Text
Here's THE masterpost of free and full adaptations, by which I mean that it's a post made by the master.
Anthony and Cleopatra: here's the BBC version
As you like it: you'll find here an outdoor stage adaptation and here the BBC version
Coriolanus: Here's a college play, here's the 1984 telefilm, here's the 2014 one with tom hiddleston
Hamlet: The Kenneth Branagh 1996 Hamlet is here, the 1964 russian version is here and the 1964 american version is here. THe 1964 Broadway production is here, the 1948 Laurence Olivier one is here. And the 1980 version is here. Here are part 1 and 2 of the 1990 BBC adaptation. Have the 2018 Almeida version here.
Henry IV: part 1 and part 2 of the BBC 1989 version. And here's part 1 of a corwall school version.
Henry V: Laurence Olivier (who would have guessed) 1944 version. The 1989 Branagh version here. The BBC version is here.
Julius Caesar: here's the 1979 BBC adaptation, here the 1970 John Gielgud one.
King Lear: Laurence Olivier once again plays in here. And Gregory Kozintsev, who was I think in charge of the russian hamlet, has a king lear here. The 1975 BBC version is here. The Royal Shakespeare Compagny's 2008 version is here. The 1974 version with James Earl Jones is here.
Macbeth: here's the 1961 one with Sean Connery. Here's the 1971 by Roman Polanski, with spanish subtitles. Here's the 1948 www.youtube.com/watch?v=ljZrf_0_CcQ">here. The 1988 BBC onee with portugese subtitles and here the 2001 one). The 1969 radio one with Ian McKellen and Judi Dench is here and the 1966 BBC version is here. The Royal Shakespeare Compagny's 2008 version is here.
Measure for Measure: BBC version here.
The Merchant of Venice: here's a stage version, here's the 1980 movie, here the 1973 Lawrence Olivier movie, here's the 2004 movie.
The Merry Wives of Windsor: the Royal Shakespeare Compagny gives you this movie.
A Midsummer Night's Dream: have this sponsored by the City of Columbia, and here the BBC version.
Much Ado About Nothing: Here is the kenneth branagh version and here the Tennant and Tate 2011 version. Here's the 1984 version.
Othello: A Massachussets Performance here, the 2001 movie her is the Orson Wells movie with portuguese subtitles theree, and a fifteen minutes long lego adaptation here. THen if you want more good ole reliable you've got the BBC version here and there.
Richard II: here is the BBC version
Richard III: here's the 1955 one with Laurence Olivier, and here's the 1995 one with Ian McKellen. (the 1995 one is in english subtitled in spanish. the 1955 one has no subtitles and might have ads since it's on youtube)
Romeo and Juliet: here's the 1988 BBC version.
The Taming of the Shrew: the 1988 BBC version here, the 1929 version here, some Ontario stuff here and here is the 1967 one with Richard Burton and Elizabeth Taylor.
The Tempest: the 1979 one is here, the 2010 is here. Here is the 1988 one.
Timon of Athens: here is the 1981 movie with Jonathan Pryce,
Troilus and Cressida can be found here
Titus Andronicus: the 1999 movie with Anthony Hopkins here
Twelfth night: here for the BBC, herefor the 1970 version with Alec Guinness, Joan Plowright and Ralph Richardson.
The Winter's Tale: the BBC version is here
Please do contribute if you find more. This is far from exhaustive.
(also look up the original post from time to time for more plays)
56K notes
·
View notes
Photo
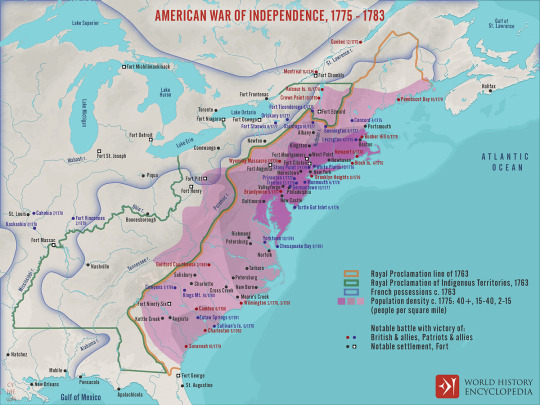
American War of Independence, 1775 - 1783
A map illustrating the course and major events during the American War of Independence (also known as the American Revolutionary War or American Revolution) between 1775 and 1783 – an armed rebellion through which thirteen of Great Britain’s colonies in North America sought independence. The insurrection stemmed from various reasons, amongst which the colonists’ grievances over taxation without representation and limitations on self-governance. Starting with the battles of Lexington and Concord in 1775, the conflict escalated into a full-scale war between the Continental Army and the forces of the British crown, and in 1778, it turned from a civil war within the British Empire into an international confrontation as France and Spain joined the colonies against Britain. The war reached its climax with the final British surrender at Yorktown in 1781, leading to the Treaty of Paris in 1783, formally recognizing the United States of America as an independent nation.
Image by Simeon Netchev
122 notes
·
View notes
Text
“Who is the third who walks always beside you? When I count, there are only you and I together But when I look ahead up the white road There is always another one walking beside you Gliding wrapt in a brown mantle, hooded I do not know whether a man or a woman -But who is that on the other side of you?”
— ― T.S. Eliot, The Waste Land and Other Poems
268 notes
·
View notes
Text
I think maybe the most important thing about Hamlet is that the line between sanity and madness has so much more to do with societal expectation than we want to admit
Like
The question of whether Hamlet and/or Ophelia are “truly” mad can’t even be asked unless you’re willing to grapple with whether their behavior—as erratic and ugly and confusing and incomprehensible as it might seem—is nevertheless a reasonable response to their situation, and that calling them “mad” is politically expedient for Claudius and Gertrude.
Grief and loneliness and fear can all make your brain and you behave in buckwild ways, it’s true, but it’s also about the crushing expectation that you won’t show any signs emotional disregulation, that you’ll continue to be a sober and rational and put-together noble when your world is falling to pieces around you. Whoever can pretend better gets to be called sane.
…god but you could do something fascinating with a production where Gertrude vehemently denies she can see the ghost while she is visibly and obviously staring directly at it
206 notes
·
View notes
Text
And then, one fairy night, May became June.
-F Scott Fitzgerald

81 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Luther’s 97 Theses
Martin Luther’s 95 Theses, credited with sparking the Protestant Reformation in Europe, have become a cultural touchstone since he posted them 31 October 1517, but the little-known 97 Theses, posted only a month earlier, are equally significant in the development of Luther’s (l. 1483-1546) vision and theology.
Learn more about Luther’s 97 Theses
39 notes
·
View notes
Text
Just finished reading Sir Gawain and the Green Knight, absolutely obsessed with arthurian legends rn. There's no greater tale in my heart.
0 notes
Photo



every line in e. a. robinson’s lancelot tore me to shreds but this one especially
3K notes
·
View notes
Photo

Why the Industrial Revolution Started in Britain
The Industrial Revolution saw a wave of technological and social changes in many countries of the world in the 18th and 19th centuries, but it began in Britain for a number of specific reasons. Britain had cheap energy with its abundant supply of coal, and labour was relatively expensive, so inventors and investors alike were lured by the possibility of profit if machines could be made that ran on coal and saved labour.
Continue reading…
39 notes
·
View notes
Text


Still reading the Lancelot grail still crazy
120 notes
·
View notes
Text




24 March 1603: death of Elizabeth Tudor, Queen of England.
29 notes
·
View notes
Photo







14 extraordinary vintage photographs that capture street scenes of London in 1894.
219 notes
·
View notes
Photo

“I can’t exactly describe how I feel, but it’s not quite right. And it leaves me cold.”
-F. Scott Fitzgerald
23 notes
·
View notes
Photo


Sam Wolfe Connelly’s illustrations for F. Scott Fitzgerald’s The Great Gatsby.
329 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Green Knight and Medieval Metatextuality: An Essay
Right, so. Finally watched it last night, and I’ve been thinking about it literally ever since, except for the part where I was asleep. As I said to fellow medievalist and admirer of Dev Patel @oldshrewsburyian, it’s possibly the most fascinating piece of medieval-inspired media that I’ve seen in ages, and how refreshing to have something in this genre that actually rewards critical thought and deep analysis, rather than me just fulminating fruitlessly about how popular media thinks that slapping blood, filth, and misogyny onto some swords and castles is “historically accurate.” I read a review of TGK somewhere that described it as the anti-Game of Thrones, and I’m inclined to think that’s accurate. I didn’t agree with all of the film’s tonal, thematic, or interpretative choices, but I found them consistently stylish, compelling, and subversive in ways both small and large, and I’m gonna have to write about it or I’ll go crazy. So. Brace yourselves.
(Note: My PhD is in medieval history, not medieval literature, and I haven’t worked on SGGK specifically, but I am familiar with it, its general cultural context, and the historical influences, images, and debates that both the poem and the film referenced and drew upon, so that’s where this meta is coming from.)
First, obviously, while the film is not a straight-up text-to-screen version of the poem (though it is by and large relatively faithful), it is a multi-layered meta-text that comments on the original Sir Gawain and the Green Knight, the archetypes of chivalric literature as a whole, modern expectations for medieval films, the hero’s journey, the requirements of being an “honorable knight,” and the nature of death, fate, magic, and religion, just to name a few. Given that the Arthurian legendarium, otherwise known as the Matter of Britain, was written and rewritten over several centuries by countless authors, drawing on and changing and hybridizing interpretations that sometimes challenged or outright contradicted earlier versions, it makes sense for the film to chart its own path and make its own adaptational decisions as part of this multivalent, multivocal literary canon. Sir Gawain himself is a canonically and textually inconsistent figure; in the movie, the characters merrily pronounce his name in several different ways, most notably as Sean Harris/King Arthur’s somewhat inexplicable “Garr-win.” He might be a man without a consistent identity, but that’s pointed out within the film itself. What has he done to define himself, aside from being the king’s nephew? Is his quixotic quest for the Green Knight actually going to resolve the question of his identity and his honor – and if so, is it even going to matter, given that successful completion of the “game” seemingly equates with death?
Likewise, as the anti-Game of Thrones, the film is deliberately and sometimes maddeningly non-commercial. For an adaptation coming from a studio known primarily for horror, it almost completely eschews the cliché that gory bloodshed equals authentic medievalism; the only graphic scene is the Green Knight’s original beheading. The violence is only hinted at, subtextual, suspenseful; it is kept out of sight, around the corner, never entirely played out or resolved. In other words, if anyone came in thinking that they were going to watch Dev Patel luridly swashbuckle his way through some CGI monsters like bad Beowulf adaptations of yore, they were swiftly disappointed. In fact, he seems to spend most of his time being wet, sad, and failing to meet the moment at hand (with a few important exceptions).
The film unhurriedly evokes a medieval setting that is both surreal and defiantly non-historical. We travel (in roughly chronological order) from Anglo-Saxon huts to Romanesque halls to high-Gothic cathedrals to Tudor villages and half-timbered houses, culminating in the eerie neo-Renaissance splendor of the Lord and Lady’s hall, before returning to the ancient trees of the Green Chapel and its immortal occupant: everything that has come before has now returned to dust. We have been removed even from imagined time and place and into a moment where it ceases to function altogether. We move forward, backward, and sideways, as Gawain experiences past, present, and future in unison. He is dislocated from his own sense of himself, just as we, the viewers, are dislocated from our sense of what is the “true” reality or filmic narrative; what we think is real turns out not to be the case at all. If, of course, such a thing even exists at all.
This visual evocation of the entire medieval era also creates a setting that, unlike GOT, takes pride in rejecting absolutely all political context or Machiavellian maneuvering. The film acknowledges its own cultural ubiquity and the question of whether we really need yet another King Arthur adaptation: none of the characters aside from Gawain himself are credited by name. We all know it’s Arthur, but he’s listed only as “king.” We know the spooky druid-like old man with the white beard is Merlin, but it’s never required to spell it out. The film gestures at our pre-existing understanding; it relies on us to fill in the gaps, cuing us to collaboratively produce the story with it, positioning us as listeners as if we were gathered to hear the original poem. Just like fanfiction, it knows that it doesn’t need to waste time introducing every single character or filling in ultimately unnecessary background knowledge, when the audience can be relied upon to bring their own.
As for that, the film explicitly frames itself as a “filmed adaptation of the chivalric romance” in its opening credits, and continues to play with textual referents and cues throughout: telling us where we are, what’s happening, or what’s coming next, rather like the rubrics or headings within a medieval manuscript. As noted, its historical/architectural references span the entire medieval European world, as does its costume design. I was particularly struck by the fact that Arthur and Guinevere’s crowns resemble those from illuminated monastic manuscripts or Eastern Orthodox iconography: they are both crown and halo, they confer an air of both secular kingship and religious sanctity. The question in the film’s imagined epilogue thus becomes one familiar to Shakespeare’s Henry V: heavy is the head that wears the crown. Does Gawain want to earn his uncle’s crown, take over his place as king, bear the fate of Camelot, become a great ruler, a husband and father in ways that even Arthur never did, only to see it all brought to dust by his cowardice, his reliance on unscrupulous sorcery, and his unfulfilled promise to the Green Knight? Is it better to have that entire life and then lose it, or to make the right choice now, even if it means death?
Likewise, Arthur’s kingly mantle is Byzantine in inspiration, as is the icon of the Virgin Mary-as-Theotokos painted on Gawain’s shield (which we see broken apart during the attack by the scavengers). The film only glances at its religious themes rather than harping on them explicitly; we do have the cliché scene of the male churchmen praying for Gawain’s safety, opposite Gawain’s mother and her female attendants working witchcraft to protect him. (When oh when will I get my film that treats medieval magic and medieval religion as the complementary and co-existing epistemological systems that they were, rather than portraying them as diametrically binary and disparagingly gendered opposites?) But despite the interim setbacks borne from the failure of Christian icons, the overall resolution of the film could serve as the culmination of a medieval Christian morality tale: Gawain can buy himself a great future in the short term if he relies on the protection of the enchanted green belt to avoid the Green Knight’s killing stroke, but then he will have to watch it all crumble until he is sitting alone in his own hall, his children dead and his kingdom destroyed, as a headless corpse who only now has been brave enough to accept his proper fate. By removing the belt from his person in the film’s Inception-like final scene, he relinquishes the taint of black magic and regains his religious honor, even at the likely cost of death. That, the medieval Christian morality tale would agree, is the correct course of action.
Gawain’s encounter with St. Winifred likewise presents a more subtle vision of medieval Christianity. Winifred was an eighth-century Welsh saint known for being beheaded, after which (by the power of another saint) her head was miraculously restored to her body and she went on to live a long and holy life. It doesn’t quite work that way in TGK. (St Winifred’s Well is mentioned in the original SGGK, but as far as I recall, Gawain doesn’t meet the saint in person.) In the film, Gawain encounters Winifred’s lifelike apparition, who begs him to dive into the mere and retrieve her head (despite appearances, she warns him, it is not attached to her body). This fits into the pattern of medieval ghost stories, where the dead often return to entreat the living to help them finish their business; they must be heeded, but when they are encountered in places they shouldn’t be, they must be put back into their proper physical space and reminded of their real fate. Gawain doesn’t follow William of Newburgh’s practical recommendation to just fetch some brawny young men with shovels to beat the wandering corpse back into its grave. Instead, in one of his few moments of unqualified heroism, he dives into the dark water and retrieves Winifred’s skull from the bottom of the lake. Then when he returns to the house, he finds the rest of her skeleton lying in the bed where he was earlier sleeping, and carefully reunites the skull with its body, finally allowing it to rest in peace.
However, Gawain’s involvement with Winifred doesn’t end there. The fox that he sees on the bank after emerging with her skull, who then accompanies him for the rest of the film, is strongly implied to be her spirit, or at least a companion that she has sent for him. Gawain has handled a saint’s holy bones; her relics, which were well known to grant protection in the medieval world. He has done the saint a service, and in return, she extends her favor to him. At the end of the film, the fox finally speaks in a human voice, warning him not to proceed to the fateful final encounter with the Green Knight; it will mean his death. The symbolism of having a beheaded saint serve as Gawain’s guide and protector is obvious, since it is the fate that may or may not lie in store for him. As I said, the ending is Inception-like in that it steadfastly refuses to tell you if the hero is alive (or will live) or dead (or will die). In the original SGGK, of course, the Green Knight and the Lord turn out to be the same person, Gawain survives, it was all just a test of chivalric will and honor, and a trap put together by Morgan Le Fay in an attempt to frighten Guinevere. It’s essentially able to be laughed off: a game, an adventure, not real. TGK takes this paradigm and flips it (to speak…) on its head.
Gawain’s rescue of Winifred’s head also rewards him in more immediate terms: his/the Green Knight’s axe, stolen by the scavengers, is miraculously restored to him in her cottage, immediately and concretely demonstrating the virtue of his actions. This is one of the points where the film most stubbornly resists modern storytelling conventions: it simply refuses to add in any kind of “rational” or “empirical” explanation of how else it got there, aside from the grace and intercession of the saint. This is indeed how it works in medieval hagiography: things simply reappear, are returned, reattached, repaired, made whole again, and Gawain’s lost weapon is thus restored, symbolizing that he has passed the test and is worthy to continue with the quest. The film’s narrative is not modernizing its underlying medieval logic here, and it doesn’t particularly care if a modern audience finds it “convincing” or not. As noted, the film never makes any attempt to temporalize or localize itself; it exists in a determinedly surrealist and ahistorical landscape, where naked female giants who look suspiciously like Tilda Swinton roam across the wild with no necessary explanation. While this might be frustrating for some people, I actually found it a huge relief that a clearly fantastic and fictional literary adaptation was not acting like it was qualified to teach “real history” to its audience. Nobody would come out of TGK thinking that they had seen the “actual” medieval world, and since we have enough of a problem with that sort of thing thanks to GOT, I for one welcome the creation of a medieval imaginative space that embraces its eccentric and unrealistic elements, rather than trying to fit them into the Real Life box.
This plays into the fact that the film, like a reused medieval manuscript containing more than one text, is a palimpsest: for one, it audaciously rewrites the entire Arthurian canon in the wordless vision of Gawain’s life after escaping the Green Knight (I could write another meta on that dream-epilogue alone). It moves fluidly through time and creates alternate universes in at least two major points: one, the scene where Gawain is tied up and abandoned by the scavengers and that long circling shot reveals his skeletal corpse rotting on the sward, only to return to our original universe as Gawain decides that he doesn’t want that fate, and two, Gawain as King. In this alternate ending, Arthur doesn’t die in battle with Mordred, but peaceably in bed, having anointed his worthy nephew as his heir. Gawain becomes king, has children, gets married, governs Camelot, becomes a ruler surpassing even Arthur, but then watches his son get killed in battle, his subjects turn on him, and his family vanish into the dust of his broken hall before he himself, in despair, pulls the enchanted scarf out of his clothing and succumbs to his fate.
In this version, Gawain takes on the responsibility for the fall of Camelot, not Arthur. This is the hero’s burden, but he’s obtained it dishonorably, by cheating. It is a vivid but mimetic future which Gawain (to all appearances) ultimately rejects, returning the film to the realm of traditional Arthurian canon – but not quite. After all, if Gawain does get beheaded after that final fade to black, it would represent a significant alteration from the poem and the character’s usual arc. Are we back in traditional canon or aren’t we? Did Gawain reject that future or didn’t he? Do all these alterities still exist within the visual medium of the meta-text, and have any of them been definitely foreclosed?
Furthermore, the film interrogates itself and its own tropes in explicit and overt ways. In Gawain’s conversation with the Lord, the Lord poses the question that many members of the audience might have: is Gawain going to carry out this potentially pointless and suicidal quest and then be an honorable hero, just like that? What is he actually getting by staggering through assorted Irish bogs and seeming to reject, rather than embrace, the paradigms of a proper quest and that of an honorable knight? He lies about being a knight to the scavengers, clearly out of fear, and ends up cravenly bound and robbed rather than fighting back. He denies knowing anything about love to the Lady (played by Alicia Vikander, who also plays his lover at the start of the film with a decidedly ropey Yorkshire accent, sorry to say). He seems to shrink from the responsibility thrust on him, rather than rise to meet it (his only honorable act, retrieving Winifred’s head, is discussed above) and yet here he still is, plugging away. Why is he doing this? What does he really stand to gain, other than accepting a choice and its consequences (somewhat?) The film raises these questions, but it has no plans to answer them. It’s going to leave you to think about them for yourself, and it isn’t going to spoon-feed you any ultimate moral or neat resolution. In this interchange, it’s easy to see both the echoes of a formal dialogue between two speakers (a favored medieval didactic tactic) and the broader purpose of chivalric literature: to interrogate what it actually means to be a knight, how personal honor is generated, acquired, and increased, and whether engaging in these pointless and bloody “war games” is actually any kind of real path to lasting glory.
The film’s treatment of race, gender, and queerness obviously also merits comment. By casting Dev Patel, an Indian-born actor, as an Arthurian hero, the film is… actually being quite accurate to the original legends, doubtless much to the disappointment of assorted internet racists. The thirteenth-century Arthurian romance Parzival (Percival) by the German poet Wolfram von Eschenbach notably features the character of Percival’s mixed-race half-brother, Feirefiz, son of their father by his first marriage to a Muslim princess. Feirefiz is just as heroic as Percival (Gawaine, for the record, also plays a major role in the story) and assists in the quest for the Holy Grail, though it takes his conversion to Christianity for him to properly behold it.
By introducing Patel (and Sarita Chowdhury as Morgause) to the visual representation of Arthuriana, the film quietly does away with the “white Middle Ages” cliché that I have complained about ad nauseam; we see background Asian and black members of Camelot, who just exist there without having to conjure up some complicated rationale to explain their presence. The Lady also uses a camera obscura to make Gawain’s portrait. Contrary to those who might howl about anachronism, this technique was known in China as early as the fourth century BCE and the tenth/eleventh century Islamic scholar Ibn al-Haytham was probably the best-known medieval authority to write on it extensively; Latin translations of his work inspired European scientists from Roger Bacon to Leonardo da Vinci. Aside from the symbolism of an upside-down Gawain (and when he sees the portrait again during the ‘fall of Camelot’, it is right-side-up, representing that Gawain himself is in an upside-down world), this presents a subtle challenge to the prevailing Eurocentric imagination of the medieval world, and draws on other global influences.
As for gender, we have briefly touched on it above; in the original SGGK, Gawain’s entire journey is revealed to be just a cruel trick of Morgan Le Fay, simply trying to destabilize Arthur’s court and upset his queen. (Morgan is the old blindfolded woman who appears in the Lord and Lady’s castle and briefly approaches Gawain, but her identity is never explicitly spelled out.) This is, obviously, an implicitly misogynistic setup: an evil woman plays a trick on honorable men for the purpose of upsetting another woman, the honorable men overcome it, the hero survives, and everyone presumably lives happily ever after (at least until Mordred arrives).
Instead, by plunging the outcome into doubt and the hero into a much darker and more fallible moral universe, TGK shifts the blame for Gawain’s adventure and ultimate fate from Morgan to Gawain himself. Likewise, Guinevere is not the passive recipient of an evil deception but in a way, the catalyst for the whole thing. She breaks the seal on the Green Knight’s message with a weighty snap; she becomes the oracle who reads it out, she is alarming rather than alarmed, she disrupts the complacency of the court and silently shows up all the other knights who refuse to step forward and answer the Green Knight’s challenge. Gawain is not given the ontological reassurance that it’s just a practical joke and he’s going to be fine (and thanks to the unresolved ending, neither are we). The film instead takes the concept at face value in order to push the envelope and ask the simple question: if a man was going to be actually-for-real beheaded in a year, why would he set out on a suicidal quest? Would you, in Gawain’s place, make the same decision to cast aside the enchanted belt and accept your fate? Has he made his name, will he be remembered well? What is his legacy?
Indeed, if there is any hint of feminine connivance and manipulation, it arrives in the form of the implication that Gawain’s mother has deliberately summoned the Green Knight to test her son, prove his worth, and position him as his childless uncle’s heir; she gives him the protective belt to make sure he won’t actually die, and her intention all along was for the future shown in the epilogue to truly play out (minus the collapse of Camelot). Only Gawain loses the belt thanks to his cowardice in the encounter with the scavengers, regains it in a somewhat underhanded and morally questionable way when the Lady is attempting to seduce him, and by ultimately rejecting it altogether and submitting to his uncertain fate, totally mucks up his mother’s painstaking dynastic plans for his future. In this reading, Gawain could be king, and his mother’s efforts are meant to achieve that goal, rather than thwart it. He is thus required to shoulder his own responsibility for this outcome, rather than conveniently pawning it off on an “evil woman,” and by extension, the film asks the question: What would the world be like if men, especially those who make war on others as a way of life, were actually forced to face the consequences of their reckless and violent actions? Is it actually a “game” in any sense of the word, especially when chivalric literature is constantly preoccupied with the question of how much glorious violence is too much glorious violence? If you structure social prestige for the king and the noble male elite entirely around winning battles and existing in a state of perpetual war, when does that begin to backfire and devour the knightly class – and the rest of society – instead?
This leads into the central theme of Gawain’s relationships with the Lord and Lady, and how they’re treated in the film. The poem has been repeatedly studied in terms of its latent (and sometimes… less than latent) queer subtext: when the Lord asks Gawain to pay back to him whatever he should receive from his wife, does he already know what this involves; i.e. a physical and romantic encounter? When the Lady gives kisses to Gawain, which he is then obliged to return to the Lord as a condition of the agreement, is this all part of a dastardly plot to seduce him into a kinky green-themed threesome with a probably-not-human married couple looking to spice up their sex life? Why do we read the Lady’s kisses to Gawain as romantic but Gawain’s kisses to the Lord as filial, fraternal, or the standard “kiss of peace” exchanged between a liege lord and his vassal? Is Gawain simply being a dutiful guest by honoring the bargain with his host, actually just kissing the Lady again via the proxy of her husband, or somewhat more into this whole thing with the Lord than he (or the poet) would like to admit? Is the homosocial turning homoerotic, and how is Gawain going to navigate this tension and temptation?
If the question is never resolved: well, welcome to one of the central medieval anxieties about chivalry, knighthood, and male bonds! As I have written about before, medieval society needed to simultaneously exalt this as the most honored and noble form of love, and make sure it didn’t accidentally turn sexual (once again: how much male love is too much male love?). Does the poem raise the possibility of serious disruption to the dominant heteronormative paradigm, only to solve the problem by interpreting the Gawain/Lady male/female kisses as romantic and sexual and the Gawain/Lord male/male kisses as chaste and formal? In other words, acknowledging the underlying anxiety of possible homoeroticism but ultimately reasserting the heterosexual norm? The answer: Probably?!?! Maybe?!?! Hell if we know??! To say the least, this has been argued over to no end, and if you locked a lot of medieval history/literature scholars into a room and told them that they couldn’t come out until they decided on one clear answer, they would be in there for a very long time. The poem seemingly invokes the possibility of a queer reading only to reject it – but once again, as in the question of which canon we end up in at the film’s end, does it?
In some lights, the film’s treatment of this potential queer reading comes off like a cop-out: there is only one kiss between Gawain and the Lord, and it is something that the Lord has to initiate after Gawain has already fled the hall. Gawain himself appears to reject it; he tells the Lord to let go of him and runs off into the wilderness, rather than deal with or accept whatever has been suggested to him. However, this fits with film!Gawain’s pattern of rejecting that which fundamentally makes him who he is; like Peter in the Bible, he has now denied the truth three times. With the scavengers he denies being a knight; with the Lady he denies knowing about courtly love; with the Lord he denies the central bond of brotherhood with his fellows, whether homosocial or homoerotic in nature. I would go so far as to argue that if Gawain does die at the end of the film, it is this rejected kiss which truly seals his fate. In the poem, the Lord and the Green Knight are revealed to be the same person; in the film, it’s not clear if that’s the case, or they are separate characters, even if thematically interrelated. If we assume, however, that the Lord is in fact still the human form of the Green Knight, then Gawain has rejected both his kiss of peace (the standard gesture of protection offered from lord to vassal) and any deeper emotional bond that it can be read to signify. The Green Knight could decide to spare Gawain in recognition of the courage he has shown in relinquishing the enchanted belt – or he could just as easily decide to kill him, which he is legally free to do since Gawain has symbolically rejected the offer of brotherhood, vassalage, or knight-bonding by his unwise denial of the Lord’s freely given kiss. Once again, the film raises the overall thematic and moral question and then doesn’t give one straight (ahem) answer. As with the medieval anxieties and chivalric texts that it is based on, it invokes the specter of queerness and then doesn’t neatly resolve it. As a modern audience, we find this unsatisfying, but once again, the film is refusing to conform to our expectations.
As has been said before, there is so much kissing between men in medieval contexts, both ceremonial and otherwise, that we’re left to wonder: “is it gay or is it feudalism?” Is there an overtly erotic element in Gawain and the Green Knight’s mutual “beheading” of each other (especially since in the original version, this frees the Lord from his curse, functioning like a true love’s kiss in a fairytale). While it is certainly possible to argue that the film has “straightwashed” its subject material by removing the entire sequence of kisses between Gawain and the Lord and the unresolved motives for their existence, it is a fairly accurate, if condensed, representation of the anxieties around medieval knightly bonds and whether, as Carolyn Dinshaw put it, a (male/male) “kiss is just a kiss.” After all, the kiss between Gawain and the Lady is uncomplicatedly read as sexual/romantic, and that context doesn’t go away when Gawain is kissing the Lord instead. Just as with its multiple futurities, the film leaves the question open-ended. Is it that third and final denial that seals Gawain’s fate, and if so, is it asking us to reflect on why, specifically, he does so?
The film could play with both this question and its overall tone quite a bit more: it sometimes comes off as a grim, wooden, over-directed Shakespearean tragedy, rather than incorporating the lively and irreverent tone that the poem often takes. It’s almost totally devoid of humor, which is unfortunate, and the Grim Middle Ages aesthetic is in definite evidence. Nonetheless, because of the comprehensive de-historicizing and the obvious lack of effort to claim the film as any sort of authentic representation of the medieval past, it works. We are not meant to understand this as a historical document, and so we have to treat it on its terms, by its own logic, and by its own frames of reference. In some ways, its consistent opacity and its refusal to abide by modern rules and common narrative conventions is deliberately meant to challenge us: as before, when we recognize Arthur, Merlin, the Round Table, and the other stock characters because we know them already and not because the film tells us so, we have to fill in the gaps ourselves. We are watching the film not because it tells us a simple adventure story – there is, as noted, shockingly little action overall – but because we have to piece together the metatext independently and ponder the philosophical questions that it leaves us with. What conclusion do we reach? What canon do we settle in? What future or resolution is ultimately made real? That, the film says, it can’t decide for us. As ever, it is up to future generations to carry on the story, and decide how, if at all, it is going to survive.
(And to close, I desperately want them to make my much-coveted Bisclavret adaptation now in more or less the same style, albeit with some tweaks. Please.)
Further Reading
Ailes, Marianne J. ‘The Medieval Male Couple and the Language of Homosociality’, in Masculinity in Medieval Europe, ed. by Dawn M. Hadley (Harlow: Longman, 1999), pp. 214–37.
Ashton, Gail. ‘The Perverse Dynamics of Sir Gawain and the Green Knight’, Arthuriana 15 (2005), 51–74.
Boyd, David L. ‘Sodomy, Misogyny, and Displacement: Occluding Queer Desire in Sir Gawain and the Green Knight’, Arthuriana 8 (1998), 77–113.
Busse, Peter. ‘The Poet as Spouse of his Patron: Homoerotic Love in Medieval Welsh and Irish Poetry?’, Studi Celtici 2 (2003), 175–92.
Dinshaw, Carolyn. ‘A Kiss Is Just a Kiss: Heterosexuality and Its Consolations in Sir Gawain and the Green Knight’, Diacritics 24 (1994), 205–226.
Kocher, Suzanne. ‘Gay Knights in Medieval French Fiction: Constructs of Queerness and Non-Transgression’, Mediaevalia 29 (2008), 51–66.
Karras, Ruth Mazo. ‘Knighthood, Compulsory Heterosexuality, and Sodomy’ in The Boswell Thesis: Essays on Christianity, Social Tolerance, and Homosexuality, ed. Matthew Kuefler (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2006), pp. 273–86.
Kuefler, Matthew. ‘Male Friendship and the Suspicion of Sodomy in Twelfth-Century France’, in The Boswell Thesis: Essays on Christianity, Social Tolerance, and Homosexuality, ed. Matthew Kuefler (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2006), pp. 179–214.
McVitty, E. Amanda, ‘False Knights and True Men: Contesting Chivalric Masculinity in English Treason Trials, 1388–1415,’ Journal of Medieval History 40 (2014), 458–77.
Mieszkowski, Gretchen. ‘The Prose Lancelot's Galehot, Malory's Lavain, and the Queering of Late Medieval Literature’, Arthuriana 5 (1995), 21–51.
Moss, Rachel E. ‘ “And much more I am soryat for my good knyghts’ ”: Fainting, Homosociality, and Elite Male Culture in Middle English Romance’, Historical Reflections / Réflexions historiques 42 (2016), 101–13.
Zeikowitz, Richard E. ‘Befriending the Medieval Queer: A Pedagogy for Literature Classes’, College English 65 (2002), 67–80.
2K notes
·
View notes

