#Cat6A External Cable
Link

#Cat6 RJ-45 UTP Wall Plate Jack White 180 degrees#Cat6 Wall Plate Jack#Cat6 UTP Wall Plate#Jacks & Couplers#Structured Cabling#Cables#Cable Wires#Cat6A External Cable#Cat6A#Cat6#Network & Data Cable
0 notes
Text
Types of Telephone Cables: All You Need to Know About Them
In today's interconnected world, telephone cables play a vital role in facilitating communication. From traditional landline connections to modern voice-over-IP (VoIP) systems, understanding the different types of telephone cables is essential for both homeowners and businesses. In this article, we will explore the various telephone cable types, their features, and their applications, providing you with a comprehensive overview of these essential communication conduits.
Coaxial Cable
Coaxial cables are commonly used for cable TV and internet connections, but they also have applications in telephone systems. These cables consist of a copper conductor surrounded by insulation, a conductive shield, and an outer protective jacket. Coaxial cables offer good signal transmission capabilities and are relatively resistant to interference. However, they are less commonly used for telephone connections compared to other cable types.
Twisted Pair Cable
Twisted pair cables are the most widely used type of telephone cable. They are composed of two insulated copper wires twisted together to form a pair. The twisting helps to reduce electromagnetic interference and crosstalk between adjacent pairs. Twisted pair cables come in two main categories: unshielded twisted pair (UTP) and shielded twisted pair (STP).
UTP
UTP cables are commonly used for residential telephone lines and Ethernet connections. They are cost-effective, easy to install, and offer satisfactory performance for voice communication. However, UTP cables may be susceptible to external interference and are limited in their transmission distance.
STP
STP cables, on the other hand, have an additional layer of shielding, typically made of foil or a combination of foil and braided wire. This shielding provides better protection against electromagnetic interference, making STP cables suitable for environments with high interference levels, such as industrial settings.
Fiber Optic Cable
Fibre optic cables revolutionized long-distance communication, including telephone systems. These cables use thin strands of optically pure glass or plastic to transmit data as pulses of light. Fibre optic cables offer numerous advantages over traditional copper cables, including higher bandwidth, faster data transmission, and immunity to electromagnetic interference.
Fibre optic cables are classified into two main types: single-mode and multi-mode.
Single-Mode Fibre
Single-mode fibre cables have a small core size, allowing for the transmission of light over long distances with minimal signal loss. They are commonly used in telecommunications networks, including long-distance telephone connections.
Multi-Mode Fibre
Multi-mode fibre cables have a larger core size, enabling the transmission of light over shorter distances. They are commonly used for local area networks (LANs) and shorter telephone connections within buildings.
Ethernet Cable
Ethernet cables are primarily used for computer networking and internet connectivity. However, they can also be utilized for Voice-over-IP (VoIP) telephone systems. Ethernet cables come in various categories, such as Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat6a, each with different performance capabilities.
Cat5e cables are the most common and offer satisfactory performance for VoIP telephone applications. Cat6 and Cat6a cables provide higher data transmission speeds and better overall performance, making them suitable for more demanding telephone and networking requirements.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of telephone cables is essential for anyone looking to establish reliable and efficient communication systems. Whether you are setting up a residential landline, a business phone network, or transitioning to a VoIP system, knowing the characteristics and applications of coaxial, twisted pair, fibre optic, and Ethernet cables will help you make informed decisions. By choosing the right telephone cable type for your specific needs, you can ensure clear voice communication, minimal interference, and seamless connectivity in today's connected world.
Disclaimer: This is generic Information & post; content about the services can be changed from time to time as per your requirements and contract. To get the latest and updated information, contact us today or visit our website.
0 notes
Link
$509.00 $ Dynamix C-C6AS-EXTBK 305m Cat6A Black S/FTP UV Stabilised Shielded External Cable. https://nzdepot.co.nz/product/dynamix-c-c6as-extbk-305m-cat6a-black-s-ftp-uv-stabilised-shielded-external-cable/?feed_id=136060&_unique_id=65a2272649e16 Features: DYNAMIX 305m Cat6A Black S/FTP Shielded External Cable. Specifications: General Brand Dynamix Cable Length 305m Test Standard ISO/IEC11801, TIA- 568C.2, YD/T1019 Insulation Material Skin-foam-skin PE – 1.330±0.05mm Diameter Inner Screening Material Aluminum Foil Drain wire Outer Screening Material Tinned copper 0.10mm – =30% Coverage Core Colour 1. White-Blue 2. White-Orange 3. White-Green 4. White-Brown Sheath Thickness 0.55±0.05mm Sheath External O.D. 7.6±0.5mm Sheath Surface Clean Sheath Material Material LDPE (complies RoHS) Sheath Colour Black Manufacturer Part No: C-C6AS-EXTBK Brand: Dynamix Product Type: – UPC – Product Family: – Shipping Weight: 18.017 kg PB Part No: CABDNX2937 Product Model: – Warranty: 60 […] #
0 notes
Text
Deciphering the Distinctions: Ethernet Cable vs. Cat6a Cable
In the digital age, fast and reliable network connections are vital. Two commonly used cable types, Ethernet cable and Cat6a cables, play a crucial role in ensuring seamless data transmission. But what are the key differences between these cables, and which one should you choose for your networking needs? In this article, we'll delve into the distinctions between Ethernet cables and Cat6a cables, helping you make an informed decision for your specific requirements.
Ethernet Cable: The Fundamental Connectivity Backbone
Ethernet cables have been the cornerstone of wired network connections for decades. These cables are well-known for their simplicity and versatility. Let's explore the fundamental aspects of Ethernet cables:
Usage: Ethernet cables are used for a wide range of applications, including connecting computers, routers, switches, and various networking devices.
Compatibility: Ethernet cables come in several categories, such as Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat6a. They are backward-compatible, meaning you can use older Ethernet cable categories for less demanding tasks.
Performance: The performance of an Ethernet cable largely depends on its category. While Cat5e cables support up to 1 Gbps (Gigabit per second), Cat6 and Cat6a offer higher data transmission speeds and better resistance to interference.
Cat6a Cable: Elevating Network Performance
Cat6a, or Category 6 Augmented, represents a significant advancement in network cable technology. It's designed to meet the demands of modern high-speed networks. Here are some key features of Cat6a cables:
Performance: Cat6a cables can deliver data speeds of up to 10 Gbps at distances of up to 100 meters, making them ideal for high-performance networking requirements.
Bandwidth: Cat6a boasts an impressive bandwidth of 500 MHz, providing the capability to support a wide range of data-intensive applications without signal degradation.
Shielding: Most Cat6a cables are fully shielded, offering enhanced protection against interference, crosstalk, and external electromagnetic disturbances.
Key Differences
Now, let's explore the key distinctions between Ethernet cables and Cat6a cables:
Purpose and Use: Ethernet cables are the broader category, encompassing various cable types, while Cat6a is a specific category designed for high-speed data transmission and is commonly used for demanding network applications.
Performance: Cat6a outperforms traditional Ethernet cables, especially in terms of data speed and bandwidth. It's the go-to choice for modern high-speed networks.
Distance: Ethernet cables are generally limited in terms of distance for achieving higher speeds, while Cat6a offers superior speed over longer cable runs, making it suitable for large office networks and data centers.
Shielding: Cat6a cables are typically fully shielded, offering superior protection against interference, which can be critical in environments with high electromagnetic interference.
Conclusion
The choice between Ethernet cables and Cat6a cables depends on your specific networking needs. Ethernet cables, including Cat5e and Cat6, remain suitable for many applications, providing a cost-effective solution for basic networking requirements. However, if you're running a high-performance network or require extended cable runs, Cat6a cables are the superior choice.
In summary, Ethernet cables are versatile and can serve well in various scenarios. Cat6a cables, on the other hand, excel in providing top-tier performance, unmatched bandwidth, and robust interference resistance. To make an informed decision, consider your network's current and future demands, and evaluate whether the enhanced capabilities of Cat6a cables are worth the investment. Ultimately, selecting the right cable type will contribute to the efficiency and reliability of your network infrastructure.
0 notes
Text
A patch cell can handle practically almost any signal
A Basic Description regarding Patch Panels
A patch panel is really a unit or system that features a good number of jacks. The jacks are frequently Shielded Keystone Jack Factory In China of the same type and they are used for routing, interconnecting, and joining circuits. It can be used for assessment. Below is some sort of basic description with patch panels. There're used in various industries.
Patch panels are usually great for smaller or large networks for the reason that allow for versatile routing. Their a considerable amount of ports are close together, making them easy to control and connect units. They also lessen the wear against your jacks and minimize enough time spent reconfiguring the actual network. Whether your network comprises of copper cables or perhaps fiber, a patch panel can make connecting and disassemblying cabling a breeze.
Choosing the right patch panel for your needs is critical to be able to ensuring optimal operation. Before buying a patch panel, take inventory of your current network devices and determine the quantity of jacks you have to have. Then, consider your current future needs when selecting a spot panel. It is additionally important to think about the size and mounting methods of your patch solar panel.
Patch panels are divided into a couple categories - entire and half-normal. Full-normal editions contain break contacts on both rows. These panels are well suited for network installation inside high-end buildings along with other high-end facilities. Normally, patch panels get between 24 as well as 48 ports. Even so, some specialty models have as much as 336 ports.
A patch cell can handle practically almost any signal. They could handle digital sound and video, and MIDI and cellular phone signals. They may also handle RF signals and cable tv. They can end up being either electronic, hardware, or electro-mechanical. Some have currency trading capabilities and can also be controlled by a strong external device. In addition, some of them may be controlled by program applications.
To avoid wire tangling, a patch panel must have cable management features. It should also manage to support a various twisted-pair cabling styles, including Cat5E, Cat6A, plus Cat7. Each of types uses numerous gauges of photographer wiring, so the patch panel must be compatible with your cabling. You can find specific area panels for shielded and also unshielded twisted-pair cabling.
Patch panels works extremely well in businesses to organize telecommunications equipment. They enable IT staff to manage the network more proficiently. They allow consumers to change wires, add or take out ports, and move communication lines. A patch panel may also be used in facts centers. These panels is usually large or modest, depending on how many ports you have.
Another great feature of any patch panel is that it can provide multiple network jacks. They can be familiar with connect several types of electronic devices, local area networks, audio as well as video equipment. They is usually used to link several computers. To get home networks, it isn't necessary, but they provide a good deal of advantages. They simplify this configuration process and make troubleshooting incredibly easier.
0 notes
Text
A Comprehensive Guide to Ethernet Cable
An Ethernet cable serves the basic purpose to connect devices to the internet. The Ethernet cable provides high reliability, high speed, high flexibility, low cost, and easy-to-install advantages. This article focus on Ethernet cable.

What is Ethernet Cable?
Ethernet cable is the most common network cable type used with wired networks. It connects network devices such as PCs, routers, and switches within a local area network (LAN). The ethernet cable resembles a traditional phone cable but is larger and has more wires. The eight insulated copper wires are split up into four pairs, and the wires are twisted around each other within each pair to reduce signal interference.

Ethernet Cable Structure
The most common ethernet cable structure is the twisted pair cable. A twisted pair cable is a type of cable made by putting two separate insulated wires together in a twisted pattern and running them parallel to each other to improve electromagnetic compatibility.Twisted pair cable reduces electromagnetic radiation from the pair and crosstalk between neighboring pairs and improves the rejection of external electromagnetic interference.
Twisted pair cables are of two types: shielded (STP) and unshielded (UTP) . STP cable contains an extra foil wrapping or copper braid jacket to help shield the cable signals from interference and transport data faster. STP cables work by attracting interference to the shield, then running it off into a grounded cable. STP cables are foil-twisted pair (FTP) and shielded/foil twisted pair (SFTP).
UTP cable is low-cost network cable built with a pair of insulated conductors twisted together and covered with a plastic jacket for protection. It has no foil wrap shielding or braided shielding screen, which makes the cable smaller in diameter. 24 AWG (short for American Wire Gauge) is the most commonly seen size of UTP cables.
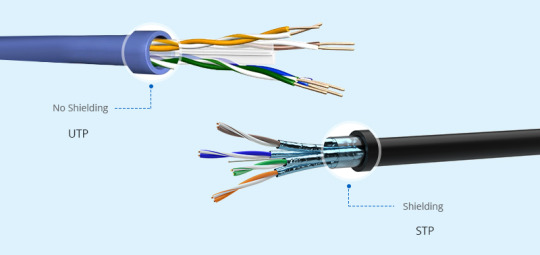
Ethernet Cable Types
The common types of ethernet cables include Cat5, Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a, Cat7, and Cat8.
Category 5 (Cat5): is the older type of ethernet cable and made up of four twisted pairs of copper wire terminated by an RJ45 connector, which has a bandwidth of up to 100 MHz, and supports 10 or 100Mbps speed.
Category 5e (Cat5e): is an enhanced version of the Cat5 cable, which indicates a lower-noise version where the potential for crosstalk is reduced. The internal interference is lower because the cable has an average of two twists per centimeter, which allows it to transmit data without significant signal degradation. Cat5e supports networks up to 1 gigabit (1000 megabits per second) and comes in shielded varieties, performing better in reducing noise.
Category 6 (Cat6): consists of four pairs of twisted copper wire but features more stringent specifications for crosstalk and system noise. A Cat6 patch cord has a bandwidth capacity of 250 MHz, which has even stricter specifications when it comes to interference and provides speeds of up to 10 Gbps.
Category 6a (Cat6a) : The "a" in Cat6a stands for "augmented". Cat6a cable can maintain higher transmission speeds over longer network cable lengths. With a stronger sheathing, the Cat6a cable is better suited for industrial environments. However, compared to Cat6 cables, Cat6a cables are thicker and less flexible.
Category 7 (Cat7): contains four individually shielded pairs inside an overall shield, called Shielded/Foiled Twisted Pair (S/FTP) or Foiled/ Foiled Twisted Pair (F/FTP). Cat7 cable does well in reducing signal attenuation and it is relatively stiff when compared to the Cat5e or Cat6a cables. The newer "Class F" cable is an ideal choice for application environments where transmission of frequencies up to 600 Mbps is required.
Category 8 (Cat8) : is the latest IEEE standard in copper Ethernet cable. The Cat8 cable can eliminate crosstalk and enable higher data transmission speeds by wrapping each twisted pair in foil. Cat8 cable can support 25GB and 40GB Ethernet, which represents a significant leap in data transfer speed.

Applications
An ethernet cable is used in telephone networks, WiFi routers, TVs, computers, video, security cameras, data centers, etc.

Conclusion
Ethernet cable is simpler, more reliable, and faster than WIFI, supporting speeds of up to a gigabit per second on the most telephone, TVs, PCs, and security cameras. Sun Telecom has over 30 years of experience in supplying Ethernet cable products. Contact us if you have any needs.
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Standard Of Cat6 And The Comparison Of Cat5
UTP CAT6 Cable is not susceptible to interference, but don’t discount Cat5e
As the newer of these two standards, Cat6 cables usually provide better insulation and enhanced performance for their internal wires, which may not be surprising. Cat5e improves the shielding of the older Cat5 standard, but Cat6 must comply with stricter crosstalk and external noise suppression standards than Cat5e.
Cat6 cables reach higher performance standards in several different ways. The most common is to use "splines". This is actually a longitudinal splitter that isolates the wires and further prevents crosstalk between the 4-wire pairs. It also has the added benefit of making Cat6 cables more durable and preventing stretching. However, this can make them stronger, so a splined Cat6 cable is not necessarily the best choice for the tightest turns.
Some Cat6 cables use separate shielding of the internal wires and use a shield or foil around the entire wire itself.
These different technologies are sometimes used alone or in combination to obtain larger or smaller shielding. This is usually indicated by the name or acronym applied to the cable, so if shielding is important to you, look for an "S" in its name.
When it comes to Cat5e and Cat6, the newer Cat6 standard provides better overall internal interference suppression, but some cables are better than others. For best performance, please pay attention to Cat6 cables that contain splines and shields, which usually comply with the Cat6a standard.
0 notes
Link

#Cat6 RJ-45 UTP Straight Through Keystone Joiner#Cat6 Keystone Jack#Cat6 UTP Keystone Jack#Jacks & Couplers#Structured Cabling#Cables#Cable Wires#Cat6A External Cable#Cat6A#Cat6#Network & Data Cable
0 notes
Text
Cat6 & Cat6A Cable plenum Rated | WESTCables
WESTCables deals in a range of CAT cables from CAT5 to CAT5e, CAT6, CAT6A, and CAT7. Plenum rated UTP cables along with STP and FTP cables at our stores are meant for utmost comfort when it comes to dealing with computing networks. Cat5 and CAT5e are relatively older versions of Ethernet cables and are replaced by CAT6 and CAT7 cables.
Specialized air vents in the buildings for the natural flow of air throughout the dimensions of the building is referred to as ‘plenum’. Such buildings have lowered ceilings and raised floor systems. Plenum rated cables best suit the purpose of patching up the computing devices over external Ethernet jackets.
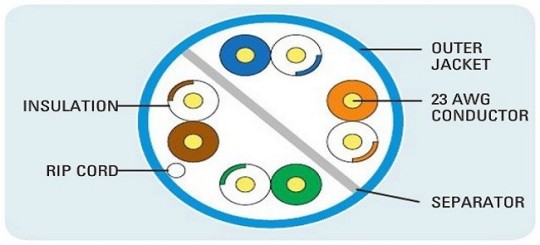
Plenum rated cables are equipped with the extra bit of shielding so that they cannot catch fire easily. They have the low smoke and low flame. They become environmentally friendly and are less toxic in comparison to many other forms of CAT cables.
UTP stands for untwisted pair cables, which is a copper cable used in telephone wiring and supports Local area networks.
CAT7 is the latest innovation in the series of patch and Ethernet cables. CAT7 are more sound and proficient in handing EMI’s and crosstalks. Additional shielding units have been added to individual wire pairs in CAT7 cable for overcoming extra pressures originating from the release of electromagnetic radiations.
CAT6 cables are less effective in handling crosstalks as compared to CAT7. CAT6 can support 10GB/s but over smaller distances as compared to CAT5e.
CAT5e and CAT6 cables show variations in frequencies as well. CAT5e has a frequency of 350MHZ whereas the category 6 patch cable has the higher frequency which is 550MHZ.
0 notes
Text
Difference between CAT5e, CAT6 , CAT6A and CAT7 cables
CAT cables are made for connecting the computing devices and fall into different categories. From CAT5 to CAT6A cables, all deal in carrying out data transmission and signal routing. CAT cables are the most important physical component in handling data transmission mechanisms.
CAT5:
CAT5 cables are now overtaken by CAT5e and CAT6 cables. They are less frequently used the set of cables to patch up computing components. In most cases, one can say they are the least effective and aren’t able to handle and organize data handling with convenience. The rate of data transfer (bandwidth) for CAT5 cable is 100MHZ.
CAT5e:
CAT5e paved their way into the cable industry with dignity and they rooted out the presence of CAT5 cables and overtook them. The most important distinguishing feature between CAT5 and CAT5e is the ability to tackle and handle crosstalks from all sources. EMI’s or electromagnetic radiations slow down the performance of data transfer between computers and from external sources on to computer networks. CAT5e Cables are insulated with the metallic copper layer in most cases, to dispense the radiations.
The radiations which are charged species (electronic flow) are a threat to the smooth execution of the data transfer mechanism and CAT5e were design as to curtail and minimize the lethal effects of data loss.
CAT5e can transfer data at a rate of 350MHZ which makes it a better choice for the users.
CAT6:
CAT6 follows CAT5e cables and they are multidimensional and more applied oriented. They can handle 10GBBASE-T along distances up to 55 meters. The data transfer (bandwidth) capability of CAT6 cables is 550 MHZ. They are insulated well enough to counter and fight out EMI’s and crosstalks.
CAT6A:
CAT6a provides can transmit data to longer distances in comparison to CAT6 cables. Cat6 cables can transfer 10GBBASE-T with bandwidths of 500 MHZ at distances as long as 100 meters.
CAT7:
Signal attenuation is reduced greatly by CAT7 cables and they are the latest in the series of CAT7 cables. CAT7 is slowly paving its way into the digital world. One can expect a higher data transfer rate of up to 600 MHZ, better transmission and smooth and safe browsing with CAT7 cables.
0 notes
Text
Data Cabling System FAQ's
Robust supporting infrastructure for the data system is imperative for any company. In case some questions are troubling you regarding the data cabling installation, this set of Frequently Asked Questions would help.
If you are setting up or moving an office, you will need an efficient and reliable data cabling company for laying down the right supporting infrastructure for the data system. Appropriate data cable installation is essential for proper functioning of your office. Answers to some Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ's) regarding the data cable installation would invariably help you.
Q. How Much Money I Will Have To Shell Out For Getting A Cabling System Installed?
A. Generally, you'll need to spend something between £25 and £120 per point, if installing a 100 point cabling network. This cost includes patch panels, outlets, cables, tray work, and installation man-hours (depending on installation complexity and cable/connector grade selected) but not the active hardware such as switches or routers, etc.
Q. How Will I Know That The Installer Is Right For The Job Or Not?
A. Make sure that the installer is certified for installing major manufacturers' cabling systems. Established manufacturers' cable systems come with a proper warranty. Such authorized installers offer active data installations.

Q. Is It Essential For The Network Cabling Installer To Have An Expertise And Experience In This Field?
A. Of course, it is essential. Though some electricians and telephone engineers possess required knowledge in network cabling they are very few, hence it is best to go for professional installers. Ask probing questions and discuss the cabling performance or network speeds and crosstalk, attenuation and return loss with them. Get details as to what kind of tester they use, the frequency range it scans at, its compliance with Cat5e or Cat6, the supplier of their cables and components and whether they would support the installation and come with a warranty.
Q. What Kind Of Cable And Connectors Should Be There In My Cabling Network?
A. Cables and connectors of at least Category 5E standard should be used. Higher standards such as Cat6 and Cat6a are also available.
Q. What Is A Cat5e Cable?
A. Cat5e is an enhanced version of Cat5 with specifications for far end crosstalk and offers the usable bandwidth of 100 MHz. 10BASE-T, 100 BASE-T, and 1000BASE-T networks can be used with this cable.
Q. What Is A Cat6 Cable?
A. Cat6 comes with more stringent specifications for crosstalk and system noise. 500 MHz of usable bandwidth is offered by this cable. 10BASE-T, 100 BASE-T, 1000BASE-T & 10000BASE-T networks are compatible with Cat6a.
Q. What Should I Go For - Category 5e Or Category 6?
A. The faster the data cable, the better it is. However, the decision depends on the requirements of your business. 5E category cable is generally ideal for most business needs. If properly installed, the system will provide a throughput of 100Mbps, and in some cases, 1000Mbps, backed by manufacturer's warranties. Correctly installed category 6, backed by a warranty, will guarantee 1000Mbps.

Q. Are Cat6 Cables Compatible With Cat5e Applications?
A. Yes. Cat6 is equipped with backward compatibility, i.e, it is compatible with all previous standard applications and thus with Cat5 & Cat5e applications.
Q. Can Desktop Computers And The Telephones Be Supported On The Data Cabling Active Data Installations Install?
A. They can be supported. Modern data cables have been designed with the latest technology and work with low-frequency voice circuits right up to Gigabit networks.
Q. What Do Mbps And Gbps Exactly Mean?
These Units Are Used To Measure Data Transfer Rates.
Mbps = Megabits per Second.
Gbps = Gigabits per Second.
Q. What Does Mhz Stand For?
MHz stands for Megahertz and refers to the frequency at which the cable transmits data.
Q. Should I Use Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSOH) Cable?
A. Yes, especially the air-conditioned buildings. LSOH is a compound used for making the sheath of a cable which prevents the emission of toxic halogen gases, in case of a fire within the building. ADI's project managers will graph out the right Data Cabling solution.
Contact us:-
Data Cabling Florida
4407 North Federal Hwy
Fort Lauderdale, Florida,33334
Phone:- 954-743-0280
External Links:-
Amazon
Angel.co
Blogger
Flattr.com
Google+
0 notes
Text
TP-Link T1700X-16TS Vs. T1700G-28TQ
Though 40G and 100G have been widely applied in big data center, 10G is still popular with small homelab. Many 10G switches on the market are designed to used with SFP transceiver module and 10G SFP+ transceiver module, while TP-Link has two 10G switches—T1700X-16TS And T1700G-28TQ, which are respectively characterized by 10GBASE-T RJ45 ports or 10/100/1000Mbps RJ45 Ports. This article will make a comparison between them.
Overview of TP-Link T1700X-16TS And T1700G-28TQ
As members of TP-Link’s T1700 Series 10G smart switches, TP-Link T1700X-16TS And T1700G-28TQ are designed to provide increased scalability, higher bandwidth, and enhanced performance. In addition, with physical stacking improving performance and simplifying management, both of them are able to provide reliable, cost-effective and resilient networking solutions for SMBs. As you can see, here are two figures. Figure 1. shows TP-Link T1700X-16TS and Figure 2. shows TP-Link T1700G-28TQ.
Figure 1. TP-Link T1700X-16TS
Figure 2. TP-Link T1700G-28TQ
TP-Link T1700X-16TS Vs. T1700G-28TQ
Similarities
Both of them support rich L2 features, including 802.1Q VLAN, Port Isolation, Port Mirroring, STP/RSTP/MSTP, Link Aggregation Groups, and 802.3x Flow Control function.
Both of them support supports L2+ feature static routing, which provides simple network segmentation by routing internal transmissions to make the flow of network traffic more efficient.
Both of them support IP-MAC-Port Binding, Port Security, Storm control, and DHCP Snooping, which help to protect the network from broadcast storms, ARP attacks, and more.
Both of them support 802.1X, which allows network clients to be authenticated through external Radius servers and the guest VLAN function allows non-802.1X clients to access specific network resources.
Both of them utilize rich QoS policies to support voice, data, and video services on one network.
Both of them support various user-friendly standard management features, such as intuitive web-based Graphical User Interface (GUI), industry-standard Command Line Interface (CLI), SNMP (v1/2/3), and RMON. Therefore, they are easy to use and manage.
Both of them support Dual Image to provide improved reliability and network uptime.
Differences
TP-Link T1700X-16TS is equipped with 12 x 10GBASE-T RJ45 ports and 4 x 10G SFP+ ports, providing 320 Gbps switching capacity. While TP-Link T1700G-28TQ is designed with 24 x 1GE ports and 4 x 10G SFP+ ports. As TP-Link T1700G-28TQ supports up to 6 units in a stack, it is able to provide 768 Gbps switching capacity.
TP-Link T1700X-16TS utilizes 10GBASE-T technology which provides a cost-effective method for migrating from current network to 10G Ethernet by using existing Cat5e/Cat6 short connections (up to 55 meters) and Cat6a/Cat7 connections (up to 100 meters). While with true physical stacking technology, up to six T1700G-28TQ units can be stacked with a single IP address, which provides enhanced scalability, simple management, and increased redundancy for high-density deployment.
TP-Link T1700X-16TS is a little larger than TP-Link T1700G-28TQ. The size of the former one is 440 x 220 x 44mm, while the latter one is 440 x 180 x 44mm.
TP-Link T1700X-16TS is designed with two smart fans. While TP-Link T1700G-28TQ utilizes a fanless design, which reduces the amount of ambient noise.
TP-Link T1700X-16TS can be used with 10GBASE-T copper SFP+ transceiver, 10G SFP+ transceiver and DAC cable. While TP-Link T1700G-28TQ can be used with Ethernet cable, 100/1000BASE-T SFP transceiver, 10G SFP+ transceiver and DAC cable.
TP-Link T1700X-16TS is more expensive than TP-Link T1700G-28TQ. You can find TP-Link T1700X-16TS at $ 950 US dollars and TP-Link T1700G-28TQ at $ 308 US dollars on Amazon.
Conclusion
From the above comparison, we can find that both TP-Link T1700X-16TS and TP-Link T1700G-28TQ have their own advantages. Before you make a decision, you’d better figure our what you most care about. If you want to use 10GBASE-T copper SFP+ transceiver, you can choose TP-Link T1700X-16TS. But if you want lower budget, then buy TP-Link T1700G-28TQ.
Originally published at: http://www.fiber-optical-networking.com/tp-link-t1700x-16ts-vs-t1700g-28tq.html
0 notes

