#if covid weren't so insanely contagious we 100% would have killed it
Text
Here we are, heading into another COVID winter. The fucker’s still here and sadly we aren’t likely to get rid of it any time soon. You kill diseases by cutting off transmission and slowly strangling them to death. We tried that. We locked down the whole world and it didn’t work.
I won’t deny that things look really ugly right now, especially with other respiratory diseases coming back. But as the sequencing results keep coming in, it’s really starting to look like something incredible happened.
Sure, the lockdowns didn’t succeed in killing COVID. That doesn’t mean they killed nothing.
Hey, I wonder how the influenza viruses are holding up?
There are two types of influenza that cause the epidemics we get every winter: A and B. (C and D don’t really get up to the same level of mischief so let’s ignore them for now.) Type A infects both animals and people, and includes things like the H1N1 bird flu pandemic strain, swine flu, et al. The H[number]N[number] format points out which subtype of two important viral proteins it has, and usually strains are reported with that code, what animal they jumped into humans from, and where they were first sequenced. Type B only affects humans, especially children. It doesn’t have subtypes like Type A. Instead it has two distinct lineages: B/Victoria and B/Yamagata.
Today’s best flu vaccines are called “quadrivalent” because they target B/Victoria, B/Yamagata, and our best guess at which two Type A’s are going to blow up this year. The guess is based on global sequencing of flu infections, so we have at least a decent idea of both past and current circulation logged in databases like GISAID and the WHO’s FluNet.
Cases went way down during the lockdowns - masking and social distancing pushed spread down to a fraction of what it usually is. Influenza in general is now back in force as people go back to their normal behavior. There’s plenty of Type A flying around. There’s been B/Victoria.
B/Yamagata has not been conclusively identified since March of 2020.
As early as 2021, flu researchers noticed the lack of new B/Yamagata sequences coming in and started to suspect something was fishy. Look at this graph of GISAID flu data by lineage:

[GISAID] [paper]
Let’s, uh, check FluNet maybe? That shows that in a typical year you see tens of thousands of cases of B/Yamagata on PCR tests. 2017 had 30,552; 2018 had 51,524. Then... 3,464 in 2019. 364 in 2020 in only 9 countries. It does seem like there are still signs of life in 2021 with 8 hits, but keep in mind these detections are based on simple PCR tests like what we do for COVID. PCR tests are exquisitely sensitive, to the point where it’s been shown that giving flu vaccines and then later using the same room to give flu tests can throw a weak positive by picking up viral RNA from the vaccine. More specifically, as of March 2022 there’s been a case of this exact thing happening with what looked like a B/Yamagata detection. So it’s going to be more reliable to look at only the results from full sequencing, where you can yeet anything that matches the vaccine ingredients and only look at wild viruses.
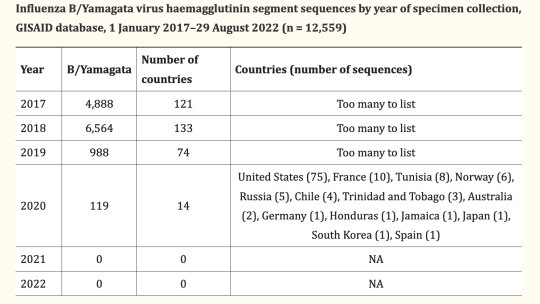
[paper]
Zero. Nothing. All signs point to we shot at COVID and blew up an entire flu lineage as collateral damage! What the fuck! We’re probably going to have to change how we do flu vaccines because fully a quarter of what they aim at looks to be gone from the face of the earth!
True, influenza B/Yamagata could still be out there somewhere that hasn’t been sequenced. Proving absence is hard. But the fact that Type A and its sibling B/Victoria are back and easy to find really does suggest it’s gone, or stomped down so far it’s near impossible to find. Time to watch and wait and feed every sample we can into the sequencers, but if we keep not finding it...
A disease is considered eradicated when we’re sure there’s no more transmission “in the wild”. For smallpox, which was also wildly contagious and also had no nonhuman reservoir, that was three years from the last known case.
Clock’s ticking.
#biology#flu#influenza#virus#medicine#if covid weren't so insanely contagious we 100% would have killed it
14 notes
·
View notes