#receptors
Text
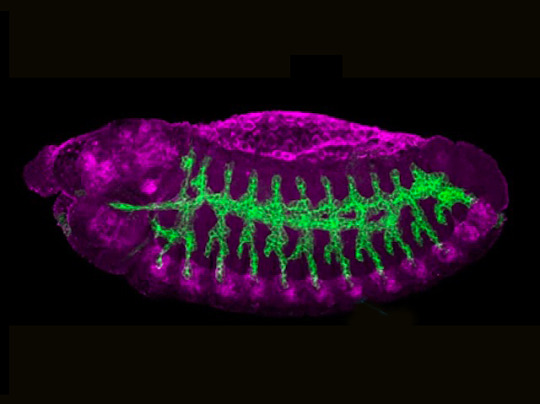
Unconventional Discovery
Greater understanding of how cell molecules interact – the conjunction of ligands and their receptors – to bring about activation of their function. This study in fruit flies reveals an unconventional mechanism for TNF receptor binding its ligands
Read the published research paper here
Image from work by Annalisa Letizia and colleagues
Department of Cells and Tissues. Institut de Biologia Molecular de Barcelona, IBMB-CSIC. Parc Científic de Barcelona, Baldiri Reixac, Barcelona, Spain
Image originally published with a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0)
Published in Nature Communications, September 2023
You can also follow BPoD on Instagram, Twitter and Facebook
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Nicotonic vs Muscarinic Receptors
Nicotinic = ionotropic
Muscarinic = Metabotropic
just think nicotinic is used where speed is crucial, like the neuromuscular junction.
Muscarinic will be found where amplification is important, like sweat glands and a lot of CNS applications. Also know that CNS also has nicotinic, which is why people use tobacco
(think about the SPEED of the tobacco high and how fast it hits 🚬💨)

17 notes
·
View notes
Text
0 notes
Text
The Role of Iron in pathogenic gram- negative bacteria; Neisseria meningitidis
Iron is essential for pathogenic growth and colonisation. Hence, it plays an important role in infections caused by bacteria. Pathogens such as bacteria isolate iron from the host through various molecules and receptors, allowing the bacteria to survive the host’s immune responses and defense mechanisms. Which the growth, replication, metabolism, and virulence of the pathogen. Due to…

View On WordPress
#Bacteria#gram-negative#infection#iron#Neisseria meningitidis#receptors#sciencearticle#scienceresearch
0 notes
Text
Hangovers and headache: a tale of receptors, mast(er) cells and neurochemical agreements
Alcohol addiction affects 283 million people globally. Crises such as terrorism, economic hardships and the coronavirus pandemic heighten alcohol intake and risky behaviors. Rehabilitation is pivotal; however, withdrawal headaches often limit recovery by driving many back to drinking. This exacerbates the addiction cycle and degrades life quality. Further research is needed, considering rising…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
How to sleep well and how to stay awake longer when awake
Our capacity for concentration, alertness, and emotional stability is reset by sleep. Consequently, it is of utmost significance.
When we are awake, what we do affects how quickly we fall asleep, whether we stay asleep or not, and how we feel when we get up the next day. Therefore, obtaining a truly good night's sleep every night is crucial.
Our neurological system and body produce more adenosine the more time we spend being awake. It induces something like a sleep urge or a hunger. Adenosine keeps progressively increasing the longer we have been awake, which is why we feel drowsy.
Adenosine is similar to caffeine. Caffeine suppresses the receptor for sleepiness when it is consumed because it binds to the adenosine receptor. Adenosine will attach to that one receptor once the caffeine wears off, causing a crash and increased fatigue (tiredness).
While caffeine can be beneficial for some people, it can also pose health risks for others. Dopamine is a neuromodulator that caffeine enhances. Dopamine is related to the neuromodulator epinephrine, which is produced from dopamine, and it tends to make us feel pleasant, driven, and energetic.
Adenosine, which is produced naturally, is what causes sleepiness. Caffeine blocks the receptor that gives us energy and raises dopamine, preventing adenosine from having its effect of making us feel drowsy. We feel more hungry when adenosine levels are high, and we don't feel hungry when adenosine levels are low.
There is a second force, known as the circadian force, that controls when we are asleep and are awake. However, light has the most influence over when we desire to sleep and wake up.
A molecule called hormone is released from one organ in the body and travels to other parts of the body, including the neurological system, where it works on other organs.
Due to the presence of the hormone cortisol in the adrenal glands, we wake up in the morning. We feel awake because of a pulse of epinephrine (adrenaline) coming from our adrenal glands and our brain. It has a tendency to alert the body's entire system. This pulse should only happen throughout the day, not in the night.
The morning is when that cortisol pulse starts to increase in intensity. Additionally, a clock is set in our bodies and nervous systems that determines when a different hormone called melatonin, which make us feel sleepy, will be released from a specific region of the brain, the pineal gland, roughly 12 to 14 hours later. There are therefore two signals: a wakefulness signal that starts the timer for the second signal, sleepy signal, and two signals altogether.
Additionally, melatonin delays the start of puberty. Melatonin releases chronically in newborns, suppressing the other brain chemicals. We tend to exit puberty about the time that we start producing melatonin at night.
One thing to bear in mind is that melatonin only aids in sleep onset; it has no effect on sleep maintenance.
Cortisol and melatonin are constantly in rhythm with one another. When that cortisol will start to rise depends on a certain factor affecting our nerve system.
As soon as we open our eyes in the morning, light enters. We have retinal ganglion cells in our eyes, known as brain neurons, that detect a certain sort of light and interact with the superchiasmatic nucleus, a clock that is located directly over the roof of our mouth and that connects to basically every cell and organ in our body.
Our body's internal clock (neurons) reacts to the specific type and quantity of light that comes from sunlight.
There will be extremely wide-ranging and detrimental impacts on cardiovascular health, dementia, metabolic effects, learning, depression, and many other things if cortisol and melatonin do not function effectively as needed.
Many anxiety and depression problems could also be brought on by a late cortisol level increase.
We should go outside and spend some time in the sun to set the circadian clock so that there is plenty of blue and yellow light hitting the retina early in the day. Artificial blue lights will work best for setting this mechanism if there are heavier dark clouds. Additionally, as blue light suppresses melatonin throughout the day, we should wear blue light blocking eyewear at night.
Sunlight prevents the pineal gland from releasing melatonin. darkness allows the pineal to release melatonin. So, we should get up, go outside and get that sunlight for at least 5 to 10 minutes on a regular basis.
We don't need to see or perceive the sun for this mechanism to function; rather, it is a subconscious process by which certain neurons, known as melanopsinganglion cells, set our central clocks by becoming activated by a specific wavelength of light that is present in the atmosphere.
Therefore, it is essential to view light in the morning, ideally sunlight, in order to create good sleep-wake rhythms and enable us to sleep well at night.
The timing of food intake, timing of exercise, and numerous pharmaceuticals and substances that one might ingest are the other factors besides light, but the light is the sole direct input to the clock.
Another structure, the intergeniculate leaflet, is located a few millimeters distant in the brain and is important in controlling the clock output during that are known as non-photic, non-light type impacts, such as exercises, feeding, and other similar activities.
According to a study, watching sunlight around the time of sunset mitigates some of the negative effects of light by delaying the release of melatonin later that evening.
Our retina and those cells become more sensitive to light the longer we have been awake.
Between 11 pm and 4 am, roughly, light enters the eyes and decreases the release of dopamine, which can impede learning and have a variety of other negative effects.
Controlling our nighttime light exposure behavior and avoiding excessive or strong light exposure in the middle of the night is one method we can support our mechanisms for good mood, mental health, learning focus, metabolism, etc.
Since most of these cells are located in the bottom half of our retina, they are observing the area around us that is visible from above. Therefore, we ought to maintain the light source nearby, either on the ground or a desk. The optimum lighting will be low-level, dim lighting because it won't excite neurons, which would change the circadian rhythm. Candlelight, campfires, and fireplaces are acceptable, and the environment can also have low lighting.
The overall amount of time spent sleeping and the time when we feel drowsy are both advanced if we switch on the lights before waking up. We want to go to bed earlier every night because of that.
Many people take afternoon naps to rest their bodies, which can be beneficial to some people but detrimental to others.
Instead of taking a nap, we can practice yog nidra, which enables us to intentionally put our body and mind into a deep state of relaxation. Depending on the practice, we may or may not fall asleep. This is carried out for periods of 10 to 30 or even 60 minutes.
It includes pausing for 10 to 30 minutes while listening to a script, and it has to do with specific breathing patterns that can significantly aid people in learning to relax in order to go asleep. It's a method of self-training that enable us to get our nerve systems to shift from the state of heightened alertness to the condition of heightened relaxation that we desire.
Dopamine and other neuromodulators can reset themselves through yoga nidra and meditation, which enhances our sleep.
#health#sleep#hormones#adenosine#dopamine#serotonin#sleepiness#caffeine#epinephrine#receptors#cortisol#pineal gland#melatonin#healthybody#cells#retina#sunlight#bluelight#subconscious#consciousness#neurons#metabolism#environment#meditation#mindset#overall health#relaxation
0 notes
Text
The Endocannabinoid System: Exploring the CB1 and CB2 Receptors
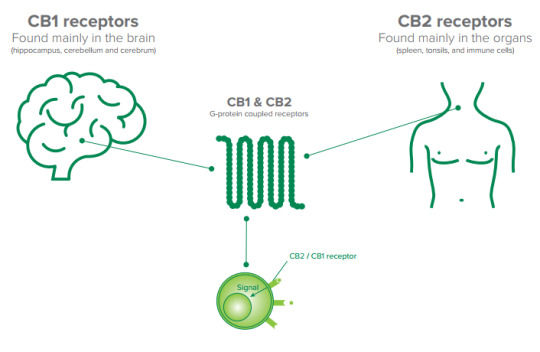
Introduction
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex network of receptors and neurotransmitters that plays a crucial role in maintaining physiological stability, also known as homeostasis. Two primary subtypes of cannabinoid receptors within the ECS are CB1 and CB2. These receptors are distributed throughout the central nervous and immune systems, and their discovery has revolutionised our understanding of how the body functions.
Discovery of Endocannabinoids
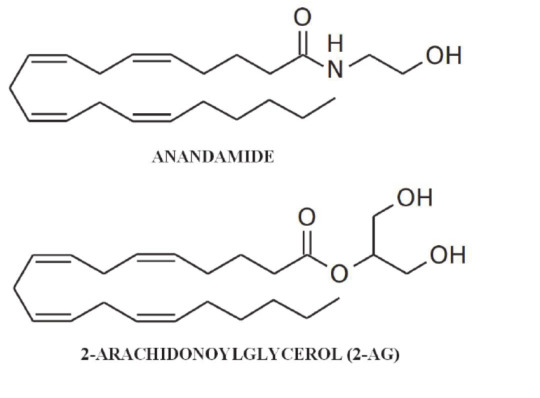
Following the identification of cannabinoid receptors, scientists embarked on a quest to uncover the substances produced naturally within the body that bind to these receptors. In the early 1990s, this pursuit led to the discovery of the first endocannabinoids, anandamide and 2-AG. Since then, three additional endocannabinoids have been isolated. These endocannabinoids, being fats, are not water-soluble, which limits their ability to efficiently move through the body. As a result, they primarily function locally.
Local Activity and Synaptic Function
One important local activity of endocannabinoids occurs when they act as the primary messengers across synapses, the gaps between nerve cells. By signalling neurons to communicate with each other through the release of neurotransmitters, endocannabinoids play a vital role in modulating the flow of neurotransmitters. This modulation ensures the smooth functioning of our nervous system. Recent research has revealed that the role of endocannabinoids in synaptic function is more significant and complex than previously believed.
Homeostasis and Disease
Endocannabinoids are produced on demand, released back across the synapse, and rapidly metabolised within cells. They are closely associated with the concept of homeostasis, helping to restore specific imbalances caused by disease or injury. The role of endocannabinoids in pain signaling has led researchers to hypothesize that their levels may be responsible for the baseline of pain throughout the body. This hypothesis opens up possibilities for using cannabinoid-based medicines in the treatment of conditions such as fibromyalgia. Furthermore, the continuous release of endocannabinoids by the body may have a "tonic" effect on muscle tightness in multiple sclerosis, neuropathic pain, inflammation, and even baseline appetite.
CB1 Receptors: The Brain's Circuit Breaker
The CB1 receptor is widely expressed throughout the brain, forming a crucial component of the ECS. When endocannabinoids bind to CB1 receptors, they act as a "circuit breaker," modulating the release of neurotransmitters. The impact of the endocannabinoid system on brain function is vast and encompasses various regions. However, it is worth noting that the brain stem, responsible for vital functions like respiration and circulation, has relatively few CB1 receptors. This scarcity explains why cannabis overdoses are not fatal. Activation of the CB1 receptor is primarily responsible for the psychoactive effects associated with cannabis consumption.
CB2 Receptors: Guardians of Immune Function
In contrast to CB1 activation, which elicits psychological and physical effects, CB2 receptor activation does not produce these effects. CB2 receptors are primarily found in blood cells, tonsils, and the spleen. From these locations, CB2 receptors regulate the release of cytokines associated with inflammation and general immune function throughout the body. Understanding the role of CB2 receptors provides insights into how the ECS influences immune responses and offers potential avenues for therapeutic interventions targeting inflammation-related disorders.
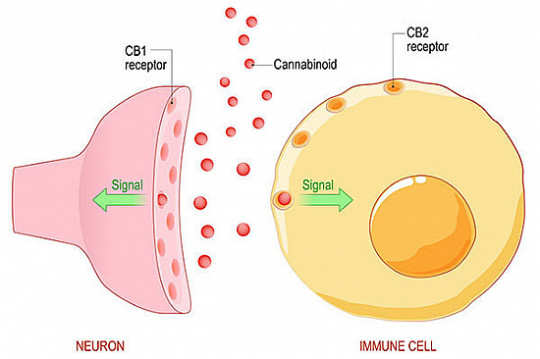
Conclusion
The discovery of the CB1 and CB2 receptors within the endocannabinoid system has unveiled a fascinating network that regulates numerous physiological processes. From modulating neurotransmitter release in the brain to controlling immune responses throughout the body, the ECS plays a vital role in maintaining homeostasis. Further research into the endocannabinoid system and its receptors will undoubtedly shed more light on their intricate functions and pave the way for novel therapeutic approaches.
#endocannabinoidsystem#endocannabinoids#receptors#health#cbd#cbdhealth#cbdoil#feelgreatagain#budandtender
0 notes
Text
Upon binding to IDA, the HAE/HSL2 receptor complex is thought to trigger the MAPK cascade, which leads to the transcriptional activation of genes encoding cell wall loosening enzymes, cell expansion, and cell separation (Figure 22.25).
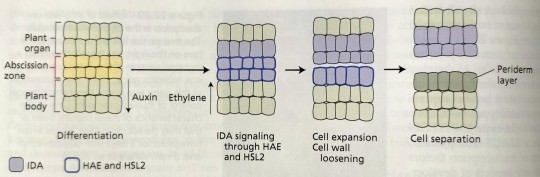

"Plant Physiology and Development" int'l 6e - Taiz, L., Zeiger, E., Møller, I.M., Murphy, A.
#book quotes#plant physiology and development#nonfiction#textbook#ida#hae#hsl2#inflorescence deficient in abscission#haesa#haesa like#kinases#plant cells#receptors#mapk#mitogen activated protein kinase#transcriptional activity#cell wall#cell expansion#cell separation#enzymes#periderm#cell differentiation
0 notes
Text
Rhamnetin decreases the expression of HMG-CoA reductase gene and increases LDL receptor in HepG2 cells
Image: Flickr
Article published in J. Pharm. Pharmacogn. Res., vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 47-54, January-February 2023.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.56499/jppres22.1507_11.1.47
Raghad R. Al-Yousef1, Manal M. Abbas1,2, Razan Obeidat2, Manal A. Abbas1,2*
1Faculty of Allied Medical Sciences, Al-Ahliyya Amman University, Amman 19328, Jordan.
2Pharmacological and Diagnostic Research Center, Al-Ahliyya Amman…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Receptors often do this by modifying the activity of other proteins or by employing intracellular signaling molecules called second messengers; these molecules then alter cellular processes such as gene transcription.
"Plant Physiology and Development" int'l 6e - Taiz, L., Zeiger, E., Møller, I.M., Murphy, A.
#book quote#plant physiology and development#nonfiction#textbook#receptors#proteins#modification#alteration#intracellular#signal molecule#cellular processes#plant cells#gene transcription
0 notes
Video
youtube
one of my favorite early chiptunes
0 notes
Audio
Silicon Scally / Receptors
0 notes
Text
Blonde teen amateur public and horny girl The Suspended Step Sis
Horny Lily Masturbating While Bathing In Shower
Hotwife getting fucked by her bull while the cuck hubby records
BBC FUCKING creamy pussy DoggyStyle & Rides For Dripping Creampie
Virtual Reality Jenna Foxx Fucks So Real
Cock sucking ebony amateur teen gets horny
Hot ladyboy masturbating on LadyboyCamTV
Sex out doors moving gay porn xxx Cute Guy Gets His Juicy Man Ass
Que Bunda Novinha
Delivering backshots in Htown
#unmoist#semipedantic#receptors#tornado-haunted#fixatives#beaming#mezzos#stylostixis#atv#essentialities#storing#boosted#disableness#Namibia#Catonic#marionettes#unobligating#vernicle#Riparii#emydes
0 notes
Text
Krang infection 43
PREV
Masterpost
NEXT





#rottmnt#krang infection comic#rise of the teenage mutant ninja turtles#rottmnt donnie#rise of the tmnt#rottmnt leo#my art#rottmnt mikey#rottmnt raph#rottmnt casey junior#cw implied brain surgery#krangified donnie#did you know you didn’t have pain receptors in your brain?
3K notes
·
View notes
