#chemistry and physics
Text
Chemistry Notes (June-July 2023)
1-Chloro-2,3-Epoxypropane
Carbohydrates
Energy and Heat Capacity Calculations
Inner Transition Metal List
Mendelevium
Order of a Reaction Ex. 3
Satisfying Octet Rule Ex. 2
Strong Acids and Water Ex. 4
Sun Facts
Vapor Pressure and Intermolecular Forces Ex. 1
X-Rays and Crystal Structures
.
Patreon
#studyblr#notes#masterlist#studyblr masterlist#studying masterlist#study masterlist#chemistry#chemistry notes#chemistry masterlist#chem#gen chem#organic chemistry#organic chemistry masterlist#chemistry master list#organic chemistry master list#astronomy#astrophysics#astrochemistry#chemistry and physics#physics and chemistry#studyblr master list#studying master list#study master list#studying resources#studyblr resources#study resources#gen chem notes#orgo#ochem
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
look, I know I've talked about this essay (?) before but like,
If you ever needed a good demonstration of the quote "Any sufficiently advanced technology is indistinguishable from magic", have I got an exercise for you.
Somebody made a small article explaining the basics of atomic theory but it's written in Anglish. Anglish is basically a made-up version of English where they remove any elements (words, prefixes, etc) that were originally borrowed from romance languages like french and latin, as well as greek and other foreign loanwords, keeping only those of germanic origin.
What happens is an english which is for the most part intelligible, but since a lot everyday english, and especially the scientific vocabulary, has has heavy latin and greek influence, they have to make up new words from the existing germanic-english vocabulary. For me it kind of reads super viking-ey.
Anyway when you read this article on atomic theory, in Anglish called Uncleftish Beholding, you get this text which kind of reads like a fantasy novel. Like in my mind it feels like it recontextualizes advanced scientific concepts to explain it to a viking audience from ancient times.
Even though you're familiar with the scientific ideas, because it bypasses the normal language we use for these concepts, you get a chance to examine these ideas as if you were a visitor from another civilization - and guess what, it does feel like it's about magic. It has a mythical quality to it, like it feels like a book about magic written during viking times. For me this has the same vibe as reading deep magic lore from a Robert Jordan book.
#off topic#literature#language#linguistics#science#science history#science fiction#fantasy#physics#atomic theory#anglish#chemistry#robert jordan#the wheel of time#uncleftish beholding
42K notes
·
View notes
Text

Astronomy I-
#physics#science#stem#mathematics#maths#math meme#science meme#physics meme#chemistry#geology#psychology#meme#funny#don’t lick the science#engineer#astronomy#space
73K notes
·
View notes
Text












Yeah I was right and there was no way I was getting the rest of this done without making you all wait another month or two, so I just went to the next good break point. We're officially past the halfway point with Astarion though, so not too much longer before you actually get to see Rolan again!
Part 1 • Previous Part • Next Part
Full page format under the cut:
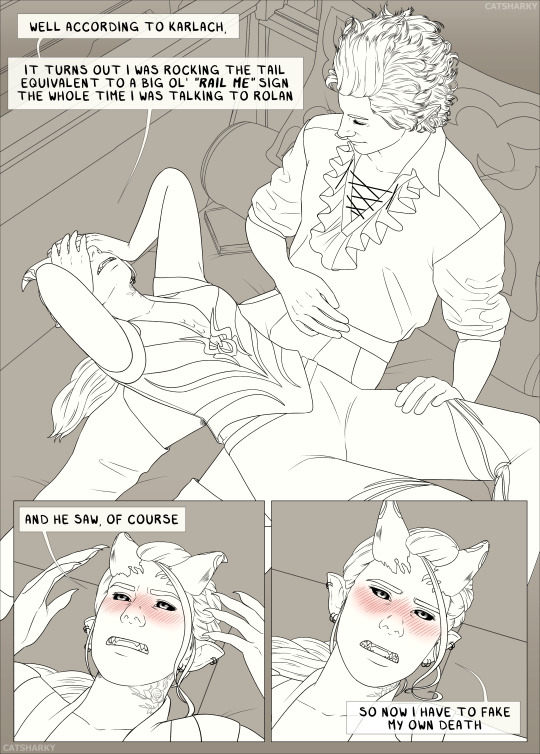



#baldur's gate 3#bg3#bg3 comic#I just really love Ember and Astarion's dynamic as well ok#He's who she canonly ends up with but the Rolan timeline is if Astarion had decided he wasn't ready for a physical relationship after all#in which case his relationship with Ember doesn't really change they just end up platonic life partners instead of romantic ones#that duo who everyone assumes are a couple because they might as well be but nah#hopefully gonna get to show off how Ember and Rolan work together once I get back to him cause I love their chemistry just as much#rolan x tav#tav x rolan#rolan x ember#bg3 astarion#astarion#my tav#sharky's tav#tav: ember#oc: ember#sharky art
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Chemical Structure of Redstone
So I was curious about what the chemical structure of Redstone looks like, and Minecraft Education Edition, albeit unintentionally, gives us a canon look into what Redstone is made of:

In Minecraft Education Edition, putting a Redstone Block into a Material Reducer shows that it's composed of 31 Carbon, 31 Uranium, and 38 Unobtanium, which we can assume to be measured in grams
Dividing the Redstone Block into Redstone Dust, each Redstone Dust is then composed of approximately 3.4 Carbon, 3.4 Uranium, and 4.2 Unobtanium
Again assuming that's measured in grams, that's 0.17 cm³ of Uranium, 1.496 cm³ of Carbon, and ???³ of Unobtanium per Redstone Dust
So what does this tell us about the chemical structure of Redstone? Basing this on Redstone Dust's composition, we can estimate that each Redstone molecule is composed of 3 Carbon atoms, 3 Uranium atoms, 4 Unobtanium atoms, a little under half of the time it binds to an extra Uranium and/or Carbon, and 20% of the time it binds to an extra Unobtanium
This also has some horrifying implications for how Redstone works:
Redstone would be extremely volatile as the radioactive decay from Unobtanium and Uranium would occasionally release Helium ions through alpha radiation, sometimes breaking apart Carbon into two Beryllium atoms (as it absorbs the extra proton and neutron from the Uranium) or merging into Oxygen
So Redstone should, in theory, be extremely flammable and potentially explosive, which implies that cave static, or the player mining Redstone with an Iron Pickaxe, could lead to a spark that causes an explosive cave-in
As Unobtanium is just a placeholder for unobtainable elements (hence the name), I'm going to estimate Unobtanium in this case as Unbinilium, the placeholder name for element 120
Why?
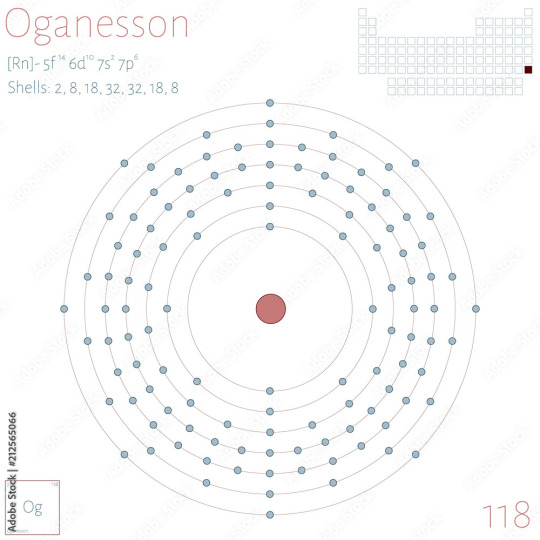
I'm estimating the Unobtanium as Redstone as being larger than the largest man-made element, Oganesson, which holds an impressive 118 protons
Each valence electron shell, from innermost to outermost, can bind with 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, and 8 shells respectively, so I'd like Unobtanium to be an element we haven't discovered yet, and consequently I'd like to jump up to the next shell
While I could estimate with element 119's placeholder, Ununennium, it would have one electron in the next shell, so Unbinilium allows for easier chemical binding
So what does this molecule look like then? Well, horrifyingly...
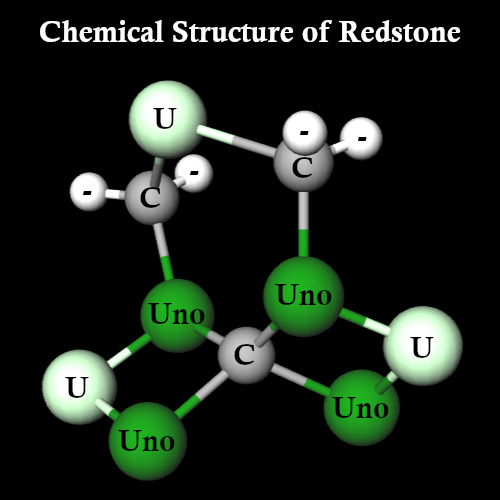
It looks like this. As Redstone forms in crystal lattices, and only two Carbon atoms are free to bind, I can absolutely see why it's so brittle that it breaks into powder.
This makes the structure of Redstone:
C3U3Uno4 (55% of molecules)
C4U3Uno4 (13% of molecules)
C3U4Uno4 (13% of molecules)
C4U4Uno4 (7% of molecules)
C3U3Uno5 (5% of molecules)
C4U3Uno5 (3% of molecules)
C3U4Uno5 (3% of molecules)
C4U4Uno5 (1% of molecules)
An extremely radioactive, flammable, and explosive compound.
#redstone#minecraft#chemistry#physics#education#i would love if someone could submit what a 2D representation of these molecules would look like#i don't actually know how to make them
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
OKAY THIS ARTICLE IS SO COOL
I'm going to try to explain this in a comprehensible way, because honestly it's wild to wrap your head around even for me, who has a degree in chemistry. But bear with me.
Okay, so. Solids, right? They are rigid enough to hold their shape, but aside from that they are quite variable. Some solids are hard, others are soft, some are brittle or rubbery or malleable. So what determines these qualities? And what creates the rigid structure that makes a solid a solid? Most people would tell you that it depends on the atoms that make up the solid, and the bonds between those atoms. Rubber is flexible because of the polymers it's made of, steel is strong because of the metallic bonds between its atoms. And this applies to all solids. Or so everybody thought.
A paper published in the journal Nature has discovered that biological materials such as wood, fungi, cotton, hair, and anything else that can respond to the humidity in the environment may be composed of a new class of matter dubbed "hydration solids". That's because the rigidity and solidness of the materials doesn't actually come from the atoms and bonds, but from the water molecules hanging out in between.
So basically, try to imagine a hydration solid as a bunch of balloons taped together to form a giant cube, with the actual balloon part representing the atoms and bonds of the material, and the air filling the balloons as the water in the pores of the solid. What makes this "solid" cube shaped? It's not because of the rubber at all, but the air inside. If you took out all the air from inside the balloons, the structure wouldn't be able to hold its shape.
Ozger Sahin, one of the paper's authors, said
"When we take a walk in the woods, we think of the trees and plants around us as typical solids. This research shows that we should really think of those trees and plants as towers of water holding sugars and proteins in place. It's really water's world."
And the great thing about this discovery (and one of the reasons to support its validity) is that thinking about hydration solids this way makes the math so so so much easier. Before this, if you wanted to calculate how water interacts with organic matter, you would need advanced computer simulations. Now, there are simple equations that you can do in your head. Being able to calculate a material's properties using basic physics principles is a really big deal, because so far we have only been able to do that with gasses (PV=nRT anyone?). Expanding that to a group that encompasses 50-90% of the biological world around us is huge.
#science#stem#science side of tumblr#stemblr#biology#chemistry#scientists#biochemistry#studyblr#physics#nature
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
The whole “scientists use big words on purpose to be exclusive” is such a bunch of anti-intellectual bullshit. Specific and concise language exists for a reason; you need the right words to convey the right meaning, and explaining stuff right is a hugely important part of science. Cultures that live around loads of snow have loads of words to describe different types of snow; cultures that live in deserts have loads of words to describe different types of sand. Complex language is needed for complex meaning.
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Victor Ninov situation is one of my favourite cases of scientific fraud because it's rare to see so straightforward an example of someone being brought low by their own hubris.
Like, okay, faking the synthesis of a previously unobserved element: it's one of the few varieties of scientific fraud that actually has a clear gameplan for getting away with it. The physical properties of unobserved elements are, in principle, predictable, and there are only so many ways to go about synthesising them. If you do your homework, it's not outside the realm of possibility that your claimed results will end up being at least mostly consistent with the results of subsequent legitimate efforts to synthesise that element, and any minor discrepancies will end up being dismissed as statistical anomalies and/or the product of sloppy experimental design. It's by no means an easy game to play, but it's a game you can conceivably win.
And Victor Ninov did it. He rolled the dice and he won – twice. His fabricated results for elements 110 and 112 were corroborated by later work, and nobody noticed that his actual data was a crock of shit. He got away with it as cleanly as he could have hoped. It was only the third time he tried it, with element 118, that he biffed it and claimed results which nobody could replicate, and this is the only reason his earlier frauds were discovered. If he'd quit while he was ahead, it's likely the first two incidents never would have come to light.
Like, they say the third time's the charm, and buddy here learned the hard way that sometimes, the opposite also holds true.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
i find it so unfair that i cant do all the science. like what do you MEAN I can't study bio and chem and biochem and atrophysics and physics and geology and climate science. what do you MEAN i have a limited lifespan and need to get out of school at some point to get a job. i want to collect the science fields like pokemon, this isn't fair
#minty's crystals#science#biology#chemistry#physics#astrophysics#astronomy#stem#I'm literally such a nerd but i want to learn EVERYTHING i want to be the MASTER OF SCIENCE#also i wanna be famous for it#something something nobel prize something something cover of time magazine#academia#chaotic academia
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
Scientist Stereotypes
Biologist: Can't do math
Theoretical Physicist: Can’t do anything but math
Geologist: Rock collection addict
Military Scientist: Meet the Engineer TF2
Archeologist: Thinks about the Roman Empire more times a day than most men think about sex
Sexologist: Thinks about sex more times a day than most men think about the Roman Empire
Chemist: A pyromaniac and/or is very fun at parties
Science Communicator: Is only fun at parties when everyone else there are nerds
Mycologist/Entomologist: They are VERY interested and passionate about gross things and THAT IS YOUR PROBLEM
Computer Scientist: gay
#science#biology#geology#physics#computer science#scientists sitcom#chemistry#archeology#sexology#entomology#mycology#military science
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Reblog this and put in the tags what country you’re from and all the science classes you took in high school (for non Americans that’s approximately when you’re 14, 15, 16, and 17 years old)
13K notes
·
View notes
Text
Comparing Intermolecular Forces Ex 7

Patreon
#studyblr#notes#medblr#medical notes#med notes#mcat#gen chem#general chemistry#gen chem notes#general chemistry notes#chemistry#chemistry notes#chem#chem notes#intermolecular forces#forces#physics#physics and chemistry#chemistry and physics#introductory chemistry#chem 2#chem 1#chemistry 1#chemistry 2#intro to chemistry
1 note
·
View note
Text
Biology rizz: I'm jealous of your heart because it's pounding inside of you and I am not.
Volcanologist rizz: damn girl are you volcanic ash and spatter? Because you’re intoxicating
Historical rizz: they’ll call me patron of the arts the way I’m paying for furry porn
Econ rizz: baby, I‘ve got the supplies, the question is, do you have the demand.
Environmental science rizz: I must be the climate crisis the way your ignoring me
Physics rizz: looks like you forgot to account for my gravitational pull
Philosophy rizz: I stopped checking for monsters under the bed when I realized society was the monster
Chemistry rizz: Call me Marie curie bc a hug without u would be life ending
#i am the funniest person alive#196#r/196#/r/196#geology memes#shitpost#chemistry#college memes#rizz#history memes#biology memes#environment#physics memes#college
754 notes
·
View notes
Text

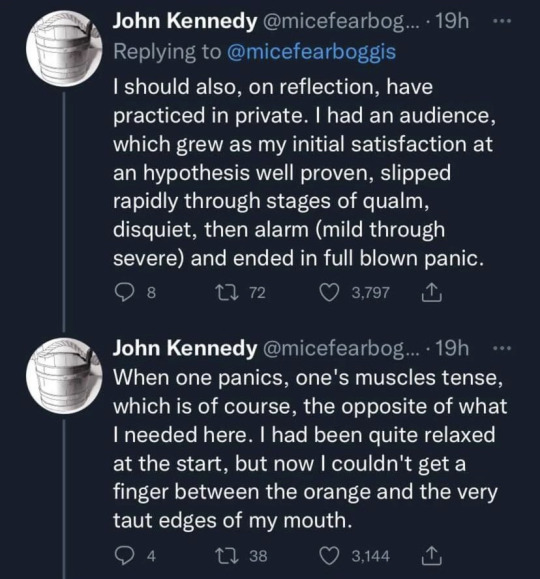

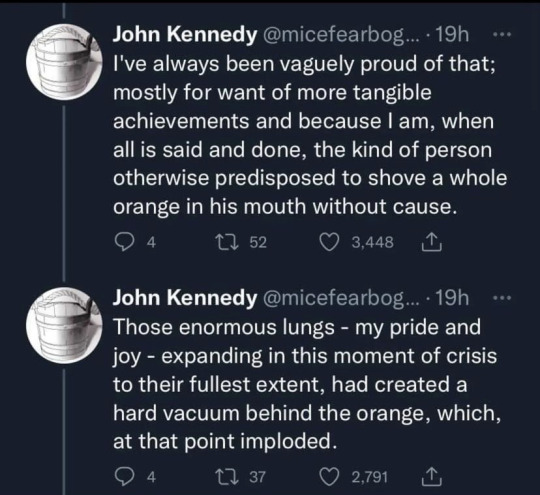
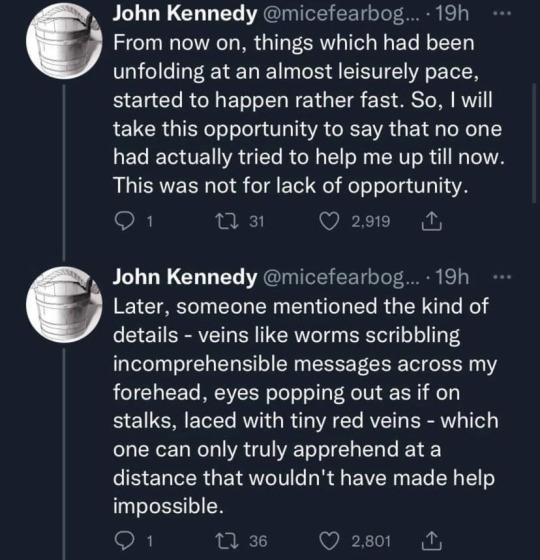




#Thank you John Kennedy for the most amusing thing I’ve read this week#science#stem#funny#Twitter#stemblr#meme#memes#Twitter meme#humour#scientists#humor#oranges#orange#physics#chemistry#biology#tw choking#tw vomiting
48K notes
·
View notes
Photo

Who else agrees?
#biology#chemistry#physics#computing#social science#sciences#studying#memes#meme#student memes#funny#comedy#science#insidesjoke#most popular#coding
2K notes
·
View notes
Text


january this january that
#studyblr#dark academia#math#mathblr#physics#study aesthetic#space#science#astronomy#astrophysics#student#telescope#light academia#physicsblr#chaotic academia#dark acadamia aesthetic#historyblr#literature#chemblr#chemistry#intp#intj#student life#winter#langblr#bookblr#study inspo#study inspiration
913 notes
·
View notes