Text
Study on neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 and other human coronaviruses
Since the outbreak, COVID-19 has had a major impact on global public health security, social stability, and economic development. WHO predicts that the number of infected people worldwide will exceed one million. Recently, three researchers from Jiang Shibo of Fudan University, Du Lanying and Christopher Hillyer of the New York Blood Center published a Review in the Journal of Trends in Immunology of Cell Press to combat SARS-CoV-2 and other human coronaviruses. And sexual antibodies (nAbs) were comprehensively summarized.
SARS-CoV-2 infection mainly causes pneumonia and upper/lower respiratory tract infections. The main clinical symptoms are fever and cough, but it is also accompanied by other symptoms such as shortness of breath, muscle pain, headache, sore throat and even acute respiratory distress syndrome and multiple organs Exhaustion. For older people with underlying comorbidities such as diabetes, hypertension or cardiovascular disease, SARS-CoV-2 infection may be more likely to cause serious and fatal respiratory diseases. So far, the impact of SARS-CoV-2 on children has been relatively mild. The virus can spread through droplets and contact. During infection, the receptor binding domain (RBD) of the S1 subunit of its S protein binds to the ACE2 receptor on the surface of the host cell, which changes the conformation of the S2 subunit, which in turn encourages the membrane fusion of the virus and the cell to invade the target cell.
NAbs induced by viruses or vaccines play a vital role in the process of antiviral infection. The research on nAbs of SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV mainly includes monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), their antigen-binding fragments (Fab), single-chain variable region fragments (scFv) or single-domain antibodies (Nbs). The S1-RBD, S1-NTD, or S2 regions prevent the S2-subunit-mediated fusion of S1-RBD with the host cell membrane, thereby inhibiting viral infection, the targets of these nAbs of SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV.
SARS-CoV nAbs
All anti-SARS-CoV antibodies are directed against their S protein, most of which are RBD regions, and also have S2 regions or S1/S2 cleavage sites. For example, mAbs isolated from SARS-CoV infected patients such as S230.15 and m396 can prevent RBD from binding to the ACE2 receptor by interacting with the viral RBD region to improve the infection of humans and civet cats. Other human mAbs such as S109.8 and S227.14 have cross-neutralizing activity against human, civet, and dog infections, and can protect mice from four different SARS-CoV strains. Human nAb 80R (scFv or mAb) can also have a neutralizing effect by preventing RBD from binding to ACE2. Although there are many nAbs that show strong neutralization and protection in cells or animal models, they have not entered clinical research, so whether these antibodies have potential cross-neutralizing activity against SARS-CoV-2 needs more Deep research.
MERS-CoV nAbs
A lot of MRS-CoV-specific nAbs have been reported before, most of which are also targeted to the RBD region of the S protein, and a small portion are targeted to the S1-NTD and S2 subunits. Among these nAbs, human mAbs or Fabs (MERS-27, m336, MERS-GD27, and MCA1 isolated from patients), humanized mAbs (hMS-1, 4C2 h), mouse mAbs (isolated from mice Mersmab1, 4C2 and D12) and Nbs (HCAb-83 and NbMS10-Fc isolated from camels) both recognize RBD regions and can neutralize pseudovirus or live virus infections. Some humanized or humanized mAbs and Nbs can protect mice, rabbits or monkeys from MERS-CoV infection. So far, only one MERS-CoV nAb (SAB-301) isolated from genetically modified cattle has entered Phase I clinical trials. Whether these antibodies have potential cross-neutralizing activity against SARS-CoV-2 also needs further study.
SARS-CoV-2 nAbs
Recently, polyclonal antibodies isolated from patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection have been used to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection, but no SARS-CoV-2 specific nAbs have been reported. Researchers are trying to find nAbs that have a neutralizing effect. After finding the next step, they will conduct in vitro neutralization or cross-neutralization experiments and in vivo animal protection tests to test their safety and effectiveness in preparation for clinical trials.
SARS-CoV-2 is closely related to SARS-CoV, and its S protein has a high degree of identity. The researchers tried to find antibodies with potential cross-neutralizing activity in SARS-CoV nAbs to combat SARS-CoV-2 infection. It is worth noting that the human neutralizing mAb CR3022 specific for SARS-CoV RBD can bind to the RBD region of SARS-CoV-2, but the neutralization is unknown.
In addition, recovered SARS patient serum or SARS-CoV S1-specific animal serum can cross-neutralize SARS-CoV-2 infection. SARS-CoV S1 RBD antibodies can also cross-react with SARS-CoV-2 RBD protein and can cross-neutralize SARS-CoV-2 infection in HEK293T cells expressing ACE2. It is a development for SARS-CoV RBD vaccine Provides a certain strategy. In the absence of SARS-CoV-2 specific vaccines and antibodies, nAbs targeting SARS-CoV RBD also have the potential to prevent and treat SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Based on the study of nAbs of SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, antibodies targeting the RBD region of S protein have better efficacy in neutralization, suggesting that the RBD region of SARS-CoV-2 should be the focus of research, except for the RBD region, and Cocktail combinations of specific antibodies in other regions of the S protein may increase efficacy and have the ability to cope with mutant strains. Rehabilitation sera are used to treat COVID-19, but care should be taken to target antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE) caused by non-neutralizing antibodies in non-RBD regions. In summary, the nAbs studies of SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV provide important guidance for the design and development of specific antibodies for SARS-CoV-2.
0 notes
Text
What occupations are most likely to get cancer?
The occurrence of cancer is not only related to genetic changes in the body but also closely related to our environment.
If a person is in an environment that is prone to cause cancer lesions for a long time, the risk of cancer will increase. Therefore, we call cancer caused by long-term exposure to carcinogens in the labor process or the working environment as "occupational cancer ".
It should be noted that occupational cancer mentioned here is what medical researchers have observed in experiments or clinical trials, and it is slightly different from the "occupational tumor" mentioned in the current occupational disease prevention and treatment law.
So, which occupations increase the risk of cancer?
These occupations are at high risk for cancer.
Firefighters, traffic police, miners, asbestos workers are vulnerable to lung cancer, pleural mesothelioma.
Firefighters, traffic policemen, and miners are often direct contacts of toxic gases and dust. Over the years, the lungs are the first to be damaged, which is why the incidence of lung cancer in this group is higher than ordinary people.
Asbestos workers are listed here separately because their situation is "worse":
1. Lungs will harden: People can breathe freely because the lungs have a certain amount of elasticity. Asbestos dust and asbestos fibers enter the lungs through the respiratory tract, which can cause pulmonary interstitial fibrosis and pleural fibrosis, leading to pulmonary sclerosis and loss of elasticity.
2. Lung cancer formation: Lung cancer or pleural mesothelioma is not uncommon among asbestos workers.
Painter, leather workers are susceptible to leukemia.
The pungent smell of paint or leather must have been tried by everyone. Most people only occasionally smell it and cannot wait to escape immediately. Compared with those painters (leather workers), you have to say that you are lucky. Those poor workers work 40 hours a week, which is probably more than most people have heard in their lifetime. To the total sum.
Paint (leather) contains a large number of volatile harmful substances, such as benzene, toluene, xylene, phenol, formaldehyde, acrylonitrile, butadiene, etc. They enter the human body through the respiratory tract, skin, and digestive tract.
In addition to causing acute and chronic poisoning, it may also induce leukemia. Although the mechanism is not clear, medical research has confirmed that paint (leather) workers have a higher risk of leukemia.
Women who often work night shifts are susceptible to breast cancer.
Many types of occupations require night shifts, such as night shift medical workers, three-shift factory workers, and night flight train crews. Statistics show that women in this group may have a higher risk of breast cancer.
This may be disrupted by the human body's physiological rhythm, making the body unable to maintain normal hormone secretion and immune function, so that cell division is more prone to error and induce cancer.
Workers involved in the production of rubber additives and pigments-vulnerable to bladder cancer
The aromatic amine used in the production of rubber is a strong carcinogen, and its carcinogenicity is much higher than that of formaldehyde.
Workers in the chemical industry producing naphthylamine, benzidine, and 4-aminobiphenyl, as well as rubber additives and pigments using naphthylamine and benzidine as raw materials, are 61 times more likely to develop bladder cancer than the general population.
So what should we do now?
If, unfortunately, your occupation belongs to the above-mentioned high-risk occupations in cancer, similar to the method of resigning and changing jobs immediately, which is not realistic for most people, what should you do to minimize the risk of disease?
1. Improve ventilation: First of all, we must improve the environment. For dust pollutants in the air, there is no more convenient and economical method than wet operation. For example: when the rock wall is excavated, use a wet rock drill; when the site is level, you can Be Equipped with a sprinkler to allow dust in the air to adhere to the sprayed water droplets. In addition to reducing harmful emissions, good ventilation is a good choice.
2. Dress yourself up: Dressing up here doesn't mean applying foundation or lipstick. Wear protective masks, goggles, and gloves before proceeding. This equipment is essential to avoid direct contact with carcinogens.
3. Adjust the biological clock: The advice for night shift workers is to strengthen your physique and adjust your biological clock to make it more suitable for night work and daytime rest.
4. Do a good physical examination: Since the occurrence and development of cancer often takes a long time, no matter whether you are engaged in a high-risk occupation, you must not ignore the risks as long as you have engaged in it, you must also be vigilant. And carry out regular anti-cancer medical examinations.
0 notes
Text
Common cell stimulation methods
As one of the basic characteristics of an organism, stress is a normal physiological phenomenon in which an organism feels and responds to external stimuli. The phototaxis of moths, the geospatial nature of eucalyptus roots, and the chemotaxis of paramecium are essential manifestations of the stress of organisms.
As the basic structural unit of the organism and the basic functional unit, the cell, it is more sensitive to the stimulation of the external environment, which will cause various physiological reactions, resulting in a large number of signal pathways and changes in protein levels. So as a researcher, how do we study the response of cells to stimuli scientifically and rigorously?
We summarized a total of 8 major categories including apoptosis, autophagy, endoplasmic reticulum stress, cell cycle, temperature, oxygen content, inflammation, oleic acid stimulation, more than 20 common cell stimulation methods and detection methods.
1, Apoptotic stimulation
Apoptosis is a fundamental biological phenomenon of cells that helps multicellular organisms remove unwanted or abnormal cells. It plays an important role in the evolution of organisms, the stability of the internal environment and the development of multiple systems. Apoptosis is not only a special type of cell death, but also has important biological significance and complex molecular biological mechanisms.
In the experiment, Staurosporine stimulation and ultraviolet (UV) stimulation are the two most commonly used methods for inducing apoptosis. The Caspase protein family is one of the most critical proteins in the process of apoptosis. For this reason, the change of Caspase protein can indirectly reflect the apoptosis.
a) Staurosporine stimulates Jurkat cells
Experimental method: Jurkat cells were used as experimental subjects. When the cell density reached 1.0×106 cells/mL, the final concentration of staurosporine was added at 1 μM, the stimulation time was 6 h, and the time gradient was sampled to detect the change of Caspase 3 protein level by Caspase 3 antibody.
Experimental results: After stimulation with staurosporine, the protein level of full-length Caspase 3 decreased with increasing stimulation time; the protein content of caspase 3 increased continuously, which indirectly reflected the occurrence and enhancement of apoptosis.
b) UV-stimulated HeLa cells
Experimental method: HeLa cells were used as experimental subjects. When the cell confluence reached 90%, the cells were stimulated with ultra-clean bench UV lamp for 2 h, the control group was under normal light culture; Caspase 12 antibody was used to detect the changes of Caspase 12 protein level.
Experimental results: After UV stimulation, the level of full-length Caspase 12 and its cleavage protein increased significantly, which indirectly reflected the occurrence and enhancement of apoptosis.
2, Autophagy stimulation
Autophagy is a process of phagocytizing its own cytoplasmic proteins or organelles and coating them into vesicles, merging with lysosomes to form autophagosomes, and degrading the contents of their encapsulation. The cells thereby achieve their own metabolic needs and the renewal of certain organelles. Starvation stress and Rapamycin treatment can cause autophagy (enhanced autophagosome formation); lysosomal inhibitors such as chloroquine or bafilomycin A1 can inhibit autophagy (inhibition of autophagosomes and Lysosomal binding). The LC3 protein, especially the lipidated LC3-II, is an autophagic membrane component that can be used for autophagosome labeling, as well as changes in both LC3-II and non-lipidated LC3-I after lipidation. It also reflects the level of autophagy in cells.
a) Serum-free culture of HepG2 and HEK293 cells
Nutrient loss caused by serum-free culture can induce autophagy in cells and form autophagosomes. Low concentrations of chloroquine can change the pH of the lysosome and prevent the binding of autophagosomes and lysosomes, thus making the autophagosomes observable.
Experimental method: HEK293 and HepG2 in the experimental group were cultured for 2 h without serum, and then exchanged with fresh medium and added with chloroquine at a final concentration of 50 μM for 24 h. The control group HEK293 and HepG2 were cultured for 2 h without serum and then exchanged with fresh medium for 24 h. The cells were collected together with the experimental group. After stimulation, the number of autophagosomes was directly observed by immunofluorescence (IF) assay with LC3 antibody or the protein levels of LC3-II and LC3-I were detected by WB assay.
EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS: IF experiments showed that LC3 protein in chloroquine-treated cells was transformed from a uniform and diffuse distribution in untreated to aggregated circular and spotted bright spot structures (autophagosomes); and WB experiments showed cell lipidation after chloroquine treatment. The LC3-II content was elevated; both experiments showed a significant increase in autophagy levels after treatment.
b) Rapamycin-stimulated 293T cells Rapamycin, a classical autophagy inducer, enhances autophagy by inhibiting the mTOR signaling pathway.
Experimental method: Cells were plated 24 h before stimulation, and stimulation was started at 70%-90% of cell confluence. 293T was stimulated by rapamycin at a final concentration of 20 nM, 100 nM, 500 nM, and a time gradient was also set. 0h, 6h, 18h, 24h; another control experiment, the same experiment, LC3 protein through IF or WB to monitor the occurrence and changes of autophagy.
c) Carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazine (CCCP) enhances mitochondrial autophagy Carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazine (CCCP) as an oxidative phosphorylation uncoupler inhibits mitochondrial electron transport chains and affects mitochondrial protein synthesis. CCCP can promote the expression of PINK1 protein. PINK1 protein further stimulates serine phosphorylation of ubiquitin molecule at 65, recruits and activates parkin, and induces mitochondrial autophagy.
Experimental method: Cells were plated 24 h before stimulation, and cell confluence was 70%-90%. Stimulation was performed using a final concentration of 10 μM CCCP for 24 h. The control was set up (CCCP diluted with DMSO, mother liquor concentration 10 mM). The protein level of the 65-terminal serine-phosphorylated ubiquitin molecule was detected by the Phospho-Ubiquitin (Ser65) antibody WB assay.
Experimental results: After CCCP stimulation, the level of serine phosphorylation at the 65th level of ubiquitin increased significantly, indicating that the level of mitochondrial autophagy is enhanced.
3. Endoplasmic reticulum stress stimulation
Endoplasmic reticulum stress (ER stress) is characterized by misfolded and unfolded protein aggregation and calcium ion balance disorder in the endoplasmic reticulum, which activates unfolded protein response, endoplasmic reticulum overload response, and caspase-12-mediated apoptosis. The death pathway can induce the protective effect of the endoplasmic reticulum chaperones such as GRP78 and GRP94, and can also induce apoptosis independently. When the endoplasmic reticulum stress occurs, the expression levels of the related proteins ATF4 and CHOP will change significantly, so it can be used for the built-in network stress detection target.
a) tunicamycin stimulates PC-3 cells
Experimental method: Tunicamycin is the main stimulator of induced endoplasmic reticulum stress. The cells were plated 24 h before the experiment, and the cell confluence was 70%-90%. The stimulation concentration was 2 μg/ml, 4 μg/ml, the stimulation time was 24 h, and the control group was added with an equal volume of DMSO. The protein level of the 65-serine phosphorylated ubiquitin molecule was detected by the CHOP antibody WB assay.
Experimental results: With the increase of tunicamycin concentration, the expression level of CHOP protein is also higher, indicating that the cell's built-in network stress level is also increasing.
b) thapsigargin stimulates HepG2 cells
Experimental method: Thapsigargin can also effectively induce endoplasmic reticulum stress. The cells were plated at 24 h before the experiment, and the cells were stimulated at 70%-90%. The final concentration was 1 μM Thapsigargin for 24 h. The control was set up and the expression level of endoplasmic reticulum stress-related protein ATF4 was detected by ELISA kit. Variety.
Experimental results: The results of ELISA showed that the protein level of ATF4 was significantly increased after thapsigargin stimulation, indicating that endoplasmic reticulum stress is occurring.
4. Cell cycle
G0 phase, G1 phase, S phase, G2 phase and M phase are five stages of the cell cycle, which regulate cell growth and division. The regulation of the cell cycle stimulates the fate of the cell.
a) Nocodazole stimulates HeLa cells
Experimental method: Nocodazole is a commonly used cell mid-term blocker that blocks the cell cycle in M phase, allowing cell cycle synchronization. HeLa cells with a final concentration of 1 μg/ml Nocodazole to a confluency of about 70% were added to the cells for 48 h, 24 h, and 16 h, respectively, and the control group was not stimulated.
b) BrdU stimulation of HeLa cells
Bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) is a synthetic nucleoside similar to thymine. It can be incorporated into the DNA of newly synthesized replicating cells. Therefore, BrdU was used to determine birth dates and monitor cell proliferation.
Experimental method: BrdU was added to HeLa cells at a concentration of 0.03 mg/ml, and cultured at 37 °C for 2 h. The cells were fixed and treated with 2 M HCl for 30 min. The control group was not stimulated. Insertion of BrdU was detected by BrdU antibody by IF assay.
Experimental results: BrdU accumulates in the nucleus, marking the cells that are proliferating.
c) CaCl2 stimulation EC109 cells
Experimental method: Cells were plated 24 h before stimulation, and the cell confluence was 70%-90% during stimulation. The cells were cultured for 0 d, 3 d, 5 d, 7 d, 10 d in the final concentration of 0.06 mM and 1.8 mM CaCl 2 . Then, ZNF750 was detected by WB experiment and IF experiment.
d) insulin stimulates HeLa cells
Experimental method: Insulin regulates cell cycle and cell proliferation through the mTOR signaling pathway. Therefore, stimulation of cells with insulin also causes changes in the cell cycle. The cells were plated 24 h before stimulation, and the cell confluence was 70%-90% at the time of stimulation. After the final concentration was 100 nM insulin stimulation for 15 min, the cells were harvested, and no stimulation control was set.
5, Temperature stimulation
Birds and mammals are known as thermostated animals because they have a well-regulated body temperature regulation mechanism and can maintain body temperature stability under changing ambient temperature. In order to maintain a constant body temperature when stimulated by a low temperature environment, the organism regulates cell metabolism through various pathways, and some protein levels may change significantly. The most typical is CIRBP, for which CIRBP is used as a low-temperature response detection index.
Low temperature stimulation
Experimental method: HepG2 cells were used as experimental materials. The cells of the same culture condition and the same number of cells were cultured at 4℃(low temperature), 25 ° C (room temperature), 37 ° C (body temperature) for 1 hour, and then the cells were collected to prepare a lysate, which was detected by WB with CIRBP antibody. Protein level of CIRBP.
Experimental results: As the temperature decreased, the higher the expression level of CIRBP protein, the stronger the response of cells to low temperature.
6, Oxygen content stimulation
Oxygen is an important material basis for maintaining the energy sources required for cell and organism activities, and is one of the keys to the body's metabolic initiation mechanism. A hypoxic environment enhances breathing intensity and inhibits physiological processes; a peroxidative environment promotes aging.
a) hypoxic stimulation
Experimental method: CoCl2 is a chemical hypoxic simulator that mimics hypoxia in a variety of cultured cells. The cells were plated 24 h before the experiment, and stimulation was started when the cell confluence was 70%-90%. Stimulated with CoCl2 solution at a final concentration of 250 μM and 400 μM for 6 h, and no CoCl2 in the control group.
. HIF1a is a major regulator of cellular responses to hypoxia. Protein levels change significantly under hypoxic conditions, and subcellular localization also changes, which can be used as a marker for hypoxic stimulation.
Experimental results: Under the treatment of CoCl2, HIF1a was detected by HIF1a antibody. The results showed that the protein level of HIF1a increased significantly, and the subcellular localization shifted from cytoplasm to nucleus, indicating that the cells responded significantly to hypoxia stimulation.
b) Peroxygen stimulation
Experimental methods: HeLa cells and HEK293 cells were used as experimental subjects; ethacrynic acid (EA) was used to stimulate cells to produce stress. The cells were plated 24 h before stimulation, and the cell confluence was 70%-90%. Stimulation was started. After adding the final concentration to 100 μM EA for 5 h, the samples were collected and no stimulation control was set. Phosphorylation of TDP43 protein is an indicator of many neurodegenerative diseases and it is also an important role for cells in responding to oxidative stress.
Experimental results: After EA stimulation, TDP43 was detected by TDP-43 antibody. The results showed that TDP-43 protein was phosphorylated (50 kDa) and cleaved into a phosphorylated fragment of TDP35 (35 kDa), indicating that the cells are responding to EA. The stimulation caused by the cells.
7,Inflammatory irritation
Inflammation is a defense response of the body to stimuli. Biological factors such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites, and other chemical factors such as acid, alkali, and decomposition products of necrotic tissue, high temperature, low temperature, radiation substances, ultraviolet rays, and mechanical damage can cause inflammatory reactions.
In the experiment, we often use the following compounds or combinations of compounds to stimulate cells to establish an inflammatory model. After inflammation occurs, the levels of PD-L1 protein and IDO1 protein in the cells change significantly, and they can be used as targets for inflammation detection.
a) PMA stimulates Jurkat cells
Experimental method: Jurkat cell density was 1.0 x 106 cells/mL. The experimental group was added to a final concentration of 10 ng/ml PMA for 2 h (PMA mother liquor was prepared in DMSO). The control group was added with an equal volume of DMSO. After 2 h, the cells were prepared to prepare lysate.
b) LPS stimulation of HepG2 / U937 / THP-1 cells
Experimental method: The cells were plated 24 h before stimulation, and the cell confluence was 70%-90% when stimulated. The experimental group was stimulated with a final concentration of 0.1 μg/ml LPS for 18-24 h, and no stimulation control was set.
c) TNF-α stimulates HUVEC cells
Experimental method: The cells were plated 24 h before stimulation, and the cell confluence was 70%-90% when stimulated. The experimental group was stimulated with a final concentration of 10 ng/ml for 18 h, and no stimulation control was set.
d) PHA+LPS co-stimulation
Experimental method: cell density 0.5x106/ml, total volume of cells per well of 6-well plate 1 x 106, final concentration of PHA 10 μg/ml, final concentration of LPS 50 ng/ml; stimulation time: PHA 30min+LPS 10min PHA 1h + LPS 30min; PHA 1d + LPS 2h; PHA 2d + LPS 1d; PHA 3d + LPS 2d.
e) CD3 monoclonal antibody stimulates Jurkat cells (T cell activation)
Experimental method: Jurkat density was 1.0 x 106 cells/ml during stimulation. The concentration of CD3 monoclonal antibody was 15 μg/ml in the experimental group. After 6 hours of stimulation, the cells were harvested and no stimulation control was set.
f) IFN-gamma stimulation A375 / A549 / HeLa cells
Experimental method: The cell density was 1.0 x 106 cells/ml during stimulation, and the IFN-gamma concentration was 15 μg/ml. After stimulation for 48 hours, the cells were harvested and no stimulation control was set. Changes in both protein levels were detected by PD-L1 antibody and IDO1 antibody.
Experimental results: IFN-gamma stimulated A375 / A549 / HeLa cells as an example. After stimulation, the protein levels of PD-L1 and IDO1 in the cells increased significantly, indicating that the cells are undergoing an inflammatory response.
8, Oleic acid stimulation
Lipid droplets are the main site of storage of intracellular neutral lipids and are research materials for lipid metabolism. Stimulation of cells with oleic acid induces the formation of lipid droplets. ADRP/Perilipin 2 is a marker of lipid droplets. Lipid droplets in cells can be well displayed by using IF assays using ADRP antibodies.
Oleic acid stimulation
Experimental method: Cells were plated 24 h before the experiment, and the cell confluence was 70%-90%. Stimulation was performed with oleic acid at a final concentration of 600 μM for 19 h. The subcellular localization of this protein was detected by an ADRP antibody.
Experimental results: After oleic acid stimulation, a large number of annular structures appeared in the cytoplasm of the cells, indicating that the number of lipid droplets in the cells increased significantly under the stimulation of oleic acid.
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Photo

Hello researchers.
The annual “1000 Free Antibodies for you” of CusAb has begun.
Actually, there are 1500 free antibodies for researchers this year.
And here is the free antibody list http://www.cusabio.com/antibody_en/
It only takes $9.9 (it is the handling fee actually), you will get 100ug of any antibody in the list. More details, please visit http://www.cusabio.com/antibody-free/ or contact me by sending emails to [email protected]
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Photo
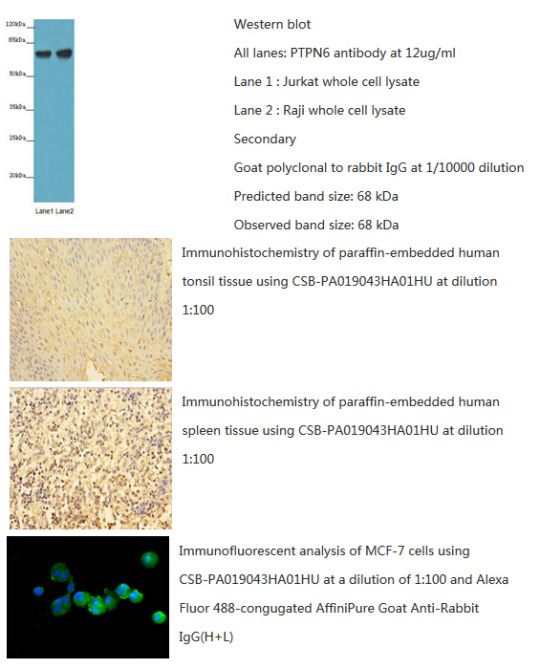
CusAb (Rabbit anti-human Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 6) polyclonal Antibody has been tested by WB, IHC and IF. The image above shows you the related results. So it can be used in your research? More details of the antibody, please refer to http://bit.ly/29OSfsu
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Link
0 notes
