#trading economics
Text
Trading economics

Yet over the last several decades, as industries have consolidated, competition has weakened in too many markets, denying Americans the benefits of an open economy and widening racial, income, and wealth inequality. Robust competition is critical to preserving America’s role as the world’s leading economy. And for consumers, it means more choices, better service, and lower prices. For entrepreneurs, it provides space to experiment, innovate, and pursue the new ideas that have for centuries powered the American economy and improved our quality of life. For small businesses and farmers, it creates more choices among suppliers and major buyers, leading to more take-home income, which they can reinvest in their enterprises. For workers, a competitive marketplace creates more high-quality jobs and the economic freedom to switch jobs or negotiate a higher wage. The American promise of a broad and sustained prosperity depends on an open and competitive economy. Get Involved Show submenu for “Get Involved””īy the authority vested in me as President by the Constitution and the laws of the United States of America, and in order to promote the interests of American workers, businesses, and consumers, it is hereby ordered as follows:Ī fair, open, and competitive marketplace has long been a cornerstone of the American economy, while excessive market concentration threatens basic economic liberties, democratic accountability, and the welfare of workers, farmers, small businesses, startups, and consumers.The White House Show submenu for “The White House””.Office of the United States Trade Representative.Office of Science and Technology Policy.Executive Offices Show submenu for “Executive Offices””.Administration Show submenu for “Administration””.

0 notes
Text
Trading economics

Great work I really enjoyed this course." - Bethany Holt I am looking forward to putting this knowledge into action. It was very thorough and detailed which I felt was quite responsible as compared to some stock trading systems courses who would sell complex systems that result in the customers demise into poverty. " What I liked about this course is that it took the time to educate the student on the terminology and the concepts behind the system. Thanks a lot for giving my life a new lesson of success!" - Robert Clyde It is only a few days & I have been able to to put together a trading strategy based on what I learned and it tested successfully. I have learned so much going through this course. " A real actionable trading strategy is followed in this course. Use economic indicators to build a low-risk and profitable system for trading the stock market in 30 minutes a day Create and test the results of your own trading strategies.Ģ000+ satisfied students from 100+ countries!!!Īre you confused from the daily bombardment of financial information by various sources? Are you irritated by the news reporters mentioning a gazillion reasons for the stock market movement, often contradicting each other? Are you tired of using adhoc strategies for trading, nervously following every market move and looking for a robust, profitable system to trade? Well, you have come to the right place. UPDATE Jan 19th 2016: Economic Indicator Trading Toolbox added. UPDATE Feb 10th 2016: Complete Trading Resource List including Top 10 must have trading websites, blogs, books, trader twitter accounts. UPDATE June 11th 2017: FREE SUPER TRADERS EBOOK including lesson and life stories of the Top 20 Super Traders of all times including George Soros, Ray Dalio, D.E.

0 notes
Text
Tom Nicholas just posted a video that summarizes like half a semester of business school and honestly teaches it better than a lot of my professors, while also ensuring the viewer is aware of the moral and ethical failings of free trade in the name of comparative advantage and global efficiency.
youtube
(Yes, for the unaware: I have a bachelor's degree in international business. I am also one of those people who graduated with a distinct distaste for much of the business world, related directly to the 'taking advantage of cheap labor and bullying less powerful entities is good, actually' model of economic theory that a lot of my classes pushed.)
#tom nicholas#education#economics#global economics#geopolitics#china#wto#united states#phoenix politics#youtube#videos#though I actually watched this on Nebula lol#comparative advantage#free trade#Youtube
352 notes
·
View notes
Note
If management finds a way to automate jobs during a strike, is that scabbing?
Peripherally.
The automation itself is more part of the general category of management strategies to restructure workflow and production methods in order to reduce the need for, and thus the power of, labor. This dates back to the origins of Taylorism itself in the 1890s as an effort to “steal the brains from underneath the cap of labor” and through to the emergence of Human Relations and Industrial Psychology in the early 20th century as a means to better control workers. So I think you could see in as essentially equivalent to classic speed-up and stretch-out efforts to maintain production at as low a cost as possible during a strike, and thus break the union.
However, the dirty truth of automation is that there is no clean way to fully substitute machinery for labor. Due to the inherent limitations of technology at any stage of development, you need labor to repair and maintain and monitor automated systems, you need labor to install and operate the machines, you need labor to design and program and manufacture the machines. (This is one reason why the job-killing predictions around automation often fall flat, because the supposedly superior new technology often requires a significant increase in human labor to service the new technology when it breaks. For example, this is why automation in fast food has proven to be so difficult and partial than expected: it turns out that self-checkout machines are actually very expensive to operate in terms of skilled manpower.) And to the extent that a given automation contract or project is being undertaken during a strike in order to break that strike, that’s absolutely scabbing.
#labor#labor history#trade unions#unions#strikes#automation#Taylorism#political economy#economic history#scabbing#labor studies
131 notes
·
View notes
Text
I know complaining about the lack of socioeconomic information on the various societies in FFXIV is a bit like complaining about my omelet not having any chocolate syrup on it. But Robert Jordan has truly brain scorched me because I can't look at the Crystarium without wanting to scream how are you a functional society, what on EARTH must your tax code look like?, followed by shaking the whole place like an etch-a-sketch until it gives me answers.
#FFXIV#Final Fantasy XIV#Shadowbriners#The Crystartium#I have spent DAYS thinking about the trade tariffs G'raha must be imposing on that god damn market#To support even a FRACTION of what his government is doing#and THEN I spent hours wondering WHO THE HELL IS MAINTAINING IS SOCIAL AND ECONOMIC POLICY#NOW THAT HE's FUCKED OFF BACK TO THE SOURCE IN ORDER TO CHASE THAT WOL DICK#*gargles furiously*#G'raha Tia
275 notes
·
View notes
Text

Free Trade Is For Peasants, Not Cartoonists
Transcript, discussion, and a gross anecdote about Hugh Hefner at: https://www.patreon.com/posts/free-trade-is-98677035
We can keep making these cartoons because lots of people support us with $1-3 pledges! Join them at patreon.com/barry
#policartoon#political cartoon#political comics#political cartoons#free trade#protectionism#economics
41 notes
·
View notes
Text
Genua nestled on the delta of the Vieux river, which was the source of its wealth. And Genua was wealthy. Genua had once controlled the river mouth and taxed its traffic in a way that couldn't be called piracy because it was done by the city government, and therefore sound economics and perfectly alright.
Terry Pratchett, Witches Abroad
#genua#witches abroad#discworld#terry pratchett#witches#travel#river#trade#laws#economics#politics#city government#power#taxes#piracy#perspective#perfectly alright
227 notes
·
View notes
Text
Countries that are no more: Republic of Venice (697AD-1797AD)
The first in a series I hope to feature on providing high level overviews of countries that existed and were influential to history or obscure and lost to most memory in time. The first up is the Republic of Venice.
Name: Serenisma Republega de Venesia (Venetian). In English this translates to the state's official name The Most Serene Republic of Venice. Also referred to as the Venetian Republic, Republic of Venice or just Venice.
Language: The official languages were the Romance languages of Latin, Venetian & later Italian. The regional dialect of Vulgar Latin in Northeastern Italy known as Veneto was the original language of Venice. This evolved in Venetian which was attested to as a distinct language as early as the 13th century AD. Venetian became the official language and lingua franca of the everyday Venetians and across parts of the Mediterranean although Latin would still be used in official documents and religious functions. Overtime, modern Italian was spoken in Venice though the Venetian language remains technically a separate language in Italy's Veneto region and the surrounding areas to this day.
Minority languages across the republic's territory included various Romance languages such as Lombard, Friulian, Ladin, Dalmatian and non-romance languages such as Albanian, Greek & Serbo-Croatian.
Territory: The republic was centered on the city of Venice founded in the Venetian lagoon on the north end of the Adriatic Sea to the northeast coast of the Italian peninsula. It also included the surrounding regions of mainland northeast Italy in the regions of Veneto and Friuli and parts of Lombardy. This became known as the terraferma or the mainland holdings of the republic. It also possessed overseas holdings in modern day Croatia, Slovenia, Montenegro, Albania, Greece & Cyprus.
Symbols & Mottos: The main symbol of Venice was its flag which had the famed Winged Lion of St. Mark. This represented the republic's patron saint, St. Mark. Mark the Evangelist after whom the Gospel of Mark in the New Testament in the Bible is named. Mark's body and holy relics were taken by Venice and said to be housed in the Basilica di San Marco (St. Mark's Basilica) in Venice itself. Variations of this flag differed during times of peace & war. During peace the winged lion is seen holding an open book and during war flags depicted the lion with its paw upon a bible and an upright sword held in another paw.
The republic's motto in Latin was "Pax tibi Marce, evangelista meus" or in English "Peace be to you Mark, my evangelist."
Religion: Roman Catholicism was the official religion of the state but Venice did have minorities of Eastern Orthodox & Protestant (usually foreign) Christian denominations at times in its territory and it also had small populations of Jews and Muslims to be found in Greek and Albanian territories during the wars with the Ottoman Empire.
Currency: Venetian ducat and later the Venetian lira.
Population: Though population varied overtime for the republic due to a variety of factors such as war & changing territory and disease & its subsequent effects. There was rough population recorded of 2.3 million people across all of its holdings in the mid sixteenth century (circa 1550-1560). The vast majority of its population was found in the terraferma of northern Italy and the city of Venice itself with its concentrated population on the islands within the Venetian Lagoon. The Greek island of Crete and the island of (Greek speaking) Cyprus were the most populous overseas possessions of the republic's territory. The rest of the population was found its various holdings in the Balkans mostly along the Adriatic coastline.
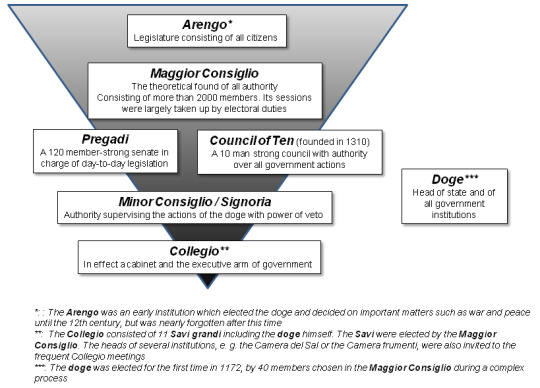
Government: The republic followed a complex mixed model of government. Essentially it could be characterized as a mixed parliamentary constitutional republic with a mercantile oligarchy ruling over it in practice. It had no formal written constitution, and this led to a degree of evolution without exactly defined roles often in reaction to happenings in its history. The resulting government became more complex overtime as institutions became increasingly fragmented in their size, scope and duties, some almost obsolete but still retained and others not fully defined. Yet, the republic managed to function quite well for most of its history. It incorporated elements of oligarchy, monarchy & limited democracy.
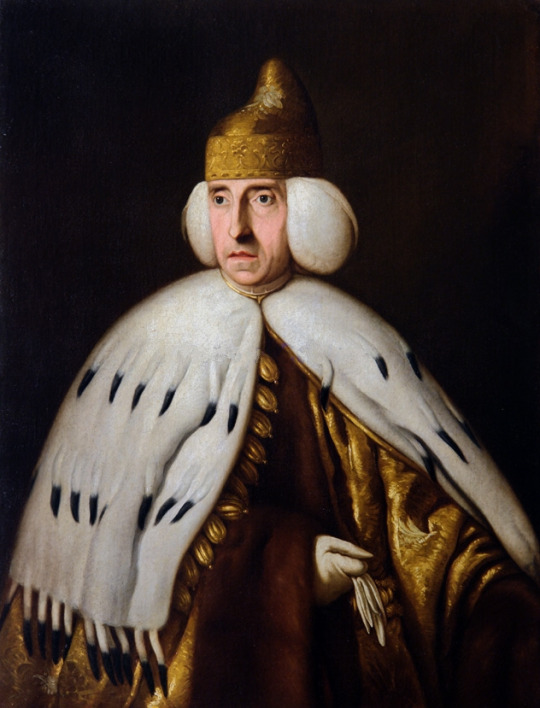
It's head of state and government was known as the Doge which is akin to the term of Duke. Though this similarity of name ends there. The Doge was neither similar to a duke in the modern sense nor was it meant as a hereditary position. The doge was rather a lifetime appointment much like the Pope for the Roman Catholic Church. Furthermore, doges were elected by the ruling elite of Venice, namely its wealthy oligarchy merchant class. The doge didn't have well defined & precise powers throughout the republic's 1,100-year history. It varied from great autocracy in the early parts of the republic to increasing regulation and restriction by the late 13th century onward. Though the doge always maintained a symbolic and ceremonial role throughout the republic's history. Some doges were forcibly removed from power and post-1268 until a new doge could be elected, the republic's rule transferred to the most senior ducal counsellor with the style of "vicedoge". After a doge's death following a commission was formed to study the doge's life and review it for moral and ethical transgressions and placed judgment upon him posthumously. If the commission found the deceased doge to have transgressed, his estate could be found liable and subject to fines. The doge was given plenty of ceremonial roles such as heading the symbolic marriage of Venice to the sea by casting a marriage ring into the sea from the doge's barge (similar to a royal yacht). Additionally, the doge was treated in foreign relations akin to a prince. It's titles and styles include "My Lord the Doge", "Most Serene Prince" and "His Serenity". The doge resided in the ducal palace (Palazzo Ducale) or Doge's Palace on the lagoonfront in Venice next St. Mark's Basilica and St. Mark's Square.
While the doge remained the symbolic and nominal head of the government, the oligarchy remained supreme overall. The supreme political organ was the 480-member Great Council. This assembly elected many of the office holders within the republic (including the doge) and the various senior councils tasked with administration, passing laws and judicial oversight. The Great Council's membership post 1297 was restricted to an inheritance by members of the patrician elite of the city of Venice's most noble families recorded in the famed Golden Book. This was divided between the old houses of the republic's earliest days and newer mercantile families if their fortunes should attain them property ownership and wealth. These families usually ranged between 20-30 total. They were socially forbidden from marrying outside their class & usually intermarried for political and economic reasons. Their economic concerns were chief to the whole of the republic and most centered on Eurasian & African trade throughout the Mediterranean Sea's basin. Members of these families served in the military and eventually rose to prominent positions of administration throughout the republic.
The Great Council overtime circumscribed the doge's power by creating councils devoted to oversight of the doge or executive and administrative functions (similar to modern executive cabinets or departments) whereas the doge became more and more a ceremonial role. The also created a senate which handled daily legislation. They also created a Council of Ten set to have authority over all government action. Other bodies were formed from this Great Council and others overtime. This resulted in intricate and overlapping yet separate bodies which found themselves subject to limitations with various checks on virtually each other's power. Essentially running as committees or sub-committees with checks on another committee's powers. These bodies weren't always completely defined in their scope and overtime their complexity led to battles to limit other's power (with limited success) along with gradual obsolescence and sometimes slow grinding administration.
Military: The military of Venice consisted of a relatively small army and a powerful navy. The famed Venetian Arsenal in Venice proper was essentially a complex of armories and shipyards to build and arm Venice's navy. The arsenal in Venice has the capacity to mass produce ships and weapons in the Middle Ages, centuries before the Industrial Revolution allowed for modern mass production in economic and military applications. Venice's military was designed towards protecting it possessions both in Italy and its overseas territories. The primary concern was to secure Venice's trade routes to the rest of Europe as well as Asia & Africa. It faced opponents' overtime ranging from the Franks, the Byzantine Empire, Bulgarians to other Italian city-states, France, Austria, the Ottoman Empire and Barbary Corsairs along with European pirates in the Adriatic and Mediterranean. It played key roles as a naval transport in other powers including throughout the Crusades. It also played a key role in the infamous Fourth Crusade which culminated in the Sack of Constantinople in 1204 AD, an event which fractured the Byzantine Empire into a half-century of civil war between successor states before a weakened revival in the mid 13th century. The Byzantine Empire would linger until the 15th century when the Ottoman Empire finally conquered its last remaining portions. Many attribute this loss to in part to its weakness still resulting from that 1204 sack lead by Venice. The Venetian military would exist until the republic's end when The French Republic's Army of Italy under Napoleon Bonaparte conquered the republic, a conquest in which the Venetians surrendered without a proper fight.
Economy: Venice's economy was based largely in trade. Namely control over the salt trade. Venice was to control salt (preservative of food) production and trade throughout the Mediterranean. It also traded in commodities associated with the salt trade routes to Eurasia and Africa. These commodities could include other foodstuffs (grains, meats & cheeses), textiles & glassware among other items.
Lifespan: 697AD-1797AD. Though the exact founding of Venice itself hasn't been determined. It is traditionally said to have taken place in the year 421 AD. At a time when Roman citizens in northeast Italy were escaping waves of Germanic & Hunnic barbarian invasions that contributed to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire. The going theory is that these Romans evaded barbarian attacks by building their homes in the Venetian Lagoon by hammering wood stakes to form a foundation which sunk into the muddy shallows and petrified. Upon which they built their homes and created a cityscape marked by streets and canals interlaced. Venice remained a community of fishermen and merchants and was nominally under the control of the surviving Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantine Empire). It avoided barbarians overrunning the land but also was removed enough from Constantinople that it was relatively autonomous and became strategically important as a port. Other islands in the lagoon also banded together with Venice in a loose confederation of sorts by the 6th and 7th centuries which increased economic productivity and security for the city. The first doge was said to have been elected in 697 AD under the name Paolo Lucio Anafesto, though there is dispute about his historicity. Anafesto supposedly ruled until 717 AD. This is traditionally regarded as the foundation of the Republic of Venice.
Venice's third doge was Orso Ipato who reigned from 726-737 and he is the first undisputed historically recorded doge whose existence was confirmed. Orso also known as Ursus was known to strengthen the city's navy and army to protect it from the Lombard Germanic invaders who had overrun and ruled Italy by that time. Though nominally part of the Byzantine Empire, by 803, the Byzantine Emperors are said to have recognized Venice's de-facto independence. Though this view is disputed somewhat, it nevertheless remained virtually independent until its collapse in 1797.
Venice also partook in the slave trade of non-Christian European populations from Eastern Europe and transferred them to North Africa, selling them to the Arab and Berber (Moors) of the Islamic world.
As the 9th century progressed, the Venetian navy secured the Adriatic and various trade routes by defeating Slavic and Muslim pirates in the region. The Venetians also went onto battle the Normans who settled in southern Italy and Sicily in the 11th century.
Venice provided naval transports for Crusaders from Western Europe starting with the successful First Crusade.
The High Middle Ages (1000AD-1350AD) saw the wealth and expansion Venice increase dramatically. However, over this period Venice gradually came into mixed relations with its former ruler the Byzantine Empire. The Byzantine Empire endured corruption, civil war and foreign invasion which saw it alternate between periods of waning power and restored power. Venice provided the Byzantines with an increased naval force when needed and many trading commodities. In exchange for this, Venice was granted trading rights within Byzantine territory and a place within the "Latin Quarter" for Western Europeans in Constantinople. The Byzantine populace though calling themselves "Romans" having taken on the political & cultural institutions of the Roman Empire which lived on in the East long after the Western half's collapse, were in fact mostly Greek by ethnicity, language and culture. Their religion was the Eastern Orthodox or Greek Orthodox branch of Christianity which was often at odds with Roman Catholics of Western Europe. Resentment at the religious and cultural differences along with the economic displacement the Venetians and other Italian merchants from Genoa & Pisa had caused in Constantinople's maritime & financial sectors contributed to the 1182 "Massacre of the Latins" in which the Byzantine Greek majority of the city rioted and slaughtered much of the 60,000 mostly Italian Catholics living within the city. Thousands were also sold into slavery to the Anatolian Seljuk Turks.
This event lingered in Venice's memory as its trade in the city was reduced for awhile. Though trade resumed between the Byzantines and the West again shortly thereafter, the event soured the perception of the Greeks to Western Europeans. This along with a subsequent power struggle for the throne of the Eastern Roman Emperor fell into Venice & Western Crusader's hands in 1202. Looking to originally ferry Western Crusaders to the Levant against the Islamic Ayyubid Sultanate of Egypt & Syria. Events transpired that devolved into Venice conspiring under its doge Enrico Dandalo along with other Western leaders and a Byzantine claimant to the throne that resulted in the first successful sacking of Constantinople in 1204. The city was ransacked, some Greek citizens murdered by the Crusaders & classical works of art destroyed or looted (most famously the four bronze horses of St. Marks in Venice) and politically, the Byzantine Empire would be temporarily fractured between competing Greek dynasties while the Crusaders along with Venice created the short-lived Latin Empire, which controlled Constantinople and its environs while Venice also acquired Greek territories which it was to hold for centuries. Venice also came into conflict with the Second Bulgarian Empire at this time as its support of the Latin Empire of Constantinople encroached on the Bulgarian's land. Eventually by the mid 13th century the Latin Empire (never fully stable) collapsed, and the Byzantine Empire was restored until the mid-15th century but forever weakened as a result of the 1204 sacking of its capital.
Venice reached trade deals with the Mongol Empire in 1221. As the century wore on, it also engaged its rival in Western Italy Genoa in some warfare.
The 14th century is generally regarded as Venice at its peak as it faced down Genoa in a number of battles and came to be the most dominant trading power in the Mediterranean, though it was impacted by the Black Death plague. Nevertheless, into the 15th and even 16th centuries, it partook in a number of wars which saw it gain territory on the Italian mainland, establishing its terraferma domain.
By the 16th late 15th and into the 16th century new threats had emerged such as the Turkish Ottoman Empire. The Ottoman capture of Constantinople in 1453 is seen as the end of the Middle Ages as the last political vestiges of the Roman Empire vanished from the world stage. However, a number of Byzantine Greeks escaped on Italian ships during the conquest of the city and others escaped Greece in subsequent years. These refugees brought with them artistic and cultural heritages that reemphasized the classical forms of Ancient Greece and Rome and lead to the Italian Rennaisance in art & other forms of culture. Ideas which emphasized humanism and spread to elsewhere in Europe overtime.
While there was a cultural flourishing in Venice and elsewhere due to the Rennaisance. There was also the first signs of economic and political decline as well from the 16th century onwards. The Ottoman dominance in the Eastern Mediterranean meant the traditional trade routes to the East were cut off by an often-hostile Muslim power. Additionally, other maritime powers in the West namely Spain & Portugal had recently begun exploring the continents of South & North America and in time France, England & the Netherlands would join in them. This decline in Eastern trade and the newfound trade routes dominated by other European states in the Americas and Asia (by way of rounding Africa) would render trade with Venice gradually obsolete. Venice would still maintain what trade it could in the Mediterranean, but it also focused on production and placed increasing importance on its Italian mainland possessions rather than just its declining position overseas in Greek territories, including the loss of Cyprus to the Ottomans in 1571. Though the Venetian navy with other Christian powers won the notable naval victory against the Ottomans in 1570 at Lepanto.
It was also involved in the Italian Wars between various rival city states and the power struggle between the Papacy, France and the Hapsburg realms of the Holy Roman Empire and Spain.
Other factors that impacted the declining trade in the 17th century included an inability to keep up in the textile trade elsewhere in Europe, closure of the spice trade to all but the Spanish, Dutch, Portuguese, French and English and the Thirty Years War (1618-1648) which impacted Venice's trade partners.
Ongoing wars including a 21-year siege of Crete by the Ottomans saw further losses. Although Venice partook in the Holy League headed by the Holy Roman Empire (under Hapsburg Austria) which saw some minor temporary gains from the Ottomans in southern Greece before losing them again in the early 18th century.
War and loss of overseas territories along with a stagnant economy was slightly offset by a somewhat strong position in northern Italy. Nevertheless, its maritime fleet was reduced to a mere shadow of its former glory and it found itself sandwiched still between Austria and France. Over the rest of the 18th century, economic stagnation and social stratification remained prevalent while Venice remained in a quiet peace. However, the French Revolution reignited war in Italy and while Venice remained neutral, it would soon get caught up in events.
The Austrians and the Piedmontese (Italian) allies were beaten by the French Republic's Army of Italy headed by an up-and-coming general named Napoleon Bonaparte. Bonaparte and the French army crossed the borders of northern Italy into Venetian neutral territory to pursue the Austrians. Eventually half of Venice's territory was occupied by France and the remainder of the mainland was occupied by Austria. By secret treaty the French and Austrians were to divide the territory between themselves (Venice was consulted in the matter). Bonaparte gave orders to Venetian doge Ludovico Manin to surrender the city to French occupation to which he abdicated his power. The republic's Major Council met one last time to officially declare an end to republic on May 12th, 1797, after 1,100 years. Venice was placed under a provisional government and ironically the French looted Venice stripping it of artworks to grace the Louvre Museum in Paris along with the Arc d'Triomphe, taking the famed four bronze horses of St. Mark's to adorn the triumphal arch in Paris, the very same horses Venice had confiscated from Constantinople in 1204. It was a symbolic end to the republic, the irony of which did not escape commentators at the time. Following Napoleonic France's final defeat in 1815 the horses were returned to Venice and St. Mark's where they remain today. Venice itself was given over to the Austrian Empire.
The Republic of Venice has a historical legacy in terms of its economic accomplishments through control of trade and its innovative mass production of ships, armaments & trade commodities. It also holds a political legacy worthy of study given it was a unique and enduring polity for 1,100 years. One that maintained a complex and at times chaotic form of government that still managed to function and endure for centuries.









#military history#middle ages#venice#venetian republic#italy#politics#political history#trade#economics#governance#commerce#ottoman empire#spain#byzantine empire#napoleon#doge#republic
64 notes
·
View notes
Text
Napoleon and Sugar Production and Trade
A little bit about how the sugar industry was transformed during the Napoleonic Wars. Specifically, how sugar beet substituted and replaced sugar cane.
From Robert M. Harveson, History of sugarbeets, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, Institute of Agriculture and Natural Resources (source)
“Sugar was only obtained from the tropical sugar cane and was prohibitively expensive for most Europeans. During the early 1800’s most sugar was obtained from the West Indies. After supplies were cut off by the English blockade of continental Europe during the Napoleonic Wars, the demand for sugar grew throughout Europe. Napoleon encouraged new research with sugar beets, and between 1810 and 1815, over 79,000 acres were put into production with more than 300 small factories being built in France.”
From R. N. Dowling, Sugar Beet and Beet Sugar:
“Napoleon I, brought real life into the new industry. As a farsighted statesman, he recognized the great advantages connected with a future beet sugar industry that would produce at home all the sugar needed by his people. For this reason he at once, by a decree of 1812, appropriated 100,000 hectares, or 247,100 acres, exclusively for the cultivation of sugar beets and 1,000,000 francs for experiments in connection with beet raising and sugar extraction.”
The trade war:
“The interest of Napoleon was due to the continental blockade that excluded all products manufactured in England and her colonies from the European markets. As a consequence the price of cane sugar rose to an extraordinary height: it was more than 30 cents per pound in the period from 1807 to 1815. Under such circumstances the erection of beet sugar factories was a very profitable investment of capital and it is, therefore, not to be wondered at that in France, as early as 1812 some 40 factories were in operation, working up 98,813 tons of beets obtained from 16,758 acres, and yielding a total output of 3,300,000 Ibs. of sugar. For the first time in the history beet sugar came to compete with the tropical product. From very modest beginnings in the first quarter of the nineteenth century the beet sugar industry grew to the enormous dimensions of today, crowding out cane sugar from the markets of the European continent and successfully competing with the tropical product in many other countries.”
(From R. N. Dowling)
Long-term impact—Sugar beet today:
“Of the current world production of more than 130 million metric tons of sugar, about 35% comes from sugar beet and 65% from sugar cane. In the USA, about 50-55% of the domestic production of about 8.4 million metric tons derives from sugar beet.”
(From Robert M. Harveson)
#Sugar beet#sugar#beets#beet sugar#napoleon#napoleonic era#napoleonic#napoleon bonaparte#first french empire#french empire#france#Napoleon’s reforms#history#1800s#agriculture#reforms#napoleonic reforms#commerce#trade#economics#economic history#University of Nebraska-Lincoln#Nebraska#sugar cane#Robert M. Harveson#Dowling#Harveson
27 notes
·
View notes
Link
116 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Vanilla Expedition (Part IV)


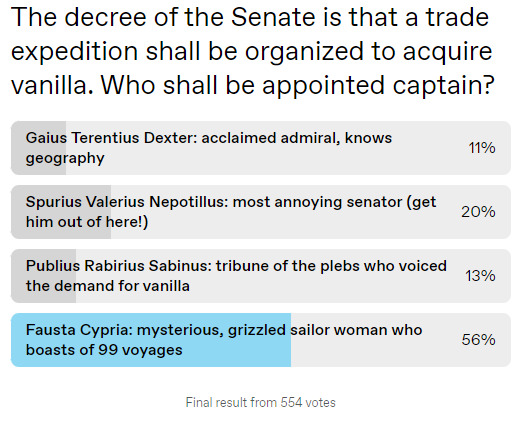
#the vanilla expedition#I restricted this list to trade goods with relatively high ratios of economic value to volume#to avoid wasting limited cargo space on stuff that isn't very valuable#but ultimately the sale value of these goods will depend on where you go looking for vanilla...#...hopefully in the correct direction!#but that will be the next poll :)
117 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Ever since Adam Smith, those trying to prove that contemporary forms of competitive market exchange are rooted in human nature have pointed to the existence of what they call 'primitive trade'. Already tens of thousands of years ago, one can find evidence of objects — very often precious stones, shells or other items of adornment — being moved over enormous distances. Often these were just the sort of objects that anthropologists would later find being used as 'primitive currencies' all over the world. Surely this must prove capitalism in some form or another has always existed?
"The logic is perfectly circular. If precious objects were moving long distances, this is evidence of 'trade' and, if trade occurred, it must have taken some sort of commercial form; therefore, the fact that, say, 3,000 years ago Baltic amber found its way to the Mediterranean, or shells from the Gulf of Mexico were transported to Ohio, is proof that we are in the presence of some embryonic form of market economy. Markets are universal. Therefore, there must have been a market. Therefore, markets are universal. And so on.
"All such authors are really saying is that they themselves cannot personally imagine any other way precious objects might move about. But lack of imagination is not itself an argument... In fact, anthropology provides endless illustrations of how valuable objects might travel long distances in the absence of anything that remotely resembles a market economy."
— The Dawn of Everything, David Graeber and David Wengrow, p.22
325 notes
·
View notes
Text
there's a very specific kind of vibe that comes with living with your friends in final year that it just does not have in first year or even second year. like as a fresher it's usually the first time any of you have lived away from home let alone with SO MANY people your age and it's terrifying and exciting and randomised to boot so it's generally carnage for a whole year in the best and worst ways, and then second year you pick who you're living with and it feels like for the first time you're doing this adult thing PROPERLY. you have a place of your own now. these are the people you've chosen to live with. studying gets serious etc. but it's still fresh. it's still new. you still don't know how to navigate it. but final year? final year is when you actually get it right. you know how to manage your time better. you know what works for you and what doesn't. studying is the main focus and you've been out in the world for three years now and it's not loud and boisterous like it was in first year and you're not exciteable and awkward like you were in second year. you're comfortable. every single one of my flatmates has their own friend group and we mainly keep to our own social circles, but we'll still meet each other back at the house after a night out and sit in the kitchen or my room to do the debrief. sometimes i'll go days not seeing either of them despite sharing a house but every now and then someone will softly call up the stairs that 'the heating's on!' or one of us will sneeze and the other two will yell 'bless you!' through the walls. the lack of interaction isn't interpreted as dislike in ways it would have been even last year, because we're all just old enough to be past that now and settled enough in our friendship not to worry about it. idk. uni is very loud and unsettling a lot of the time so it's been really sweet to see how almost boringly comfortable final year is.
#like my day today was literally drag myself out of bed at 10am to meet my econ friends bc we're in a group together#and i spent two hours with them writing a fucking TRADE REPORT before coming home#and the rest of the day was kinda lost. i showered. i put a wash on. i had a nap. i mainly stayed in my room#which sometimes is the End Of All Things but today was quite nice#and i can hear in their rooms how my flatmates are doing the exact same thing. pottering about and getting on with uni#and we've barely spoken all day but earlier my one flatmate ran into my room all excited to show me her nails#bc she's been teaching herself to do gels and it took her 2 hours but im still one of the first people she wanted to show#and just now we all went to use the bathroom at the same time and it led to one of our Stair Sessions#where we all inexplicably just gather on the stairs and chat for no reason with a cup of tea#idk it's just nice. it's such basic shit but i can't belive in first year i used to spend EVERY DAY with these girls#and we were one single friendship group and that was all we had#and then in second year one girl branched off bc she lived in a studio and got into her societies#but me and the other girl lived together again and it was the same thing of she was a friend before she was someone i lived with#and weirdly that can actually be detrimental to a dynamic. but this year we're all just very solidified and confident in ourselves#and where we stand and yes we all have our own friendship groups outside of the house now#but there's still that love and simple comfortableness around each other that you only get with time and a hell of a lot of proximity#and a sense of being settled that maybe is just what happens as you get older#idk it's just really nice. if i had this exact same day in first year (doing economics and barely leaving my room)#it would've been a really bad depressive day for me so the fact i can find such contentment from it now is really heartening#i love my little life here im very proud of what ive been able to achieve :)#hella goes to uni#feeling nostalgic because SOME BITCH decided to ribs post
21 notes
·
View notes
Note
Sliiightly unrelated, and I absolutely don’t mean this condescendingly (and I don’t mean to keep bothering you either, feel free to ignore ofc) — I’m just in the dark. When you say ‘Trade work’ and ‘learn a trade’… what do you mean by a trade? The only thing that comes to mind with ‘trade’ is being a plumber, woodworker, etc but I’m pretty sure that’s not what you meant ahejdydj
It is! Due to the push for young people to go to college and get jobs that utilize those degrees, the United States has actually seen a concerning decrease across the decades of people who are qualified to do trade work such as plumbers and electricians, etc. As a result, the population in those trades is aging quickly, and we are anticipating that there won't be enough people to do those jobs very soon. A lot of them are nearing retirement age. Thanks to that demographic shift, young people entering those trades are a very high demand, and in many areas, the pay for such a job can be like 50,000 a year, which can be a solid living wage on par with something like teaching. And in most cases, the apprenticeships are paid, which is definitely a consideration for people who don't want to deal with student loans.
@thisarenotarealblog, any input?
#trade services#trade work#plumbing#electricians#vocational work#trade school#united states#economics#Anonymous#phoenix answers asks
58 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
The Biden administration announced a rule Tuesday to cap all credit card late fees, the latest effort in the White House push to end what it has called junk fees and a move that regulators say will save Americans up to $10 billion a year.
The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau’s new regulations will set a ceiling of $8 for most credit card late fees or require banks to show why they should charge more than $8 for such a fee.
The rule would bring the average credit card late fee down from $32. The bureau estimates banks brought in roughly $14 billion in credit card late fees a year.
“In credit cards, like so many corners of the economy today, consumers are beset by junk fees and forced to navigate a market dominated by relatively few, powerful players who control the market,” said Rohit Chopra, director of the bureau, in a statement.
President Joe Biden planned to highlight the proposal along with other efforts to reduce costs to Americans at a meeting of his competition council on Tuesday. The Democratic president is forming a new strike force to crack down on illegal and unfair pricing on things like groceries, prescription drugs, health care, housing and financial services.
The strike force will be led by the Justice Department and the Federal Trade Commission, according to a White House statement.
The Biden administration has portrayed the White House Competition Council as a way to save people money and promote greater competition within the U.S. economy.
The White House Council of Economic Advisers produced an analysis indicating that the Biden administration’s efforts overall will eliminate $20 billion in annual junk fees. The analysis found that consumers pay about $90 billion a year in junk fees, including for concerts, apartment rentals and auto dealers.
The effort appears to have done little to help Biden politically ahead of this year’s presidential election. Just 34 percent of U.S. adults approve of Biden’s economic leadership, according to a new survey by The Associated Press-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research.
Sen. Tim Scott, R-South Carolina, criticized the CFPB cap on credit card late fees, saying that consumers would ultimately face greater costs through higher interest rates and less access to credit.
“It will decrease the availability of credit card products for those who need it most, raise rates for many borrowers who carry a balance but pay on time, and increase the likelihood of late payments across the board,” Scott said.
Americans held more than $1.05 trillion on their credit cards in the third quarter of 2023, a record, and a figure certain to grow once the fourth-quarter data is released by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corp. next month. Those balances are now carrying interest on them, which is the highest it has been since the Federal Reserve started tracking the data back in the mid-1990s.
Further, more Americans are falling behind on their credit card debts as well. Delinquency rates at the major credit card issuers such as American Express, JPMorgan Chase, Citigroup, Capital One and Discover have been trending upward for several quarters. Some analysts have become concerned Americans, particularly poorer households hurt by inflation, might be taking on too much debt.
“Overall, the consumer is credit healthy. However, the reality is that there are starting to be some significant signs of stress,” said Silvio Tavares, president and CEO of VantageScore, one of the country’s two major credit scoring systems, in an interview last month.
The growth of the credit card industry is partly why Capital One announced it would buy Discover Financial last month for $35 billion. The two companies, which are two of the largest credit card issuers, are also two companies whose customers regularly carry a balance on their accounts.
This is not the first time policymakers have weighed in on credit card fees. Congress in 2010 passed the CARD Act, which banned credit card companies from charging excessive penalty fees and established clearer disclosures and consumer protections.
The Federal Reserve issued a rule in 2010 that capped the first credit card late fee at $25, and $35 for subsequent late payments, and tied that fee to inflation. The CFPB, which took over the regulation of the credit card industry from the Fed after it was established, is proposing going further than the Fed.
The bureau’s proposal is similar in structure to what the bureau announced in January when it proposed capping overdraft fees to as little as $3. In that proposed regulation, banks would be required to either accept the bureau’s benchmark or show regulators why they should charge more, a method that few bank industry executives expect to use.
Biden has made the elimination of junk fees one of the cornerstones of his administration’s economic agenda heading into the 2024 election. Fees that banks charge customers have been at the center of that campaign, and the White House directed government regulators last year to do whatever is in their power to further curtail the practice.
In another move being highlighted by the White House, the Agriculture Department said it has finalized a rule to stop what it deems to be deceptive contracts by meat processors and to ban retaliation against small farmers and ranchers that work together in associations.
#us politics#news#pbs#president joe biden#2024#Consumer Financial Protection Bureau#credit cards#late fees#junk fees#Rohit Chopra#Federal Trade Commission#department of justice#White House Competition Council#White House Council of Economic Advisers#Sen. Tim Scott#Federal Deposit Insurance Corp#federal reserve#youtube#videos#economy#economics
13 notes
·
View notes
Note
You talked in an earlier post* about economists' attitudes about mercantilism. Where do the physiocrats fit into this? What were they trying to do, what do current economists think of them, and how accurate is their assessment?
*https://www.tumblr.com/racefortheironthrone/741771031361077248/why-do-economists-need-to-shut-up-about
First of all, thank you for including the link! It really helps.

Ok, so let's talk about the physiocrats. This was a pre-Smithian school of economists from France in the 18th century, and they are somewhat complicated to assess because their ideas are a strange mix of surprisingly accurate and completely batshit:
unlike the mercantilists, who they really didn't get along with, the physiocrats thought that growth and especially the circulation of wealth (as opposed to achieving a positive balance of trade and deepening capital pools as the means of driving development) was the most important goal of economic policy.
unlike the mercantilists and the classical economists, the physiocrats believed in the labor theory of value...but only for agricultural labor. The reason they called themselves "physiocrats" is that they believed all wealth came from nature, and that all industrial and commercial and other forms of labor were "unproductive appendages" that existed parasitically off of agricultural labor. This is particularly insane, given that they were writing on the very eve of the Industrial Revolution but well after the Commercial Revolution, so they were well aware that European countries had been making increasingly large amounts of money from stuff that wasn't agriculture. This, they felt, was cheating.
in terms of policy prescriptions, the physiocrats' main agenda items were free trade in grain - they firmly believed that any form of government intervention (say, during a famine to prevent starvation and bread riots) was inherently counterproductive and an unwarranted inference in the natural right of producers to maximize profits, which would eventually lead to higher production and lower prices - and a flat tax on property.
This school of thought was initially quite influential duiring the early stages of the French Revolution, but broke down almost immediately when there was a bad harvest and food prices shot up through the roof, because when large numbers of starving people who have just gone through a revolution and now have weapons and believe they have a right to use them to defend their lives and their freedom see the rational self-interest of grain merchants jacking up the price of their daily staple by 400%, they respond by killing them and putting their heads on pikes and taking the food by force. In that scenario, any government is going to react through intervention if only out of their own rational self-interest. Hell even the ancien régime knew enough to do that, and now the government is run by a bunch of Jacobins.
I would describe their reputation among contemporary economists as one of outwardly-polite condescension of the "well, bless your heart" school of southern gentility. They did hit on some ideas that later economists would run with, but at the end of the day they aren't Big Daddy Adam Smith so they are a mere footnote. But then again, contemporary economists are surprisingly ignorant about the history of economic thought, so it's to be expected.
#political economy#physiocrats#french revolution#mercantilism#history of economic thought#economics#advocating free trade in grain during a famine is a really bad idea
15 notes
·
View notes