#cognitive bias codex
Photo

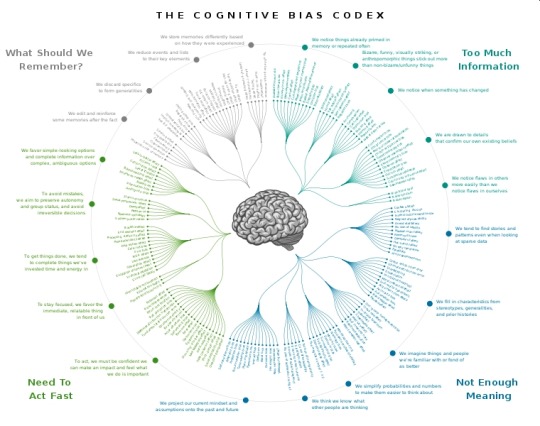
Cognitive Bias Codex, sure is a few o them huh
0 notes
Text
This is really cool. I want a poster of this for my class. Even though a poster wouldn't have hyperlinks explaining each one which is partially what makes this super cool.
0 notes
Text
Microsoft Azure Fundamentals AI-900 (Part 4)
Introduction to Azure OpenAI Service
Generating natural language
Generating code
Generating images
What is generative AI
Artificial intelligence - imitates human behavior by relying on machines to learn and execute tasks without explicit directions on what to output
Machine Learning - models take in data like weather conditions and fit the data to an algorithm to make predictions
Deep Learning - model of layers of algorithms in the form of artificial neural networks
Generative AI - model can produce new content based on what is described in the input.
Describe Azure OpenAI
Microsoft partnered with OpenAI to deliver on three main goals
Utilize Azure’s infrastructure, security, compliance, and regional availability to help users build enterprise grade apps
Deploy Open AI model capabilities in Microsoft products (Azure AI included)
Use Azure to power all of OpenAI's workplads
Introduction to Azure OpenAI Service
Pre-trained generative AI models
Customization capabilities; the ability to fine-tune AI models with your own data
Built-in tools to detect and mitigate harmful use cases so users can implement AI responsibly
Enterprise-grade security with RBAC and private networks
Understand Azure OpenAI workloads
Machine learning
Computer vision
Natural Language Processing
Conversational AI
Anomaly detection
Knowledge mining
Text completion - generate and edit text
Embeddings - search, classify, and compare text
Azure OpenAI’s relationship to Azure AI Services
Azure’s Machine Learning Platform
Cognitive Services
Applied AI Services
Vision
Speech
Language
Decision
Azure Open AI Service
How to use Azure OpenAI
GPT4
GPT3
Codex
Embeddings - Special format of data representation that can be easily utilized by machine learning models and algorithms.
DALL-E
Completion - Allow you to see text responses as you type
Chat - use the assistant setup to instruct the model about how it should behave.
Understanding OpenAI’s natural language capabilities
Generative Pre-trained transformer models are excellent at understanding and generating natural language
Azure OpenAI is powered by GPT3.5-turbo and GPT4
Summarizing text
Classifying text
Generating names or phrases
Translation
Answering questions
Suggesting content
Understanding OpenAI code generation capabilities
build unit tests for the code
Summarize functions already written
Explain sql queries or tables
Convert code between languages
GitHub Copilot
OpenAI partnered with GitHub to create copilot
Integrates codex as a plugin into IDE’s like visual studio code
It can suggest how to write or finish a method based on some text you type
Understand OpenAI’s image generation capabilities
Original images generated by providing a text prompt
The more detail in the prompt, the better quality and more desired result
Provided an image, edits can take place based on the user’s request.
It requires uploading the image and selecting a transparent mask to inform the model where to edit.
Prompts are used to describe the edit
This requires uploading an image and then providing how many variations you required
Subjects and backgrounds along with other elements are moved around the image.
Describe Azure OpenAI’s access and responsible AI Policies
Fairness - AI systems shouldn’t make decisions that discriminate against or support bias of a group or individual
Reliability and Safety - AI systems should response safely to new situations and potential manipulation
Privacy and Security - AI systems should be secure and respect data privacy
Inclusiveness - AI systems should empower everyone and engage people
Accountability - People must be accountable for how AI systems operate
Transparency -AI systems should have explanations so users can understand how they’re build and used
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Photo
being in a human vessel is tough work
thanks wikipedia
friendly reminder to donate to platforms (and humans) you trust and use frequently, in whatever capacity you can
#wikipedia#wiki#cognitive bias#psych#psychology#neuro#neurology#computer science#compsci#science#meaning#politics#code#codex#information#it#technology#tech#artificial intelligence#AI#diagram#information design#design#consciousness#philosophy#theory of mind
23 notes
·
View notes
Photo

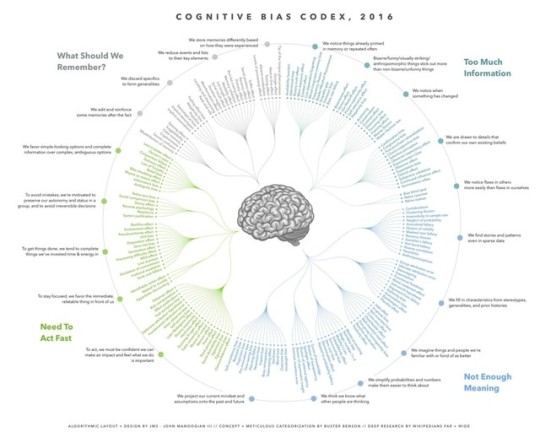
Cognitive Bias Codex (2016)
1 note
·
View note
Text
I think there is huge misconception about the understanding of the Fi function.
The misconception seems to come that most people think that having values will automaticaly asses you as an Fi user, which is completely false. To put it, my correct understanding of the Fi function is that it asses moral ethic code, usualy behavour codex or moral beliefs. Usualy how to treat the weak, or defend whatever it values (Closed people to him for example) and do it best to give It's warmth to them, that's Fi.
The Fi function when it goes on lower levels of the cognitive stack will result in more selfishness, and less experience with emotional situations. However that does not mean he is an emotionless robot incapable of having feelings, it that it has focus on another function on It's primary focus so less attention will be given to Fi function, resulting in less warmth expression and probably less care about moral codex beliefs.
Lets put examples.
Here is the guy, who enjoys, and puts values in scientifical research, basicaly random nerdy science guy. He will put emotional importance and value on his science because he preceives as It's truth and enjoys to work with logical patterns and figuring how scientifical formulas and It's mechanics works.
Sure, It is Fi when I mentioned Emotional value (Because Logic is impersonal), but is hes really Fi when he enjoyes working on logical patters and figuring out scientifical forumals and their mechanics and does not put priority to give warmth to others or morals? It's simple, It's a Ti guy user who puts value on logical patterns.
And sure, it does not have to be Science specificaly, but I just used it as an example.
I could give with an sport athlete who enjoys playing football, and he prioritises his emotional value on physical stimulation, which will make him a Se user, not Fi just because "He puts emotional value", which is the huge misconception of Fi I'm talking about.
Point being here, Fi function is not some superflexible superfunction capable of valuing everything to make you an Fi user, thats simply not how it works. Because if it is how it is really described to be, everyone here in the forum would be a Fi dominant user, not just the forum but the entire earth population, it just seems that there is huge bias with the IxFP Fi dominant slapping on the MBTI typology fandom.
I created this thread, because I want to know whether my conception of the Fi function is correct or is it I am the one who seems to have misconception regarding the Fi function? https://www.typologycentral.com/forums/showthread.php?t=104220&goto=newpost&utm_source=dlvr.it&utm_medium=tumblr
6 notes
·
View notes
Photo
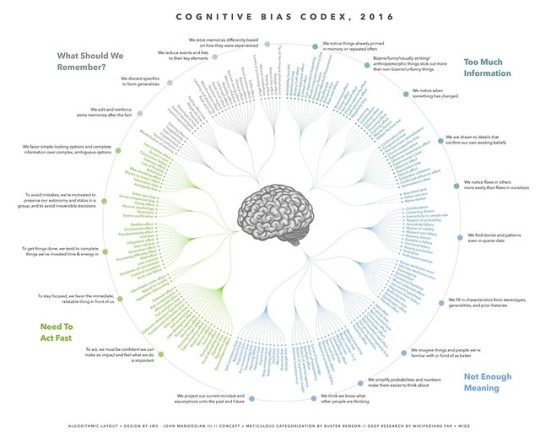
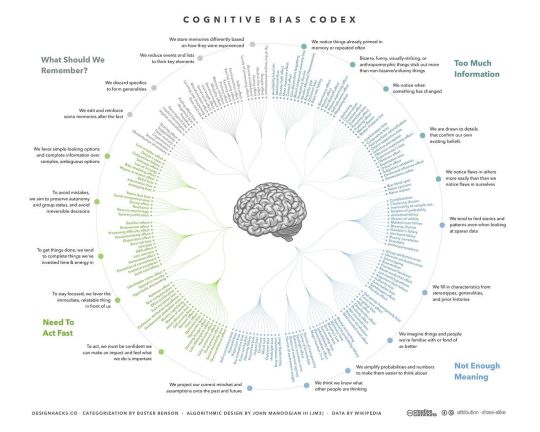
Cognitive bias codex, 2016
Cognitive bias cheat sheet: https://medium.com/better-humans/cognitive-bias-cheat-sheet-55a472476b18
Colinha para Vieses Cognitivos: https://medium.com/@altruismoeficaz/colinha-para-vieses-cognitivos-da69c9607c29
1 note
·
View note
Text
Cognitive bias codex: 200 rules of everyday thinking
A new codex boils them down to 4.

Nearly 200 cognitive biases affect our decision-making.
The sheer amount of biases should teach us humility.
And we should recognize the essential role they play in life, as well.
Aside from mythical spiritual figures and biblical kings, humans are not objective in how they react to the world. As much as we would like to be fair and impartial about how we deal with the situations that arise on a daily basis, we process them through a complex series of internal biases before deciding how to react. Even the most self-conscious of us cannot escape the full spectrum of internal prejudices.
Brain biases can quickly become a hall of mirrors.
(via Cognitive bias codex: 200 rules of everyday thinking - Big Think)
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Explore: The Cognitive Bias Codex The more you know about cognitive biases, the more you realize how biased you can be -- which itself is probably some kind of bias. Here’s a cool visual diagram on 188 biases linked to their Wikipedia pages. - Jacob https://www.instagram.com/p/CWFF5xZlM5p/?utm_medium=tumblr
1 note
·
View note
Text
Module 3
Hello, and welcome back, this week we had three assignments all together and as always more things to do within them so lets dive in!
Assignment 1:
This week we started with a video lecture by the professor during this, we discussed perception, and what the problems of perception are and what the two processing pathways are as well. So with that, the two problems of perception are that there can be too much input for us to process and understand and there is more information in the world than we can even possibly hope to perceive. I also feel like this goes back to the fact that we are not easily able to multitask so if we attempt to take in too much information we may miss some important information.
As previously mentioned as well there are two processing pathways as well. These are the bottom up processes and the top down processes as well. The bottom up process is driven by sensory information from the physical world while the top down process is active in seeking and extraction of sensory information by our knowledge, beliefs, expectations and goals.
Next, we watched another lecture from a different professor who was teaching under grads at MIT and this video was filmed in the spring of 2018. The video in general is called 1.2 - How Can We Study the Human Mind and Brain? Marr’s Level’s of Analysis and it was published by MITCBMM. Overall I felt the video was interesting and obviously the professor is really knowledgeable on the subject she is speaking on I just unfortunately did not take any notes on her lecture I just listened but I quite enjoyed her presentation and I am sure you will too.
youtube
That was it for our first assignment of course of the discussion post we did for this one that I usually do not share, but next is assignment 2!
Assignment 2:
This assignment was fairly easy, we had a few articles to read and our discussion post to answer. So it wasn’t too bad so lets dive in.
First article is called How do our brains reconstruct the visual world? written by Alex Burmester. The article itself was very interesting, it explains how our eyes works and how it pairs with the brain to give us our vison. I found it to be very interesting and informational. I was also lucky enough to learn a bit more about this in another class I am in as well! The author also included an interesting graphic as well which if you don’t want to read the article, I will share it below!

Next we moved on to read ‘Noisy’ neurons put a limit on visual perception, which was written by Adam Hadhazy. This article was also quite interesting and informational and I am sure you will enjoy it, so feel free to read it yourself!
We then moved on to the final article of this assignment which was called Brain’s limits lead to unconscious choices in what we see and remember written by Melissa Healy. This article ended up explaining how our brains limit could also limit what we see and remember. But, with the brain doing this it’s all from an unconscious perspective, so its not anything we can truly control.
That is it for assignment 2 and now on to assignment 3!
Assignment 3:
We started off by reading Cognitive bias cheat sheet written by Buster Benson. This article goes through and explains what cognitive biases are and problems of biases and what could be possible solutions for them as well. One thing I loved about this article is the small comic it starts with because it is so true and it is what so many of us do!

Source of the comic
Then we ended up looking at the cognitive bias codex, it starts with a basic bias and then goes into a more specific bias and then you get the answer of what the bias could be, not necessarily what it is.
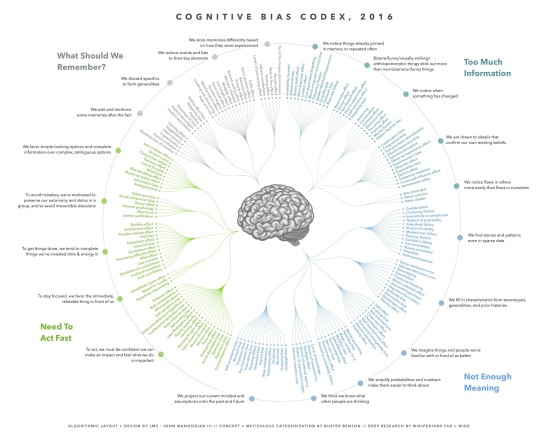
Overall it is a very detailed wheel and a bit hard to read but it was definitely very interesting to look over especially since you tend to recognize some of the biases on there.
Overall that was it for this module, as always I will share the review sheet and I will see you for the next one!

0 notes
Text
PSYCHOLOGY OF PEOPLE ANALYTICS
The attention to people analytics has increased enormously over the last few years. Many organizations have established people analytics teams, and several promising start-ups have developed software that can help HR with people analytics.
The assumption is that if we have access to the right data, if we have the right analysis tools and clever people to interpret the data, we will be able to predict human behavior – and that these predictions will be used in a sensible way in organizations. I have some doubts.
It is time to have a closer look at the psychology of people analytics.
Inspiration
Two books were a great inspiration, and a must-read for HR professionals and people analytics specialists.
On number one “Thinking, fast and slow” of Nobel prize winner Daniel Kahneman. Looking at the numbers that were sold of this book, you would expect almost everybody has read this book (or at least: has bought this book). When I studied experimental psychology (from 1975-1981) Kahneman was already famous. I still remember the famous article he published in 1974 with his colleague Amos Tversky: Judgment under uncertainty – heuristics and biases. I quote from this article: “The reliance on heuristics and the prevalence of biases are not restricted to laymen. Experienced researchers are also prone to the same biases when they think intuitively. For example, the tendency to predict the outcome that best represents the data, with insufficient regard for prior probability, has been observed in the intuitive judgments of individuals who have had extensive training in statistics”.
On number two “The art of thinking clearly”, written by Rolf Dobelli. His book is less scientific, but certainly a worthwhile read with many good lessons. In 99 chapters, he describes the most common thinking errors, with interesting examples.
I also used the list of cognitive biases on Wikipedia. A great and extensive list. This list inspired Buster Benson to cluster these cognitive biases in categories, which he describes in his excellent article Cognitive bias cheat sheet. Based on this article John Manoogian made a very interesting and informative infographic, the Cognitive Bias Codex.
0 notes
Photo

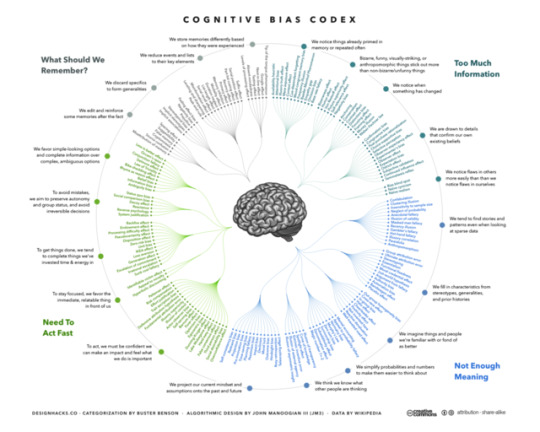
Cognitive Bias Codex | #Infographic | #HighGradeArt
8 notes
·
View notes