has attacked, Pelley requested Zelenskyy what he thought Putin was attempting to perform by killing civilians.
North Korea’s vows to expand its nuclear stockpile have also elevated fears of a world battle. Hours into the New Year, leader Kim Jong Un called for an “exponential increase” in his regime’s nuclear arsenal, in a sign of “deepening animosity” in course of the US, South Korea and Japan, stated The Guardian. As international relations have deteriorated in recent times, critics of U.S. international primacy have regularly warned that a new chilly struggle was brewing. During the unique Cold War, American leaders and citizens knew that survival was not inevitable. World-rending violence remained an all-too-possible vacation spot of the superpower contest, right as much as its astonishing end in 1989.
The Sino-Soviet border conflict was a seven-month undeclared navy border warfare between the Soviet Union and China on the height of the Sino-Soviet split in 1969. The most severe of these border clashes, which introduced the world's two largest communist states to the brink of war, occurred in March 1969 in the neighborhood of Zhenbao (Damansky) Island on the Ussuri (Wusuli) River, close to Manchuria. Exercise Mainbrace brought together 200 ships and over 50,000 personnel to follow the protection of Denmark and Norway from the Soviet attack in 1952. The train was jointly commanded by Supreme Allied Commander Atlantic Admiral Lynde D. McCormick, USN, and Supreme Allied Commander Europe General Matthew B. Ridgeway, US Army, during the autumn of 1952.
The potential for absolutely the destruction of the human species may have contributed to both American and Soviet leaders avoiding such a situation. Many army leaders who had fought in Vietnam supported it, realizing that those who volunteered to serve and fight in a warfare were often simpler in combat than those who had been merely drafted into service. Despite the strategic failures of the AVF in Afghanistan and Iraq, most navy leaders today insist upon preserving the AVF somewhat than institute conscription. The good economist, Milton Friedman, hailed the creation of an AVF as a momentous step toward nationwide progress. Friedman argued that a conscription pressure was finally one by which its members had been slaves until the battle ends (or they die).
However, the USSR noticed the SDI idea as a major risk, since a unilateral deployment of the system would enable the US to launch a large first strike on the Soviet Union with none fear of retaliation. The same month, the US despatched a submarine with nuclear-armed ballistic missiles to South Korea for the primary time in decades, prompting North Korea’s defence minister to warn that this might meet its authorized situations to be used of nuclear weapons. Ukraine’s Western allies are supplying weapons and different materiel, however have ruled out the idea of imposing a no-fly zone. EU international locations are offering air defense methods, but have balked at Ukraine’s request for fighter jets.
War crimes were perpetrated in World War I. Chemical weapons had been used within the war despite the Hague Conventions of 1899 and 1907 having outlawed using such weapons in warfare. The Ottoman Empire was liable for the Armenian genocide, during the First World War, in addition to different war crimes. Insofar as one of the major results of sanctions has been to send tens of hundreds of middle-class Russians into exile, they really help Putin by weakening a potent base of political opposition. As for the oligarchs, they could have misplaced their yachts, however they’re not about to pick up their guns. "Putin," stated a senior British army source on Tuesday, "just isn't about to assault Nato. He just wants to turn Ukraine right into a vassal state like Belarus." Eastern European countries like Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania or Poland - once part of Moscow's orbit in Soviet times - are all now Nato members.
“We can look forward to destruction here, just as the opposite nations in the Second World War.” This perception didn’t keep him or his successors from meddling in third world international locations, from Guatemala to Indonesia, the place the Cold War was brutal. But U.S. leaders, regardless of party, acknowledged that if the United States and the Soviet Union squared off directly, nuclear weapons would lay waste to the American mainland. More than some other presidential statement since Sept. 11, 2001, Mr. Biden’s warning signaled the beginning of a model new period in American overseas coverage. Throughout my grownup life and that of most Americans today, the United States bestrode the world, essentially unchallenged and unchecked. Although “great energy competition” grew to become the watchword of Pentagonese, the phrase may as easily indicate sporting rivalry as explosive conflict.
The Strategic Defense Initiative Organization (SDIO) was arrange in 1984 throughout the United States Department of Defense to supervise the Strategic Defense Initiative. At the time the US nuclear arsenal was restricted in measurement, primarily based within the United States, and relied on bombers for supply. "Dropshot" included mission profiles that may have used 300 nuclear bombs and 29,000 high-explosive bombs on 200 targets in one hundred cities and cities to wipe out 85% of the Soviet Union's industrial potential in a single stroke. Between seventy five and one hundred of the 300 nuclear weapons have been focused to destroy Soviet combat aircraft on the bottom. The AVF model will simply be inadequate to produce the army with the force ranges that will be required to go up against China’s 2.18 million-man navy or Russia's a couple of million-man drive.
In July, North Korea detained a young US military soldier, Travis King, who crossed the border from South Korea without permission. The disaster got here “during a very tense time with the North”, mentioned BBC News. Today the United States is once more assuming the first burden of countering the ambitions of governments in Moscow and Beijing. When it did so the first time, it lived in the shadow of world struggle and acted out of a frank and healthy worry of another. These questions will be requested during a battle, so they must be asked prematurely. Even those who think the United States ought to struggle for Ukraine or Taiwan have an interest in educating the public about the stakes of nice power battle in the nuclear and cyber age.
Providing Kyiv with MIG-29 fighter jets and different probably game-changing weapon techniques might help turn the tide. What would a world struggle imply for these superpowers not at present twisted up in the conflict? In the case of China, the world’s second largest superpower, it’s unclear—even although the Chinese Communist Party has been critical of the U.S.’s role in the conflict, suggesting that NATO encroachment has provoked Russia, Cross says. But western leaders nonetheless worry Russia could presumably be poised to make a full-scale invasion of Ukraine. European Command that practiced command and management procedures, with emphasis on the transition from solely typical operations to chemical, nuclear, and conventional operations during a time of struggle. He argues the media has oversimplified Ukraine's counteroffensive by focusing an extreme quantity of on the theatre of the front line, the place the gains have been marginal, and less on the substantial successes of missile strikes in Crimea and the focusing on of Russian warships.
Mark Cancian believes that “after about nine months of intense peer conflict, attrition would grind the U.S. armed forces right down to one thing resembling the navy of a regional power." That is until the United States can embrace a complete warfare ethos—as it did on the planet wars. Exercise Reforger (from the REturn of FORces to GERmany) was an annual exercise carried out in the course of the Cold War by NATO. The Warsaw Pact outnumbered NATO all through the Cold War in conventional forces, and especially in tanks and armoured automobiles. Therefore, within the event of a Soviet invasion, so as not to resort to tactical nuclear strikes, NATO forces defending against a Warsaw Pact armored spearhead would have to be shortly resupplied and changed. Although he later believed in disarmament treaties slowly blunting the hazard of nuclear weaponry by reducing their quantity and alert standing, he also believed a technological resolution might enable incoming ICBMs to be shot down, thus making the US invulnerable to a primary strike.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Space Situational Awareness Market Qualitative & Quantitative Study
Space Situational Awareness Market, Solution (Services, Payload Systems, and Software), Orbital Range (Near-Earth and Deep Space), End Use (Commercial, and Government & Military), Object, Capability and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East and Africa and South America)
Market Overview
The global Space Situational Awareness market size is projected to reach USD 2 billion by 2026 at a CAGR of 4.6% from USD 1.5 billion in 2021 during the forecast period 2021-2028.
Space Situational Awareness (SSA) is a term which refers to keeping a track of object in the orbit of earth and predicting their position at a given time in space. It not just tracks the position of the objects but also identify multiple objects in the orbit and also reck the orbit followed by them. Its most important contribution is that it allows to predict the particles that might collide with earth.

Due to the recent surge in demand for earth observation imagery and analytics along with the increased number of space exploration mission are some of the factors that have supported long-term expansion for Space Situational Awareness Market.
The COVID-19 pandemic is causing widespread concern and economic hardship for consumers, businesses, and communities across the globe. Halted supply chain, new import export regulations, the manufacturing ability all of these factors were witnessed by the sector.
Request For Free Sample Report: https://www.delvens.com/get-free-sample/space-situational-awareness-market-trends-forecast-till-2028
Regional Analysis
North America is expected to be the largest market during the forecast period. Due to the recent regulation of US government and its focus to track missiles, nuclear warhead.
Competitive Landscape
Key Players
L3Harris Technologies
Lockheed Martin Corporation
Kratos Defense & Security Solutions, Inc.
Parsons Corporation
Peraton
To Grow Your Business Revenue, Make an Inquiry Before Buying at: https://www.delvens.com/Inquire-before-buying/space-situational-awareness-market-trends-forecast-till-2028
Recent Developments
In September 2021, A USD 2.8 million Department of Defense funding was received by Kratos Defense and Security Solutions for a prototype development effort so as to provide commanders with quick access to space-related situational awareness data.
In August 2021, Telespazio UK was awarded a Service contract by the European Space Agency to run the science operations centers of the astronomy, heliophysics, and fundamental physics missions.
Reasons to Acquire
Increase your understanding of the market for identifying the best and suitable strategies and decisions on the basis of sales or revenue fluctuations in terms of volume and value, distribution chain analysis, market trends and factors
Gain authentic and granular data access for Space Situational Awareness market so as to understand the trends and the factors involved behind changing market situations
Qualitative and quantitative data utilization to discover arrays of future growth from the market trends of leaders to market visionaries and then recognize the significant areas to compete in the future
In-depth analysis of the changing trends of the market by visualizing the historic and forecast year growth patterns
Direct Purchase of Research Report at: https://www.delvens.com/checkout/space-situational-awareness-market-trends-forecast-till-2028
Report Scope
Space Situational Awareness Market is segmented into solutions, end use, object, orbital range, capability and geography.
On the basis of Solutions
Services
Space weather
Space weather forecasts and warnings
Radiofrequency interference notifications
Near-earth object detection
Disposal/end-of-life-support
Tracking space debris
Re-entry predictions
Orbit determination
space surveillance and tracking (SST)
Launch and Early Orbit Phase
On-Orbit Conjunction Assessment
Mission Support & Navigation
De-orbit Support
Collision Avoidance and Mitigation
Space Traffic Coordination & Safety
Deep space Detection and tracking
Breakups and Seprations
Space Object Identification
Launch Detection
Payload systems
Ground Based systems
Radar Sensor
Telescope
Space based sensors
Satellite
Datalinks
Software
Orbit determination tool kit
ComSpOC
Space data center
Space event generator
Joint space operations center
On the basis of Capability
Detect, Track, and Identify (D/T/ID)
Threat warning and assessment
High altitude nuclear detection
Orbital ASAT
Directed energy attack
Jamming
Others (Cyber Attack, Direct Ascent ASAT)
On the basis of Object
Mission-related debris
Rocket bodies
Fragmentation debris
Functional spacecraft
Non-functional spacecraft
Others
On the basis of Object
Mission-related debris
Rocket bodies
Fragmentation debris
Functional spacecraft
Non-functional spacecraft
Others
On the basis of End-User
Commercial
Government & Military
On the basis of Region
Asia Pacific
North America
Europe
South America
Middle East & Africa
About Us:
Delvens is a strategic advisory and consulting company headquartered in New Delhi, India. The company holds expertise in providing syndicated research reports, customized research reports and consulting services. Delvens qualitative and quantitative data is highly utilized by each level from niche to major markets, serving more than 1K prominent companies by assuring to provide the information on country, regional and global business environment. We have a database for more than 45 industries in more than 115+ major countries globally.
Delvens database assists the clients by providing in-depth information in crucial business decisions. Delvens offers significant facts and figures across various industries namely Healthcare, IT & Telecom, Chemicals & Materials, Semiconductor & Electronics, Energy, Pharmaceutical, Consumer Goods & Services, Food & Beverages. Our company provides an exhaustive and comprehensive understanding of the business environment.
Contact Us:
UNIT NO. 2126, TOWER B,
21ST FLOOR ALPHATHUM
SECTOR 90 NOIDA 201305, IN
+44-20-8638-5055
0 notes
Text
Military Optronics Surveillance and Sighting Systems Market: Growth Overview
Sub-national conflicts involving strong cross-border dynamics are commonly witnessed across the globe, making it critical for nations to ensure military strength and advance their defense systems. In view of this, several countries have increased their defense budgets, especially for border security. This has increased the deployment of integrated observation equipment, fire control systems, mobile vehicle surveillance systems, and other such equipment, which is expected to bolster the global military optronics surveillance and sighting systems market.

Triton Market Research’s report estimates that the market will display a CAGR of 5.70% in the forecast years from 2023 to 2030. Military optronics surveillance and sighting systems enable rapid & early detection of illegal border activities and offer strong situational awareness by tracking movement across rough terrains, thus preparing armies for combat. Also, along with traditional warfare equipment, many countries are focusing on the R&D of modern warfare equipped with AI and other technologies, thus advancing market prospects.
Beyond Borders – Evaluating Regional Markets’ Performance
North America and Europe occupy key positions in the global market, which can be accredited to the presence of large-scale arms manufacturers and other key market players in these regions. Whereas, the Asia-Pacific military optronics surveillance and sighting systems market is also expected to flourish due to an increased focus on domestic manufacturing and extensive investments in R&D.
Israel, an important market in the Middle East and Africa, is a major supplier of advanced military systems, such as missiles, drones, radar systems, and others, and exported weapons worth over $345 million to 16 countries in 2020. On the other hand, in most Latin American countries, specific drug control units have been highly militarized to tackle the growing threat from transnational crime & drug trafficking organizations. This has necessitated the demand for guns, armored vehicles, clothing, and tactile equipment, to facilitate logistical support.
Military Optronics Surveillance and Sighting Systems Market Segmentation
Military Laser Systems is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.99% in the Machinery segment during 2023-2030
Fiber lasers, semiconductor diode lasers, solid-state lasers, and CO2 & other gas lasers are some of the laser systems used in the military. They are used for target designation & tracking, guidance, and range finding, and are also used in conjunction with squad weapons. Vectronix by Safran Group is a widely used military laser system; the high-performance handheld equipment is embedded with high resolution & superior quality optics.
Aerial is estimated to grow at a 6.03% CAGR in the Medium segment during the forecast period
Modernization of aerial warfare is being witnessed with the addition of combat aircraft and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). They are generally used for surveillance, target acquisition, intelligence gathering, and also for transporting aircraft ammunition. Advanced technologies like multispectral imaging are being increasingly used in UAVs. Besides, the use of some emerging technologies, such as hyperspectral imaging and infrared thermography, will offer lucrative opportunities for the growth of this segment.
Seismic and Acoustic Sensors held a revenue share of $4217.22 million in the Product Type segment in 2022
Seismic and acoustic sensors are used in the military because of their ability of identifying & tracking targets in non-LoS conditions and carrying out missions in a docile manner. These sensors are used in numerous applications, such as defense security, monitoring, and surveillance. They are also being used in several modern surveillance sensor systems called unattended ground sensors (UGS). A UGS has inbuilt sensors with magnetic, acoustic, seismic, and infrared capabilities. The combination of features from various sensor technologies largely optimizes their target recognition ability.
What Our Experts Say
Stealth technology presents growth scope due to growing investments by countries to gain a tactical advantage over enemy forces. Also called low observable technology, it is a core element of modern military warfare to make one’s own forces discreet and ideally invisible to the enemy. Some well-known stealth aircraft include the F-22 Raptor by Lockheed Martin Corporation and Chengdu J-20 by Chengdu Aerospace Corporation.
Also, there is an enhanced focus on developing defense systems with hypersonic technology. There are two main types of hypersonic weapons, which include hypersonic glide vehicles and hypersonic cruise missiles. The latter travel 5 times faster than the speed of sound, and on a lower trajectory in the atmosphere, potentially reaching a target more quickly. Moreover, these missiles can tackle the opponents by further compressing their counter-responses. As a result, major world powers are in a race to develop hypersonic military warfare. Further advancement of such technologies presents growth opportunities for the military optronics surveillance and sighting systems market.
FAQs:
Q 1) Which are the leading and fastest-growing regions in the global market?
North America (leading) and the Asia-Pacific (fastest-growing).
Q 2) Which industry components are covered in the market report?
Raw Material Suppliers, Manufacturers, Defense OEM/Prime Contractors, and End-users.
#military optronics surveillance sighting systems market#aerospace#defense industry#triton market research#market share reports#market share trends
0 notes
Text
Saturday, April 29, 2023
Consolidation
(WSJ) Industrial consolidation is a serious problem, especially when it comes to the companies that supply arms to the Pentagon. The number of major arms suppliers is down to just five, the number of fixed-wing aircraft suppliers has fallen from eight to three since the end of the Cold War, major shipbuilders are down from eight to two, three companies make 90 percent of the missiles, and the overall defense industrial base fell from 69,000 vendors in 2016 to 55,000 vendors as of 2021. This can cause bottlenecks; take, for instance, the only domestic source of black powder, a factory in Louisiana. Black powder is needed in small amounts for 300 kinds of munitions to detonate larger explosives, which is a problem, because that factory exploded in June of 2021, eliminating the sole supplier. That’s an issue if, for example, you’ve hypothetically got a land war in Europe. The Pentagon spent $3.5 million to help upgrade and fix it up, and shipments should resume this summer.
Cigarette Smoking Declines
(1440) The number of US adults who smoke cigarettes dropped to an all-time low last year, according to new data released yesterday from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Preliminary findings from a survey of more than 27,000 adults show 11%, or 1 in 9 adults, reported smoking in 2022, down from 12.5% in 2021 and in 2020. Cigarette smoking—linked to cancer, heart disease, lung diseases, and more—has been declining since the mid-1960s when 42% of US adults identified as active smokers.
U.S. to open immigrant processing centers in Latin America
(Washington Post) The Biden administration said Thursday that it will set up new immigration processing centers in Colombia and Guatemala as part of a wider hemispheric effort to curb human smuggling and the soaring number of illegal crossings at the U.S. southern border. Secretary of State Antony Blinken and Homeland Security Secretary Alejandro Mayorkas described plans for the centers and announced other preparations the administration is making in anticipation that illegal crossings—already near record levels—will surge even higher when the White House lifts pandemic-era border controls on May 11. Speaking to reporters at the State Department, Blinken and Mayorkas said the centers will encourage migrants to avoid smugglers and seek to come to the United States legally by boosting refugee admissions, increasing family reunification visas and expanding other lawful channels. Migrants who disregard those pathways will face stiffer consequences if they cross the U.S. border illegally, including fast-tracked deportations, a five-year ban on reentry and possible criminal charges, they said.
Argentina Shifts to the Yuan
(Foreign Policy) Argentina will officially start paying for Chinese imports in yuan rather than dollars, Argentine Economy Minister Sergio Massa announced on Wednesday. Argentine authorities hope the currency deal will help ease the country’s diminishing dollar reserves, which is critical to the stability of the country’s financial system. The country has one of the world’s highest inflation rates: It is currently more than 100 percent for the first time in three decades. Many banks are even having to build new vaults to hold all of the country’s currency deposits. Argentina is not the first Latin American country to switch to the yuan. Brazil recently signed an agreement with China to trade in yuan and reals instead of dollars. China is Brazil’s largest—and Argentina’s second-largest—trading partner. Both countries hope trading in yuan will decrease their dependency on the U.S. dollar as Chinese investment in the region grows; Beijing, meanwhile, hopes the moves will provide further momentum in its efforts to globalize the yuan.
The Pope in Hungary
(AP) Pope Francis plans to outline his vision for the future of Europe during a three-day visit to Hungary starting Friday, with Russia’s war in Ukraine, migration flows and Hungary’s tense relations with Brussels looming large over the pontiff’s weekend journey. Hungarian officials say Francis’ pilgrimage was designed primarily to let the pope minister to the country’s Catholic community and to encourage its members in their faith. Francis is also set to meet with some of the 35,000 Ukrainian refugees who have remained in Hungary after 2.5 million fled across Ukraine’s border with Hungary’s early on in Russia’s invasion. It will be another opportunity for Francis to raise immigration as a topic and to reiterate his belief that European countries should, within their means, open their arms and borders to people fleeing poverty as well as conflicts.
NATO: Ukraine allies sent 1,550 combat vehicles, 230 tanks
(AP) NATO allies and partner countries have delivered more than 98% of the combat vehicles promised to Ukraine during Russia’s invasion and war, the military alliance’s chief said Thursday, giving Kyiv a bigger punch as it contemplates launching a counteroffensive. Along with more than 1,550 armored vehicles, 230 tanks and other equipment, Ukraine’s allies have sent “vast amounts of ammunition” and also trained and equipped more than nine new Ukrainian brigades, NATO Secretary-General Jens Stoltenberg said. More than 30,000 troops are estimated to make up the new brigades. Some NATO partner countries, such as Sweden and Australia, have also provided armored vehicles. “This will put Ukraine in a strong position to continue to retake occupied territory,” Stoltenberg told reporters in Brussels.
Russia Digs In
(Reuters) When Ukraine’s military paused to regroup towards the end of 2022, extensive Russian fortifications designed to slow any Ukrainian advances started to spring up along, behind and sometimes far removed from the front lines. Satellite images of thousands of new defensive positions reviewed by Reuters show Russia has been digging in at key strategic points in readiness for an offensive by a Ukrainian military rearmed with state-of-the-art Western weapons. Stretching from the Russian city of Voronok down through eastern Ukraine and southwest to the Crimean Peninsula, new trenches, anti-vehicle barriers and revetments for equipment and material have appeared, said Brady Africk, an open-source intelligence researcher and an analyst at the American Enterprise Institute. Africk said his research showed Russian anti-vehicle ditches and barriers such as “dragon’s teeth”—concrete pyramid blocks set in staggered rows to block tanks—were common in Ukraine. Mine fields are common too. The fortifications, though, like other aspects of the war, will leave scars well after the last shell is fired, Africk said, telling of how another researcher found a mark he was having trouble interpreting on the terrain in a satellite photo of Ukraine.
Foreign companies in China face growing scrutiny, pressure
(AP) Foreign companies are under growing pressure in China from anti-corruption, security and other investigations as President Xi Jinping’s government tightens control over business. This week, Bain & Co. said police questioned staff in its Shanghai office. Last month, the corporate due diligence firm Mintz Group said its Beijing office was raided by police who detained five employees. Also last month, an employee of a Japanese drug maker was detained on spying charges and the government announced a security review of memory chip maker Micron Inc. Business groups have said global companies are shifting investment plans to Southeast Asia, India and other economies. The investigations come at a time when China’s relations with Washington, Europe and Tokyo are strained by disputes about human rights, Taiwan, security and technology.
Hong Kong’s economy is recovering, but its freedoms are not
(AP) Like most people in Hong Kong, taxi driver Leung Tat-chong says it feels like the city is recovering after years of protests, crackdowns and pandemic restrictions, while it also has changed forever. He’s earning almost as much as he did before the pandemic. But, Leung said, the city has been divided since the 2019 protests, in which hundreds of thousands of people marched, and many battled police, in opposition to a government they saw as a proxy for Beijing. Leung sometimes doesn’t turn on the radio in his cab because the news or a public affairs program could get his customers cursing. He watches what he says in front of friends to avoid starting fights. Living in Hong Kong today means juggling contradictory feelings. In 20 interviews, many said that when they focus on business indicators and everyday life, they see a recovery gathering pace after years of travel restrictions. But when it comes to anything political, the openness and freedoms that were once hallmarks of the Chinese-ruled former British colony seem permanently gone.
Tanker tit for tat
(AP/Foreign Policy) Masked Iranian navy commandos conducted a helicopter-borne raid to seize a U.S.-bound oil tanker in the Gulf of Oman, footage aired by Iran's state television showed Friday. The capture on Thursday of the Turkish-managed, Chinese-owned Advantage Sweet represents the latest seizure by Iran amid tensions with the U.S. over advancing nuclear program. According to Iranian state media, the country’s navy said it took the ship after it had collided with an Iranian boat, injuring several crew members. However, the Financial Times reports that the move came just days after the United States ordered a tanker carrying Iranian oil headed for China to be redirected to Washington. Thursday’s maritime seizure was the fifth commercial vessel taken by Iran in the last two years.
Looting, Roadblocks: Paramilitary Is a Scary Neighbor in Sudan’s Capital
(NYT) In the 12 days since war broke out in Sudan, the residents in the capital of Khartoum have learned to survive, living side by side with armed fighters. Civilians negotiate with a feared paramilitary faction at roadblocks for safe passage, grudgingly share food and water with them, and sometimes receive warnings about an upcoming battle—giving residents time to either bolt or run back inside and lock their doors. The fighters have moved into homes and taken over stores and hospitals, alternatively terrifying and wooing civilians. In one neighborhood, a resident said, they handed out milk. In another, they invited community members to share in the spoils of their looting. In another, they turned vigilantes, punishing petty criminals. “Apparently they don’t have anyone that gives them orders so they’re just doing their thing,” said Dania Atabani, who lives in Khartoum. The paramilitary group, the Rapid Support Forces, was part of a military-led government as recently as this month, but is now combating the regular army for power in Sudan, a northeast African country of 45 million people surrounded by seven nations.
Too many people take too many pills
(Economist) As a pharmacist in a big hospital in Adelaide, Emily Reeve would often see patients overwhelmed by the number of drugs they took each day. “They’d say ‘I take so many medicines that I rattle when I walk’,” she recalls. Dr Reeve’s patients are not unusual, at least in the rich world. About 15% of people in England take five or more prescription drugs every day. So do 20% of Americans and Canadians aged 40-79. Not all those prescriptions are beneficial. Half of older Canadians take at least one that is, in some way, inappropriate. A review of overprescribing in England in 2021 concluded that at least 10% of prescriptions handed out by family doctors, pharmacists and the like should probably not have been issued. And even properly prescribed drugs have side effects. The more medicines someone takes, the more they will experience. A recent study at a hospital in Liverpool found that nearly one in five hospital admissions was caused by adverse reactions to drugs. The Lown Institute, an American think-tank, reckons that, between 2020 and 2030, medication overload in America could cause more than 150,000 premature deaths and 4.5m hospital admissions. Getting people off drugs is unfamiliar terrain for modern health systems, which are mostly set up to put patients on them. Medication overload persists for several reasons. One, particularly in America, is advertising, which oversells the benefits of medicines. Lack of unified personal health records is another. A cardiologist may prescribe drugs for a patient without knowing what the doctor treating his lungs may have put him on. Perhaps the most common reason is that patients are not told when to stop taking a drug, or forget.
0 notes
Text
Military Antenna Market Trends, Share, Scope and Forecast by 2030
The market study covers several perceptions of the market, with market dynamics, value chain, pricing analysis, competition analysis, regional and segmental growth comparison, and macro-economic and industry growth analysis, alongside segment-level projections in a comprehensive manner. Increasing technological advancements, growing need for modern battle equipment, rising demand for innovative communication systems, increasing security concern, modernization of the military equipment, rise in terrorist activities, attack prone border, increasing demand for high - frequency military aircraft are few of the factors driving the market. The marketS are combined with advanced applications like multifunctional radars, 3D drones, etc. which provide better surveillance for accurate target tracking. However, the high cost involved in the development of the device is one of the main challenges for the development of the market. The global market is segregated on the basis of Application as Electronic Warfare, Navigation, Telemetry, Communication, Surveillance, and SATCOM. Based on the Frequency band the market is segmented in Ultra-High Frequency, Super High Frequency, Extremely High Frequency, High Frequency, and Very High Frequency. Based on Platform the market is segmented in Ground, Marine, and Airborne. Based on Type, the market is segmented in Loop Antennas, Aperture Antennas, Travelling Wave Antennas, Dipole Antennas, Monopole Antennas, and Array Antennas.
The global market report provides geographical analysis covering regions, such as North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and the Rest of the World. The market for each region is further segmented for major countries including the U.S., Canada, Germany, the U.K., France, Italy, China, India, Japan, Brazil, South Africa, and others.
View Complete Report@ https://marketreportslibrary.com/report/ad0093/military-antenna-market
The global Military Antenna market has been segmented as below:
By Application
Electronic Warfare
Navigation
Telemetry
Communication
Surveillance
SATCOM
By Frequency band
Ultra-High Frequency
Super High Frequency
Extremely High Frequency
High Frequency
Very High Frequency
By Platform
Ground
Handheld Antennas
Body Worn Antennas
Unmanned Ground Vehicle (UGV) Antennas
Base Station Antennas
Vehicle Antennas
Manpack Antennas
Marine
Shipboard Antennas
Submarine Antennas
Unmanned Marine Vehicle (UMV) Antennas
Airborne
Aircraft Antennas
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Antennas
Missile Antennas
By Type
Loop Antennas
Aperture Antennas
Travelling Wave Antennas
Dipole Antennas
Monopole Antennas
Array Antennas
By Region
North America
Europe
Asia-Pacific
Rest of the World
By Company
Harris Corporation
Cobham plc
Comrod Communications AS
Terma A/S
RAMI
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation Maxar
Technologies Norsat International Inc.
Kymeta Corporation
Viasat Inc.
Ruag International Holding Ltd.
Lockheed Martin Corporation
Aselsan A.S.
Ball Corporation
Nd Satcom
Thales Group
Gilat Satellite Networks
Micro-Ant
Sat-Lite Technologies
Datapath, Inc.
Hanwha-Phasor
Viking Satcom Ltd.
Honeywell International Inc.
General Dynamics Corporation
The report covers the below scope:
Global market sizes from 2019 to 2025, along with CAGR for 2020-2025
Market size comparison for 2020 vs 2025, with actual data for 2020, estimates for 2021 and forecast from 2021 to 2025
Global market trends, covering a comprehensive range of consumer trends & manufacturer trends
Value chain analysis covering participants from raw material suppliers to the downstream buyer in the global market
Major market opportunities and challenges in forecast timeframe to be focused
Competitive landscape with analysis on competition pattern, portfolio comparisons, development trends and strategic management
Comprehensive company profiles of the key industry players
Request a Sample of this Report: @ https://marketreportslibrary.com/request/sample/ad0093/military-antenna-market
Explore other reports from ”Information and Communication, Technology ” sector @
Contact Us:
Avinash
Market Reports Library
1 note
·
View note
Text
Military Optronics Surveillance and Sighting Systems Market: Growth Overview
Sub-national conflicts involving strong cross-border dynamics are commonly witnessed across the globe, making it critical for nations to ensure military strength and advance their defense systems. In view of this, several countries have increased their defense budgets, especially for border security. This has increased the deployment of integrated observation equipment, fire control systems, mobile vehicle surveillance systems, and other such equipment, which is expected to bolster the global military optronics surveillance and sighting systems market.
Triton Market Research’s report estimates that the market will display a CAGR of 5.70% in the forecast years from 2023 to 2030. Military optronics surveillance and sighting systems enable rapid & early detection of illegal border activities and offer strong situational awareness by tracking movement across rough terrains, thus preparing armies for combat. Also, along with traditional warfare equipment, many countries are focusing on the R&D of modern warfare equipped with AI and other technologies, thus advancing market prospects.

Beyond Borders – Evaluating Regional Markets’ Performance
North America and Europe occupy key positions in the global market, which can be accredited to the presence of large-scale arms manufacturers and other key market players in these regions. Whereas, the Asia-Pacific military optronics surveillance and sighting systems market is also expected to flourish due to an increased focus on domestic manufacturing and extensive investments in R&D.
Israel, an important market in the Middle East and Africa, is a major supplier of advanced military systems, such as missiles, drones, radar systems, and others, and exported weapons worth over $345 million to 16 countries in 2020. On the other hand, in most Latin American countries, specific drug control units have been highly militarized to tackle the growing threat from transnational crime & drug trafficking organizations. This has necessitated the demand for guns, armored vehicles, clothing, and tactile equipment, to facilitate logistical support.
Military Optronics Surveillance and Sighting Systems Market Segmentation
Military Laser Systems is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.99% in the Machinery segment during 2023-2030
Fiber lasers, semiconductor diode lasers, solid-state lasers, and CO2 & other gas lasers are some of the laser systems used in the military. They are used for target designation & tracking, guidance, and range finding, and are also used in conjunction with squad weapons. Vectronix by Safran Group is a widely used military laser system; the high-performance handheld equipment is embedded with high resolution & superior quality optics.
Aerial is estimated to grow at a 6.03% CAGR in the Medium segment during the forecast period
Modernization of aerial warfare is being witnessed with the addition of combat aircraft and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). They are generally used for surveillance, target acquisition, intelligence gathering, and also for transporting aircraft ammunition. Advanced technologies like multispectral imaging are being increasingly used in UAVs. Besides, the use of some emerging technologies, such as hyperspectral imaging and infrared thermography, will offer lucrative opportunities for the growth of this segment.
Seismic and Acoustic Sensors held a revenue share of $4217.22 million in the Product Type segment in 2022
Seismic and acoustic sensors are used in the military because of their ability of identifying & tracking targets in non-LoS conditions and carrying out missions in a docile manner. These sensors are used in numerous applications, such as defense security, monitoring, and surveillance. They are also being used in several modern surveillance sensor systems called unattended ground sensors (UGS). A UGS has inbuilt sensors with magnetic, acoustic, seismic, and infrared capabilities. The combination of features from various sensor technologies largely optimizes their target recognition ability.
What Our Experts Say
Stealth technology presents growth scope due to growing investments by countries to gain a tactical advantage over enemy forces. Also called low observable technology, it is a core element of modern military warfare to make one’s own forces discreet and ideally invisible to the enemy. Some well-known stealth aircraft include the F-22 Raptor by Lockheed Martin Corporation and Chengdu J-20 by Chengdu Aerospace Corporation.
Also, there is an enhanced focus on developing defense systems with hypersonic technology. There are two main types of hypersonic weapons, which include hypersonic glide vehicles and hypersonic cruise missiles. The latter travel 5 times faster than the speed of sound, and on a lower trajectory in the atmosphere, potentially reaching a target more quickly. Moreover, these missiles can tackle the opponents by further compressing their counter-responses. As a result, major world powers are in a race to develop hypersonic military warfare. Further advancement of such technologies presents growth opportunities for the military optronics surveillance and sighting systems market.
#Military Optronics Systems Market#Military Sighting Systems Market#Military Surveillance Systems Market#Aerospace and Defense#Defense Industry#market research report#market research reports#triton market research
0 notes
Text

On Cue From Washington: Ukraine Conflict Shows Europe's 'Dependence on US' Has Never Been Greater
— Svetlana Ekimenko
Following Washington's lead, Europe sprang into action and rolled out sanctions against Moscow to "punish" it for its military operation in Ukraine. The EU also rustled up military and financial aid for Kiev, pressing ahead with restrictions on Russia that backfired plunging it into an unprecedented and largely self-inflicted energy crisis.
Europe has never been as dependent on Washington as it is now, a US media report has highlighted.
European Union allies have all found themselves firmly positioned “in Washington’s slipstream”, following directions from the Biden administration when it comes to the Ukraine conflict, the outlet stated. European allies are slavishly following the signals coming out of Washington regarding their next moves on the Ukraine conflict, added the report.
As Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky's recent visit to the US confirmed, Washington plans to continue using Kiev as a proxy for an indirect war against Russia, Kremlin spokesman Dmitry Peskov emphasized. US assistance to Kiev is already on track to top $100Bln in 2022, and there is more where that came from. Biden is expected to sign off on an comprehensive spending bill in the coming days, after Congress passed the Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2023. The bill, worth nearly $1.7 trillion, funds the federal government through the 2023 fiscal year, ending on 30 September 2023. This spending bill includes nearly $45Bln in aid for Ukraine and North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) allies.
One could say that, yet again, the proof is in the money, as Washington positions itself as intent on pursuing a dominant role in siphoning funds and funneling weapons to fan the flames of the Ukraine conflict. The 46th POTUS also signed off on sending to the Kiev regime the much-coveted Patriot missile-defense system.
'Reading Cues From Washington'
European Union leaders recently pledged billions more euros to prop up Kiev, clinching an agreement to unblock an €18Bln ($19Bln) Package to Ukraine next year, circumventing a veto introduced by Hungary. However, they are left “reading cues from Washington” about what line of action to take in the coming months, the US media report emphasized.
France, for example, has delivered rocket launchers, Crotale (air defense batteries), and equipment to Ukraine and "will send more early next year", French President Emmanuel Macron said on 20 December. But the questions said to be at the back of the EU leaders’ minds are: how much more firepower is to be routed to Ukraine and where is the fine line which if we were to cross it would cause the conflict to escalate uncontrollably?
As European countries have relatively limited stocks of weaponry and ammunition, the regime in Ukraine is heavily dependent on Washington for military supplies. Accordingly, Zelensky opted for Washington as the destination of his first in-person visit earlier in December to plead the case for more weapons.
“The whole war effort has been a complex orchestra, but it’s been conducted from Washington,” the report quoted Rosa Balfour, director of international peace organization Carnegie Europe, as saying.
Mixed Messages
After US Army Gen Mark Milley, chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, said during an appearance at the Economic Club of New York a month ago that a victory by Ukraine might not be achieved militarily, and that there may be a window for Kiev’s negotiations with Russia, the Biden administration went into damage-control mode, indicating that peace talks were not currently on the table.
However, at his joint press conference with US President Biden at the White House, Zelensky claimed “there can’t be any just peace” in Ukraine, pressuring Washington to provide even more weapons and cash to his regime. The Ukrainian leader’s words flew in the face of a remark delivered by Biden just minutes prior, in which the US president insisted Zelensky was “open to a just peace”.
Moscow has repeatedly indicated that it is ready for talks, but Kiev has imposed a ban on them at the legislative level, with Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov underscoring that it was "obvious that Kiev is not ready for dialogue."
Furthermore, there have been growing fears in the White House that a substantial number of Republicans may no longer be ready to write any more "blank checques" to Ukraine when the new Congress convenes in January.
Within Europe, commitment to aiding Ukraine and sanctioning Russia has come at a heavy price. The continent is in the midst of an unprecedented and largely self-inflicted energy crisis after restricting the purchase of Russian oil, gas, coal and electricity to “punish” Moscow for its military operation in Ukraine. Restrictions have triggered a sharp increase in energy costs, and threaten the region with deindustrialization. This has prompted citizens in countries such as Germany and the Czech Republic to protest against the sanctions that have been fueling the cost of living crisis. Therefore, further military and monetary aid to Ukraine, which can only prolong the conflict, may serve to exacerbate the tensions and fuel more popular resentment.
Whenever blame for the ongoing conflagration is placed at Moscow's door, as has been repeatedly the case on the part of Washington and its allies among the so-called collective West, President Vladimir Putin has reiterated the fact that his country is open to talks with all stakeholders on a peaceful conflict settlement in Ukraine. However, they have so far refused to negotiate.
"The policies of our geopolitical opponents, aimed at splitting up Russia, are at the root of the Ukrainian conflict," the Russian president explained.
0 notes
Text
Electronic Warfare Market Size Current And Future Industry Trends, Forecast Till 2029 Worth USD 37.60 Billion, Exhibiting a CAGR of 5.56%
The global electronic warfare market size was valued at USD 23.45 billion in 2021 and reached USD 25.74 billion in 2022. The market is expected to reach USD37.60 billion by 2029, exhibiting a CAGR of 5.56% during the forecast period. Rising geopolitical conflicts and increasing adoption of warfare technology may propel market growth. Fortune Business Insights™ presents this information in its report titled “Electronic Warfare Market, 2022-2029.” In addition, rising defense expenditures and the procurement of advanced weapons are expected to elevate the industry's growth.
Information Source:
Report Coverage
The report provides a detailed analysis of the top segments and the latest trends in the market. It comprehensively discusses the driving and restraining factors and the impact of COVID-19 on the market. Additionally, it examines the regional developments and the strategies undertaken by the market's key players.
Segments
Electronic Support Segment to Dominate Owing to Strong Demand for Surveillance and Intelligence
By domain, the market is segmented into electronic attack, electronic protection, and electronic support.
The electronic support segment is expected to dominate the market due to the rising demand for surveillance and intelligence equipment. Furthermore, rising demand for reconnaissance equipment is expected to enhance market progress.
Jammers Segment to Dominate Owing to its Strong Demand
By equipment, the market is categorized into jammer, antenna, radar warning receiver, directed energy weapon, anti-radiation missile, Counter Measure Dispenser System (CMDS), Directional Infrared Countermeasure (DIRCM), self-protection electronic warfare (EW) suite, and others.
The jammers segment is expected to dominate the market share due to its strong demand. The rising focus on portable warfare is likely to enhance the adoption of warfare systems. These factors may enhance industry growth.
Land-based Segment to Grow Owing to Military Modernization and Rising Defense Budgets
As per platform, the market is classified into air-based, sea-based, and land-based.
The land-based segment is expected to gain the highest market share due to military modernization. Furthermore, increasing defense budget is expected to enhance the adoption of land-based EW systems.
Regionally, the market is clubbed into North America, Asia Pacific, Europe, and the Rest of the World.
Driving Factors
Rising Threat of Remotely Triggered Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs)to Boost Market Growth
Electronic warfare is used to control the electromagnetic (EM) spectrum to analyze, detect, and track potential threats. It enables countries to undertake effective strategies to avoid upcoming attacks and enhance safety. The rising threat of remotely triggered Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs) is expected to enhance the adoption of EW systems. Furthermore, the emergence of new warfare tactics, such as asymmetric war and hybrid war techniques, is expected to drive the electronic warfare market growth.
However, the high cost associated with the manufacturing of warfare systems is likely to hinder the market’s progress.
Regional Insights
High Defense Spending to Enhance Industry Growth in North America
North America is expected to dominate the electronic warfare market share due to high defense spending. The market in North America stood at USD 8.41 billion in 2021 and is expected to gain a huge portion of the global market share. Furthermore, the allocation of defense budgets by the U.S. is expected to increase the adoption of the product. For example, the U.S. government allocated nearly USD 3.17 billion for 45 EW programs conducted across platforms and military service departments. These factors are likely to boost market progress in the coming years.
In Europe, the rising investment in modern warfare techniques is expected to enhance the adoption of the product. Further, major players in the region are expected to enhance the industry prospects.
In Asia Pacific, the rising expenditure in the defense sector from India, China, Australia, and Japan is expected to enhance the product demand. These factors may propel market progress.
Competitive Landscape
Players Develop Advanced Products to Elevate Brand Image
Prominent companies operating in the market develop advanced products to elevate their brand image. For example, Raytheon Technologies developed three advanced electronic Next Generation Jammers (NGJ) for the U.S. Navy EA-18G Growler EW jets in July 2021 for a contract of USD 171.6 million. This strategy may allow the company to offer advanced EW systems and enhance its brand image globally. Furthermore, companies devise partnerships, acquisitions, mergers, acquisitions, and expansions to enhance their market position globally.
Key Industry Development
February 2022: Aselsan produced and designed a land-based radar EW system named KORAL. It includes two trucks and complex and conventional hostile radar systems used for multiple target signals in wide frequencies.
0 notes
Photo
“War is the art of deception,” says one source in the Ukrainian armed forces. “We deceived them good.” The Kharkiv offensive/ miracle some are calling it sounds like something out of a film! They saw an in, tricked the Russians into thinking they were attacking one line, but encircled them instead & took back 1000 square Km! Ukraine have taken back Kharkiv, Balakliya & Izyum pushing Russia back to the Oksil river … next Kupyansk (a key rail hub for supplying Russian forces to the south)!!! Reports state Russian soldiers fled in civilian clothes on stolen bicycles & cars! A Ukrainian military intelligence source says that the success of the offensive was contingent on American-supplied harm anti-radiation missiles, which home in on the emissions of Russian air-defence radar and other equipment. It also relied on surface-to-air systems that threatened Russian aircraft: like Germany’s Gepard, a set of anti-aircraft guns on tracks. As a result Russia was reluctant to deploy air power; when it did, it suffered losses. Unconfirmed reports suggest that at least 1 Russian fighter jet & 2 helicopters were downed during Ukraine’s operation. Russian aircrafts have reportedly struggled to distinguish between Russian and Ukrainian units in the pell-mell of fighting, with frontlines shifting rapidly. “They are blind, and we see everything,” claims the Ukrainian official. 💙💛🙌🏼 #ukrainewar #slavaukraini #fuckputin https://www.economist.com/europe/2022/09/09/ukraine-seizes-the-initiative-in-the-east (at 𝐅𝐔𝐂𝐊 𝐘𝐎𝐔) https://www.instagram.com/p/CiUnHSeKgp21sn6zBRW6qG0dwXjFhSyUojv6ag0/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
1 note
·
View note
Video
youtube
(via US military learning from Russian troops using cell phones in Ukraine)
Russian troops are proving that cell phones in war zones are a very bad idea
"If I can find you, I can target you."
BY JEFF SCHOGOL | PUBLISHED MAY 13, 2022 12:50 PM
NEWS
TECH & TACTICS
A Task & Purpose photo composite showing a 2011 photo of Russian soldiers in the southern Russian city Stavropol laid over a screenshot of Ukraine via Google Maps. (Danil Semyonov/Getty Images/Google Maps).SHARE
It’s been a nightmare scenario for U.S. commanders for years: An amphibious readiness group sails stealthily towards its objective, one reckless Marine or sailor goes topside and uses a personal cell phone to check Facebook, revealing the position of the assault ship. The Chinese or Russians quickly detect the cell phone signal in the middle of the ocean and realize they can’t miss. The enemy fires its anti-ship ballistic or cruise missiles at Pfc./Seaman Schmuckatelli as he posts a meme and suddenly the entire ship along with thousands of sailors and Marines are lying on the ocean floor.
To some, this type of scenario may seem as hyperbolic as warnings that wearing white socks in combat could give away your location to the enemy, but Russian troops in Ukraine have shown the perils of using cell phones in modern-day warzones.
The Ukrainians claim to have killed 12 general Russian officers since late February, in part because the Russians have resorted to using cell phones when their communications systems break down.
“It is not hard to geo-locate someone on a phone talking in the clear,” retired Army Gen. Ben Hodges, former commander of U.S. Army Europe, told the New York Times.
Subscribe to Task & Purpose Today. Get the latest in military news, entertainment, and gear in your inbox daily.
When Russian troops cross into Ukraine, their cell phones emit a roaming signal that connects to Ukraine’s cellular network, allowing the Ukrainians to triangulate where the Russians are by using the closest three cell towers, said Artem Starosiek, CEO of Molfar, an open-source intelligence community based in Kyiv.
“So, the Ukrainian special services automatically receive information with the ID number of the device, roaming number, and, of course, the location of the person,” Starosiek told Task & Purpose. “Fortunately, Russians are quite naive and ignorant about using mobile devices, so they often call home, turning on their phones and connecting to the Ukrainian stations.”
The Russians have also given away their positions by stealing Ukrainian iPhones, which can be tracked using the Find My iPhone app, even when the phones are turned off, Starosiek said.
One Ukrainian man was able to use the “Find My” feature on Apple products to track the Russian troops who stole his AirPods, The Times of London reported. Vitaliy Semenets has posted on Instagram the path of the Russians as they retreated from Kyiv into Belarus and then repositioned in the Russian city of Belgorad, near Ukraine’s eastern border.
Amid numerous reports that the Ukrainians can track and target Russian troops when they use cell phones, one question remains: Why don’t the Russians destroy Ukraine’s cellular network?
The answer: They need it, said James Lewis, a technology expert with the Center for Strategic and International Studies think tank in Washington, D.C.
“That’s ridiculous, but that’s where it is,” Lewis told Task & Purpose. “The Russians need 3G and 4G for their comms to work. They didn’t set up the independent communications networks that the Americans or Chinese might have set up.”
While the Russians had developed encrypted communications handsets for their special operations forces, those handsets were not widely distributed among Russian troops before the latest invasion of Ukraine, Lewis said.
Corruption could be another factor that has played into why the Russian military has proven to be so poor at using secure communications, he said.
“There are good examples – not always public – of the Russians identifying a security goal and then allocating, in one case, $10 billion to it; and $5 billion of it ended up in Switzerland,” Lewis said.
The Russians also did not adequately plan for the invasion because they honestly thought that the Ukrainians would welcome them as liberators, he said. The combined effects of the corruption, poor planning, and resulting logistical problems is that there are now many images online showing Russian troops using cell phones or even the type of unencrypted walkie talkies that you could purchase at toy stores.
Looking at the Russian failures in Ukraine so far, it’s tempting to think the militaries of NATO members wouldn’t make the same mistake, but they have. In November, Polish troops that had been deployed to the border with Belarus left the dating apps on their cell phones on. Just across the border in the city of Grodno, the Belarusians knew exactly how far away the Polish troops were.
U.S. troops are far from immune to unintentionally revealing their positions by using mobile devices. In 2018, a company that gathers data from consumer fitness devices such as FitBits revealed that American service members were essentially drawing GPS maps of their bases in the Middle East and Afghanistan every time they went running.
Later that year, the Defense Department banned troops from using cell phones, fitness trackers, and other devices that use geolocation features, and now many offices in the Pentagon require people to leave their cell phones in lockers outside. A subsequent New York Times investigation revealed that companies can track people’s smartphones inside the Pentagon by using software on mobile phone apps.
The Russians’ experience in Ukraine is a warning to U.S. troops about what can happen if they act carelessly. In 2020, a bored Marine lance corporal got his entire artillery unit “killed” during an exercise at Marine Corps Air-Ground Combat Center Twentynine Palms, California, when he used his cell phone to take a selfie, Military.com reported.
“The Marine Corps understands signature management must be incorporated into planning efforts and training,” said Marine spokesman Maj. Gregory Carroll, who added that the Corps will soon release its new doctrine on information warfighting.
“A passive way to deny the opponent vital information is to selectively alter or suppress the visual, electromagnetic, and digital signatures emanating from friendly forces,” Carroll said. “This includes implementing operations security measures, communication discipline, camouflage, counterintelligence, and signature management.”
Soldiers are also trained to turn off Bluetooth and Wi-Fi radios when not using them, encrypt sensitive files, and only download trusted apps, said Maj. Andrew Harshbarger, a spokesman for Army Training and Doctrine Command. Soldiers’ mobile devices can also be disabled and confiscated when necessary.
The U.S. military has been concerned about troops inadvertently revealing their positions by using cell phones long before Russia attacked Ukraine in late February.
Commanders have known for years that U.S. troops forces have lost their fieldcraft skills at hiding their electronic, thermal, infrared, and visible signatures, said retired Gen Robert Neller, the former Marine Corps Commandant.
“We need to make the adversary work to find us – we can’t make it easy for them to find us,” Neller told Task & Purpose.
Neller recalled how Marines used to stay in touch with their families while in the field and on deployments by sending and receiving mail. While modern technology has made it easier for troops to stay in touch with loved ones, it has also created a new series of problems.
A few years ago, the I Marine Expeditionary Force conducted an exercise to find out which part of the base had the largest electromagnetic signature, he said.
“The most readily apparent thing from high overhead was the billeting area, where people were living, because they all were using their phones,” Neller said.
While Marines have improved at concealing their electronic signatures, they need to remain concerned about unintentionally revealing their positions, said Neller, who noted that even PlayStations can be detected by adversaries because they are networked.
“I don’t understand why people don’t understand,” Neller said. “If I can find you, I can target you; and if I can target you, I can shoot you; and if I can shoot at you, I can kill you. It’s pretty simple.”
0 notes
Text
Aircraft Carrier Market Share, Trend Key Players Size, Regional Outlook and Forecast - 2027
Aircraft Carrier Market Research Report: Information by Type (Conventional-Powered and Nuclear-Powered), Configuration (Catapult-Assisted Take-Off but Arrested Recovery, Short Take-Off but Arrested Recovery, and Short Take-Off but Vertical Recovery), Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East & Africa, and Latin America)—Forecast till 2027
Aircraft carrier market is estimated to witness a CAGR of approximately 3% during the forecast period 2018 to 2023.
The aircraft carrier is a floating military base consist of a fleet of fighter jets and military personnel, radar absorbent material, catapult system, missile launching systems, and anti-submarine warfare capabilities. Moreover, they are recognized for mobility, versatility, and competencies.
The aircraft carrier market has been estimated to witness steady growth during the forecast period. Moreover, China is an emerging country in the market and is expected to be the major contributor to the global market growth. Companies are looking forward to developing the aircraft carriers with a higher capacity than the conventional aircraft carriers.
Currently, in May 2018, it was reported that China was looking forward to launching its first domestically manufactured 'Type 001A' aircraft carrier, by 2020. This carrier is expected to be larger than the Liaoning aircraft carrier and feature improvements in design and its engines. The new vessels features include an overall length of 320m and a planned displacement of 85,000 tons. Moreover, China is also developing another aircraft carrier in Shanghai. It is expected that China would develop 4 to 5 aircraft carriers by 2020. The country is aggressively building on its sea power because of the ongoing conflicts in the South China Sea.
Key Players
The key players in aircraft carrier market are Thales Group (France), Fincantieri S.p.A (Italy), BAE System (U.K), Huntington Ingalls Industries Ltd. (U.S.), Navantia (Spain), Wincanton Plc (U.K), Leonardo S.p.A (Italy), Northrop Grumman Corporation (U.S.), General Atomics (U.S.), Babcock International Group PLC (U.K), and United Shipbuilding Corporation (Russia).
Scope of the Report
This study provides an overview of the global aircraft carrier market, tracking two market segments across five geographic regions. The report studies key players, providing a five-year annual trend analysis that highlights the market size, volume, and share for North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), the Middle East & Africa, and Latin America. The report also provides a forecast, focusing on the market opportunities for the next five years for each region. The scope of the study segments the global aircraft carrier market by its type, configuration, and region.
By TypeConventional-powered
Nuclear-powered
By Configuration
Catapult-Assisted Take-Off but Arrested Recovery (Catobar)
Short Take-Off but Arrested Recovery (Stobar)
Short Take-Off but Vertical Recovery (Stovl)
By Region
North America
Europe
Asia Pacific
The Middle East and Africa
Latin America
Full Report @ https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/aircraft-carrier-market-6133
0 notes