#houston 1977
Text
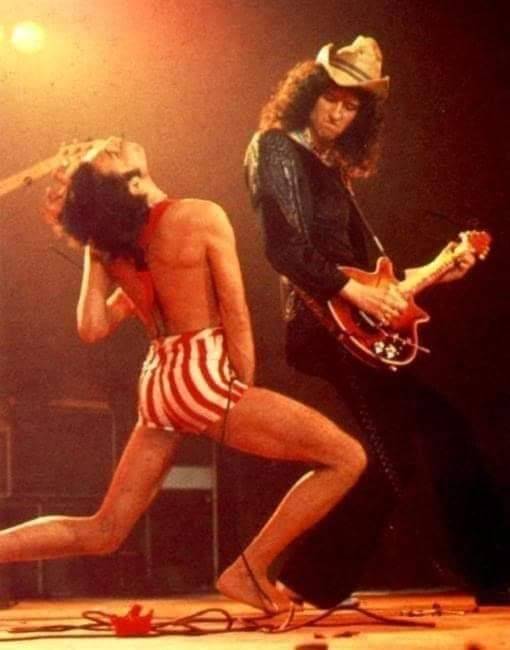

Today - February 26th, 1977 - Queen Story!
Houston, TX, USA, Sam Houston Coliseum
'A Day A The Races' tour
📸➡️ Source photo: RockinHouston.com
#1977#a day at the races tour#a day at the races album#freddie mercury#queen band#london#zanzibar#legend#queen#brian may#john deacon#freddiebulsara#roger taylor#usa#houston
50 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Hills Have Eyes (1977) - Spanish Poster
#the hills have eyes#the hills have eyes 1977#susan lanier#robert houston#john steadman#michael berryman#1977#1970s movies#wes craven#horror movie poster
93 notes
·
View notes
Text
#yours is a generation of girls that do not have to do this #and frankly I recommend you don’t #james tiptree jr you were so real for writing #that a freed population would find the literature of the past#so unrelatable #a bit pathetic #the fuck were they on about honestly #we don’t appreciate the sufferings of our mothers #and I hope our daughters will think ours are unrealistic
obsessed with these tags by @xn3city on this post. We should talk about Tiptree... I need everyone to know I love Tiptree SO much.
Also you really put into words why I think everyone should read older feminist literature. Yes, it's not wholly relevant in this day and age. Yes, that is the point.
#please talk to me about 1977 Hugo Award winning novella Houston do you read#PLEASE talk to me about the screwfly solution sometimes i think about it and my brain glitches#james tiptree jr#book talk
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
Year-End Poll #28: 1977

[Image description: a collage of photos of the 10 musicians and musical groups featured in this poll. In order from left to right, top to bottom: Rod Stewart, Andy Gibb, The Emotions, Barbra Streisand, Hot, Kenny Nolan, Thelma Houston, Rita Coolidge, Alan O'Day, Mary MacGregor. End description]
More information about this blog here
Another good year for the commercial peak of soft rock on the top of the charts. With Evergreen, we're also seeing one of the first instances of the big soundtrack hit in pop music (we'll see an even larger staple of this phenomenon next year). Along with the prolific songwriter (and Swan in Phantom of the Paradise) Paul Williams, Barbra Streisand won the Academy Award for Best Original Song that year, making Streisand the first woman to receive an award as a composer.
The fusion of disco with other genres continues to grow in popularity this year, as seen with Rita Coolidge's cover of Jackie Wilson's (Your Love Keeps Lifting Me) Higher and Higher.
#billboard music#billboard poll#tumblr poll#1970s#1970s music#1977#rod stewart#andy gibb#the emotions#barbra streisand#hot#kenny nolan#thelma houston#rita coolidge#alan o'day#mary macgregor
46 notes
·
View notes
Text

0 notes
Text

LaRue Burbank, mathematician and computer, is just one of the many women who were instrumental to NASA missions.
4 Little Known Women Who Made Huge Contributions to NASA
Women have always played a significant role at NASA and its predecessor NACA, although for much of the agency’s history, they received neither the praise nor recognition that their contributions deserved. To celebrate Women’s History Month – and properly highlight some of the little-known women-led accomplishments of NASA’s early history – our archivists gathered the stories of four women whose work was critical to NASA’s success and paved the way for future generations.
LaRue Burbank: One of the Women Who Helped Land a Man on the Moon
LaRue Burbank was a trailblazing mathematician at NASA. Hired in 1954 at Langley Memorial Aeronautical Laboratory (now NASA’s Langley Research Center), she, like many other young women at NACA, the predecessor to NASA, had a bachelor's degree in mathematics. But unlike most, she also had a physics degree. For the next four years, she worked as a "human computer," conducting complex data analyses for engineers using calculators, slide rules, and other instruments. After NASA's founding, she continued this vital work for Project Mercury.
In 1962, she transferred to the newly established Manned Spacecraft Center (now NASA’s Johnson Space Center) in Houston, becoming one of the few female professionals and managers there. Her expertise in electronics engineering led her to develop critical display systems used by flight controllers in Mission Control to monitor spacecraft during missions. Her work on the Apollo missions was vital to achieving President Kennedy's goal of landing a man on the Moon.
Eilene Galloway: How NASA became… NASA

Eilene Galloway wasn't a NASA employee, but she played a huge role in its very creation. In 1957, after the Soviet Union launched Sputnik, Senator Richard Russell Jr. called on Galloway, an expert on the Atomic Energy Act, to write a report on the U.S. response to the space race. Initially, legislators aimed to essentially re-write the Atomic Energy Act to handle the U.S. space goals. However, Galloway argued that the existing military framework wouldn't suffice – a new agency was needed to oversee both military and civilian aspects of space exploration. This included not just defense, but also meteorology, communications, and international cooperation.
Her work on the National Aeronautics and Space Act ensured NASA had the power to accomplish all these goals, without limitations from the Department of Defense or restrictions on international agreements. Galloway is even to thank for the name "National Aeronautics and Space Administration", as initially NASA was to be called “National Aeronautics and Space Agency” which was deemed to not carry enough weight and status for the wide-ranging role that NASA was to fill.
Barbara Scott: The “Star Trek Nerd” Who Led Our Understanding of the Stars

A self-described "Star Trek nerd," Barbara Scott's passion for space wasn't steered toward engineering by her guidance counselor. But that didn't stop her! Fueled by her love of math and computer science, she landed at Goddard Spaceflight Center in 1977. One of the first women working on flight software, Barbara's coding skills became instrumental on missions like the International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE) and the Thermal Canister Experiment on the Space Shuttle's STS-3. For the final decade of her impressive career, Scott managed the flight software for the iconic Hubble Space Telescope, a testament to her dedication to space exploration.
Dr. Claire Parkinson: An Early Pioneer in Climate Science Whose Work is Still Saving Lives

Dr. Claire Parkinson's love of math blossomed into a passion for climate science. Inspired by the Moon landing, and the fight for civil rights, she pursued a graduate degree in climatology. In 1978, her talents landed her at Goddard, where she continued her research on sea ice modeling. But Parkinson's impact goes beyond theory. She began analyzing satellite data, leading to a groundbreaking discovery: a decline in Arctic sea ice coverage between 1973 and 1987. This critical finding caught the attention of Senator Al Gore, highlighting the urgency of climate change.
Parkinson's leadership extended beyond research. As Project Scientist for the Aqua satellite, she championed making its data freely available. This real-time information has benefitted countless projects, from wildfire management to weather forecasting, even aiding in monitoring the COVID-19 pandemic. Parkinson's dedication to understanding sea ice patterns and the impact of climate change continues to be a valuable resource for our planet.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
#NASA#space#tech#technology#womens history month#women in STEM#math#climate science#computer science
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Pretty Boy Live in Santa Fe, 1977
Part 1/3 Also on Ao3 here

For @harringrove-relay-race. Very happy with how part 1 turned out, and there will be more to come. Thanks to @foxxtastic for the intro and next up will be something stunning from our fearless Relay Race leader @half-oz-eddie
Rated M / 5k words / Part 1/3

Part 1: Into Hades
Rolling Stone Magazine - May 2002
Billy Hargrove arrived after I did, in his lovingly maintained blue Camaro, the subject of his song, “Lady Blue.” “Lady Blue” was recently named #93 on Rolling Stone’s Top Love Songs of the Century.
“I wrote, ‘She’s the wind in my hair, the rumble in my soul.’ I thought it was so obvious,” He laughed, his blue eyes still boyish. “My niece made it her wedding song, I said ‘Really? It’s about a fuckin’ car!’”
He showed me several pictures of his niece, the supermodel Tyler Sinclair. It seems good looks run in the family. He suggested the diner and he ordered waffles, winking when I mentioned that we’ll be here a long time.
The decades have been kind to him, maybe a few more lines. It’s not hard to imagine him stepping right back onto the stage, as if no time has passed at all.
“A little extra glitter on the eyes,” He said with a smile, “to hide my crows feet. That’s all I need.”
I ask what he’s going to wear to the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame ceremony for Kaleidoscope's induction and his smile dims only for a moment.
“I think I should pull out some old costumes. You know, the butterfly still fits.”
He was referring, of course, to the sheer butterfly cape costume that nearly had him thrown off the stage in Houston Texas in December 1976. He caved to putting on a pair of silvery shorts rather than the nude underwear it was designed with. He later wore it with the nude underwear on the inside cover of Kaleidoscope, the album that will be inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame in just a few short weeks. Kaleidoscope was his last album with the iconic Glam Rock band Pretty Boy, which famously broke up at the height of their career while touring for the album, onstage.
It’s not often that a band is inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame and there’s a question if all of them will even show up.
“I’ll be there,” Hargrove said, fiddling with the silver band on his middle finger. “I have no problem with seeing him.”
The him is, of course, the lead guitarist and other lead singer of Pretty Boy, Steve Harrington.
Steve Harrington invites me to his oceanfront house in Malibu later that afternoon.
“I haven’t decided if I’m going to go,” He said thoughtfully, his brown eyes darting around the room.
When I mention that Billy is going to go, he seems surprised.
“He didn’t say he was going to punch me, did he?” Harrington smiled, but it doesn’t seem like much of a joke.
For one of the most famous rock stars of the 70s, Harrington is shockingly low key. He wears a t-shirt and slouchy linen pants, and he jokes that he ought to have shaved when I take out my camera. The house is stunning but empty, with miles of blank white walls and overstuffed white furniture.
“I’m looking for a little peace,” He shrugs, “I used to have all these pictures up, all this furniture… It was too much.”
It was hard not to see him as an artist without a muse. He drifted listlessly, picking things up and putting them down as we talked. So it was a surprise to me to hear that he’s been recording.
“I may never release it but… Yeah,” He laughed, “Music. After all this time. Bet you didn’t know.”
He picks up a rare photo from the piano. It’s from the early days of Pretty Boy, before Billy Hargrove. Harrington has his arm around his bandmate, Eddie Munson. Their drummer Chrissy Cunningham is balanced precariously across their shoulders, laughing and cringing at the same time. Bassist Robin Buckley smirks from the corner of the frame, messy bangs in her eyes.
“Who knew, right?” He asked no one, shaking the frame a little.
There are no pictures of Billy Hargrove.
“That’s a… a long story,” He said, when I asked.
But I have time. I tell him Rolling Stone will pay for it. At least that makes him laugh.

It was just by chance that Pretty Boy’s last concert was filmed.
“We were meant to just film in Vegas,” The director, Argyle Molina-Zapata, sat down with me after a private screening of Pretty Boy Live in Santa Fe, 1977, “But there was a freak rainstorm, and I couldn’t get my camera’s out of the back. The crowd was digging it, refused to leave. I remember when Billy hit the high note for ‘Mother Make Me,’ there was this lightning crack… brilliant.”
Molina-Zapata shook his head, “But the footage, what I got of it, was awful. Awful! So I begged Murray to let me come with them to Santa Fe.”
Murray was Murray Bauman, famed tour manager, who handled the Boys, later Pretty Boy from their first album Starfire, all the way to Kaleidoscope.
“And I was lucky,” Argyle nodded, “They had that extra tour bus.”
The tour busses are featured in the first few minutes of the film. They roll around the corner, one reading Billy Blue (Billy’s original stage name was Billy Blue before he dropped the Blue), and the other, Steve’s Six (Named after Steve’s best friends from his hometown.)
“They were nightmares,” Murray Bauman’s voice crackled over the phone, “Nightmares on tour. Separate buses. Separate hotels. Fuck me, I swear to god at one point they wanted separate stages. And the label caved on almost all of it. Fucking nightmare.”
It’s almost impossible to imagine it when you see them on stage together. There’s something electric that passed between Billy Hargrove and Steve Harrington, something that drove crowds wild. They gravitate towards each other on the stage, orbiting like planets until they can share the same mic. They can’t seem to stay apart.
It’s hard to see exactly what happened that night.
“I’ve watched it a million times,” Argyle laughed, “But the only two people who can really say what happened are Billy and Steve.”
What you can see is this: Steve tearing into “Pride & Prejudice”, the lead off Kaleidoscope and the last song of the night.
Billy was trembling, visibly shaking as he sang and Steve harmonized along.
What can I say, if you ask me to walk away?
Baby, there’s no words for you.
Baby. I don’t know what to do.
Billy danced closer, joining Steve, his handheld mic loose at his side.
Can you ever put away your pride?
Is it worth it to not have me at your side?
I guess it must be, because I’m yours,
Regretfully,
Baby.
Billy leans in, sharing Steve’s mic for the bridge.
Is it really a mystery?
What I mean to you, and you mean to me?
Is it really, baby?
Billy shook his head, curls bouncing. He looked into Steve's eyes. He smiled. Steve looks at Billy, and Billy looks at him. It almost looks like Billy mouths something, but bootleg footage also has appeared where it looks like Billy just nodded. Steve goes a little shell shocked, hand freezing on his guitar, falling out of sync.
And then Steve turned away and left the stage, handing his guitar to a stagehand. Billy turned to the crowd, his expression strangely triumphant. He was always magnetic on stage, but this moment transcends that. It somehow feels like he’s getting everything he wants.
So I guess I’m losing you,
You promised me you would and it’s true.
Baby, there’s no words for you.
Baby. I don’t know what to do.
Steve Harrington hasn’t performed in public since 1977.

“None of us knew what was going to happen that night,” Chrissy Cunningham curled up next to her husband, Eddie Munson, on the large white couch of their Seattle home.
They’re a handsome couple still, draped in rock and roll finery. He toyed with the edge of her scarf, and she curled his long hair around her long fingers.
“We had some of our own shit going on at the time so…” Munson shrugged, “Maybe we were distracted.”
Their living room was crowded and verdant, every spare flat surface covered in plants. Their partner, former record executive Jason Carver, puttered in the kitchen in an apron that read Plant Papa.
“Yeah,” Chrissy smiled, “We had some stuff going on at the same time. But still… It seemed like they were getting better. Didn’t it seem like they were getting better?”
Munson shrugged, “The thing about Billy and Steve… they were soulmates. You don’t write music like that and not… it was like they had a second language, just for them. They were soulmates, I really believe that. Everything they did, everything that happened… they could only hurt each other that badly if… yeah.”
When I ask what they did to each other, Eddie and Chrissy just scooted closer together, like teenagers in a slasher, hiding from the killer. She laid a hand over his leg, her two stone diamond ring catching the sunlight.
“Steve never wanted Billy to be in the band,” Eddie shook his head, “but Jim had a soft spot for Billy. And Steve had… I mean Jim was…”
“Jim was like a father. To all of us.” Chrissy’s knee jiggled.
“We were this little tiny band from Nowhere, Indiana,” Eddie nodded, “And Jim believed in us.”
“I was just a junior exec at the time. I was put on the Kaleidoscope tour in case of catastrophic failure, which by the way it was,” Jason Carver is making risotto while we speak, the steam curling the lock of hair that falls over his face. “But it wasn’t my fault although I was high as hell on coke half the time. I guess I deserved to get fired. But Jim was the real deal. Gold records out the ass, best wife in the world, and his daughter, I mean… she was something else.”
They’re referring, of course, to Jim Hopper, producer on Kaleidoscope as well as Billy Blue and The Boys’ records, and the father of pop superstar Eleven aka Jane Hopper.
“Jim was…” Steve Harrington’s eyes always got a little misty talking about Jim, staring out over the ocean. “Yeah, I guess he was a little like my dad. My own parents were always gone. Which is like… I grew up so privileged so like I’m not saying… I just mean I grew up mostly by myself. And we were just so lucky he even agreed to listen to us when we got to LA.”
“I remember that night,” Joyce Hopper’s voice was raspy, cigarette-y in the way only old movie stars are. She’s a gorgeous woman in jeans and a gardening hat, speaking to me while she tends to her garden at her home in Castellammare. “He came home and said, ‘I have the next ones, the next big ones. Fuck, Joyce, they’re brilliant. Unpolished, but brilliant.’”
When I ask about when Jim discovered Billy Hargrove she just laughed.
“If Steve and the rest of The Boys were unpolished, Billy Hargrove was a fucking ten carat diamond,” She said. “But Steve’s band was Jim’s, and he could polish them up how he wanted. And then when he thought they were just right for it… he set the diamond.”
Jim Hopper was a big man, larger than life both in appearance and in personality. His fingerprints are all over some of the best hits of the decade.
Watching him on old interviews, there’s an immediacy to his presence that leaps off the screen.
“My daughter is the one who really found him. She snuck out with her sister and wandered God knows where. And she just… found him. Called me the next morning, saying ‘Dad, you have to hear this guy.’ He was playing in this… terrible club,” Jim said, tapping his cigar on the table of Merv Griffin’s set. “Absolute shithole, pardon my french. And he’s got a great voice, you’ve heard his voice, right?”
“I have,” Merv said.
“I had to get him out of there. He was a star.”
Billy Hargrove was a teenage runaway from San Diego when he came to LA in 1971.
“I had a girl’s backpack from my stepsister, eight dollars, and an extra pair of underwear. By the end of the next week? I had two more dollars,” Billy laughed. “But I got lucky. I met Heather.”
Heather Holloway was a showgirl at Wildwoods, a nightly revue. She found Billy at the backdoor, and took him to her apartment.
“She saved me,” He frowned. “Whenever I needed her most.”
Heather Holloway, Billy Hargrove’s first and only wife, died in 1979.
“I got a job singing at Sugar, this great gay club downtown. It was in the late afternoons, so I had a crowd of about… two. But those two brought two more,” Billy smiled, “Heather would talk me up to all the promoters. He’s a singer, he’s great, you’ll love him, he’s so cute.”
“He was an instant hit,” Sugar’s manager, Bob Newby, tells me by phone as well. “I did have to keep a couple of creeps off him, when he just started he was only nineteen. But even if you closed your eyes… he was a hit.”
“Guys used to think that because I was a part of the entertainment, I was fair game. And let me tell you, the novelty of that wears off mighty quick,” Billy shakes his head.
He shares a diary entry from his late wife of a night in April 1972. He came to her home with blood all over his face.
“Some guy thought because I was a fag…” Billy’s mouth twisted, but he went on, cradling the little marble notebook in his hand. “He could do whatever he wanted to me. When I fought back… he cracked a bottle over my head.”
He’s not just a piece of meat. He’s a person. I don’t understand these people. I just don’t understand, Heather Holloway wrote. I cleaned him up and he’s sleeping now.
The next diary entry is from a day later. April 12. Billy and I drove to Vegas and got married. When we spoke in the morning he said he was afraid for me too, even though I’m careful with the girls. He’s afraid of the cops trying to bust up the Wildwoods and picking me up. At least this way, he says. He and I can come home to each other. Look out for each other. Always. The groom wore band aids and his great velvet pants. The bride wore lavender. It was perfect.
“And lucky too. Because within a month… I met Jim,” Billy smiled. “And my whole life changed.”
Upside Down Records signed Billy Blue, unagented, in1972 and he spent the next year working on his debut album with Jim Hopper.
“I didn’t even realize, when it happened,” Billy shook his head. “A couple of girls came by after a show, wanting to talk to me, wanting to meet me. That wasn’t that unusual. But they were young, far too young to get into the club. And the little one, she was asking all these weird questions. Did I have an agent? Did I know if I had enough songs for an album? Weird fuckin’ questions. And then she said I have to meet someone. To be honest, I thought she was coked out of her mind when she said, ‘You have to meet my dad.’”
“I was not,” Eleven promised me, “coked out of my mind. But that’s just Billy.”
Eleven aka Jane Hopper, meets me backstage at one of her shows. She’s dressed in slouchy leather pants, to match her sister and drummer Kali Hopper.
“I knew he was something special. My dad was always talking about the IT factor. That thing that made a person something special. But I didn’t get it until I saw Billy Blue singing on that tiny stage,” She smiled. “He didn’t just have the IT factor. He was IT.”
It’s odd then, that Billy Blue’s first album had a surprisingly tepid response. His first single, in 1973, “Let Alone,” came in at only 26th for the month of April on the pop charts.
“People liked it,” Billy shrugs, “But I don’t think they knew what to do with it. You have my songs, these like… little pop love songs and ballads. I wasn’t that strong of a writer at the time. It was like half my songs, half covers. And so they’d book me, expecting fucking… Peter Frampton. And here comes this big queer with glitter on his nipples.”
But the lyrics of “Let Alone” would hint at his later songs, a hallmark simplicity that shone off his raw voice and poetry that hinted at a troubled past.
And if you were meant to care for me
You would, and that’s how it has to be
You said I couldn’t go on without you
Ha, look at me, looking brand new
At the same time, The Boys’ song “Paper Girl,” penned by Harrington, was number one.
She’s my paper girl
She’s my paper girl
Wakes me up every morning, right on time
She got me smiling, got my head in a whirl
Picture perfect, paper girl
“Billy didn’t have much commercial appeal. Sex appeal, yes,” Jason laughed, toying with Chrissy’s hair. “But for sales? That’s where The Boys came in.”
“I hated that name,” Eddie said, “To start with we were half girls.”
The Boys had already had a somewhat successful tour under their belt by the time Jim suggested a collaboration with Billy Hargrove.
“It was a nice, short tour,” Steve Harrington glances away when I ask about the first tour.
“It was a nightmare. Balls to the wall nightmare,” Robin Buckley’s voice is a warm crackle over the phone. “Steve went on like thirty overlapping benders at once.”
Her partner, soap actress Vickie Carmichael cackles behind her, at their home in Salt Lake City.
“The thing about Steve is… well… he’s never found a good way of coping with himself,” Robin huffs. “Music was about as close as he ever got. But in those early days, he just kept looking for more and more.”
“You don’t think it was about-” Vickie asked, just barely into the phone.
“No.”
“It was about Nancy,” Eddie said confidently when I mentioned their first tour. “Nancy, Nancy, Nancy.”
The Boys got their start in the late sixties, beginning with Eddie and Steve. Eddie gave Steve guitar lessons, which turned into some talent show performances. They used to practice at Eddie’s Uncle’s trailer.
“That’s where we got the name,” Eddie nodded, “My uncle used to just call us that, and it stuck.”
“I don’t even remember,” Chrissy said.
“That’s not how we got the name,” Steve shook his head, when I mention Eddie. “It was our first gig, after we got Chrissy and Robin. Robin put it down after the headliner kept asking when ‘you boys’ would go on, and kept addressing it to Chrissy’s chest. She blew him out of the fucking water.”
Nancy Wheeler was there that night, writing about local bands for a tiny column in the school paper.
“She was beautiful. Smart. So smart. Could hear her talk forever,” Steve said, eyes falling.
Steve Harrington and Nancy Wheeler were married in 1972 after they graduated high school.
“Steve made his own choices,” Chrissy shook her head.
That summer, the Boys plus one drove to LA and Nancy Wheeler took a job at Women’s Day Magazine and later, Rolling Stone. Steve Harrington and The Boys got a “steady gig” at La Bonita Rosa on the strip, playing for drunks every night from seven to eight.
“I really liked playing at La Bonita,” Steve said. “The audience, right there. You could smell the sweat. You could see on their faces if you were bombing. And we used to bomb. A lot. But it was a great place to try things. Experiment. We played there for about a year but… it felt too short.”
Within the year they had met Jim Hopper, who got them into the recording studio and sold their demo nearly on the spot to Upside Down Records.
“They had a great sound. They had got this way of playing. Smooth like a polished stone. Everything sounds good sitting in a frame like that,” Jim said in an interview with Rolling Stone in 1981. “Their songs were… catchy, but basic. But they had the sound.”
Upside Down records set the Boys on a US tour after “Paper Girl,” and “Joy to Love You,” both charted.
“It was like… overnight. One day we’re in a studio, messing around. Kid stuff. I was nineteen,” Steve Harrington shookhis head. “But…”
“That tour,” Chrissy trails off, playing with her ring again.
“I…” Steve Harrington scratched his nose. “I was losing it. Majorly losing it. It felt like we had just moved to LA and we were already neck deep. I mean, I had a number one fucking song. And for some reason I got it in my head to call my mom. She told the maid she wasn’t home. And I could hear her over the phone. My mom. So yeah. I lost it. Lost about half my damn mind on that tour. And people will say it was because of Nancy, because we got married just out of high school, and she wasn’t supportive… but that wasn’t true. Nancy saved me.”
“Nancy never wanted him to be in the band. But… she also didn’t seem to care that much either,” Eddie shook his head, “It’s… complicated. Love is supposed to be. Simple. Like the chords of a song. 1-3-5.”
Jason Carver rolled his eyes at that, “Then what are we?”
Eddie grinned, “We’re a band.”
Nancy Wheeler met me on a Thursday in New York City, slim sunglasses dominating her small porcelain face. We get lunch at her favorite deli shop, and she perches at the counter, loafers dangling. She’s an editor at The New Yorker now, but she still has a soft spot for rock and roll, as evidenced by the Grateful Dead t-shirt under her blazer.
“That tour. I didn’t even know anything was wrong. He just came home with a funny look on his face, saying, ‘We’re headlining.’ So I said, ‘That’s great, Steve.’ He just kept… saying it. It was starting to piss me off, if I’m being honest,” She shook her head. “I should have known something was wrong.”
“I wish she had stopped me. But how could you know right? Hindsight is always 2020,” Steve Harrington said. “I mean, she was my wife. How could she not want me home? But that’s just… sorry. That’s not fair to put on her. I chose to go.”
“I flew out to meet them when they were in Indianapolis, visited my family, and I came a day early to see him,” She smiled warmly, and then it fell. “He was… Well, first, Eddie Munson tried to intercept me at the hotel, so I wouldn’t see him. I told him, ‘I’m here to see my fucking husband.’”
Steve Harrington didn’t add any more details about the tour, just shrugged when I asked.
“He was coked up like you wouldn’t believe,” Robin scoffed. “She walked in on him with two girls and coke all over his… well.”
“I just asked him. Do you want to come home? Do you want to get help? Or not?” She purses her lips. “And so he came home and we found a rehab place near Hawkins.”
“The tour kind of… fell apart. Obviously. We had lost our lead singer and guitarist to fucking… Hawkins, Indiana,”
Everything stopped for the Boys. Upside Down offered to let them out of their two album contract, but Steve couldn’t afford to pay it down.
“Rehab,” He shrugged. “Is expensive.”
Right as it seemed that everything would be over for the Boys, things were looking up for Billy Blue.
“Jim was always saying, ‘the record is selling alright, the songs are getting there but he needs a… push,’” Joyce said. “‘He’s so close. So close. He’s a star.’”
“He always believed in me,” Billy smiled, toying with his ring again. “Always. Even when I threw a jug of milk at his head.”
Joyce laughed when I asked about that moment, “He came home saying, ‘He milked me, Joyce. But he’ll fix the song tonight.’”
“And I did,” Billy said. “And the album was going alright. I did a little tour, socal and the southwest. And then one night, Jim brings me this song. He said, ‘I want you to tell me what’s missing from this.’”
The song was, of course, the Boys’ biggest hit, “Hades.” Steve Harrington’s first version was called, “To Orpheus” and the chorus goes:
Don’t turn back don’t look behind you baby
I’m close, I’m right behind
The future's so bright, and I want you to take me
Wanna be holding your hand when I make it across the line.
“It was fine, but just kind of… nothing. It was supposed to be about Eurydice, but it was so… nothing. She just loved Orpheus and that was it. There were no insides to her. She was going to follow him to her doom,” Billy shook his head. “That’s not right.”
This was not the version that made it to the recording booth, of course. The Boys’ single, “Hades featuring Billy Blue,” came out in 1975. The actual chorus goes:
Turn back on me and I won’t forgive you baby
Don’t want you to see me like this
Up ahead is bright, and I want you to take me
If you’re strong enough to cross that finish line
“‘Hades,’ was a real step forward for the Boys. Gone were the teenybopper tunes,” Steve Harrington’s biographer and personal friend Dustin Henderson wrote in his book The Pretty Boy. “Their first album got the kids dancing. But the second proved that they actually had something to say.”
“Still hate it,” Steve Harrington said. “I wrote that song in rehab. It was deeply, deeply personal to me.”
“He came out, all ready. He wanted to start recording right away,” Robin sighed. “Like I mean the next day. All these songs, just pouring out of him. But the label had lost faith in us. And they certainly weren’t going to let us start recording with a guy who had only just earned his thirty day sober chip.”
“The song wasn’t ready,” Billy shook his head. “But I guess he was. Jim said he needed this. So Jim asked if I would come and like… pitch some stuff as a personal favor. Songwriting credit, that’s all it was supposed to be. Get the songs moving, get them going.”
Steve Harrington takes a long time to continue speaking about it.
“I felt it, writing for that album. I felt proud of those songs. They didn’t belong to anyone else but me,” He toyed with some piano keys while we talked, and then finally sat down and began to play something tuneless and half formed.
“That album was all about Nancy,” Chrissy said. “I mean. I know it. You know it. Nancy knew it. And she kind of hated it. But-”
“You can’t leave your husband right as he gets out of rehab,” Nancy said to me, toying with her wedding ring. “When he writes all these songs about how you’re the only thing… Steve was always like that. Heart wide open. That’s why when he met Billy. I almost thought… it would all be okay. That sounds fucked up but. I thought they could save each other. That the music could save him.”
“It was just a songwriting credit,” Billy raised his hands. “Jim swore up and down. I was just gonna come in there and sit down with this guy Steve. But when I walk into the studio, there’s two mics set up.”
“I was the Boys’ only singer,” Steve Harrington shook his head. “And to be absolutely honest, I was kind of a jackass about it. So to have some guy come in and say he’s gonna sing me my song… well…”
“Steve was the only one who would ever argue with Jim, And he let him have it that day,” Eddie laughed. “He called him the most low down, dirty, rat bitten bastard in California, and that he would die rather than give up his band to someone else.”
“I did not want his band. I did not know his band. And I did not care. And his song sucked. And I told him so. And then I sang it. Better.” Billy smiled.
“Billy was…” Chrissy shook her head. “Incredible.”
I ask Steve what Billy was like that first day in the studio.
“He was,” Something passed over his face. “Alright. He has a great voice, alright.”
“I was good. Better. Best.” Billy smiled.
“But he didn’t understand the song. He wanted Eurydice to… doubt. To think she wasn’t going to get out,” Steve slammed his hands on the keys. “It’s been… almost twenty years. I still don’t understand it.”
I asked why he let Billy stay. But Steve doesn’t have an answer.
“They were like oil and water, right away,” Chrissy said.
“Yeah, but oil on the water can catch fire,” Eddie shrugged.
“Jim asked me to stay,” Billy looked away from me, down at his waffles. “It was a favor to the label.”
“If Billy said louder, Steve said mute,” Robin snickered. “It was kind of great, actually. Finally someone called King Steve on his shit. One day I came in and they were arguing over how close the microphone should be to your throat. Almost got in a physical fight over a fucking microphone. I mean, I love Steve. But he always thinks he’s like… the babysitter. It’s his job to do everything for everybody.”
“Like who was this guy? Really? He came into my studio with no shirt on, most of the time still half smashed from the night before, and he thinks he can make all these changes. But Jim keeps telling me it’s just business, the label thinks it’s good business.” Steve frowned, and then smiled, and then frowned again.
“Yeah, I never wore shirts back then. Or underwear,” Billy said with a grin. “I was a rockstar!”
“Steve fought for every song on that album,” Nancy Wheeler patted her lips primly with a napkin. “He only lost on one.”
“Billy Hargove has songwriting credit and lead vocals on “Hades.” Dustin Henderson wrote.
“Billy was all over that album. He’d make some minor suggestion, maybe this chord instead of that, this word is better. And Steve would flip out, yell at him, yell at Jim, threaten to storm out… and then two days later quietly tell me to change the chord, he’d start singing the new words. Billy was there with us about every single day,” Eddie said.
“Of course, it was our biggest hit,” Chrissy laughed. “Everything but that song, Steve did what he wanted. Oh we had Billy in the studio, making suggestions. But Steve did what he wanted except for ‘Hades.’ Jim said that song is the album, and he wouldn’t cut it.”
“Jim was always right,” Steve closed the piano. “The bastard.”
Hades exploded onto the radio in late 1975. They didn’t have the same distribution as their first record, but the Boys had another hit.
“Billy had this way of singing it. Still does. He broke four mics when we recorded it. Singing so loud I had to keep an eye on the cymbals to stop them from shaking. You can feel him, right in your chest.” Chrissy giggled. “Like he was trying to wake all the dead from Hades. If anyone could, he could.”
“It’s a really, really great song,” Robin said.
This song belongs to Billy Blue, Rolling Stone wrote in 1976. The only question now is, what will The Boys do next?
“I remember that article. Fucking… Harrington said that he basically wrote the whole song. But he said, ‘the label thought bringing Billy in was a good idea,’” Billy gets tense for the first time. “I’m not saying I was like… I just mean. It would have been nice. To treat me like an equal. I’m more than just a singer. I’m not just… a piece of meat.”
“Billy was really pissed about that article. I remember, the day after the article came out, we were getting breakfast at this tiny place off La Cienega. Steve had this car back then, a big maroon BMW, and Eddie had got him a vanity plate when he bought it. Stupid thing it said, ‘BIGBOY.’ Anyway, We’re having breakfast, and we hear this screech outside, like an accident,” Robin Buckley gets uncharacteristically quiet as she goes on through this story. “Billy’s car is parked halfway out of the parking lot, and he comes in like a bull in a charge. Billy… he wasn’t some wimpy guy. He was small, but he was strong as hell… He came right over and grabbed Steve by his collar and lifted him right off the counter. And he said, I’ll never forget it because Steve used to recite it from memory, yell it at me, ‘Tell me I’m not dreaming. Is that Steve fucking Harrington? The lead singer of the Boys. Hey man, I love your song ‘Hades.’ How’d you get your voice to sound halfway decent for once?’”
“I don’t remember that,” Steve Harrington said flatly when I asked.
“And Steve used to be a fucking dick in high school. So he starts getting real bitchy, shoving Billy off him, asking what his problem is, why he’s such a dick all the fucking time, when it’s not even his band. And Billy said something like, ‘No one wants your shit band. Not with you in it,’” Robin paused for a moment. “And they just. Stare at each other. Like… daring each other to do something.”
Billy just shrugs when I ask, “I was pissed. I gave this guy a number one hit, and he still wanted to treat me like some… airhead singer the label brought in as a stunt. I’m not just a singer. I’m not a piece of meat. I’m a person.”
When I ask Steve about that day he’s pretty quiet, deflated at his piano. He only wants to talk about the song. The music. Can’t seem to talk about Billy any other way.
“He sang it like he not only knows Orpheus can’t save him, but that he won’t. It was supposed to be hopeful. A happy ending.” Steve said.
“So you still hate the song?” I asked.
“No, I don’t. It’s brilliant. And that’s the whole problem.”

To be continued...
Next up is Half-Oz-Eddie's piece at 7:00 pm. GET HYPE!
#harringrove relay race#harringrove#billy x steve#billy hargrove#steve harrington#harringrove fic#steve x billy#harringrovefic#harringrovefanfic#harringrove fanfiction#harringrove fanfic#stranger things#my writing#DJATS au#Daisy jones and the six au#tw drugs
86 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Premiering now the first fully complete remaster of Queen Live in Houston 1977, done by some amazing people, come drop by if you're free and a fan of this show! ❤️
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
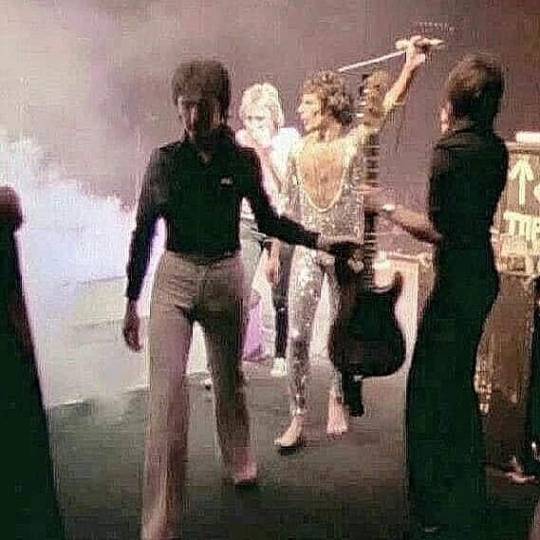

December 11th, 1977 - Queen Story!
Queen perform at the Summit, Houston, USA, during 'News Of The World Tour'#usa
41 notes
·
View notes
Text

Sex kitten summit meeting! Jayne Mansfield and Éva Gábor photographed at the Cotillion Ball at the Shamrock Hilton in Houston Texas in November 1960. Imagine partying with this fun duo! Effervescent coquette Éva Gábor (11 February 1919 – 4 July 1995), youngest and most talented of the three much-married fabulously ridiculous Hungarian American socialite, elite courtesan and surgically-enhanced glamourpuss Gábor sisters, was born on this day 105 years ago. While she’s inevitably described as “famous for being famous”, Gábor was a gifted and sparkling comedic actress of stage, screen and TV (especially in 1960s sitcom Green Acres; seek out the film Paris Model (1953) for further evidence), possessed a distinctive campy voice (she memorably did voice-overs for the Disney films The Aristocats (1970) and The Rescuers (1977)) – and the boss lady behind her own successful wig range! Gábor may also have been bisexual: in his 2019 book Finding Zsa Zsa: The Gabors Behind the Legend, author Sam Staggs suggests that Eva enjoyed a long liaison with Marlene Dietrich. Apparently, Francesca Hilton (Zsa Zsa Gábor's daughter and Eva’s niece) alleged to Staggs that her aunt was secretly a lesbian. Considering Éva was married five times and had a long romance with Glenn Ford, her commitment to Sapphism seems unlikely. But who knows? To complicate things, Eva was widely rumoured to be Merv Griffin’s “beard” later in life. Let’s hope it’s true! Anyway, my favourite Éva Gábor memory: circa 1989 when her more volatile older sister Zsa Zsa was famously arrested for slapping a traffic cop’s face, the cable network Nick at Nite promoted their reruns of Green Acres with an ad proclaiming, “Remember – this is Éva, not Zsa Zsa! Eva will not harm you!”
#eva gabor#jayne mansfield#lobotomy room#sex kitten#kitsch#the gabor sisters#green acres#old showbiz#old hollywood#glamour#international sex kitten#starlet#glamour queen#glamourpuss#retro#camp
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cancelled Missions: NASA's October 1977 Space Shuttle Flight Itinerary
"Soon after President Richard Nixon gave his blessing to the Space Shuttle Program on January 5, 1972, NASA scheduled its first orbital flight for 1977, then for March 1978. By early 1975, the date had slipped to March 1979. Funding shortfalls were to blame, as were the daunting engineering challenges of developing the world's first reusable orbital spaceship based on 1970s technology. The schedule slip was actually worse than NASA let on: as early as January 32, 1975, an internal NASA document (marked 'sensitive') gave a '90% probability date' for the first Shuttle launch of December 1979.
In October 1977, Chester Lee, director of Space Transportation System (STS) Operations at NASA Headquarters, distributed the first edition of the STS Flight Assignment Baseline, a launch schedule and payload manifest for the first 16 operational Shuttle missions. The document was in keeping with NASA's stated philosophy that reusable Shuttle Orbiters would fly on-time and often, like a fleet of cargo airplanes. The STS Utilization and Operations Office at NASA's Johnson Space Center (JSC) in Houston had prepared the document, which was meant to be revised quarterly as new customers chose the Space Shuttle as their cheap and reliable ride to space.
The JSC planners assumed that six Orbital Flight Test (OFT) missions would precede the first operational Shuttle flight. The OFT flights would see two-man crews (Commander and Pilot) put Orbiter Vehicle 102 (OV-102) through its paces in low-Earth orbit. The planners did not include the OFT schedule in their document, but the May 30, 1980 launch date for their first operational Shuttle mission suggests that they based their flight schedule on the March 1979 first OFT launch date.
Thirteen of the 16 operational flights would use OV-102 and three would use OV-101. NASA would christen OV-102 Columbia in February 1979, shortly before it rolled out of the Rockwell International plant in Palmdale, California.
As for OV-101, its name was changed from Constitution to Enterprise in mid-1976 at the insistence of Star Trek fans. Enterprise flew in Approach and Landing Test (ALT) flights at Edwards Air Force Base in California beginning on February 15, 1977. ALT flights, which saw the Orbiter carried by and dropped from a modified 747, ended soon after the NASA JSC planners released their document.
The first operational Space Shuttle mission, Flight 7 (May 30 - June 3, 1980), would see Columbia climb to a 225-nautical-mile (n-mi) orbit inclined 28.5° relative to Earth's equator (unless otherwise stated, all orbits are inclined at 28.5°, the latitude of Kennedy Space Center in Florida). The delta-winged Orbiter would carry a three-person crew in its two-deck crew compartment and the bus-sized Long Duration Exposure Facility (LDEF) in its 15-foot-wide, 60-foot-long payload bay.
Columbia would also carry a 'payload of opportunity' - that is, an unspecified payload. The presence of a payload of opportunity meant that the flight had available excess payload weight capacity. Payload mass up would total 27,925 pounds. Payload mass down after the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm hoisted LDEF out of Columbia's payload bay and released it into orbit would total 9080 pounds.

A page from the STS Flight Assignment Baseline document of October 1977 shows payloads and other features of the first five operational Space Shuttle missions plus Flight 12/Flight 12 Alternate
During Flight 8 (July 1-3, 1980), Columbia would orbit 160 n mi above the Earth. Three astronauts would release two satellites and their solid-propellant rocket stages: Tracking and Data Relay Satellite-A (TDRS-A) with a two-stage Interim Upper Stage (IUS) and the Satellite Business Systems-A (SBS-A) commercial communications satellite on a Spinning Solid Upper Stage-Delta-class (SSUS-D).
Prior to release, the crew would spin the SBS-A satellite about its long axis on a turntable to create gyroscopic stability and raise TDRS-A on a tilt-table. After release, their respective solid-propellant stages would propel them to their assigned slots in geostationary orbit (GEO), 19,323 n mi above the equator. Payload mass up would total 51,243 pounds; mass down, 8912 pounds, most of which would comprise reusable restraint and deployment hardware for the satellites.
The TDRS system, which would include three operational satellites and an orbiting spare, was meant to trim costs and improve communications coverage by replacing most of the ground-based Manned Space Flight Network (MSFN). Previous U.S. piloted missions had relied on MSFN ground stations to relay communications to and from the Mission Control Center (MCC) in Houston. Because spacecraft in low-Earth orbit could remain in range of a given ground station for only a few minutes at a time, astronauts were frequently out of contact with the MCC.
On Flight 9 (August 1-6, 1980), Columbia would climb to a 160-n-mi orbit. Three astronauts would deploy GOES-D, a National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) weather satellite, and Anik-C/1, a Canadian communications satellite. Before release, the crew would raise the NOAA satellite and its SSUS-Atlas-class (SSUS-A) rocket stage on the tilt-table and spin up the Anik-C/1-SSUS-D combination on the turntable. In addition to the two named satellites, NASA JSC planners reckoned that Columbia could carry a 14,000-pound payload of opportunity. Payload mass up would total 36,017 pounds; mass down, 21,116 pounds.
Following Flight 9, NASA would withdraw Columbia from service for 12 weeks to permit conversion from OFT configuration to operational configuration. The JSC planners explained that the conversion would be deferred until after Flight 9 to ensure an on-time first operational flight and to save time by combining it with Columbia's preparations for the first Spacelab mission on Flight 11. The switch from OFT to operational configuration would entail removal of Development Flight Instrumentation (sensors for monitoring Orbiter systems and performance); replacement of Commander and Pilot ejection seats on the crew compartment upper deck (the flight deck) with fixed seats; power system upgrades; and installation of an airlock on the crew compartment lower deck (the mid-deck).
Flight 10 (November 14-16, 1980) would be a near-copy of Flight 8. A three-person Columbia crew would deploy TDRS-B/IUS and SBS-B/SSUS-D into a 160-n-mi-high orbit. The rocket stages would then boost the satellites to GEO. Cargo mass up would total 53,744 pounds; mass down, 11,443 pounds.
Flight 11 (December 18-25, 1980) would see the orbital debut of Spacelab. Columbia would orbit Earth 160 n mi high at 57° of inclination. NASA and the multinational European Space Research Organization (ESRO) agreed in August 1973 that Europe should develop and manufacture Spacelab pressurized modules and unpressurized pallets for use in the Space Shuttle Program. Initially dubbed the 'sortie lab,' Spacelab would operate only in the Orbiter payload bay; it was not intended as an independent space station, though many hoped that it would help to demonstrate that an Earth-orbiting station could be useful.
ESRO merged with the European Launcher Development Organization in 1975 to form the European Space Agency (ESA). Columbia's five-person crew for Flight 11 would probably include scientists and at least one astronaut from an ESA member country.
Flight 12 (January 30 - February 1, 1981), a near-copy of Flights 8 and 10, would see Columbia's three-person crew deploy TDRS-C/IUS and Anik-C/2/SSUS-D into 160-n-mi-high orbit. Payload mass up would total 53,744 pounds; mass down, 11,443 pounds.
JSC planners inserted an optional 'Flight 12 Alternate' (January 30 - February 4, 1981) into their schedule which, if flown, would replace Flight 12. Columbia would orbit 160 n mi above the Earth. Its three-person crew would deploy Anik-C/2 on a SSUS-D stage. The mission's main purpose, however, would be to create a backup launch opportunity for an Intelsat V-class satellite already scheduled for launch on a U.S. Atlas-Centaur or European Ariane I rocket. An SSUS-A stage would boost the Intelsat V from Shuttle orbit to GEO.
NASA JSC assumed that, besides the satellites, stages, and their support hardware, Columbia would for Flight 12 Alternate tote an attached payload of opportunity that would need to operate in space for five days to provide useful data (hence the mission's planned duration). Payload mass up would total 37,067 pounds; mass down, 17,347 pounds.

Space Shuttle Flights 13 through 18 would include the first orbital mission of the OV-101 Enterprise (Flight 17), during which astronauts would retrieve the LDEF payload deployed during Flight 7.
Flight 13 (March 3-8, 1981) would see three astronauts on board Columbia release NOAA's GOES-E satellite attached to an SSUS-D stage into a 160-n-mi-high orbit. OV-102 would have room for two payloads of opportunity: one attached at the front of the payload bay and one deployed from a turntable aft of the GOES-E/SSUS-D combination. Payload mass up would total 38,549 pounds; mass down, 23,647 pounds.
Flight 14 would last 12 days, making it the longest described in the STS Flight Assignment Baseline document. Scheduled for launch on April 7, 1981, it would carry a 'train' of four unpressurized Spacelab experiment pallets and an 'Igloo,' a small pressurized compartment for pallet support equipment. The Igloo, though pressurized, would not be accessible to the five-person crew. OV-102 would orbit 225 n mi high at an inclination of 57°. Mass up would total 31,833 pounds; mass down, 28,450 pounds.
Flight 15 (May 13-15, 1981) would be a near-copy of Flights 8, 10, and 12. OV-102 would transport to orbit a payload totaling 53,744 pounds; payload mass down would total 11,443 pounds. The JSC planners noted the possibility that none of the potential payloads for Flight 15 — TDRS-D and SBS-C or Anik-C/3 — would need to be launched as early as May 1981. TDRS-D was meant as an orbiting spare; if the first three TDRS operated as planned, its launch could be postponed. Likewise, SBS-C and Anik-C/3 were each a backup for the previously launched satellites in their series.
Flight 16 (June 16-23, 1981) would be a five-person Spacelab pressurized module flight aboard OV-102 in 160-n-mi-high orbit. Payloads of opportunity totaling about 18,000 pounds might accompany the Spacelab module; for planning purposes, a satellite and SSUS-D on a turntable behind the module was assumed. Payload mass up would total 35,676 pounds; mass down, 27,995 pounds.
Flight 17, scheduled for July 16-20, 1981, would see the space debut of Enterprise and the retrieval of the LDEF released during Flight 7. OV-101 would climb to a roughly 200-n-mi-high orbit (LDEF's altitude after 13.5 months of orbital decay would determine the mission's precise altitude).
Before rendezvous with LDEF, Flight 17's three-man crew would release an Intelsat V/SSUS-A and a satellite payload of opportunity. After the satellites were sent on their way, the astronauts would pilot Enterprise to a rendezvous with LDEF, snare it with the RMS, and secure it in the payload bay. Mass up would total 26,564 pounds; mass down, 26,369 pounds.
For Flight 18 (July 29-August 5, 1981), Columbia would carry to a 160-n-mi-high orbit a Spacelab pallet dedicated to materials processing in the vacuum and microgravity of space. The three-person flight might also include the first acknowledged Department of Defense (DOD) payload of the Space Shuttle Program, a U.S. Air Force pallet designated STP-P80-1. JSC called the payload 'Planned' rather than 'Firm' and noted somewhat cryptically that it was the Teal Ruby experiment 'accommodated from OFT [Orbital Flight Test].'
The presence of the Earth-directed Teal Ruby sensor payload would account for Flight 18's planned 57° orbital inclination, which would take it over most of Earth's densely populated areas. Payload mass up might total 32,548 pounds; mass down, 23,827 pounds.
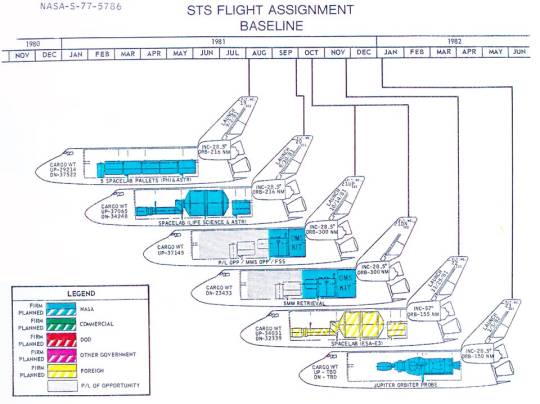
Space Shuttle Flights 20 through 23 would include the first mission to make use of an OMS kit to increase its orbital altitude (Flight 21), the first European Space Agency-sponsored Spacelab mission (Flight 22), and the launch of the Jupiter Orbiter and Probe spacecraft (Flight 23)
Flight 19 (September 2-9, 1981) would see five Spacelab experiment pallets fill Columbia's payload bay. Five astronauts would operate the experiments, which would emphasize physics and astronomy. The Orbiter would circle Earth in a 216-n-mi-high orbit. Payload mass up would total 29,214 pounds; mass down, 27,522 pounds.
Flight 20 (September 30-October 6, 1981), the second Enterprise mission, would see five astronauts conduct life science and astronomy experiments in a 216-n-mi-high orbit using a Spacelab pressurized module and an unpressurized pallet. JSC planners acknowledged that the mission's down payload mass (34,248 pounds) might be 'excessive,' but noted that their estimate was 'based on preliminary payload data.' Mass up would total 37,065 pounds.
On Flight 21, scheduled for launch on October 14, 1981, Columbia would carry the first Orbital Maneuvering System (OMS) Kit at the aft end of its payload bay. The OMS Kit would carry enough supplemental propellants for the Orbiter's twin rear-mounted OMS engines to perform a velocity change of 500 feet per second. This would enable OV-102 to rendezvous with and retrieve the Solar Maximum Mission (SMM) satellite in a 300-n-mi-high orbit.
Three astronauts would fly the five-day mission, which would attain the highest orbital altitude of any flight in the STS Flight Assignment Baseline document. JSC planners noted that the Multi-mission Modular Spacecraft (MMS) support hardware meant to carry SMM back to Earth could also transport an MMS-type satellite into orbit. Payload mass up would total 37,145 pounds; mass down, 23,433 pounds.
On Flight 22 (November 25 - December 2, 1981), Enterprise might carry an ESA-sponsored Spacelab mission with a five-person crew, a pressurized lab module, and a pallet to a 155-to-177-n-mi orbit inclined at 57°. Payload mass up might total 34,031 pounds; mass down, 32,339 pounds.
During Flight 23 (January 5-6, 1982), the last described in the STS Flight Assignment Baseline document, three astronauts would deploy into a 150-to-160-n-mi-high orbit the Jupiter Orbiter and Probe (JOP) spacecraft on a stack of three IUSs. President Jimmy Carter had requested new-start funds for JOP in his Fiscal Year 1978 NASA budget, which had taken effect on October 1, 1977. Because JOP was so new when they prepared their document, JSC planners declined to estimate up/down payload masses.
Flight 23 formed an anchor point for the Shuttle schedule because JOP had a launch window dictated by the movements of the planets. If the automated explorer did not leave for Jupiter between January 2 and 12, 1982, it would mean a 13-month delay while Earth and Jupiter moved into position for another launch attempt.
Almost nothing in the October 1977 STS Flight Assignment Baseline document occurred as planned. It was not even updated quarterly; no update had been issued as of mid-November 1978, by which time the target launch dates for the first Space Shuttle orbital mission and the first operational Shuttle flight had slipped officially to September 28, 1979 and February 27, 1981, respectively.
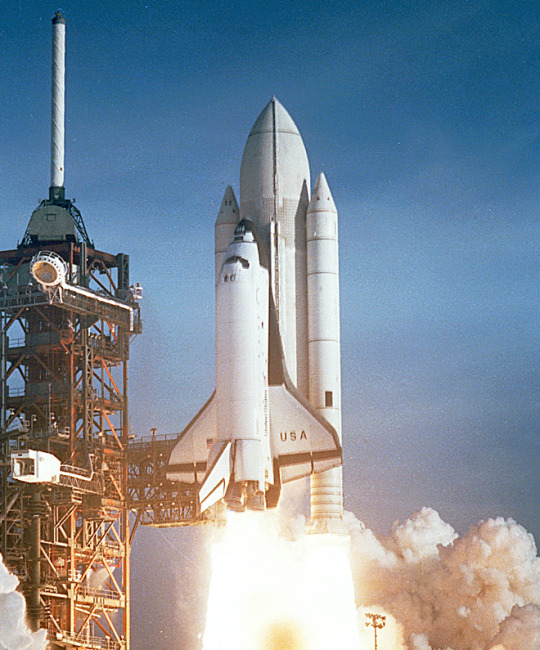
The Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia lifts off at the start of STS-1.
The first Shuttle flight, designated STS-1, did not in fact lift off until April 12, 1981. As in the STS Flight Assignment Baseline document, OV-102 Columbia performed the OFT missions; OFT concluded, however, after only four flights. After the seven-day STS-4 mission (June 27 - July 4, 1982), President Ronald Reagan declared the Shuttle operational.
The first operational flight, also using Columbia, was STS-5 (November 11-16, 1982). The mission launched SBS-3 and Anik-C/3; because of Shuttle delays, the other SBS and Anik-C satellites planned for Shuttle launch had already reached space atop expendable rockets.
To the chagrin of many Star Trek fans, Enterprise never reached space. NASA decided that it would be less costly to convert Structural Test Article-099 into a flight-worthy Orbiter than to refit Enterprise for spaceflight after the ALT series. OV-099, christened Challenger, first reached space on mission STS-6 (April 4-9, 1983), which saw deployment of the first TDRS satellite.
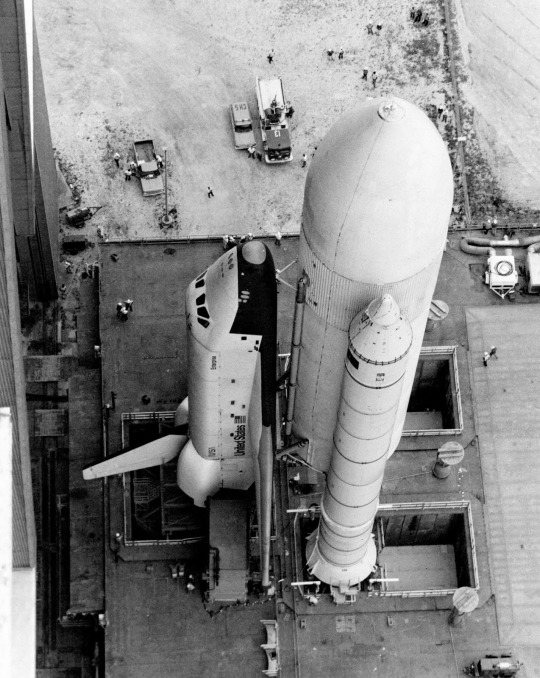

NASA put OV-101 Enterprise to work in a variety of tests and rehearsals (such as the 'fit check' shown in the image above), but did not convert it into a spaceflight-worthy Orbiter.
The voluminous Spacelab pressurized module first reached orbit on board Columbia on mission STS-9 (November 28- December 8,1983). The 10-day Spacelab 1 mission included ESA researcher Ulf Merbold and NASA scientist-astronauts Owen Garriott and Robert Parker. Garriott, selected to be an astronaut in 1965, had flown for 59 days on board the Skylab space station in 1973. Parker had been selected in 1967, but STS-9 was his first spaceflight.
The 21,500-pound LDEF reached Earth orbit on board Challenger on STS-41C, the 11th Space Shuttle mission (April 6-13, 1984). During the same mission, astronauts captured, repaired, and released the SMM satellite, which had reached orbit on 14 February 1980 and malfunctioned in January 1981. Challenger reached SMM without an OMS kit; in fact, no OMS kit ever reached space.
STS Flight Assignment Baseline document assumed that 22 Shuttle flights (six OFT and 16 operational) would occur before January 1982. In fact, the 22nd Shuttle flight did not begin until October 1985, when Challenger carried eight astronauts and the West German Spacelab D1 into space (STS-61A, October 30 - November 6, 1985). Three months later (28 January 1986), Challenger was destroyed at the start of STS-51L, the Shuttle Program's 25th mission.
In addition to seven astronauts — NASA's first in-flight fatalities — Challenger took with it TDRS-B, NASA's second TDRS satellite. The Shuttle would not fly again until September 1988 (STS-26, September 29 - October 3, 1988). On that mission, OV-103 Discovery deployed TDRS-C. The TDRS system would not include the three satellites necessary for global coverage until TDRS-D reached orbit on board Discovery on mission STS-29 (13-18 March 1989).
Following the Challenger accident, NASA abandoned — though not without some resistance — the pretense that it operated a fleet of cargo planes. The space agency had at one time aimed for 60 Shuttle flights per year; between 1988 and 2003, the Shuttle Program managed about six per year. The most flights the Shuttle fleet accomplished in a year was nine in 1985.
Shuttle delays meant that JOP, renamed Galileo, missed its early January 1982 launch window. It was eventually rescheduled for May 1986, but the Challenger accident intervened. Galileo finally left Earth orbit on 18 October 1989 following deployment from OV-104 Atlantis during STS-34 (October 18-23, 1989).
Between the time JOP/Galileo received its first funding and the Challenger explosion, NASA, the White House, and Congress had sparred over how the Jupiter spacecraft would depart Earth orbit. Eventually, they settled on the powerful liquid-propellant Centaur-G' rocket stage.
Citing new concern for safety following Challenger, NASA canceled Centaur G'. Galileo had to rely on the less-powerful IUS, which meant that it could not travel directly to Jupiter; it had instead to perform gravity-assist flybys of Venus and Earth to reach its exploration target. Galileo did not reach the Jupiter system until December 1995.
LDEF had been scheduled for retrieval in March 1985, less than a year after deployment, but flight delays and the Challenger accident postponed its return to Earth by nearly six years. On mission STS-32 (January 9-20, 1990), astronauts on board Columbia retrieved LDEF, the orbit of which had decayed to 178 n mi. LDEF remains the largest object ever retrieved in space and returned to Earth.
During reentry at the end of mission STS-107 (16 January-1 February 2003), Columbia broke apart over northeast Texas, killing its international crew of seven astronauts. This precipitated cancellation of the Space Shuttle Program by President George W. Bush, who announced his decision on 14 January 2004.
The end of the Space Shuttle Program was originally scheduled for 2010, immediately following the planned completion of the International Space Station. In the event, STS-135, the final Space Shuttle mission, took place four years ago (July 2011), three months after the 30th anniversary of STS-1. The Orbiter Atlantis lifted off on 8 July with a four-person crew — the smallest since STS-6. It docked with the International Space Station to deliver supplies and spares and landed in Florida 13 days later."
Article by David S. F. Portree: link
source, source
NASA ID: S77-5784, S77-5785, S77-5758
#STS-1#STS-2#STS-3#STS-4#STS-5#STS-6#STS-7#STS-8#STS-9#STS-10#STS-11#STS-12#STS-13#STS-14#STS-15#STS-16#STS-17#STS-18#STS-19#STS-20#STS-21#STS-22#STS-23#Space Shuttle Columbia#Columbia#OV-102#Space Shuttle Enterprise#Enterprise#OV-101#cancelled
29 notes
·
View notes
Text

'for colored girls who have considered suicide / when the rainbow is enuf' by Ntozake Shange, «Playbill», Equinox Theatre, Houston, TX, November 19, 1977 [Marjorie Randal National Women's Conference Collection, Box 1, Folder 11, UH Libraries Exhibits, University of Houston, Houston, TX]
With: Deborah Arceneaux, Laura Booker, Jan Crain, Dannette Johnson, Barbara Marshall, Leslie Mays, and Brenda Sers
Direction: Bruce Bowen
#graphic design#art#theatre#theater#play#brochure#cover#ntozake shange#deborah arceneaux#laura booker#jan crain#dannette johnson#barbara marshall#leslie mays#brenda sers#bruce bowen#playbill#equinox theatre#university of houston libraries#university of houston libraries exhibits#uh libraries exhibits#1970s
27 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Elaine de Kooning (American, 1918-1989), Portrait of Houston Woman, 1977. Oil on canvas, 24 x 29 7/8 in.
283 notes
·
View notes
Photo








Queen - News Of The World Tour
Live at The Summit, Houston, 11th December 1977
#freddie mercury#roger taylor#john deacon#brian may#queen#queen band#news of the world#my gif#my edit
336 notes
·
View notes
Text
Disabled actors with ungiffed roles (of course any roles are welcomed) for disability pride month:
Michael J. Fox (1961) - has Parkinson's Disease - Designated Survivor (2018), See You Yesterday (2019).
Mat Fraser (1962) - has thalidomide-induced phocomelia - Loudermilk (2017-2020).
Daryl Mitchell (1965) African-American - is paraplegic - Fear the Walking Dead (2018-2023).
Warwick Davis (1970) - has spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita - Willow (2022-2023).
Selene Luna (1971) Mexican - has dwarfism - Mayans M.C (2022-2023).
Cherylee Houston (1974) - has Hypermobility Ehlers-Danlos syndrome - Coronation Street (2010-2023).
Callan Mulvey (1975) ¼ Maori, ¾ Scottish - is blind in one eye - has been in a lot of things including Last King of the Cross (2023), Firebite (2021-2022), Till Death (2021), and Mystery Road (2020).
Shannon Murray (1976) - is paraplegic - Viewpoint (2021), Get Even (2020).
Kurt Yaeger (1977) - is a leg amputee - Another Life (2021).
Katy Sullivan (1979) - is a double leg amputee - Dexter: New Blood (2021-2022).
Jamie-Lynn Sigler (1981) Cuban / Ashkenazi Jewish, Romaniote Jewish, Sephardi - has multiple sclerosis - Big Sky (2021-2023).
Prince Amponsah (1985 or 1986) Ghanaian - is a double arm amputee, with his right arm amputated above the elbow and his left arm amputated below the elbow - Avacado Toast the series (2022) and Station Eleven (2021-2022).
Rana Daggubati (1984) Telugu Indian - is blind in one eye - Rana Naidu (2023).
Rick Glassman (1984) Jewish / Italian - is autistic - As We See It (2022), Not Dead Yet (2023).
Ali Stroker (1987) - is paraplegic and bisexual - Echos (2022), Only Murders in the Building (2021-2022), Ozark (2022).
Josh Thomas (1987) - is autistic, has ADHD, and is gay - Everything’s Gonna Be Okay (2020-2021).
Jillian Mercado (1987) Domincian - has spastic muscular dystrophy - The L Word: Generation Q. (2019-2023).
Ruth Madeley (1987) - has spina bifida - The Almond and the Seahorse (2022).
Tim Renkow (1989) Mexican Jewish - has cerebral palsy - Jerk (2019-2021).
Melissa Johns (1990) - is an arm amputee - Grantchester (2021-2022).
Steve Way (1990) - has muscular dystrophy - Ramy (2019-2022).
James Moore (1992) - has cerebral palsy - Emmerdale (2018-2023).
Arthur Hughes (1992) - has an upper limb indifference - The Innocents (2018).
Madison Ferris (1992) - has muscular dystrophy - Panic (2021).
RJ Mitte (1992) - has cerebral palsy - The Unseen (2023).
Mei Kayama (1994) Japanese - has cerebral palsy - 37 Seconds (2019).
Ryan J. Haddad (1995) Lebanese - has cerebral palsy - The Politian (2019-2020).
Lauren Spencer / Sitting Pretty Lolo (1996) African-American - has Lou-Gehrig’s disease - The Sex Lives of College Girls (Season 2).
Annabelle Davis (1997) - has dwarfism - Hollyoaks (2023).
Kayla Cromer (1998) - is autistic - Everything’s Gonna Be Okay (2020-2021).
Micah Fowler (1998) - has cerebral palsy - Speechless (the latter seasons!)
Daniel Monks (?) - is quadriplegic - Sissy (2022).
Matthew Jeffers (?) - has dwarfism - New Amsterdam (2018-2023).
Ben Mehl (?) - has macular degeneration called Stargardt's disease, which causes one to lose central vision- You (2021).
Gloria May Eshkibok (?) Mohawk, Ottawa, Irish, French - is Two-Spirit (she/her) and has one eye - OChiSkwaCho (2018).
Zack Weinstein (?) - is quadriplegic - Sing It! (2016).
Angel Giuffria (?) - is a congenital arm amputee - To the Dust (2022), Good Trouble (2022), Impulse (2019).
Joci Scott (?) - is paraplegic - Smash or Pass (2023).
Jacob Mundell (?) - congenital hand amputee - The Expanse (2021-2022).
+ HERE'S MY DISABLED FC MASTERLIST FOR MORE!
+ let me know if you have suggestions!
+ let me know if anybody wants suggestions with youtube content!
51 notes
·
View notes
Text
46 years ago
Weirdos/Germs show at Mabuhay Gardens, San Francisco, October 1977.
Belinda Carlisle, Alice Bag and Penelope Houston in the audience.

#punk #punks #punkrock #womenofpunk #history #punkrockhistory #otd
32 notes
·
View notes