#like early Christians in rome
Text
People complain about Christians stealing pagan culture like they forget that the early Christians were in a pagan dominated culture and that the people who were becoming Christians willingly early on were of those cultures.
#I say willingly because it didn't take that long until kingdoms were forcing people to be of Christianity#Just like every other religion ever#Like I'm not saying “the way later Christians used saints as stand ins for pagan gods was 100% natural and shit#Just that Christianity wasn't (and still isn't) a solid ridged set of beliefs and values#and that people will bring often aspects of their previous beliefs with them#Such as Saturnalia morphing into Christmas overtime#Ffs I better not do a theology paper next year and find out everything here is just wrong#Also I'm more speaking about Christianity pre orthodox/catholicism spilt#Before it was the state religion of Rome#Theology#Early Christianity#Please someone correct any misconceptions I gsce#Have#Fuck I hate my keyboard so much on my phone I need to download a better one#But afraid it could be worse#Also I hated myself for saying pagan culture#But like this is more targeted at the people who would only know those preexisting religious beliefs as pagans (and Judaism)#I had a rant about Constantine but had to chillax it to this#It's 3am
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Yo Gentiles! Looks like I'm going to need to give some of you a crash course on what antisemitic language looks like, because I've been seeing entirely too much of it from some of you here on Tumblr.
Now, I think it's time for a Jewish history lesson, because I've been seeing way too many Nazi-related conspiracy theories going around. If you hear contradictions to the basic information that I am about to share (i.e., if you hear someone saying that the Jewish people are "a race that originated in Europe"), it is likely that you are hearing a white supremacist, anti-Jewish conspiracy theory.
So, here's the basics of Jewish history. Jews are indigenous to the Levant have been there for thousands of years. The Levantine people that Jews descended from have been in that area of the Levant since the Bronze Age. Jews as a distinct people have been there since the Late Bronze Age. Before it was Palestine it was the Kingdom of Judah, then Judea, and then Judaea, and that is literally where we are from. The word Jew means "a person from the Kingdom of Judah." The Romans renamed the area Syria-Palaestina (which they borrowed from the Greek name Palestina) in the 2nd century CE after destroying the Second Temple in Jerusalem and leading another campaign to try to eradicate the Jewish people (guess what, we're still here, motherfuckers).
And even after the Romans tried to annihilate us, even after they scattered many of us into European diaspora, many Jews came back, again and again over the ages, and there have nearly always been Jewish communities in the region throughout history.
And if you come for me or try to dispute any of this history with white supremacist bullshit, I am a Jew who has studied way more Jewish history than you. And as politely as possible, you can take your white supremacist conspiracy theories and fuck off into the sun.
Okay, with all that out of the way, let's get into it!
Gloves are coming off, because this is just a sampling of the Nazi dogwhistles I've been seeing here on Tumblr about the Jewish civilians who were tortured, murdered, and worse:
- If you say shit like, "The Jews got what they deserved"...
GUESS WHAT? You're talking like a white supremacist, and you need to fucking check yourself.
- And if, on the other hand, you say shit like, "The reports were probably overblown. I think those were paid actors. I don't think those Jews were murdered. No Jewish children were killed. No Jewish bodies were desecrated" blahblahblah...
GUESS WHAT? You get to sit with the Nazis at their table for lunch.
- If you tell Jews "go back to Europe where you came from"...
GUESS WHAT? Not only are you telling the descendants of Jewish refugees to go back to the Spanish Inquisition, the Russian pogroms, and the Nazi gas chambers, as I explained in this post, but you are also repeating a white supremacist conspiracy theory about the origins of European Jews.
Jews are a Levantine people from the area of the Middle East currently called Israel (formerly called the Kingdom of Judah, and then Judea). While there was some emigration to Europe during the late Roman Republic and the early days of the Roman Empire, the first mass migration of Jews to Europe was a forced migration. Gentiles from the Roman Empire dragged us there as captives after 70 CE, the year Rome destroyed the Second Temple.
- And if you're telling yourself that there are "good Jews" and "bad Jews," and those Jewish civilians were "bad Jews," so they deserved to be tortured and killed...
GUESS WHAT? You're spouting white supremacist ideology.
Antisemitism takes a long time to deprogram.
A lot of gentiles grow up with anti-Jewish ideology that they have never questioned.
And a lot of Christians are kept ignorant about Jewish history because preachers and priests fear it would make Christians question the many inaccuracies in the Bible.
But the first step in noticing antisemitic beliefs is to notice when you start singling people out *because* they are Jewish.
And I have been seeing some of you gleefully celebrating the murder of Jewish civilians *because* they are Jewish.
And that is antisemitism.
That is one step closer to the next generation of Jews getting shoved into the gas chambers. And there are only 16 million of us left in the entire world. We're 0.2% of the world's population. And we cannot afford another Holocaust.
And if your response to me saying that is, "Well, those Jews deserve it."
Guess what. You are making it easier for Nazis and white supremacists to spread hatred and commit acts of violence against Jewish people. And you will have to live with that blood on your conscience.
So...
If you are a gentile, and you see other gentiles repeating these kinds of white supremacist dogwhistles about Jewish people, here's how you can help:
1. MOST IMPORTANTLY: Help them direct their focus away from attacking random Jewish people online and towards helping Palestinians.
Actions that people can take right now are contributing to verified charities and relief organizations that help the people of Gaza. Some organizations that are verified by CharityNavigator.org and CharityWatch.org are:
Anera (92% rating on Charity Navigator)
Palestine Children's Relief Fund (97% rating on Charity Navigator)
Doctors Without Borders (98% on Charity Navigator)
2. Call that shit out. Tell people that they're being antisemitic, and explain that Jew-hatred is dangerous to Jewish people. Antisemitism gets Jews attacked and it gets Jews killed. In the US, many synagogues require round the clock security to protect against white supremacists who want to murder Jews. In Pittsburgh, my old home town, a group of Nazis from north of the city planned the murder of Jewish congregants at Tree of Life Synagogue, and so far only one of them (the gunman) has been arrested and convicted of the murders. The others are still at large.
3. Explain to them that it is antisemitic to celebrate someone's death *because* they're Jewish. ALSO, it is antisemitic to blame a random Jewish person for the actions of ANY government, whether that be the Israeli Government or the US Government.
4. Explain to people that they're not going to solve this conflict by posting antisemitic statements and memes online. All they will do is alienate the Jewish people in their lives and make those Jews feel scared and unsafe. And they will contribute to this current wave of antisemitism.
Antisemitic hatred doesn't help Palestinians. All it does is put Jewish people around the world in danger.
#tl;dr if you celebrate the murder of jews *because* they are jews you are an antisemite - end of story#just fyi - i will be monitoring the comments so if anyone posts anything antisemitic i will delete your comment and block you#antisemitism tw#jumblr
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
One of the things I hear a lot from Gentile witches and neo-pagans who want to work with Lilith or claim to work with Lilith, is that she is actually a Mesopotamian goddess, usually either Ishtar/Inanna or Erishkigal, and that it was the Jews, with their horrible patriarchy juice, who slandered her and cast her down, and so the Jews do not deserve to say what happens to her and it isn't antisemitism to work with her, or to completely ignore what the Jews say about what she is in a Jewish context.
Lilith is not Ishtar or Erishkigal. However, there is a Mesopotamian figure that is pretty stinking analogous to Lilith, and is probably her folkloric ancestor, by which I mean the idea of Lilith probably comes from this Mesopotamian figure. In fact, Lilith almost certainly is either a Jewish version of this figure, or, they are both descended from the same Near Eastern and Mediterranean basin folkloric figure. That figure is Lamashtu.
Lamashtu is, much like Lilith, the supernatural embodiment of maternal and infant mortality, a figure of power and terror, who functions as a way to embody and cope with the profound dangers that are pregnancy, childbirth, and infancy without effective medical care. the Mesopotamians never worshiped Lamashtu, but they did seek to appease her, including making symbolic gifts to her, to keep her from visiting them, and killing them or their children.
An interesting side note is that there is also a Mesopotamian figure who specifically opposes Lamashtu and functions as the protector of pregnant women and infants, and that figure is Pazuzu, a wind spirit, who ruled over other wind spirits, including ones called the Iilu in the Akkadian language. Akkadian is a Semitic language, related to Hebrew, and this word is probably a cognate of Lilith, but the Iilu probably have no relationship to the figure of Lilith except her name. You might know Pazuzu as the demon featured in the movie, The Exorcist, and ironic fate for a mythological protector of women and children.
Anyway, if you'll remember, I implied above that the Lamashtu/Lilith figure, was present in various guises throughout the Mediterranean basin and the Near East, so there are of course figures analogous to both of them throughout the region, such as Lamia of Greece, and the Strix of Rome.
So if you really really want to work with a figure who functions as the supernatural embodiment of maternal and infant mortality, Lamashtu, Lamia, or the strix would all be excellent options that don't come from an extant closed religious practice. All the baby killing, none of the antisemitism and cultural appropriation.
While all three figures are almost certainly descended from the same folkloric root, they're all subtly different, because as stories and characters travel, they change. as such, they all have particular good points about them as figures of veneration.
Lanashtu is the OG bad bitch, who commanded fear, respect, and offerings, like a mythological mafiosa, collecting protection money.
Lamia has attached to her the story that she was one of Zeus's dubiously willing lovers, who was screwed over first by Zeus, the embodiment of patriarchical rule, then by a jealous Hera, the embodiment of patriarchal marriage, so if what attracted you to Lilith was the story from the Alphabet of Ben Sira, about a victim of the patriarchy getting her own back through violent vengeance, Lamia might be the girl for you. With her however, the emphasis is less on her murder of children, then on her seducing and eating men, though she does also get strongly associated with killing children, especially boys.
And the strix is particularly interesting, because the word comes down to us in the modern Italian word for witch, striga. Indeed, one of the theories as to where the witch figure came from in Early Medieval, and then Early Modern Christianity, was as the strix demon made human. This might explain the close association between Early Modern Witchcraft and infant mortality, including Italian stories of witches causing infants to die seemingly natural deaths, so that they could dig them up and eat them after their funerals, something that ties these human supposed witches very closely to demonic folkloric antecedents. If you are looking for a figure of unfairly maligned female power, the strix and her close association with later human witches, might be the one for you.
All three of these figures, much like Lilith herself, are reflections, both of the power women wielded even within patriarchal societies, over the process of pregnancy, birth, and childrearing, and also the powers of death and loss that everyone was subject to. There is something powerful, transgressive, and even healthy in acknowledging the fears and dangers presented by this death and loss,and for some people, that might take the form in venerating the underlying powers. If this is something that would be spiritually meaning for you, and you wish to work with such a figure, and you are not Jewish, please respect the fact that Lilith is part of a closed religious practice, and remember that Lilith has sisters, in other parts of the Mediterranean basin and the Near East, who are not from extant closed cultures, and who might serve your needs better anyway.
666 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Marble Head of Apollo Unearthed in Greece
The excavation, carried out by a group of students of the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki in the archaeological site of Philippi Kavala, brought to light important findings. Among other things, they discovered a rare head of Apollo dating back to the 2nd or early 3rd century AD.
The statue dates back to the 2nd or early 3rd century AD and it probably adorned an ancient fountain.
Natalia Poulos, Professor of Byzantine Archaeology, led the excavation, which included fifteen students from the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki (11 undergraduates, 2 master’s, and 2 PhD candidates), Assistant Docent Anastasios Tantsis, and Professor Emeritus of Byzantine Archaeology Aristotle Mendzo.
Archaeologists say, this year the excavation continued east of the southern main road (decumanus) at the point where it meets the northern axis of the city (the so-called “Egnatia”). The continuation of the marble-paved road was revealed, on the surface of which a coin (bronze phyllis) of the emperor Leo VI (886-912) was found, which helps to determine the duration of the road’s use. At the point where the two streets converge, a widening (square) seems to have been formed, dominated by a richly decorated building.
Archaeologists say evidence from last year’s excavations leads them to assume it was a fountain. The findings of this year’s research confirm this view and help them better understand its shape and function.
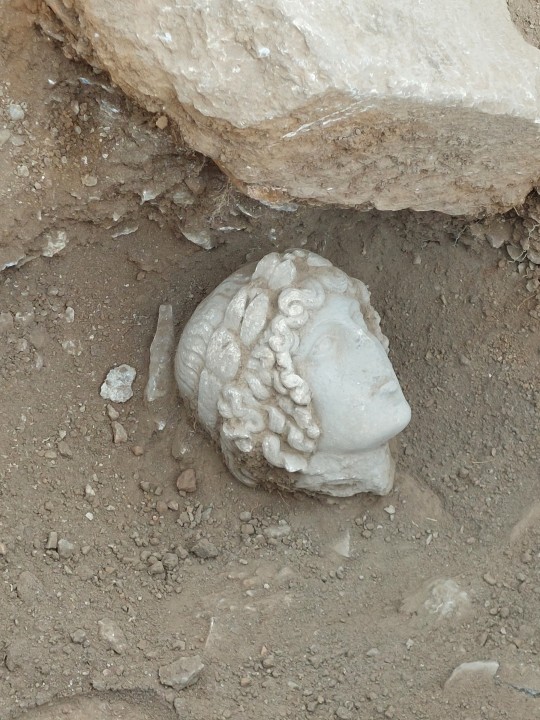

The research of 2022 brought to light part of the rich decoration of the fountain with the most impressive statue depicting Hercules as a boy with a young body.
The recent excavation (2023) revealed the head of another statue: it belongs to a figure of an ageneous man with a rich crown topped by a laurel leaf wreath. This beautiful head seems to belong to a statue of the god Apollo. Like the statue of Hercules, it dates from the 2nd or early 3rd century AD and probably adorned the fountain, which took its final form in the 8th to 9th centuries.

In classical Greek and Roman religion and mythology, Apollo is one of the Olympian gods. He is revered as a god of poetry, the Sun and light, healing and illness, music and dance, truth and prophecy, and archery, among other things.
Philip II, King of Macedon, founded the ancient city of Philippi in 356 BC on the site of the Thasian colony of Crenides near the Aegean Sea. The archaeological site was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2016 for its outstanding Roman architecture, urban layout as a smaller reflection of Rome itself, and significance in early Christianity.
By Oguz Buyukyildirim.


#The Marble Head of Apollo Unearthed in Greece#Philippi Kavala#marble#marble statue#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#ancient greece#greek history#greek art
192 notes
·
View notes
Note
hey, i find your posts about historical fiction pretty interesting, do you have any recs?
anon this is the most beautiful and validating ask i have ever received. absolutely of COURSE I have recs. not gonna be a lot of deep cuts on this list but i love all of these books and occasionally books do receive awards and acclaim because they are good. in no particular order:
the cromwell trilogy by hilary mantel. of course i gotta start with the og. it’s 40 million pages on the tudor court and the english reformation and it will fundamentally change you as a person and a reader
(sub rec: the giant, o’brien by hilary mantel. in many ways a much shorter thematic companion to the cromwell trilogy imo. about stories and death and embodiment and the historical record and 18th century ireland. if you loved the trilogy, read this to experience hils playing with her own theories about historical fiction. if you are intimidated by the trilogy, read this first to get a taste of her prose style and her approach to the genre. either way please read all four novels ok thanks)
lincoln in the bardo by george saunders. the book that got me back into historical fiction as an adult. american history as narrated by a bunch of weird ghosts and abraham lincoln. chaotic and lovely and morbid.
the everlasting by katy simpson smith. rome through the ages as seen by a medici princess, a gay death-obsessed monk, and an early christian martyr. really historically grounded writing about religion and power, and also narrated with interjections from god’s ex boyfriend satan. smith is a trained historian and her prose slaps
(sub rec: free men by katy simpson smith. only a sub rec bc i read it a long time ago and my memory of it is imperfect but i loved it in 2017ish. about three men in the woods in the post revolutionary american south and by virtue of being about masculinity is actually about women. smith did her phd in antebellum southern femininity and motherhood iirc so this book is LOCKED IN to those perspectives)
a mercy by toni morrison. explores the dissolution of a household in 17th century new york. very different place and time than a lot of morrison’s bigger novels but just as mean and beautiful
(sub rec: beloved by toni morrison. a sub rec bc im pretty sure everyone has already read beloved but perhaps consider reading it again? histfic ghost story abt how the past is always here and will never go away and loves you and hates you and is trying to kill you)
an artist of the floating world by kazuo ishiguro. my bestie sir kazuo likes to explore the past through characters who, for one reason or another (amnesia, dementia, being a little baby robot who was just born yesterday, etc), are unable to fully comprehend their surroundings. this one is about post-wwii japan as understood by an elderly supporter of the imperial regime
(sub rec: remains of the day by kazuo ishiguro. same conceit as above except this time the elderly collaborator is incapable of reckoning with the slow collapse of the system that sheltered him due to britishness.)
the pull of the stars by emma donoghue. donoghue is a strong researcher and all of her novels are super grounded in their place and time without getting so caught up in it they turn into textbooks. i picked this one bc it is a wwi lesbian love story about childbirth that made me cry so hard i almost threw up on a plane but i recommend all her histfic published after 2010. before that she was still finding her stride.
days without end by sebastian barry. this one is hard to read and to rec bc it is about the us army’s policy of genocide against native americans in the 19th century west as told by an irish cavalry soldier. it is grim and violent and miserable and also so beautiful it makes me cry about every three pages. first time i read it i was genuinely inconsolable for two days afterwards.
this post is long as hell so HONORABLE MENTIONS: the amazing adventures of kavalier & clay by michael chabon, the western wind by samantha harvey, golden hill by frances spufford, barkskins by annie proulx, postcards by annie proulx, most things annie proulx has written but i feel like i talk about her too much, the view from castle rock by alice munro, the name of the rose by umberto eco, tracks by louise erdrich
#honestly will probably be coming back with additions bc this is just based on whats currently on my bookshelf#made this post while staring at the copy of mirror & the light i keep on my desk as some kind of hilary mantalisman#send me your address so i can explain my passions etc etc#histfic
161 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hey-o! Tis the season for people to talk about how the holidays were "actually pagan" and I'm on the hunt for sources about how that's really not the case, if you have any you'd recommend!
Okay, so the problem is there are so many weird "Christmas is stolen!" bullshit memes going around, it's so hard to just give you a comprehensive list of sources. Christmas celebrations have evolved as the religion has spread, and different things come from different times...
The key here is to go for academic sources. This is a question of history, and a well supported historical research is going to tell you whether they're operating from primary, secondary or tertiary sources.
So while I can't give you a simple list, let me give you a couple of examples off the top of my head and give you tips on how to investigate any the dumb claims that get passed around.
Christmas being in December: So a lot of people go for the "Christmas is in December so it can steal from [INSERT SOLSTICE CELBRATION]" is ahistorical... because we know exactly why Christmas is in December. Because the guys who made the decision argued with each other and left behind written documentation. The two big names you need to look up are Clement of Alexandria (who pitched January 6th) and Hippolytus of Rome (who proposed December 25th). This is around the turn of the third century, and you can find both of their writings. Some folks have questioned the authenticity of some of Hippolytus of Rome's writings, but Clement of Alexandria's seem well supported. These were internal arguments about when the birth of Christ took place within the early church, and when they settled on late December. There are reasons for this, and you can read their arguments (it largely has to do with the importance of when Jesus was conceived -- they wanted that to be an important date and then added nine months to it). Importantly though, because linear time is a thing, this means Christmas was set in December before the Christianization of the Germanic and Norse tribes... so anyone who says Christmas was set to December to correspond with Yule doesn't understand the concept of "coincidences."
The Christmas Tree: The Christmas tree was invented in 16th century Germany. That's... that's just written down all over the place. Now, there are legends about Martin Luther being the first who did it -- but I'm pretty certain that's just an embellishment that got added on. There are preceding traditions where part of an evergreen was brought into the home as a part of solstice traditions (though some will claim the Egyptians did this? Which is wild -- likely misinterpreting their use of palm fronds as the same thing), but the act of taking a whole ass tree, cutting it down, putting it in your house, and decorating it? That's 16th century Germany all the way. You can rabbit hole so many sources on that one, but honestly just pick apart the citations on the Wikipedia page. Putting a branch in your house and dragging a whole tree in are very different acts.
Jesus's story is copied from [INSERT RANDOM GOD]: There are so many of these, and some are just downright disrespectful to major world religions (the Krishna version of the meme especially). The answer is... just see if what the meme is saying about the god is supported by the mythology. Like I've seen ones that says Dionysus was "born of a virgin." If you know anything about the Greek gods, you're probably already laughing on the floor. Horus gets dragged into this too, because Gerald Massey was trying to pull a "White Goddess but with Dudes." But any serious research on Horus will tell you the supposed parallels aren't supported by the mythology.
So sorry, this wasn't so much sources you can use as it is how to look for them to begin with. Because there's just so, so much. This isn't even covering cases of syncretism, where pre-existing cultural traditions got continued post-Christianization. Because it's almost always the case that if a pre-Christian practice endured post Christianization, it's because people decided to keep doing it -- not because the church was trying to "steal" it. The latter means there was some mustache twirling plan behind it, when the former means (usually) the church went "Well, they're paying their tithes and saying it's for Jesus, so who gives a shit?"
I'm just going to finish this off with linking to my podcast episode on this, along with Ocean Keltoi's great Yule video on the topic. Hopefully that helps.
youtube
188 notes
·
View notes
Text

Love in the Changing History of Ancient Rome
The love between a merchant's son and a gardener slave is a striking example of the fluctuating history of homosexuality in the Roman Empire. It stands as a symbol of hope and resistance in the late Roman Republic or early Imperial period. While not necessarily accepted, romantic relationships between men from different social strata were not uncommon. The two men likely had to live their love clandestinely and discreetly.
In the early Roman Republic, homosexuality between men was accepted and even considered normal. Mythology and art depicted relationships between men and gods that celebrated homosexuality. Several Greek and Roman gods and goddesses were associated with homosexuality, such as Eros, the god of love, who was often depicted with a young man.
However, Roman laws became increasingly repressive over time. In the 1st century BC, laws like the Lex Scantinia and the Lex Iulia de Adulteriis prohibited homosexual relationships between free men and between married men or men in domestic partnerships. The Lex Papia Poppaea granted tax benefits to married men and women, which led more people to marry and made homosexuality less acceptable.
The reasons for the tightening of these laws were multifaceted, including the rising influence of Christianity in the centuries after Christ, which viewed homosexuality as a sin. Additionally, homosexuality was believed to undermine the discipline of the Roman army and the traditional family.
Attitudes changed once more in the Late Antiquity. Homosexuality became increasingly accepted in Roman society, particularly due to the growing influence of paganism, which led to greater tolerance of homosexuality.
The polytheistic nature of paganism may have contributed to this reacceptance of homosexuality during a time when Christianity was no longer the dominant religion. In a polytheistic religion, there is no single source of authority that could prohibit homosexuality. Instead, there are many different gods and goddesses associated with various values and beliefs. Additionally, it was a period of change and uncertainty, during which people may have become more open to new ideas and convictions.
Text supported by Chat GPT 3.5 and Bard
These images were generated with StableDiffusion v1.5. Faces recalculated with inpainting.
#LoveInHistory#LGBTQHistory#gayart#AncientRomeLove#LoveKnowsNoBounds#HistoricalLove#Inclusivity#gaycomic#TimelessLove#ancientrome#mankissman#boykissboy#gayman#gay
213 notes
·
View notes
Text

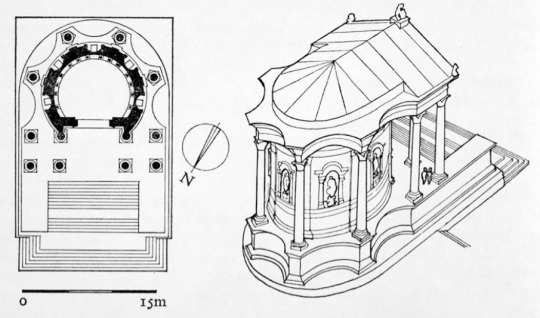


The Temple of Venus in Baalbek (Heliopolis), Lebanon was built in the 200s CE to honor the goddess of love, sex and fertility. Venus was derived by the Romans from the Greek goddess Aphrodite, who herself was inspired by the Near Eastern goddess Astarte. This temple's cult likely incorporated elements of both Roman Venus and the local Astarte.
The temple itself has many novel and unique features found nowhere else in Classical architecture. Five semicircular exedrae run along the outer wall, framing arched niches decorated with carved doves and seashells that probably contained statues in ancient times. Above each niche a festoon of leaves and fruit hangs, symbolizing fertility. The pentagonal column bases are without parallel in antiquity, and no other examples are known. The interior is less well preserved, but it can be safely assumed by the lavishness of the construction that it was once sumptuously decorated with paintings, statues, colored marbles and golden ornaments.
The temple has an eventful history, being also a site of persecutions of early Christians under Julian the Apostate, the last pagan emperor of Rome. Sozomen, a late antique historian, says in his Ecclesiatical Histories:
The inhabitants of Heliopolis, near Mount Libanus, and of Arethusa in Syria, seem to have surpassed them in excess of cruelty. The former were guilty of an act of barbarity which could scarcely be credited, had it not been corroborated by the testimony of those who witnessed it. They stripped the holy virgins, who had never been looked upon by the multitude, of their garments, and exposed them in a state of nudity as a public spectacle and objects of insult. After numerous other inflictions they at last shaved them, ripped them open, and concealed in their viscera the food usually given to pigs; and since the swine could not distinguish, but were impelled by the need of their customary food, they also tore in pieces the human flesh.
I am convinced that the citizens of Heliopolis perpetrated this barbarity against the holy virgins on account of the prohibition of the ancient custom of yielding up virgins to prostitution with any chance comer before being united in marriage to their betrothed. This custom was prohibited by a law enacted by Constantine, after he had destroyed the temple of Venus at Heliopolis, and erected a church upon its ruins."
Whether Sozomen's account is an exaggeration or not, there is archaeological evidence that the temple was indeed converted into a church, dedicated to Saint Barbara. According to the (comparatively late) Christian legend, Barbara was the daughter of a Heliopolitan dignitary, Dioscorus, who still worshipped the old gods. When he learned that she had been baptized, he killed Barbara and was immediately struck by lightning. Up til the present day, Saint Barbara is invoked if people want to be protected against lightning.
Because the monument continued to be in use, the temple of Venus is comparatively well-preserved. Unbroken religious activity has continued on almost the same site since antiquity, and there's still a small mosque next to the temple of Venus. The Greek-Orthodox church of Baalbek, which is close by, is still dedicated to Saint Barbara.
69 notes
·
View notes
Text
What do Shax and a 30-year-old Sandman comic have in common? Puns. The answer is always puns.
While I've recently revealed Shax does actually know how to spell, (she's just really old), the "angle" message Shax throws through the window to demand the "angel" one was a little trickier, because it's not Middle English, or even Old French, it's probably the oldest pun in Good Omens... it's latin.

Good Omens Season 2, Episode 5, 2023
Fortunately, a time travelling Neil Gaiman left answers for us in his 1995 Sandman special "Sandman midnight theatre." See for yourself.

Sandman Midnight Theatre, Neil Gaiman, Matt Wagner, Teddy Kristiansen, 1995
"Still, they have some illuminated manuscripts in their library which throw fascinating light on early church history. "Not angels, but angles" eh? I've been angling for permission to browse through their manuscript collection for yonks."
Appropriate for an English reverend to be curious about "Angels and not Angles". It's THE earliest christian pun, attributed to Pope Gregory the Great in the 6th century CE.

Oxford reference essential quotations
It comes from a historical account of the pope walking through a market in Rome, and seeing some exotic slave children (i.e. fair hair and blue eyes, and light skin) from what is now the England, and asking where they were from. The master replied that they were "Angles" (Angli in latin) and the pope declared them to be "Angels" (Angeli) instead, which, in latin at that time would have been a pun.
This history from Bede actually influenced a lot of the christian world, so we could conceivably make the point that fair blonde and blue eyed angels comes from the idea that they looked liked the English (who were not christian, but pagan at the time of being newly conquered). Aziraphale's looks in the originsl Good Omens are probably a direct result of the lineage in art of this 1,500 year old pun.
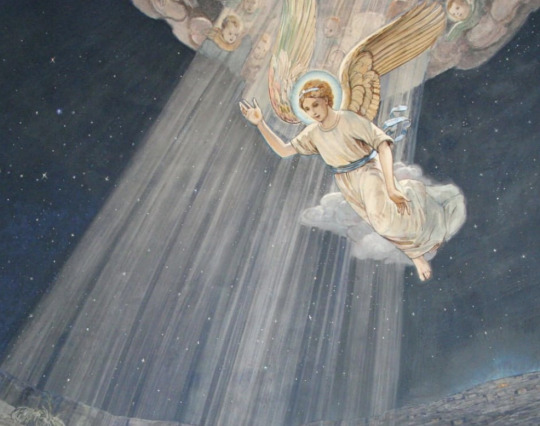



Depictions of angels, 1100 years apart
Which raises the question: if Shax is asking for the Angel Gabriel with her note, the pun doesn't make any fucking sense.
Jon Hamm plays Gabriel as an "American", specifically not English like the rest of the cast. He does have blue eyes, but as far as Shax is concerned, Gabriel's eyes are violet, not really a human colour. Shax could just actually be stupid (I guess?) and not realize that in modern English that constitutes a mistake (boring), or that Americans succeeded in 1776 (hilarious). But here's a quirkier theory: Shax knows what she's talking about, and she's gunning for Maggie.
If you look really closely, demons show up and start hanging around the street earlier in the ball than you would guess. Once a fair number have amassed, they stay waiting for Shax to lead them. However, even though she hasn't shown up yet, they eagerly chase Maggie down the street from her shop. They're only stopped by Crowley, and Maggie gets safely into the ball.

Once inside, she has quite a stunning change of costume, highlighting her blonde hair and blue eyes:

There's so much more evidence to suggest that Maggie isn't really a normal human, but this post is long enough. What I will say is that it's subtle, but once the demon attack really gets going (no thanks to Maggie), Shax and the other demons never look for Jim once, even when he leaves the mezzanine. They concentrate all their efforts on Aziraphale, Maggie and Nina, and never mention Gabriel again.
While Maggie is a Scottish name, and she clearly has some links to Scotland if a random pub in Edinburgh is buying records from her in Soho, she does have a distinctly English accent, and lest we forget...

———————————————
thanks as always to @embracing-the-ineffable and @thebluestgreen for the tasty links and sounding board.
#good omens meta#good omens 2#art director talks good omens#go season 2#go meta#good omens season two#good omens season 2#good omens#go2#good omens prime#nina and maggie#anthony j crowley#jimbriel#crowley x aziraphale
74 notes
·
View notes
Text
If Caravaggio were alive today today, he would have loved the cinema; his paintings take a cinematic approach. We filmmakers became aware of his work in the late 1960s and early 1970s, and he certainly was an influence on us. The best part for us was that in many cases he painted religious subject-matter but the models were obviously people from the streets; he had prostitutes playing saints. There’s something in Caravaggio that shows a real street knowledge of the sinner; his sacred paintings are profane.
Martin Scorsese on Caravaggio
Michelangelo Merisi, known to most of us as “Caravaggio,” was born on September 29, 1571 in Milan, Italy, to parents who were from the small town of Caravaggio. In the span of his 38 years long life he revolutionised painting with innovations like a unique use of chiaroscuro - with dark shadows contrasting with dramatic areas of light - and a deep sense of realism that later inspired the Baroque movement. But most of all, he developed such an iconic style that most of us can probably look at a painting and know if it’s a Caravaggio, or Caravaggio-inspired.

Merisi spent the first few years of his life in Milan, studying painting, and later moved to Rome, where his early talent impressed Cardinal Del Monte, who introduced the young painter to other high-profile Catholic figures who became commissioners of some of Caravaggio’s best work. It seemed there was no end to the artist’s creative genius. Caravaggio, much to his patron’s delight, would pump out one masterpiece after another. It seemed the more out of control his personal life became (cheating, brawling and murder were standard fare), the more his art would become more refined, more potent.
In the long list of masterpieces he left behind, both secular and religious works stand out. But it is perhaps in his religious works that the artistic transition of the master is more evident. Caravaggio is, in fact, known to have changed his style after harsh personal life experiences led him to reassess his outlook on life.
In May of 1606 Caravaggio took part in a deadly brawl in Rome and was charged with murder. He fled to Malta, in search of asylum from the Order of Saint John, a Catholic order dedicated to helping the sick and the poor. The order commissioned some of the most important late life works of the Milanese artist.
It is in these works that we notice the shift in Caravaggio’s art, from a strong focus on aesthetics to an interest in the spirituality of his subjects, which critics believe was motivated by his own introspection.

On the streets surrounding the churches and palaces, brawls and sword fights were regular occurrences. In the course of this desperate life Caravaggio created the most dramatic paintings of his age, using ordinary men and women - often prostitutes and the very poor - to model for his depictions of classic religious scenes.
By representing biblical characters in a naturalistic fashion, typically through signs of aging and poverty, Caravaggio's populist modernisation of religious parables were little short of trailblazing. Although not without his critics within the church, by effectively humanising the divine, Caravaggio made Christianity more relevant to the ordinary viewer.
For some, though, his art was too real. Bare shoulders, plunging necklines, severed heads; this raw humanity didn’t always fly in 17th century Rome. As a result, many of his pieces were rejected as altar pieces and as church hangings. One such piece, the Madonna of Loretto (now hanging in a church in Rome) was widely criticised upon its unveiling. The people of the day were shocked to behold the Mother of God leaning nonchalantly against a wall in her bare feet while holding baby Jesus in her arms.

It is ironic that the very art that today we consider “classical” and “iconic” to the Catholic faith was considered questionable and perhaps void of modesty and virtue. Yet, the fact remains that no individual artist has made such a lasting impression on the world of modern art. Truly, many have called Caravaggio the “first modern artist”. It is no surprise, then, that his style has sparked both widespread admiration and imitation throughout the centuries.
Before Pope John Paul II refined a theology of the body beautiful, Caravaggio's paintings suggested a reverence for the inherent beauty of human form.
Troubled though he may have been, his art speaks eloquently of the dignity of the mundane. Though the original medium may be weathered and cracked, the message of beauty still echoes down the centuries. And this same beauty still fuels, escapes and reduces artists to relentless seekers as surely and as forcefully as it did in Caravaggio's life.
#scorsese#martin scorsese#quote#art#artist#caravaggio#art history#aesthetics#modern#sacred#profane#rome#catholic church#christian#beauty#realism#art of the mundane
400 notes
·
View notes
Text
Stephen Shoemaker has talked at length about the eschatological nature of early Islam in other books and articles; he makes some very interesting points in The Apocalypse of Empire (which is not just about Islam, although it discusses Islam at length in two chapters), synthesizing some points made by other scholars.
Scholarly trend to view Islam as a movement that was from the beginning pragmatic, not apocalyptic. Other scholars try to portray Muhammad as basically a national unifier/Arab empire-builder, with religion as a tool secondary to this aim. This seems to amount to not taking early Islam as it portrays itself very seriously, and indeed in some cases seems to be almost an apologetic project to try to help make early Islam more relevant to the present day.
Snouck Hurgronje(sp?) argued that early Muslims saw Muhammad's appearance itself as a sign the end of the world was at hand, and that Muhammad would not die before its arrival. He and other scholars after him saw other elements of his message as more or less accessories to his concern with the impending end of the world.
Projects of empire-building and apocalypticism are not necessarily opposed! The rest of this book furnishes examples from Byzantium, Rome, Zoroastrianism. For a contemporary example, we might look at ISIS. It was relatively common in the ancient near east to think the eschaton would be realized through imperial triumph, and that the end of history was imminent. Indeed, Muhammad's religious beliefs probably played a significant role in the dynamism and success of his nascent polity.
Later Islamic tradition like the biographies deemphasized the urgent apocalypticism (again, not unlike Christianity!). But the Quran is rife with warnings of impending judgement and destruction ("the Hour"), and incorporates Christian apocalyptic material like the parable of the rich fool from Luke. Shoemaker furnishes lots of quotes like "The matter of the Hour is as a twinkling of the eye, or nearer," and "The Lord's judgement is about to fall," etc. Astronomical events will predict the Hour's arrival; doubters will soon be proved wrong, etc.
Perspectives from the New Testament help us understand why different passages portray the urgency of the Hour differently; the historical Jesus probably preached an imminent apocalypse, but the Gospels were compiled later, so they can be more ambivalent. Likewise later Muslims, when compiling the Quran, would have to deal with the fact that the "urgent" end of the world hadn't arrived yet; though the strong eschatological perspective persisted (as it did in Christianity, too), there was an effort to try to moderate some of these embarrassing passages.
Some early hadith and other early traditions corroborate the impending eschaton, emphasizing the link between his appearance and the end of the world. "According to another tradition, Muhammad offered his followers a promise (reminiscent of Matt. 16:28, 24:34) that the Hour would arrive before some of his initial followers died. In yet another tradition, Muhammad responds to questions about the Hour’s timing by pointing to the youngest man in the crowd and declaring that 'if this young man lives, the Hour will arrive before he reaches old age.'"
Donner argues the conquests were an effort to establish an interconfessional "community of the Believers" that included Jews and Christians, requiring only belief in God and the last day. According to him, Muhammad and his earliest followers didn't even think of themselves as a separate religion; rather, their earliest community was a loose confederation of Abrahamic monotheists who shared Muhammad's apocalyptic aoutlook, and who were trying to establish a righteous kingdom in preparation for the end. Cf. the Constitution of Medina, which seems to be a very early source. It has a dramatic discontinuity with the ethnic and religious boundaries established in later Islam. Traditionally held to be a brief experiment that ended with Muhammed expelling the Jews from Medina, Donner argues that in fact Muhammad's community remained confessionally diverse for decades, including Jews and Christians into the Umayyad period. Indeed, a lot of their early successes may have been aided by their nonsectarian outlook.
Only under Abd al-Malik(!) does Islam begin to consolidate, and a new Arab ethnic identity crystallizes that distinguishes Muslims from outsiders they ruled.
In variant readings of the Quran we can glimpse a view not unlike that of the early Christians, where the Kingdom of God had its inception in Jesus's works; here, the conquests of the early followers of Muhammad are part of an the initiation of the end times. Muhammad is the "seal of the prophets" in this reading because the world is about to end.
So the picture that emerges from all this is that Muhammad was an apocalyptic preacher and reformer, very much like Jesus, who wasn't aiming to found a new religion necessarily. But he preached that the world was ending, and as part of his preaching on this subject he led the creation and rapid expansion of a new polity meant to unite the community of believers. Only once he died, and the world failed to end, and his followers had to consolidate their gains and transform them into an actual, durable state did a coherent scripture (the Quran) and a coherent religious identity (Islam) emerge, both strongly affected by the new social, cultural, and political contexts his followers found themselves in. The turning point seems to be the reign of Abd al-Malik, around fifty years after the death of Muhammad, when the oral traditions of the original community of believers are approaching their expiry date, and a new generation (and new converts) need a worldview and a political system that is relevant to their present circumstances. This is extremely comparable to the transition from early Jesus-traditions to the Gospels finally being written down in the second century, when the last people who knew Jesus directly, or who knew the Apostles directly, were dying, and the community had to transition to a form that could survive indefinitely, or else be forgotten.
69 notes
·
View notes
Text
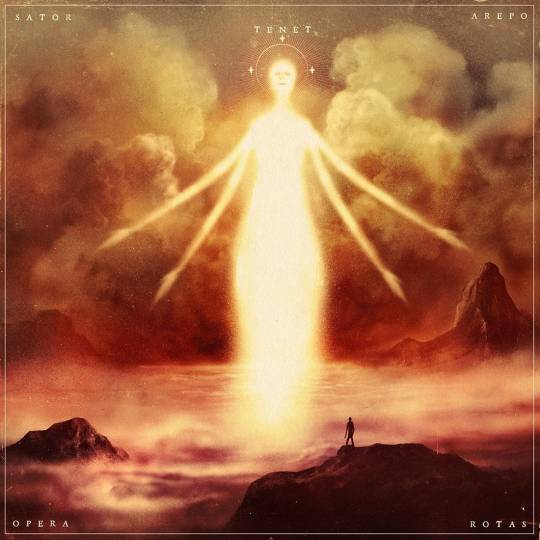


The Sator Square (or the Rotas-Sator Square, or the Templar Magic Square)
Sator square, early Latin word puzzle or cryptogram. It is the most well-known example of a lettered magic square, with 25 letters that make up a five-by-five grid of acrostic Latin palindromes. The words found in a sator square are SATOR (“sower” or “planter”), AREPO (an unknown word, possibly a name), TENET (“to hold”), OPERA (“work” or “care”), and ROTAS (“wheels”). These words are often arranged in this order, but examples have also been found beginning with ROTAS and ending with SATOR; this variant is called a rotas square.
When the five words of a sator square are read horizontally, vertically, forward, in reverse, from bottom to top, or from top to bottom, they form a sentence: sator arepo tenet opera rotas. This sentence has been translated in numerous ways, with the most commonly cited being “The sower, Arepo, works (or holds) the wheels with care.” If read boustrophedon (Greek: “to turn like oxen”; zigzag) with the central word repeating, it can be read as sator opera tenet, tenet opera sator, which has been translated as “as you sow, so you shall reap” and, with a more religious bent, “the Creator preserves his works.” Such a reading has the advantage of eliminating the obscure AREPO, which occurs nowhere else in Latin. (Few of these readings apply to the rotas square.)
The oldest complete example of this cryptogram was a rotas square found in the ruins of Pompeii in 1936. This finding, carved into a column of Pompeii’s Palestra Grande, can be dated to before 62 CE, when an earthquake destroyed the structure. (A fragmentary rotas square was found at Pompeii in 1925.) Other rotas squares have been found throughout the Roman world, from Manchester, England, to the border city of Dura-Europos (now in Syria).
After the fall of Rome and the spread of Christianity throughout Europe, the rotas square was supplanted by the sator square, possibly because the square then began with sator (“sower”), referring to the parable of the sower in Matthew 13. Another Christian connotation was that the grid’s middle word, both vertically and horizontally, is always TENET, which can be read as the two arms of a hidden cross.
The sator square’s origin as a Latin puzzle became increasingly irrelevant as the symbol took on magical properties in European folklore. In the 12th century it could be found in medical books, often as a cure for rabies and fever. Sufferers were advised to carve the square’s words into the crusts of bread before ingesting it. The sator square was also often used as a charm for good fortune in medieval times. In the centuries following, it was adopted as a ward against fires; it was inscribed on the walls of German buildings to prevent their destruction. Sator squares accompanied European settlers to the Western Hemisphere, proliferating throughout North and South America in the 18th and 19th centuries. In the Allegheny and northern Appalachian mountains, German settlers continued to use sator squares as magic cures and prophylactics into the 20th century.
Beginning in the 19th century, Christian thinkers and puzzle enthusiasts tried to decode possible hidden meanings in the sator square. Perhaps the most popular was the Pater Noster theory, which finds the Latin name of the Lord’s Prayer, Pater Noster, written twice in cross form as well as four residual letters (two each of the letters a and o), which can be read as alpha and omega, the first and last letters of the Greek alphabet and how God identifies himself in the Book of Revelation. Independently proposed in the mid-1920s by three separate authors, the Pater Noster theory fell into disfavour with the discovery of the Pompeii rotas squares. Some academics have found a basis for the square’s origin as a Jewish symbol, pointing to the Hebrew letter tau as the central symbol rather than the cross. They also point to the large population of Jews who settled in Pompeii prior to and during the 1st century. Another theory places the square’s origins in Pythagoreanism and Stoicism. Others have argued it is a gnostic symbol developed from Egyptian words and imagery. Many such arguments hinge on tenuous theories about the meaning of AREPO, and no theory of the square’s origins has been widely accepted. It has even been noted that another magic square (ROMA-OLIM-MILO-AMOR), which does not form a sentence, was found at Pompeii, and, thus, the 1st-century Romans possibly just found magic squares to be fun.
49 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Ghosts in the Middle Ages
The medieval Church informed the people's religious imagination during the Middle Ages (c. 476-1500) and the world was therefore interpreted - even by heterodox Christians - through the Church's lens. Ghosts – referred to as revenants – were no exception in that the Church defined such apparitions as souls in purgatory requiring human intervention to find eternal peace.
In the Early Middle Ages (c. 476-1000), there was no consensus on the meaning of ghostly appearances since, following the biblical injunction to "test all spirits", it was usually thought that such an apparition was a demon. As the Church began to emphasize the reality of purgatory, however, the concept of the ghost-as-soul-in-purgatory gained more ground.
The souls most likely to return to haunt the living were those whose burial rituals were not performed correctly or who had unfinished business which required closure; suicides, women who died in childbirth, or people who died suddenly and tragically without time for confession and absolution. Another reason, often entwined with these, was the need of the living to properly say goodbye and let the deceased person go. Elaborate rituals developed to enable the living to cope with the loss of death, release their memories of the dead in order to lay a ghost to rest, and move on with life.
Ghosts in the Ancient World
In the Early Middle Ages, the Church distanced itself from the concept of ghosts as understood by pagan Rome – as the disembodied spirits of the dead – and interpreted them as demonic entities. The biblical epistle of I John 4:1-3 warns believers that not every spirit is "from God" and they should be carefully evaluated for demonic origin. If an apparition appeared in the form of one's departed loved one, it was most likely a demon assuming that shape in order to damn one by tempting them to question God's plan.
The Church taught that God was in ultimate control of every aspect of one's life and that, when one died, there was a place for every soul in the afterlife – in heaven, hell and, eventually, the in-between of purgatory – just as there had been in the social hierarchy of life. A ghost threatened that understanding because it was not only out of place but had returned to where it no longer belonged. If God actually was in control, how did a ghost slip its assigned place in the afterlife to return to the living? The answer, reflecting the I John 4 passage, was that the apparition was not a 'ghost' but a demon in disguise.
Prior to the rise of Christianity, ghosts were understood as a natural – albeit uncomfortable and unwanted – aspect of human existence. The pagan belief systems held to the same understanding of ghosts that the Church would eventually adopt – that spirits of the dead could return to ask help from the living in completing unfinished business, to punish the living for incomplete or inadequate funerary rites, or because some aspect of their death left them unsettled – but this concept was at first resisted by the medieval Church.
In ancient Egypt, people could write letters to the dead addressing problems ranging from why the writer was being haunted or experiencing misfortune to asking where some treasured artifact or document had been placed. In Greece, the continued existence of the dead depended on the memory of the living as expressed in monuments and rituals. The more vibrant the memory, the more vital the spirit in the afterlife. This same paradigm was understood and observed by the Romans who developed societies a citizen paid into which, upon one's death, ensured proper funerary rites and continued remembrance. An apparition, in all three of these belief systems, was a sign that the soul of the deceased was not at rest and some action was required on the part of the living.
The Church had to distance itself from this understanding in the same way it did with all other aspects of pagan thought in order to make its message completely new. Ghosts were demonized in the same way women, cats, attention to personal hygiene, and anything else valued by the pagans were.
Continue reading...
28 notes
·
View notes
Note
I wanna riff off the Ancient Rome ask with my own, but instead of Rome it's Greek babey!!!!
So the old Byzantine Emperors had a bodyguard group called the Varangian guard. They were foreigners to the Empire and loyal only to the Emperor.
Hob is one such guard. He was kidnapped at an early age when his village was attacked by Norsemen. Since then he's fought his way around Europe before being invited into the guard. He's not big on the whole Christianity thing, but he can at least enjoy serving such a pretty Emperor.
On the flip side, Dream is miserable. As Emperor, his head is constantly in peril of being put on the pike. He's got to keep his neighbors from spilling into his territory, he's got to keep trade lines to the east open for business, even the church threatens to break apart and there will be riots in the streets. There already have been when two factions of chariot fans joined forces and nearly burned down Constantinople.
Fortunately, he has his guard around him. Men who can't and won't be bought off or forced into killing him due to the machinations of the other noble houses or even his own siblings. Hob is one of the few he trusts absolutely with his life.
Hob accompanies him to church, where even he is not permitted a weapon. Hob watches over him when he visits the bathhouse and is the only one allowed in the room when he bares his Imperial person so to speak. He even is the sole guard positioned inside the royal bedchamber to watch over the king as he sleeps. He does his job well enough and speaks so little to the various other nobles and Imperial family members that there is little thought of him. He just does his job really well.
What they don't know is Hob has grown to be more than just a body guard. He's Dream's closest companion. He has been given a thorough education in Latin and Greek, how to read and write, he's even sat in on a few philosophy and poetry lessons to better entertain his employer.
In turn, Dream has allowed himself to be less guarded around Hob. They've talked and chatted about loves lost and won. About Dream's idea of the soul being blind until it's had a true, satisfying love. Hob wants to be that love and as such has also been satisfying his Emperor with not only his company but his body as well. It is a sin in the church, but Dream doesn't care. He's an Emperor after all.
This all changed when a Persian assassin snuck into the palace and attempted to kill the Emperor to provoke a war the Byzantines were sure to lose. The assassin was killed by Hob before he could make his attempt on his Emperor's life, but the damage is done. He locks himself in the imperial apartments, refusing to come out except for the high holy days when he spends all his time in church. He refuses to attend senate meetings. He communicates only through Hob. He is completely isolated from the rest of the world.
Some of the noble families titter and gripe about how close a foreign heathen is to the Emperor. How closely he stands to the throne when Dream does make his scant few public appearances. But the Emperor is safe at least. Just so long as Hob can continue to pay the Persians off that is.
🎸
Oh poor Dream, I don't envy him! Except for the fact that he has Hob protecting him 24/7. That is a pretty enviable position to be in!
I really like the emperor/guard situation. The intimacy of that relationship. And there's something especially intimate in the fact that Hob is a foreigner here with absolutely no loyalty or interest elsewhere. It's like he's totally focused on Dream. At this point he doesn't even really have a home to go back to: Dream is his home, his family, his everything. Maybe that's too much for the members of the court and maybe they don't like how close the emperor has become to this common indentured bodyguard. Frankly, Hob doesn't care. He doesnt care about anything in the world, except for Dream.
As much as he hates to see the love of his life so scared and helpless, locked away in his rooms like a precious jewel... it is admittedly a great convenience for Hob to have him in one place all the time. They spend so much of their time in privacy, they become quite used to expressing their love and living a simpler, more domestic life. Sometimes Dream almost seems to forget his troubles when he's lying in his luxurious bed with his head on Hob’s chest.
It isn't only himself he's keeping safe, of course. If Dream isn't in any danger then neither is Hob. Seeing Hob wrestling with that assassin and finally finishing him off was one of the worst moments of Dream’s life. He was terrified that the one man he loves would be killed, all for his sake.
Hob is safe in the imperial apartments with Dream. No assassins will piece their iron doors. Hob may be paying the Persians off, but Dream is paying for Hob’s safety too. And it's worth it. Every moment of Hob’s safety is worth whatever Dream has to give.
42 notes
·
View notes
Text
Here is my master list. Of course, I will be adding as I go. So far, it's all about Jensen and the characters he brings to life for us all to enjoy. My messages are open if you would like to send requests. I'm always looking for some good ideas.
Most of my writing I release 2 weeks early over on my Patreon. I also have started exclusive series over there as well.
Jensen Ackles
She's Mine
Birthday Boy
First Con
Catching His Eye
When In Rome
It Worked
Dean Winchester
Wanna Touch?
Good Girl -MOC Dean
Say My Name
Payback
Seeing Red -Demon Dean
Death Confession
Beau Arlen
Handcuffs and piercings
Luck of the Irish
You're Been a Bad Girl
Soldier Boy
Dirty Boy
Sorry... Not Sorry
Modern Lady
Mini Series
Who Doesn't Love Piercings
All I see is Red
Christian Kane
Meeting Texas
#jensen ackles#soldier boy#beau arlen#dean girl#dean winchester#the boys tv#big sky#spn fanfic#supernatural#jensen ackles smut#spnfamily#soldier boy smut#beau arlen smut
253 notes
·
View notes
Note
Did ancient peoples (such as the Romans, Greeks) believe their Gods were the gods of all men (ala Christianity/Islam) or just specifically THEIR gods? Might a Roman except that Zeus is real but far away and foreign?
Yes and no.
On the one hand, the ancient Mediterranean world could get very local - this is the god of this river, this is the goddess of this forest, this is the patron diety of this polis and there's the temple where they live. One interesting example of this attitude was the Roman tradition of evocatio deorum, a prayer that the Romans would make to the god(s) of a foreign city that they were besieging. In this prayer, they would promise to build a bigger temple in Rome than the one in the diety's home city if they would abandon the defenders for Team Rome:
"Thee too, Queen Juno, who now dwellest in Veii, I beseech, that thou wouldst follow us, after our victory, to the City which is ours and which will soon be thine, where a temple worthy of thy majesty will receive thee."
Likewise, the Romans could get really into gods who they saw as cool and exotic -Isis was a big hit, so was Cebele, so was Mithras, and so forth. As the quote above indicates, to a significant extent, the Roman attitude was that the inclusion of foreign gods made Rome spiritually stronger.
On the other hand, classical paganism had a strong tendency to syncretism. And while this could lead to a more tolerant attitude to foreign gods ("hey, they're just like us!"), it could also lead to an oddly colonialist attitude in which people would translate foreign gods that had the same or similar jobs to their own, erasing some real differences between them:
hence the Romans borrowed the Greek Pantheon but insisted that Ares is actually Mars, Zeus is actually Jupiter, Hera is actually Juno.
the Romans wouldn't stop saying that the Germans worshipped Jupiter (Odin) and Mars (Thor) and Venus (Freya).
the Greeks got into it too, with Herodotus constantly calling Thoth Hermes, and so forth.
On yet a third hand, the Romans could get extremely insistent that everyone in the Empire partake in religious rituals of the Imperial cult, which they saw as spiritually necessary for the prosperity and security of the Roman Empire - which frequently led to violent conflict with monotheistic cultures. Whether in the case of the Jewish-Roman Wars or the persecution of early Christians or the Manicheans in the eastern Empire, the Roman army could go from zero to cultural genocide very fast indeed.
91 notes
·
View notes