#cholestatic liver disease
Text
Cholestatic Liver Diseases Symptoms, Causes, Treatment - Best liver transplant surgeon in India

Cholestasis liver disease is a condition that affects the liver. It happens when your liver's bile flow is slowed or stopped.
#Cholestatic Liver Diseases Symptoms#Liver Diseases Symptoms#Best liver transplant surgeon in India#liver transplant surgeon in India#Best liver transplant surgeon
0 notes
Text
Liver biochemical and function tests – Blood tests commonly obtained to evaluate the health of the liver include liver enzyme levels (alanine aminotransferase [ALT], aspartate aminotransferase [AST], alkaline phosphatase, gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase), tests of hepatic synthetic function (albumin, prothrombin time/international normalized ratio [INR]), and the serum bilirubin level. (See 'Common liver biochemical and function tests' above.)
Initial evaluation of abnormal liver biochemical and function tests – The initial evaluation includes obtaining a history to identify potential risk factors for liver disease and performing a physical examination to look for clues to the etiology and for signs of chronic liver disease. Subsequent testing is determined based on the information gathered from the history and physical examination as well as the pattern of liver test abnormalities (table 4 and algorithm 1). (See 'Initial evaluation' above.)
●Patterns of liver test abnormalities – Liver biochemical test abnormalities can often be grouped into one of several patterns: hepatocellular, cholestatic, or isolated hyperbilirubinemia. Patients with a hepatocellular process generally have a disproportionate elevation in the serum aminotransferases compared with the alkaline phosphatase, while those with a cholestatic process have the opposite findings. The serum bilirubin can be prominently elevated in both hepatocellular and cholestatic conditions and therefore is not necessarily helpful in differentiating between the two. Abnormal tests of synthetic function may be seen with both hepatocellular injury and cholestasis. (See 'Patterns of liver test abnormalities' above.)
●Patients with elevated serum aminotransferases – In the setting of hepatocyte damage, ALT and AST are released from hepatocytes, leading to increased serum levels. The differential diagnosis for elevated serum aminotransferases is broad and includes viral hepatitis, hepatotoxicity from drugs or toxins, alcoholic liver disease, hepatic ischemia, and malignant infiltration. The evaluation should take into account the patient's risk factors for liver disease as well as findings from the physical examination that may point to a particular diagnosis. The evaluation often involves testing for viral hepatitis and autoimmune disease (table 4). Occasionally, a liver biopsy may be required. (See 'Elevated serum aminotransferases' above.)
●Patients with cholestasis – Cholestasis may develop in the setting of extrahepatic or intrahepatic biliary obstruction (table 5). In patients with cholestasis, the alkaline phosphatase is typically elevated to at least four times the upper limit of normal. Lesser degrees of elevation are nonspecific and may be seen in many other types of liver disease, such as viral hepatitis, infiltrative diseases of the liver, and congestive hepatopathy. Patients with a predominantly cholestatic pattern typically undergo right upper quadrant ultrasonography to further characterize the cholestasis as intrahepatic or extrahepatic. (See 'Elevated alkaline phosphatase' above.)
The presence of biliary dilatation on ultrasonography suggests extrahepatic cholestasis which may be due to gallstones, strictures, or malignancy. The absence of biliary dilatation suggests intrahepatic cholestasis. There are numerous possible causes of intrahepatic cholestasis (table 5), including drug toxicity, primary biliary cholangitis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, viral hepatitis, cholestasis of pregnancy, benign postoperative cholestasis, infiltrative diseases, and total parenteral nutrition. Subsequent testing to identify the underlying cause may include checking antimitochondrial antibodies, magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography, computed tomography, endoscopic ultrasonography, and/or endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (algorithm 1). (See 'Evaluation of elevated alkaline phosphatase' above.)
●Patients with isolated hyperbilirubinemia – The evaluation of isolated hyperbilirubinemia begins with determining whether the hyperbilirubinemia is predominantly conjugated (direct hyperbilirubinemia) or unconjugated (indirect hyperbilirubinemia). An increase in unconjugated bilirubin in serum results from overproduction, impairment of uptake, or impaired conjugation of bilirubin. The evaluation of unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia typically involves evaluation for hemolytic anemia as well as obtaining a history to determine if the patient has Gilbert syndrome. In a patient with a history consistent with Gilbert syndrome (eg, the development of jaundice during times of stress or fasting), normal serum aminotransferase and alkaline phosphatase levels, and mild unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia (<4 mg/dL), additional testing is not required. (See 'Isolated hyperbilirubinemia' above and 'Unconjugated (indirect) hyperbilirubinemia' above.)
An isolated elevation in conjugated bilirubin is found in two rare inherited conditions: Dubin-Johnson syndrome and Rotor syndrome, as well as other genetic bile transport disorders in children. Dubin-Johnson syndrome and Rotor syndrome should be suspected in patients with mild hyperbilirubinemia (with a direct-reacting fraction of approximately 50 percent) in the absence of other abnormalities of standard liver biochemical tests. Normal levels of serum alkaline phosphatase and GGT help to distinguish these conditions from disorders associated with biliary obstruction. Differentiating between these syndromes is possible but clinically unnecessary due to their benign nature. (See 'Conjugated (direct) hyperbilirubinemia' above.)
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Get Accurate Liver Function Tests at PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad,India
Your liver is a vital organ responsible for filtering toxins, producing proteins, and regulating blood sugar. Regular liver function tests (LFTs) are crucial for monitoring its health and detecting potential problems early. PACE Hospitals, a leading Multi-Super Speciality Hospitals in Hyderabad, offers comprehensive LFT services to help you stay informed about your liver health.
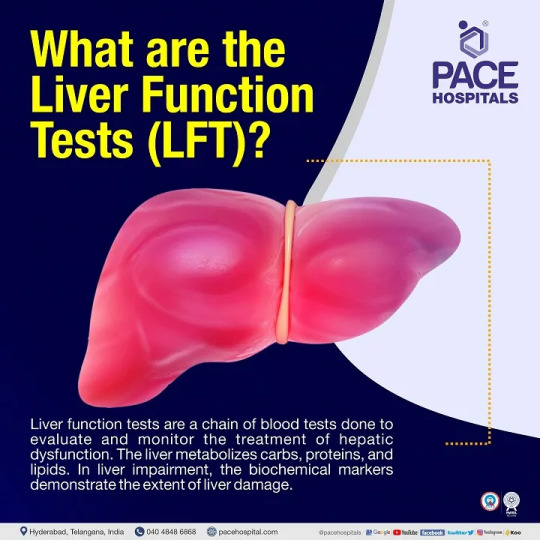
Why Choose PACE Hospitals for Liver Function Tests?
State-of-the-Art Diagnostics: Our NABL-accredited laboratory utilizes advanced technology to ensure accurate and reliable test results.
Experienced Medical Staff: Our team of qualified doctors and technicians will guide you through the testing process and interpret the results effectively.
Focus on Patient Care: We prioritize your comfort and well-being, offering a seamless testing experience.
Benefits of LFTs at PACE Hospitals:
Early Detection of Liver Issues: Identify potential problems like hepatitis, fatty liver disease, or cirrhosis at an early stage, allowing for timely intervention.
Monitoring Treatment Progress: Track the effectiveness of ongoing treatment for existing liver conditions.
Improved Overall Health: By maintaining optimal liver health, you can safeguard your overall well-being.
PACE Hospitals - Your Partner in Liver Care
PACE Hospitals understand the importance of proactive healthcare. PACE Hospitals is committed to providing comprehensive liver function testing services to empower you to take charge of your liver health.
Liver Function Test Indication :
The indication of liver function blood tests usually includes the following:
Screening: They are prescribed as a sensitive screening modality for liver dysfunction in suspected and high-risk individuals.
The pattern of disease: Liver function tests are helpful to recognise the way of liver disease, e.g.,
Differentiating between acute viral hepatitis and various cholestatic disorders and chronic liver disease.
Assess severity: They are helpful in assessing the severity and predicting the outcome of certain diseases like primary biliary cirrhosis.
Follow-up: They are helpful in the follow-up of certain liver diseases and valuable for evaluating responses to therapy like autoimmune hepatitis.
Abnormal lft blood test may indicate subclinical liver disease, guiding additional diagnostic examination. After hepatic dysfunction is identified, liver test abnormalities may imply the underlying liver illness, such as hepatitis, biliary obstructions, or infiltrative liver disease.
Blood tests for liver function may not be cost-effective for screening healthy, asymptomatic people for liver disease. A panel of tests (aspartate aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, albumin) is preferred to a single test for screening since it is more sensitive and specific for liver disease.
Schedule Your LFT Today!
Contact PACE Hospitals to schedule your liver function test in Hyderabad India. Our friendly staff will guide you through the process and ensure a smooth experience.
0 notes
Text
Single-cell and spatial transcriptomics reveals the human liver immunological landscape and myeloid dysfunction in PSC.
Background: Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a serious immune-mediated cholestatic liver disease characterized by bile retention, biliary tree destruction, and progressive fibrosis leading to end stage liver disease and transplantation. There is an unmet need to understand the cellular composition of the PSC liver and how it underlies disease pathogenesis. As such, we generated a comprehensive atlas of the PSC liver and a reference healthy liver dataset using multiple multi-omic modalities with functional validation. Methods: In this work, we employed single-cell (12,000 cells), single-nuclei (23,000 nuclei) and spatial transcriptomics (1 sample by 10x Visium and 3 samples with multi-region profiling by Nanostring GeoMx DSP) to profile the cellular ecosystem in 5 patients with PSC. Transcriptomic profiles were compared to 100k single cell transcriptomes and spatial transcriptomics controls from 24 healthy neurologically deceased donor (NDD) livers. Flow cytometry and intracellular cytokine staining was performed to validate PSC-specific differences in immune phenotype and function. Results: PSC explants with cirrhosis of the liver parenchyma and prominent periductal fibrosis were associated with a unique population of hepatocytes which transformed to a cholangiocyte-like phenotype. Those hepatocytes were surrounded by diverse immune cell populations, including monocyte-like macrophages, liver-resident and circulating natural killer (NK) cells. Cytokines released by inflamed cholangiocytes and fibrosis-resident hepatic stellate cells and endothelial cells recruited CD4+T-cells, dendritic cells, and neutrophils to PSC liver tissues. Tissue-resident macrophages, by contrast, were reduced in number and exhibited a dysfunctional inflammatory response to LPS and IFN-{gamma} stimulation. Conclusions: We present the first comprehensive atlas of the PSC liver and demonstrate hyper-activation and exhaustion-like phenotypes of myeloid cells and markers of chronic cytokine expression in late-stage PSC lesions. http://dlvr.it/St3l9w
0 notes
Text
Severe side effects of C-GEST-200
Abdominal pain
Sleepiness
Absence of menstrual periods
Itching
Flatulence
Nausea
Depression
Breast tenderness
Abnormal vaginal bleeding
Altered menstrual cycle
Edema (swelling)
Change in body weight
Changes in cervical secretion
Cholestatic jaundice
Injection site reactions (pain, swelling, redness)
Red spots or bumps
Acne
Hair loss
Excessive hair growth on face
Anaphylactic reaction
Fever
Insomnia (difficulty in sleeping)
Soreness
Diarrhea
Vaginal irritation
Vaginal dryness
Dementia
Deep vein thrombosis (blood clot in the legs)
Myocardial infarction
Stroke
Pulmonary embolism
Breast cancer
How to use C Gest Softgel capsule Capsule
Take this medicine in the dose and duration as advised by your doctor. Swallow it as a whole. Do not chew, crush or break it. C Gest 200mg Softgel capsule is to be taken with food.
Safety advice

Alcohol
CONSULT YOUR DOCTOR
It is not known whether it is safe to consume alcohol with C Gest 200mg Softgel capsule Capsule. Please consult your doctor.

Pregnancy
SAFE IF PRESCRIBED
C Gest 200mg Softgel capsule Capsule is safe to use during pregnancy. Most studies have shown low or no risk to the developing baby.
Breast feeding
SAFE IF PRESCRIBED
C Gest 200mg Softgel capsule Capsule is safe to use during breastfeeding. Human studies suggest that the drug does not pass into the breastmilk in a significant amount and is not harmful to the baby.

Driving
UNSAFE
C Gest 200mg Softgel capsule Capsule may decrease alertness, affect your vision or make you feel sleepy and dizzy. Do not drive if these symptoms occur.

Kidney
CONSULT YOUR DOCTOR
There is limited information available on the use of C Gest 200mg Softgel capsule Capsule in patients with kidney disease. Please consult your doctor.

Liver
CONSULT YOUR DOCTOR
There is limited information available on the use of C Gest 200mg Softgel capsuleCapsule in patients with liver disease. Please consult your doctor.
What if you forget to take C Gest Softgel capsule Capsule?
If you miss a dose of C Gest 200mg Softgel capsule Capsule, take it as soon as possible. However, if it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and go back to your regular schedule. Do not double the dose.
#c pharm ceutical top pharma companies in india#top 1000 pharma companies by market cap#list of top pharmaceuticals stocks in india
1 note
·
View note
Text
Study provide new insights into why cholestasis causes cognitive issues
Study provide new insights into why cholestasis causes cognitive issues
Patients with cholestatic liver disease such as primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) can experience significant impairment of bile flow and may develop neurological symptoms including fatigue and cognitive decline. Little is known about why these symptoms develop in some patients, and there is no current therapy. In a new study in The American Journal of Pathology, published by Elsevier,…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
The Signs Of Childhood Cholestasis
If your child exhibits cholestasis symptoms, you should consult with your doctor. By evaluating total bile acid serum, they can assist you in determining the optimum treatment. They will also examine your child's growth to verify that he is not in danger. If he is, your doctor may decide to deliver the baby early to lessen the baby's danger. This may be done vaginally or via cesarean section, depending on your child's symptoms and test results.
Itching is one of the most common symptoms of cholestasis. A few essential medications, such as ursodeoxycholic acid, which lowers bile levels in the blood, can alleviate this condition. Ursodeoxycholic acid can be started promptly in pregnant women and toddlers. It successfully treats the disease in around three out of every four women and even relieves itching in approximately 25% of affected women. While UDCA has been used to treat cholestasis during pregnancy, its mechanism of action remains unknown. It can cause problems for the mother, baby, and child, and a child with cholestasis may need constant monitoring during pregnancy.
Cholestasis occurs during pregnancy when the liver fails to digest fats effectively. Bile, a fluid that breaks down lipids, is usually produced by the liver. Bile accumulates and leaks into the bloodstream when the gallbladder cannot drain properly. This produces severe itching, mainly if it occurs at night.
Yellowing of the skin is a common symptom of cholestasis, a liver condition. It can produce severe itchiness, particularly on the hands and soles of the feet. Pale feces, dark urine, and nausea are also possible symptoms. Treatment for cholestasis in a child may include bile acid-lowering medication and periodic pregnancy monitoring. Complications like stillbirth and respiratory distress syndrome might occur if left untreated. In severe cases, doctors may prescribe a c-section before the child's due date.
The fundamental cause of cholestasis is liver immaturity. However, it can also be caused by liver damage or other factors such as medicines. Although cholestasis can afflict people of any age, young children are more vulnerable.
Yellowing mucous membranes in babies are an essential indicator of cholestasis and should prompt additional assessment and therapy. A Kasai hepatic portoenterostomy, usually performed before 30 to 45 days of age, is the most successful treatment for cholestatic newborns. However, if this is not done immediately, there is a risk of liver failure or injury.
Cholestasis symptoms can include an irregular mucous membrane and skin discoloration. This is related to low oxygen levels in the blood. Icterus, an early symptom of liver illness, can also result from the disease.
Several risk factors can cause elevated bilirubin levels in children. Infections are among these. These infections can be bacterial or viral, depending on the cause. Herpes simplex, for example, is a common illness that can cause jaundice in youngsters. Galactosemia, a severe condition that can affect children, is another risk factor.
Furthermore, several hereditary illnesses can induce jaundice in youngsters. However, the majority of these disorders are quite rare. Premature neonates with impaired liver development are also at risk of jaundice.
Jaundice is a symptom of elevated bilirubin levels in the blood. This happens when the liver isn't working correctly, and too much bilirubin is secreted into the blood. A doctor will order a blood test to measure bilirubin levels and other substances. If these levels are high, the youngster must consult a specialist.
Depending on the problem's etiology and the disorder's symptoms, there are several therapy options for cholestasis in children. Treatment generally focuses on preventing problems, alleviating symptoms, and reducing bile acids. Surgery may be recommended in extreme situations.
Cholestasis symptoms in children range from moderate to severe. Slow development, severe itching, and splenomegaly are common symptoms. Symptoms may appear at any point throughout the first few weeks of life. Based on the symptoms, the doctor will propose a treatment plan. In rare circumstances, genetic abnormalities or infections can cause the illness. Idiopathic cholestasis affects a small number of newborns with no known cause. On the other hand, specific gene mutations are linked to up to 25% of newborn cholestasis instances.
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Effect of Extracorporeal Albumin Dialysis (ECAD) on Pruritus Using MARS Versus New Adsorbent Recirculation (OPAL)
Abstract
Extracorporeal Albumin Dialysis (ECAD) is a therapy option for pruritus in cholestatic liver disease. The aim was to evaluate the feasibility for ECAD using two different devices. A subgroup with intractable pruritus of a prospective randomized crossover study in liver patients was analyzed. Randomly subjects received either MARSTM first and new HepalbinTMCluster12 albumin dialysis (OPALTM) second or vice versa. Visual Analogue Score, total bile acids as well as albumin binding function were measured before and after each treatment. 8 subjects suffering from cholestatic liver disease and pruritus were enrolled. Subjects in both arms were comparable. Albumin dialysis could reduce albumin bound toxins, the binding function of patient’s albumin improved in OPAL, but not in MARS. Which one of the biomarker changes are responsible for the improvement of pruritus remains unknown and requires more research. The procedure was safe in all subjects.
Read More About This Article: https://crimsonpublishers.com/gmr/fulltext/GMR.000600.php
Read More Crimson Publishers Google Scholar Articles: https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=en&user=kHTkZusAAAAJ&cstart=20&pagesize=80&citation_for_view=kHTkZusAAAAJ:e5wmG9Sq2KIC
0 notes
Text
Complications In Pregnancy - A overview

Most pregnancies are without complications but this is not the norm. Complication can risk the health of mother, foetus or both. This is the reason why antenatal checkups are always recommended by obstetricians everywhere so that the complication is diagnosed early and managed appropriately.
TO ENUMERATE SOME COMPLICATIONS :-
- High blood pressure:- Gestational hypertension, pre-eclampsia, eclampsia and chronic hypertension
- Anaemia
- Gestational diabetes
- Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP)
- Infections
- Preterm labour
- Miscarriage
- Still birth
- Ante partum haemorrhage
HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE
Blood pressure above systolic > 140mmHg and / or diastolic > 90mmHg diagnosed any time during pregnancy. This is associated with higher risk of many other complications such as premature birth, low birth weight (IUGR), antepartum haemorrhage, still birth.
Patient with high blood pressure must observe for warning signs blurring of vision, severe headache not even releaved by paracetamol, right side upper abdominal / epigastric pain, abnormal body movements.
It is therefore very important to control blood pressure in pregnancy through medications.
ANEMIA:-
Anemia is a condition in which number of red blood cells or haemoglobin concentration with in the body is lower than normal WHO anemia classification in pregnancy
mild anemia 9-10.9g/dl
moderate anemia 7-8.9g/dl
severe anemia <7gm
Having anemia in pregnancy can make you feel tired, weak and pale all the time. National Iron Plus Initiative recommends iron folic acid (IFA) supplimentation of 100mg elemental iron and 500mcg of folic acid every day for at least 100 days starting after the first trimester at 14-16 weeks of gestation for all non-anemic pregnant women followed by same dose for 100days post partum.
GESTATIONAL DIABETES
Hormonal changes from pregnancy can cause the body to not make enough insulin, or if it does then it is not used efficiently with the lack of insulin the glucose builds up in the blood which cause diabetes or high blood sugar.
On 75gm OGTT test value of 140-199mg is diagnosed as gestational diabetes and value > 200mg is diagnosed as overt diabetes.
Controlling gestational diabetes is important as it can lead to high blood pressure, IUGR, large infant which increases the risk for caesarean delivery.
INTRA HEPATIC CHOLESTHAISIS OF PREGNANCY (ICP)
ICP is the most common liver disease of pregnancy. It is a reversible cholestatic disease presenting typically in the second and third trimester of pregnancy and is characterized by itching of the palms and soles, elevated serum aminotransferases and / or elevated serum bile acid levels (>=10micromol/l) with spontaneous relief of laboratory abnormalities and symptoms promptly after delivery but no later than one month post partum.
ICP is relatively benign to women, but it is reported to have important fetal implications.
ICP has been found to be associated with increased risk of preterm delivery, meconium staining of amniotic fluid, fetal bradycardia, respiratory distress and fetal demise.
So the itching of hand and palm or sudden onset of itching all over the body any time in second and third trimester should not be ignored and must be reported to your obstetrician at the earliest.
INFECTION
Many infections such as bacterial, viral, parasitic and sexually transmitted infection can occur during pregnancy and may lead to complications. These infection can pass from mother to infant during delivery or from the mother to the foetus during pregnancy. It can contribute to miscarriage, low birth weight, birth defects, still birth, and maternal health complication, if not treated in time.
PRETERM LABOUR
When labour begins before 37 weeks of pregnancy, it is called preterm labour. It can lead to complications as brain and lungs, might not be fully developed .
Miscarriage
Miscarriage is loss of pregnancy during the first 20 weeks of pregnancy. Approximately 10% of all pregnancy ends up in miscarriage and 90% of miscarriage occur before 16 weeks. Sign if miscarriage include vaginal bleeding, fluid or tissue passing per vaginum and cramping.
STILL BIRTH
Still birth is the loss of pregnancy after 20 week of pregnancy. Infections, maternal health issues, problems with placenta and chromosomal abnormalities can contribute to still birth.
ANTE PARTUM HAEMORRHAGE
Placenta previa:- Placenta is an organ that develops in the uterus during pregnancy and provides oxygen and nutrients to the growing baby along with removing waste from its blood.
Placenta previa is a condition in which placenta partially or wholly covers the opening between the uterus and vagina (cervix). The main symptom of placenta previa is vaginal bleeding without any pain or cramp. Visiting your doctor immediately is strongly recommended in such a condition.
Placental abruption:- A serious pregnancy complication in which the placenta detaches from the womb (uterus). The condition can deprive the baby of oxygen and nutrients. symptoms include vaginal bleeding, abdominal pain and back pain mainly in the last 12 weeks of pregnancy Patient must contact the treating doctor immediately.
Although complications can not be prevented, regular health check ups and prenatal care can help in strengthening the health of both the mother and the child.
Are you looking for the best pregnancy and delivery doctor in Solan, You are the right place. Shri Balmukund Apex Hospital is one of the best Private Hospitals in Solan, Himachal Pradesh who have an experienced doctor’s team. Visit today for more details.
Article Resource - https://www.sbah.in/complications-in-pregnancy
#Top Hospital In Solan#Best Hospital In Solan#Private Hospitals in Solan#Multispeciality hospital in Solan#24x7 Medical Emergency Service Solan#Best gynaecologist hospital in solan#Best Gynecologists in Solan#Gynaecologists in Solan#Gynaecologist & Obstetrician Doctors in Solan#Gynaecologist Doctors in Solan
0 notes
Text
FIB-4: Fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) Index for Liver Fibrosis; noninvasive estimate of liver scarring in HCV and HBV patients, to assess need for biopsy.
When to use: Patients with any known risk factors for liver disease, including chronic hepatitis, alcoholic liver disease, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and the cholestatic and metabolic liver diseases. Patients with known liver fibrosis should have their fibrosis trended over time to evaluate for progression or stabilization.
Liver fibrosis often progresses non-linearly, so it is important to be able to re-assess fibrosis trends in individual patients over time, and invasive re-assessments carry significant risk to patients. FIB-4 allows for non-invasive liver fibrosis assessment.
FIB-4 was developed in patients with HIV and HCV co-infection.
FIB-4 was developed to correlate with Ishak levels of fibrosis (by biopsy) with 3 levels:
0-2 (mild fibrosis)
3-4 (moderate fibrosis)
5-6 (severe fibrosis/cirrhosis)
Low fibrosis scores may be appropriate candidates for medical management and may not require liver biopsy if FIB-4 scores continue to stay low. Severe fibrosis/cirrhosis scores may need liver biopsy for confirmation of cirrhosis unless there are other clinical or imaging signs of progression to end-stage liver disease.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Forever Changed: Random Reflections
Forever Changed: Random Reflections
100. That’s how many posts I’ve written on here. 100! Y’all don’t know me well enough to know how huge that is. I almost never stick to anything that I start. When I first started this blog, I never would have imagined how therapeutic it would prove to be. I just wanted somewhere to write my updates for my family and somewhere to put my random thoughts. You see, when you have chronic…

View On WordPress
#autoimmune#autoimmune disease#autoimmune liver disease#autoimmune warrior#cholestatic liver disease#chronic disease#chronic illness#chronic pain#coronavirus#depression#immune-compromised#liver disease#mental health#my autoimmune life#pbc#rare autoimmune liver disease#rare disease#rare liver disease
0 notes
Link
“...The case was reported to Italian sanitary authority (AIFA, Agenzia Italiana del Farmaco) and patient was warned about re-exposure to the vaccine.
The new mRNA vaccines protect against infectious diseases by triggering immune response. In registration trials, no cases of hepatitis were recorded [2]. The association between vaccine and autoimmune manifestations has been reported in different settings [3, 4, 5, 6]. Our patient didn’t develop autoantibodies, nor liver histology showed typical signs of autoimmune damage. Nevertheless, two factors suggest immune mediated hepatitis: the first is the timeline from vaccine to liver alteration which may correspond with the development of the immune response. The second, is the excellent response to steroids. Besides these hypotheses, the pathogenetic mechanism of this possible form of hepatitis is obviously to be clarified. Drugs can induce toxic hepatitis [7], SARS-CoV-2 infection has been associated with the development of autoimmunity [3] and there are also cases of drug-induced hepatitis with features of autoimmunity [8]. Similarly to the case reported by Bril F. et al [1], eosinophils infiltrate was present at histology; this feature is more often observed in toxic or drug related liver injury but also in autoimmune hepatitis [7]. Our patient had non underlying chronic liver disease but only an intermittent observation of mild hypertransaminasemia related to hyperlipidaemia. With regard to the previous use of ginkgo-biloba, it seems unlikely related to hepatitis as it was discontinued about 100 days before the onset of jaundice. Moreover, antioxydant properties of ginkgo-biloba has been described to prevent liver fibrosis in patients with chronic viral hepatitis [9] and, although potential hepatic toxicity has been proposed [10], it has never been reported to cause severe liver damage before.
We are aware that a clear causality between vaccine and hepatitis can’t be established and our aim is not to discourage clinicians from investigating other causes or questioning the importance of vaccination against COVID-19. Despite this and in the light of the previous case, we believe it is important to inform the scientific community as we could be facing a possible immune mediated hepatitis, induced by vaccine and presenting in with different features, which shows excellent response to steroid therapy.”
#covid-19 vaccine#covid-19#sars-cov-2#hepatitis#family medicine#internal medicine#print this off later#molecular mimicry
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
The action on the curve, being a function of dose, covers survival of the organism with a deficiency state to typical health and wellness, toxicity, and also death.In chelation fondness chromatography, elution is accomplished with EDTA or EGTA for a fast group-specific elution.Chelating agents generating soluble steel complicateds are likewise called sequestering agents.GBCAs can be classified into acyclic and macrocyclic representatives based on the nature of the chelating moiety.High relaxivity is also critical for MRI contrast agents.
They are normally organic substances, yet this is not a necessity, as when it comes to zinc and its usage as an upkeep treatment to avoid the absorption of copper in individuals with Wilsons disease., with a humic acid or a protein). Steel chelate substances prevail parts of plant foods to give micronutrients.7 to 17.
What is Hard Water? Tough water lugs minerals like magnesium as well as calcium.We describe exactly how chelation therapy functions prior to diving right into several of its less standard uses to see whether it's actually effective.Another typical indication of innovative Pb poisoning is the lead paralysis in the most energetic muscles, particularly for the radial nerve with wrist decrease, which is sluggish and also not constantly full in healing after cessation of exposure.
Sillanpää, reports a 17% to 30% of EDTA reduction, in three plants of triggered sludge of surface pulp and also paper mills.The opportunity of finding EDTA biodegrading task in ground water and also dirt would certainly be of interest, considering that in this substratum photolysis might not comprise a destruction option.EDTA triggers disturbance of the outer membrane, given that it can eliminating its magnesic and also calcic divalent cations, with the subsequent loss of considerable quantities of lipopolysacharide, which consequently, make cells vulnerable to the action of many compounds such as detergents, proteases, lipases and also lysozymes.Regarding to dental human exposure, Fe(III)-EDTA salts are thought about secure and utilized as an iron supplement source.
However, a number of pet researches showed Gd deposition was likewise discovered in minds adhering to [ GdDOTA] − management, so the growth of much safer, extra inert GBCAs is needed.However, combination therapy with deferasirox as well as deferoxamine did not show additive (or synergistic) iron excretion in an iron-overloaded gerbil model, recommending that the chelators may simply contend for an usual iron pool.The chelating agents are uncommon root causes of liver injury, the only agent convincingly connected to causing distinctive acute liver injury with jaundice being penicillamine which usually root cause of an immunoallergic, primarily cholestatic liver disease with a brief incubation duration.
Because a chelant is insoluble in water as well as acid, a chelant is the only effective method to do away with the deposits.Toxicity is generally a function of either the steel chelate or of the ligand getting rid of important steel ions.Their chelating capacity towards Fe and also Al was examined in aqueous option, by spectroscopic and also potentiometric methods, and they confirmed to be strong sequestering agents for these metal ions without depletion of Zn, a crucial biometal.Thus, as compared with previously reported analogues, each ligand possesses an additional totally free amino group all set for additional functionalization.
Once they're infused into the blood stream, they circulate with the blood, binding to metals.GBCAs can be categorized right into macrocyclic and acyclic agents based on the nature of the chelating moiety.Chelation therapy is a secure procedure when correctly administered.Furthermore, several bacterial pressures specifically resistant to Heavy steels and also chelants were isolated and also chosen.
Phosphonates likewise function as sequestering representative for metal ions like iron, zinc, manganese.the as well as copper phosphonate particles which had adsorbed on calcium carbonate particles are launched when crystals collapse and they are offered to duplicate very same work again as well as again.The professional indications consist of heart disease (due to injury to myocytes) and arrythmias (as a result of harm to the cells of the cardiac conducting system). Scientific Efficacy of Iron Chelators.Consequently, a chelator particle that binds to all 6 sites totally suspends the "cost-free" iron.
1 note
·
View note