Text
HEALTH EDUCATION 2-4-19 THEORIES OF TEACHING + LEARNING BEHAVIORISM TEAM CLASSICAL CONDITIONING IVAN PAVLOV - Learning process that occurs through associations of a neutral stimulus with something and the response would come out. CONNECTIONISM THEORY EDWARD THORNDIKE REINFORCEMENT THEORISTS - Trial + Error - Relationship between stimulus and response. CONNECTIONISM AND ITS 3 LAWS 1. LAW OF EFFECT - Satisfying results = increase in certain response - Unsatisfying results = decrease in response 2. LAW OF READINESS - Ready to learn = satisfied in learning - Ready to learn but does not learn = ANNOYED STUDENT - Not ready to learn and does not learn = ANNOYED STUDENT 3. LAW OF EXERCISE - If you don’t use it, you lose it. ROLE OF THE TEACHER 1. Respond with reinforcement 2. Motivate student to learn 3. Repeat + Emphasize OPERANT CONDITIONING BF SKINNER - Method of learning that occurs through rewards and punishments for behavior. - Specific consquences are associated with voluntary behavior. BEHAVIORISM THEORY JOHN WATSON (CONTIGUITY THEORIST) - series of activites for one response - Acquisition of new behavior based on environmental condition. - Behavior can be CONTROLLED or MODIFIED based on antecedents and consequences of a bheavior. BEHAVIOR - Was obvious and practical - Was muscle movement - Results of a series of conditioned reflexes all emotion and thought is a result of behavior learned through conditioning ASPECTS OF BEHAVIORISM 1. Anyone can be trained for a task 2. Behavior is acquired by conditioning 3. Behavior is OBSERVABLE and MEASURABLE CONTIGUITY THEORY EDWIN RAY GUTHRIE - Combination of stimuli which has accompanied a movement will on its recurrence tend to be followed by that movement. ASPECTS OF CONTIGUITY THEORY 1. In order for conditioning to occur, the organism must actively respond. 2. Instruction must present very specific tasks. 3. Exposure to many variations in stimulus patterns is desirable in order to produce a generalized response. 4. Last response in a learning situation should be correct since it is the one that will be associated. CLASSICAL CONDITIONING = Simple signal learning BEHAVIORISM = explains only simple behavior FOR BEHAVIORIST: LEARNING PROCESS = very simple LEARNING: Drill Practice Memorization Behaviors that are rewarded are more likely to occur. CLASSICAL CONDITIONING - involuntary responses can be achieved by conditioning. CONNECTIONISM - trial and error relationship between stimulus and response. OPERANT CONDITIONING - learning is reinforced by rewards or punishments. BEHAVIORISM THEORY - new behavior is acquired based on environmental conditions. CONTIGUITY THEORY - learning will occur regardless of whether reinforcement is given, so long as the conditioned stimulus and the response occur together. II. COGNITIVE TEAM Cognitive Psychology and School of thought COGNITIVE PSYCHOLOGY - study of HOW OUR BRAINS WORK in the process of perceiving, thinking, remembering, and learning (BREUR, 1993) INFORMATION PROCESSING - sometimes used to describe this field of study. FOCUS OF CT: MENTAL PROCESS that are responsible for behavior and its meaning. INSIGHT LEARNING: Wolfgang Kohler - sudden realization of the solution of any problem without repeated trials or continuous practices. - Used CHIMPANZEES named sultan, put him in a cage and give sticks and put bananas outside and play with them and figured out to put sticks together to get banana CHARACTERISTICS OF INSIGHT LEARNING 1. Insight represents seeing CLEARLY jnto the essence of a situaion 2. It is NOT a step by step process but patially by unconscious procrss STAGES OF INSIGHT LEARNING 1. PREPARATION - problem cannot be solved - Data gathering 2. INCUBATION - problem is put on hold - Problem work on unconsciously 3. INSIGHT - suddenly theirs is a mental represntjon of soulftuon or eureka or AHA moment 4. VERIFICATION - Solution checked FIELD THEORY (Kurt Lewin) - learning is a process of perceptual organization of one’s life space involving insight - examines patterns of interaction between the individual and the total field (ENVIRONMENT) FIELD THEORY b = F(pe) Behavior F P E ——> INSERT LEWINS THEORY OF LEARNING Overcome the barrier and pass the restraining force to achieve goal. Psychological, you versus you. DISCOVERY THEORY (Jerome Bruner) - Learners are encouraged to build on past experiences and knowledge. - Learning makes use of INTUITION, IMAGINATION, CREATIVITY to search for new information to discover, facts, correlations, and new truths. PRINCIPLES OF DISCOVER LEARNING MODEL 1. PROBLEM SOLVING - instructors should guide and motivate learners to seek for solutions. 2. LEARNER MANAGEMENT - instructors should allow participation to work either alone or with others and learn at their own pace. 3. INTEGRATING AND CONNECTING - instructors should teach learners how to combine prior knowledge with new and encourage them to connect to the real world. 4. INFORMATION ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION - discovery learning is process-oriented and not content-oriented. 5. FAILURE AND FEEDBACK - learning doesnt only occur when we find the right answers. It also occurs through failure. ADVANTAGES - Encourages motivation, involvement and creativity - Learner’s pace is priority - Promotes autonomy and independence - Ensures higher levels of retention SCHEMA THEORY (David Rumelhart) - active strategy coding technique necessary for facilitating the recall if knowledge. SCHEMA/SCHEMATA - are knowledge structures that are syored in memory. ALL KNOWLEDGE IS PACKAGED INTO UNITS units = schemata tall dark handsome ASSIMILATION THEORY (David Ausubel) - people learn best when they can link, or assimilate new information with previous knowledge. PRINCIPLES OF ASSIMILATION THEORY 1. SUBSUMPTION - new material is related ti releventa ideas in existing cognitive structure on substansive non verbatim basis 2. SUPERORDINATE LEARNING - new information on top of already known info. Connecting new info to alreafy learned info 3. PROGRESIVE DIFFERENTATION- increass tge stabilit and clarity if anchring 4. INTEGRATIVE RECONCILIATION - new concepts and relationhshipd and Similarities and difference are substantively uncorporated into cognivtivr sturucture. are 5. OBLITERATIVR SUBSUMPTION - meaningfully learned mayerial cannot be recalled un the precise form in which it was originally learned due to the subsuption if the new mateial undr a broader class or cincept. 6. ADVANCED ORGANIZERS - big picture before going on into details. Statements made at te behining of class to help students activate prior knowledge. COMMONCONETPCT Learning is acquisition of knowlege. Learning is the process whereby novices become experts. Metacognition is thinking about one’s thinking. A process learners use to gauge their thinking while reading, studying, trying to learn, or problem solving. Memory: the more we connect new info to old, the more we ruminate over the new info, and te more frequently we recall Transfer is the ability to take info learned in one situation and apply it to another. Cognitive learning theories are the predominant bsis for approcahes in learning. Old thiugt: behaviorism New learning: congitive Learning active application .
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
Manila City is one of the densest city in the Philippines as of today. It is notable for such its unruly physical and economic growth. Rural migrants had pour in the metro desperate for search of work and life. These people settle in margin of the land but when nothing, they build make shift home on stilts above Manila Bay and Pasig River. Discussing about NEIGHBORHOOD AND BUILT ENVIRONMENT. Esteros, railways, garbage dumps, bays, rivers and its tributaries and other public areas such as sidewalks, highway, and parks. The Capital is currently facing various adversities that include mainly, provision for public health service, housing, water system, sewage service, garbage management, transportation, and education. Everything is insufficient due to high increase of migrants and the people of the city itself. I cannot blame the city for this but I think if this is the case, the government needs to prioritize the city to cater all the needs in improving the knowledge and health of individuals, family and communities. As dramatic increase in population over the past two decades that put effect on the urban community, I cannot emphasize how its ECONOMIC STABILITY is going. I have encountered a post that Manila City ranks top 3 among the richest cities here in the philippines. I pressume that despite of the population increase, Manila remained multi-faceted. It remained as the center of commercial, cultural, political and social industry and manufacturer of diverse products. In my own percepts, the reason why it did not hog top to Rank 1 because in Makati it centers to investments to like malls, estates and such but in Manila it’s like all life status dwells in here and ‘some’ benefits go to the people with nothing in return. There is no doubt that Manila is also the center for EDUCATION, and I myself is the evidence. I came all the way from Laguna just to study here because I do believe that the quality of education is high. Since the spanish era, top universities like UST, ADMU, DLSLM, UP, PUP and other universities along the U-belt have been established. Not just for education that it excels but in sports as well that improve not just the concentration of higher education but extra curricular activities. These schools offer courses that are not available in other places as to why people really go here in manila for college. I also observed that there are lots of public schools and science schools which is good most especially for our young children who is not privileged enough to study. Public HEALTH and HEALTHCARE is provided by private corporations since majority of the hospitals in manila are privately owned. Just like in Education, people from south and north go to manila for the quality of healthcare. San Lazaro Hospital is a hospital that I always hear about ever since I was a child who manages cases for communicable diseases. The headquarters for WHO Country Office and DOH is designated at NCR. Around 6 hospitals are also accredited by Joint Commission International and based on my my research, with its multitude health workers and health providers, NCR has the lowest rate of malnutrition but I don’t really believe because it is occupied by nearly slums and squatter areas wich I think unprivileged individuals reside. Talking about SOCIAL AND COMMUNITY CONTEXT. I think the metropolitan area sufficiently and unsufficiently caters this depending on various circumstances and districts. Manila has 16 cities and designated as the Global Power City, it has a very significant role to finance, media, art, commerce, fashion, research, technology, education and entertainment concluding that all lifestyles are here. Housing in Manila varies from high-end to low-end. Condominiums and High-rise buildings have risk due to their elevation and having less number of windows. Starting a family as well in this type of housing would not contribute greatly to social developmental characteristics of a child. Another type of housing are those of along esteros that is detrimental to an individual’s health. No proper ventilation, weak structure, exposed to areas such as contaminated rivers and dumpsites. I also wanna take on consider the improper waste disposal of these people living in manila especially along P. Noval St. here in Sampaloc. Garbage are not tightly disposed, leaving leaks and unwanted odor. When it comes to public safety, the city also houses the Philippine National Police. I strongly believe that if there is a mutual give and take relationship with the people and government we could create a better place to live in. It will all start from the self, the practice of honesty, generosity and discipline.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
ASSESSMENT Assessing is a continuous process carried out during all phases of nursing process. All phases of the nursing process depend on the accurate and complete collection of data. - Assessment (collect data, organize data, validates data, document data) - Diagnosis - Planning - Implementation - Evaluation - Documentation *** COLLECTION OF DATA - Data collection is the process of gathering information about a client’s health status. - DATABASE - All info about the client. Includes the HH, physical ass, the physicians history, physical exam, result of lab, diagnostic test, and all material contributed by other health personnel. MEDICAL VS NURSING ASSESSMENT Medical Assessment - target data pointing to pathologic condition. What is damaged organ. Nursing Assessment - focus on the patients response to health problems, what happened to the patient and balances observed. TYPES OF DATA Subjective Data (Overt) Objective Data (IPPA) Primary Source (consider mental capability) Secondary Source (family members, client records) use many as much as possible Complete and updated 1. Medical record 2. Records of therapies IN DATA COLLECTION CONSIDER: - Time - Needs of patient - Developmental stage - Physical surroundings( privacy, temp, noise) - Past and present coping patterns (be self confident and know what things to act to not inflict trauma) DATA CHARACTERISTICS Complete - must be comprehensive Factual- Accurate -what only happen Relevant- MODALITY METHODS Interviewing -health hostory Physical assesment - IPPA OBSERVATION - To gather data using senses - eg. laboured breathing, pallor or flushing, pain a lowered side rail, functioning of an equiipment, environment and people in it. INTERVIEW - Get the history of patient using open ended question for patient to elaborate further. - Planned communication or conversation with a purpose. - Types of questions and setting report is important. 4 PHASES OF NURSING INTERVIEW PREPARATORY PHASE - Nurse collects info from previous chart. - Ensure environment is conducive. - Arrrange seating - 3-4 ft apart - Interviewer at 45 degrees - Allow adequate time INTRODUCTORY PHASE - Nurse introduce self - Identifies purpose of interview - Ensure confidentialty of info - Provide for patient needs before starting WORKING PHASE - Nurse gathers info for subjective data - Excellent communication skills are needed - Active listening - Eye contact - Open ended questions TERMINATION PHASE - Inform patient when nearing end of interview - Ensure patient knows what will happen with info - Offer patient chance to ask anything - Summarizing, reflecting DATA GATHERING PROBLEMS RELATED TO DATA GATHERING - Inappropriate organization of data base - Omission of pertinent data - Inclusion of irrelevant or duplicated data - Failure to establish rappor and partnership - Recording an interpretation of data rather than observed behavior - Failure to update the database - Sources of bias (previous informant, first impression) ORGANIZING DATA - Nurses uses a written or computerized format for arranging the data systematically. VALIDATING DATA Validating - act of double checking. Verifies understanding of info. Comparison with another source. Patient or family member, record of other notes of healthcare team. SKILLS COMMUNICATION SKILLS - Important role in nurse-client relationship - Exchange of info between individual ENCODING - Process of formulating a message for transmission to another person. DECODING - Process of searching through ones memory experience and knowledge base. INTERACTIONAL SKILLS - Actions that are used during the decoding and encoding process to obtain and disseminate info, develop relationship and promote understanding of self and others. - Listening, attending, paraphrasing, leading, questioning, reflecting, ectc LISTENING/ATTENDING - Giving the client full and undivided attention. - Eye contact, lean forward, quiet area, unhurried manner. PARAPHRASING - Restating the client’s basic message to test whether it is understood. DIRECT LEADING - To obtain specific info or begin interaction. FOCUSING - Helping the client to zero in on a subject or get in touch with feelings. QUESTIONING - Gathering specific info on a topic. - Open ended questions. REFLECTING - Empathy with clients thoughts and feelings. SUMMARIZING EMPOWERING THE PATIENT - Inquire about the patient’s perspective. - Express interest in the person, not just the problem. - Follow the patients lead. - Elicit emotional content. - Share info with the patient. - Make clinical reasoning transparent to the patient. - Reveal the limits of your knowledge (not allowed to explain and interpret) BARRIERS TO EFFECTIVE CLIENT INTERACTION 1. False reassurance 2. Interrupting or changing the subject 3. Passing judgement 4. Cross exam 5. Technical terms 6. Sensitive issues ADAPTING THE INTERVIEW FOR SPECIAL PATIENTS 1. Silent patients 2. Confusing patient 3. Patient with altered capacity- surrogate informant 4. Talkative patient 5. Crying patient 6. Angry or disruptive patient 7. Dying patient - Interview across a language barrier - Patients with physical functional impairment; hearing, vision, cognitive disabilities GUIDELINES WITH AN INTERPRETER - When ask question, should be short and simple. - Choose trained interpreter. - Mutual understanding with patient. - Must be able to verify - Be patient - Arrange room GUIDELINES FOR BROACHING SENSITIVE TOPICS - Single most important rule is to be nonjudgemental. - Explain why you need to know certain info. - Find opening questions for sensitive topics. - Finally consciously acknowledge. THREE DIMENSIONS OF CULTURAL COMPENTENCIES - Self awareness - Respectful communication - Collaborate partnership ETHICS AND PROFESSIONALISM: BUILDING BLOCKS OF PROFESSIONAL ETHICS IN PATIENT CARE - Nonmalificence or primum non nocere “first do no harm” - Beneficence - do good - Autonomy - right to choose and refuse - Confidentiality - right for privacy HEALTH HISTORY AND PHYSICAL ASSESSMENT COMPLETE HEALTH HISTORY - Biographical data - Reason for seeking care (chief complaint) - History of present illness - Past health - Accidents and Injury - Hospitalization and operations - Family History - Review of system - Functional assessment (daily living act) - Perception of health HISTORY 1. Welcome the patient - ensure comfort 2. Use open ended questions 3. List of issues (chief complaint, specific req) 4. Clarify the patient’s expectations CHIEF COMPLAINT - Reason why the patient is brought to hospital. BIOGRAPHICAL DATA - Name, Age, Birthplace, Gender, Marital status, Occupation etc. COMPONENTS OF HISTORY - SOCIAL HISTORY - FAMILY HISTORY - REVIEW SYSTEMS HISTORY OF PRESENT ILLNESS - OPQRSTA - Onset, Progression, Quality, Radiation, Scale, Timing, Associated symptoms HPI: Analysis of the Symptom Provoked, Quality, Region, Severity, Time PAST MEDICAL HISTORY - Medical conditions that the patient has chronically diseases and that they see a doctor for. PAST SURGICAL HISTORY - Previous operations that patient may had. MEDICATION - Include all meds the patient is on - Include dosages and how often the patient takes it. ALLERGIES - Make sure to ask about medication and reaction. SOCIAL HISTORY - Occupation - Marriage status - Tobacco use - Alcohol use - Illicit drug use - Immunization status - If pertinent, STD history FAMILY HISTORY REVIEW OF SYSTEM - Group asymtomatology based on system profile. - Other problems other than chief complaint. PHYSICAL ASSESSMENT THORACIC (heart and lungs) - INSPECTION - PERCUSSION - PALPATION - AUSCULTATION ABDOMEN - IN, AUS, PERC, PALPA - Do not alter bowel sounds ASSESS SEQUENCING - Head to Toe BASIC KNOWLEDGE 1. Types of an operation of equipment needed fro the particular exam. 2. Preparation of the setting. 3. Perfomance of IPPA. PREPARE PHYSICAL SETTING PREPARING ONESELF - Wash your hands - Wear gloves - If pin or sharp objects is used discard - Wear mask or goggles PREPARING THE PATIENT - Start on the area with less pain - Right side of the patient INSPECTION - Ensure good lighting - Perform at every encounter with your client - Always compare both sides of the body PALPATION - Skill of assessing the client through the sense of touch to determine specific characteristics of the body. - Characteristics: Texture, Consistency - Temp> strength, moisture, mobility, degree of tenderness, organ Finger pads - fine discrim Ulnar/palmar- postion, consistency, texture Dorsal- temp GENERAL GUIDELINES 1. Fingernails short 2. Hands temp 3. Procede from light to mode to deep Light - pulses, to ilicit pain 1cm Moderate - 1-2cm use palmar surface Deep - 2-4cm palpate visceral organ like liver, hypogastric PERCUSSION - Tap body parts to produce sound waves - Use fingerpads - Elicit pain - Size and shape - Density - Abnormal masses and reflexes Direct - sinus tenderness Indirect - lung percussion Plexemeter dom and plexir non dom Blunt percussion- organ tenderness PERCUSSION SOUNDS Resonance Flatness Dullness Tympanism INSERT TABLE ——> PERCUSSION NOTES AND THEIR CHARACTERISTICS AUSCULTATION - Listening to sounds produced by the body - Instrument: Stethoscope Diaphragm- high pitched sounds, heart, lungs, abdoment Bell- low pitch
1 note
·
View note
Text
https://www.scribd.com/mobile/doc/13624745/thesis-English-Teen-Obesity-THEYAN
3 notes
·
View notes
Photo








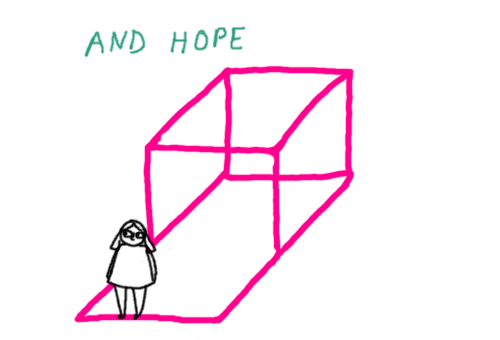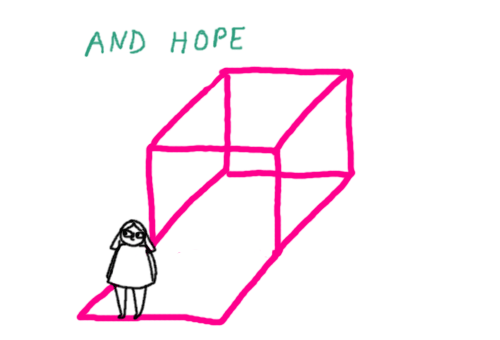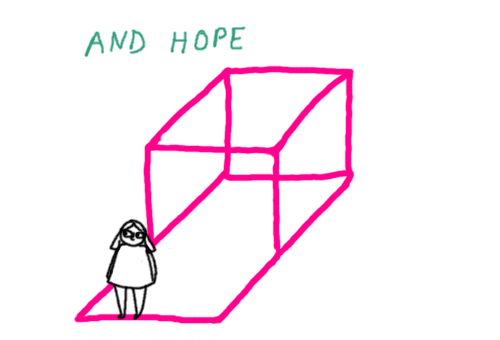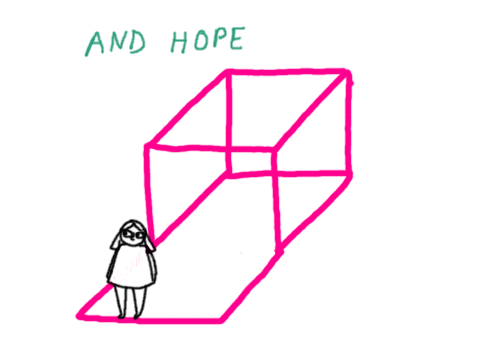
I found these gifs I made a while back for a site that’s not running anymore, so I thought I’d post them here. It’s a description of psychiatric symptoms and states of mind using a pink box and some other stuff.
1M notes
·
View notes
Text
Date a girl who says things like:
•drive safe
•text me when you’re home safe
•choke me harder
•I can’t wait to see you
•I’m proud of you
385K notes
·
View notes
Quote
It’s like I look at you, and I wanna give you every single part of me. I love you more than I did yesterday and I will love you even more tomorrow.
And I wish tomorrow came sooner (via miranda-michelle)
243 notes
·
View notes











