#the golden age
Text


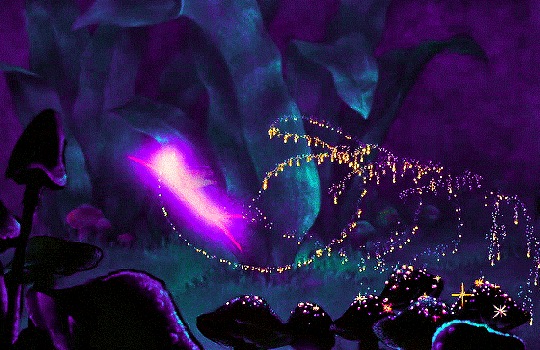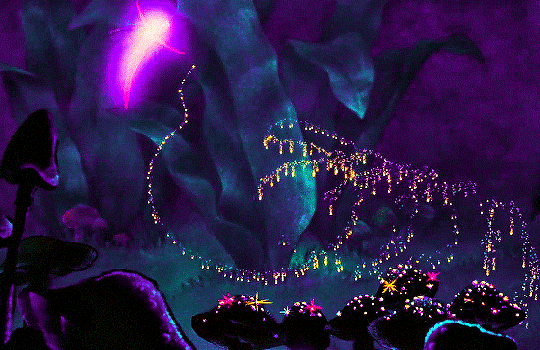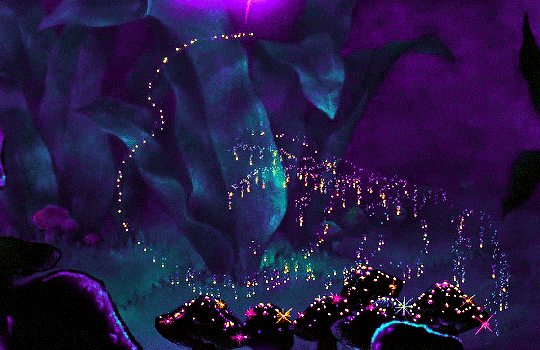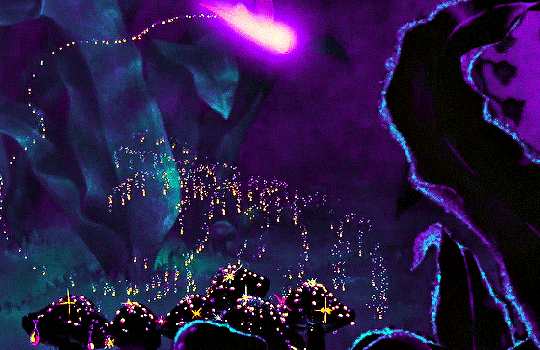
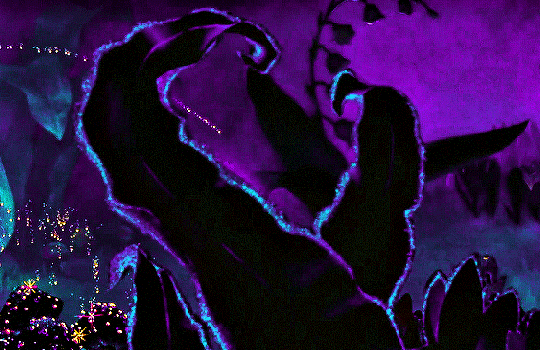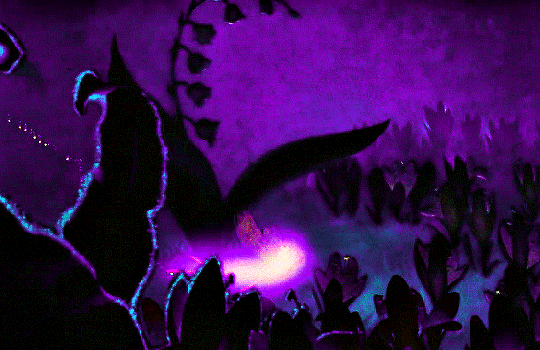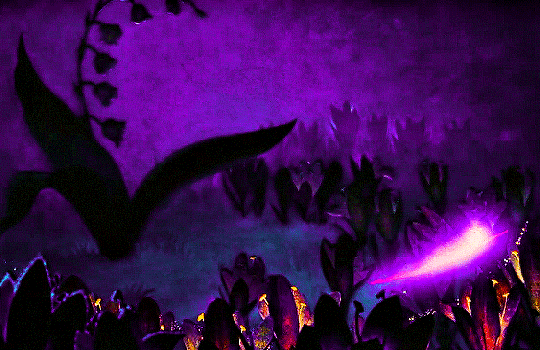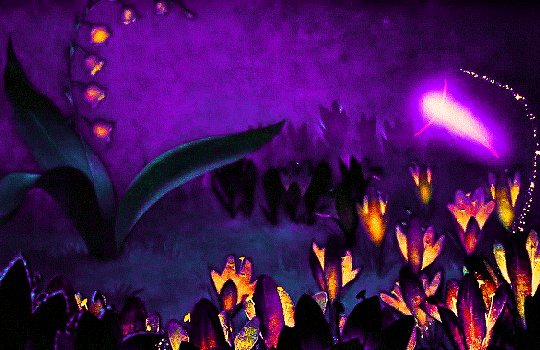
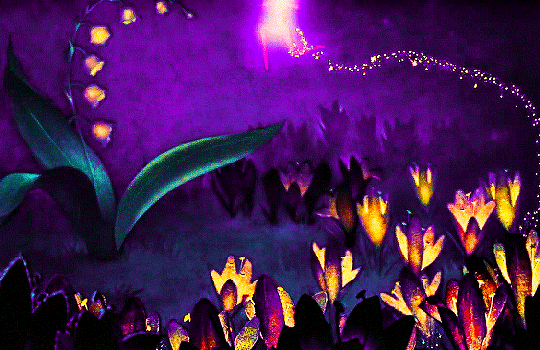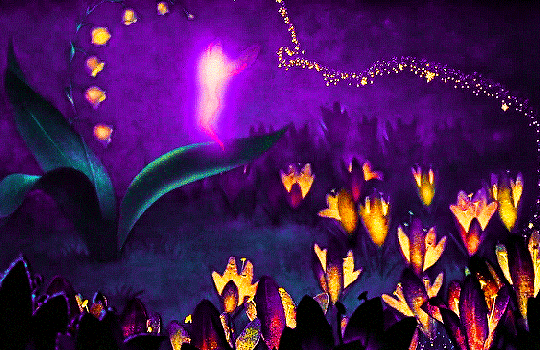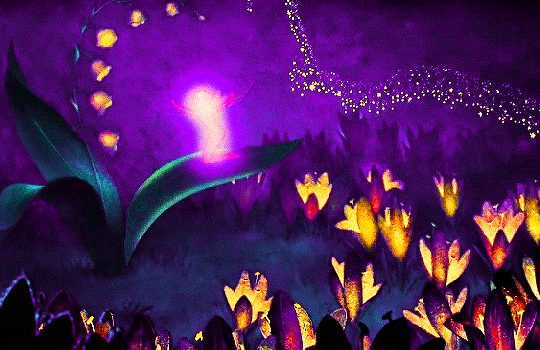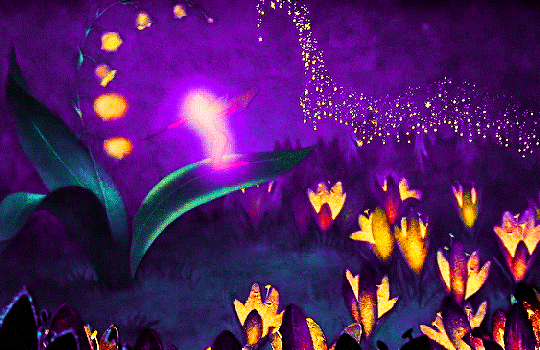

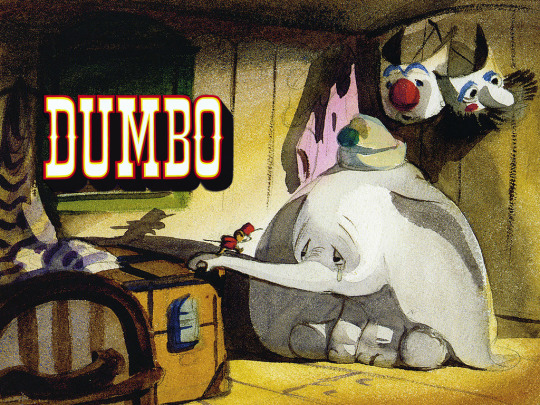
FANTASIA (1940)
#fantasia#fantasiaedit#disneyedit#dailyanimatedgifs#dailyfilmsource#1940s#*mine#disneyfeverdaily#disneygifsdaily#disneynetwork#fyeahdisney#fyeahmovies#animationsdaily#animationedit#filmtvdaily#filmedit#moviegifs#cartoonedit#dailyflicks#the golden age
960 notes
·
View notes
Photo




𝙳𝚒𝚜𝚗𝚎𝚢 𝚌𝚘𝚗𝚌𝚎𝚙𝚝 𝚊𝚛𝚝Iᴛʜᴇ ɢᴏʟᴅᴇɴ ᴀɢᴇ (1937 - 1942)
#ask and you shall receive#disney eras#disney#the golden age#disney animation#disney concept art#concept art#art#artwork#animation art#illustration#snow white and the seven dwarfs#pinocchio#pinocchio 1940#fantasia#dumbo#dumbo 1941#bambi#mine
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
sometimes i think about narnia and i vibrate out of my skin like...
you walk into a world you cannot understand, frozen and dying, and it is you who thaws it. you who kills the witch, you who breaks the stone table, you who slays the wolf. it is you who is crowned and it is you who wails for two worlds when the wardrobe doors shut behind you.
your skin never sits quite right and your teeth are too dull. there are wars in your bones and decades in your eyes before you can reach the telephone on the wall.
you are king. you are queen. they won't let you read the newspapers at breakfast.
it calls you back from beyond a train and from within paint. begs with bloody palms and salt-crusted cheeks. takes from you all that you can give - and sends you back.
you watch your sister fade.
you are a child twice and an adult once. and when you stand in your home again, with crushed bones and the smell of coal still in your nose, you watch them sneer at your sister.
your sister is the sun above you. she is, beautiful and stone-cast, alive in a world you could never stomach. she smiles, still, and stretches her skin over human bones.
she is no longer a friend of narnia. do you tell them it is her who has to bury you all and the stars that are falling from the skies in shards?
#narnia#narnia fanfiction#narnia fic#the problem of susan#susan pevensie#peter pevensie#edmund pevensie#lucy pevensie#the kings and queens of old#the golden age#the lion the witch and the wardrobe#prince caspian#the voyage of the dawn treader#the last battle
7K notes
·
View notes
Note
I have a question about Zeus and Kronos. SEVERAL actually. Their relationship gets more confusing the far you dig into it.
How did the ancient Greeks see their relationship? How did they see the whole conflict between the Gods and the Titans?
In modern works, Kronos and the Titans are almost always portrayed as evil, monstrous tyrants, and Zeus and the Olympians as the young heroes that bring them down.
However, in Greek Mythology, Kronos' reign was the Golden Age, an utopic and paradisiac time of peace, happiness and prosperity, and Zeus is the main responsible for bringing pain, disease, and death to humankind through Pandora.
And to make matters more confusing, patricide was a huge sin in ancient Greek culture.
Was Zeus and Kronos' story a heroic tale of order overcoming chaos, or a tragic "Paradise Lost" type of scenario? Is Zeus a hero for deposing his father, or fallen hero that only escaped divine retribution because he himself is a god? Who was in the right in the conflict between Olympians and Titans? How am I supposed to interpret Hesiod's Theogony?
This is a very complex question that opens the door to many, many possibilities. But long story short: in the Olympians vs Titans conflict, the Titans were definitively in the wrong, and yes we are supposed to root for the Olympians.
Remember, the Olympians are supposed to be the "big goods" of Greek mythology - or at least, mostly positive figures. The enemies of the Olympians are by extension our enemies because the Olympians represent order and civilization. The Gigantomachy is the best representation of that, as the Giants were literaly designed to kill and destroy and nothing else. Same thing with Typhon, chaos and terror embodied.
Now what was the problem with the Titans? Long story short, many things. But what we have to understand is that the Titans are being supposed to represent... yes chaos in a way, but also a more brutal, primitive form of the universe. Yes the Titans are gods like the Olympians - but they are not the same kind of gods. Older, rougher. For example take the Olympians - they are kings and queens over the principles they control. Poseidon rules over the sea but is not the sea ; Zeus' decisions control the weather but he is not the weather. When we go by the Titans, however, we have beings such as Helios who was the literal sun or Oceanos who was the literal ocean. The Titans reflect the primal forces of nature, the rough and brutal, less humanized elements, more personifications and embodiments than deities as we understand them today. So what was the object and purpose of the Titanomachy? The "taming" and ordering of the world. Some Titans sided with the Olympians, and thus became more human and more "ordered" and found a place for themselves within an organized world. Themis for example, who as the embodiment of the Law and of Justice, would of course choose the Olympians' side. Also note that, outside of Themis, none of the Titans reflected any concept or principle part of a civilization. The Titans were violence (Iapetos whose name means "piercer", and Kronos who castrated his own father), the Titans were animals (many are the titans with strong animal motifs), the Titans were the sea and the moon and the sun and the light and the earth... They were literaly born out of the sky and earth. But what came with the Olympians? When Zeus got onto the throne, he started creating new gods through his many marriages and alliances: he brought forth Apollo of the art, Athena of wisdom and peace, Artemis of the hunt of the wild, Hermes of all the sciences, and the Horai, and the Muses, and sometimes even the Moirai themselves. Zeus organized the world and brought many of the concepts we cherish so much today.
Not only was the problem with the Titans that they were primordial and brutal forces of nature, but the problem with the specific Titans that went at war against the gods is that they literaly refused to let fate be and time pass. Kronos' flaw and fault is the most common of all mythology: fighting an oracle, trying to destroy a prediction, trying to avoid his fate. He was foretold he would be overthrown by his son. Not destroyed, not mutilated, certainly not killed (because gods cannot die, they are immortal), but just overthrown. And he refused this. He refused to have his throne taken away from him - he refused to let generations change, to let youth come. He had obtained his throne for right reasons (he punished the sins of his father) and yet through bad means (mutilating his own father). As such he got the throne but was fated to let it go, and know a "lesser" version of what he had inflicted upon his father. But he refused this.
Not only that, but he actually ended up repeating the mistakes and crimes of his father Ouranos. By not just bringing a stasis, but by literaly causing a regression. Imprisoning back the Cyclops and Hekatoncheires he had set free ; and then swallowing back into his belly the children he brought forth, literaly reversing the natural cycle of time. So Zeus' war against Cronos was justified to allow the world to continue its own maturation, and evolve further. And from a world of brutality, barbary and regression, we reached an age of order and civilization.
Now let's take the second side of the problem - the whole "Ages of Mankind".
It should be recalled that the Ages of Mankind story comes from Hesiod's "Of Works and Days", not from his "Theogony". And "Of Works and Days" is not supposed to just be a cosmogony like the Theogony, but rather a didactic work. It isn't about mythology per se, as the true topic of the work is agriculture, and all sorts of advices on how to take care of your field, woven with philosophical and moralist lessons about the importance of hard work. The mythological story woven in the work is meant to be an illustration of why humanity has to work, and is tied to all sorts of socio-philosophico messages, making it closer to a fable in many ways. It should also be taken into account that the "Ages of Man" story is tied in "Of Works and Days" to the legend of Prometheus, Epimetheus and Pandora. A legend also told in "Theogony"... but with slightly different details. For example, in the Theogony the story is very misogynistic as the curse of Zeus is... literaly women. As in, women are evil, and that's it. The version of "Of Works and Days", slightly less misogynistic, is the one with the famous Pandora jar later turn Pandora 's box, and there the evil is contained within the jar and is all a convoluted plan to force the "clan" of Prometheus to end up cursing the humanity they favored. Hesiod was never afraid of contradicting himself - even within the Theogony you have opposite stories, such as how in one part the Moirai are aughters of Zeus and Themis, in another daughters of Nyx that predated Zeus.
Anyway, all of that being said, I want to point out something important: in the Ages of Man storyline by Hesiod, Zeus is not supposed to be the one that caused the misery of mankind. At least not directly. It is true that the Golden Age and the first humanity is said to have existed/been formed under the rule of Cronos, while the Silver Age, which was a downgrade, occured when Zeus arrived on the throne. But the text does not say that Zeus was the one who caused the downgrade of humanity. There is definitively a change, an evolution, but it doesn't mean it is Zeus that "corrupted" humanity. In fact, the text does say that Zeus kept around the first humanity as powerful spirits to help, guide and enrich the following humanity. And Zeus' "rule" is not all bad, as there is a mention of one of the humanities brought forth under him being the Heroic Age, which is considered one of the best humanities after the Golden Age. The legend isn't actually about Zeus "ruining" humanity in any way, as the message Hesiod tries to give here is rather that humanity is living through a sort of natural decline... Yes, Hesiod was quite pessimistic, and honestly you can hear a bit of the old as time rant "Young people are doing everything bad, the world is getting worst and worst, wasn't it better before?". You can literaly hear Hesiod doing his youth-hating-grandpa-rant through his tale.
Afterward, we have to consider the whole Prometheus-Pandora-Zeus triangle... And this is where things get tricky and dual. Now I can't possibly embrace the full scope of the implications of the Prometheus legend. There is a reason he is such an inspiring and powerful figure even today - and Prometheus is one of the most complicated entities of all of Greek mythology. But here is the thing I wanted to say... Yes Hesiod does say and explain that Zeus created all sorts of evil he inflicted upon humanity because he was unhappy with being deceived by Prometheus. In "Of Works and Days" it is an especially strong point because the entire text is about explaining why humanity has to work so hard, and why labor is needed by humanity, and why if we have benevolent deities we must still be burdened by chores and toil. And in general this is an answer to the very same problem that the Genesis of the Bible poses: Why would a benevolent god inflict us a life of suffering? Why do we have to work to eat and why isn't the superior power providing us, if they love us so much?
In the Biblical text, this is explained by the original sin, and by all this being a punishment for humanity's original flaw. But in the Greek texts we have something very different - as it is inflicted... to punish Prometheus? That's what Hesiod's text tells us and/or implies, by making the equation "Zeus got tricked by Prometheus, he got mad, and as a result he unleashed evils on humanity". This is what led to so many readings of Zeus as some sort of petty tyrant who wounded humanity to just get back at Prometheus. And this is partially true in Hesiod's myth... But not the whole truth. Because Hesiod insists on a very important fact: he stands as both a human speaking to other humans, and thus he cries over the misfortune of humanity and our suffering, and he explains it comes from Zeus and thus it is why it is unescapable... But he also stands as a devout Greek, as a herald of the gods' words, as someone inspired by the Muse - meaning he also has to point out that Zeus was in the right. This is why, when you compile the dual legends in "The Theogony" and "Of Works and Days", you get a very ambiguous Prometheus, more of a anti-villain by Ancient Greeks standards.
For example, the idea that Zeus got mad upon discovering he had been cheated by Prometheus is a misconception when it comes to the Hesiodic text. When you read Hesiod's text in the Theogony, what does it say? It says that Zeus was not fooled by Prometheus' trick, during the partition of the cow (when it was time to decide which part of food ent to the gods, which part went to humanity). No, Zeus, as king of the gods and superior god, is all-knowing and all-seeing, and the text does say he did knew of Prometheus' trick as soon as he laid eyes on the divided cow. He did play along with Prometheus' trick, but he got massively angry - not at being cheated, no... he got angry at the idea that Prometheus had rigged the game, and had tried to deceive him. See this as some sort of betrayal - he entrusted Prometheus with doing a fair share, and he discovers the Titan had rigged the game. Similarly, when Prometheus stole the fire, Zeus got angry because it was a theft - a theft opposing his law and decisions, an act of rebellion against his position as a king - and yes he would dislike humanity, because now they literaly had a stolen good that they were not supposed to have. Remember that Zeus is a god of justice whose deal was punishing criminals and enacting the law - so of course, a cheater, a scammer and thief like Prometheus would displease him, especially when he is not just a rebel that opposes Zeus' very rule... but also who threatens the cosmic order.
I said it before - in Ancient Greece everything was about balance ad harmony. Humanity had to be "balanced". And the actions of Prometheus literaly placed humanity out of balance. When the partiton of food came, Prometheus rigged the game so that humanity would have the best part. As a result, Zeus had to inflict an "handicap", a "flaw" to humanity so that they wouldn't be too overpowered. This was the removal of the fire. But then Prometheus stole the fire back, making humanity over-powered again. And so Zeus decided to bring the ultimate "handicap", the ultimate "flaw", the ultimate "evil" that would never go away... Because that's another thing with this legend. Zeus never takes away what had been given by the gods. When the partition of food was done, Zeus did not fight it. Zeus removed the fire yes, but when Prometheus gave it back, he did not remove it again. Once something is gifted, it cannot just be snatched back - again, Zeus respects the laws, the promises, the customs. A choice is a choice, a gift is a gift. Which is why, to weaken humanity, Zeus had to GIVE something instead of remove it. And this gift was A) in Theogony, Pandora. Because the Theogony's misogynistic take on the Pandora myth is that SHE was evil because women are by nature evil and ruin humanity. B) in Of Works and Days, the gift of the jar containing all the evils and misfortunes. Which, as I said, was a clever plan to have Prometheus' own family balance his over-powering of humanity by having THEM bring upon humanity something bad. As a way to even things out. When Hesiod evokes the person that brought misfortune upon humanity, when he describes the source of all the evils mankind has to suffer through, he doesn't speak of Zeus... He speaks of Epimetheus. Or of Pandora. But not Zeus. Zeus isn't the "culprit" in Hesiod's texts - rather it is either Pandora (for, misogynistic time, women are inherently curious and curiosity - and women in general - is evil), or Epimetheus (for being a dummy who gets seduced by pretty appearances, doesn't think of anything before acting, accepts any shining gift and is too naive for his own good, trusting both his enemies and the people he doesn't know). Oh yes, the human in Hesiod will cry and lament that Zeus is persecuting humanity... But he will make it clear it was the fault of Prometheus and Epimetheus (Pandora doesn't get much of the "culprit" treatment" because she is either seen as A, the evil Epimetheus brought into the world, B, just a tool and extension of Zeus' own will, and so not an actual "culprit").
The final piece of the puzzle that allows us to understand a bit more the tale of Hesiod is that we have to recall what was the worst crime ever in Ancient Greece. Hubris: for humanity to believe itself equal or above the gods. This was the manifestation of the Greeks' immense fear of unbalance and disharmony, when the low humans tried and believed themselves to be above their natural condition, about to rival with the immortals who were perfect in body and mind (well... absolutely perfect in the religion, much more flawed in the myths and literary works). And all the actions of Prometheus worked on bringing forward humanity close to hubris. By giving them a food better than the gods', by leaving them the full mastery of fire - especially since at the time it was the early humanity, the "golden age", those long-lived, happy, careless, ageless humans that were basically Tolkien's elves - Prometheus was literaly building rivals for the gods. Remember that what Prometheus did was seen as an act of rebellion and disobediance towards Zeus' order, ruling and position... Betrayal of his king, so to speak. Zeus had to inflict on humanity something so that they wouldn't get too overpowered or too similar to gods - he had to inflict on them something that would remind them that they were mortals, not gods, and that the world did not belong to them.
And THIS is where the "Silver Age" problems come from. As I said before, when Hesiod uses Cronos and Zeus to evoke the Golden and Silver Age, he uses them more as chronological markings than anything. By making the Golden Age Cronus' era, Hesiod places this humanity in the far, far, far away distant past, in a time beyond what is mythical - in a time before the actual organized time of the gods people knew, before what humans understood of humanity. And Hesiod insists in his texts that the ills and the worries brought by either Pandora's presence among humanity (Thegony) or by the jar of Pandora (Of Works and Days) are what caused humanity's downfall as they started aging, and falling sick, and losing their happiness, and living shorter... So long story short, it isn't because Zeus became king of the gods that the Golden Age became the Silver Age. It is rather because of the chain of events started by Prometheus - it is because of all the punishments Zeus had to took against the rebellious and cheating Prometheus that the original humanity became another. So... while yes, Zeus did send the evil, the texts of Hesiod also make it clear it is kind of Prometheus' fault. Hence the anti-villain status: yes he tried to favorite and help humanity, and thus is our hero... But he also tried to destroy the order of the world and is the reason we were cursed in the first place, so he is still a villain. Mind you, in the times after Hesiod the Greeks would come to gain a much more positive view of Prometheus - but I am focusing here only on Hesiod since it is what the question is about.
The best metaphor I would have would be : all those incidents we have today when we favorize and protect one species in an ecosystem because it is "cute"... and by doing so, we ruin the entire ecosystem. This is literaly what Prometheus did, as the trickster-rebel, and what Zeus had to fight as the god of order and balance. (And again, we have an Hesiod that is literaly doing grandpa rants about how the "good ol' times" were better and the "youth today is crap", so of course he would offer us a myth where the established order and ruling monarchy is praised, while the rebellious opposition is demonized... with the nuance that the rebellious opposition protected us humans, and thus we have this very ambiguous territory.) It is no wonder that in modern fiction dealing with Prometheus, a question arises that was first brought forward by commentators of Greek myths: did Prometheus act out of excessive love for humanity, or more to get at Zeus? Both options are possible: in "The God Beneath the Sea" for example Prometheus is this tragic figure of someone who loved too much humanity and tried to protect it at all costs... But in the French novel "Prometheus the revolted" by Janine Teisson, he is more presented as a cunning, exploitative schemer that uses humanity as a tool to discreetly try to get back at Zeus, because while he sided with him, he could never fully accept his new king due to his older Titan alliegeance. Which interpret is correct? We can't tell, because the older record is just very ambiguous...
As a final, final note, we have to bring in more "outside-the-text" context to the whole situation. Because these stories were told within a society that had an established hierarchy, an established religion and established morals differing from our own, hence why we can lack some key information to get the nuance. For example, in "Of Works and Days", Hesiod cries and laments about one of the punishments of Zeus against humanity - hiding the grain of plants below the earth, and forcing humans to work to grow their crops and their food. A punishment which is nuanced when you remember something from Greek religion that the text does not speak about: Zeus was one of the favorite gods of farmers and crop-growers, and seen as their ally, because he was a god of fertility and agriculture. Zeus was the god of weather - but of good, fertile, helpful weather. Zeus sent the fertile rain that made the plants grow and the earth alive ; and he also sent all the sunlight needed for fruits to mature and plants to be healthy. This was in fact part of his dicotomy with Hades - Hades kept the grain under the earth to protect it, and then Zeus helped it grow into a plant above the soil. (And yes, this is tied to the Persephone legend in some ways). When you know that, you realize that Zeus might have cursed humans with having to work hard and search hard for their food... But he also clearly helps them to do so by sending the weather needed for the crop to grow well.
Just like how he is said to destroy the various humanities of the Ages of Man one by one to punish them or due to other incidents... But he then grants them some pretty sweet things. Like how the Golden Age humans became Greek-equivalent of guardian angels, benevolent semi-divine entities, or how the men of the Silver Age were said to be among the "Blessed" in the afterlife, and supposedly to dwell in some sort of paradise...
Of course the issue is infinitely more complex, and there's entire books written about this, so this is just a fragment of synthesis. But to return to the original question... Cronos, and the other Titans, were not at fault for oppressing humanity or being tyrants, no. From what Hesiod gives us to read, the Titans in fact had nothing to do or didn't care about humanity in the first place - since before Zeus' time we have no record of any god mingling with humans. We'd have to wait for the Olympians for humanity to become "interestng" or even "desirable" in the yes of the gods. No, Kronos' true crime was a cosmic one. The Titans had to be overthrown because they refused the natural flow of time and the natural evolution of the world, because they repeated the same oppression they had delivered the world from (Ouranos'), because they had enforced a stagnation and even a regression, perfectly symbolized by the image of the father swallowing the babies as soon as they are out of their mother's belly. The gods do grow - but they grow trapped within their father's stomach in a perverse, reverse pregnancy, and in a mirror of how Ouranos' lust also prevented life from spreading forth into the world. And we'd have to wait for Zeus to force a new "birth", through making his father vomit, for the gods to finally be able to accomplish their purpose in life - change the world and make the universe go forward...
As a final note, and I think this is something Jean-Pierre Vernant said (but a lot of what I said above comes from Jean-Pierre Vernant): Zeus overthrowing Cronos is a symbol of the rule of brute strength and violent tyranny being stopped. How did Cronos reached the throne? By castrating his father. How did he maintain his rule? By imprisoning his siblings and devouring his own children. What happened when he was challenged? A cosmic war. And Cronos ruled alone as sole king over the universe. But when Zeus came into the world... He was first of the gods, yes, but he still shared the world with his brothers, so that there were three "kings of the world". His first instinct was to ave sex once he was king, yes, but he didn't just "have sex". He symbolically or officially married the most important goddesses (Themis, the Law/Justice, Mnemosyne, Memory, Metis, Prudence/Wisdom) to bring forth the embodiments of order and peace: the Horai, the Charites, the Muses, the Moirai, Athena... And, unlike Cronos who had imprisoned his siblings as soon as he was king, Zeus accepted and rewarded his allies among the Titans, making entities such as Themis, Helios or Hecate first-rank deities in the new pantheon. AND, while he did overthrow his father, it was in the result of a long war, without any brutal mutilation, and what he merely did was imprison him - and perhaps even latter forgave him and released him according to some stories. So we are definitively into a much better rule than the predecessor.
#greek mythology#greek gods#titans#hesiod#zeus#prometheus#pandora#the ages of man#the ages of humanity#the golden age#greek myths#kronos#cronus
116 notes
·
View notes
Text

Page from JSA: The Golden Age Book Four. 1994. Art by Paul Smith.
#dc comics#dc universe#justice league#justice society of america#the golden age#green arrow#aquaman#the flash#challengers of the unknown#doom patrol#martian manhunter#paul smith#james robinson#richard ory
45 notes
·
View notes
Text
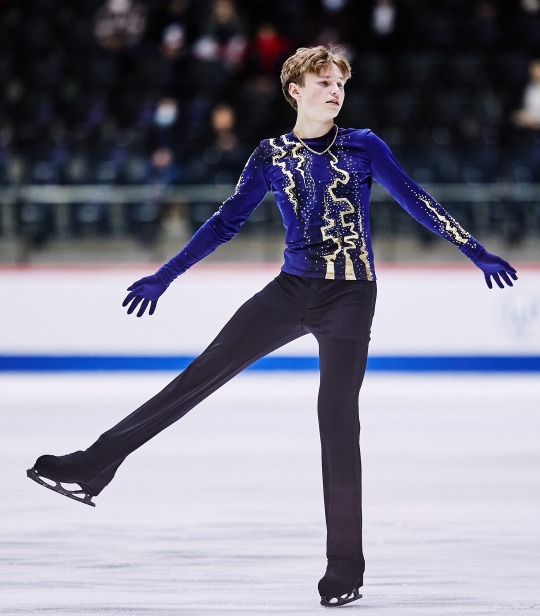
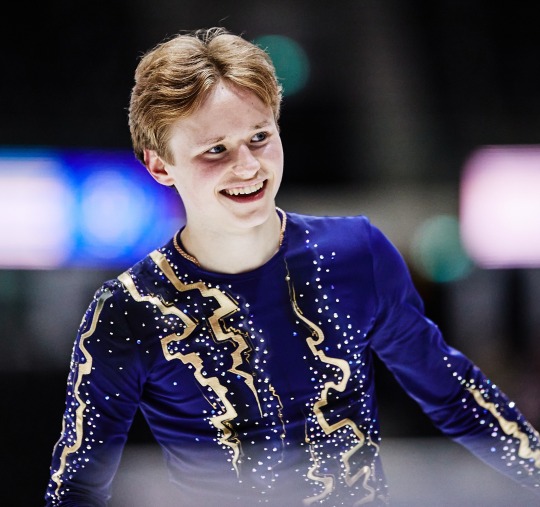
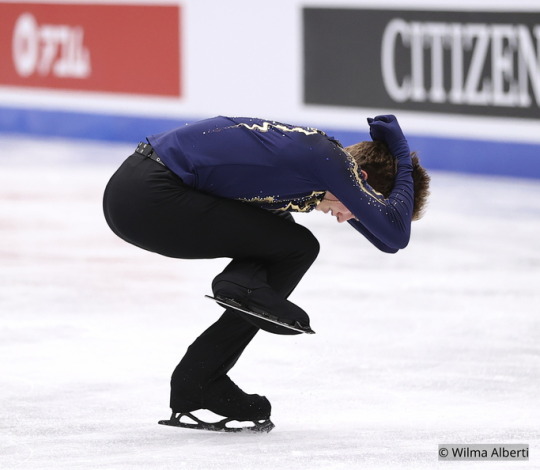
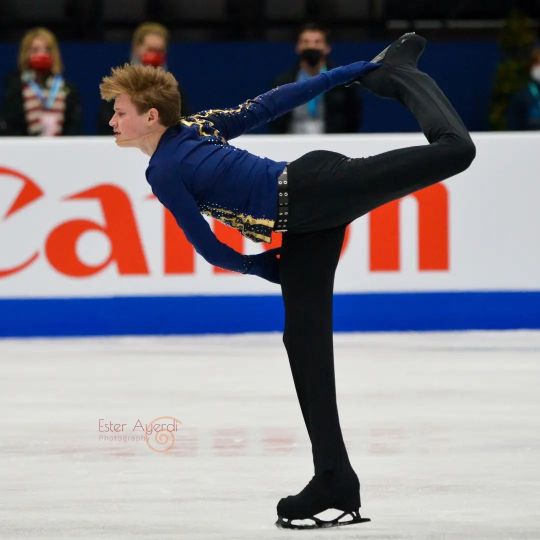





Ilia Malinin skating to music by Autograf and Woodkid for his free program at the 2022 Junior Worlds, 2022 US Nationals and 2022 Worlds.
(Sources: 1, 2, 3 and 4)
#Definitely one of his better costumes imo#Ilia Malinin#Figure skating#United States#Autograf#Woodkid#The Golden Age#2021–2022#2022 US Nationals#2022 Worlds#2022 Junior Worlds#Men
25 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Golden Age
1875
Ar by Edward John Poynter (1836-1919)
212 notes
·
View notes
Text

I'm re-listening to Archive 81 and rediscovered one of my most favorite scenes <3.
Yes, Daniel Powell. If you leave this outpost, I will come with you.
#archive 81#rat and dan#daniel powell#archive 81 season 2#the city#left of the dial#the golden age#dead signals#artists on tumblr#digital art#fanart#podcast fanart#2d art#drawings#digital artwork#digital illustration#ratty
22 notes
·
View notes
Photo

the Silver Age rises
Golden Age #4
#green lantern#the flash#aquaman#martian manhunter#dc comics#green arrow#adam strange#doom patrol#robotman#elasti girl#negative man#elongated man#atom#metamorpho#justice league of america#JLA#dc#the Golden Age#golden age#silver age
349 notes
·
View notes
Text





17 notes
·
View notes
Text

GOLDEN
#my art#berserk#griffith#guts#berserk fanart#the golden age#landscape#shhhhh i definitely did not reupload this
132 notes
·
View notes
Text
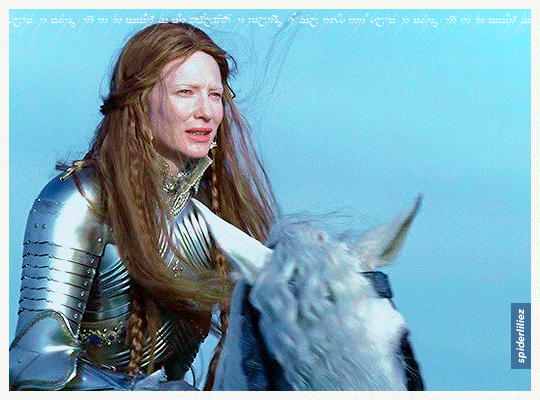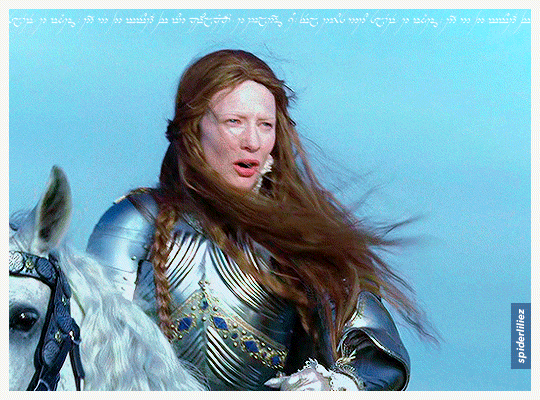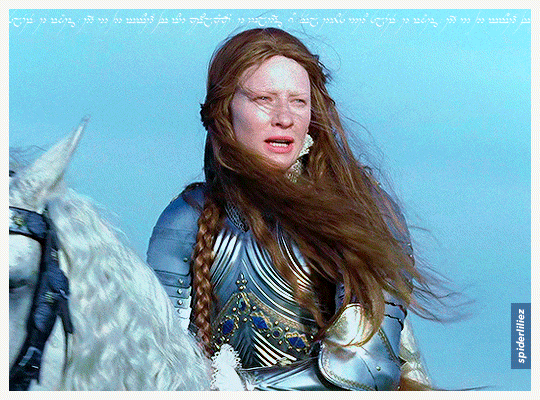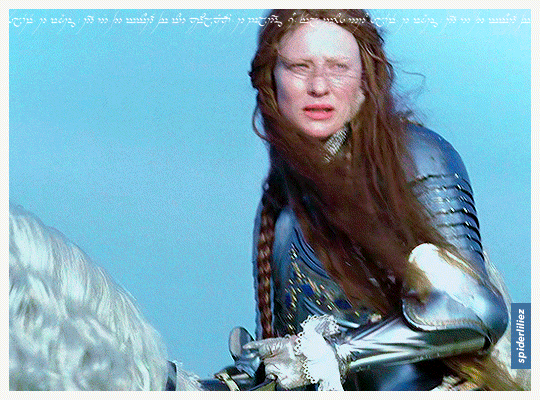


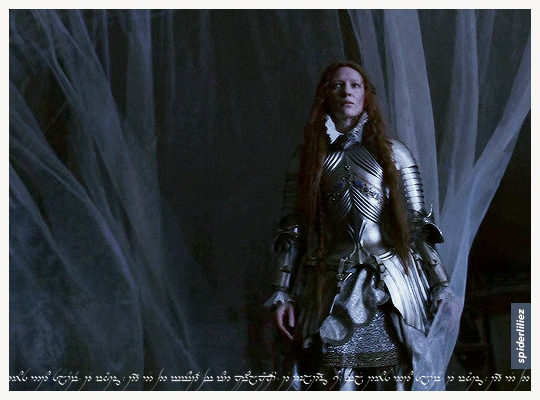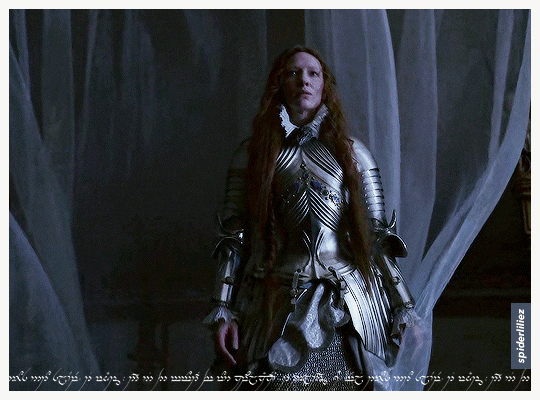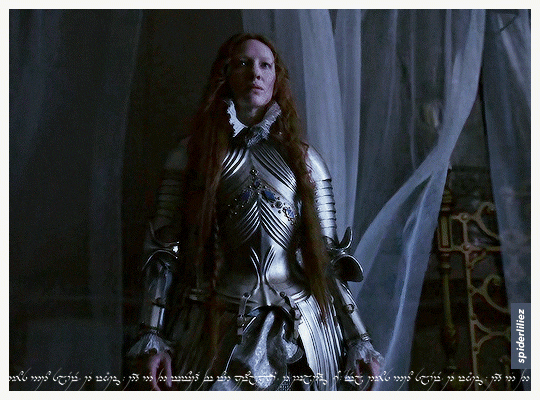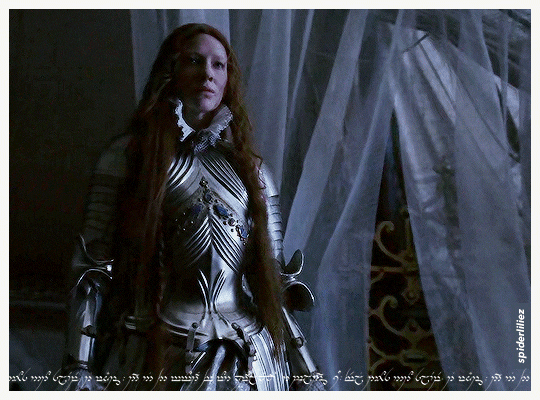
Our Galadriels in Armour!
The great Cate Blanchett and Morfydd Clark ✨
THE RINGS OF POWER (2023)
ELIZABETH: THE GOLDEN AGE (2007)
[+] MORFYDD [GIF Collection] 🌸
[+] CATE [GIF Collection] 🌻
[+] ..more on Galadriel ✨
[+] ..more on Queen Elizabeth I ✨
#MORFYDD FOR DAYS#Morfydd Clark#Cate Blanchett#Galadriel#Queen Elizabeth I#The Rings of Power#The Lord of the Rings#Elizabeth#Elizabeth The Golden Age#The Golden Age#TROP#LOTR#Tolkien
27 notes
·
View notes
Text

🗡️ girl knight but make it lucy pevensie 🗡️
#myart#mine#lucy pevensie#narnia#tcon#the lion the witch and the wardrobe#narnia the golden age#the golden age#cs lewis#girl knight#character desigb#gouache#painting#art#illustration
60 notes
·
View notes
Text



The Golden Age #3
Writer: James Robinson
Artist: Paul Smith
Inker: Paul Smith
Colors: Richard Ory
16 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Concept art for The Golden Age (1993) by Paul Smith.
#the golden age#the golden age 1993#jsa#justice society of america#justice society#all star squadron#all-star squadron#rex tyler#hourman#libby lawrence#liberty belle#jonathan law#tarantula#the tarantula#paul smith#dc#dc comics#dcedit#comicedit#comicsedit#u can reblog#PRETTIEST LITTLE TARANTULA I EVER DID SEE
70 notes
·
View notes
Text
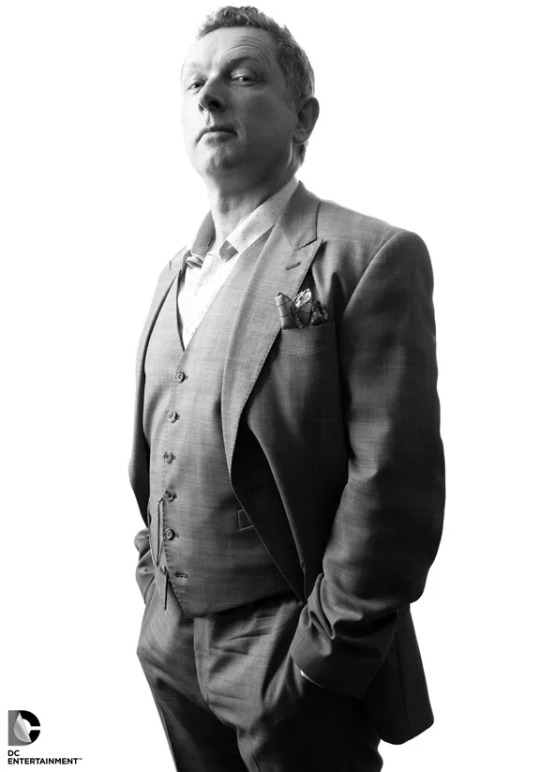




Happy birthday to James Robinson!
5 notes
·
View notes