#las vegas review journal
Text


Paramore at When We Were Young Festival by Ellen Schmidt for the Las Vegas Review-Journal
#tour 2022#paramore#hayley williams#joey howard#when we were young fest#when we were young#when we were young festival#ellen schmidt#las vegas review journal
89 notes
·
View notes
Text
[excerpt:]
In an earnings call with investors, [executive chairman and CEO of Madison Square Garden Company] Dolan said U2’s success has spurred interest in the entertainment world.
“The incredible response to U2’s run at Sphere has only increased interest from the artist community to play the venue, and we’re having conversations with artists across a wide variety of genres, including discussing runs of varying lengths,” he said. “We expect to host two additional residencies in the second half of this fiscal year (January through June) and look forward to sharing more details.”
Las Vegas Review-Journal | November 9, 2023
#just to add to my prev post..#tho if H’s doing it I assume it won’t be until the later half of 2024#we’ll see..#rumours#the sphere#las vegas review journal#09.11.23#news
1 note
·
View note
Text
Las Vegas, be careful with Oakland A's owner, John Fisher because he will NOT SPEND MONEY
Get ready, Las Vegas. When John Fisher comes to your town, you better prepare yourself. After reading over some Las Vegas media this week, it does seem that most in the area understand the many financial issues that come along with rooting for a team owned by John Fisher. I have also seen some who are just happy getting a baseball team, while others believe that there is a chance of Las Vegas…

View On WordPress
#Atlanta#Atlanta Braves#California#Cobb County#Dave Kaval#Georgia#John Fisher#Las Vegas Aviators#Las Vegas Review Journal#Minor League Baseball#MLB#Nevada#Nevada Independent#Oakland#Oakland As#Oakland Coliseum
0 notes
Text
HELLS ANGELS RETALITION
OAKLAND — A Hells Angels associate has been charged with witness retaliation for allegedly targeting a former member of the outlaw biker club who took the witness stand in a major racketeering trial over the summer, according to court records.
Samuel Holquin, 49, was indicted by a federal grand jury last week on two counts of witness retaliation and two counts of making false statements to the…

View On WordPress
#Biker News#california#hells angel associate#hells angels#hells angels interviews#hells angels mc#HELLS ANGELS RETALITION#hells angels supporter#insane throttle#las vegas news#motorcycle clubs explained#motorycle club videos#review journal#sonoma#sonoma hells angels
0 notes
Text
Las Vegas investigative reporter Jeff German stabbed to death outside his home, police looking for suspect, authorities say
Las Vegas investigative reporter Jeff German stabbed to death outside his home, police looking for suspect, authorities say
2022-09-05 16:10:43
LAS VEGAS, Nevada — A Las Vegas investigative reporter was stabbed to death outside his home and police are looking for a suspect, authorities said.
The video above is ABC13’s 24/7 livestream.
Las Vegas Metropolitan Police officers found journalist Jeff German, 69, dead with stab wounds around 10:30 a.m. Saturday after authorities received a 911 call, the Las Vegas…
View On WordPress
#investigative journalist Jeff German death outside home#Las Vegas Metropolitan Police#las vegas reported stabbed#Las Vegas Review-Journal
0 notes
Text

Free Aspirin & Tender Sympathy at Union 76, Las Vegas Strip. Undated c. 1958. Slide scan by Charles Phoenix.
Alan Post’s Union 76 opened circa ‘57. The phrase “Free Aspirin, Tender Sympathy” appeared in their print advertising that summer, but the earliest dated visual we have of the sign is a traveler's 8mm film from Fall 1958. The sign was referenced in the newspaper later that year:
“A service station attendant got some of his own ‘free aspiring and tender sympathy’ last night on the Strip after he was slugged twice with a crescent wrench by two teenagers who attempted to rob him.”
– Man Slugged by Two Teenagers. Review-Journal, 12/9/58.
The S&H Green Stamps section of the sign was in place through the mid 60s when the station was owned by Wayne Nickerson. That section of the sign lost its neon in the 70s, and was used for painted lettering of later owners names: Jay G. Manning, 70's, and Kenneth L. Lehman, 80s til closing in 2001.
Film from Danita Courtney. Dated Oct. 1958 by performer names in the film. Trees on either side of the sign are about the same size as the Charles Phoenix image.
532 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Neighborhood Playhouse was (and still is) a noted drama school at 340 East 54th Street, known for teaching Sanford Meisner's approach to acting. Here, on June 21, 1956, C&W singer June Carter, who was taking lessons at the Playhouse, did a bit while others watched. From left to right, are Jerry Summers, Hollywood, Calif., Robert Fuller, Hollywood, Calif., Larry Storch, Broadway and television comedian, Julie Wilson, starring in the Broadway production, "The Pajama Game," and Miss Carter. Other alumni of the school include Gregory Peck, Robert Duvall, Kim Basinger, Carol Channing, Jeff Goldblum, Allison Janney, and Grace Kelly.
Photo: Associated Press via Las Vegas Review-Journal
#vintage New York#1950s#drama schools#Neighborhood Playhouse#acting schools#Sanford Meisner#June Carter Cash#Larry Storch#Julie Wilson
37 notes
·
View notes
Text
478. 93 things about 1993, part 5

(part 4)

26. G.I. Joe and Barbie's voiceboxes get switched.
A group of performance artists switched the voiceboxes of about 300 G.I. Joe and Teen Talk Barbie. This was later referenced in the Simpsons episode Lisa Vs. Malibu Stacy:

Poor Celeste.

27. Bill's Half Brother

Leon died in 2009 at the age of 70. He and Bill met a few times! 1

28. The first dreidel in space
Spun by Jeff Hoffman.

29. Lawrence comes out in For Better or for Worse (April 10th)


Lawrence, Michael's friend in the strip came out of the closet in the spring of 1993. Of course, people got mad and demanded the strip be pulled from their local papers:
In the next few weeks, Lawrence, who is 17, will also reveal his sexual orientation to his mother and stepfather. Reader beware; the next two sentences give away plot details. His mother will insist Lawrence is mistaken, and his stepfather will throw Lawrence out of the house. He will spend a lonely night in a doughnut shop until Mike locates him and brings him home for a reconciliation with his famiy.
The plot line has already proved too rich for some tastes. Universal Press Syndicate editorial director Lee Salem says about 20 of some 1,400 newspapers subscribing to “For Better or For Worse” have asked for backup material that can be substituted for the Lawrence strips, and eight have canceled the comic outright.
Lynn Johnston, the Canadian cartoonist who writes and draws the 14-year-old strip, says she knew she was entering a sensitive area, but she’s a little surprised by the scope of the negative reaction.
“What I wrote was kind; it was caring,” she says. “It explored both sides of the issue.”
[...]
Thomas Mitchell did. He’s the editor of the Las Vegas Review-Journal, one of the newspapers pulling the Lawrence panels in favor of backup material.
“We had a pretty little heated argument among ourselves,” he says.
Mitchell finally decided parents shouldn’t abruptly find themselves explaining the material to their children over the morning Rice Krispies.
“It’s the comics page, man. Give me a break,” he says. “It’s an interesting topic. Teenage homosexuality: How do you handle it; how do you talk about it?”
Mitchell says he wouldn’t object to a feature story on the subject, possibly illustrated by strips from “For Better or For Worse.”
Bob Hansen of Enfield probably wishes he was getting Mitchell’s newspaper. Hansen is a Courant subscriber who called the paper Monday to complain about the tack Johnston’s strip had taken.
“I’m very upset about it,” he says. “Comics, in the first place, comics are for fun.”
Hansen says he doesn’t object to homosexuals, but he objects to having homsexuality pushed at people who aren’t interested in hearing about it. In particular, he disliked Lawrence’s remark, in Monday’s episode, insisting he isn’t confused about his orientation: “Everybody else is confused.” 2

For the record, I obsessed over For Better or for Worse almost as much as I did Funky Winkerbean. Good to know Lawrence had a good ending as the strip wound to the end in the Summer of 2008.

30. Dana Carvey almost becomes the host of Late Night.
He said no when offered. 3

(eBay user 3d-ology)
31. Addy becomes an American Girl
There was some controversy among the company whether Addy would be "too real" for kids:
Indeed, the story of Addy may be too heavy for the frail shoulders of a doll, and it clearly represents a dramatic shift in the tone of these children's books. While the other dolls face such traumas as wild bears, sailing during a storm or even choosing between loyalty to the crown of England or the patriots of the new Colonies, none can really compare with watching your brother being whipped by a cruel overseer because he "done run off." In "Meet Addy," the first of her series, she escapes from slavery with her mother, after they are forcibly separated from the rest of the family.
Pittsburgh novelist Connie Porter, who was hired to write the Addy books, is aware of the criticism. "Some people don't want to see a character in slavery -- that's ridiculous," she said. "You can run the risk of being so politically correct that you can lose whole periods of history. Children are more ready to talk about these things than some adults are."
Porter, who met twice with the advisory board to discuss story content and the use of dialect, said that she has not trivialized slavery in any way. If anything, she has made it more real to a modern child than it might have been before, she said. "I tried to show how a black child would be treated during the day at the age of 9," she said. "That she had a job like a grown person. Addy works all day worming tobacco plants. She also serves occasionally for the master, who treats her with indifference. At one point they treat her badly. She's a piece of property." 4
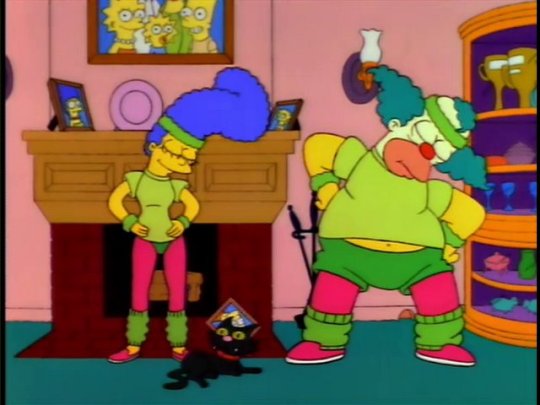

32. Krusty gets canceled, but marge doesn’t say anything. (May 13th)
Y'all Ever notice that Marge has no lines in the classic Simpsons episode "Krusty Gets Canceled"? She's there, but no lines. According to the DVD commentaries, Al Jean said that Julie Kavner felt uncomfortable being in an episode with so many celebrity guests, describing it as "tasteless". I guess she changed her mind through the years.
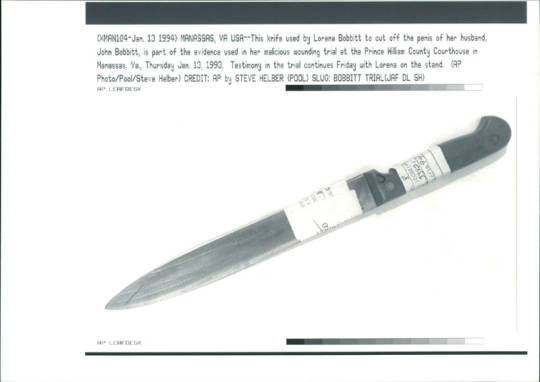
33. Lorena Bobbit copycats
In a four-month period, at least three men besides John Bobbitt had their genitals trashed by angry women. In April, a 29-year-old woman in Milwaukee partially severed her boyfriend's penis after he announced that he wanted to break up, reported the Milwaukee Journal. In Waynesville, N.C., in July, Cynthia Mason Gillett, 28, was charged with setting her husband's genitals on fire while he slept after an argument, reported the Charlotte Observer. In April, Jose Dogelio, 31, was shot in the penis by a woman he was "flashing" on a street in Dasmarinas, Philippines, according to the Manila newspaper, People's Journal. 5
Cynthia was put on probation in January of 1994 because her husband refused to testify against her. She doused his genitals in nail polish and caught them on fire! 6 I could not find Jose's condition.
When I was a kid and I'd see pieces about Lorena and John Bobbit on the news, I pictured Lorena cutting John's penis off with scissors.
Facebook | Etsy | Retail History Blog | Twitter | YouTube Playlist | Random Post | Ko-fi donation | instagram / threads @thelastvcr | tik tok @ saleintothe90s
Barker, Jennifer, and Medianews Group. “Former Paradise Resident Ritzenthaler, Clinton’s Half-Brother, Dies.” Chico Enterprise-Record (blog), January 14, 2009. https://www.chicoer.com/20090114/former-paradise-resident-ritzenthaler-clintons-half-brother-dies/. https://archive.is/YqjO4 .
Hartford Courant. “COMIC TACKLES CONTROVERSIAL ISSUE AS CHARACTER ANNOUNCES HE IS GAY.” March 31, 1993. https://www.courant.com/1993/03/31/comic-tackles-controversial-issue-as-character-announces-he-is-gay/. https://archive.is/dZIGX
Carter, Bill. 1995. The Late Shift: Letterman, Leno, and the Network Battle for the Night. New York: Hyperion. 225-226.
Rosenfeld, Megan. “WHOLESOME BABES IN TOYLAND.” Washington Post, May 24, 1993. https://www.washingtonpost.com/archive/lifestyle/1993/05/24/wholesome-babes-in-toyland/b4ed92ca-1571-4ec9-9290-4dfb4ded0b7b/.
Shepherd, Chuck. “1993: THE YEAR OF THE WEIRD.” Washington Post, December 26, 1993. https://www.washingtonpost.com/archive/opinions/1993/12/26/1993-the-year-of-the-weird/cca1ec6a-5dc9-4be6-9087-e26abe3c657f/.
Tulsa World . “Woman Who Burned Mate Gets Probation.” January 22, 1994. https://1ft.io/proxy?q=https%3A%2F%2Ftulsaworld.com%2Fnews%2Fwoman-who-burned-mate-gets-probation%2Farticle_910a1d92-ff60-57f9-af48-af57d99ad8e2.html
#1993#Lorena bobbit#teen talk barbie#barbie#bill clinton#for better or for worse#dana carvey#american girl dolls#Krusty gets canceled#marge simpson
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
FITFWT23: LAS VEGAS RECAP
Concert number: 22
Date: 1 Jul 2023
Place: THE CHELSEA AT THE COSMOPOLITAN
Capacity: 3,000
Venue: [ducks] [tashfrisco] [floor shaking with Silver Tongues] [exterior] [oli crump] [oli crump]
Livestream: FULL, PARTIAL
Louis’ tweet
LTHQ Twitter and Instagram
Concert Group Photo: [x] [lthq] [x] [x]
Fashion: Palace Skateboards t-shirt, Adidas Gazelle red shoes [Helen Seamons] [Martine Rose football shorts]
Lithograph
Openers: Andrew Cushin, The Snuts
Setlist [annotated… Mikey]
Photos: [x] [x] [city sign] [x] [zak’s mum] [x] [smiling gifs] [HQ] [HQ] [HQ] [HQ] [HQ] [HQ] [x] [x] [gifs] [x] [HQ football] [HQ] [Steve Aoki] [HQ] [x]
Videos: [x]
Speeches: I don’t mind admitting I’ve had a little bit too much fun in Vegas
Outro: Human, by The Killers
Press: Review Journal, astr0mag, astr0mag review, sunlightmagazine
Trends: zouis and Tumblr
Misc: AFHF 2023 IG post, Louis liked Andrew Cushin’s post, Krystle’s beauty products, Louis liked Hotwax’s IG post. Of note, this concert occurred on the day that Twitter’s “rate limit exceeded” error occurred. Matt D’s post. Steve Aoki shares photos and Louis comments. Riccardo. Jack Grealish.
23 notes
·
View notes
Text

Paramore at When We Were Young Festival by Ellen Schmidt for the Las Vegas Review-Journal
#paramore#hayley williams#tour 2022#when we were young#when we were young festival#when we were young fest#las vegas review journal#ellen schmidt
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
Las Vegas Review-Journal | September 22, 2023
Updated September 25, 2023
By John Katsilometes
The music universe seems to be visiting Vegas this weekend. But a performer not in town is creating buzz around the amps.
Harry Styles is in the center of reports from informed individuals he will be the next Sphere headliner announced. This is not formally confirmed, but word is Styles would launch his series in March.
Styles and Phish have been name-dropped consistently among those familiar with The Sphere’s booking plans. Trey Anastasio’s band was held up as a top contender for New Year’s Eve. Not anymore. Phish has announced four NYE dates at Madison Square Garden to close the calendar.
Combining yet-to-be-formalized plans, look for Phish at The Sphere in April, after Styles.
Styles has also been held up as a performer for the Super Bowl halftime show at Allegiant Stadium in February. Such an appearance would serve as a wonderful way to announce a show in Vegas. But those who know Styles’ plans say he is not planning on performing at the Super Bowl.
But Styles is an apt fit for The Sphere. It’s far easier to list the reasons why he’d play the glorious globe than not. In 2022, Styles sold out a 15-show residency at Madison Square Garden. He’s a hitmaker, with “Harry’s House” winning the Grammy Award for Album of the Year.
The first single from that album, “As It Was.” was the No. 1 song internationally by Billboard calculations.
Also, Styles’ sequined bodysuits and boas delight all variety of fan.
And Styles is managed by Irving Azoff’s Full Stop Management entertainment agency. Azoff, who runs the company with his son Jeffrey, is entertainment industry royalty. Azoff the elder is reportedly involved in booking The Sphere as a consultant with venue partner Madison Square Garden Entertainment.
Another of Azoff’s clients: U2. At The Sphere, everything comes full circle.
#this is from september but maybe relevant again now..#(not the super bowl part tho)#harry#the sphere#rumours#las vegas review journal#22.09.23#25.09.23#link#m
1 note
·
View note
Text
Las Vegas seems addicted to handing over taxpayer money to sports teams
Las Vegas loves to do big things. They love their casinos, and they really love handing over millions of taxpayer dollars to rich owners of professional sports teams. With the most recent news of the Oakland A’s wanting taxpayer money from the city of Las Vegas, I thought I would quickly go over some of their most recent deals to build sports teams a new home. To be fair to Las Vegas, they…

View On WordPress
#Allegiant Stadium#Investigative Post#Las Vegas#Las Vegas Raiders#Las Vegas Review Journal#Las Vegas Sun#LVSportsBiz#MLS#MLS2LV#Money Pit#Nevada#Nevada Independent#NFL#Oakland As#Oakland Raiders#TIF District#UNLV#USAToday
1 note
·
View note
Text
MARION, Kan. (AP) — A small newspaper and a police department in Kansas are at the center of a dispute over freedom of speech that is being watched around the country after police raided the office of the local newspaper and the home of its owner and publisher.
Officials with the Marion Police Department confiscated computers and cellphones in the Friday raid, prompting press freedom watchdogs to condemn the actions of local authorities as a blatant violation of the U.S. Constitution’s protection for a free press. The Marion County Record's editor and publisher, Eric Meyer, worked with his staff Sunday to reconstruct stories, ads and other materials for its next edition Wednesday.
A search warrant tied Friday morning raids, led by Marion Police Chief Gideon Cody, to a dispute between the newspaper and a local restaurant owner, Kari Newell. She is accusing the newspaper of invading her privacy and illegally accessing information about her and her driving record and suggested that the newspaper targeted her after she threw Meyer and a reporter out of her restaurant during a political event.
While Meyer saw Newell's complaints — which he said were untrue — as prompting the raids, he also believes the newspaper's aggressive coverage of local politics and issues played a role. He said the newspaper was examining Cody's past work with the Kansas City, Missouri, police as well.
“This is the type of stuff that, you know, that Vladimir Putin does, that Third World dictators do," Meyer said during an interview in his office. "This is Gestapo tactics from World War II.”
Cody said Sunday that the raid was legal and tied to an investigation.
The raids occurred in a town of about 1,900 people, nestled among rolling prairie hills, about 150 miles (241 kilometers) southwest of Kansas City, making the small weekly newspaper the latest to find itself in the headlines and possibly targeted for its reporting.
Last year in New Hampshire, the publisher of a weekly newspaper accused the state attorney general’s office of government overreach after she was arrested for allegedly publishing advertisements for local races without properly marking them as political advertising. In Las Vegas, former Democratic elected official Robert Telles is scheduled to face trial in November for allegedly fatally stabbing Las Vegas Review-Journal reporter Jeff German after German wrote articles critical of Telles and his managerial conduct.
Meyer said that on Friday, one Record reporter suffered an injury to a finger when Cody wrested her cellphone out of her hand, according to the report. The newspaper's surveillance video showed officers reading that reporter her rights while Cody watched, though she wasn't arrested or detained. Newspaper employees were hustled out of the building while the search continued for more than 90 minutes, according to the footage.
Meanwhile, Meyer said, police simultaneously raided his home, seizing computers, his cellphone and the home’s internet router.
But as Meyer fielded messages from reporters and editors as far away as London and reviewed footage from the newsroom’s surveillance camera, Newell was receiving death threats from as far away, she said. She said the Record engages in “tabloid trash reporting” and was trying to hush her up.
“I fully believe that the intent was to do harm and merely tarnish my reputation, and I think if had it been left at that, I don’t think that it would have blown up as big as it was,” Newell said in a telephone interview.
Newell said she threw Meyer and the Record reporter out of the event for Republican U.S. Rep. Jake LaTurner at the request of others who are upset with the “toxic” newspaper. On the town's main street, one storefront included a handmade “Support Marion PD” sign."
The police chief and other officials also attended and were acknowledged at the reception, and the Marion Police Department highlighted the event on its Facebook page.
LaTurner's office did not immediately return phone messages left Sunday at his Washington and district offices seeking comment.
Newell said she believes the newspaper violated the law to get her personal information as it checked on the status of her driver's license following a 2008 drunken driving conviction and other driving violations.
The newspaper countered that it received that information unsolicited, which it verified through public online records. It eventually decided not to run a story because it wasn’t sure the source who supplied it had obtained it legally. But the newspaper did run a story on the city council meeting, in which Newell herself confirmed she'd had a DUI conviction and that she had continued to drive even after her license was suspended.
A two-page search warrant, signed by a local judge, lists Newell as the victim of alleged crimes by the newspaper. When the newspaper asked for a copy of the probable cause affidavit required by law to issue a search warrant, the district court issued a signed statement saying no such affidavit was on file, the Record reported.
Cody, the police chief, indicated that probable cause affidavits were used to get the search warrants. When asked for a copy, Cody replied in an email late Sunday that the affidavits would be available “once charges are filed.”
Cody defended the raid, saying in an email to The Associated Press that while federal law usually requires a subpoena — not just a search warrant — to raid a newsroom, there is an exception “when there is reason to believe the journalist is taking part in the underlying wrongdoing.”
Cody did not give details about what that alleged wrongdoing entailed.
Cody, who was hired in late April as Marion’s police chief after serving 24 years in the Kansas City police, did not respond to questions about how police believe Newell was victimized.
Press freedom and civil rights organizations said that police, the local prosecutor's office and the judge who signed off on the search warrant overstepped their authority.
“It seems like one of the most aggressive police raids of a news organization or entity in quite some time,” said Sharon Brett, legal director for the American Civil Liberties Union of Kansas, adding that it seemed “quite an alarming abuse of authority."
Seth Stern, director of advocacy for Freedom of the Press Foundation, said in a statement that the raid appeared to have violated federal law, the First Amendment, “and basic human decency.”
“The anti-press rhetoric that’s become so pervasive in this country has become more than just talk and is creating a dangerous environment for journalists trying to do their jobs," Stern said.
Meyer said he has been flooded with offers of help from press freedom groups and other news organizations. But he said what he and his staff need is more hours in the day to get their next edition put together.
Both he and Newell are contemplating lawsuits — Newell against the newspaper and Meyer against the public officials who staged the raid.
Meyer also blames the home raid for stressing his 98-year-old mother enough to cause her death on Saturday. Joan Meyer was the newspaper's co-owner.
As for the criticism of the raid as a violation of First Amendment rights, Newell said her privacy rights were violated, and they are “just as important as anybody else’s.”
11 notes
·
View notes
Photo
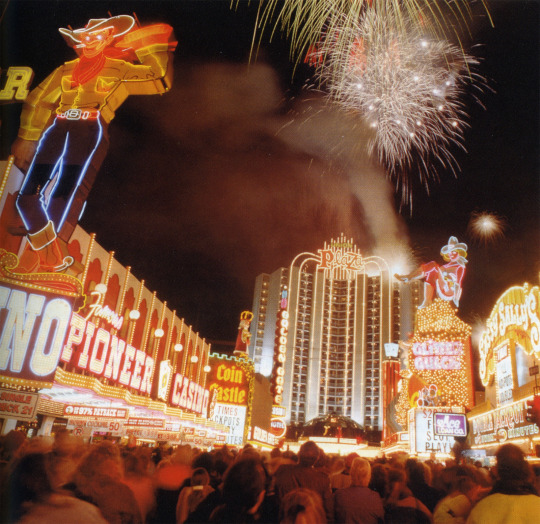

Fireworks from the top of Plaza Hotel, New Year 1990
Photo by John Gurzinski, Las Vegas Review Journal.
463 notes
·
View notes
Text
When Russian troops seized control of the Chernobyl nuclear power plant last year, following the invasion of Ukraine, President Volodymyr Zelensky called it “a declaration of war” against Europe. Others warned that Russia’s reckless seizure of the plant could trigger a nuclear disaster to rival Chernobyl’s 1986 radiological accident.
Their fears seemed well-founded when, on the night of the invasion, sensors began reporting sudden spikes in radiation levels in the Chernobyl Exclusion Zone (CEZ)—a 1,000-square-mile forested zone around the plant where radioactive soil from the 1986 disaster had settled.
Forty-two sensors recorded spikes that night and the next morning—some at levels hundreds of times higher than normal. The State Nuclear Regulatory Inspectorate of Ukraine (SNRIU) eased concerns that nuclear material had leaked from the plant, however, when it said the spikes were likely due to “resuspension” of radioactive soil stirred up by Russian military vehicles—an explanation widely accepted by many nuclear experts and the media.
But a group of environmental radiation experts disputes this conclusion. In a paper published in June by the Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, they detail why there’s no way soil resuspension could have caused the spikes and speculate that interference from an electronic warfare weapon was behind the surge instead.
Now, in what is becoming a deepening mystery, noted cybersecurity researcher Ruben Santamarta says he believes something else was the cause—data manipulation, possibly through a cyberattack.
Based on patterns he found in the spikes—batches of sensors geographically distant from one another recorded spikes at the exact same moment, while sensors closer to them recorded no elevation—he thinks a remote hacker or someone with direct access to the server processing the data manipulated the numbers.
After an extensive review of the data and other materials, Santamarta says he finds it hard to believe the explanation about soil resuspension was ever considered plausible. And he is surprised that authorities never bothered to examine the data for patterns or, if they did, kept that information from the public. He thinks those patterns discount theories about interference from electronic weapons, and he plans to present his findings at the BlackHat security conference in Las Vegas next week.
“I have collected a significant amount of evidence by different means, including OSINT [open source intelligence], hardware and software reverse engineering, and data analysis of the radiation levels,” he says “I think it is enough to seriously consider the possibility that these radiation spikes were fabricated.”
If Santamarta is right, his finding could have far-reaching implications for radiation-monitoring systems around the world, says a former nuclear safety official who asked to remain anonymous in order to speak freely about the matter. If the data was manipulated, it could undermine trust in radiation-monitoring systems or change how data from them gets reported publicly. Data from radiation monitors is often distributed publicly in near real time so that governments and nuclear experts can actively monitor conditions in populated cities and around nuclear facilities. But this creates a risk that hackers or others could alter data to trigger public alarm before proper verification can occur.
Monitoring Networks
Russian troops entered the CEZ early on the morning of February 24 last year because it’s the shortest and most direct route from Russia-friendly Belarus to Kyiv, Ukraine’s capital 80 miles south of the plant. But some feared Russia’s interest in Chernobyl was more than strategic. They worried the military could cause a disaster using radioactive waste at the plant or drum up false claims that Ukraine was building a dirty bomb there.
After a day-long battle with Ukrainian troops and three hours of negotiations to establish parameters for Russia’s occupation of the plant, Russia took control of Chernobyl’s facilities. At 8:40 pm local time, 10 minutes after the SNRIU indicated that Russia had formally taken control of the plant, seven monitoring stations in the CEZ suddenly began reporting elevated radiation levels. The readings ranged from two to five times the normal radiation rate each sensor had historically detected, but one station showed a level eight times higher than normal.
Ukraine has two networks of sensors to monitor radiation at Chernobyl. A set of 10 sensors inside the plant is operated by the state-owned nuclear energy company Energoatom. A second network, known as a radiation-monitoring and early-warning system (the Ukrainian acronym for it is ASKRS), consists of about 68 battery-powered GammaTracer detectors spread throughout the CEZ (with a few positioned outside it). This network is managed by the State Specialized Enterprise Ecocenter (Ecocenter, for short), under the State Agency for the Management of the Exclusion Zone.
These detectors continuously record ambient gamma radiation levels in the CEZ, process the readings to calculate an average, then transmit that figure once an hour (or every two minutes in an emergency) to a base station in the Ecocenter’s office in the town of Chernobyl, about 10 miles from the plant. The data is transmitted via radio over a dedicated channel using a SkyLink protocol.
The data then gets analyzed and processed with DataExpert software and a custom Ecocenter program before being posted to the Ecocenter’s website. It’s also distributed to the SNRIU, the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)—the UN body that monitors nuclear programs around the world—and other governments.
The data can be difficult to find on Ecocenter’s site, so a Ukrainian nonprofit called SaveEcoBot scrapes it and republishes the data on its own site for easier access. It’s these two sites that many people around the world were using to track radiological conditions at Chernobyl in real time on the day of the invasion, and that triggered alarm when people began posting screenshots of them on Twitter.
The Spikes
Radiation levels at Chernobyl are measured as “ambient dose equivalent” rates—essentially the amount of energy, due to ionizing radiation, that the human body would absorb if exposed to the level of radiation a sensor detects. Dose rates are reported as microSieverts per hour (aka μSv/h).
Following the first spikes at 8:40 pm on February 24, 2022, the next cluster of spike occurred at 9:50 pm, when 10 different sensors reported elevated radiation levels, as well as one that had been in the earlier cluster.
More cluster spikes occurred at 10:20 pm, 11:30 pm, and 11:50 pm, involving nine, six, and five sensors, respectively, and then the pattern switched. From 12:01 am to 12:20 am on February 25, there were several spikes involving just one or two sensors each time. Then at 9:20 am, 10 sensors spiked simultaneously, including one that increased nearly 600 times its normal radiation reading. At 10:40 am, nine sensors spiked. And at 10:50 am, the last spike occurred with a single sensor. This sensor spiked three times in all. Called Pozharne Depo, its baseline reading of 1.75 μSv/h spiked to 8.79 (at 8:40 pm), 9.46 (at 9:50 pm), and 32.2 (at 10:50 am the next morning). The sensors may have continued spiking, but the Ecocenter website stopped updating its data.
Like other European countries, Finland carefully tracks Ukraine’s radiation levels. According to Tero Karhunen, a senior inspector with STUK, Finland’s radiation and nuclear safety authority, if ambient dose rates rose above 100 μSv/h for more than 48 hours, it would generally trigger an evacuation of affected regions.
Two sensors nearly reached that threshold at 93 μSv/h, but then they and all the other sensors stopped reporting updates—or at least the Ecocenter stopped posting updated data to its website. It’s not clear why this stopped. The invasion caused internet disruptions in Ukraine, but this would not have prevented the sensors from transmitting their data to the base station; it would only have prevented the Ecocenter from publishing new data to its website.
Yet the Ecocenter did continue to publish new data for some sensors. Shortly after the sensors spiked, online updates of data from 30 of them stopped; but data for the remaining ones continued until they stopped updating at different times. Most of the sensor data was updating online again the following Monday, February 28—at which point all the sensors were reporting normal radiation levels. But by March 3, Ecocenter had stopped posting data altogether.
This may be because Russian troops began stealing and damaging equipment at Chernobyl—including the server and software Ecocenter used to receive and process sensor data. In a French TV news interview after Russian troops left Chernobyl at the end of March, Mykola Bespalyi, head of the Ecocenter’s central analytical lab, showed an empty cabinet that had housed the server, explaining that the center had lost its connection to the radiation sensors in the CEZ. Data transmissions only restarted in June when the IAEA and others helped Ukraine restore the radiation-monitoring system.
Official Response
The spikes were initially attributed to shelling. In a news story published about an hour after the spikes began, an unnamed Ukrainian official said Russian shelling had hit a “radioactive waste repository” and implied that radiation levels had risen as a result. Anton Herashenko, advisor to Ukraine’s Interior Ministry, then warned that the attack could send radioactive dust into Belarus and the EU.
But the next morning, on February 25, the SNRIU said the cause of the spikes couldn’t be determined. Later it released a statement saying Ecocenter experts attributed the spikes to topsoil stirred up—or “resuspended”—by military equipment. At that point, media attention turned to ongoing battles elsewhere in Ukraine, and talk of the spikes dropped.
Not everyone bought the explanation, however. Karine Herviou, deputy director general in charge of nuclear safety at France’s Institute for Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety, told reporters there was no coherent explanation for the spikes, though her group later issued a statement saying they didn’t have any information “to confirm or refute” the SNRIU’s assertion about soil resuspension.
Bruno Chareyron, a nuclear physics engineer and laboratory director for France’s nongovernmental Commission for Independent Research and Information on Radioactivity, also scoffed at the soil explanation. Instead, he told reporters at the time that the spikes might be the result of interference—from a cyberattack.
If you look at a map showing the places where the results had been increasing, “there was no logic” to the soil suspension explanation, he now says. And given that Russia had been prolifically hacking Ukrainian systems at the time of the invasion, it was reasonable to wonder whether a cyberattack had resulted in false data.
Hours after the SNRIU’s statement, the IAEA released its own. Apparently accepting that the radiation spikes were real, the agency said the elevated radiation levels posed no threat to the public. Oddly, though, it referred to the spikes as topping out at 9.46 μSv/h—a figure it received from Ukraine’s nuclear regulator. But the agency only had to look at the Ecocenter’s website to see that some sensors were reporting levels magnitudes higher than this at 58 and 65 μSv/h.
Only some of the GammaTracers are considered “regulatory” sensors—meaning the SNRIU is required to submit data from them to the IAEA. At least three of these regulatory sensors were among those reporting exceptionally high data spikes. But it appears that the SNRIU didn’t provide data from those sensors to the IAEA. It’s not clear why; the SNRIU didn’t respond to inquiries from WIRED.
Notably, there was chatter on Twitter at the time, among nuclear and radiation experts, that the spike data might be erroneous. But if the sensor readings being reported by Ecocenter on its website were accurate, then contrary to the IAEA’s statement that the spikes posed no threat to the public, “this would have been a very dangerous situation for the people in the area,” Chareyron says.
Why did the IAEA only reference the lower radiation spikes in its statement and not the higher ones? The IAEA, after asking WIRED to submit questions in writing, didn’t respond to this or any of the other detailed questions submitted to it, including whether it attempted to investigate the veracity and cause of the spikes.
In the US, the National Security Council followed events in Chernobyl closely but did not respond to repeated requests to discuss the mystery around the radiation spikes.
Soil Suspension, Debunked
As noted, Mike Wood, a professor of applied ecology at the University of Salford in the United Kingdom who studies environmental radiation, including in the CEZ, examined the spike data with four colleagues and ruled out soil resuspension as the cause.
Wood says there isn’t enough radiation in the CEZ soil to cause the level of spikes that occurred—not to mention that military vehicles traveled primarily on asphalt and hardened dirt roads, not in places where loose soil would have been stirred up.
“Even with conservative assumptions, you cannot get anything like the rises that we’ve seen in those dose rate spikes,” he says.
What’s more, experts told WIRED that if soil resuspension were the cause, the radiation levels should have dropped gradually over days as the soil and dust resettled. Instead, many of the sensors were back to reporting normal levels within 30 minutes to a couple of hours after reporting a spike, despite heavy military traffic continuing in the region.
There was also no uniformity or expected patterns to the spikes. Instead of sensors spiking at different times as radiation levels near them rose, multiple sensors in different locations spiked at exactly the same time. Some sensors reported spikes 12 to 38 times their baseline level, others 300 times above baseline. The sensor that spiked nearly 600 times its base level was 18 miles southeast of the plant, located along what Wood calls a “minor” road where “there is no logical explanation as to why there would be significant military activity.”
Olegh Bondarenko, director of the Ecocenter until 2011, agrees with Wood’s conclusions and calls the air suspension explanation “fantastical.” But he doesn’t think Wood’s alternate theory—that the spikes were caused by interference from electronic warfare weapons—was the cause either.
Electronic Warfare
Electronic warfare weapons are used as jamming devices to hinder or block an enemy’s communications and signals.
But Karhunen says Finnish researchers conducted limited tests on the effects of electronic warfare weapons on radiation sensors and found that they could also cause sensors to report false readings up to 30 μSv/h—300 times the base levels for the test systems.
William Radasky, former chair of an International Electrotechnical Commission subcommittee on electromagnetic weapons and their effects, says interference can cause data spikes and, depending on a weapon’s strength, permanently damage sensors. If a weapon were close to a radiation detector when it was fired, “they would probably kill the electronics used with the sensor,” says Radasky, who has conducted research for the US government and military on effects of electromagnetic pulses on defense systems and the electric grid. The pulses wouldn’t interfere with the sensors’ ability to detect radiation, but they would affect the electronics that are used to translate the radiation signals from the sensor into saved data and then transmit that data to the Ecocenter. It’s worth noting that the IAEA visited Chernobyl after Russian soldiers left and reported that many radiation-monitoring stations were damaged and out of service. The agency never identified which sensors or explained the nature of the damage, however.
But if such weapons can produce spikes in the sensor data, that still doesn’t explain the anomalous nature of the spikes, Radasky and Bondarenko say. There were no reports of other equipment in the CEZ being affected by electromagnetic weapons. And radiation sensors in other parts of Ukraine where fighting occurred—and presumably where electromagnetic weapons would likely have been used—did not experience spikes.
Most significantly, sensors that showed spikes in their data were near sensors that didn’t record spikes, and the geographical distance between sensors that spiked defied logic. Many of the sensors that showed simultaneous spikes in the CEZ were more than 30 kilometers apart. Radasky says it would be possible to have a single weapon affect sensors geographically apart, but only at limited distances.
“The most powerful [electromagnetic weapon] I know about could create a high field over [only] a kilometer,” he says. “There is no way to simultaneously affect widely dispersed sensors … from a single weapon.”
If troops dispersed throughout the CEZ carried portable electromagnetic weapons and fired them at the same time, it would be possible to affect sensors far apart, Radasky says. “But … the likelihood that they would have set off those weapons at the exact same moment, causing simultaneous spikes, seems highly unlikely,” he says, noting that a pulse generally lasts for one microsecond.
This, plus patterns that Santamarta found in the spikes, “really does sound like … this is a hacking attempt and not an electromagnetic weapon attack,” Radasky says.
Bondarenko agrees. Every other explanation is “practically implausible or impossible.” It would have been easy, he says, to “write a script that causes certain sensors to elevate at a certain time and then to go back to normal at a certain time.”
Jan Vande Putte, a lead radiation specialist at Greenpeace Belgium, led a team that visited Ukraine last July to measure radiation levels in one part of the CEZ. He agrees that none of the other given explanations are plausible. But he cautions that Santamarta’s theory of data manipulation, while convincing, is still speculation without a forensic investigation to support it.
“I have seen so many examples of coming to wrong conclusions,” he says.
Data Manipulation
Santamarta began looking at the issue last year, after a non-Ukrainian nuclear engineer who has done research in the CEZ asked him to consider whether the sensors could have been hacked. Santamarta specializes in critical infrastructure vulnerabilities and in 2017 found unpatched flaws in radiation-monitoring systems that would let someone falsify data with the aim of simulating a dangerous radiation leak.
He studied the type of sensors used in Chernobyl—a model made by the France-based company Saphymo (later purchased by Bertin Technologies)—and obtained raw sensor data Ecocenter posted to its website, which contained time stamps identifying when each sensor spiked.
He identified 42 radiation sensors that reported spikes in four different patterns—patterns that he says support his assertion that the radiation spikes were fabricated. In the first pattern, 18 sensors reported spikes before going offline. In the second pattern, 17 sensors each reported spikes two times. The second spike was always incrementally higher than the first. For example, a monitoring station called Buryakovka showed a moderate spike on the night of February 24, from 2.19 to 3.54 μSv/h. But at 9:20 am the next morning, it shot up to 52.7 μSv/h.
The third pattern involved two sensors that each spiked three times. The fourth pattern involved five sensors that experienced two spikes—the first spike occurred at 8:40 pm and the second at 11:30 pm the night of the invasion. In each case, the second spike involved a lower value than the first spike—in other words, the second reading was still higher than the baseline level, but lower than the earlier spike. For example, a sensor station called Gornostaypol normally reported a baseline of .092 μSv/h, but during the first spike at 8:40 pm it shot up to .308 μSv/h and at 11:30 pm it reported a level of .120 μSv/h—about midway between the two.
Santamarta believes the patterns strongly suggest that someone wrote code to inject false data into the Ecocenter’s DataExpert database at intervals. The code then posted the false data to the Ecocenter’s website while suppressing legitimate data that came in from the sensors.
“After characterizing the spikes, which are clearly structured, it’s difficult not to assume some kind of human intervention behind them,” he says.
WIRED sent the State Agency for the Management of the Exclusion Zone a list of detailed questions about the patterns Santamarta found and asked whether it had conducted any investigation to determine the cause of the spikes. The agency declined to answer most of the questions and said it was unable to answer others because the events occurred when Russian forces controlled the CEZ and Ecocenter personnel weren’t in a position to know what occurred or to carry out “any corrective actions on the systems.”
Because Ecocenter staff weren’t present, “there is almost no information about the situation around the sensors and servers of Ecocenter in the described period,” Maksym Shevchuk, deputy head of the state agency, said in an emailed statement that his agency translated into English. He noted that any data transmitted by the sensors during that time was automatically received and “automatically transmitted in ‘as-is’ mode” to “various departments outside the exclusion zone,” suggesting that any data posted to the Ecocenter website and transmitted to the IAEA was automatically processed and sent without involvement from Ecocenter staff.
With regard to Santamarta’s findings, Shevchuk said his agency’s “competence does not include the assessment of hypotheses and assumptions on this topic coming from third parties,” and he therefore can’t comment on them.
Who and Why
Santamarta doesn’t speculate in his presentation about who was behind the manipulation if it occurred—he wanted to focus on finding a sound technical and plausible explanation of the cause. But there are two obvious suspects—Russia and Ukraine—both of which have means and motive.
Russia has repeatedly threatened a nuclear event to assert dominion in the conflict and, some argue, to warn NATO against getting involved. And Russian authorities have made numerous claims before and after the invasion that Ukraine was developing a radioactive dirty bomb. A Russian scientist told state media that Russian troops seized Chernobyl to prevent Ukraine from creating a dirty bomb, and the radiation spikes could have been used as “evidence” of illicit nuclear activity on the part of Ukraine.
What’s more, in an April 2022 report about the war, Microsoft revealed that Russian hackers affiliated with the FSB intelligence service had breached a Ukrainian “nuclear safety organization” in December 2021 and stolen data for three months with the aim of obtaining data that would support Russia’s disinformation claims about Ukraine, including claims that it was building a dirty bomb. The report didn’t identify the organization, but the breach shows that Russia had a particular interest in hacking nuclear organizations in Ukraine with the aim of supporting its disinformation campaign.
These suggest a potential method and motive for Russia. But there’s a hitch in this theory. After Ukrainian officials cited the spikes in their denunciation of Russia’s “reckless” seizure of the plant, Russian Ministry of Defense spokesperson Igor Konashenkov denied that any spikes had occurred. He didn’t say how he knew this, but Bondarenko believes Russian troops likely carried handheld radiation meters with them into the CEZ, where they may have gotten very different readings from those the Ukrainian sensors were reporting. A Russian scientist also told Russian media that once data from the CEZ sensors started being posted online again “it would be clear that the radiation situation at Chernobyl was under control.”
If Russia planned to use the spikes to bolster claims that Ukraine was building a dirty bomb at Chernobyl, why didn’t it seize the opportunity to further that claim, instead of disputing that the spikes were real.
As for Ukraine’s potential motives, on the day of the invasion and for days after, Ukraine was struggling to secure timely financial and military aid from Europe. Radiation spikes could have helped underscore the potential nuclear threat to EU leaders if they didn’t act quickly to help Ukraine expel Russian troops.
But there’s another possible motive as well. A Chernobyl worker may have inadvertently revealed it in an interview with the Economist after Russian troops left Chernobyl at the end of March.
He told the publication that during the occupation of the plant, Chernobyl staff had “exaggerated the threat of radiation” to Russian troops, identifying “problematic areas” that they should avoid—all as part of a “cheeky plan” to control where the soldiers went. He didn’t mention the radiation spikes, but they could conceivably have been part of this plan.
After Russian troops left Chernobyl, workers also told reporters that some of the troops had exhibited signs of radiation poisoning—they “developed huge blisters and were vomiting after ignoring warnings about digging trenches in radioactive soil.” Reporters have not been able to independently verify the claims. The IAEA conducted tests after the soldiers left and determined that the digging would not have posed a radiation threat to the soldiers, raising questions about whether the reports of radiation sickness were falsified to instill fear in Russian soldiers.
It may be noteworthy that, in June of this year, as tensions around the Zaporizhzhia plant heated up during Russia’s occupation of that facility, Moscow ordered its troops to halt the automatic transmission of data from the plant’s radiation sensors. The sensors continued to monitor radiation levels, but the data was manually collected from the sensors by IAEA staff.
Verifying Spikes
There were a number of ways to verify the veracity of the spikes when they occurred last year, but there’s no sign anyone in Ukraine questioned the integrity of the data or ordered an investigation. Vande Putte says this was never discussed when his Greenpeace group traveled to Ukraine.
More than two dozen wireless sensors in the CEZ have aerosol filters attached to them that detect radiation levels in the air. Karhunen says the filters are “a hundred million times more sensitive” to small changes in radiation than the digital sensors. Before the invasion, Chernobyl workers collected the filters once a week to test them in a lab. These could have been tested to see if they detected the same radiation levels as the digital sensors. But it seems this didn’t happen during the Russian occupation of the plant when the activities of Chernobyl workers were strictly curtailed, and it’s not clear if the filters were collected and tested afterward. Vande Putte says the Russians left land mines behind in the CEZ, and this may have made it too dangerous for workers to collect the filters after they left.
Once the occupation ended, it would also have been possible to conduct a forensic investigation. Even though the Ecocenter data server, and any digital evidence of manipulation it contained, was no longer available because the Russians stole the server, investigators could have extracted data from the memory of the digital sensors in the CEZ—land mines permitting—to see if data stored in the devices matched what was posted to the Ecocenter website. If it didn’t, this could have bolstered the theory that the data was manipulated on the Ecocenter server. It’s not clear anyone did this, however. Ukraine’s computer emergency response team would likely have been involved in such an investigation, but a source with knowledge of the CERT’s activities says the organization never received a request to investigate the Ecocenter’s systems, and the Ecocenter didn’t respond to WIRED’s inquiries.
It’s possible Ukraine and the IAEA didn’t investigate the spikes because they simply had other more pressing things to address—for example, an ongoing crisis at the Zaporizhzhia nuclear plant. The State Scientific and Technical Center for Nuclear and Radiation Safety told WIRED that it did do a radiological survey after Russian troops left Chernobyl, but this was to determine if Russian forces had absconded with any nuclear materials or planted them in occupied regions to leave behind a nuclear hazard, according to Yuliya Balashevska, who headed the survey. The survey focused only on Kyiv and southeast border regions, and Balashevska said her organization has no access to the Chernobyl sensors and could not have examined them if it wanted to do so.
It may be the case that authorities simply never questioned the authenticity of the spikes and therefore saw no reason to investigate.
Santamarta, however, believes the IAEA and Ecocenter didn’t investigate because of the potential geopolitical implications if such an investigation reached “an inconvenient conclusion” that risked adding “more complexity to an already extremely complicated situation.”
Either way, he, like everyone else WIRED interviewed, says the truth about what occurred is more important than whatever the findings might reveal about who was involved.
Although it’s not clear whether, 18 months after the invasion, evidence still exists that could resolve the mystery of the radiation spikes. Greenpeace’s Vande Putte says an investigation is merited, and that Santamarta’s research is high-quality and “very valuable” as a starting point.
The implications, if the cause was intentional data manipulation, are global, given the potential precedent for manipulating sensors in other regions.
“The truth in these matters is really important. Where did it go wrong? Was it purely technical? Was it deliberate?” he says. “We need to get to the bottom.”
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
3 notes
·
View notes