#sarscov2
Text
PSA: Covid Effects and Complications
Alright fekkers this is how we’re doing public health announcements now that society is collapsing :))
This isn’t a post to tell you to avoid it, but to ask you to read the headings and make sure you make an informed decision if you wanna go out and get infected. If you do take risks, remember to avoid very young/old/pregnant/unwell/vulnerable people, test regularly and wear a mask (yes, they work).
Covid is Not Just A Respiratory Illness
COVID-19 routinely affects organs throughout the body, not just the respiratory system, including the brain, heart, liver, GI tract, endocrine system and skin (Gupta et al., 2020)
Covid can be seen as a blood clotting disorder masquerading as a respiratory illness. (Janardhan et al., 2020)
Covid Causes Brain Damage
Mild Covid infection shows significant orbitofrontal cortical atrophy (shrinking of parts of the brain) and cognitive decline (Crunfli et al., 2022)
Mild COVID-19 infection can cause impaired neurogenesis (nervous tissue growth), myelin and oligodendrocyte (nerve insulation) loss and increased neurotoxic molecules around the central nervous system (Fernández-Castañeda et al., 2022 *preprint)
MRIs of 401 patients done before and after Covid infection showed reduction in global brain size, grey matter loss (orbitofrontal cortex and parahippocampal gyrus) and cognitive decline. (Douaud et al., 2022)
COVID increases the risk of neurodegenerative disorders- Alzheimer’s disease risk is 3.5x increased; Parkinson’s disease risk is 2.6x increased; ischaemic stroke risk is 2.7x increased and intracerebral haemorrhage (bleeding in the brain) risk is 4.8x increased. (Zarifkar et al., 2022)
Risks of cognitive deficit, dementia, psychotic disorders, and epilepsy or seizures are increased for at least 2 years following Covid infection. (Taquet et al., 2022)
In 25% of mild Covid cases, visuocontructive cognitive deficits are seen, associated with changes in brain structure and metabolism. (de Paula et al., 2022)
Hospitalised Covid patients cognitive loss is similar on average to that sustained with 20 years ageing, and equivalent to losing 10 IQ points. (Hampshire et al., 2022)
People reportedly recovered from Covid show decreased intelligence and significant cognitive deficits. (Hampshire et al., 2021)
Covid Causes Alzheimer’s-like Pathology and Accelerates Existing Alzheimer’s Disease
Covid invades cognitive centers of the brain and induces Alzheimer’s-like neuropathology (Shen et al., 2022)
Covid is associated with accelerated progression of Alzheimer’s disease (aaic.alz.org)
Covid produces proteins that form cytotoxic aggregates which damage neuronal cells, which parallels Alzheimer’s disease mechanism (Charnley et al., 2022)
COVID increases the risk of neurodegenerative disorders- Alzheimer’s disease risk is 3.5x increased; Parkinson’s disease risk is 2.6x increased; ischaemic stroke risk is 2.7x increased and intracerebral haemorrhage (bleeding in the brain) risk is 4.8x increased. (Zarifkar et al., 2022)
Risks of cognitive deficit, dementia, psychotic disorders, and epilepsy or seizures are increased for at least 2 years following Covid infection. (Taquet et al., 2022)
Covid Causes Kidney Damage
Mild Covid infection is associated with increased risk of kidney damage (Bowe et al., 2021)
Covid infection triples risk of End Stage Kidney Disease, requiring dialysis or kidney transplant (Bowe et al., 2021)
Covid Causes Diabetes
Covid patients have a 40% increased risk of being diagnosed with diabetes after first infection (Xie et al., 2022)
Covid infection is associated with an 81% increase in Diabetes incidence for 12+ weeks following infection (Rezel-Potts et al., 2022)
Mild Covid infections increase risk of Type 2 Diabetes development (Rathmann et al., 2022)
Covid infection leads to an average of 42% increased risk of Type 1 Diabetes across all ages. Risk increases most in pediatric patients- by 584%. (Quedan et al., 2022)
Covid Causes Cardiovascular Illness
Covid infection, even when mild, substantially increases risk of cardiovascular illness up to at least 1 year later (Xie et al., 2022)
Capillary density (how many small blood vessels are present) is reduced by 41% in sufferers of Long Covid 18 months after Covid infection (Osiaevi et al., 2022)
Acute Covid infection results in 6x increase in cardiovascular diagnosis; 11x increase in pulmonary embolism (blood clot in lung); 6x increase in atrial arrhythmias (abnormal heartbeat); 5x increase in venous thromboses (blood clot in vein). (Rezel-Potts et al., 2022)
A spike protein found on Covid-19 virus particles uses the body’s immune response to damage and inflame heart muscle cells. (heart.org)
People with Covid exhibited increased risks and 12-month burdens of incident cardiovascular diseases, including cerebrovascular disorders, dysrhythmias, inflammatory heart disease, ischemic heart disease, heart failure, thromboembolic disease and other cardiac disorders. Risk were evident even in those without prior cardiovascular disease. (Xie et al., 2022)
Risk of stroke more than doubles even with mild or asymptomatic Covid infection. Median time of stroke is 2 months after Covid diagnosis. (Tu et al., 2021)
Covid infection increases heart attack risk by 3-8x and stroke risk by 3-6x (Katsoularis et al., 2021)
Covid infection increases risk of deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism and bleeding in the months following acute illness (Katsoularis et al., 2022)
Long Covid is associated with presence of microclots throughout the body. (Pretorius et al., 2021)
Long Covid patients may face an increased risk of abnormal blood clotting. (uclh.nhs.uk)
Covid Accelerates Biological Ageing
Accelerated biological ageing is seen in Covid infection (Cao et al., 2022)
Covid Damages the Immune System
Covid causes T-cell exhaustion, meaning the immune system is less able to fight off pathogens (Loretelli et al., 2021)
Previous infection with earlier SARS2 strains can lead to impaired immune responses to Omicron (Reynolds et al., 2022)
Covid infects and kills T-lymphocytes (key cells of the immune system), causing low T-lymphocyte counts 1(Guan et al., 2020), 2(Shen et al., 2022)
Long Covid patients show reactivation of latent Epstein-Barr (can cause MS) and Varicella Zoster (can cause shingles and Ramsey Hunt syndrome) viruses (Klein et al., 2022 *preprint)
2.8% of Long Covid patients reported Varicella Zoster Virus reactivation, leading to shingles, following Covid infection. Primary risk factors for VZV reactivation are age and immunodeficiency. (Davis et al., 2021)
Covid infection causes immunodefiency in recovered patients by downregulating a specific protein on B Cells (a type of immune cell). (Jing et al., 2021)
Covid Causes the Body to Attack Itself (Autoimmunity)
Covid causes production of autoantibodies which target the immune system, vascular cells, coagulation factors and platelets, connective tissue, and organ systems, including lung, the central nervous system compartment, skin, gastrointestinal tract and other tissues. (Wang et al., 2021)
Asymptomatic Covid infection can lead to severe Ulcerative Colitis (an inflammatory bowel disease). (Mora et al., 2022)
Mild Covid infection can produce significant levels of autoantibodies for 7+ months. (Bhadelia et al., 2021)
Covid infection precedes new appearance of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. (Galleoti and Bayry, 2020)
Covid infection linked to development of vasculitis, arthritis, lupus and sarcoidosis. (Gracia-Ramos et al., 2021)
Autoantibodies linked to Lupus, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Guillain-Barré syndrome, immune thrombocytopaenia and autoimmune haemolytic anaemia found in patients following Covid infection. (Moody et al., 2021)
In a group of non-hospitalised healthcare workers with Covid, 54% tested positive for autoantibodies- these targeted skin, smooth muscle, neutrophils (a type of white blood cell of the immune system) and gastric parietal cells (cells in the gut). (Richter et al., 2021)
Covid May Affect Both Male and Female Fertility
COVID-19 virus can be found and continues to replicate in the testes even after death (Costa et al., 2022 *preprint)
COVID-19 infects the testes and damages spermatogenesis (sperm production) (Ma et al., 2020)
Covid virus particles found in penis tissue of men infected 6-8 months earlier, who later experienced erectile dysfunction (Kresch et al., 2021)
Study shows total sperm number lower in men infected with Covid at 3 month follow up (Best et al., 2021)
Testes of Covid patients show significant seminiferous tubular injury and reduced Leydig cells- cells that produce testosterone. (Yang et al., 2020)
11 of 26 (42%) men with mild/moderate Covid infection showed incidental (asymptomatic) epididymitis on Doppler ultrasound - a condition that can cause infertility (Carneiro et al., 2021)
A case of premature ovarian failure due to Covid infection (Madaan et al., 2021)
Another case of premature ovarian insufficiency in a 34-year-old following Covid infection (Wilkins and Al-Inizi, 2021)
Ovarian injury, including declined ovarian reserve and reproductive endocrine disorder, can be observed in a study of women in China infected with Covid. (Ding et al., 2021)
Study finds men who had seemingly fully recovered from Covid infection developed decreased sperm count and motility and abnormally shaped sperm. (Ghosh et al., 2022)
Covid Causes Erectile Dysfunction
Covid virus particles found in penis tissue of men infected 6-8 months earlier, who later experienced erectile dysfunction (Kresch et al., 2021)
A Long Covid survey found 15% of men reported sexual dysfunction and 3% reported a decrease in genital size. (Davis et al., 2021)
Prevalence of erectile dysfunction 3x as common in men after Covid infection (28% vs 9% in controls) (Sansone et al., 2021)
Prevalence of erectile dysfunction in Thai men reported as 65% following Covid infection (Harirugsa et al., 2021)
Another study showing risk of erectile dysfunction triples following Covid infection. (Katz et al., 2021)
Study finds that Covid infection leads to 6-fold increased risk of erectile dysfunction, which worsens men’s mental health. (Hsieh et al., 2022)
Covid Causes Autonomic Nervous System Dysfunction
30% of 4000 Long Covid patients met the criteria for a diagnosis of Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome, a type of dysautonomia (Davis et al., 2021)
Dysautonomia (autonomic nervous system dysfunction) may be responsible for fatigue and hypoxia in Long Covid patients. (Barizien et al., 2021)
Covid infection frequently causes abnormalities in autonomic nervous system tests, as well as worsening pre-existing dysfunction. Abnormalities included orthostatic intolerance, fainting, heachaches, burning pains, excessive sweating and lightheadedness. (Shouman et al., 2021)
67% of Long Covid patients have moderate-to-severe autonomic dysfunction, regardless of severity of initial Covid infection. (Larsen et al., 2022 *preprint)
Covid infection could result in gastric dysmotility and paralysis (stomach and intestines become unable to move food through). (Coles et al., 2022)
Covid Can Seriously Harm Children
SARS2 causes increased hospital admissions, mortality rate and absolute numbers of deaths in children, compared to Influenza (Shein et al., 2022)
Asymptomatic infection in children can lead to a serious, multiorgan hyperinflammatory syndrome (Riphagen et al., 2020)
An epidemic of hepatitis in healthy children could be linked to previous COVID-19 infection (science.org)
Pulmonary dysfunction persists even in children considered to be recovered from Covid (Heiss et al., 2022 *preprint)
Covid leads to a 3x increased risk of psychotic disorders in children (Taquet et al., 2022)
Children are twice as likely to develop epilepsy or seizures following Covid infection, compared to following other respiratory infections (Taquet et al., 2022)
Children are at an increased risk of epilepsy, encephalitis, nerve, nerve root and plexus disorders up to at least 2 years after Covid infection (Taquet et al., 2022)
Intracranial (brain) bacterial infections have increased during the Covid pandemic, occuring during or just after Covid infection. One Michigan children’s hospital reports a 236% increase. (Khuon et al., 2022)
235,000 children in England have Long Covid symptoms lasting 12+ weeks that affect their daily life (ONS.gov.uk)
21% of Year 13 pupils missed 4+ weeks of school due to Covid for the 21/22 academic year in England (suttontrust.com)
Children and teens who’ve had Covid are at greater risk for blood clots, heart problems, kidney failure, and Type 1 diabetes (Kompaniyets et al., 2022)
5.2 million children have lost a parent or caregiver to Covid infection. (Unwin et al., 2022)
Covid infection leads to an average of 42% increased risk of Type 1 Diabetes across all ages. Risk increases most in pediatric patients- by 584%. (Quedan et al., 2022)
Covid Can Endanger Pregnancy and the Growing Baby
Covid infection during pregnancy increases risk of preterm delivery (Edlow et al., 2022)
Covid infection at delivery increases risk of stillbirth (DeSisto et al., 2021)
Covid infection during pregnancy increases risk of neurodevelopmental disorder diagnosis in babies by 2.17x during first year of life (Edlow et al., 2022)
Risk of severe Covid infection is higher in pregnant women. (Rad et al., 2021)
Newborns born to mothers who had recovered from Covid 10+ weeks prior to birth show viral mRNA and proteins in their stool and signs of intestinal inflammation. (Jin et al., 2022)
Covid infection destroys the placenta, starving the baby of oxygen, resulting in increased risks of stillbirth and neonatal deaths. (Schwartz et al., 2022)
Covid Can Lead to Development of New Allergies
Mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS) may be triggered by Covid infection, resulting in new allergies and risk of anaphylaxis. (Afrin et al., 2020)
Mast cell activation symptoms are increased in Long Covid (Weinstock et al., 2021)
Covid Worsens Mental and Psychological Health
Covid diagnosis associated with increased risk of mental health diagnosis and neurocognitive decline (Xie et al., 2022)
Risks of cognitive deficit, dementia, psychotic disorders, and epilepsy or seizures are increased for at least 2 years following Covid infection. (Taquet et al., 2022)
Covid Reinfection is Common and Increasingly Detrimental to Health
Reinfection with Covid increases risk of hospitalization, death and long covid by more each time 1(Al-Aly et al., 2022 *preprint), 2(World Health Organisation)
Covid reinfections are common. Mean time between 1st and 2nd infection is 79 days, and between 2nd and 3rd infection is 65 days. (Al-Aly et al., 2022 *preprint)
Covid reinfection is possible as soon as 19 days after initial infection. (Ren et al., 2022)
Long Covid is Common, Serious and Potentially Disabling
1 in 5 (20-30%) develop a new health condition following Covid infection (Bull-Otterson et al. 2022)
Just below 1 in 10 (9.3%) triple vaccinated people are not recovered 4-8 weeks after Omicron infection in the UK (ONS.gov.uk)
1 in 7 (14%) of 11-18 year olds have symptoms 15 weeks after COVID-19 infection (Stephenson et al., 2021)
Long Covid causes disability and unemployment (theguardian.com)
Two million days of healthcare staff absences were lost to Long Covid during the first 18 months of the pandemic in England (the guardian.com)
On average, healthcare staff absent with Long Covid are off for more than 80 days in England (theguardian.com)
A US Long Covid group reports that 44% of those affected are out of work (longhauler-advocacy.org)
235,000 children in England have Long Covid symptoms lasting 12+ weeks that affect their daily life (ONS.gov.uk)
21% of Year 13 pupils missed 4+ weeks of school due to Covid for the 21/22 academic year in England (suttontrust.com)
The proportion of people unemployed and not seeking work due to Long Covid has doubled in the past year in the UK (theguardian.com)
Long Covid survey of nearly 4000 finds 45% required a reduced work schedule and 22% could not work due to illness (Davis et al., 2021)
88% of Long Covid sufferers experience cognitive dysfunction and memory problems (Davis et al., 2021)
80,000 people estimated to have left employment due to Long Covid by March 2022 in UK (Reuschke and Houston, 2022)
2.9 million people of working age in the UK have had, or currently have, Long Covid (Reuschke and Houston, 2022)
Long Covid has over 200 symptoms spanning 10 organ systems. (Davis et al., 2021)

Graph via @davidsteadson on Twitter
Vaccination Does Not Fully Prevent Long Covid
16% of Covid infections lead to Long Covid after 3 vaccinations (Azzolini et al., 2022)
Just below 1 in 10 (9.3%) triple vaccinated people are not recovered 4-8 weeks after Omicron infection in the UK (ONS.gov.uk)
Vaccination only reduces risk of Long Covid by 15%. (Al-Aly et al., 2022)
Covid Persists in the Body after Initial Infection
Covid can persist throughout the body and brain even following mild/asymptomatic infections, for at least 230 days (Chertow et al., 2021 *preprint)
COVID-19 can persist within the gut for at least 7 months after infection 1(Gaebler et al., 2021), 2(Natarajan et al., 2022)
Residual COVID-19 virus has been found in the appendix and breast tissue, 175- and 462-days post-infection, respectively (Goh et al., 2022 *preprint)
COVID-19 virus can persist in the eyes after initial infection (Armstrong et al., 2021)
COVID-19 virus can be found and continues to replicate in the testes even after death (Costa et al., 2022 *preprint)
Covid virus particles found in penis tissue of men infected 6-8 months earlier, who later experienced erectile dysfunction (Kresch et al., 2021)
Viral Persistence Can Cause Serious Illness Many Years Later
We do not know the long term effects of Covid Infection and Persistence.
Persistent Hepatitis C infection increases risk of Hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer) (Mitchell et al., 2015)
Persistent Human Papillomavirus (HPV) infection causes cervical cancer (Sudenga et al., 2013)
Persistent HIV infection leads to immunodeficiency and AIDS (Pauza, 1988)
Persistence of Epstein Barr Virus (EBV) can cause development of multiple sclerosis (Ruprecht, 2020)
Persistence of varicella zoster virus (VZV), which causes chickenpox, can result in shingles and Ramsey Hunt Syndrome (Gershon et al., 2015)
These effects of Covid are not easy to learn about, but it is essential that people know the risks. This is not fearmongering- it is not “what if”s and “maybe”s- these are events that are happening right now, around the world.
#psa#public health#covid#covid infection#coronavirus#coronavirus infection#covid-19#covid19#sarscov2#sars-cov-2#pandemic#covid pandemic#coronavirus pandemic#lockdown#pandemic response#long covid#covid long hauler#pasc#clinically vulnerable#clinically extremely vulnerable#research#covid research#wear a mask#public information#public health information#world health organisation#cdc#ukhsa#covid response#viral persistence
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Weekly COVID-19 Update for 2023-12-24
COVID is still airborne, and COVID still very much isn't over.
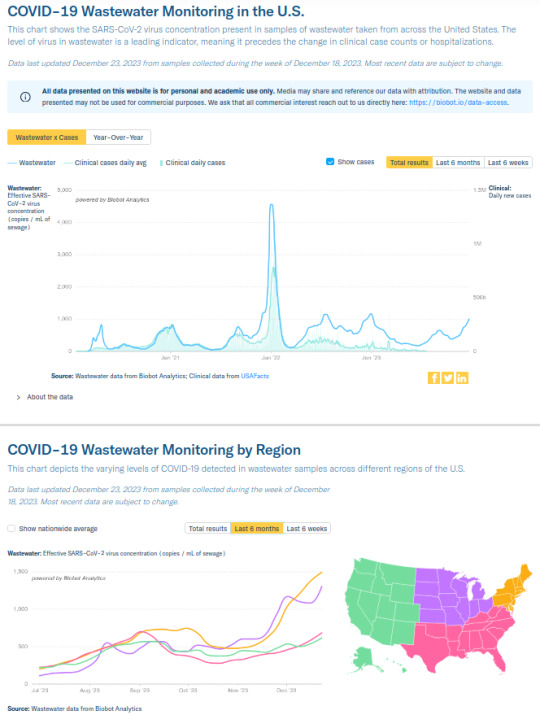
Northeastern and Midwestern USA SARS2 virus levels in wastewater are *soaring*, Northeast is currently at 1500 copies/mL (~750 copies indicates a strong surge), and Midwest is at 1300 copies/mL. Southeastern and Western USA are maintaining relatively lower levels between 600 and 700 overall, but both are still climbing. See https://biobot.io/data for county-specific data as results can vary widely between locales.
How to reduce your risk of infection? The SARS2 virus is airborne and can spread like smoke, so #MaskUp with an #N95 or better, avoid superspreader events and locations, and stay up-to-date on your boosters. Do it for yourself, so you don't catch SARS-CoV-2, and for others, so you don't spread SARS-CoV-2. Even if you're fully vaccinated, your risk of developing #LongCOVID following an infection is lower but not zero, and multiple reinfections increase your odds of negative health outcomes. Plan A always should be to prevent an infection from developing by wearing a respirator with a good seal around your mouth and nose (FFP2, FFP3, KN95, N95, N99, P100, etc.).
Holiday tips:
-If someone tells you that COVID is over, you might ask them why, if we didn't consider COVID to be over in 2020 or 2021, when the COVID wastewater levels were lower, why should we consider it over now, when the virus is circulating in even higher amounts?
-"Fewer cases" doesn't mean much when most of the at-home rapid tests don't get counted in official records, and the most accurate PCR tests are neither freely available nor given to everyone getting on a plane or attending classes.
-"Fewer deaths" also means less when you remember that about 1,200,000 of the most vulnerable people already have died from it, COVID-19 remains the #3 cause of death in 2023 (behind heart disease and cancer, the risk of both of which may be increased by COVID), and the risk of a Long COVID/post-acute COVID syndrome (PACS) disability or other potentially life-shortening organ damage (brain, kidney, lung, immune, etc.) isn't measured just by the death count. Also, the USA's life expectancy still hasn't recovered from the drop it experienced following the start of the pandemic.
source: https://biobot.io/data
source: https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/news/20231006/these-are-the-top-10-causes-of-death-in-the-us
source: https://publichealth.jhu.edu/2022/covid-and-the-heart-it-spares-no-one
source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33914346/
source: https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/nation/2023/11/29/average-us-life-expectancy-increased-not-pre-covid/71738611007/
#covid#pandemic#corona#coronavirus#sarscov2#publichealth#science#disease#covidisntover#virus#medicine#sars2#covidisairborne#covidisnotover#health#lifeexpectancy
47 notes
·
View notes
Text

Proactive, preventative protection is partisan.
Wear a mask. The air is toxic.
918 notes
·
View notes
Link
Whether or not deer could act as long-term reservoirs for these obsolete variants is still unknown, as scientists continue to collect and analyze new data.
The study, published January 31 in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, represents one of the most comprehensive studies to date to assess the prevalence, genetic diversity and evolution of SARS-CoV-2 in white-tailed deer.
"One of the most striking findings of this study was the detection of co-circulation of three variants of concern—alpha, gamma and delta—in this wild animal population," said Diego Diel, associate professor of population medicine and diagnostic sciences at Cornell.
Over the course of the pandemic, deer have become infected with SARS-CoV-2 through ongoing contact with humans, possibly from hunting, wildlife rehabilitations, feeding of wild animals or through wastewater or water sources.
Continue Reading
130 notes
·
View notes
Link
Most SARS-CoV-2 patients experience anosmia, or a loss of smell, which can linger for months after recovery. According to olfactory epithelium samples taken from 24 biopsies, T cell-mediated inflammation continues in the olfactory epithelium even after SARS-CoV-2 has been removed from the tissue, indicating a mechanism for long-term post-COVID-19 smell loss.
The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 is thought to harm the olfactory epithelium, a specialized tissue involved in smell sense that runs along the top of the nasal cavity (SARS-CoV-2). The olfactory epithelium comprises three key components: odor-detecting olfactory receptor cells, a sustentacular cell layer for support, and basal stem cells that replenish the cells continually.
Continue Reading
78 notes
·
View notes
Text
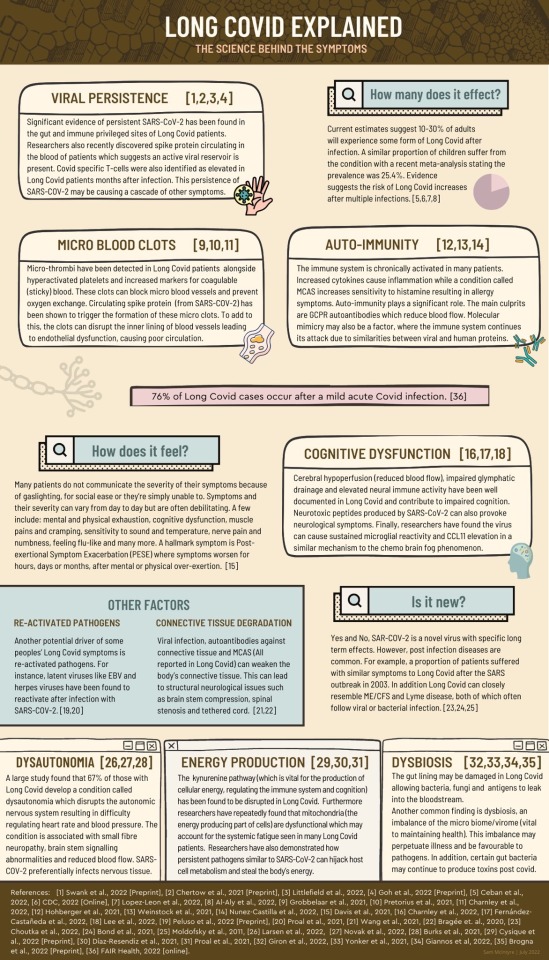
Long Covid Explained: The Science Behind the Symptoms (Infographic)
Source: @SamMc413 on Twitter (thread contains links to data sources listed at bottom) & PDF version
See also: Symptoms and risk factors for long COVID in non-hospitalized adults (Nature, August 2022)
139 notes
·
View notes
Text
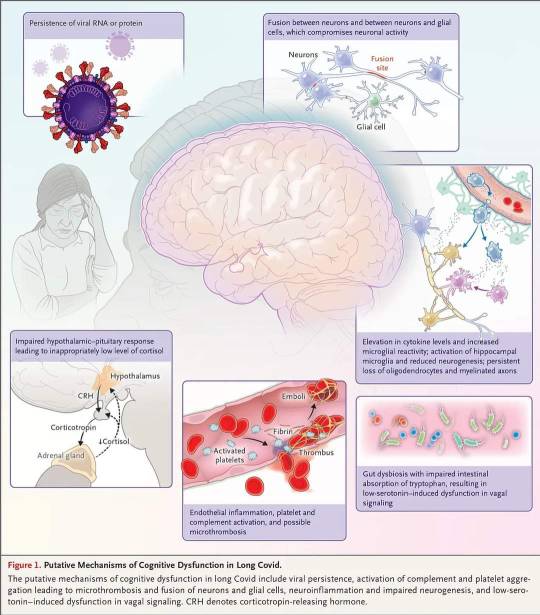
#LongCovid and Cognitive Deficits by @EricTopol
"None of this is good news for Long Covid and the brain, folks."
https://erictopol.substack.com/p/long-covid-and-cognitive-deficits?utm_campaign=post&triedRedirect=true
#psychiatry #neuroscience #BrainHealth #Neurology #brain #SARSCoV2 #COVID19 #CentralNervousSystem #NervousSystem #BrainFog
#Long COVID#psychiatry#Neuro Science#Brain#Brain Health#Neurology#SARSCOV2#COVID19#Brain Fog#central nervous system#nervous system
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
🌡️⚖️ Bacterial Pneumonia: Lessons from the Past, Relevance to COVID-19 🦠🔍
The 1918 influenza pandemic taught us about the significant role of bacterial pneumonia, overshadowing the primary viral infection. This knowledge remains relevant to COVID-19.
🧪 Unveiling the Evidence: Autopsy findings showed that secondary bacterial infections were the primary cause of death during the 1918 pandemic.
⚙️ Viral-Bacterial Interplay: Combining influenza viruses with bacteria led to severe disease, highlighting their synergistic effects.
💡 Pandemic Preparedness: Recognizing the importance of bacterial pneumonia is vital in preparing for future outbreaks. Preventing, diagnosing, and treating bacterial pneumonia should be prioritized.
😷 Finding Balance: While masks are essential in curbing the spread of COVID-19, excessive and indiscriminate usage may have drawbacks. Research has raised concerns about certain mask types potentially increasing respiratory infections.
💪 Navigating Complexity: We need a comprehensive approach that balances mask usage with overall health considerations to create a resilient society.
🌍🤝 Building a Healthier Future: By learning from history, we can prioritize public health, prepare for future pandemics, and minimize unintended consequences. Let's stay vigilant and #StopTheSpread.
#psa#public health#covid#covid infection#coronavirus#coronavirus infection#covid-19#covid19#sarscov2#sars-cov-2#pandemic#covid pandemic#coronavirus pandemic#lockdown#pandemic response#long covid#covid long hauler#pasc#clinically vulnerable#clinically extremely vulnerable#research#covid research#wear a mask#public information#public health information#world health organisation#cdc#ukhsa#covid response#viral persistence
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
THINKING: How to articulate the reality of how COVID spreads- you know, that it's NOT JUST DROPLETS/SPITTLE THAT INFECT YOU, that SARS-CoV-2 [the virus causing COVID-19] can remain suspended in these pretty much invisible tiny bits of moisture, floating like smoke/mist.
This is why it is not only important to mask, but that the mask covers your nose etc. and also why the filtration of indoor air and ventilation of shared spaces makes a difference.
so uh LOL OK MEMES why not?! like literally what is there to lose???
So I made… this.
All Your Base Are Belong To Us, except it's about COVID, so, All Your Breath Are Belong To Us.
All your breath are belong to us
For great justice,
put on fitting mask
Wear mask,
you know what you doing,
put on fitting mask
For a chance to survive,
clean your air
The audio in the post here is what I'm using for the slideshow that'll be a video with COVID related memes, but, more content is needed before the vid can be completed (have Other Things I'm working on/dealing with, so, this vid hasn't been highest priority, but, it would be good to complete it).
Examples of what'd be part of this slide show:
Good idea…
Are these droplets?
Darmok and Jalad at 2 metres!
COVID is airborne! (I choose you, SARS-CoV-2!)
COVID is Airborne, my dudes
Mask up, live long, and prosper
WEAR MASK [Goncharov reference]
So, suggestions for memes (I may make them) and/or links to relevant COVID PSA materials (but public domain) are welcome!
Guidelines I've had as I've put memes together,
no bigotry (sexism, racism, ableism, trans-antagonism, etc.)
not targeting specific people (it should not be personal, AND many issues are systemic, AND, times change so a reference to an individual becomes out of date, AND, internationally, people might not get a reference, like, "Who's Bonnie Henry?")
avoiding product placement (e.g. memes based on an ad campaigns)
ideally, entertain and inform (a meme about "wear mask" can just be funny, but, it can also contain good info e.g. importance of fit)
And: If you're not familiar with AYBABTU, this is the video I'm emulating.
#COVID is airborne#COVID is NOT over#COVID is ongoing#COVID floats like smoke#COVID#COVID19#COVID 19#SARS-CoV-2#SARSCoV2#SARS CoV 2#pandemic#PLAGUE#mask#masks#masking#MASK UP#my ocs
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
Implications
Additional SARS pandemics are therefore expected, like those associated with influenza. Influenza viruses are at present vastly more diverse than SARS-CoV-2, but over decades we are likely to see significant diversification of SARS lineages, if IBV’s history is to guide us. The frequency of these future pandemics is unpredictable, as is their severity. Establishing the “SARS” category as proposed here is necessary for proper preparation for such future events.
Influenza pandemics have all been self-limiting, and early in the first COVID-19 pandemic it was regularly interpreted in a similar manner, i.e. as something that will naturally dissipate. More recently that has shifted towards an acceptance of “endemicity”, where “endemicity” is sold as a state of constant circulation that is not overtly disruptive to normal societal functioning rather than the actual scientific definition, which is constant circulation of the pathogen, and which tells us nothing about its impacts on humans.
If we are to instead view the first COVID-19 pandemic as the initial, and so far appearing to be permanent introduction of an entirely new type of pathogen (SARS) in the human population, and to accept the possibility of many novel SARS serotypes and strains appearing in the future, a rather different picture emerges. So far Omicron exhibits the lowest mortality rate of all sarbecoviruses known to have infected humans, but SARS-1 was much more severe than SARS-2, and the evolution of the first SARS2 serotype was towards more severe disease27 and current data suggests a similar trajectory within many Omicron lineages28.
Therefore it cannot be assumed that all future pandemic serotypes/strains will be “inconsequential”, or even tolerable (where “tolerable” has now been established to mean anything that does not break healthcare systems to the point where refrigeration trucks need to be called in to store the dead bodies), as subsequent iterations of viral evolution that gain a strong fitness advantage due to major antigenic innovations could revert to substantially more pathogenic states, as commentators have previously warned4,25. An understanding of the course of SARS-CoV-2 evolution so far as having already spawned two separate pandemics is needed to raise awareness of and prepare for these possibilities.
9 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Big props to the legend #DJBobbito for doing his part to keep the community safe and modeling what someone with their humanity intact looks like! We see you keeping folks safe to @perfectlyclaire! • “We both was wearing masks because the pandemic is not over, and while we're both healthy, we care about those in our community who may not have a strong immune system to defend against infection, sickness and at worst death. I appreciated her thoughttulness and willingness to be covid cautious!” @koolboblove • #ThisIsWhatSolidarityLooksLike #CovidCautious #CovidIsNotOver #sarscov2 #LongCovid #DisabilityJustice #Immunocompromised #Ableism #Eugenics #CovidDenial #CapitalismKills #HipHop #WearAMask https://www.instagram.com/p/CnjK5xtuJLG/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
#djbobbito#thisiswhatsolidaritylookslike#covidcautious#covidisnotover#sarscov2#longcovid#disabilityjustice#immunocompromised#ableism#eugenics#coviddenial#capitalismkills#hiphop#wearamask
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube


les vérités cachées ne le sont plus
#big pharma est toujours en bonne santé#big pharmla#covid&corruption#covid de sens#covid au cerveau#mon ministre est sinistre#mon infirmier est un fumier#sarscov2#christine cotton#scandale sanitaire#Youtube
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Per ora sembra funzionare per i topolini, per cui no a facili entusiasmi. Però la strada verso la prevenzione del contagio per via nasale è interessante.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Researchers Develop a Machine Learning Model to Predict Whether a COVID-19 Test Might be Positive or Not

A study from Florida Atlantic University used machine learning to provide new evidence for understanding how molecular tests and serology tests are correlated and what features are most useful in COVID-19 testing. This could be useful in helping healthcare providers prioritize testing and treatment for patients most likely to have the virus.
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)-related new coronavirus illness (COVID-19) first appeared in Wuhan City, China, in 2019, and it spread swiftly around the world. Over 515 million COVID-19 cases and more than 6 million fatalities have been reported worldwide as of May 2022. The major way that COVID-19 infection spreads from an infected person to a non-infected person is by aerosol droplets from their coughing or sneezing. Asymptomatic people may potentially transmit the disease. SARS-CoV-2 has an incubation period of 2 to 14 days, with most people showing symptoms within 12 days after infection.
Continue Reading
#bioinformatics#covid19#sarscov2#pandemic#machinelearning#artificial intelligence#medical diagnostics#scicomm#stem#meded#science news
54 notes
·
View notes
Text
Masterpost on Mask Efficacy Reseach in Covid-19
Sick of hearing that masks don’t work? Me too :)))) here’s some research studies showing that they do for next time Karen starts Karening.
(Correct as of August 2022)
A general respiratory viruses review (there are many more but that’s a post for another day):
A review of studies showing mask wearing prevents respiratory virus transmission including SARS, influenza, bird flu and Covid-19.
Wang et al., 2021 doi: 10.1002/mds3.10163
Animal models and masks with Covid-19
This study placed hamsters in separate cages and measured transmission of Covid-19 from an infected hamster to a healthy one. Surgical masks were shown to decrease infection rates.
Chan et al., 2020 doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa644
Mathematical models/simulations and masks with Covid-19
Mathematical modeling demonstrates mask ability to reduce transmission and mortality. It shows even masks of low efficacy can do this transmission rate is low or decreasing.
Eikenberry et al., 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.idm.2020.04.001
Mathematical modelling shows that higher quality face masks can protect the wearer from Covid-19, but two-way masking is better than one-way masking.
Bagheri et al., 2021 doi: 10.1073/pnas.2110117118
Researchers made a cough aerosol simulator to test how well different masks blocked the aerosol. N95 masks blocked 99%, surgical masks blocked 59%, cloth masks blocked 51% and face shields blocked only 2%.
Lindsly et al., 2021 doi: 10.1080/02786826.2020.1862409
Medical grade respirator masks are able to filter particles the size of Covid-19, while poorer quality masks are still able to filter larger aerosol particles which likely contain the virus.
Robinson et al., 2022 doi: 10.1080/02786826.2022.2042467
A model based on close-contact behaviour on the Subway showed that virus exposure could be reduced by 82% if all passengers wore surgical masks.
Liu et al, 2022 doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129233
Community settings and masks with Covid-19
A study looking back at 124 households in Beijing found that when one family member had Covid-19, risk of secondary infections within the household decreased by 79% if the infected member started masking before symptoms.
Wang et al., 2020 doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2020-00279
In Hong Kong, in the period studied, masking compliance was 96.6% and Covid-19 incidence was significantly lower per million people than in countries with less mask compliance.
Cheng et al., 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.04.024
A study of 211 Covid-19 cases and 839 controls in Thailand showed that consistent mask wearing was independently associated with reduced risk of Covid-19 infection.
Doung-ngern et al., 2020 doi: 10.3201/eid2611.203003
Introduction of mask mandates in states across the US was associated with a decline in Covid-19 infection growth rates.
Lyu and Wehby doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2020.00818
A randomised trial in nearly 350,000 people in Bangladesh found that mask wearing significantly reduced symptomatic Covid-19 infections.
Abaluck et al., 2021
In US counties with masking mandates, daily case incidence declined by 35% in 6 weeks compared to matched counties without masking mandates.
Huang et al., 2022 doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2021.01072
An outbreak of Covid-19 on the USS Theodore Roosevelt, which carried 382 men, showed that those that wore face coverings were 70% less likely to become infected.
Payne et al., 2020 doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6923e4
A study of mask wearing in 20 million people, alongside Covid-19 infection data from 92 regions showed that mask wearing corresponds to a 19% reduction in Covid-19 reproductive number, R.
Leech et al., 2022 doi: 10.1073/pnas.2119266119
Young children wearing masks was associated with a 13% reduction in risk of childcare program closure due to Covid-19, meaning more in-person education.
Murray et al., 2022 doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.41227
Healthcare settings and masks with Covid-19
A hospital in Massachusetts managed to decrease rates of Covid-19 infection amongst 10,000 staff with universal masking, despite increasing rates of infection in the community.
Wang et al., 2020 doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.12897
A North Carolina health provider showed that epidemiological curve of healthcare-aquired Covid-19 infections was flattened in healthcare workers following a universal masking policy. This was despite increasing community incidence.
Seidelman et al., 2020 doi: 0.1017/ice.2020.313
A study of 29 general hospitals in Israel found that hospital-acquired Covid-19 infections among healthcare workers only started to decline following a universal masking mandate for all staff, patients and visitors.
Temkin et al., 2021 doi: 10.1017/ice.2021.207.Epub
A systematic review of 13 studies in healthcare and the community found that probability of Covid-19 infection for mask wearers was 7%, compared with 52% for non-mask wearers.
Alihsan et al., 2022 doi: 10.1101/2022.07.28.22278153
Properly fitted N95 masks alongside high quality air filtration can protect from Covid-19 infection for long periods, even with high viral loads at close range.
Landry et al., 2022 doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiac195
This study shows masks were able to block the exhalation of virus particles by individuals infected by Covid-19 in Brazil.
Mello et al., 2022 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0264389
“But masks can harbour bacteria and fungi and give you pneumonia”
This is most likely referring to the study by Park et al., 2022 doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-15409-x
However, if they actually read the paper they would find that:
Most fungi found were on the outside of the mask. Most fungi were opportunistic pathogens (only a danger to immunocompromised), rather than pathogenic.
Most bacteria were non-pathogenic in humans. Of the bacteria that were potentially pathogenic, most were commensal (normally found within the body) or opportunistic (don’t cause harm unless immunocompromised).
The article does not recommend against mask use, only repeated use of the same mask in immunocompromised individuals.
The paper points out that masks reduce transmission of Covid-19.
The paper points out that pathogenic bacteria and fungi are detectable on many materials we use in daily life.
And if you’re really worried about what’s on your mask:
Masks can be sterilized with steam or hot water without compromising their efficacy.
Rahman et al., 2022 doi: 10.3390/polym14071296
“But studies show that masks don’t work”
The most commonly cited evidence of this is a Danish study on the effectiveness of adding a mask mandate.
Bundgaard et al., 2021 doi: 10.7326/M20-6817
This study found that there was no significant difference in infection rates in 4000 Danes, between those recommended masks and those not recommended masks.
However, the study has many limitations which may explain why results differ from the majority of mask studies:
Infection rates reported in the study were not comparable with rates reported in the Danish population at the time.
Fewer people were infected in the masked group, but not to a level of statistical significance. The authors state that results are inconclusive, as opposed to concluding that masks provide no protection.
Only surgical masks were given to participants, which have a limited ability to protect the wearer from airborne viruses vs aerosolised viruses due to their loose fit.
The study only assessed how effectively the masks protected the wearer, not how well it reduced transmission to others.
In the group where masks were recommended, only 46% reported wearing their masks completely as recommended. I.e. more than half of this group did not always wear a mask.
The authors themselves state that the findings should not be used to conclude that mask recommendations in the community would not be effective in controlling Covid-19 spread.
“But masks make it hard to communicate!”
Data is mixed on expression recognition, but some studies show masks have no detrimental effect. Also, context and additional non-verbal cues are often not considered in studies.
A study of children aged 7-13 found that face masks did not impair ability to infer emotions.
Ruba and Pollack, 2020 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243708
Also, clear face masks are available, including clear surgical masks and clear respirators.
“But masks reduce oxygenation”
Wearing a face mask does not cause low O2 nor high CO2 at rest or during activity.
Shein et al., 2021 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247414
Gas exchange is not significantly affected by the use of surgical mask, even in subjects with severe lung impairment.
Samannan et al., 2020 doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202007-812RL
THAT graph that anti-maskers love to show

“Fig. 3. Correlation between Infection Rate and Annual Mask Usage generated from discarded face masks. (USA: United States of America; UK: United Kingdom)”
This graph actually comes from a paper on microplastics from face mask disposal, as opposed to anything epidemiological.
Shukla et al., 2022 doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134805
This graph does not accurately show the Annual Mask Usage (AMU) of each country to an accuracy that could ever be used in a paper with an epidemiological focus.
The authors did not account for variable mask usage in different countries and they use no real world data used on this. Instead, variation in Annual Mask Usage (AMU) is estimated by considering the population of each country in rural vs urban areas, and the presumed acceptance of masks in each area, which is constant for each country (10% in rural areas vs 80% in urban). Basically, this graph shows no accurate data on mask wearing in each country.
The authors also state that there is a correlation between AMU and infection rate. However, the country with the greatest population in the world, China, counters this trend. Equally, the data for India and Brazil, which also have a large proportion of the global population, also contradict this conclusion. This would explain why the authors never attempted to provide statistical tests to prove the correlation that they have supposedly found.
I think that about sums it up, but feel free to add more!
#at some point ill get around to a post about why you should give a fuck about not getting covid in the first place#but not rn lol#masks#mask wearing#wear a mask#masks stop covid#mask research#anti maskers#mask hesitant#antimask#antimaskers#mask masterpost#masterpost#research masterpost#information masterpost#public health#pandemic#covid-19#coronavirus#sarscov2#sars-cov-2#covid pandemic#global health#long covid#psa#covid19#covid#surgical mask#ffp2#ffp3
7 notes
·
View notes
Photo

#StarWars, the #Mandalorian (Disney+) encourages others to keep their distance and never remove your mask. Be like the Mandalorian. #SARSCoV2 #Covid #N95 https://www.instagram.com/p/CnL_aEiriq7/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
2 notes
·
View notes