#openaccess
Text

Arthritic diseases are a group of conditions that cause inflammation and pain in the joints. The most common types of arthritic diseases are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
2. Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that is caused by the breakdown of cartilage in the joints. Cartilage is a soft tissue that cushions the ends of bones in a joint.
Visit: https://symbiosisonlinepublishing.com/rheumatology-arthritic-diseases/
#rheumatology#Rheumatoid#rheumatoidarthritisproblems#arthritis#arthritisawareness#arthritispain#arthritisrelief#pathophysiology#PainManagement#osteoarthritis#osteoporosis#rheumatoidarthritis#lupus#gout#jointpain#RheumaticHeartDisease#journals#journal#publicjournal#openaccess#openaccessjournal#pubmed#peerreviewed#peerreview#symbiosisonlinepublishing
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

𝐋𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐬𝐭 𝐫𝐞𝐯𝐢𝐞𝐰 𝐛𝐲 𝐊𝐚𝐫𝐠𝐛𝐨 𝐑𝐁, 𝐞𝐱𝐩𝐥𝐨𝐫𝐞𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐩𝐨𝐭𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐢𝐚𝐥 𝐨𝐟 𝐩𝐬𝐲𝐜𝐡𝐞𝐝𝐞𝐥𝐢𝐜-𝐚𝐬𝐬𝐢𝐬𝐭𝐞𝐝 𝐭𝐡𝐞𝐫𝐚𝐩𝐲 𝐢𝐧 𝐭𝐫𝐞𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐚𝐥 𝐡𝐞𝐚𝐥𝐭𝐡 𝐝𝐢𝐬𝐨𝐫𝐝𝐞𝐫𝐬
#mentalhealth#menshealthmonth#heraldscholarlyopenaccess#heraldopenaccess#openaccess#mentalillness#mental therapy#therapy#mental health#neurology
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

#InternetArchive#digitallibrary#WaybackMachine#books#movies#music#software#preservation#openaccess#knowledge#history#research#substack#substackinc#madscientistwriting
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
firefox
Finally making the transition to firefox.
Help a girl out, other than unpaywall what are some of the other add-ons that can help skip over paywalls on news sites or for research articles
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Exercise and EEG

Our paper titled ‘Effects of Exercise on Electroencephalography-Recorded Neural Oscillations: A Systematic Review’ is available on a gold open-access basis from ‘International Review of Sport and Exercise Psychology’ (IRSEP).
In Figure 1, you can see the exercise modalities that were featured in this systematic review, which was first-authored by Leti Hosang.
Gold open access from: https://tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/1750984X.2022.2103841
#electroencephalography#eeg#neurophysiology#psychophysiology#neuroscience#brain#science#exercise#exercisescience#research#review#systematicreview#article#publication#openaccess#irsep
0 notes
Text

dayitwa.com
"Dayitwa Education for Social Bookmarking is a pioneering initiative aimed at harnessing the power of social bookmarking to revolutionize education and foster social change. Through Dayitwa, individuals and communities are provided with a platform to curate and share educational resources, ranging from articles and videos to academic papers and online courses. By leveraging the collective intelligence of users, Dayitwa promotes collaboration, knowledge sharing, and continuous learning.
#EducationForAll#CommunityLearning#DigitalLiteracy#OnlineCourses#STEMEducation#SocialJustice#LifelongLearning#OpenAccess#InclusiveEducation#GlobalCitizenship#EnvironmentalEducation#EmpowermentThroughKnowledge#CulturalHeritage#WellnessEducation#EntrepreneurshipSkills#CriticalThinking#DigitalSkills#21stCenturySkills
1 note
·
View note
Text

Celebrate National First Generation College Day! This book is an open access (freely available) collection of useful info for first-gen students in US colleges and universities. Search SouthernSearch for the title: Bridges: United States Academic for First-Generation and International College Students or go direct to https://directory.doabooks.org/handle/20.500.12854/42470
0 notes
Text
Setkání na téma Open Science v Národní technické knihovně
Na začátku června se v Národní technické knihovně konala první česká událost s názvem „National EOSC Tripartite Event“ následovaná Národním dnem otevřené vědy. Obě akce měly za cíl přivést k jednomu stolu všechny zúčastněné strany a poskytnout jim aktuální informace o evropské politice v oblasti otevřené vědy a stavu implementace EOSC v České republice.
V rámci příkladů dobré praxe na akci vystoupila také ředitelka Nakladatelství Munipress Alena Mizerová, která prezentovala aktivity Masarykovy univerzity v oblasti Diamond Open Access.
Otevřený přístup k vědeckým publikacím (Open Access) je totiž jedním z pilířů otevřené vědy, takže téma Open Access v Česku nemohlo chybět. Z našeho pohledu se bohužel přehnaně zdůrazňovaly tzv. transformační dohody (transformative agreements), které jsou bezesporu významné a aktuální, diskuzi kolem Open Access však nelze redukovat jen na ně. (Více o tomto tématu v některém z dalších příspěvků.)
Od roku 2020 se mluví o přístupu Diamond Open Access, což je model vědeckého publikování, v němž časopisy nevybírají poplatky ani od autorů, ani od ��tenářů (více např. zde). Právě tento způsob se ukazuje jako nosný pro ideály open science a získává si větší a větší podporu v rámci Evropy (viz nedávné rozhodnutí Rady EU o otevřeném vědeckém publikování).
Masarykova univerzita vydává 45 „diamantových open access“ časopisů, z nichž mnohé mají velmi dobrou pověst a jsou indexovány předními vědeckými platformami. Z diskuze, která se na toto téma rozvinula, vyplynulo, že by bylo velmi vhodné „diamantový“ přístup podporovat i v Česku, ale chybí data o financování těchto časopisů. Munipress se v tomto ohledu rozhodl hozenou rukavici zdvihnout, spojit síly s dalšími českými vydavateli „diamatových“ odborných časopisů a chybějící data poskytnout. Věříme, že to bude další krok na cestě nejen k uznání, ale také k podpoře Diamond Open Access přístupu v České republice.
0 notes
Photo

🖤🧡❤️💛➡️ 3rd Rail Print @3rdrailprintspace Last Saturday workshop was real fun! It was such a lovely group. Thanks to everyone that came and spent the day printing t-shirts with us. If you are interested in learning screen printing, check our beginners workshop on out website! You can choose in between paper, fabric and tshirt. NEXT T SHIRT WORKSHOP:20TH OF MAY #openaccess #artstudio #printmakingstudio #screenprintingstudio #printmaking #print #screenprinting #screenprint #fabricprinting #paperprinting #workshop #printingworkshop #screenprintingworkshop (at 3rd Rail Print Space) https://www.instagram.com/p/Crdu0NwIn7Y/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
#openaccess#artstudio#printmakingstudio#screenprintingstudio#printmaking#print#screenprinting#screenprint#fabricprinting#paperprinting#workshop#printingworkshop#screenprintingworkshop
0 notes
Photo

Happy National Freedom of Information Day! 🎉📚💡 On this important day, we recognize the essential role of access to information in promoting transparency, accountability, and good governance. Let's celebrate the power of knowledge and the importance of free and open access to information. Together, let's continue to protect and defend the right to know, and uphold the principles of democracy and freedom. We are committed to promoting transparency and accountability in all that we do. Join us in championing the cause of freedom of information and making the world a more informed and just place.
1 note
·
View note
Text

Some of the most common neurological disorders include:
Stroke: A stroke is a sudden loss of brain function caused by a blood clot or bleeding in the brain.
Multiple sclerosis: Multiple sclerosis is a chronic disease that affects the central nervous system. It is characterized by inflammation and damage to the myelin sheath, which is a protective layer that surrounds nerve fibers.
Visit: https://symbiosisonlinepublishing.com/neurology/
#symbiosisonlinepublishing#researchstudy#research#openaccess#peerreview#pubmed#journal#journals#trypanosomiasis#encephalitis#meningitis#myastheniagravis#myopathies#melancholy#bipolardisorder#parkinsonsresearch#parkinsons#parkinsonsdisease#alzheimers#Schizophrenia#epilepsy#spinalcord#centralnervoussystem#peripheralnervoussystem#peripheralneuropathy#neurologicaldisease#neurologia#neurologicaldisorder#neurologist#neurological
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Journal of Reproductive Medicine, Gynaecology and Obstetrics (ISSN: 2574-2574) Issue released with "6" articles. Online now!
Impact factor - 1.44*.
Read, Follow & Share:
#heraldopenaccess#openaccess#reproductivemedicine#reproducción#gynaecology#obstetrics#journal#viral trends#top trends#tumblr trends#trending#trendingnow#viral online#viral on social media
0 notes
Text
Lupine Publishers | Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy our Technique Description
Abstract
Objective: To describe step-by-step technique in Robot Assisted Radical Prostatectomy of our transperitoneal posterioranterior technique for prostatic dissection with preservation of the endopelvic fascia, preservation of the puboprostatic ligaments and dorsal venous complex.
Materials and Methods: Description of our surgical technique over 80 patients who underwent RARP and the characteristics group from 2016 to 2019 excluding the rest of cases who went to different surgical approach and technique for robot-assisted radical prostatectomy.
Results: The mean age was 63 years old, 7% of patients were overweight and 7.5% had obesity. The mean pre-operative prostate volume was 42.620 cc, mean prostatic specific antigen (PSA) of 10.414.8 ng/dl. The mean console time was 198±47. The surgical margins were positive in 13.75% of the patients. Complications were recorded in the peri-operative period, five (6.2%) Clavien-Dindo I and six (7.5%) Clavien-Dindo II.
Conclusions: After 8 years of experience in our center we have modified our technique of robot assisted radical prostatectomy, improving our results, following different worldwide concepts in the prostatic dissection. Even if necessary, to increase the number of cases we have find an easier way to reproduce with acceptable results.
Keywords: Robotic Radical Prostatectomy, Prostate Dissection, Transperitoneal Approach
Introduction
In the past year’s robot assisted laparoscopic surgery is becoming more easily available in Latin America, in México was introduce by our department in Mexico, City in 2013 we accomplished the first robot assisted radical prostatectomy. At the beginning we started performing an anterior technique, which is, in most centers the standard of treatment for localized prostate cancer.
The technique varies depending on the place of learning or according to initial proctoring and preferences. Twenty years ago, was introduced the laparoscopic approach, at that time was usual the retrograde dissection starting with the apex. Guillonneau et al., described the mixed technique modifying the Mountsouris technique where they used and antegrade and retrograde approaches in 7 standardized steps. [1]After in 2003 following several years of evolution in the robotic radical prostatectomy technique the Frankfurt group published a case series of their robot-assisted technique using ascending and descending techniques for prostate approach [2]. In 2012 Asimakopuolus et al., described their intra fascial dissection of the neurovascular bundle [3]. Several approaches since that time have been created. In this article we describe our technique, which has been modified since our initial experience from 2011, after learning the lateral anterior approach in France, and then modifying to a mixed technique in between anterior and the Bocciardi approach[4].
Materials and Methods
Description of our surgical technique over 80 patients who underwent RARP and the characteristics group from 2016 to 2019 excluding the rest of cases who went to different surgical approach and technique for robot-assisted radical prostatectomy at the same time.
Technique step-by-step
We include a single surgeon experience over 80 cases from January 2016 up to December 2019 of Robotic Assisted Radical Prostatectomy, following the next description of the technique.
Port placement and Docking
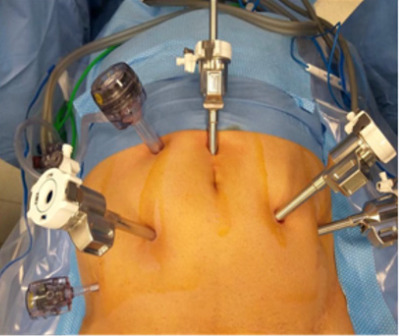
The trocars placement starts once needle Veress insufflation of the cavity is performed. We use a four-arm X da Vinci robotic system (Intuitive Surgical, Sunnyvale, CA, USA). First robotic trocar is placed one centimeter higher to the umbilicus, two da Vinci X ports on the left side, first one, four cm to the left of the camera trocar and the second one, four more centimeters according to the anterior axillar line. On the right side, one more robotic port (8 mm) four centimeters from the camera port in a horizontal line. Two more accessory ports for the assistant are placed, one 12 mm port in a triangle between the camera port and first robotic port on the right, and a 5 mm port down and 3 centimeters upper the iliac crest (Figure 1).
TransperitonealPosterior Dissection
Sigmoid dissection is performed to allow enough space in the rectovesical area. Upper traction is done by the prograsp instrument in the middle line in between bladder fatty tissue and the line of the rectum. We follow the vas deferens reflection to start the perineotomy through the pouch of Douglas. Reaching the vas deferens we transected, we follow them laterally for each side preparing the seminal vesicles, as the description of Montsouris technique. The next step is to dissect the full posterior base of the prostate, opening the Denonvilliers fascia reaching the apex of the prostate area where the urethra can be visualized, once we finish the medial space in between the prostate and the rectum, we start the nerves bundles preservation. By manipulating the right vesicle with the fourth arm, we expose the angle of the vesicle tip and the base of the prostate. The inferior and superior portions of the lateral face of the prostate are dissected. Then we reproduce the same on the left seminal vesicle, up traction to expose the base of the prostate and we perform the nerve sparing on an antegrade way, if necessary we place 5 mm clips coming from one of the assistant ports to avoid the bleeding from the capsular arteries going through the prostate and to control the prostatic pedicles. We can reproduce different degrees of preservation, intrafascial, inter or extrafascial [5,6] (Figure 2). Once posterior base and lateral walls of the prostate are finished, we tract the seminal vesicles and perform a forward an up dissection in direction of the bladder neck, leaving the most anterior prostate bases (left and right) the closer to the start of the bladder neck, at this time we release the seminal vesicles and we move to the lymph node dissection, once accomplished the approach goes anteriorly.
Transperitoneal Anterior Dissection
We go traditionally anteriorly to create the Retzius Space with a parietal peritoneum incision, down the level of Cooper Ligament; we identify all the anterior prostate suspension structures by removing the fatty tissue that surrounds it. The bladder at this time has been pull up by the forth arm, we perform and incision at the lowest medial level of the puboprostatic ligament without opening the endopelvic fascia but very near to the lateral prostate capsule, we do respect the maximum length of the puboprostatic ligaments [7].
The endopelvic fascia is preserved, we go laterally to the prostate capsule from the initial incision up to the level of the bladder neck anteriorly and laterally, because of the previous down to up dissection and nerve sparing form the posterior dissection we can easily visualized the nerves already spared. The same steps are reproduced in the right side, sparing the endopelvic fascia, and the maximum length of puboprostatic ligament, going down till the bladder neck shape appears (Figure 3). Once both sides accomplished, we do a close traction by the fourth arm Prograsp and decreased the bladder catheter balloon to 5 cc. A U inverted incision on the anterior wall of the bladder is done, a very spare bladder neck is accomplished by cutting the posterior bladder neck area, following deeper to a fully access to the previously dissected seminal vesicles, this step allows a very well neck sparing technique [8].
Lateral Prostate and Apex
Next step is to move the prostate lateral dissection toward the apex, going close and down to the dorsal venous complex, without cutting it or suturing it, we follow the angle going down to the level of the urethra respecting the anatomical position of the plexus over the urethra, the plexus stays at the level of the respected puboprostatic ligaments and rounded endopelvic fascia. We correctly identified the urethra diameter and transected with the maximum length possible. The Denonvilliers fascia bellow properly dissected avoids posterior reconstruction. For the urethral – bladder anastomosis a van Velthoven technique is perform using a 3-0 V-Loc [9]. Finally we use the same V-Loc suture from each side of the anterior line of suture to recreate a suspension-like hammock stitches; this is accomplished by using the end tip of the suture from the lateral portion of the neck bladder to the previous position of the puboprostatic ligament, with this we enhance hypothetically, better continence. A Foley 18 fr catheter is placed with 15 cc inside, finalizing the procedure. Prostate is removed through the camera incision port.
Results and Discussion
The patients were aged between 44 and 86 years old (mean: 63 years old). The most common co morbidity was high blood pressure (n=17), seven percent of patients were overweight and 7.5% had obesity. The mean pre-operative prostate volume was 42.620 cc (range: 9.3-115), mean prostatic specific antigen (PSA) of 10.414.8 ng/dL (range: 0.9-131) and mean positive cores per biopsy were 4.93 (range: 1-12). The mean console time was 19847 minutes (range 120-400) and intraoperative blood loss was 368263 (range 50-1300). The uretro-vesical anastomosis was performed with the van Velthoven technique in 80 patients (100%). In 17 (21.3%) patients a closed suction drainage was placed. [10] Five (6%) patients required blood transfusion, and none required conversion to an open approach [11] (Table 1). No major complications were recorded in the peri-operative period, five (6.2%) Clavien-Dindo I and six (7.5%) Clavien-Dindo II.
The RARP Gleason score were 6 in 36 (45%), 7 in 26 (32.5%), 8 in 7 (8.8%), 9 in 9 (11.3%) and 10 in 2 (2.5%) patients. The T clinical stage and D’Amico risk group is described in Table 2. Pelvic lymph node dissection was performed as follows: 9 (11%) standard/ obturator, 23 (28%) extended and 11 (13%) super extended. The surgical margins were positive in 11 (13.75%) patients. The most common positive surgical margin was at the level of prostatic apex. [12]We found a positive Pearson correlation between RARP Gleason score and positive surgical margins (r=0.539, p=0.01). The mean hospital stay were 3 days (2-7 days), and the urethral catheter was removed in a mean period of 51 day (5-10 days) [13,14].
Respecting, as other authors, the puboprostatatic ligaments and the santorini complex as well as the endopevic fascia we can spare much more the prostate fossa, avoiding too much invasion on the pelvic structures. [15] Our final stich for an anterior suspension, keeps part of the anatomy form the bladder to the ligaments. As demostrated by Galfano et al., we bealive that starting the radical prostatectomy through the pouch of Douglas is an easier way to improve later during the procedure a most precise definition to the bladder neck as also a better definition of the anterior anatomical structures, and maybe is also a proper start if we want to fully perform a robotic retzis sparing radical prostatectomy [16].
Conclusions
We decide after four years of performing transperitoneal anterior dissection approach and base in different worldwide leaders and techniques for robotic radical prostatectomy, that some of the steps in the learning curve could be challenging, we started posteiror dissection with good overall outcomes and a good reproducible technique. Due to hight evolution in the technique we decide to follow steps to simplify the bladder neck approach. With posterior dissection, we can reproduce, from the vesicle tip and going laterally up to the body of the prostate a very fine neurovascular bundle dissection. Going thought the Retzius space with the previous posterior dissection gives a clear anatomical landmark to define a proper bladder neck sparing and to approach the Santorini plexus from behind and below avoiding anatomical damage and excessive blood loss. Different techniques have been described for robot assisted radical prostatectomy, and the preference and expertise of surgeon allows making different possibilities to the surgical robotic approach.
For More Lupine Publishers Open Access Journals Please visit our Website:
https://lupinepublishers.com/index.php
For more Journal of Urology & Nephrology Studies articles please click here:
https://lupinepublishers.com/urology-nephrology-journal/
#lupine publishers#lupine group#open access journals#nephrology#urology#renal system#journal of urology & nephrology studies#lupine journals#openaccess#submissions#manuscripts#articles
0 notes
Photo
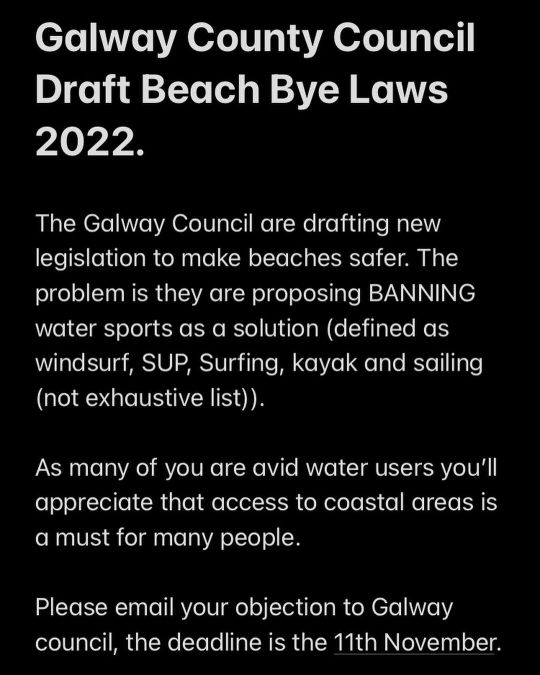
PLEASE HELP BEFORE 11th NOVEMBER!! Galway County Council have draft beach user legislation. Included in this is a proposal to BAN all watersports! Surfing, sailing, windsurfing, kitesurfing etc. You can help by submitting an email to Galway county council (emails in images). There are two draft emails and contact details for the Council, courtesy @rusheenbay. Also two screenshots of the draft document. . #stopthebans #stop #coastalaccess #coast #westcoast #west #openaccess # (at Black Sheep Surf Co- Online Surf Store) https://www.instagram.com/p/CkswzEEDsDk/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
0 notes