#ribon original
Photo

Akazukin Chacha "summer postcard" -- Ayahana Min (Ribon Original August 1993)
#ayahana min#min ayahana#akazukin chacha#ribon#ribon original#furoku#furoku: postcard#season: summer#my collection
140 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cinderella no Kaidan by Ichijou Yukari
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
How about I start the side blog with this post?
If you are a fan of Osamu Tezuka you must know that he was friends with one of the greatest Brazilian comic artists, Mauricio de Sousa.

I didn't see anywhere other than Brazilian sources commenting on this.
A few years ago MSP (Mauricio de Sousa Produções) was going to finish a story about the Amazon rainforest that Tezuka was writing but with his passing the manga is incomplete, but MSP never touched in the subject since, the project will probably never be completed, I believe it is in limbo.
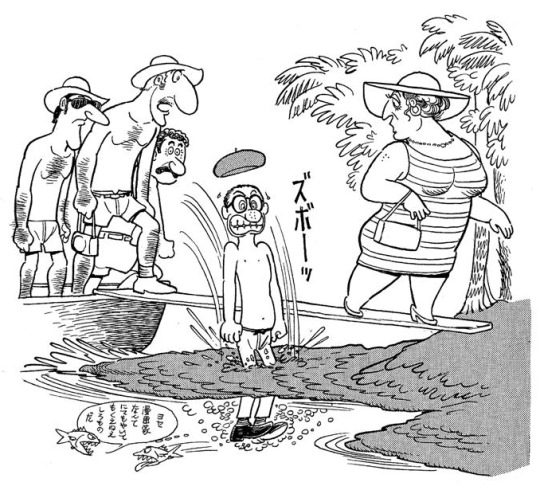

The only project with the Amazon rainforest that actually happened is the crossover between Turma da Mônica and the Tezuka characters.



The editions I have:



Source about the amazon rainforest manga: JBOX
#osamu tezuka#side blog#tezuka osamu#brazil#mauricio de sousa#amazon rainforest#Astro Boy#ribon no kishi#princess knight#uran#tetsuwan atom#A princesa e o cavaleiro#kimba the white lion#jungle taitei#kimba o leão branco#turma da monica#Turma da Monica Jovem#Osamu Tezuka X Mauricio de Sousa#Original post
38 notes
·
View notes
Text

Series: Good Morning Call
Artist: Yue Takasuka
Publication: Ribon Magazine (04/2002)
#good morning call#yue takasuka#takasuka yue#nao yoshikawa#yoshikawa nao#hisashi uehara#uehara hisashi#00s manga#shoujo manga#shoujo#manga fashion#00s aesthetic#ribon magazine#my scans#tfw I’m stupid and originally forgot to put the name of the publication
49 notes
·
View notes
Text

Baobab Studios Inks Partnership With Disney Television Animation For Young Adult Animated Series For Disney+.
Baobab Studio award winning VR studio has announced that they have inked a creative partnership with Disney Television Animation, under the partnership Baobab Studios will develop with Disney TVA upcoming young adult animated series films and specials for Disney+.
The announcement was part of the promotion of Osnat Shurer (Walt Disney Animation Studios "Moana" Franchise") as Co-Chief Creative Officer.
The upcoming animation slate at Baobab Studios which includes "The Witchverse" created by Eric Darnell (Dreamworks Animation "Madagascar" Franchise) inspired on the Baba Yaga VR short film, and "InterCats" created by Darnell and Pamela Ribon (Walt Disney Animation Studios "Moana",Anaapurna Animation "Nimona") joins Disney Television Animation's Young Adult Animated content for older audiences which includes 20th Television Animation and Disney TVA collaboration with stop-motion musical comedy "Rhona Who Lives By The River" created by Emily Kapnek (Nickelodeon Animation Studios "As Told By Ginger") with Karen Gillian (Marvel Studios "Guardians Of The Galaxy" Franchise) as EP and VA and Danny Elfman (Netflix Wednesday) as EP and songwritter & composer, "Fantasy Sports" inspired by the graphic novel series by Sam Bosma ("The Owl House", Cartoon Network Studios "Steven Universe" Franchise) with NBA LeBron James company SpringHill Media, a upcoming NDA animated musical comedy series created by Molly Knox Ostertag's (Anaapurna Animation's "Nimona", "The Owl House") and forest animated comedy "Duckie".
#Baobab Studios#The Witchverse#Witchverse#InterCats#Eric Darnell#Pamela Ribon#Disney Television Animation#Disney+#Disney Plus#Disney+ Originals#Disney Plus Originals#Disney+ Original Series#Disney Plus Original Series#Disney+ Original Animated Series#Disney Plus Original Animated Series
18 notes
·
View notes
Text




Yahoo mes petits dangos! 😚
ça fait un petit moment que je n'ai plus rien posté et je m'en excuse. J'avoue m'être plus focalisé sur mon travail ainsi que mon activité dans le cosplay dernièrement... MAIS! ça ne veux pas dire que je n'ai rien fait depuis... juste pas eu le temps de poster, hu hu 😏
Après ce ne sont pas des dessins grandioses car, je n'avais pas non plus trop le temps pour me poser chez moi au calme pour faire des choses énormes et propres... mais, ça ne saurait tardé! J'ai quelques projets en cours et je cherche aussi à m'améliorer en même temps (surtout à la tablette numérique). Et en attendant, je vais vous poster quelques gribouillages des derniers mois...
Notamment des dessins que je laissais sur l'ardoise de mon collègue de bureau pour égayer son retour au bureau 😉
Et on commence par ces trois dessins, dans l'ordre vous retrouverez :
* Ma mascotte principale Pixie
* Une de mes mascottes secondaires Ribon
* Une autre de mes mascottes secondaires Akai
* Ma version chibi pour Halloween
Sur ce, je vous dis au prochain post pour d'autres dessins (que ce soit à l'ardoise ou pas), en attendant que je progresse sur certains projets, hé hé 💖
#oc#original character#chibi art#chibi#mascot#mascotte#me#myself#halloween#pixie#ribon#akai#witch#ardoise#slate
0 notes
Text
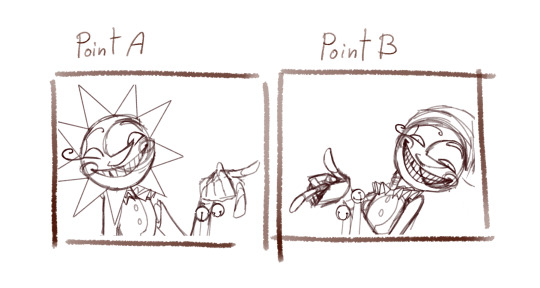
So, someone asked for a tutorial of this animation so, why not?
I need to say first that I'm not a profesional animator, I'm a selftaught artist and I'm terrible at teaching/making tutorials so maybe this isn't the best example of how to animate.
Having said that, this was my process:
I first drew the important key frames, in other words, where I wanted point A and point B to be. No details, only body and head (I have no save of the original frames but basically no bells or ribons nor ruffles)
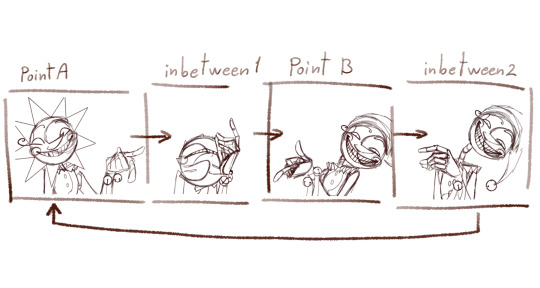
Then I needed a frame in betwen to conect them
I added a bounce effect duplicating the images, squeezing and stretching it a little (I have no save of this part but I have a video on my phone from january of last year, sorry it looks a little bad, I had to crop it)
I slowed it down so you can see the bounce

It's just like 3 frames each bounce
Now, to animate all the frames I started from A to inbetween 1,
then later to point B and closed the loop with inbetween 2.
To make this easier I drew a "rute" on the background
It looked something like this
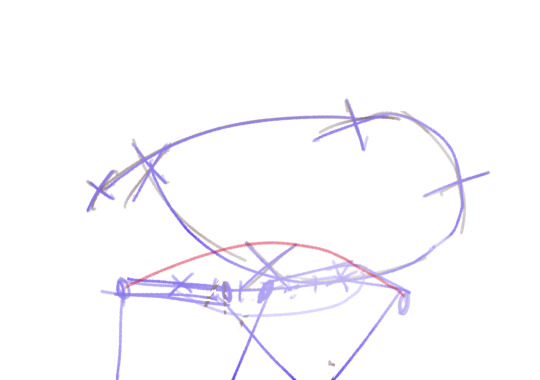
and with the animation

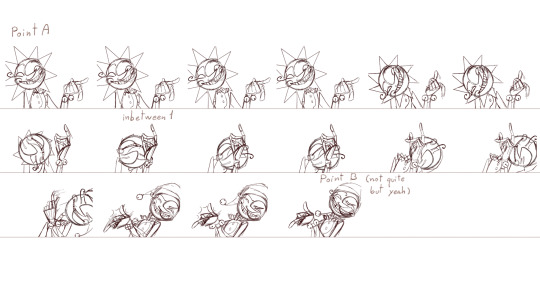
It's a process of trial and error. While you are drawing the frame you don't actually know if it's the correct pose (unless you are some kind of god), so you have to draw the inbetweens, check how it looks in movement, spot where it lack/exceeds frames or where it needs more space between frames... untile it's finished and you get something like this.

As you can see only 8/46 frames aren't drawn. These 8 frames are little "stops" for the images so the character is still.
Some of these frames has the character still but something else is moving, like Moons hat.
Finally, I got to animate the details: sunrays, hat, bells, etc. Each of these objets has its own physics and this part enters more in how I belive the physics would behave like having in mind the mass of the objet and the inertia.
Example:
The hat has a lot of inertia because fast movement so: it moves faster and it takes time to stop.
The ribons and ruffles has less inertia because even though it is still fast is a slower movement so: it moves fast BUT stops fast.
Note to add: the faster and objet moves the less frames it needs to be drawn, sometimes it may need to draw the character/object deformed to look right. The slower it moves the more frames you'll have to draw and the more precision you'll need to make it look right.
Some cursed frames:
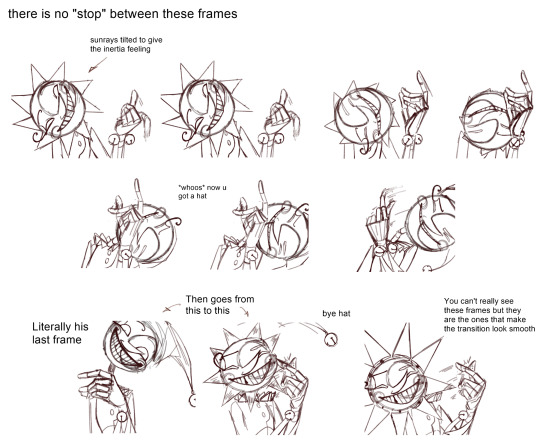
Some "still" frames:

Another note to add: this is animated at 24fps, this means every 1 second has 24 images. Most cartoons and movies are animated at 24-25 fps, this not only aplies to 2d animation but also 3d and stopmotion.
Fun fact: the human eye perceives between 30-60 fps, however animating at 30 fps or more can give an unnatural feeling to the animation.
At last, here is the animation clean up that I never finished

I added a couple of frames to make it a lil' more smooth.
Hope this crapy tutoria helped somehow.
Now I'm going to bed and hope when I see this in the morning it looks decent.
714 notes
·
View notes
Text
TMM Character Bios over All Versions
At long last, my collection of TMM bios, both transcribed and translated.
Sorted by source here.
Sorted by person here.
Collection of pictures of chara bio stickers, mostly from (expired) auction/sale listings online here.
List of sources:
Manga-related:
Manga character info page: that page that appears at the beginning of each volume of the manga. Very short. Does not change over time (with one exception), so sometimes it doesn't highlight the character's main personality trait…
Manga character info page (a La Mode): Same as above, but for a La Mode. Only appears in volume 2. (Note: Re-Turn does not have one of these)
A La Mode Intro Boxes: the little character bio charts that Berry and Tasuku get in A La Mode chapter 1
PS game manual: manual from the PS game. Contains the most direct ages for all characters and the only info on game-exclusive characters.
2002 Anime-related:
Profile stickers: square stickers with a picture of the girl on the front and a little chart of character info on the back. Comes in 2 distinct styles: One with a headshot of the character inside a heart on the front and the back printed in the character's theme color, and the other with a sparkly full-body shot + closeup of their head on the front and the back printed in red/hot pink.

2002 Anime Fanbook: artbook/fan guide for the original anime. Character pages have 2 taglines, a short bio, and a chart containing information similar to the stickers. Not well edited, so there's some inconsistent formatting/punctuation.
2002 Anime Insert from the TMM New Artbook: small section on the original anime within the New season 1 artbook. Character pages have a tagline, a short bio, and a chart containing information almost identical to the 2002 fanbook. The text for the bios are similar to the 2002 fanbook, but with more kanji and some editing for consistent style.
TMM New-related:
TMM New website character page: page on the official TMM site that has designs, birthdays, and short bios for all major characters. The one source that lists Seiji as a major character.
TMM New season 1 artbook: artbook with background information on season 1 of New. Only contains info on what appears in season 1, but the 2002 insert has spoilers for that whole series. Character pages have a tagline and a short bio which is very similar but not identical to the bio from the website.
If you want to see some of my thoughts on the info here + interesting changes/differences I noticed, that's below the cut!
It's obvious the original anime was aimed at kids and the new one is aimed at adults because sources related to the original manga and anime use lots of kana instead of kanji and have furigana on all kanji they do use. New-related sources use way more kanji and have no furigana.
Possibly related to this, older TMM stuff tends to use ミュウプロジェクト (Mew Project) vs New, which uses 「μ」プロジェクト (μ Project).
The original TMM fanbook has spotty editing which is especially visible in the charts. There's lots of small inconsistencies, like some words being spelled slightly differently (e.g., らっきょ instead of らっきょう for Pudding's least favorite food) and punctuation being inconsistent between the girls (e.g., items in lists being separated by interpuncts ・ except for Pudding's special skills, where it's inexplicably a comma 、). The biggest, most glaring issue is actually with a section I'll be posting slightly later, but I'll go ahead and list it here too: out of all official sources, the TMM Fanbook is the ONLY one who lists the Mew Mews' attacks as begining with リボン (ribon) instead of リボーン (riboon). This would be conclusive evidence in the Ribbon/Reborn debate if I didn't have the suspicion it's just a typo no one double-checked…
The stickers are in a slightly weird place continuity-wise since they have anime art on the front but refer to some manga-only information on the girls (e.g., Pudding having a pet monkey).
Speaking of the monkey, apparently at the time the stickers were coming out, Mia Ikumi had yet to finalize Annin's name, since here the monkey is called Mapo (i.e., mapo tofu)
The sticker bios have some otherwise-unseen info on character backstories: specifically, we find out that Mint's dad is a CEO and her mom runs a school, Zakuro's father is a producer and her mother is a model, and that Keiichirou is an orphan taken in by the Shiroganes at age 14. Also, apparently Ryou lives in the room above the cafe and Keiichirou lives in the secret basement.
Keiichirou seems to get way more impressive intros as time goes on. The manga bio comically undersells him, calling him "a waiter", and the PS game book only calls out his cooking skills, although Masha's bio drops the bomb that Keiichirou's the one who built him for Ryou. The 2002 fanbook mostly makes a point of how considerate he is, in contrast to the 2002 insert in the New artbook, where he's explicitly referred to as a researcher on cryptids/UMA. The New bios on the website and artbook go one step further and call him a "leading" researcher in the field!
Moe and Miwa's personalities seem to have changed or even reversed between the OG anime and New. Originally both Moe and Miwa are mostly defined by how they react to Ichigo. I.e., Ichigo says/does something weird (usually related to Mew Mew stuff or Aoyama), then Moe calls her out and Miwa either plays peacemaker or ends up joining in with Moe. So Moe snarky, Miwa gentler. New attempts to give them goals/personalities outside of this, so Moe becomes a "soothing" person with an interest in psychology and Miwa becomes a practical aspiring writer. I can only assume the writer thing is based on her writing Keiichirou a poem in the one episode where she and Moe get crushes on him and Shirogane, but I have no idea where Moe's career goal came from, much less how she became the "nice" one… I have to assume it's from her cutesy name??? Or maybe they thought that the one with blond curls looked "nicer/gentler" than the brunette with very short hair??? Weird.
The girls + Masaya (and Seiji, who is now in college so that he remains an older brother!) are aged up for New, but Ryou still seems to be the same age, which kind of makes the whole situation much funnier. Ichigo already had zero respect when he was slightly older, but now he's basically just one of her classmates. …of course, there's still room for him to be 16-17 instead of 15…
Sidenote: Ryou is consistently referred to as shonen/boy, which strikes me as funny despite making sense for his age. The narrator also doesn't respect him. Keiichirou gets seinen/young man, which trends a little older.
Ichigo gets referred to as ドジ (doji) in the '02 Fanbook which made me double-take since I'd usually associate it much more with Lettuce… I'd usually translate it to "clumsy", but in this case it's clearly going more for ditsy, flighty, disorganized, etc. so I went with "scatter-brained". The New bios do call Lettuceドジ, and I just used clumsy there.
Buling knowing kenpo/martial arts sure shows up more than I expected considering how little relevance it has to the actual show…
Zakuro, at least in the '02 anime, is supposed to be good with computers apparently! It shows up in her Fanbook bio as well as in one of the stickers (hobby: the internet). The internet being framed as a cool and mysterious thing for a smart character to know feels very 90s to early oughts, so maybe that's why it got dropped from her New characterization once everyone has smart phones… Saying someone's hobby is "the internet" reads more as neet or maybe influencer nowadays, as opposed to Cool Hacker or whatever. But I guess you could argue this is precedent for he inexplicable technological/manufacturing skills when she helps Minto make the prototype windmill thing?
In the stickers, there's a split between the Mew Mews favorite foods vs favorite sweet, but later on the sweets get lumped into favorite foods, which is how it's listed in the Fanbook and '02 Insert. But this does obscure the fact that Lettuce is the only one of them who just straight out has sweets as her favorite foods (shortcake, crepe cake), probably related to the fact that "cooking" and "making sweets" are listed as her special skills. 煮物/nimono (boiled or stewed food) is only added to her list of favorites in the Fanbook.
Weird that we never see Tasuku and Buling interact since he's explicitly compared to a monkey lmao.
#Tokyo Mew Mew#Tokyo Mew Mew a La Mode#Tokyo Mew Mew New#Ichigo Momomiya#Minto Aizawa#Retasu Midorikawa#Buling Huang#Zakuro Fujiwara#Ryou Shirogane#Keiichirou Akasaka#Masaya Aoyama#Translation#Meta#sort of
129 notes
·
View notes
Text
Shoujo Manga’s Golden Decade (Part 1)
Shoujo manga, comics for girls, played a pivotal role in shaping Japanese girls' culture, and its dynamic evolution mirrors the prevailing trends and aspirations of the era. For many, this genre peaked in the 1970s. But why?

Manga stands as one of Japan's primary cultural exports, deeply ingrained in the local culture and enjoyed by individuals of all ages and genders across various genres. Conventionally, manga is divided into two editorial segments: shonen (targeted at boys) and shoujo (targeted at girls). While shonen manga, propelled by hits like "Dragon Ball," "Slam Dunk," "Naruto," and "One Piece," has achieved global popularity, girls' comics, with their own international sensations such as "Sailor Moon," hold a crucial position in the market. The evolving landscape of girls' manga serves as a fascinating lens through which to observe the shifting fashionable aspirations and beauty ideals within Japanese society.
Shoujo manga has a rich history, dating back to the early 20th century. However, it truly gained recognition in its modern form in the late '50s and early '60s when prominent Japanese publishers introduced shoujo manga anthologies such as Kodansha's Nakayoshi and Shoujo Friend, as well as Shueisha's Ribon and Margaret. The acclaimed "godfather of manga," Osamu Tezuka, is often credited with creating the first modern shoujo, "The Princess Knight," in 1954, and the first shonen, "Astro Boy," in 1952.
A distinguishing feature of shoujo manga is that it is created by and for girls. But, in the '50s, this wasn't the case, and male artists dominated the shoujo field, which was considered an entryway to the manga business. By the 1960s, that would change as publishers recognized that women creators possessed a unique proficiency in crafting narratives centered around female experiences. Female manga-kas resonated with readers in a way that many male artists couldn't, marking a crucial shift in the landscape of shoujo manga.
The Volleyball Craze
A notable display of how shoujo could mirror societal trends unfolded in the '60s. In 1964, the Tokyo Olympics marked a new beginning for post-war Japan, and the female volleyball team, known as Toyo no Majou (the Oriental Witches), achieved stardom by clinching victory in the finals against the Soviet Republic. This triumph triggered a nationwide "volleyball boom," resonating particularly within the shoujo manga realm.
Shueisha's Ribon, historically the leader in the shoujo manga field, started publication in 1955. Still, the editorial house would only begin to make its series available in standalone tankobon format almost 15 years later through the now iconic Ribon Mascot Comics imprint. The first series to be made available by the imprint was Chikako Ide's "Viva Volleyball."
Simultaneously, over at Kodansha, Shoujo Friend was also eager to capitalize on the boom. Editors commissioned a title about the sport from illustrator Akira Mochizuki and novelist Shiro Jimbo. The final project, "Sign wa V," became a multimedia success, being quickly adapted into a live-action TV drama that achieved very high ratings.
While "Viva! Volleyball" and "Sign wa V" enjoyed success in their time, they did not etch themselves into the collective memory. The true shoujo sports manga blockbuster, a cross-generational classic universally known in Japan, is Chikako Urano's "Attack No. 1," serialized from 1968 to 1970 in Weekly Margaret.

It became the first shoujo manga title to surpass ten tankobon volumes (it had a total of 12 volumes), and it was forever immortalized thanks to its 1970 anime adaptation, which reached huge ratings on Japanese TV. Everything about "Attack No. 1" -- from the original manga to the cartoon adaptation to the anime's theme song, which sold over 700k copies as a single -- was a success.
The story of a high school girl trying to become the best player in her school, in Japan, and, eventually, in the world became a phenomenon setting the stage for the '70s "golden era of shoujo."
The Shoujo Lost Years
Until the '70s, manga carried the stigma of being a guilty pleasure, often viewed as a "poison" meant to dumb down young readers. Despite a few discerning individuals recognizing the medium's potential, manga critics, enthusiasts, and tastemakers — predominantly men — largely disregarded female-centric comics. Shoujo manga, despite its immense popularity, faced the harshest criticism.
Because society and critics downplayed shoujo, influential shoujo manga-kas from the '50s and '60s, such as Hideko Mizuno, do not enjoy the same level of recognition as their shonen counterparts from that era.

Hideko Mizuno and a page of one of her most celebrated works, "Fire."
Mizuno was one of the first women to create manga, worked as an assistant to Osamu Tezuka, and was behind several massive hits that had a significant impact on women in the '50s, '60s, and '70s. In fact, the most iconic shoujo manga-kas from the '70s golden period directly mention her as an influence. She fought to include romance -- now the essential element in girls' manga -- in her works back when such topics were deemed inappropriate by male editors.
Mizuno's repertoire was vast: she wrote mangas about little girls and their poneys, magic adventures, and romcoms based on Audrey Hepburn's movies, and she drew the first sex scene in a shoujo manga. The manga in question was "Fire," a teen-targeted manga featuring a rebellious American rocker, which broke new ground by having a male character as its focal point. Alongside other notable female artists from the '60s, Mizuno laid the groundwork for the '70s shoujo explosion, during which girls' comics took center stage.

In 1960's "Hoshi no Tategoto" (left,) Hideko Mizuno created the first shoujo love story. Serialized in Weekly Margaret between 1964 and 65, "Shiroi Troika," set during the Russian Revolution, was the first historical shoujo manga.
A contributing factor to this "golden period" was the emergence of several shoujo mangas as unstoppable hits, selling millions of copies and becoming cultural phenomena. These titles, considered masterpieces, continue to be read and known by multiple generations.
The BeruBara Boom
"Attack No. 1"'s success spread far and wide, forcing Japanese society to take note of the potential of the shoujo segment. Right after this historic success, Shueisha's Weekly Margaret hit the jackpot once again with another epoch-defining manga hit, Ryoko Ikeda's "The Rose of Versailles," which debuted in 1972. Set in the years preceding and during the French Revolution, it weaved together historical figures like Marie Antoinette and fictional ones, like the iconic Lady Oscar, a handsome noblewoman raised as a boy to succeed her father as the commander of the Royal Guard at the Palace of Versailles.

The first volume of the original comic had Marie Antoinette on the cover as Margaret's editors believed she'd be the favorite character. However, the androgynous Lady Oscar turned into a fan fave and the absolute star of the series, which is reflected on the cover of most rereleases since then, including the 2013 bunko version seen above.
When talking about shoujo manga classics from the '70s recognized by literally everyone in Japan, "Rose of Versailles" is probably the first name that comes to mind. It was a hit that really defined the era and impacted the country as a whole. While Marie Antoinette is seen around the world as a tragic, out-of-touch figure, in Japan, many women and girls see her as an aspirational historical fashion icon. While Sofia Coppola's 2006 film "Marie Antoinette" solidified this among younger generations, it was Ikeda's gentle portrait that made her a character loved by so many across all age groups.
When conceptualizing the story, Ikeda was heavily inspired by Stefan Zweig's "Marie Antoinette: The Portrait of an Average Woman," which she read while in high school. Once in college, in the late '60s, she, like millions of others, was heavily involved with the Marxist student movements. These references led to a historical romance that touched on heavy and revolutionary themes, which was atypical for a shoujo manga, a segment that, back then, was primarily catered to elementary school-aged girls.
Because of its unorthodox concept, Margaret's editors were unsure about the series. But right from the start, "BeruBara" (derived from the original Japanese title, "Berusaiyu no Bara"), serialized between 1972 and 1973, was an explosive hit, quickly turning into Weekly Margaret's most popular series. It was compiled in 10 tankobon volumes published, which sold tens of millions of copies.
In 1974, after the original manga had finished its serialization, Takarazuka Revue, an all-female theatrical troupe, announced a stage adaptation of the story.

Posters of the first three Takarazuka adaptations, from between 1974 and 1975. Since then, the Revue has adapted the manga 11 times, with a new run scheduled for 2024.
The Revue was established in 1913 by the owner of Kansai's leading railway company, Hankyu, to boost tourism to the city of Takarazuka, his line's last stop. It was a huge success, and soon, the group had its own luxurious theater as well as its very exclusive academy where young ladies underwent an arduous audition process to become Takaraziennes. In 1934, a second Takarazuka theater opened in Tokyo.
However, in the early 1970s, Takarazuka faced stagnation, with declining ticket sales attributed to the growing popularity of alternative entertainment forms such as cinema and television.
In 1973, Shinji Ueda, who had risen through the Takarazuka ranks as a director, made his debut as a playwriter in the company with a musical based on ancient Japanese history. While thinking about his next project, he decided to check out a manga popular with some Takarazuka fans, "Rose of Versailles," and he quickly realized it was the perfect theme for an adaptation. Lady Oscar, who had lady-like features but was also as handsome as a man, was the embodiment of the male role-playing Takaraziennes. Ueda reached out to Ryoko Ikeda, who, as an admirer of the troupe, quickly granted the rights.
But Ikeda and Ueda's excitement wasn't shared by many. Most of the Takarazuka team were skeptical about a play inspired by something as vulgar as a manga. Fans of the original were also highly protective of its characters and entirely against a live adaptation.
Amid this climate of distrust, the play opened at the end of August 1974 at the Takarazuka Grand Theater. The reaction after the first night was extremely positive. Soon, Takarazuka's "Rose of Versailles" was the hottest ticket in all of Japan, with the press breathlessly covering the "BeruBara boom" that led thousands of people to stand hours in line to get tickets to the coveted performances in Kansai and Tokyo. Ikeda herself was shocked by the media phenomenon when she returned from an overseas trip and had hundreds of reporters awaiting her at the airport.
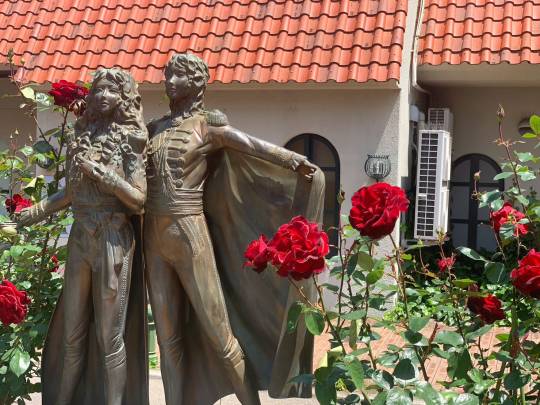
A statue of Lady Oscar and Andre surrounded by rose bushes sits outside the Takarazuka Grand Theater in Hyogo, Japan.
The "BeruBara" phenomenon single-handedly reversed Takarazuka's fortunes, leading to record-shattering ticket sales for the company. The Takarazuka Academy, which had seen declining applicants, suddenly became highly sought-after again, originating the saying "Todai in the East, Takarazuka in the West," comparing it to Tokyo University, the most prestigious university in Japan. The phrase underscored the desirability and prestige associated with a position at the troupe.
Ultimately, the success of "The Rose of Versailles" propelled Takarazuka back to the pinnacle of the entertainment industry, a position it maintains to this day. The brand continues to hold great esteem among women of all ages in Japan, with Takarazuka's stage adaptations, derived from Broadway musicals, movies, novels, and shoujo manga, consistently selling out. Notably, various adaptations of "BeruBara" have collectively sold over 5 million tickets since 1974.
Following the manga and Takarazuka adaptation's explosive success, the anime debuted in 1979. While the anime received acclaim, Ikeda herself was not entirely satisfied, mainly due to the treatment of her favorite character, Andre, who played a significant role in the manga but had a minor presence in the animated version, which focused almost entirely on the manga's most popular character, Lady Oscar.

In 2013, celebrating Margaret's 50th anniversary, new special chapters of "BeruBara" were published. The first new story in 40 years resulted in Margaret magazine selling out across the country.
"BeruBara" remains a prominent franchise in Japan, spawning numerous licensed products, sequels, and spin-offs. Ryoko Ikeda, known for other successful series, continues to garner widespread respect and media attention. However, while almost everything related to "The Rose of Versailles" turned into a hit, there was an exception.
In March 1979, a few months before the anime premiere, a live-action film adaptation debuted with great fanfare. Fittingly for such a hot property, the movie was one of the most ambitious productions in Japanese cinema, with a substantial 1 billion yen budget.
The Palace of Versailles granted permission to shoot in its interior. The film was filmed in English, with a European cast. The project was helmed by France's hottest movie director, Jacques Demy. Demy wasn't respected only in the West but also in Japan, where his two most important films, "The Umbrellas of Cherbourg" (1964) and "The Young Girls of Rochefort (1967)," were also hits. In fact, to this day, both flicks remain popular among trend-conscious Japanese as examples of stylish oshare movies that fully capture aspirational girls' culture (alongside, among others, Sofia Coppola's "Marie Antoinette"). Demy, the mind behind dreamy, girly movies, seemed like the perfect choice to turn this blockbuster shoujo classic into a live-action film.
The movie had the backing of three gigantic domestic corporations: Toho, the leading Japanese movie distributor; Nihon Terebi (NTV), one of the main TV stations; and cosmetic giant Shiseido. NTV and Shiseido made sure the movie had one of the most extensive marketing campaigns Japan had ever witnessed. The TV station aired specials and segments on this grand production. Meanwhile, Shiseido made the star of the movie -- British actress Catriona McCall, who played Oscar -- the face of its spring campaign, promoting its new Red Rose lipstick. Catriona was plastered on billboards across the country, made media and department store appearances, and starred in luxurious TV spots.

On the left, Lady Oscar and Marie Antoinette adorn the cover of Margaret in 2016, over 40 years after the end of the original serialization. On the right, Oscar models Dolce & Gabanna new collection for high-end fashion magazine Spur in 2014, celebrating 40 years of the conclusion of the original manga.
Back then, Kanebo, the second biggest local cosmetic company, was in fierce competition with Shiseido. TV ads from both companies had a tremendous impact, propelling singles to the top of the charts, and there was a battle on which commercial would feature the biggest hit. But, in the spring of 79, the focus of the fight changed. As a response to the Catriona "Rose of Versailles" campaign, Kanebo also hired a British beauty, actress Olivia Hussey, and launched a "Super Rose lipstick" with the tagline "You are more beautiful than a rose." The cosmetics war was another proof of the chokehold "The Rose of Versailles" had in the decade.
But, when the movie finally premiered, it was a flop. Critics hated it. Japanese fans thought the adaptation was weak and lacked impact. Catriona, in particular, was very criticized for not conveying Oscar's androgynous charm, which perfectly balanced masculinity and femininity. With the well-received anime premiering just a few months later, the expensive movie adaptation ended up being outshined and forgotten. It became only a costly footnote in its history.

An exhibition in Tokyo celebrates 50 years of BeruBara in 2022.
(It's worth noting that Kanebo clearly won the CM war. The "You Are More Beautiful than a Rose" song they commissioned from singer Akira Fuse became a considerable hit).
Movie aside, "The Rose of Versailles" is one of Japan's most beloved comics. From its debut in 1971 to its film and anime adaptation in 1979, it remained front and center in the country's mind throughout the whole decade. Its impact was felt in different fields, from the cosmetic business to the publishing business, from live theater to TV. It also forever changed how shoujo manga was perceived and remains one of the country's most beloved properties.
Ace-Scoring Manga
The 1970s marked a turning point for shoujo manga, as it began to gain recognition beyond its traditional audience, propelled not just by critical acclaim but by commercial success. The era witnessed the emergence of several blockbusters that captured the public's imagination. Notable among them were Yoko Shoji's "Seito Shokun," a tale centered on the daily exploits of a mischievous high-schooler, and Waki Yamato's "Haikara-san ga Toru," a love story set in the Meiji period featuring a tomboy with a lady-like demeanor. These manga were significant hits during their publication in Shoujo Friends, becoming best-selling titles.
Some shoujo classics from the '70s are still in publication today, appealing to a diverse readership spanning multiple generations. Suzue Michi's "Glass Mask," serialized in Hana to Yume since 1976, remains a cultural phenomenon with 49 tankobon volumes, over 55 million copies sold, an anime adaptation, a live-action drama, and a stage play. Similarly, Chieko Hosokawa's "Crest of the Royal Family," chronicling the adventures of a young American girl transported to ancient Egypt, has been a consistent presence in Princess magazine since 1976, boasting 69 volumes and over 45 million copies sold to date.
But, when talking about definitive shoujo classics from the '70s, titles that were historical successes, influenced everything going forward, and are known by everyone, three titles come to mind. We already explored one of these, "The Rose of Versailles." One of the other three is "Ace wo Nerae."

Following the monumental success of "Attack No. 1," the prospects of another shoujo sports manga achieving similar heights of popularity seemed improbable. However, Weekly Margaret defied expectations once more in 1973 with the release of Suzumika Yamamoto's "Ace wo Nerae" ("Aim for the Ace"), a compelling narrative focused on tennis that swiftly captured the nation's attention.
Japan and tennis already had some prior history. The first Japanese Olympic medalist was a tennis player, Ichy Kumagae, in 1920. Emperor Akihito met his commoner wife, Michiko, at a tennis match, and they initially bonded over their love for the sport. But, in the 70s, the country was taken over by an unprecedented tennis boom. At high schools across the nation, tennis became the most popular after-school activity. Fashion magazines like JJ and Popeye dedicated pages and pages to "tennis fashion." At the same time, trendy young adults decked in clothes from sports brands populated Shibuya and other stylish districts in Tokyo.
There were several contributors to the tennis boom. But the remarkable success of "Ace wo Nerae," which first conquered girls before dominating the nation, played a part in it.
The manga follows the journey of Hiromi Oka, a high school student initially plagued by insecurities but propelled into the world of tennis through the encouragement of her coach. "Ace wo Nerae" portrays her growth from a hesitant newcomer to a world-class tennis player, navigating challenges and discovering hidden potential along the way.

From left to right: Madame Butterfly, lead character Hiromi Oka and coach Jin Murakata as depicted in the anime. Madame Butterfly, a rich wealthy student who was gentle and a world-class tennis player, is a fan favorite character.
In 1973, "Ace wo Nerae" was adapted into an anime. Despite initial modest ratings, the anime gained popularity through reruns. Encouraged by this, NTV decided to remake the cartoon. The second adaptation, which debuted in 1978, was an immediate hit. Concurrently, Weekly Margaret revived the manga series, which, after being first finalized in 1975, ran again from 1978 to 1980, spanning a total of 18 volumes.
Since "Ace wo Nerae," several hit mangas focused on tennis -- both shoujo and shonen -- were published. But, thanks to the success of its anime and the intragenerational support for the manga, the original work by Suzumika Yamamoto is still considered one of the defining and most beloved works about the sport. Its role in propelling tennis culture as part of the oshare youth culture of the '70s also defines its impact.
Japan Wants Candy
Following the monumental multimedia success of "The Rose of Versailles" and "Ace wo Nerae," the third shoujo sensation of the '70s is "Candy Candy."

Initially published in Nakayoshi, the story started taking shape when editors at the magazine sought a work of literary excellence akin to beloved classics popular among girls, like "Heidi" and "Anne of Green Gables." They enlisted Keiko Nagita, writing under the pen name Kyoko Mizuki, and paired her with one of the magazine's most famous artists, Yumiko Igarashi. The collaborative effort resulted in the creation of "Candy Candy," centered around an American, blond, blue-eyed orphan named Candice "Candy" White Ardlay.
"Candy Candy" epitomized various shoujo directions prevalent in the '70s. The protagonist, a white girl with lustrous blonde hair, embodied the fascination with Western culture during a time when Japanese youth held a keen interest in Europe and the United States. The manga's narrative style, characterized by its dramatic tone and intricate plot twists, also aligned with the prevalent storytelling preferences of the era.

Candy Candy was such a resounding success that it became the first manga to achieve an initial print run of over 1 million copies of one of its paperback compilations.
Debuting in 1975, "Candy Candy" swiftly captured the hearts of Nakayoshi's readers, leading to unprecedented success. The subsequent anime adaptation by Toei in the following year propelled the franchise into the realm of a cultural phenomenon, sending manga tankobon sales skyrocketing. The seventh volume of the "Candy Candy" compiled paperback reportedly became the first Japanese manga to achieve an initial print run of over 1 million copies. Additionally, Nakayoshi's sales surged, surpassing those of Shueisha's Ribon for the first (and only) time.
The adventures of young Candy were also licensing gold. With over 100 licensed products, the "Candy Candy" doll alone sold 2 million units, solidifying Bandai's position as Japan's premier toymaker, a status it continues to uphold to this day. The resounding success of "Candy Candy" forged a lasting alliance between Kodansha's Nakayoshi, Toei Animation, and toymaker Bandai, which led to the iconic "Sailor Moon" franchise in the 1990s.
While "Candy Candy" concluded its run in 1979, its appeal extended far beyond its original target demographic, captivating kids, teenagers, and adults alike, thus contributing significantly to the manga and anime's widespread acclaim and enduring popularity.
However, a protracted legal dispute between Igarashi and Nagita has prevented the commercialization of any "Candy Candy" related products since the late 1990s, including reprints of the manga and re-broadcasting of the anime. The lawsuit arose from Igarashi's unauthorized licensing of merchandise based on the franchise, falsely asserting sole ownership of the copyright. Although Igarashi was initially credited as the lead artist in Nakayoshi during the manga's publication, the court ultimately ruled in Nagita's favor, emphasizing that Igarashi's artistic foundation was built upon Nagita's written work.

A collection of "Candy Candy" freebies offered by Nakayoshi magazine in the '70s. During the publication of the series, Nakayoshi would eclipse Ribon's sales for the one and only time in its history, (image credit)
Consequently, any commercial exploitation of Yumiko Igarashi's "Candy Candy" artwork necessitates the approval of both Igarashi and Nagita, a challenging prospect given the existing feud. Nagita, on the other hand, can profit from "Candy Candy" as long as she doesn't include any illustrations, which allowed her to release a book sequel in 2010. However, due to the dispute, one of the most beloved works in Japanese manga history is currently out of print. The lawsuit also blocks the anime from being aired or distributed. But, despite the almost two-decades-long media ban, "Candy Candy" remains widely known and beloved across Japan, a testament to its staying power.
While smash hits like "Candy Candy," "Ace wo Nerae," "Rose of Versailles," "Seito Shokun," "Hikara-san ga Tooru," and "Glass Mask," among others were key pieces into shoujo finally earning the respect it deserved, the rise of a revolutionary group of artists during the '70s was another critical element in shoujo's rise: the Year of 24 Group.
Part 2
#1970s japan#1970s#vintage shoujo#shoujo manga#lady oscar#rose of versailles#ace wo nerae#candy candy
41 notes
·
View notes
Text



From now until April 2nd 2023 Fujii Mihona will be selling a variety of things on her BOOTH page as part of the virtual event, NEOKET4. Featured in this pretty solid line up are a variety of physical items from GALS!! and Ryuu-ou Mahoujin such as mirrors, acrylic keyholders, acrylic stands, t-shirts, can badges, tapestries, pillows, and more (including an umbrella which sold out almost instantly).
Now this brings us to the digital works Fujii-sensei is releasing;
An original GALS!! anthology (which is more like a one-shot)
A Ryuu-ou Mahoujin prologue which begins the Chi no Maki arc (with the series gaining an "official" English-language name for the first time, Magic Circle of the Dragon Kings).
Interestingly the description for the GALS!! anthology states in English that it will be receiving an English translation in the future with news to come so stay tuned, I guess!
At this stage there are no plans to release these digital works in a physical form, but if these plans change they will be announced through Fujii's official channels.
All NEOKET4 releases from Fujii Mihona's "Studio Mihonacchi" circle are available for a limited time only, with sales ending April 2nd, so please get in quick if you'd like to order (I think at this point it's way too late to bother saying she was manning her own digital stall this evening, as it's all over... but she was at one point which is awesome).
I had already ordered the one thing I definitely had to buy from this event, which was the Rino acrylic stand (I have a soft spot for Ryuu-ou Mahoujin) but I'll probably also get the digital manga as I really want to check out Ran with dark hair in the GALS!! anthology and omg am I ever keen to read more Ryuu-ou Mahoujin.
Anyway I don't have a lot of insight on this event or these items on a Friday night, I just thought I should give them a quick shout-out because I am always down for a popular 90s Ribon artist to make some noise on Pixiv/BOOTH!
#gals!#gals#gals!!#chou gals kotobuki ran#super gals#ryuuou mahoujin#magic circle of the dragon kings#fujii mihona#mihona fujii#manga news#shoujo manga#merch#merchandise#i absolutely love the cover of the anthology#the fruit pics are just too darn cute#i wish i could justify owning the lil mirrors#but i would 100% break them within 5 minutes of getting them#and i think the ran stand is cute but i cannot justify 6k yen on a stand#it took a couple of days for me to even psych myself up to spend 3k yen on the rino one#and i adore her#so#anyway zzzz#enjoy#go shop if you like this stuff and can afford it#you're supporting releases directly from fujii mihona herself which is a cool thing to do
117 notes
·
View notes
Text
Phantom Thieves, Magical Idols, and Strong Heroines: The Legacy of Tanemura Arina

Shoujo manga artist Tanemura Arina might be best known for magical girl stories, but that wasn’t her original plan. In the chat column for her manga Full Moon O Sagashite, she mentions, “I’ve always wanted to draw an ordinary story. When I made my debut, I didn’t intend to draw fantasies at all.” However, no matter her early plans, the author, illustrator, and character designer has created some of manga’s best-loved shoujo works by combining the aesthetics of fantasy aimed at young girls with complex themes.
Tanemura began her manga career at the young age of 18 in 1996 when her short story “Niban Me no Koi no Katachi” debuted in Ribon Original magazine. Her early one-shots garnered a lot of praise, and she received about 500 fan letters after her first publication. Tanemura channeled the thoughts and feelings she had gone through fairly recently as an adolescent into stories her young readers could relate to, and described herself as “a delinquent student who would work on manuscripts during class.”
One year later, she released her first series, I.O.N. The story follows Tsuburagi Ion, who has always recited the letters of her first name for luck and one day finds the letters activate her telekinesis. I.O.N. established many of the hallmarks of Tanemura’s work: complicated love triangles; girls who encounter a magical element in their lives; and a tragedy they need to overcome, leading to acceptance and self-actualization.
Read it at Anime Feminist!
#arina tanemura#full moon o sagashite#idol dreams#i.o.n#phantom thief jeanne#kamikaze kaitou jeanne#articles
41 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Marmalade Boy "summer postcard" -- Yoshizumi Wataru (Ribon Original August 1993)
#marmalade boy#yoshizumi wataru#Wataru Yoshizumi#ribon#ribon original#furoku#furoku: postcard#season: summer#my collection
51 notes
·
View notes
Text





Penguin Brothers by Shiina Ayumi
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Rurouni Kenshin Original Soundtrack Vol.1
Track No.12 - Aiiro no Ribon
#るろうに剣心#rurouni kenshin#ruroken#samurai x#kenkao#kenshin x kaoru#himura kenshin#kenshin himura#kamiya kaoru#kaoru kamiya#himura kaoru#kaoru himura#anime couple#manga couple#anime ost#anime#manga#my bias#my otp#my edit
19 notes
·
View notes
Text

Majo wa Koi ni Hen Shiteru art piece illustrated by series mangaka, Eri Kumaki. Included within a notebook taken from Monthly MonMon Magazine.
#majo wa koi ni hen shiteru#魔女は恋にヘンしてる#eri kumaki#kumaki eri#ruby#00s manga#shoujo manga#shoujo#magical girl manga#magical girls#mahou shoujo manga#mahou shoujo#mahoucore#kawaii#my scans#so i bought this lot of furoku on Mercari and this notebook came with it#turns out they were all from a chinese magazine!#it features a lot of japanese shoujo manga but also features original chinese works as well#it actually features a mix of works originally featured in ciao and ribon magazine#but I think all of the Japanese works featured within are from shogakukan publishing#i may have butchered the name of the magazine#i hope not#anyway this artwork is rare and info in this series is sparse in english so i thought it would be cool to share
80 notes
·
View notes
Text
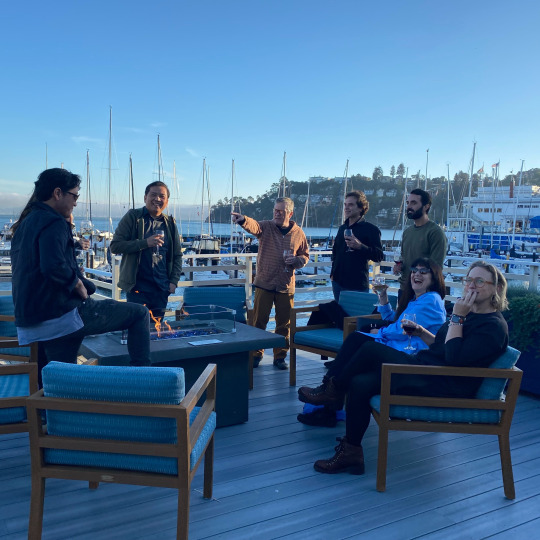


Rhona, Wiz, Lunella and Magda will give you the angst and drama but the InterCats will give you the laughs. The team at Baobab Studios had a blast this week at an offsite as they continue to develop our 'Intercats' series! 😼
InterCats coming soon to Disney+! 🐈 📽️ 🛜
#InterCats#Eric Darnell#Pamela Ribon#Baobab Studios#Disney+#Disney Plus#Disney+ Originals#Disney Plus Originals#Disney+ Original Series#Disney Plus Original Series#Disney+ Original Animated Series#Disney Plus Original Animated Series
13 notes
·
View notes